Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 36625228
Câu hỏi ôn tập chương 1
1. Giải thích khái niệm dữ liệu (data)
- Là dữ kiện có thể lưu trữ được và có một hàm nghĩa ngầm định nào đó.
2. Giải thích khái niệm thông tin (information)
- Là tập các dữ liệu được tổ chức (xử lý dữ liệu để nó mang lại một ý nghĩa nào đó trong một ngữ cảnh cụ thể.
3. Định nghĩa về cơ sở dữ liệu (CSDL) -
Một tập hợp các dữ liệu có liên quan với nhau trong một lĩnh vực cụ
thể. - A database is a collection of related data.
4. Định nghĩa về Hệ quản trị CSDL (DBMS)
- Một gói / hệ thống các phần mềm giúp cho việc tạo và duy trì cơ sở dữ liệu trên máy tính một cách thuận lợi.
5. Liệt kê tên một vài hệ quản trị CSDL
- SQL-Sever, DB2, Paradox, Informix, Oracle.
6. Các thành phần của một hệ CSDL
- Một DBMS ( hệ quản trị CSDL ) và một CSDL ( có thể gồm cả chương trình ứng dụng.
- DBMS ( meta-data + database ). 7. Siêu dữ liệu là gì
- Hệ CSDL không chỉ lưu CSDL mà còn lưu trữ định nghĩa về cấu trúc dữ liệu và các ràng buộc
trong catalog. Thông tin được lưu trữ trong catalog được gọi là siêu dữ liệu.
8. Trình bày các loại đối tượng sử dụng CSDL
- Người quản trị CSDL ( DBA- Database Administrator )
- Người thiết kế CSDL ( Database designer )
- Người dùng cuối ( End user )
- Phân tích viên hệ thống ( System Analyst )
- Lập trình viên ứng dụng ( Application Programmer )
9. Nêu nhiệm vụ của DBA, Database designer, System Analyst, Application Programmer - DBA:
+ cấp quyền khai thác CSDL
+ xem xét việc sử dụng CSDL và thu hồi tài nguyên
+ bảo mật và thời gian đáp ứng yêu cầu của hệ thống - Database designer:
+ Hiểu yêu cầu của người dùng và tạo thiết kế đáp ứng yêu cầu.
+ Xác định dữ liệu cần lưu trong CSDL và cấu trúc CSDL.
- System Analyst: xác định yêu cầu của người dùng và xây dựng bản đặc tả cho những giao tác
đáp ứng yêu cầu người dùng.
- Application Programmer: cài đặc đặc tả thành chương trình, kiểm tra, dò lỗi, ghi sưu liệu và
bảo trì những thao tác này. 10.
Mô hình dữ liệu là gì ( Data Model )
- Một tập hợp các khái niệm dùng để mô tả cấu trúc của cơ sở dữ liệu lOMoARcPSD| 36625228
11. Giải thích 3 loại mô hình: mô hình mức khái niệm, mô hình dữ liệu mức logic và mô hình dữ liệu mức vật lý
- Mô hình dữ liệu mức cao ( mức khái niệm ): cung cấp các khái niệm gần với cách người dùng
cảm nhận về dữ liệu.
- Mô hình dữ liệu mức thấp ( mức vật lí ): mô tả cách dữ liệu được lưu trữ trên máy tính.
- Mô hình dữ liệu mức logic: mức trung gian giữa 2 mức trên để người dùng có thể hiểu nhưng
cũng gần với cách dữ liệu được tổ chức trên đĩa cứng. Mô hình này giấu đi chi tiết lưu trữ dữ
liệu trên đĩa nhưng có thể cài đặc trên máy tính (Ví dụ: Mô hình quan hệ, mô hình phân cấp, mô hình mạng) 12.
