Preview text:
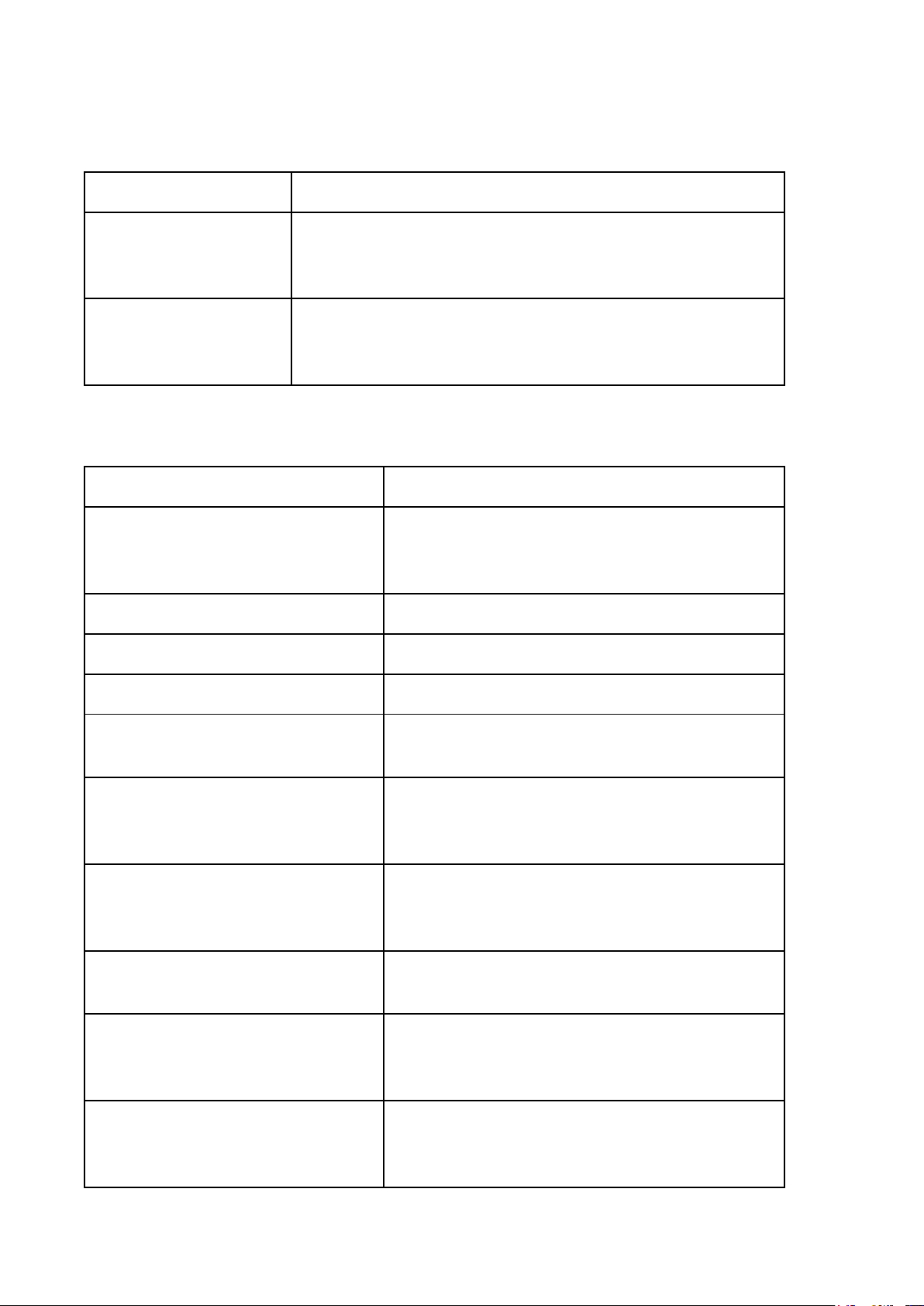
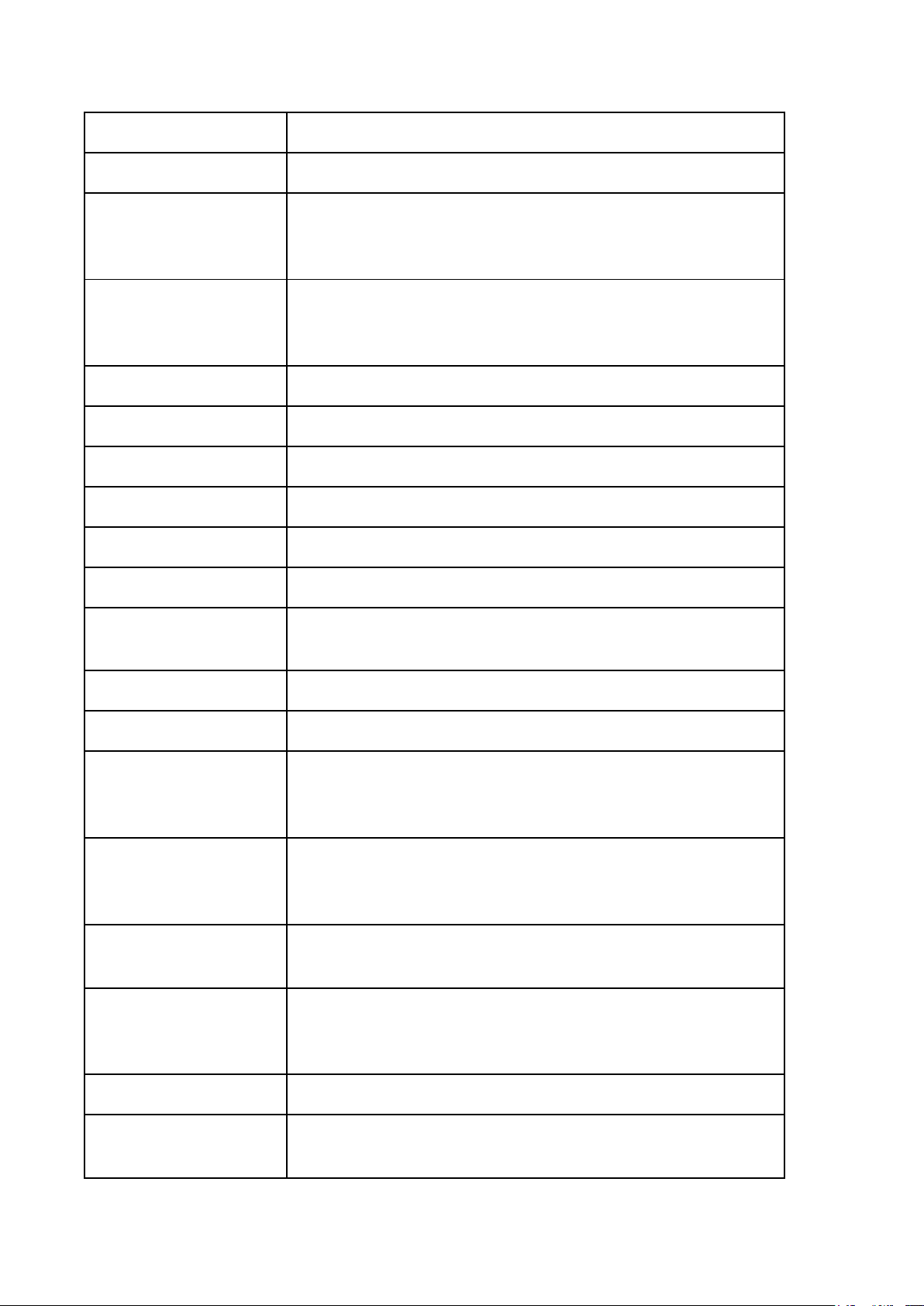
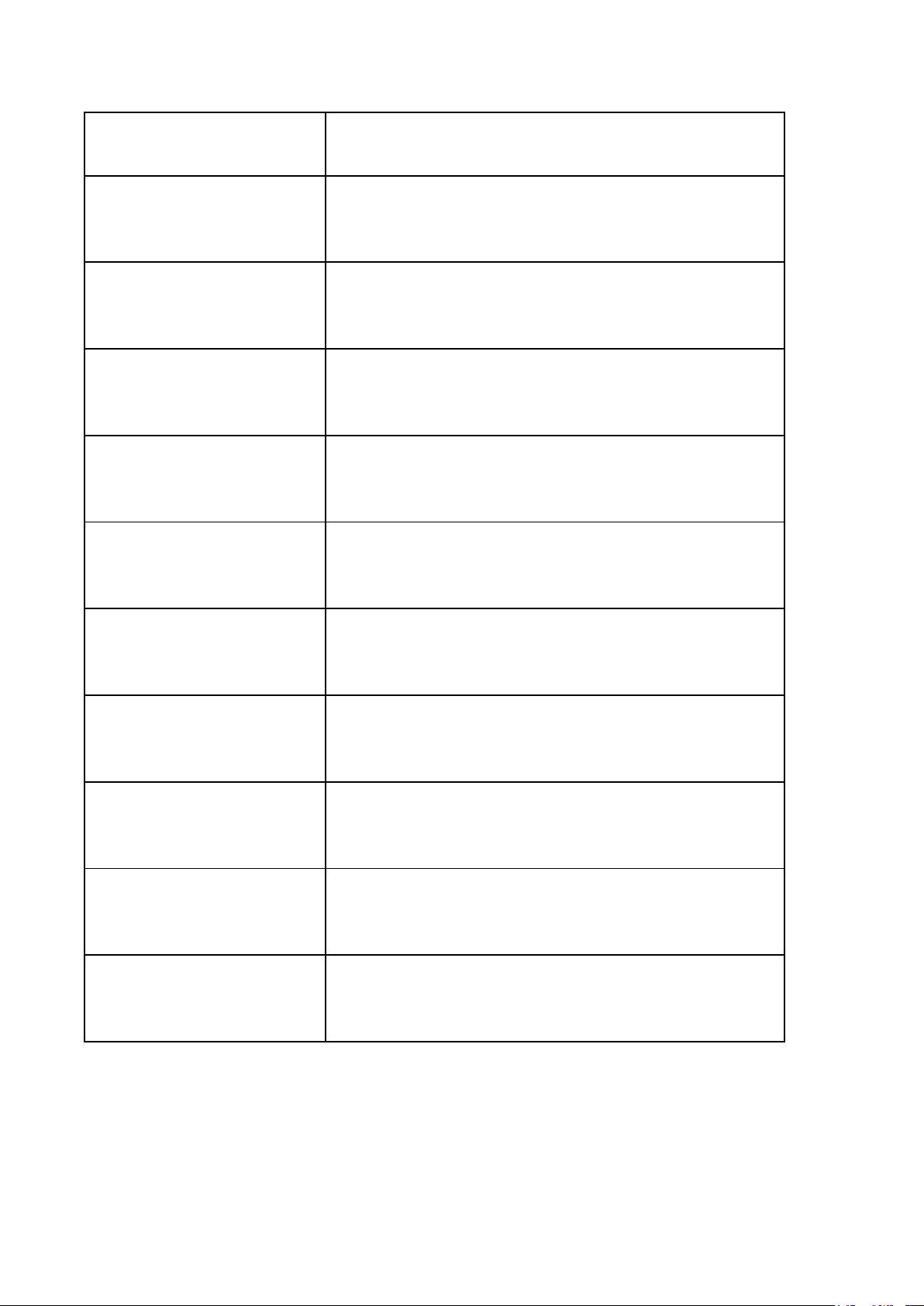
THEORY OF STATE LESSON 1: Nhập môn Legal words Descriptions
Deductive Arguments Diễn dịch
(begins with a general proposition and ends with either a
general or a particular proposition.) Inductive Argument Quy nạp
(begins with a particular proposition and ends with either a
general or a particular proposition.)
LESSON 2: THE ORIGINS AND EVOLUTION OF STATES (Nguồn gốc nhà nước) Legal words Descriptions Law Luật
(A system of rules that regulates the conduct of a community) Customary law Tập quán pháp Precedent Án lệ Legal documents
Văn bản quy phạm pháp luật Legal system Hệ thống pháp luật
(A set of rules or laws, procedures.) State Nhà nước
