






Preview text:
AMERICAN CULTURE
UNIT 1: SYMBOLS AND HOLIDAYS
Module 1A: American Symbols
A/ The Flag of the United States. The British flag.
Before the American Revolution, it was the flag of the thirteen American colonies. The “Great Union Flag”
the flag of the American army during the Revolutionary War.
(The flag of England was in the corner, the red and white stripes
were symbol for the 13th American colonies)
Betsy Ross made the first American flag (The corner
13 white stars in a field of blue, 7 r ed and 6 white stripes)
The flag during the War of 1812
Had 15 stars and 15 stripes for 15 states
Francis Scott Key wrote a song about the American flag
(The “Star – Spangled Banner” became the national anthem of the US)
The US grew and admitted more states to the Union
13 stripes (for 13 original colonies) 50 stars (for 50 states)
White: purity, innocence; Red: bravery, valor, streghth; Blue: justice, perseverance
The Pledge of Allengiance is a promise of loyalty to the United States
NguyenDoHoangKhanh – 02000066
B/ More American Symbols
The Declaration of Independence - The delegates of the 13 th colonies planned it - Thomas Jefferson wrote it
- declared the independence of the colonies from England The Liberty Bell
- rang out on July 4th (when Congress adopted and the delegates signed
the Declaration of Independence)
symbol of the Declaration of Independence
(in the State House, Philadelphia) The Statue of Liberty
- A gift of friendship from France in 1884 - Now
symbol of freedom for new immigrants to this coutry The American eagle
the official emble of The US
- appears on the Presidental flag and some coins The donkey and the elephant
- appeared in political cartoons
symbols for the Democratic (donkey) and Republican (elephant) Parties Uncle Sam
- original appeared in political cartoon.
unofficial symbol of the U.S. government
NguyenDoHoangKhanh – 02000066
Module 1C: More National Holidays Date of Calendar Holiday Purpose celebration date
The celebration of the calendar new New Year’s Day January 1 January 1 year Martin Luther The 3rd Monday
The memberance of the civil rights January 15 King, Jr Day in January leader’s birthday February 12 The 3rd Monday (Lincoln)
A birthday celebration for 2 famous Presidents Day in February February 22 Presidents (Washington)
The rememberance of past wars and a Memorial Day The last Monday May 30
day to visit military and family graves (Decorated Day) in May (for the death) Independence July 4 July 4
The birthday of the United States Day The first The first Monday
A celebration of the industrial spirit Labor Day Monday in in September and the dignity of work September The second
The rememberance of Christopher Columbus Day Monday in October 12 Columbus and his spirit of October achievement The honoring of Americans who Veterans Day November 11 November 11
fought in wars and a promise to work (Armitice Day) for peace (die and still live) The fourth The fourth
A day to gather friends, feast, and give Thanksgiving Day Thursday in Thursday in thanks November November
The celebration of the birth of Jesus Christmas Day December 25 Decemeber 25 Christ
NguyenDoHoangKhanh – 02000066 UNIT 2: AMERICANS
Module 2A: Famous Presidents 1. George Washington:
- 1st President (1789 – 1797) fouding (birth)
- a farmer in the colony of Virginia
- served as a military leader in the Revolutionary War
- be often called “the Father of Our Country.”
- an American politician ans soldier
- the 1st to sign the US Constitution - never abused power
“It is our true policy to steer clear of permanent alliance, with any portion of the foreign world.” – G.Washington 2. Thomas Jefferson:
- 3rd Presidents (1801 – 1809) growth (expansion)
- a farmer and a lawyer in Virginia
- a scientist, an inventor, a philosopher, and an architect
- could communicate in French, Italian, Spanish, Latin and Greek
- many of his ideas became basic principles of the government of the US
- “all men are created equal”
- was credited with the expansion the country to the west - helped developing democracy Democratic Party
- the author of the Declaration of Independence
“We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are
endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty
and the pursuit of Happiness.” – Thomas Jefferson 3. Abraham Lincoln:
- 16th President (1862 – 1865) preservation
- grew up in Kentucky in a log cabin
- Illinois congressman against slavery
- self-educated lawyer, legislator
- created with holding the country together during the civil war
NguyenDoHoangKhanh – 02000066
- was instrumental in the abolishment of slavery
- established Thanksgiving as a national holiday
- 1865, he was shot by an actor – John Wilkes Booth
“A house divided against itself cannot stand." I believe this government cannot endure,
permanently half slave and half free.” – Abraham Lincoln 4. John F. Kennedy:
- 35th President for only 3 years (1961 – 1963)
- the 1st Roman Catholic and the youngest President in the history
- supported the ideas of Martin Luther King, Jr fought for civil right s, fair housing, and programs to stop poverty
- asked for more money for education and medical care for elderly people - 1963, he was assassinated
“And so, my fellow Americans: ask not what your country can do for you — ask what you
can do for your country. My fellow citizens of the world: ask not what America will do for
you, but what together we can do for the freedom of man.”