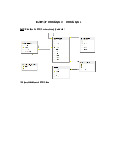
Trình bày kiến trúc 3 mức của 1 hệ CSDL
Kiến trúc 3 mức giúp tách biệt các ứng dụng người dùng với CSDL vật lý
- Mức vật lisL Sử dụng mô hình dữ liệu vật lý để mô tả cấu trúc lưu trữ vật lý của CSDL
- Mức logic/quan niệm: Giấu đi chi tiết về cấu trúc lưu trữ vật lý. Dùng mô hình dữ liệu logic để
mô tả cái gì được lưu trữ trong CSDL và mối quan hệ giữa các dữ liệu đó.
- Mức ngoài/view: Mô tả một phần của CSDL cho một nhóm người dùng quan tâm và giấu đi
phần còn lại của CSDL khỏi nhóm người dùng đó 13.
Tính độc lập dữ liệu là gì?
- Là khả năng thay đổi lược đồ tại một mức của hệ CSDL mà không phải thay đổi lược đồ tại mức cao hơn kế tiếp 14.
Trình bày tính độc lập dữ liệu vật lý và tính độc lập logic
- Vật lý: là khả năng thay đổi lược đồ vật lí mà không phải thay đổi lược đồ quan niệm. Vì vậy
lược đồ ngoài cũng không cần phải thay đổi.
- Logic: là khả năng thay đổi lược đồ quan niệm mà không phải thay đổi lược đồ ngoài hay chương trình ứng dụng Assignment(GROUP)
1. Define the following terms and give an example for each term: data, database,
DBMS, database system, DBA, end user, meta-data.
-Data: mean known facts that can be recorded and that have implicit meaning (For example,
consider the names, telephone numbers, and addresses)
- Database: The collection of related data with an implicit meaning is a database.
Ex: -model standard: high, weight, name; concert: light, music, day, artists.
-DBMS: is a collection of programs that enables users to create and maintain a database. lOMoARcPSD| 36625228
Ex: MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle Database, and Microsoft Access.
-Database system: The DBMS software together with the data itself. Sometimes, the
applications are also included.
-DBA: the person who is a chief administrator to oversee and manage resources.
-End user: The end users of a database may perform business transactions (for example, a
customer buys a camera) or events may happen (for example, an employee has a baby) that cause
the information in the database to change.
-Meta-data: The database definition or descriptive information is also stored by the DBMS in
the form of a database catalog or dictionary.
Ex: author, date created, date modified, and file size.
2. What are the responsibilities of the DBA and the database designers?
-The DBA is responsible for authorizing access to the database, coordinating and monitoring
its use, and acquiring software and hardware resources as needed. The DBA is accountable for
problems such as security breaches and poor system response time. In large organizations, the
DBA is assisted by a staff that carries out these functions -The database designers:
+ Identifying the data to be stored in the database and for choosing appropriate structures to
represent and store this data.
+ Interacting with each potential group of users and developing views of the database that
meet the data and processing requirements of these groups.
3. What are the different types of database end users?
- Naïve or parametric end users - Casual end users - Sophisticated users - Standalone users
Naive end users need to learn very little about the facilities provided by the DBMS; they
simply have to understand the user interfaces of the standard transactions designed and
implemented for their use. Casual users learn only a few facilities that they may use repeatedly.
Sophisticated users try to learn most of the DBMS facilities in order to achieve their complex
requirements. Standalone users typically become very proficient in using a specific software package. lOMoARcPSD| 36625228 EXCERCISES
a. If the name of the ‘CS’ (Computer Science) Department changes to ‘CSSE’
(ComputerScience and Software Engineering) Department and the corresponding prefix for the
course number also changes, identify the columns in the database that would need to be updated.
The following columns will need to be updated. Table Column STUDENT Major COURSE Course Number and Department SECTION Course Number PREREQUISITE
Course Number and Prerequisite Number
b. b. we should split the following columns into two columns: Table Column Split Columns COURSE CourseDept and CourseNumber CourseNum SECTION CourseDept and CourseNumber CourseNum PREREQUISITE CourseNumber CourseDept and CourseNum PREREQUISITE PrerequisiteNumber PreReqDept and PreReqNum
Note that in the COURSE table, the column CourseDept will not be needed after the above
change, since it is redundant with the Department column.