(A political entity that has sovereignty over a
defined territory and its population.) Divine Right Theory Thuyết Thần Quyền
(The idea that the right to rule comes from God) Patriarchal Theory Thuyết Gia Trưởng
(The state originates from the family.) Social Contract Theory
Thuyết Khế ước xã hội
(Present the State as a product of the mutual agreement of men) Force Theory Thuyết bạo lực
(One person/small group claimed control over
an area and forced ALL within it to submit to
the person’s/group’s rule)
Marxism-Leninism of state origin Thuyết nhà nước của Marxism - Lenin
Socio-economic Patterns
Hình thái kinh tế xã hội Primitive commune Công xã nguyên thủy Slavery possession Chiếm hữu nô lệ Feudal Phong kiến Capitalist Tư bản chủ nghĩa Communism Cộng sản chủ nghĩa Social power Quyền lực xã hội
(is a central element in analyzing human
society and how it is organized.) Political power Quyền lực chính trị
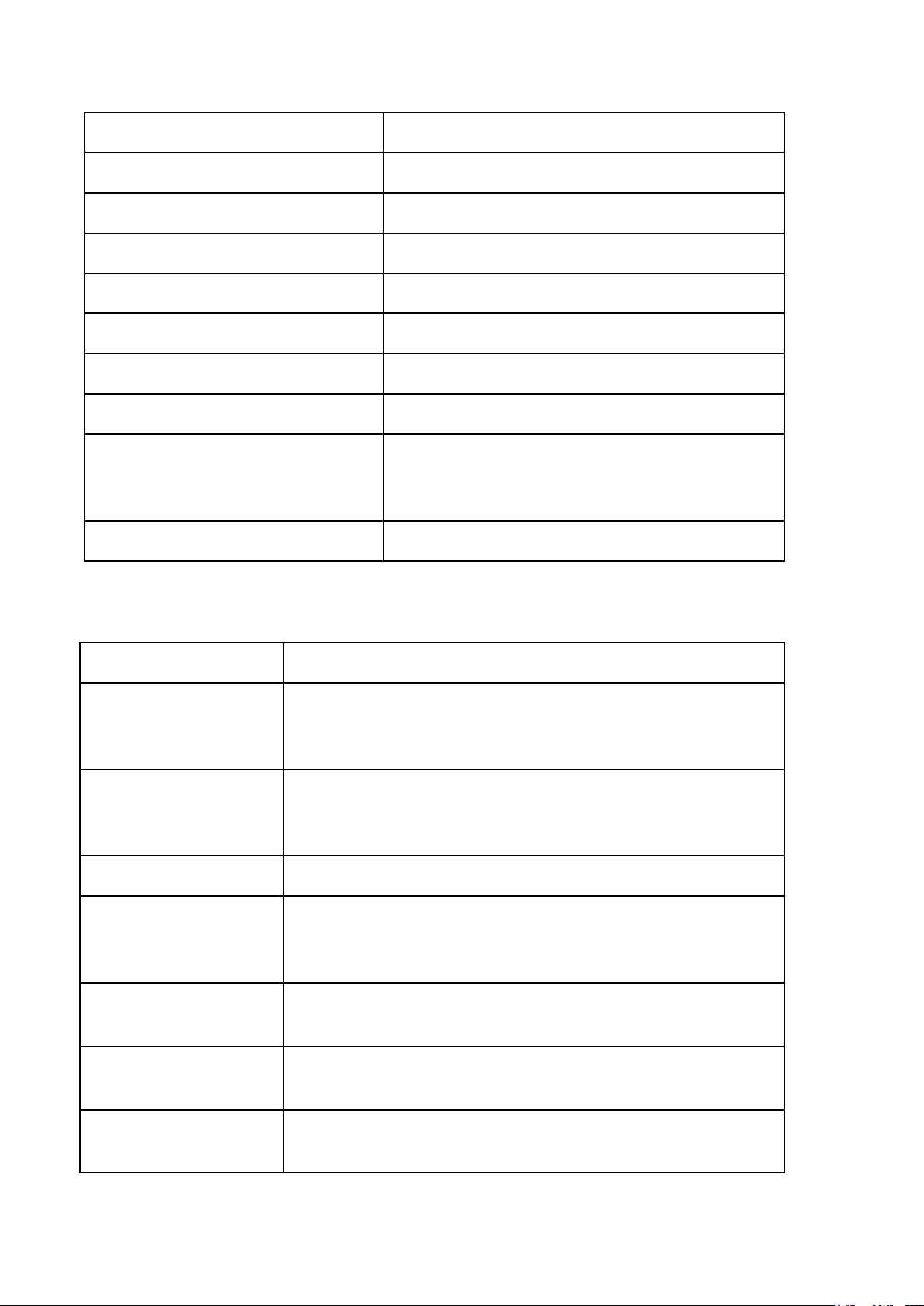
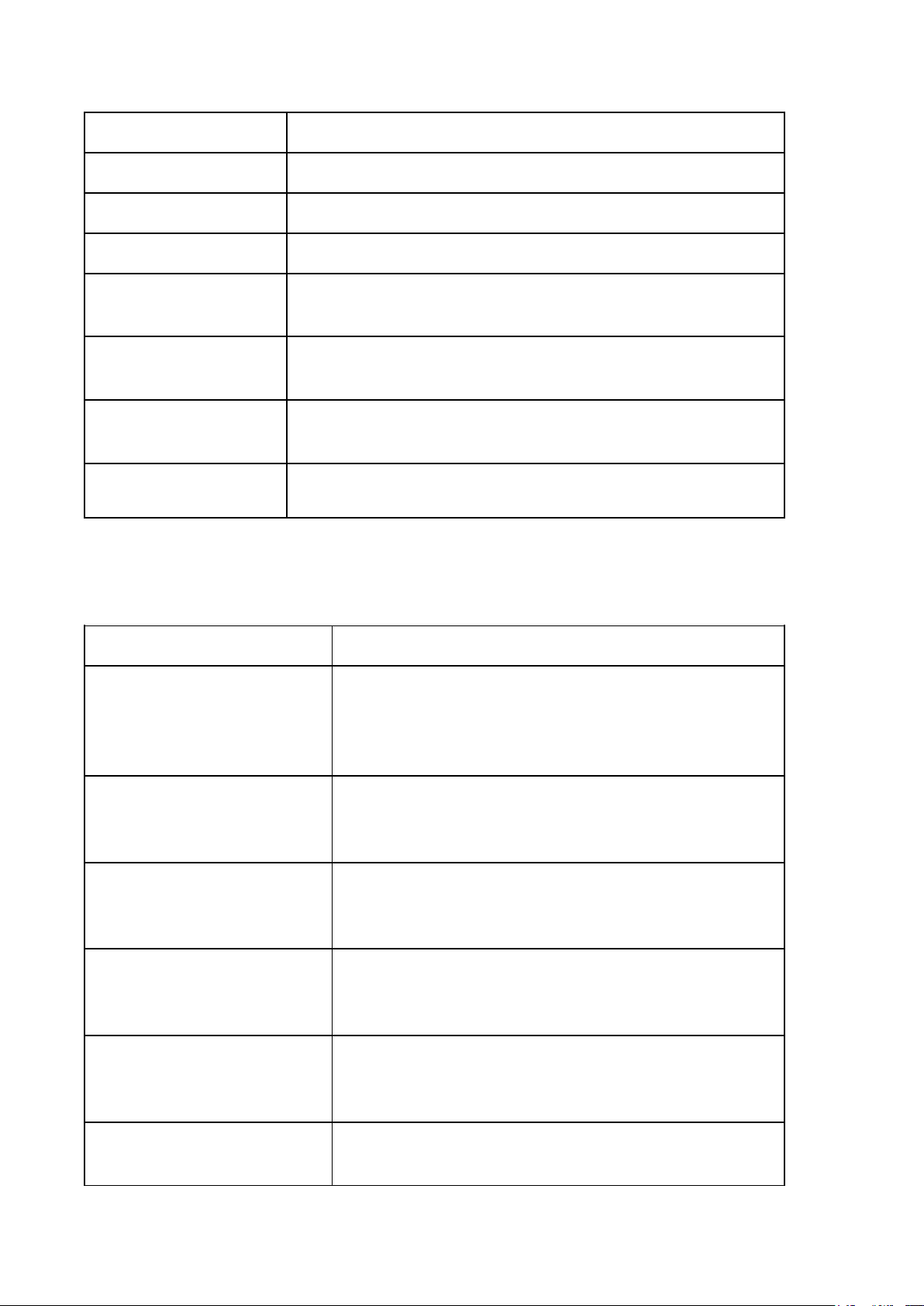
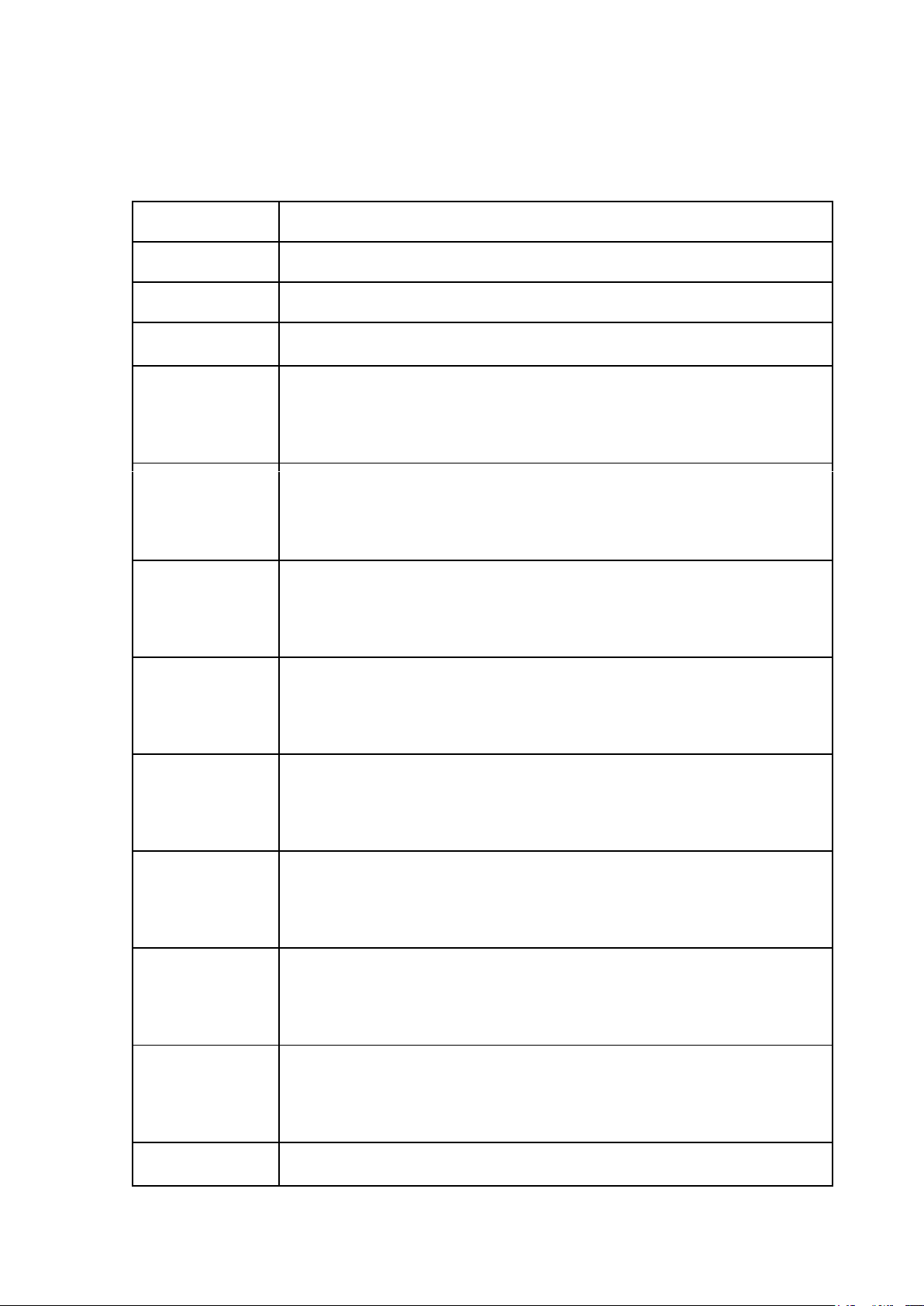
LESSON 3: THE NATURE OF THE STATE (Bản chất nhà nước) Legal words Descriptions Power Quyền lực
(a relationship between two social actors or entities (groups and individuals) ) Nature of the state Nguồn gốc nhà nước
(internal relations and rules that play a decisive role in the state’s basic development) Class nature
Tính giai cấp (the essential nature of a state) Economic power Quyền lực kinh tế
(The ability to control all resources of the economy and society.)
