
Preview text:
Phase diagrams - consultation
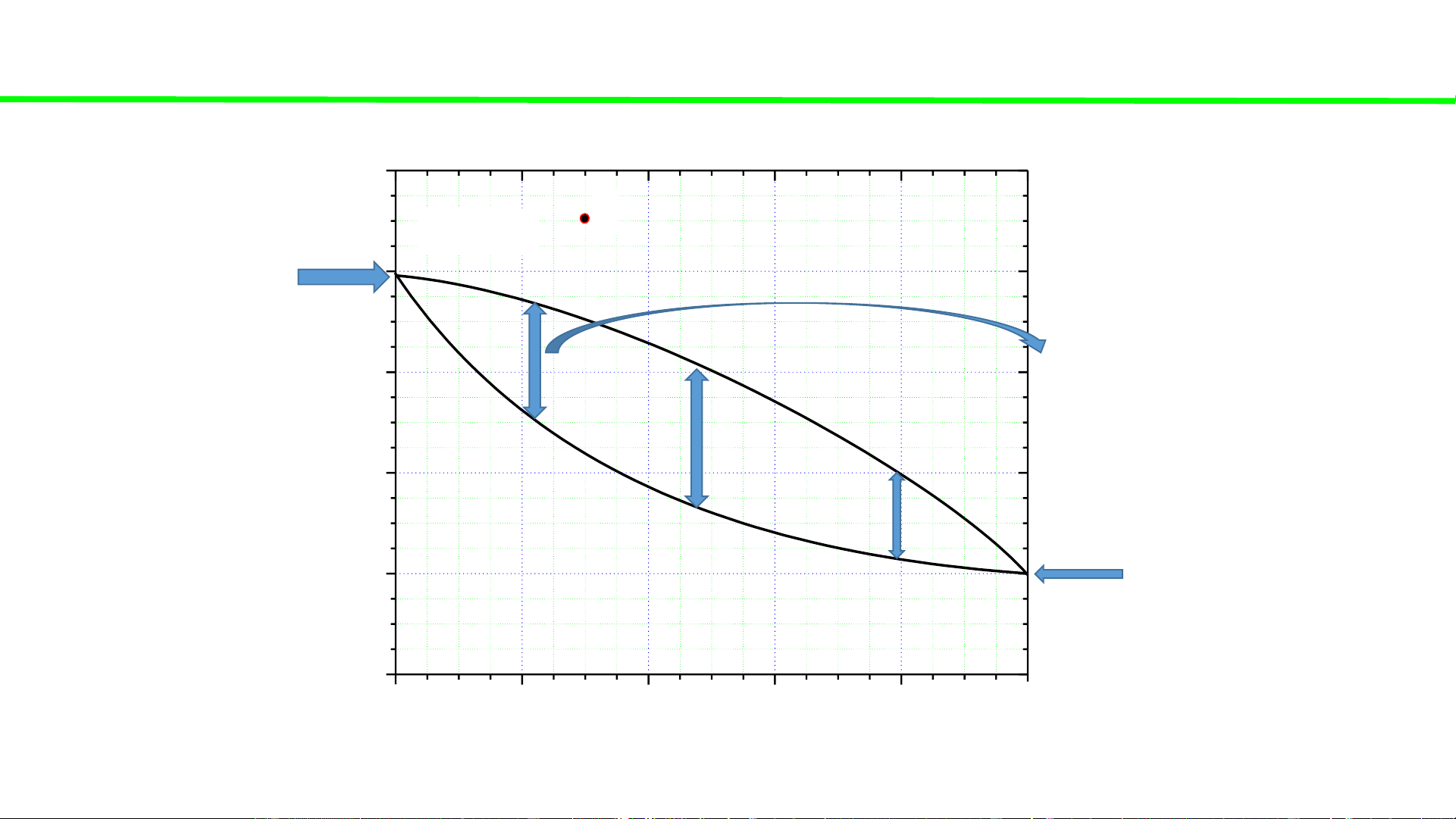
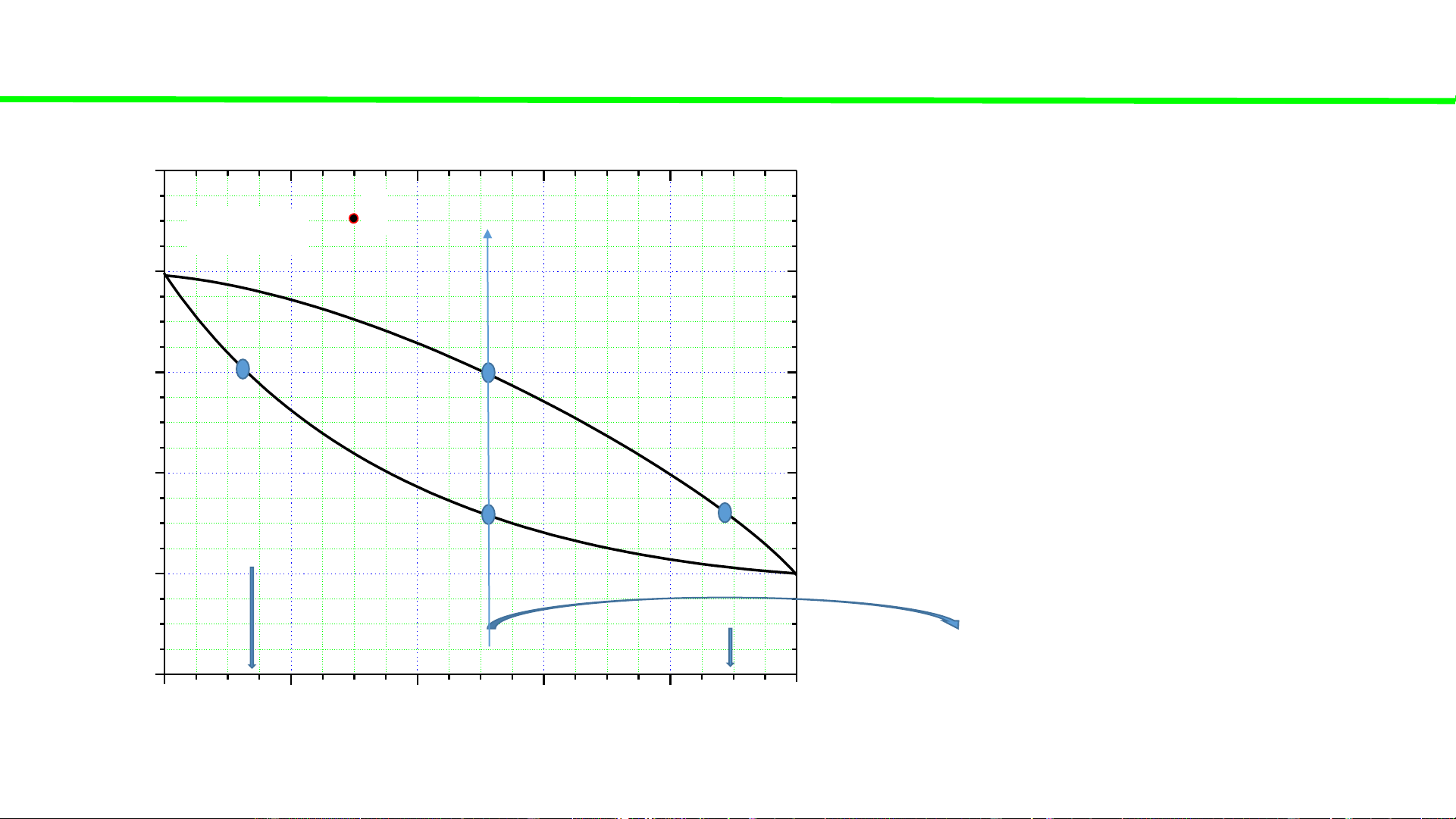
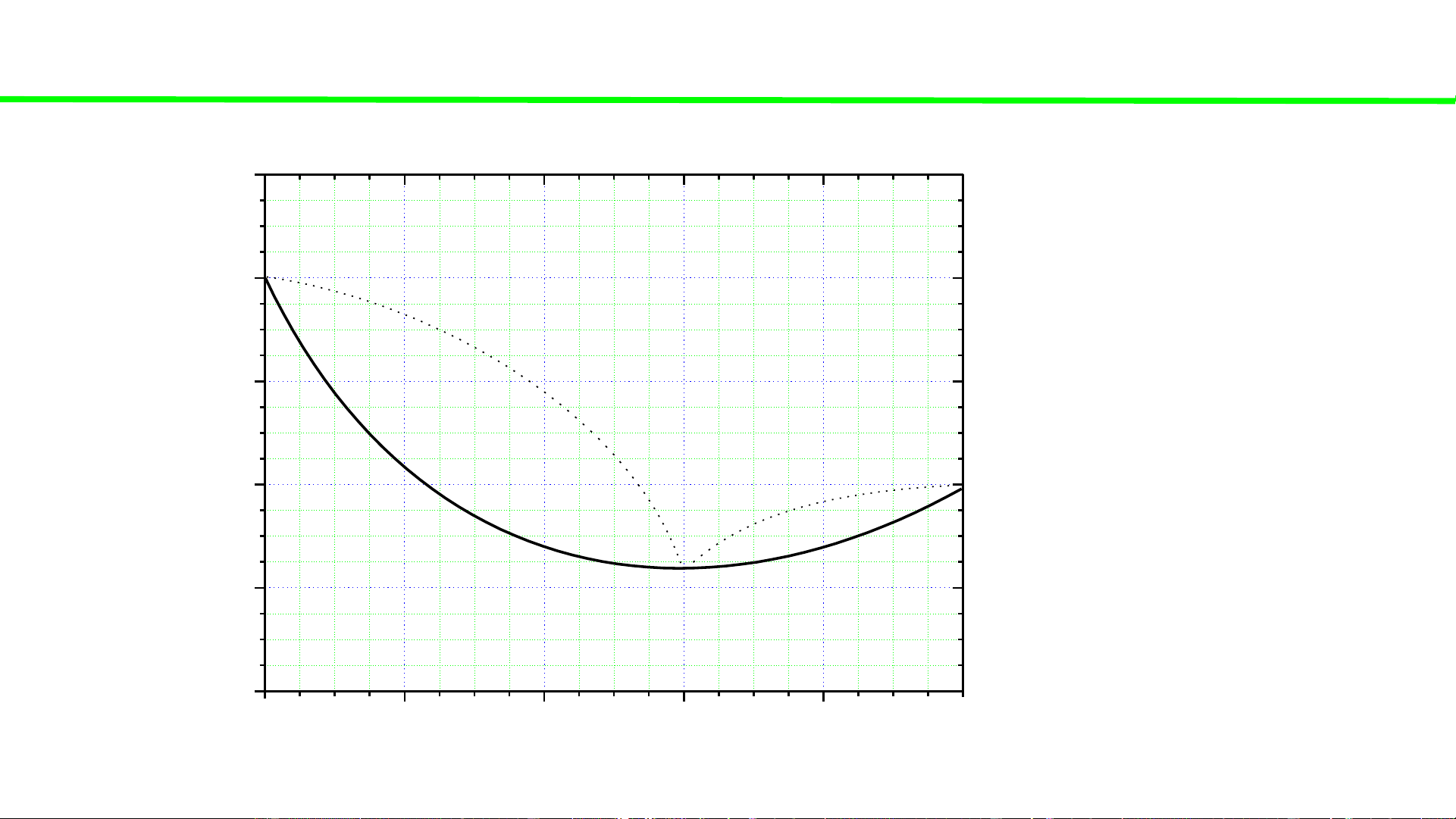
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2 totally miscible liquids without azeotrope 100 tan lẫn điểm đẳng phí Q Boiling point of P const 80 pure liquid A - 0 Boiling temperatures fix TA
of solutions (A+B) – 60 varied, but C o 0 00 0 40 T, T T T B ( A B ) A 20 Boiling point of pure liquid B - 0 0 fix TB 0 20 40 60 80 100 A % B B B
Compiled by RNDr. Ngo Manh Thang, CSc., Dr. rer. nat.
