



Preview text:
CHAP 4: ACCRUAL ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS (KT dồn tích)
1. Explain the accrual basis of accounting and the reasons for adjusting entries
- Divides the economic life into artificial time periods: Periodicity asumption (Giả định thời gian)
- Gennerally a month, a quarter, a year.
- Fiscal year: accounting time period that one year long (Năm TC) vs Calendar year
The revenue recognition principle (ghi nhận doanh thu):
Recognize revenue in which the performance obligation is satisfied (maybe not received cash)
Ex: service provide in June but be paid in July
The expense recognition principle (ghi nhận chi phí):
Match Expense – Revenue _ Matching Principle
Accrual versus cash basis of accounting:
- Accrual-Basis Accounting: record when events occur
- Cash-Basis Accounting: record at time receive cash (not accordance with GAAP)
The need for adjusting entries:
- Ensure 2 principles are followed (Revenue & Expense) - Require when prepare FS
- All adjusting entries include: 1 income statement account & 1 balance sheet account - Some reasons:
+ Some events are not recorded daily. Ex: the use of supplies and the earning of wages
+ Some costs are not recorded because it expires with the passage of time. Ex: the use of
buildings and equipment, rent and insurance.
+ Some items may be unrecorded. Ex: utility service bill.
Types of adjusting entries:
- Deferrals (trì hoãn):
+ Prepaid Expense (CP trả trước): expense paid in cash before they are used.
+ Unearned Revenues (DT chưa thực hiện): cash received before services are performed.
- Accruals (dồn tích):
+ Accrued Revenues (DT dồn tích): revenue for services performed but not yet received in cash.
+ Accrued Expenses (Nợ tồn đọng): expenses incurred but not yet paid.
2. Prepare adjusting entries for deferrals:
a. Prepaid expense/ Prepayment (CP trả trước): expense paid in cash before they are used.
- expense prepaid so asset increased (debit)
- They are the cost that expire either:
+ Passage of time: rent, insurance + Through use: supplies
(Not require daily entries)
An adjusting entry for prepaid expenses results in: an increase (a debit) to an expense account
and a decrease (a credit) to an asset account (Debit T expense & Credit asset)
Supplies: recognize at the end of the accounting period.
Debit T expense: debit Supplies Expense => overstated Credit asset: credit Supplies
Insurance: at the end, Insurance Expense increase (debit) & Prepaid Insurance decrease (credit)
Debit T expense: debit Insurance Expense
Credit asset: credit Prepaid Insurance
Depreciation: “useful life” - allocate cost to period in which it is used not the actual change in asst’s value.
Debit T expense: debit Depreciation Expense
Credit asset: credit Accumulated Depreciation
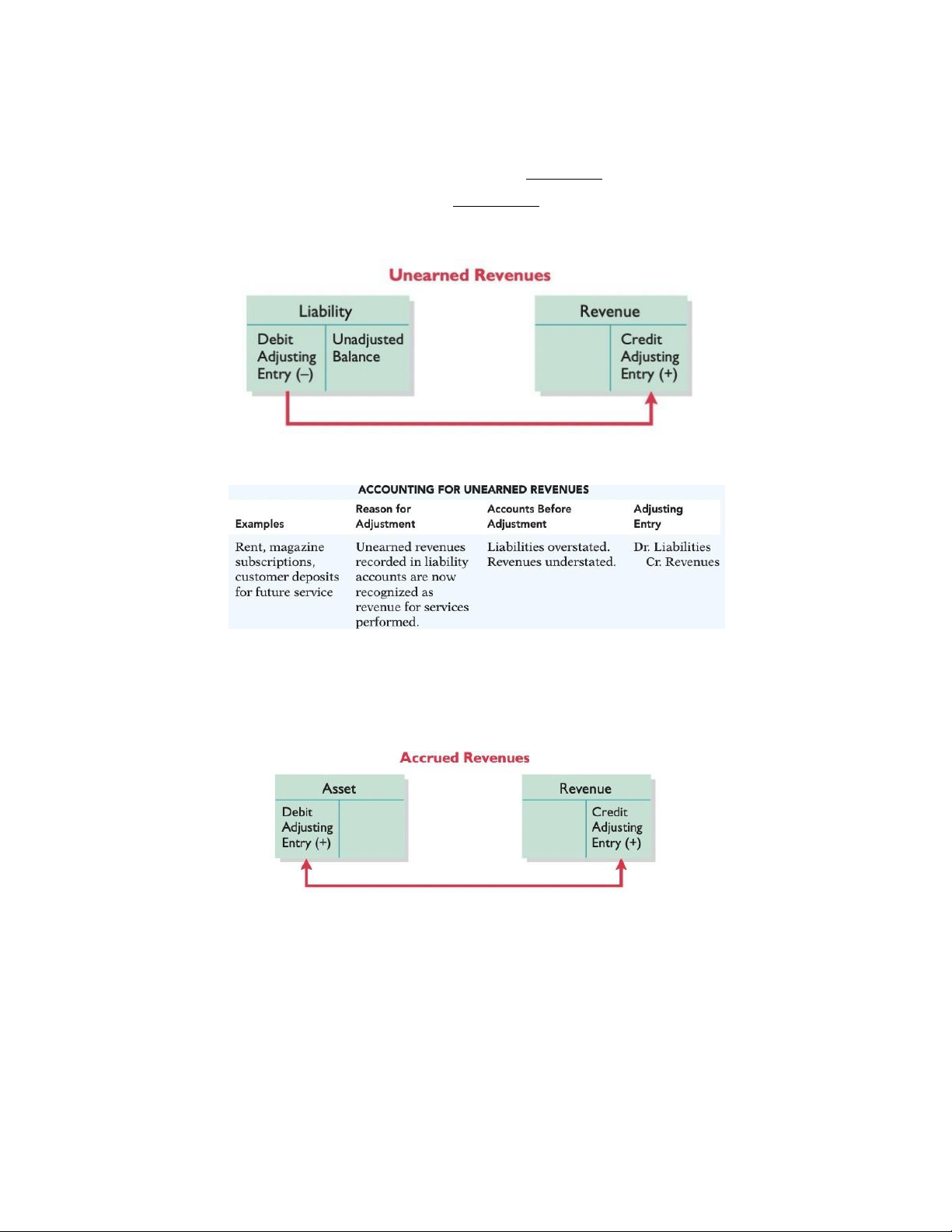
b. Unearned Revenues: (DT chưa thực hiện): cash received before services are performed.