Module 2B: The history of Immigration 1500’s
25 million “native Americans” (Indians) lived in North and South America 1600’s
the largest immigrant group to settle in the North (farmer, fishermen, traders)
- many immigrants from Scotland, Ireland, France, Holland, Germany,
Sweden, and Poland most: Protestants 1700’s
- The Spanish settled mainly in the Southwest (California) (managers, priests,soldiers) 1600’s to
American slave traders captured black Africans force them to work on 1800’s plannations
- About 3.5 million Irish Cathlics left poverty and discrimination work in 1820 to
America (coal miners, railroad, canal builder) 1880 - Many Germans
farmers, laborers, and businessmen
NguyenDoHoangKhanh – 02000066 1850 to
100,000 poor Chinese came to work in mining camps and on the railroad 1870 1880 to
25 million Europeans immigrants to America 1930 1940’s
The US welcomed thousands of refugees after the WWII 1950’s 1960’s
Abolished quotas for immigrants from non-European nations (from Asia and 1970’s Latin American)
Module 2C: Historical Figures
1. Henry Ford was an automobile manufacturer and the first to sell cars with eight-cylinder engines.
2. Samuel Clemens wrote newspaper stories and spoke on issues such as the responsibility
of the white man toward other people. He was the author of Tom Sawyer, Huckleberry Finn, and other famous stories.
3. Eleanar Roosevelt was the wife of a President. She worked for many causes. As a U.N.
delegate, she was a leader in the fight for human rights.
4. Susan B. Anthony led the battle for women’s rights, espeacially the right to cote. She
fought against slavery and for Black rights. She was for prohibition.
5. Hideyo Noguchi made discoveries about polio and other diseases. His work led to avaccine for yellow fever
6. Bejamin Franklin was a Fouding Father of the US. He wrote, published, created useful
inventions, worked on the Declaration of Independence and the US Constitution, and was a diplomat to other countries.
7. John James Audubon loved nature and painted pictures of birds. A society named after him works to protect birds.
8. Lawrence Welk was a TV host and band leader. He represented American values such as
cooperation, hard work, honesty, and healthy living
9. Duke Ellington wrote jazz and music for opera, ballets, shows, and films. He was the creator of big and jazz.
NguyenDoHoangKhanh – 02000066
10. Clara Barton started the American Red Cross. She worked to help the victims of wars and natural disasters.
11. Thomas A. Edinson created machines for stock brokers and telegraph services, the light
bulb, the movie projector, the phonograph, and other useful inventions,
12. Cesar Chavez led the protests of field workers against grape and lettuce growers and
began the United Farm Workers of America. His union continues to organize boycotts and protest the use of pesticides. UNIT 3: GEOGRAPHY
Module 3A: The Geography of the United States
A/ The position and the size of the U.S.
- The 4th largest country in the world in land area (after Russia, Canada, and China)
- 48/50 states are in the middle of the North American continent btw the Atlantic Ocean on
the east and the Pacific Ocean on the west.