Phase diagrams - consultation
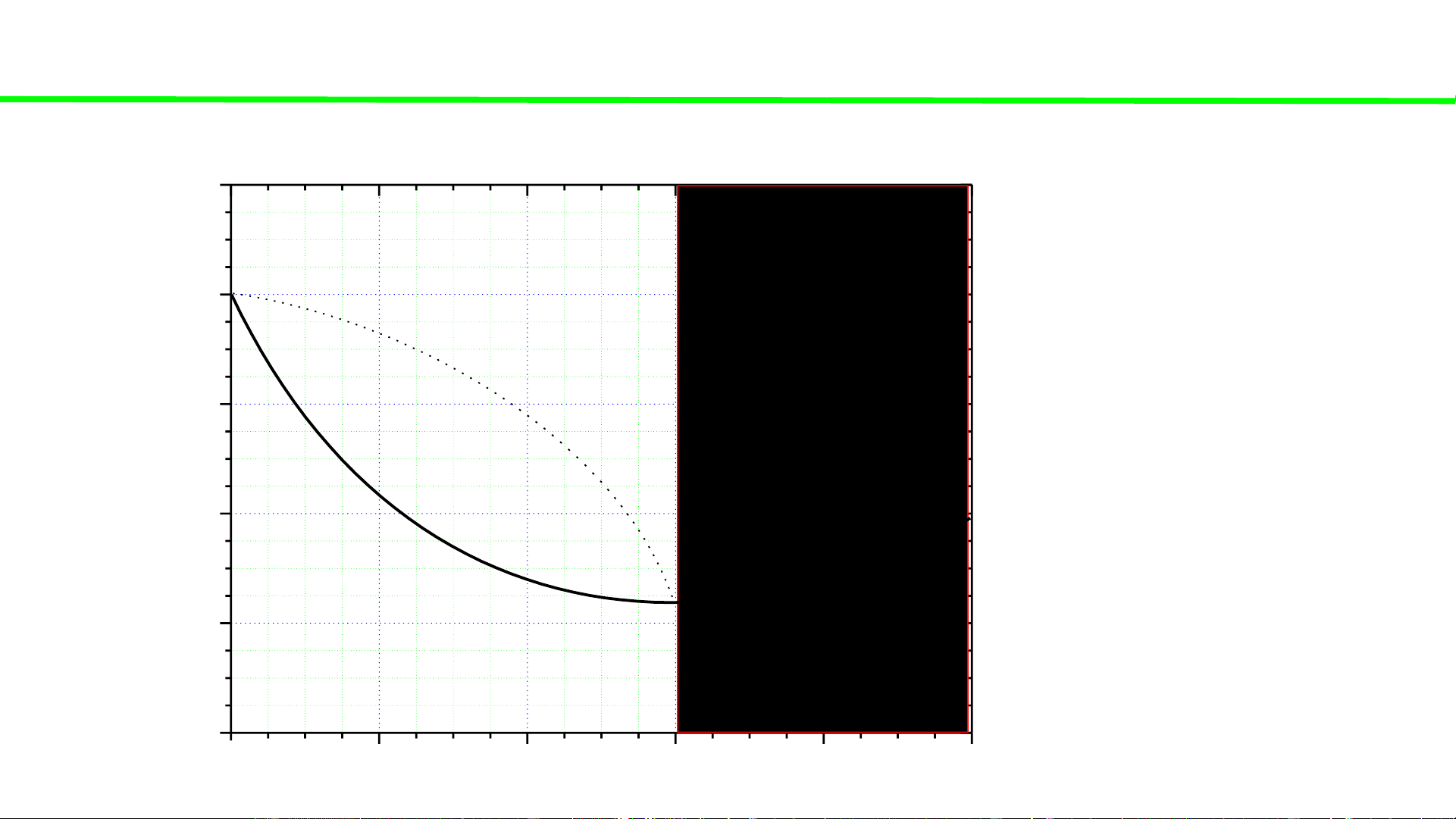
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2 totally miscible liquids without azeotrope 100 Q P const
Cooling of gaseous mixture Q 80
Condensation starts, ca. 70oC 60
Condensation continues, T C o
Total condensation ca. 45oC 40 T, 20 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 A % B B B
Compiled by RNDr. Ngo Manh Thang, CSc., Dr. rer. nat.