increase (crediting) a liability account called “unearned revenue”
Debit liabilities: debit Unearned Service Revenue => overstated
Credit T revenues: credit Service Revenue => understated
3. Prepare adjusting entries for accruals:
a. Accrued Revenue (DT dồn tích): revenue for services performed but not yet received in cash.
Debit T Assets: debit Account Receivable
Credit T revenues: credit Service Revenue
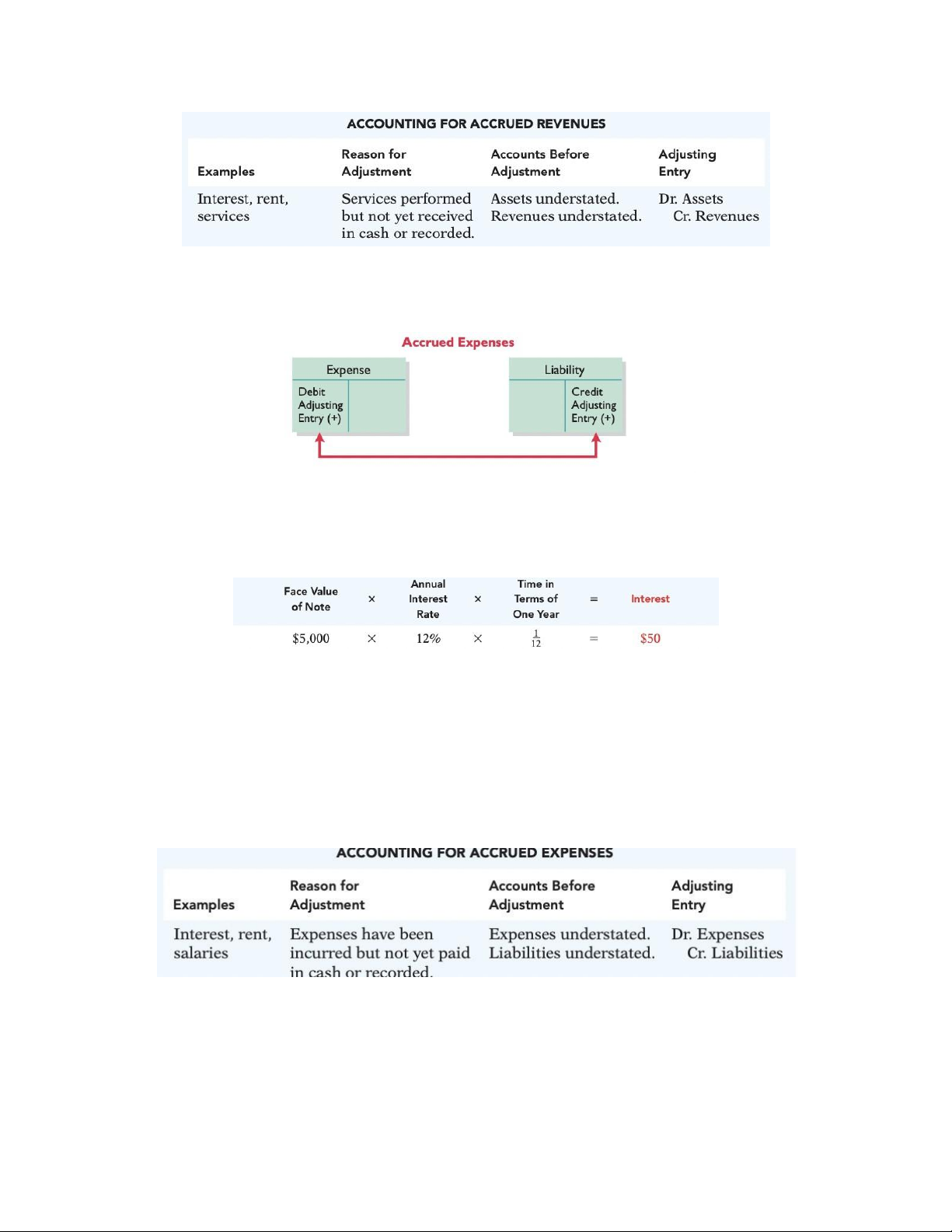
b. Accrued expenses (Nợ tồn đọng): expenses incurred but not yet paid.