Economic orientation Kinh tế thị trường định hướng xã hội chủ nghĩa
(market economy followed by a socialist oriented economy) Economic sectors
Sự phân chia nền kinh tế của một quốc gia thành các lĩnh
vực sản xuất hoặc dịch vụ khác nhau. Political power Quyền lực chính trị
(Refers to the authority and ability to influence or control
the actions, policies, and decisions of a state or government.) Ideological power
Quyền lực tư tưởng (Refers to its ability to influence
societal beliefs, values, and norms through various methods.) Social nature Tính xã hội Concept of a state
Khái niệm về nhà nước
(political organization that has special public power. It was
founded and existed due to the requirements of class
conflict settlement and public services.) Features of a state
Đặc điểm của nhà nước Population Dân số
(The group of people who are the members or citizens of a state) Territory Lãnh thổ
(The area in which a state’s rule applies.) Sovereignty Chủ quyền Government Bộ máy nhà nước
(The organization within a state that controls the actions and policies of the state.)
Special public power Quyền lực công cộng đặc biệt People and territory
Phân chia dân cư theo lãnh thổ thành các đơn vị hành chính management Sovereignty Chủ quyền quốc gia Law
Ban hành luật và quản lý đất nước bằng pháp luật Tax Thuế Natural Law Luật tự nhiên
(a system of moral principles and rules that are inherent in
human nature, universal, immutable, and independent of state enactment.) Positive Law Luật thực định