Phase diagrams - consultation
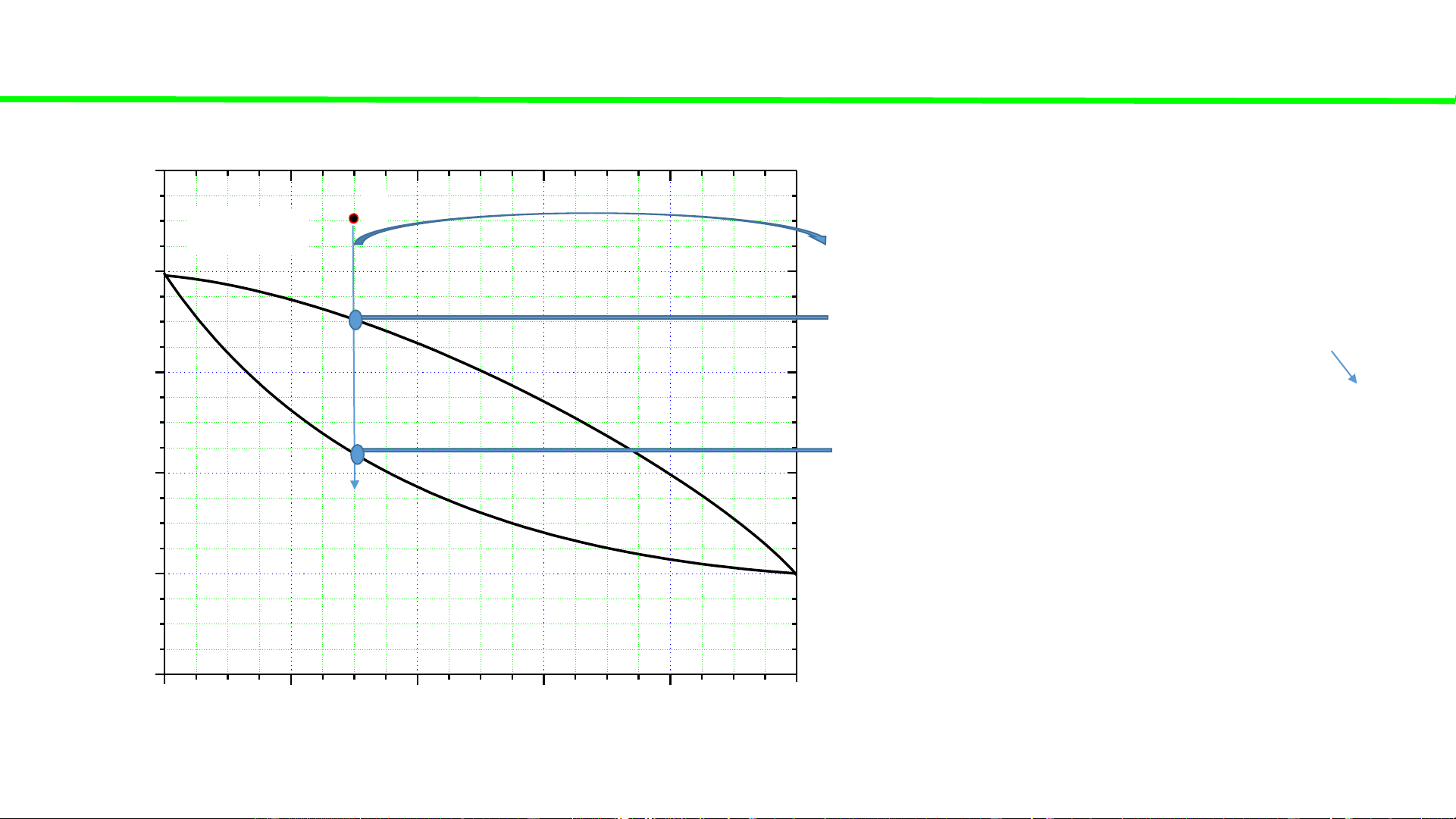
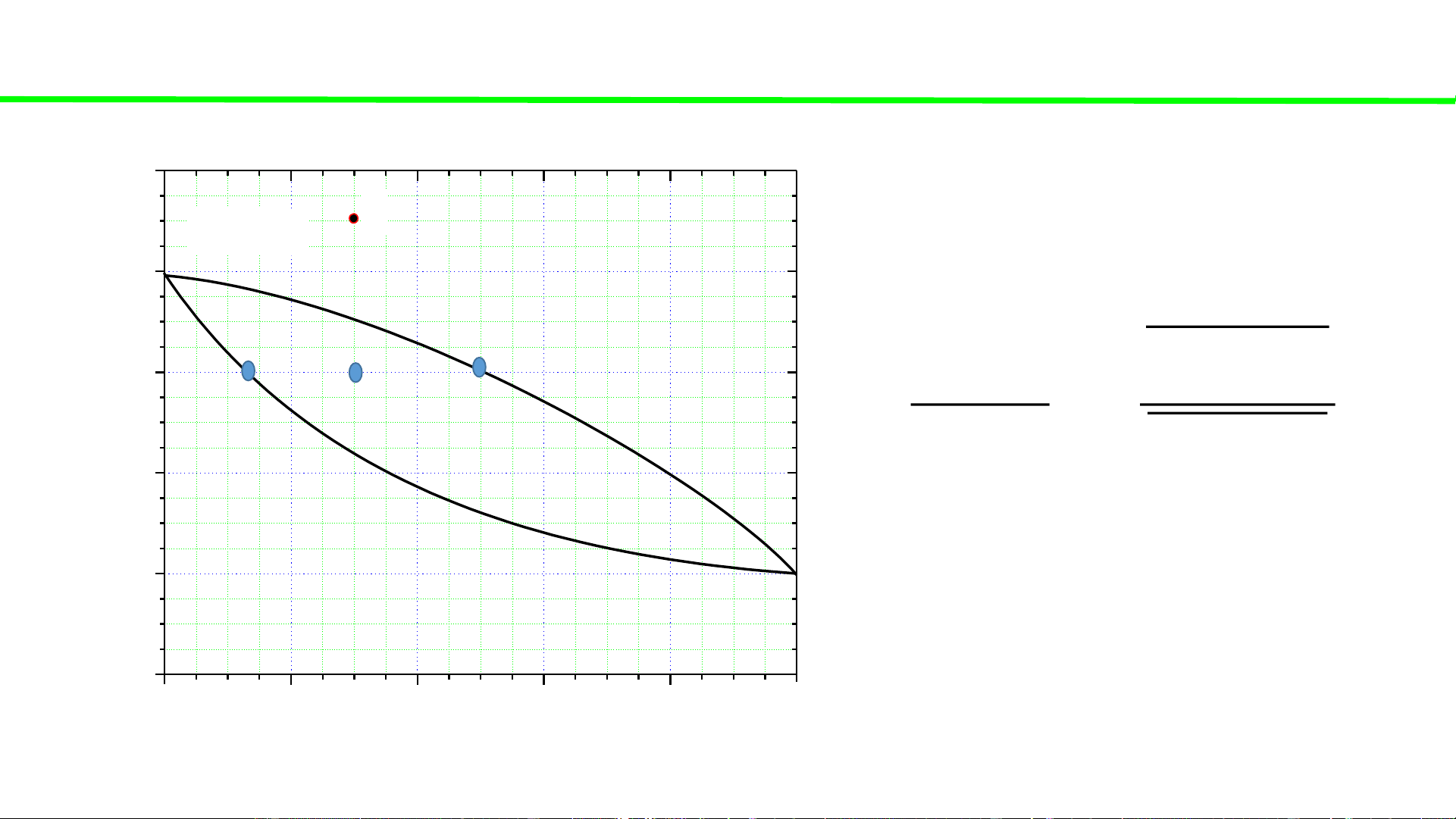
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2 totally miscible liquids without azeotrope 100 Q P const
Cooling of gaseous mixture Q 80 1st liq.
Condensation starts, ca. 70oC droplet 60
Condensation continues, T C Last gas o
Condensation ends ca. 45oC 40 T, buble 20 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 A % B B B 6% B 74% B
Phase diagrams - consultation