- The island state of Hawaii is in Pacific Ocean (youngest state – 50th state)
- The state of Alaska is northwest of Canada (Artic Oc. – 49th state) - The east coast the west coast: 3000 miles (4800km) - The Canadian border (north)
the Mexican border (south): 1500 mile s (2400km) Canadian border 1500 miles (2400 km) Pacific Ocean Atlantic Ocean Mexican border West coast East coast 3000 miles (4800 km)
NguyenDoHoangKhanh – 02000066
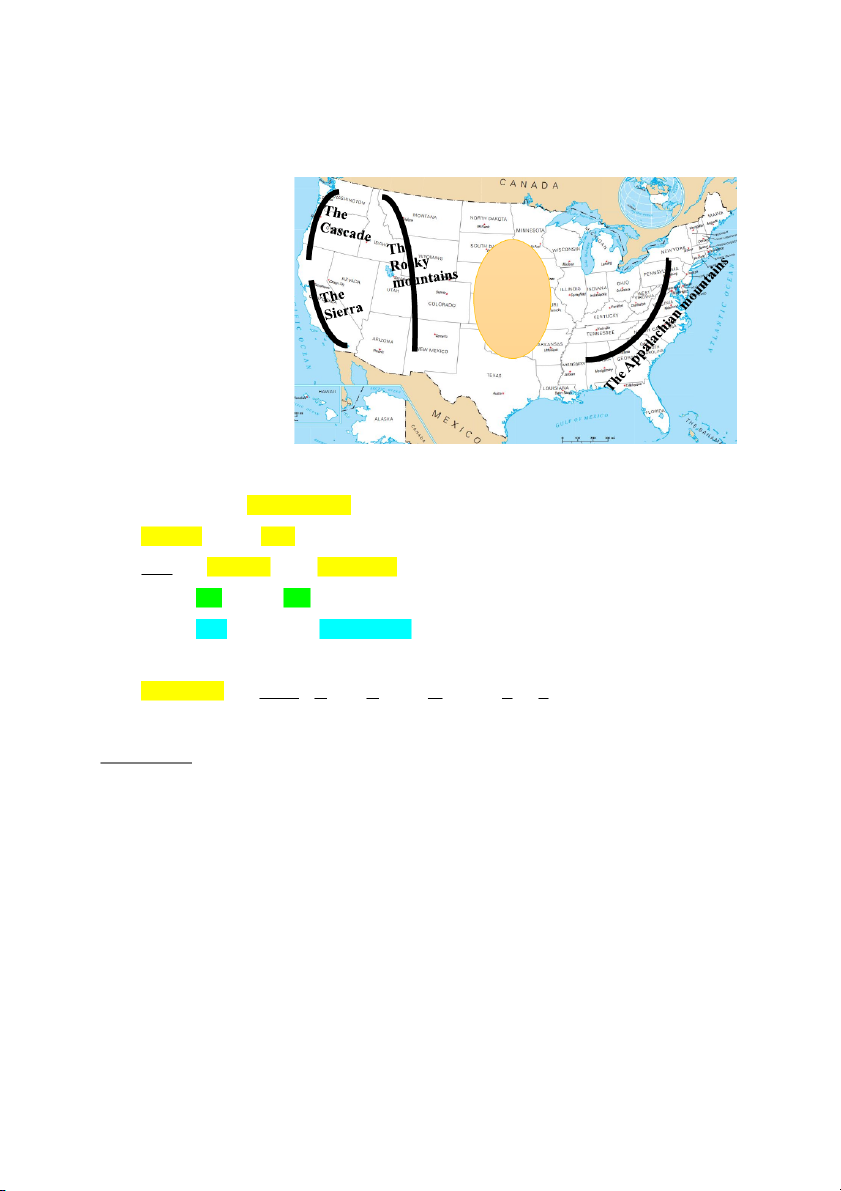
B/ The mountain, river and lake system of the U.S. 1. The Mountain:
- 2 main mountain ranges: Appalachian mountain (in the east) Rocky mountain (in the west) The Great - another mountain chain Plain west of the Rocky: Sierra Cascade - btw them the Great Plain 2. The river:
- The longest river is the Mississippi
- The Missouri and the Ohio flow into the Mississippi into the Gulf of Mexico
- The west: the Colorado & the Rio Grande - River to the east flow east - River to the west flow into Pacific ocean 3. The lake:
- The Great Lakes (the North): Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, Superior - The Great Salt (the West) in the desert area
Module 3B: Famous places 1. Washington D.C.
- Before 1800, the capital of the US is New York city
- G. Washington first took office in New York city in 1789 - Capital in Philadelphia - 1790: Washington DC the capital of the US - D.C.: district of Columbia
- The district derived from Christopher Columbus
- Washington: named after President G. Washington
NguyenDoHoangKhanh – 02000066
- Not belong to any state, but in federal district
The US Capitol (Capitol Building): Congress – the Senate and the House of
Representative – meet in this building ad makes the laws of the land
The Library of Congress: has copies of all books with a US Copyright
The National Archives: saw 2 important original documents – the Declaration of
Independenceand the US Constitution
The Washington Monument: was built in 1848 – 1885 in honor of G. Washington (1st President of the US)
The Jefferson Memorial: built in 1938 – 1943 in memory of Thomas Jefferson (3rd President of The US)
The Lincoln Memorial: built in honor of Abraham Lincoln, a statue of Lincoln & 2
murals with symbols of freedom ad justice, 2 huge stone tablets Lincoln’ s important speeches
The White House: at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue, built in 1792 – 1800, official residence
and work place of the President
2. New York (capital: Albany) Statue of Liberty
Empire State Building: the name is derived from “Empire State” (NY’s nickname)
Brooklyn Bridge: one of the oldest suspension bridges in the US
Central Park: fifth largest park in New York city; most visited urban park in the US,
estimated 37.5 – 35 million visitors annually and one of the most filmed locations in the worlds Time Square:
Gateway Arch: on Mississippi River
Golden Gate Bridge: suspension bridge, symbol of San Francisco and the US
Universal Studio (in California) Module 3C: The states 5 biggest states: 5 smallest states: - Alaska - Rhode Island - Texas - Delaware - California - Connecticut - Montana - Hawaii - New Mexico - New Jersey
NguyenDoHoangKhanh – 02000066 s
NguyenDoHoangKhanh – 02000066