(the body of law formally enacted or recognized by the
state and enforced through state authority.) International Law Luật quốc tế
(a system of legal principles and rules that govern relations
between states and other subjects of international law.) Rule of Law
Nguyên tắc pháp quyền/Nhà nước pháp quyền
(a principle of governance in which all persons and
institutions, including the state itself, are subject to and accountable under the law.) Sociological
Cách tiếp cận xã hội học perspectives
(view law as a social phenomenon shaped by social
structures, power relations, culture, and social practices.) Legal Pluralism Đa nguyên pháp luật
(the coexistence of multiple legal systems or normative
orders within a single social or political space.)
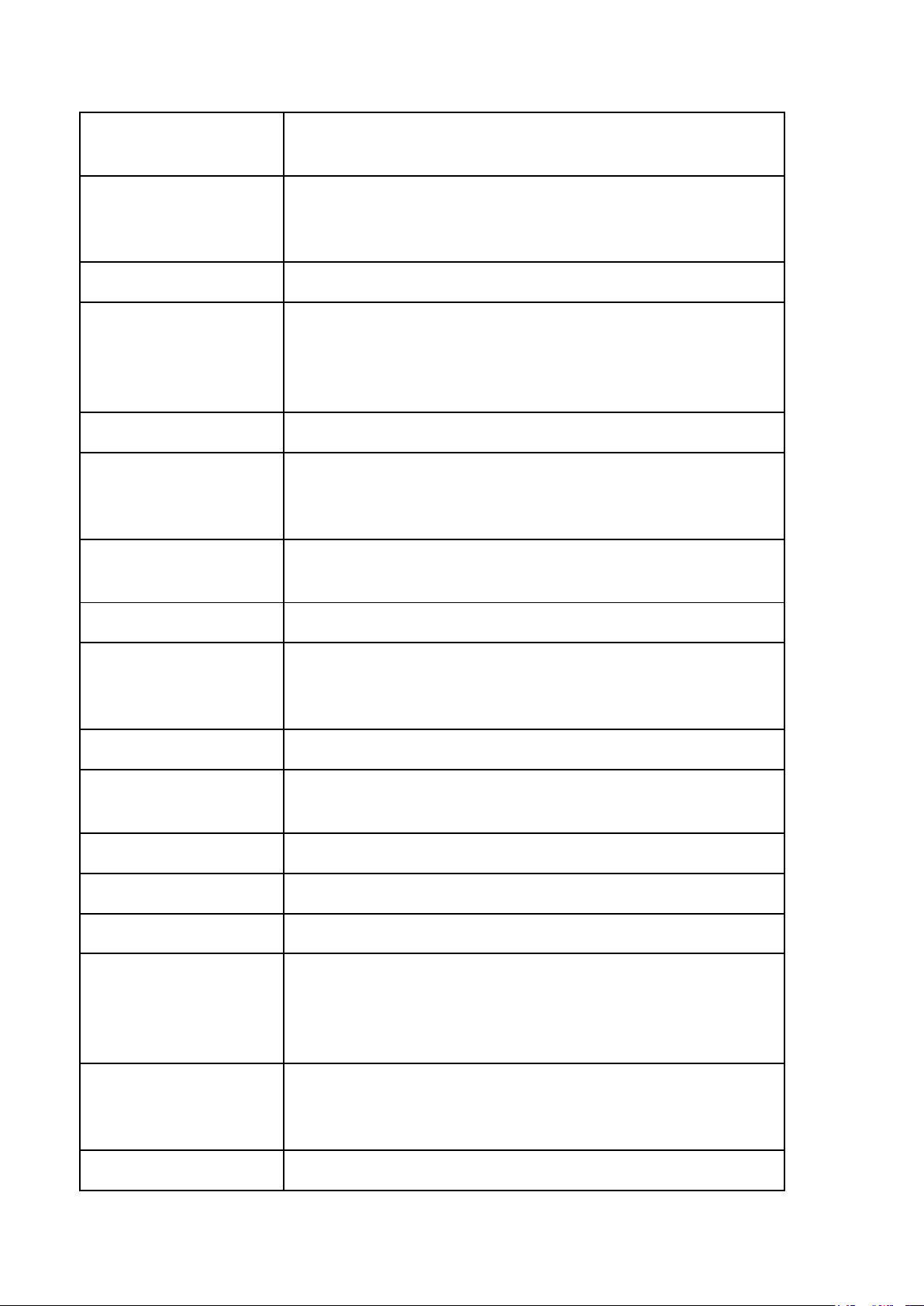
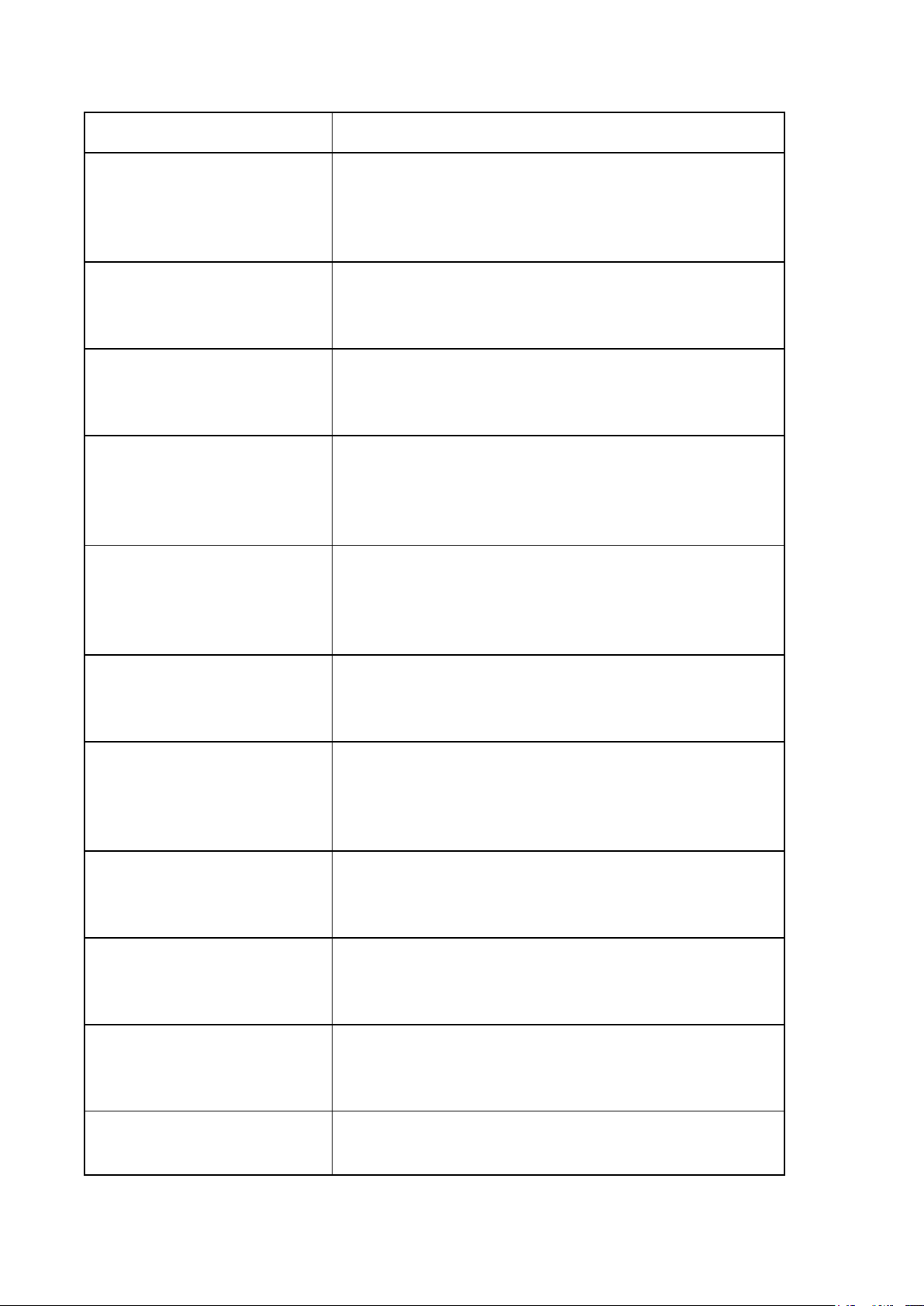
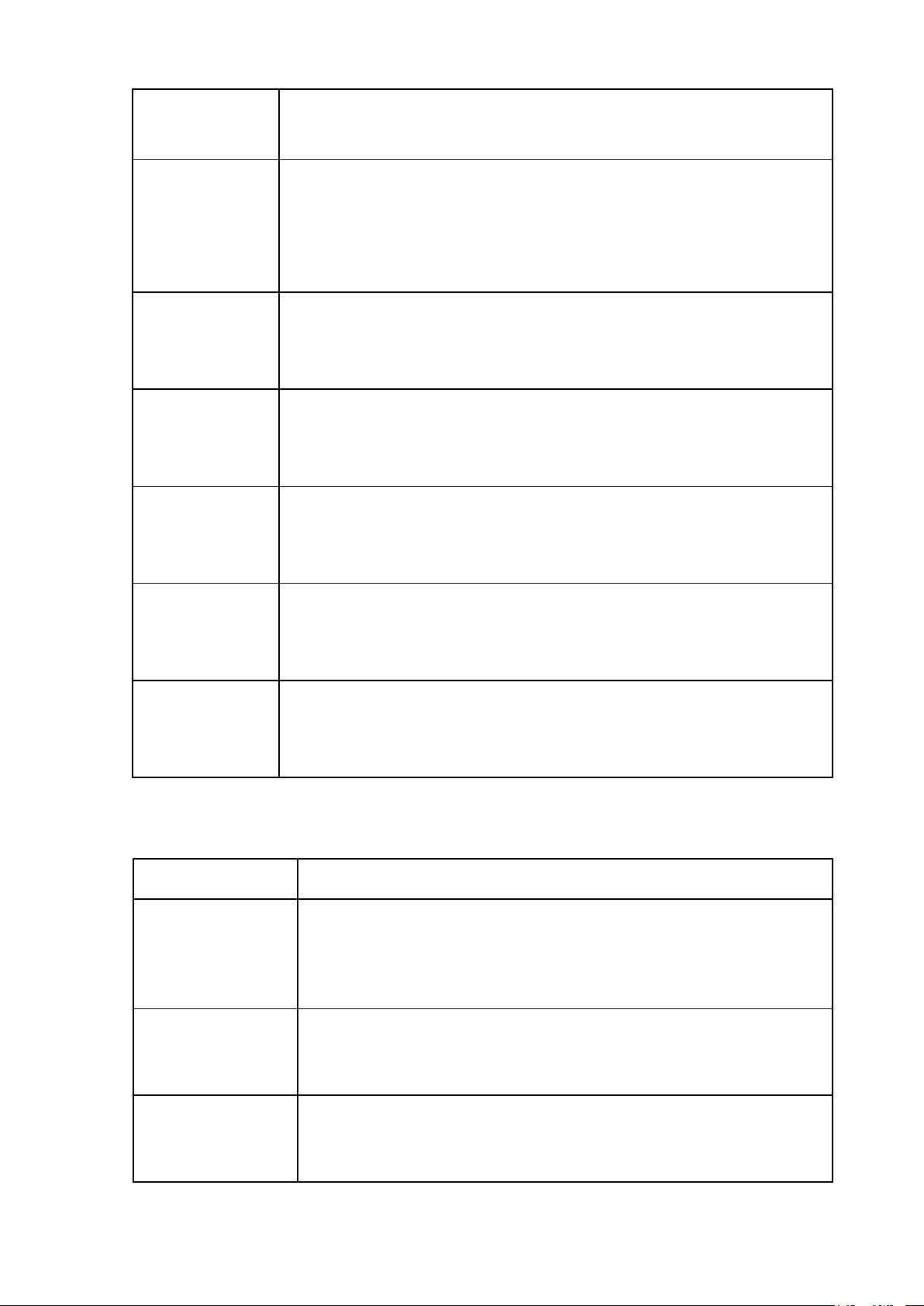
LESSON 4: TYPES OF STATE, FUNCTIONS, AND ORGANIZATION OF THE
STATE (Kiểu nhà nước, chức năng và tổ chức nhà nước) Legal words Descriptions Type of state Kiểu nhà nước
(characterized by the state that reflects the class nature,
social role, conditions for the emergence, existence, and
development of the state in a certain socio-economic form. The basis of the
Cơ sở tồn tại của nhà nước state’s existence
(the fundamental and objective economic, social, and
ideological conditions that give rise to the State and ensure
its existence and development, independent of individual
will or subjective intentions.”)