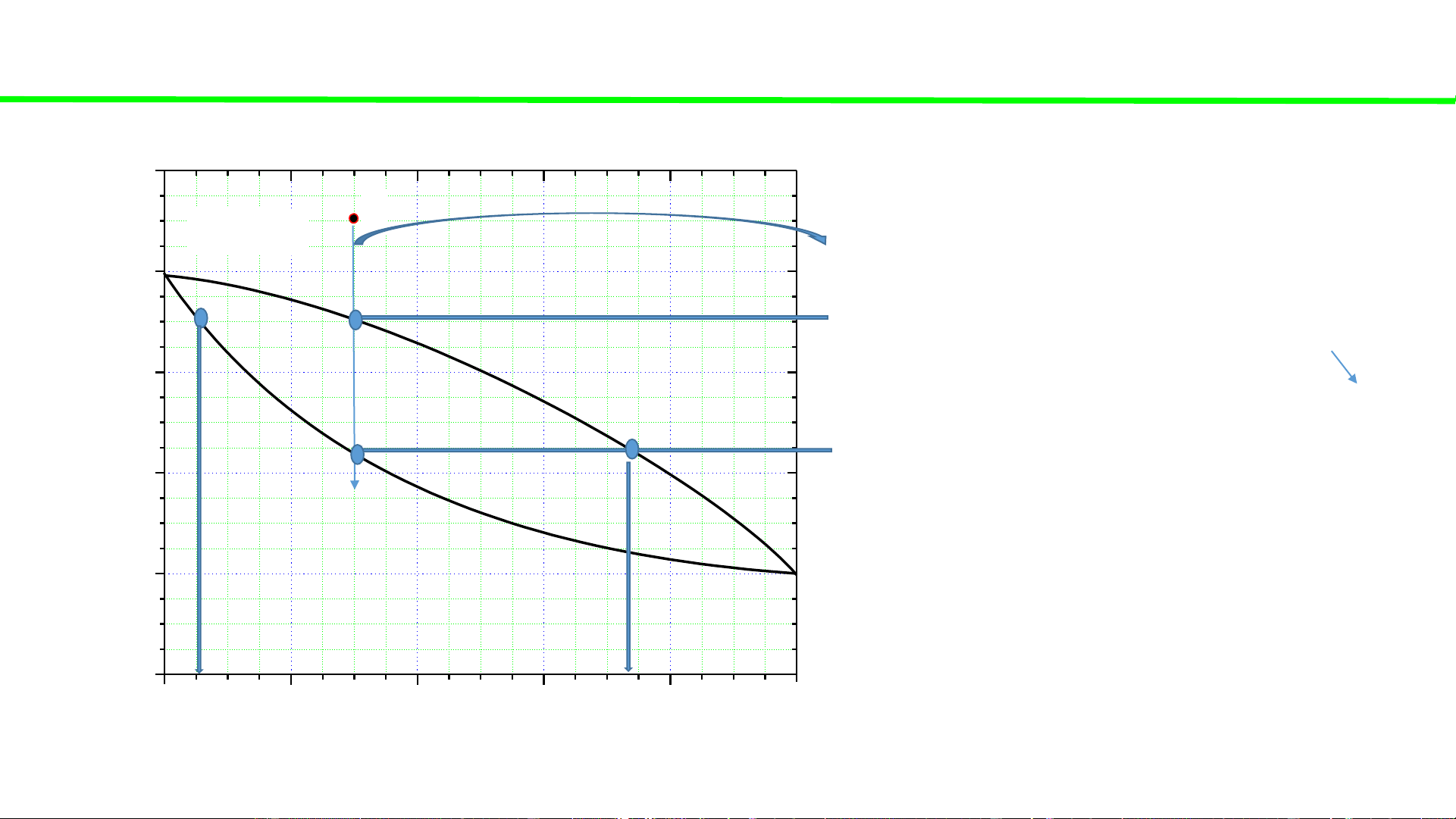
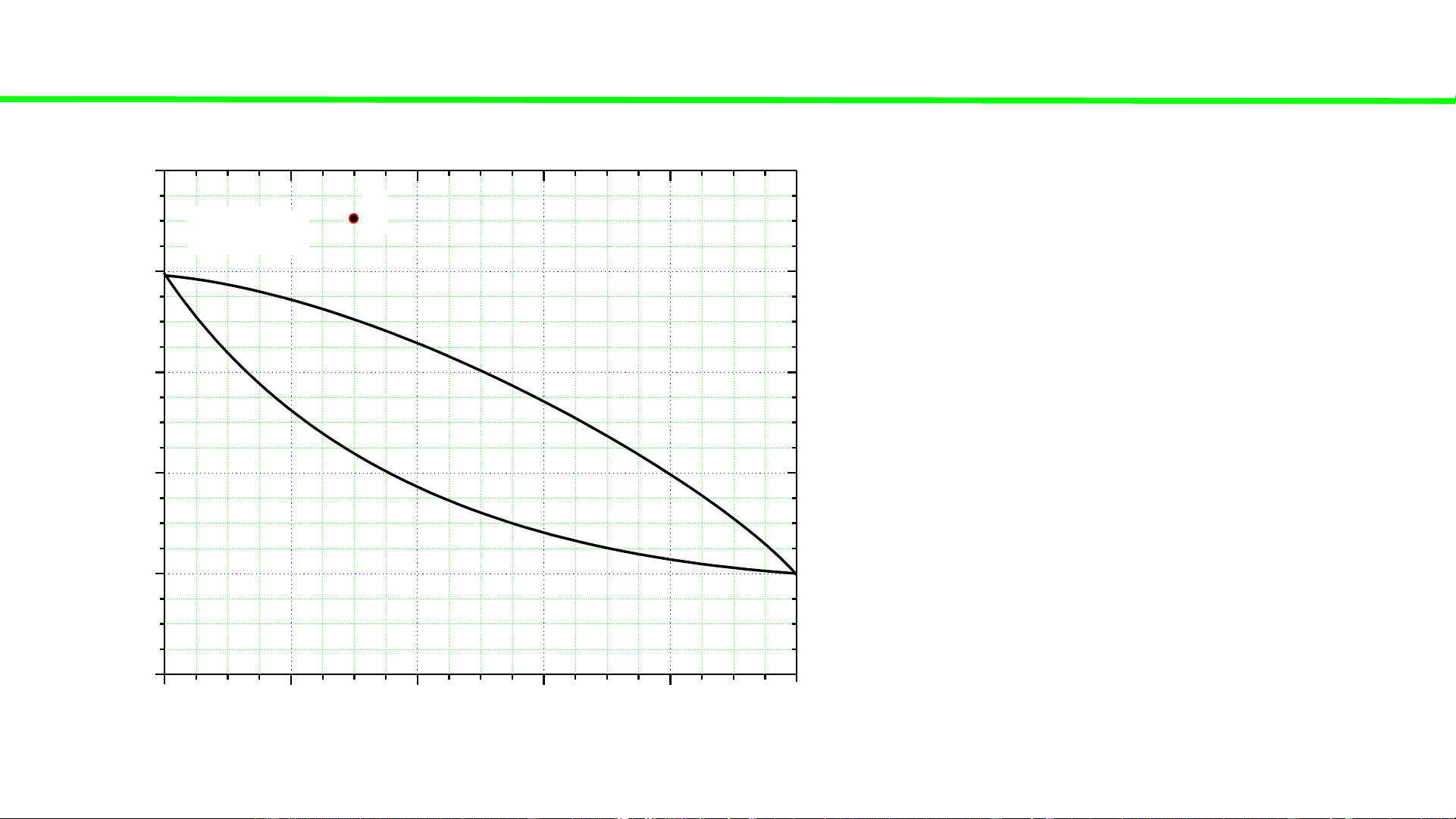
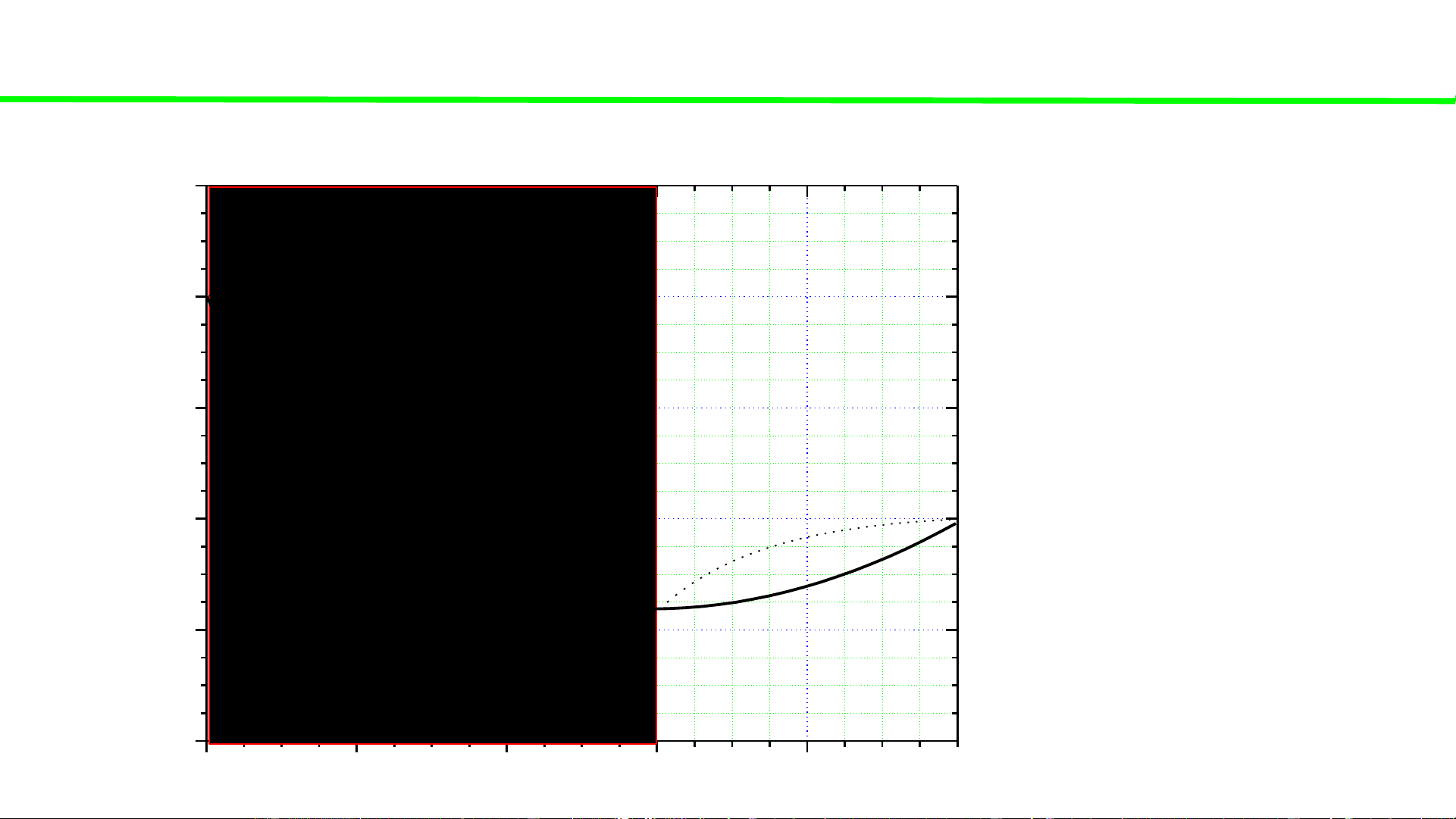
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2 totally miscible liquids without azeotrope 100 Q P const 80 60
Total vaporization, ca. 60oC C o boiling continues, T 40 T,
boiling solution starts, ca. 32oC 20 Q2
heating of liquid solution Q2 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 A % B B B
Compiled by RNDr. Ngo Manh Thang, CSc., Dr. rer. nat.
Phase diagrams - consultation
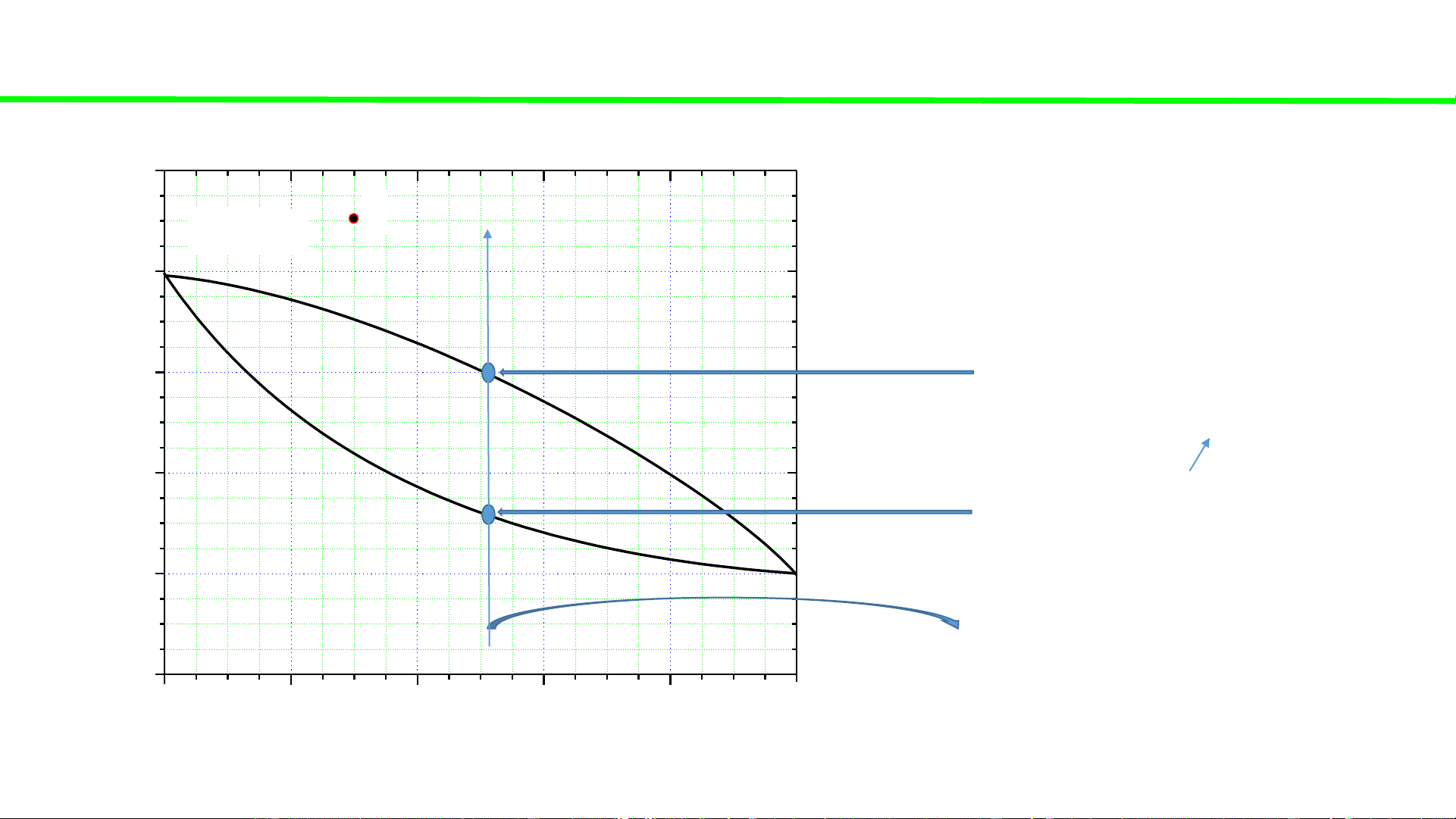
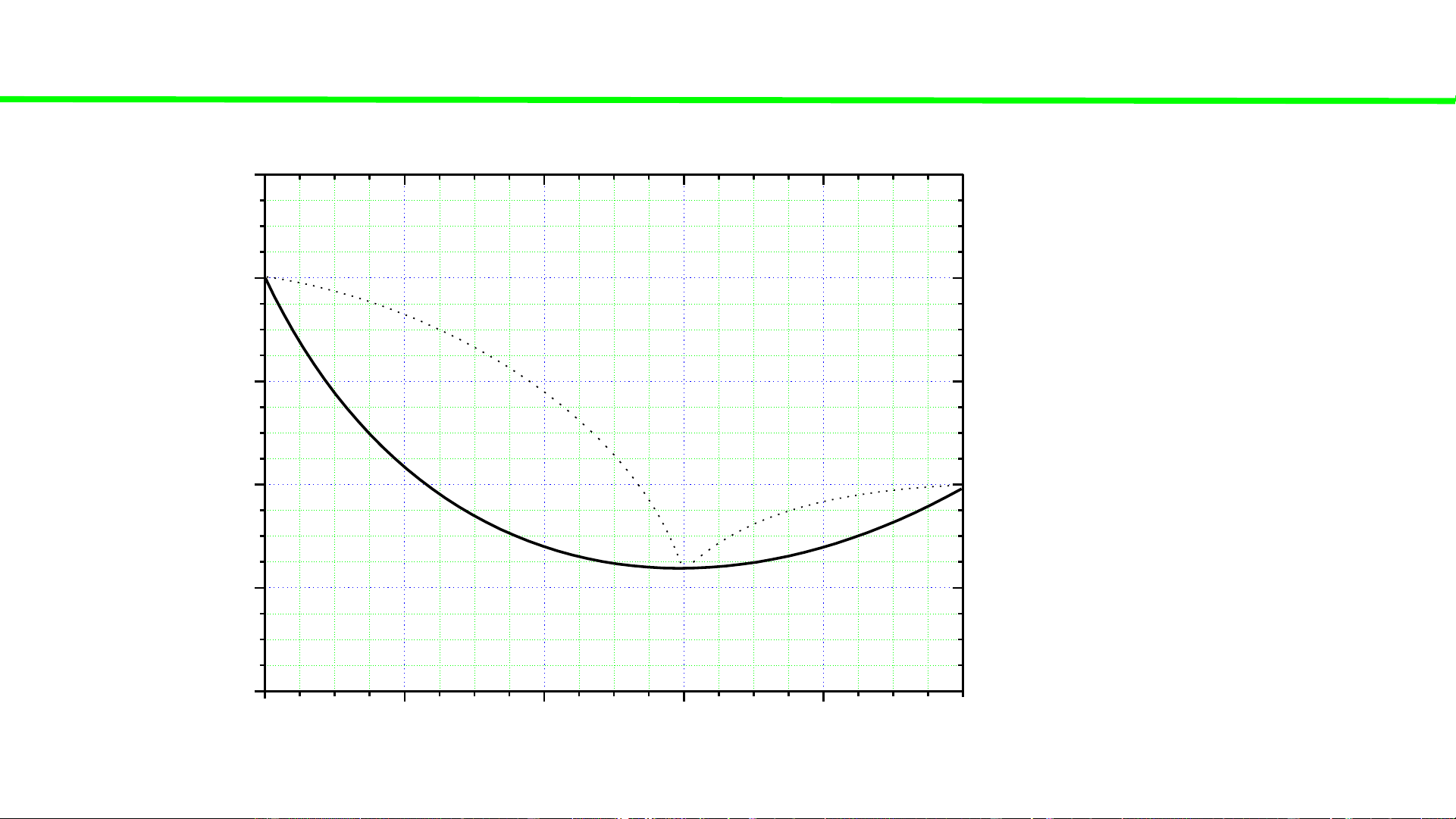
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2 totally miscible liquids without azeotrope 100 Q P const 80 60 1st gas C o Last bubble 40 T, liq. drop 20 Q2
heating of liquid solution Q2 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 A % B B B 14% B 90% B
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2 totally miscible liquids without azeotrope 100 Q
The weights of phases inside could P const 80 be calculated 60 m Q g L L 60 60 60 60 Q g C 60 60 o m Q L 40 g 60 T, 60 60 20 m m m L 60 g 60 Q 60 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 A given % B B B
Compiled by RNDr. Ngo Manh Thang, CSc., Dr. rer. nat.
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2 totally miscible liquids without azeotrope 100 Q P const
Total separation by fractional 80 Bottom of the
distillation possible. distillation tower
Necessary a suitable distillation 60 device / tower. C o 40 T, 20 top of the distillation tower 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 A % B B B
Compiled by RNDr. Ngo Manh Thang, CSc., Dr. rer. nat.