Economic foundation Cơ sở kinh tế
(The economic basis is the entire financial life of a social
organization model, with the core being ownership relations.) Social foundation Cơ sở xã hội Ideological
Cơ sở tư tưởng/ý thức hệ foundation Slave-possession Nhà nước chủ nô States Feudal States Nhà nước phong kiến Bourgeois States Nhà nước tư sản Socialist States
Nhà nước xã hội chủ nghĩa
Functions of the state Chức năng của nhà nước
(The main areas of activity that a state undertakes to fulfill
its purpose and address the needs of its society)
The Classification of Phân loại các chức năng của nhà nước Functions of The State
Legislative Function Chức năng lập pháp Executive Function Chức năng hành pháp Judicial Function Chức năng tư pháp Economic function Chức năng kinh tế Social function Chức năng xã hội Coercion Cưỡng chế Inducement/ Giáo dục/Thuyết phục persuasion State apparatus Bộ máy nhà nước State organs Cơ quan nhà nước Repressive State
Bộ máy nhà nước tổ chức theo kiểu trấn áp Apparatus
(Primarily enforces social order through physical force and the threat of violence) Ideological State
Bộ máy nhà nước tổ chức theo tư tưởng Apparatus
(Shapes individual consciousness and behavior through
ideology, subtly influencing beliefs and values) Centralization Tập trung quyền lực
(The act of consolidating power under central control.) Decentralization Phân quyền
(the process of redistributing or dispersing functions and
powers away from a central authority.) Deconcentration Phân cấp quyền lực Montesquieu’s
Học thuyết tam quyền phân lập của Montesquieu Theory of separation of powers National Assembly Quốc Hội President Chủ tịch nước The Government Chính Phủ
People’s Council and Hội đồng nhân dân và Ủy ban nhân dân People’s Committee People’s Court Tòa án nhân dân System People’s Procuracy Viện kiểm sát nhân dân System Regional Khu vực
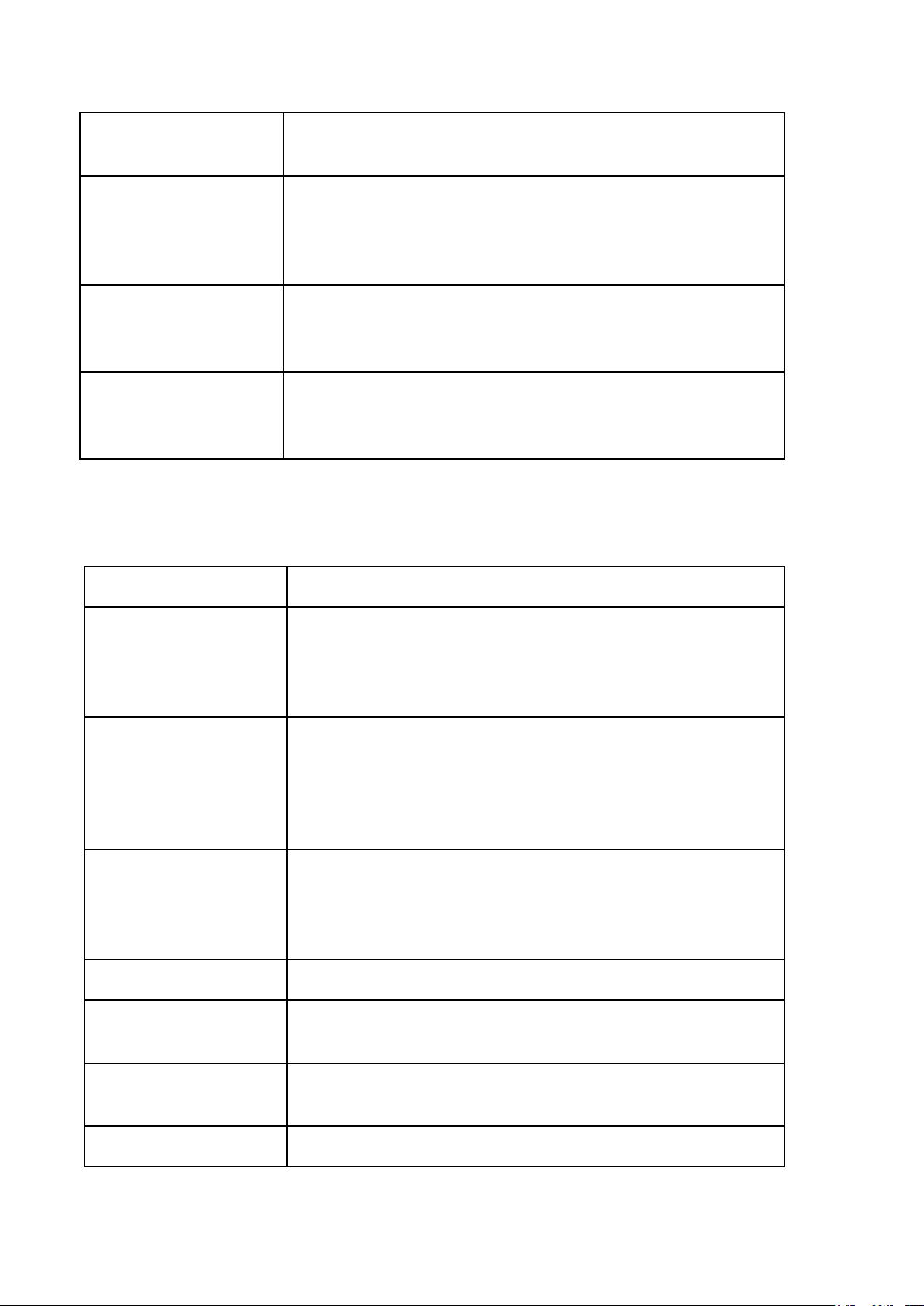
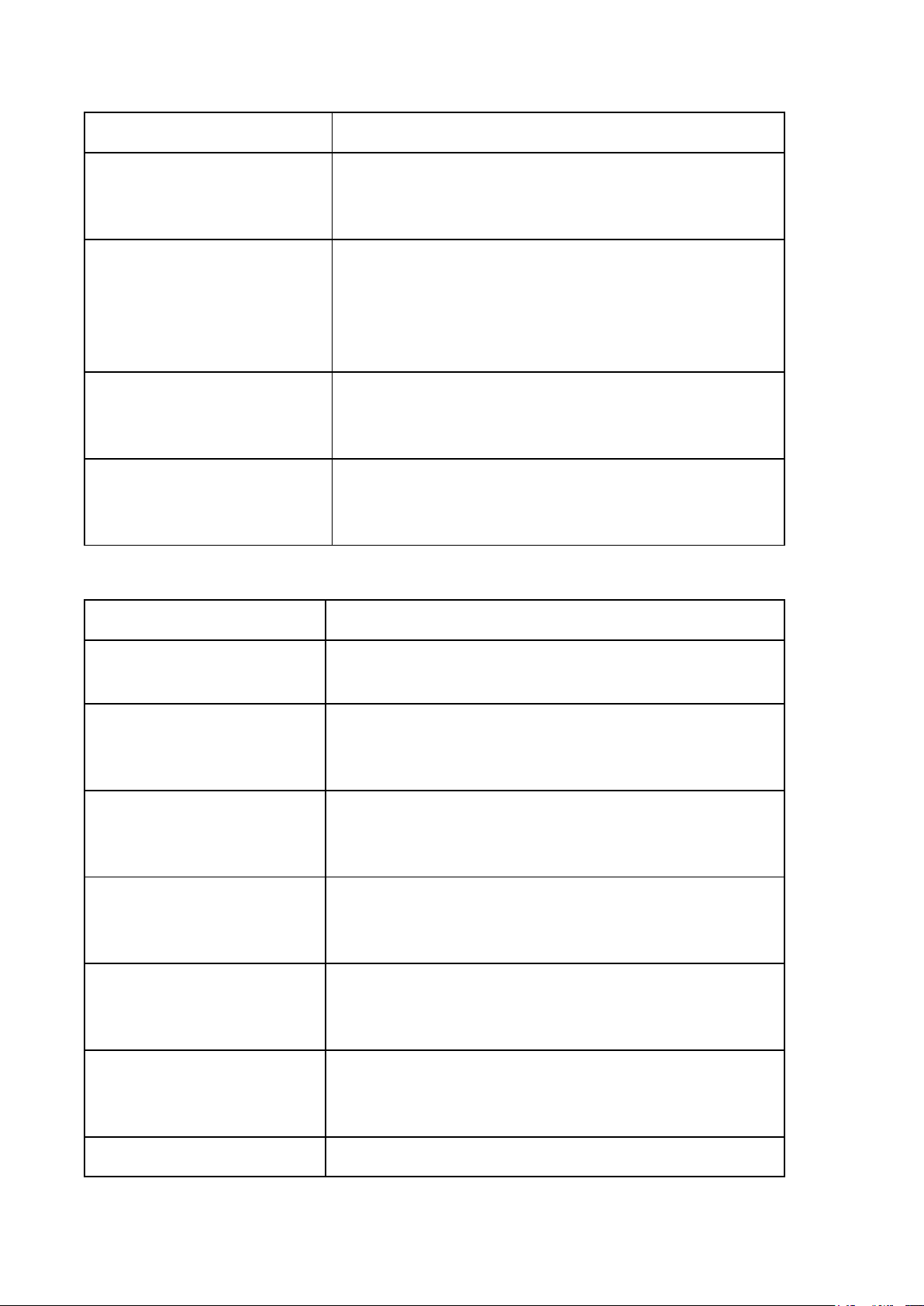
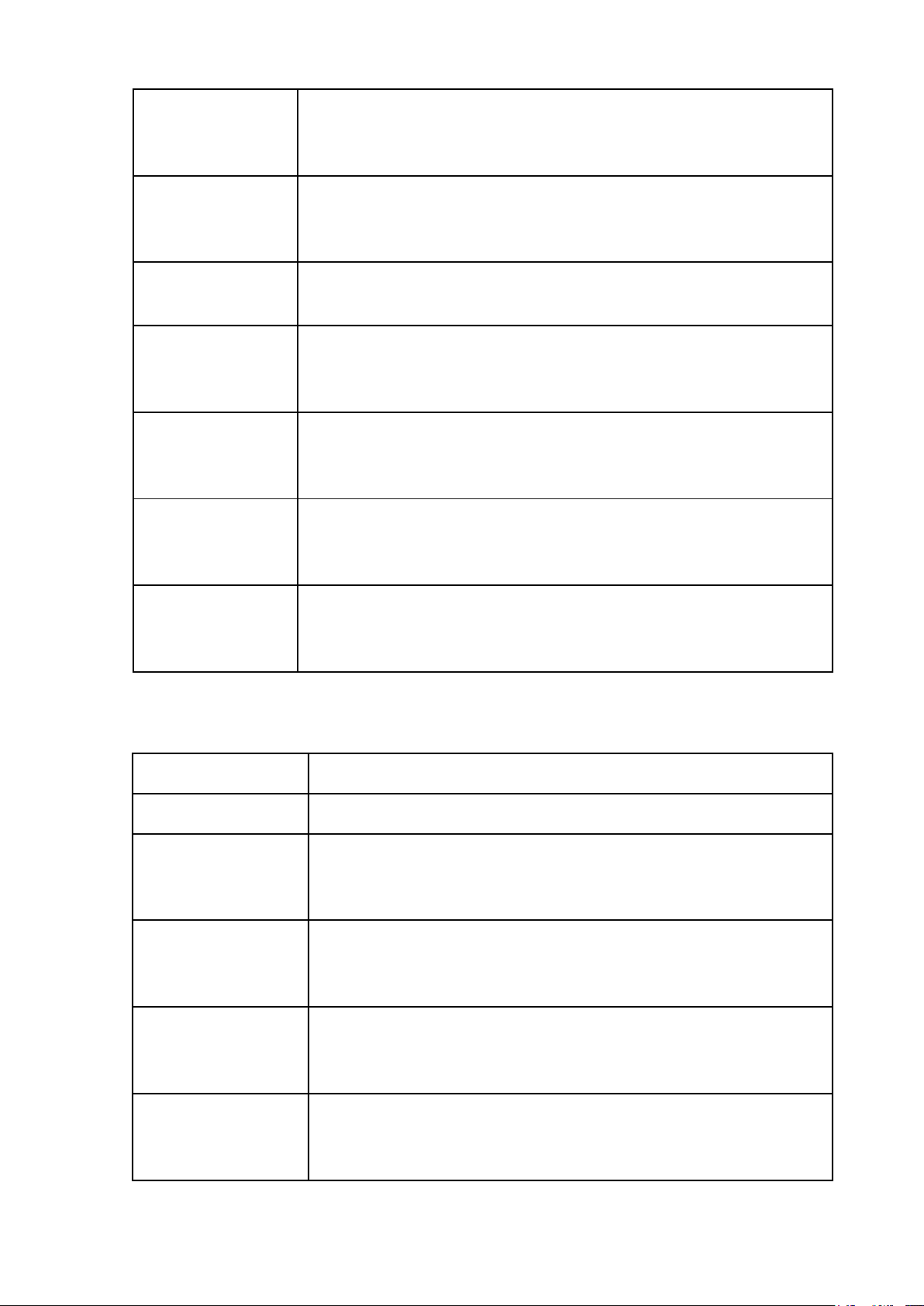
LESSON 5: FORM OF STATE (Hình thức nhà nước) Legal words Description Form of state Hình thức nhà nước
(The way state power is organized and exercised,
including the form of government, the structure of the
state, and the political regime.)
Form of government/State Hình thức chính thể Regime
(The way supreme state organs are established,
organized, and related to one another.) Structure of the state
Hình thức cấu trúc nhà nước
(The territorial organization of state power and the
relationship between central and local authorities. Political regime Chế độ chính trị
(The methods, means, and ways by which state power is exercised in society.) Mode of power
Phương thức thực hiện quyền lực
(How state power is exercised in practice, including
democratic or coercive methods.) Absolute monarchy Quân chủ chuyên chế
(a form of government in which all state power is
concentrated in the hands of the monarch.) Divine right
Thuyết thần quyền / Quyền lực thần thánh
(The belief that a monarch’s authority comes directly
from God and cannot be questioned by human institutions.)
Constitutional monarchy Quân chủ lập hiến
(A form of government in which the monarch’s
power is limited by a constitution and law.) Hierarchy Quan hệ thứ bậc
(Hierarchy refers to a system of organization based
on ranked levels of authority.) Dualistic Monarchy Quân chủ nhị nguyên
(a form of constitutional monarchy in which state
power is shared between the monarch and the parliament.) Republic System Thể chế cộng hòa
(a form of government in which state power belongs
to the people and is exercised through elected representatives.) Republic Aristocracy Cộng hòa quý tộc
(a form of republic in which political power is held by a privileged elite class.) Presidential System Cộng hòa tổng thống
(a form of government in which the president is both
head of state and head of government and is
independent of the legislature.) Republic Parliament Cộng hòa đại nghị