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2
totally miscible liquids with azeotrope 100 P const gaseous solution
The azeotrope behaves 80 during heating / cooling as a pure 60 compound! o p e C r o ,
It boils / condenses at a 40 e o t T
constant temperature & a z
vaporizes / condenses at 20 e the same composition. liquid solution 0 azeotrop 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 A B xB
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2
totally miscible liquids with azeotrope 100 P const gaseous solution
Total separation by 80
fractional distillation at constant pressure 60 impossible! o p e C r o , Just a portion of one 40 e o t T component could be a z
separated. Its remaining 20 e
& the 2nd component liquid solution create the azeotrope 0 azeotrop 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 solution. A B xB
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2 totally miscible liquids with azeotrope 100 P const gaseous solution
Total separation by 80
fractional distillation at constant pressure 60 impossible! Just C a portion of o , 40 component A could be T separated. Remaining A
& whole amount of B in 20 liquid solution the azeotrope solution. 0 A azeotrope
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical liquid-vapour equilibrium, 2 totally miscible liquids with azeotrope 100 P const
Total separation by 80 gaseous solution
fractional distillation at constant pressure 60 impossible! Just a portion of C o , component B could be 40 T separated. Remaining B
& whole amount of A in 20 liquid solution the azeotrope solution. 0 azeotrope x B B