(a form of government in which the government is
established by and responsible to the parliament) Fusion of power
Sự tập trung / hợp nhất quyền lực
(the concentration or combination of legislative and
executive powers in one body.)
Semi-presidential System
Cộng hòa hỗn hợp / bán tổng thống
(a form of government combining elements of
presidential and parliamentary systems.) Unitary State Nhà nước đơn nhất
(a state in which sovereignty is centralized and
applied uniformly throughout the territory.) Federal State Nhà nước liên bang
(a state formed by the union of semi-autonomous
states or regions with shared sovereignty.) Autonomous regions Vùng tự trị
(territorial units within a state that are granted a
certain degree of self-governing authority in political,
administrative, cultural, or legal matters, while
remaining under the sovereignty of the central state.) Democratic regime Dân chủ
(state power belongs to the people and is exercised for the people. Antidemocratic regime Phi dân chủ
(state power is exercised without or against popular participation.)
LESSON 6: RULE OF LAW (Nhà nước pháp quyền) Legal words Descriptions Natural Law
is a system of law that is determined by nature, and so is universal. Positive law
Law actually and specifically enacted or adopted by a
proper authority for the government of an organized jural society Rule of law Nhà nước pháp quyền
(the supreme power of law in society, regulating the
behavior of all subjects, including state officials.) Supremacy Tính tối thượng
(the highest authority or overriding power of law over
all individuals and institutions.) Regular law Pháp luật chung
(general and ordinary laws applied equally to all members of soc) Arbitrary power
Quyền lực tùy tiện / chuyên quyền
(the exercise of power based on personal will rather than legal rules.) Predominance of legal
Sự chi phối của tinh thần pháp luật spirit
(The values and principles of law guide state action and social behavior.)
Equality before the law
Bình đẳng trước pháp luật
(all individuals are subject to the same laws without discrimination.) Control State Power
Kiểm soát quyền lực nhà nước
(mechanisms that prevent abuse of power by state authorities.) Freedom from
Không tham nhũng / Tự do khỏi tham nhũng Corruption
(governance free from bribery, abuse of office, and misuse of public power.) Order and Safety
Trật tự và an toàn xã hội
(Order and safety refer to a stable social condition
ensured by law and public authority.) Fundamental Rights
Quyền cơ bản / Quyền con người cơ bản
(basic rights inherent to all individuals and protected by law.) Open Government Chính phủ mở
(a system of governance characterized by
transparency, accountability, and public participation.) Stable Enforcement of
Thực thi pháp luật ổn định Laws
(the consistent and predictable application of legal rules) Justice in Civil and
Công lý trong pháp luật dân sự và hình sự Criminal Laws
(fair adjudication and protection of rights in both civil and criminal matters.) Informal Justice Công lý phi chính thức
(dispute resolution mechanisms outside the formal court system.) Rule by Law Pháp trị
(The use of law as an instrument of control by those in
power, rather than as a limitation on power.) THEORY OF LAW
LESSON 8: GENERAL ISSUES ABOUT LAW, SOURCES OF LAW Legal words Description Law
A system of established, general rules Command
A desire/wish of a superior with authority Order
A desire normally with love, care Morality Đạo đức
(Principles or standards concerning the distinction between right
and wrong or good and bad behavior.) The doctrines
Các học thuyết pháp luật of law
(theoretical systems and schools of thought that explain the origin,
nature, role, and development of law.) Natural law
Học thuyết pháp luật tự nhiên Theory
(law is based on universal moral principles inherent in human
nature and superior to enacted law.)
Contemporary Các trường phái pháp luật đương đại schools
(modern legal theories developed in the contemporary period to
explain law in relation to society, politics, and economics.) Legal
Học thuyết pháp luật thực chứng Positivism
(views law as a system of rules created and enforced by the state, Theory
separate from moral considerations.) Generality Tính phổ biến
(The characteristic of law being applicable to all subjects in similar circumstances.) Compulsion Tính cưỡng chế
(The binding force of law that obliges subjects to comply with legal rules.) Promulgation
Ban hành / Công bố (pháp luật)
(The formal act of officially issuing or announcing a law by a competent authority.) Clarity Tính rõ ràng, minh bạch
(Tính rõ ràng của pháp luật đòi hỏi quy định pháp luật phải cụ thể,
dễ hiểu và không mơ hồ.)
Guaranteed to Được bảo đảm thực hiện bằng cưỡng chế nhà nước be
(Law is guaranteed to be implemented through coercion when the implemented
state uses compulsory measures to ensure compliance.) through coercion
Sources of law Nguồn của pháp luật
(the formal forms through which legal rules are created and expressed.) Delegated
Văn bản pháp luật được ủy quyền / Lập pháp ủy quyền legislation
(legal rules made by an authority under powers delegated by the legislature.) Judicial
Quyết định tư pháp / Án lệ decisions
(rulings issued by courts that may serve as legal guidance or sources of law.) Equity Lẽ công bằng
(principles of fairness used to supplement or correct the strict application of law.) Scientific
Bình luận khoa học pháp lý
Commentaries (scholarly interpretations and analyses of law provided by legal scholars.) LESSON 9: LEGAL NORMS Legal words Descriptions Legal norms Quy phạm pháp luật
(general rules of conduct issued or recognized by the state,
regulating social relations and guaranteed for implementation by state power.) General
Tính bắt buộc chung / Tính cưỡng chế chung compulsion
(the binding force of legal norms that applies to all subjects within their scope.) Contains legal
Chứa đựng quyền và nghĩa vụ pháp lý rights or legal
(provisions on legal rights and legal obligations of subjects.) obligations Issued or
Do nhà nước ban hành hoặc thừa nhận recognized by
(issued or recognized by the state through competent the state authorities) Guaranteed
Được nhà nước bảo đảm thực hiện implementation
(guaranteed to be implemented by the state through by the state
organizational, economic, and coercive measures.) Presumption Giả định pháp lý
(legal assumption recognized by law until proven otherwise.) Hypothesis
Giả định (của quy phạm pháp luật)
(The part of a legal norm that specifies the conditions under which the norm applies.) Regulation
Quy định (điều chỉnh pháp luật)
(The legal guidance or direction of behavior prescribed by a legal norm.) Disposition
Quy định (phần quy định của quy phạm pháp luật)
(the part of a legal norm that defines the rights and obligations of subjects.) Sanction Chế tài
(the part of a legal norm that prescribes legal consequences for violations.)
LESSON 10: LAW SYSTEM (Hệ thống pháp luật) Legal words Descriptions Branch of law Ngành luật Legal institution Chế định pháp luật
(A number of legal norms have similar general characteristics
to regulate a corresponding group of social relations) Procedure Law
Luật tố tụng / Pháp luật tố tụng
(The procedures and methods by which substantive law is
enforced and disputes are resolved.) The system of
Hệ thống văn bản pháp luật legislative
(the hierarchical structure of legal documents issued by state documents authorities.) Normative legal
Văn bản quy phạm pháp luật documents
(are written instruments issued by competent authorities
containing generally binding legal rules.) Legislative Văn bản pháp luật documents
(legal instruments issued by state authorities to regulate social relations.) Codes and Laws Bộ luật và Luật
(legislative documents enacted by the legislature with the
highest legal validity after the Constitution.) Resolutions Nghị quyết
(legal documents adopted by competent authorities to decide
important issues or provide legal norms.)
Joint Resolutions Nghị quyết liên tịch
(legal documents jointly issued by two or more competent authorities.) Ordinances Pháp lệnh
(legislative documents issued by standing bodies of the
legislature when the legislature is not in session.) Order Lệnh
(legal documents issued by competent authorities to direct specific actions.) Decision Quyết định
(legal documents issued by state authorities to apply law to specific cases.) Decree Nghị định
(normative legal documents issued by the government to detail the implementation of laws.) Circular Thông tư
(legal documents issued by ministers or heads of agencies to
guide the implementation of laws and decrees.) Joint Circulars Thông tư liên tịch
(legal documents jointly issued by multiple authorities to guide law enforcement.) Legality Tính hợp pháp
(compliance with the law and legal procedures.)
Regulated subject Social relations in a certain area of social life that regulated by law
Regulated method The way the law affects the behaviour of subjects participating
in social relations within the scope of regulations of that legal industry. Reasonableness Tính hợp lý
(the fairness, rationality, and appropriateness of legal rules or decisions.) LESSON 11: LEGAL RELATION Legal words Descriptions Legal relation Quan hệ pháp luật
(a social relationship regulated by legal norms, in which
the parties involved possess corresponding legal rights and obligations.)
Subject of legal relations Chủ thể của quan hệ pháp luật
(individuals or organizations that participate in legal
relations and possess legal rights and obligations.
Object of legal relations Khách thể của quan hệ pháp luật
(the interests, material or immaterial benefits that legal
relations aim to regulate or protect.) Content of legal
Nội dung của quan hệ pháp luật relations
(consists of the legal rights and legal obligations of the subjects involved.) Subject legal capacity
Năng lực pháp luật của chủ thể
(the ability of a subject to have legal rights and legal obligations.)
Capacity for legal acts
Năng lực hành vi pháp luật Legal problems Sự biến pháp lý Legal acts Sự kiện pháp lý Subjective legal acts
Can be influenced by human will Objective legal acts
Cannot be influenced by human will Legal event Sự kiện pháp lý
(circumstances or occurrences recognized by law that
give rise to, change, or terminate legal relations.)
LESSON 12: LAW IMPLEMENTATION AND LAW APPLICATION Legal words Descriptions Law implementation Thực hiện pháp luật
(an active process with the purpose of connecting legal
provisions to life, becoming actual legal acts of legal subject) Obey the law Tuân theo pháp luật
Compliance with the law (Subject refrain from performing acts that prohibited by law) Implementing laws Thi hành pháp luật
(Subjects doing things according to the requirements of the regulations) Using laws Sử dụng pháp luật
(Subject has the right to exercise or not to exercise
his/her rights as prescribed by the law) Applying laws Áp dụng pháp luật
(a form of law enforcement in which the state ensure
the capacity to exercise the rights, obligations
prescribed by law of competent state agencies,
authorities or social organizations)
LESSON 13: VIOLATION OF LAW AND LEGAL LIABILITY Legal words Descriptions Violation of law Vi phạm pháp luật
(an unlawful act or omission committed by a subject
with fault, infringing upon social relations protected by law.) Legal liability Trách nhiệm pháp lý
(the obligation of a subject who commits a violation
of law to bear adverse legal consequences imposed by the state.)
Unilateral will/ forces
Ý chí đơn phương của nhà nước
(the state’s authority to impose legal consequences
without the consent of the violating subject.)
Adverse consequences/state
Hậu quả pháp lý bất lợi / Biện pháp cưỡng chế nhà coercive measures nước
(s (Sanctions imposed by the state to punish violations and restore legal order.)