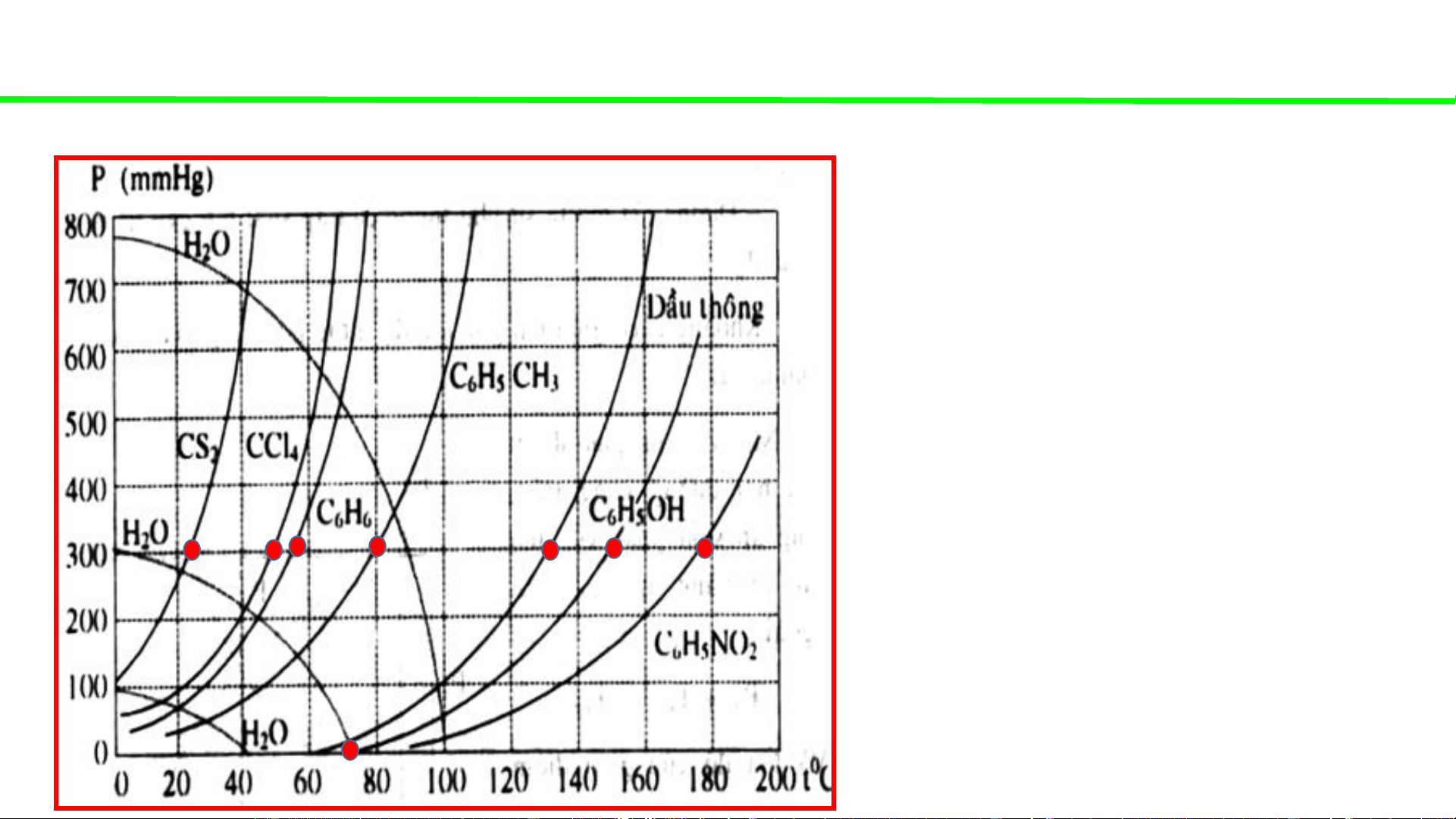
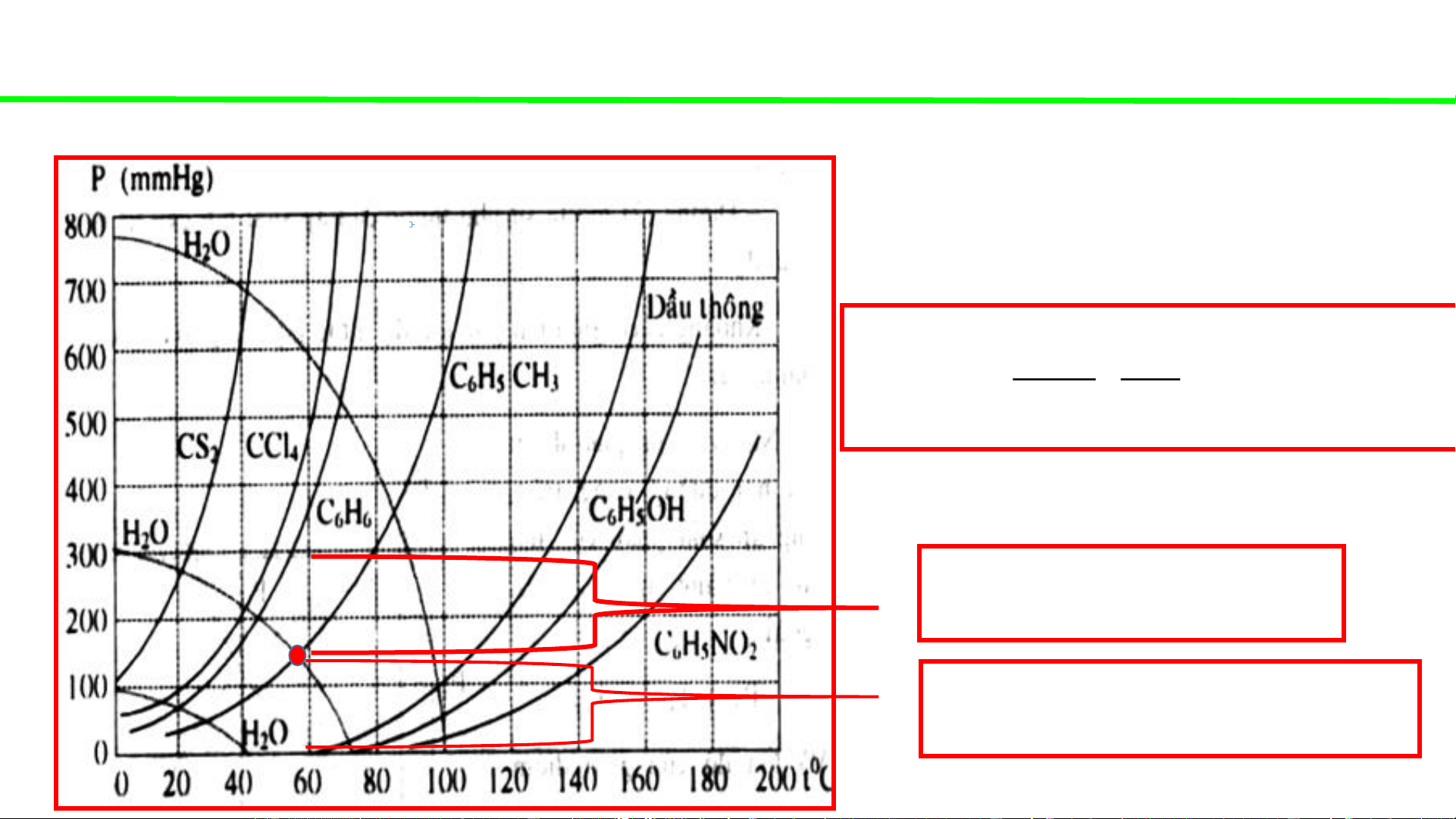
Phase diagrams - consultation
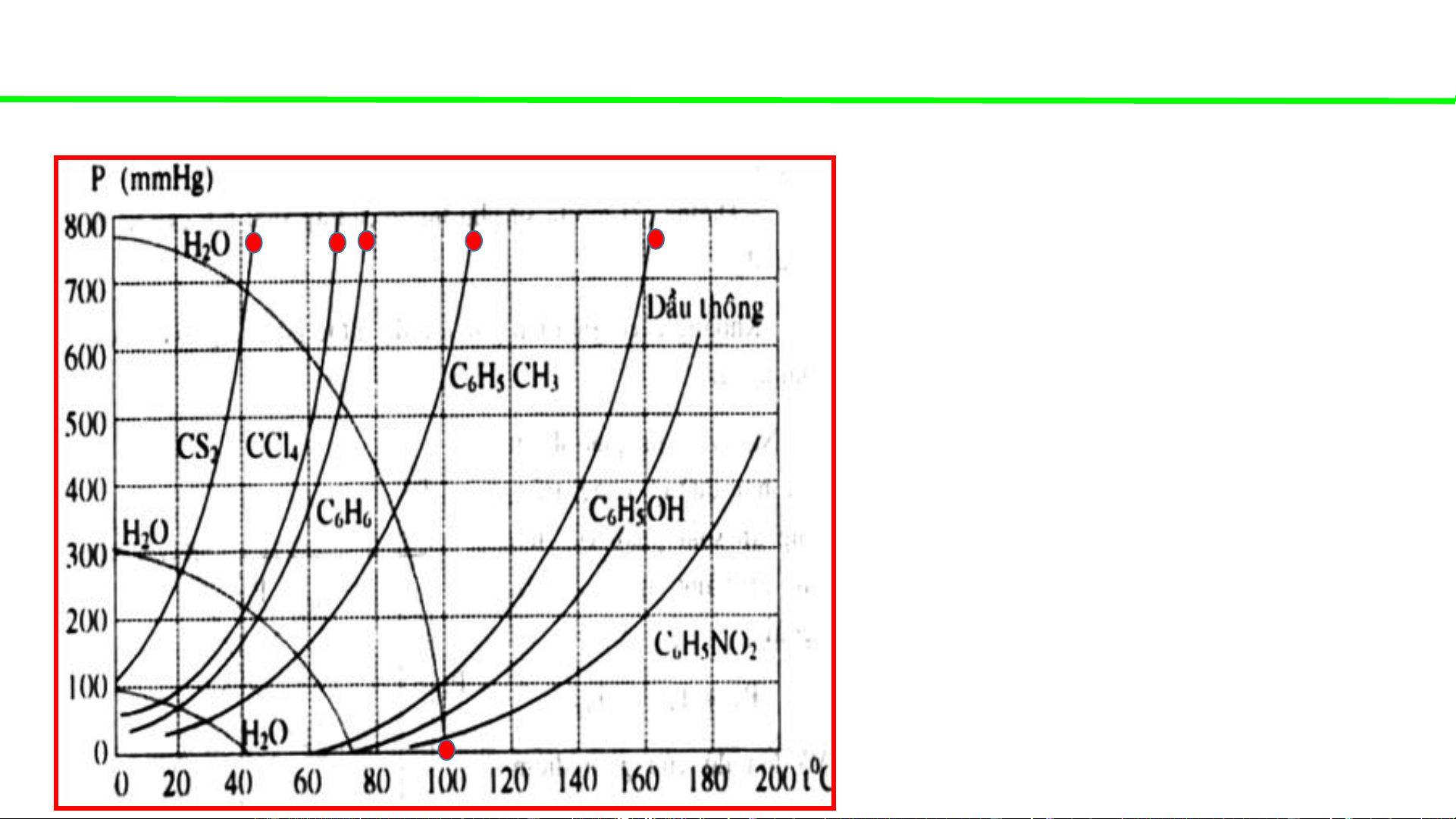
Typical pressure-temperature diagrams of water & some organic solvents
When the external pressure is
atmospheric (1atm – 760mmHg)
Water boils at 100oC
CS boils at ca. 42oC 2
CCl boils at ca. 68oC 4
C H boils at ca. 78oC 6 6
C H CH boils at ca. 110oC 6 5 3
Pine oil boils at ca. 162oC
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical pressure-temperature diagrams of water & some organic solvents
When the external pressure is
atmospheric (1atm – 760mmHg)
System (H O+CS ) boils at 2 2 41oC
System (H O+CCl ) boils at 2 4 65oC
System (H O+C H ) boils at 2 6 6 69oC
System (H O+C H CH ) boils at 2 6 5 3 85oC
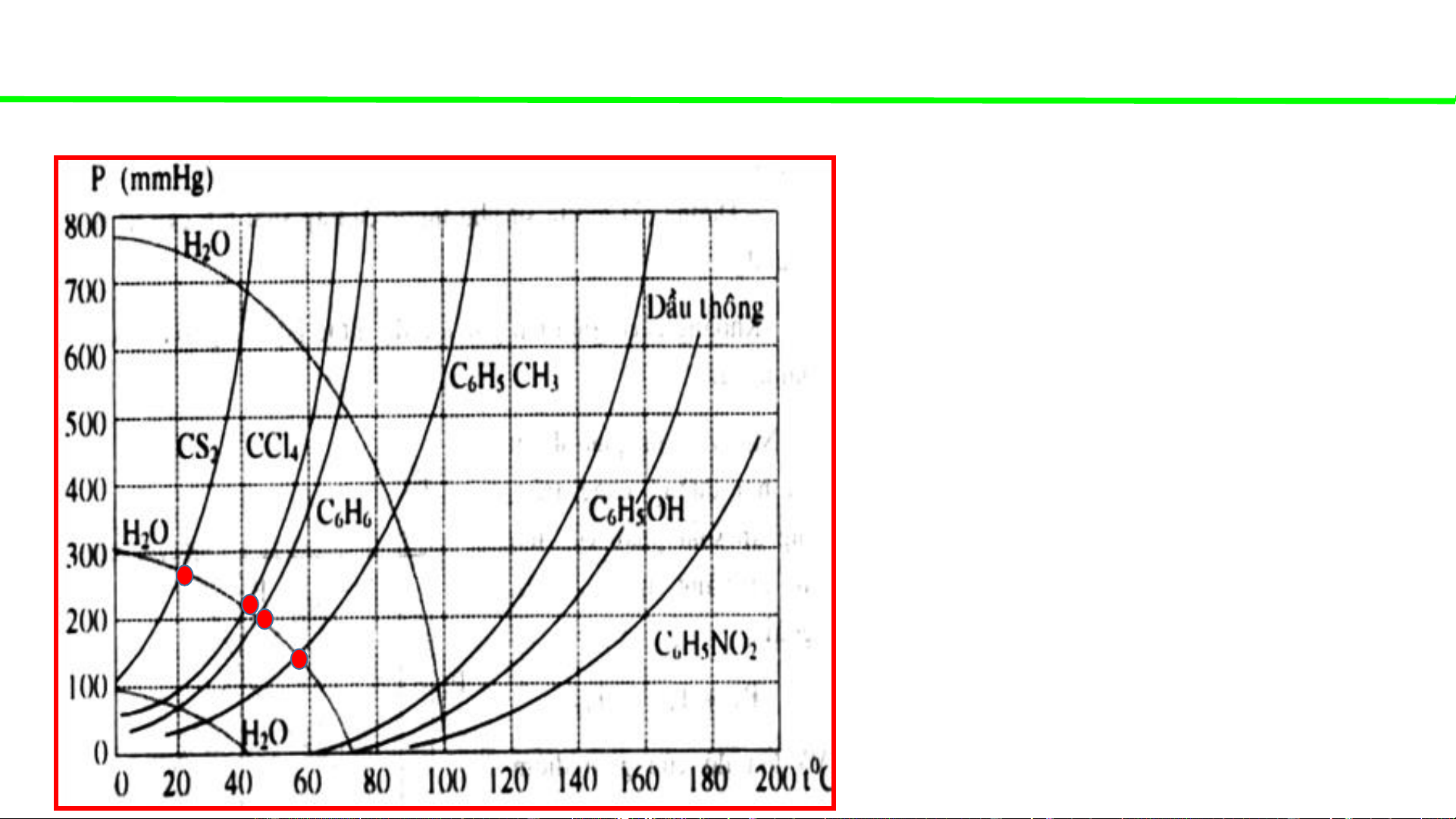
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical pressure-temperature diagrams of water & some organic solvents
When the external pressure is 300mmHg
Water boils at ca 72oC
CS boils at ca. 22oC 2
CCl boils at ca. 48oC 4
C H boils at ca. 55oC 6 6
C H CH boils at ca. 80oC 6 5 3
Pine oil boils at ca. 132oC
C H OH boils at ca. 150oC 6 5
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical pressure-temperature diagrams of water & some organic solvents
When the external pressure is 300mmHg
System (H O+CS ) boils at 2 2 ca. 22oC
System (H O+CCl ) boils at 2 4 ca. 42oC
System (H O+C H ) boils at 2 6 6 ca. 45oC
System (H O+C H CH ) boils at 2 6 5 3 ca.56oC
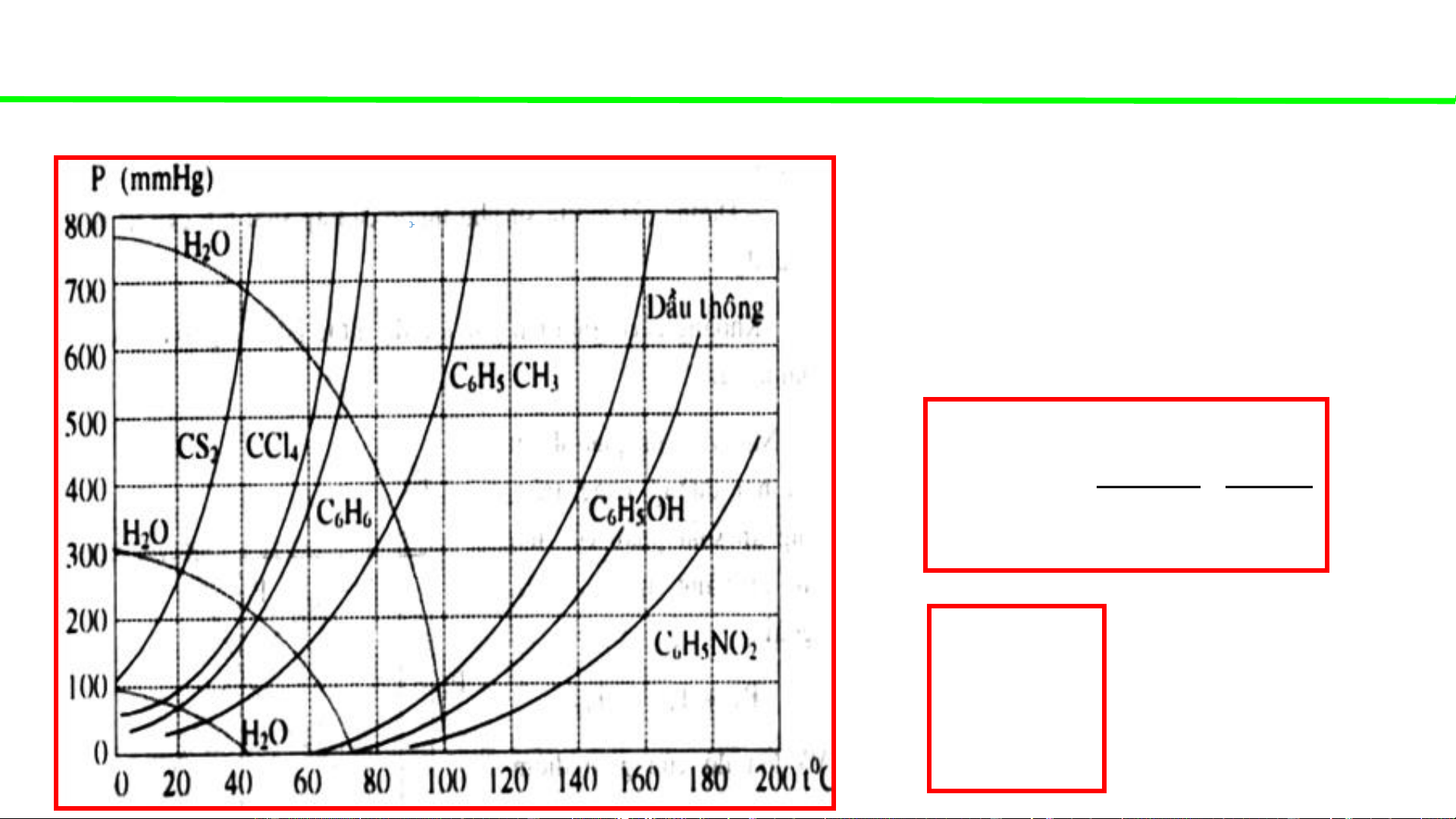
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical pressure-temperature diagrams of water & some organic solvents
The minimal amount of water (kg)
for purifying 1 kg of an organic
solvent A (with mole mass M by A steam distillation): P0 H O 18 g 2 . H O 2 P0 M A A 0 P At boiling temp. of H 2O the corresponding 0 and P mixture! A
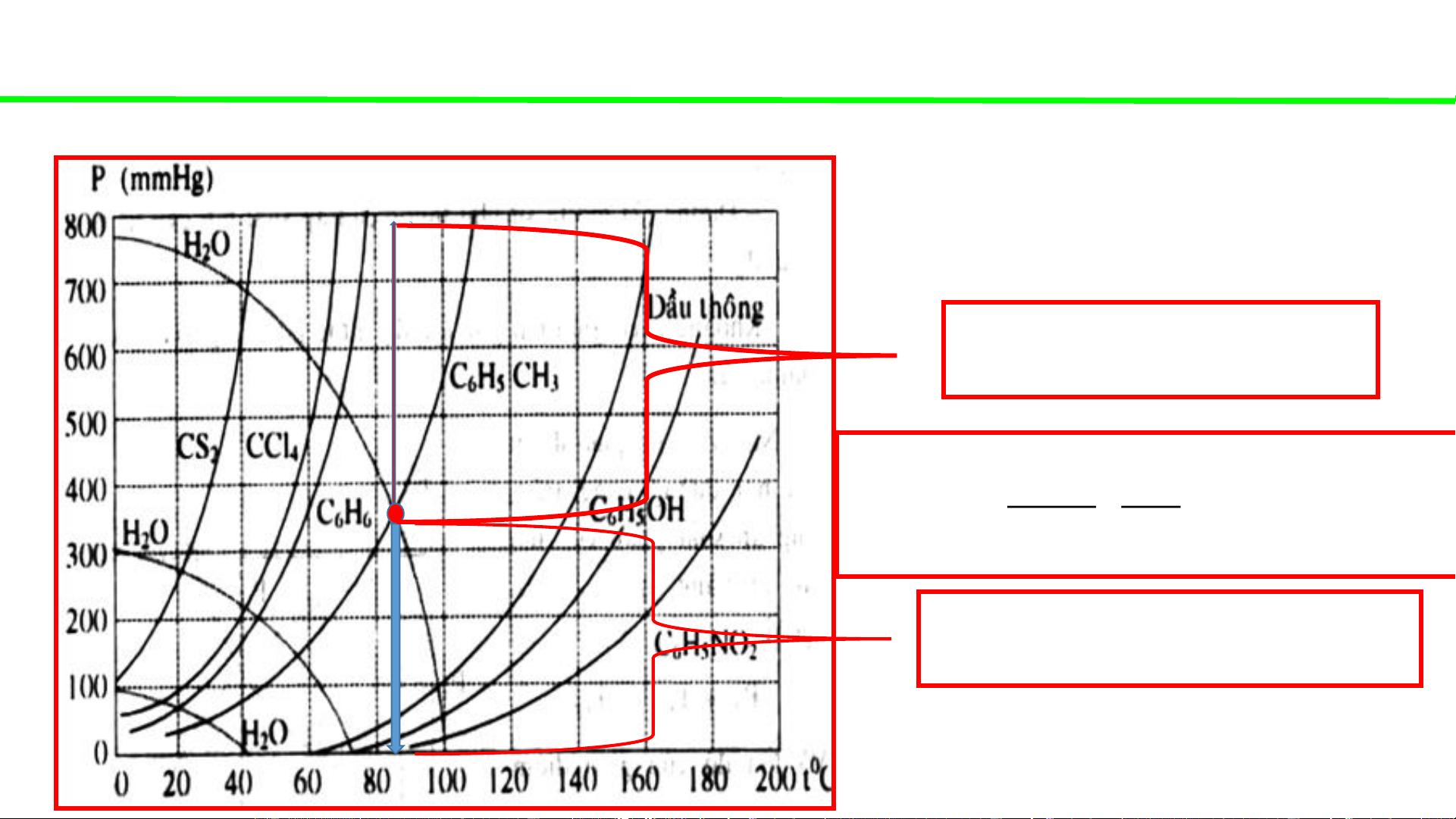
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical pressure-temperature diagrams of water & some organic solvents
Steam distillation of toluene under
atmospheric pressure 760 mmHg P0 410 mmHg H O 2 410 18 g . 2292 . 0 kg H O 2 350 92 P0 350 mmHg C H CH 6 5 3
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical pressure-temperature diagrams of water & some organic solvents
Steam distillation of toluene under
atmospheric pressure 300 mmHg 160 18 g . 2236 . 0 kg H O 2 140 92 P0 160 mmHg H O 2 P0 140 mmHg C H CH 6 5 3
Phase diagrams - consultation
Typical liquid-liquid equilibrium of 2 totally (partially) immiscible components 120
T > 110oC totally miscible P const 100 Q
110oC ≥ T ≥ 30oC partially miscible 80
T ≤ 30oC totally immiscible C o , 60 T system Q is homogeneous system Q is a liquid 40 solution with conc. 80% B at temperature 100oC 20 0 20 40 60 80 100 A B % B
Phase diagrams - consultation
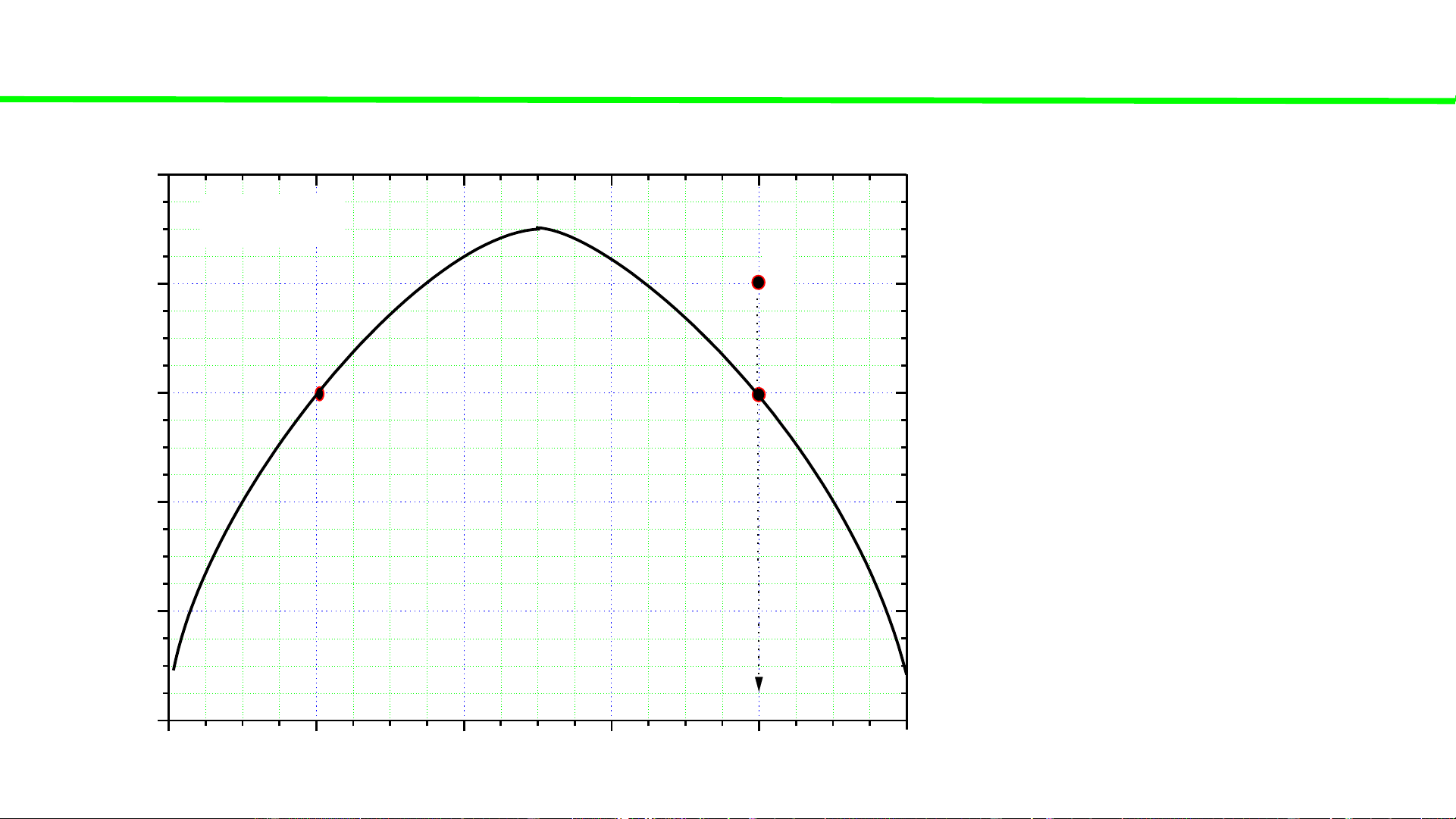
Typical liquid-liquid equilibriu
m of 2 totally (partially) immiscible components 120 P const Q Cooling system Q 100 system Q becomes 80 heterogeneous at 80oC C o ,
At 80oC, the solubility of 60 T A in B is 20% (A), and
the solubility of B in A is 40 20% 20 0 20 40 60 80 100 A B % B