interest, taxes, utilities and salaries Debit T Expense: debit Expense
Credit T Liabilities: credit Payable Accrued Interest:
Debit T Expense: debit Interest Expense
Credit T Liabilities: credit Interest Payable Accrued salaries:
Debit T Expense: debit Salaries & Wages Expense
Credit T Liabilities: credit Salaries & Wages Payable
Note: Understated – indicates a reported amount < true amount
Overstated – indicates a reported amount > true amount
Summary of basic relationships:
4. Prepare an adjusted trial balance and closing entries:
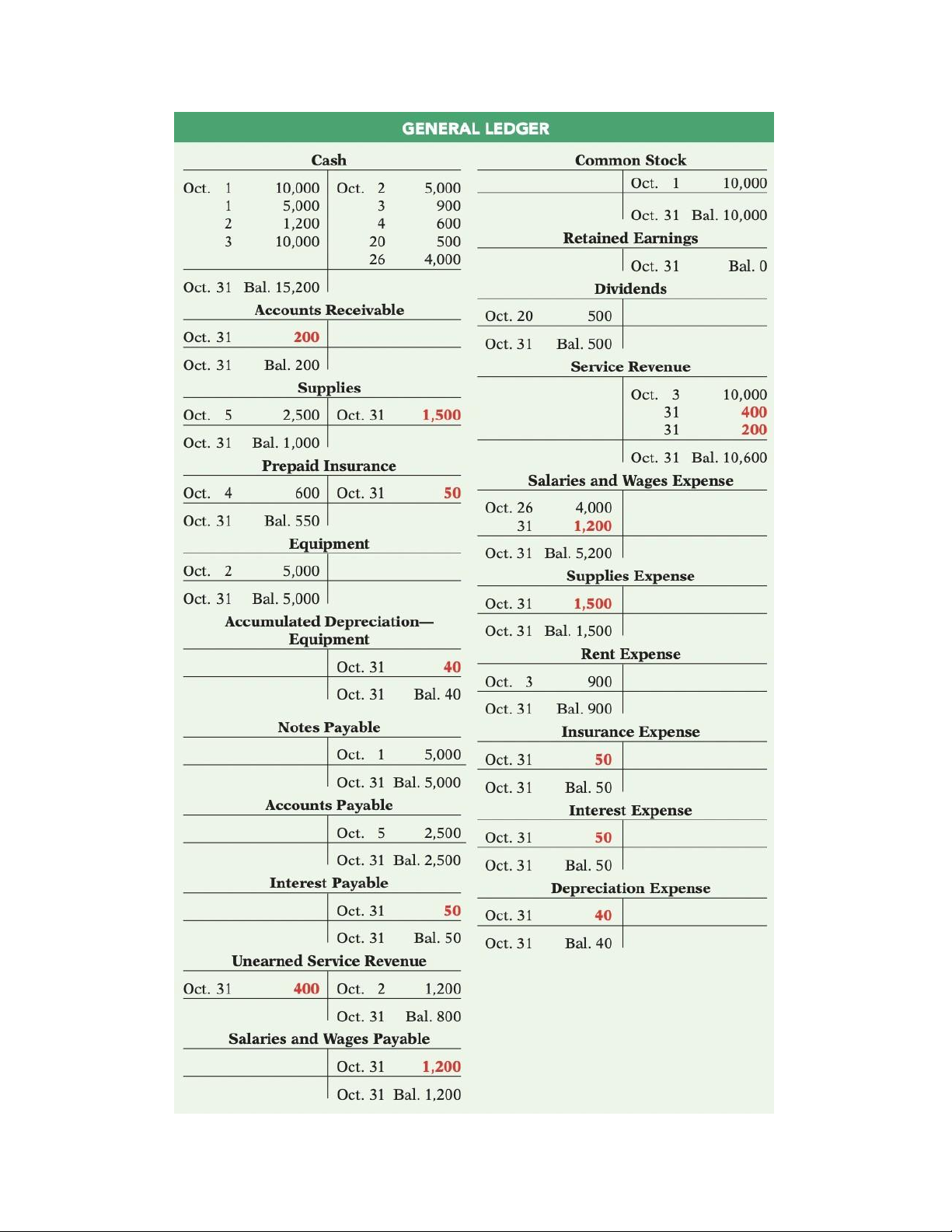
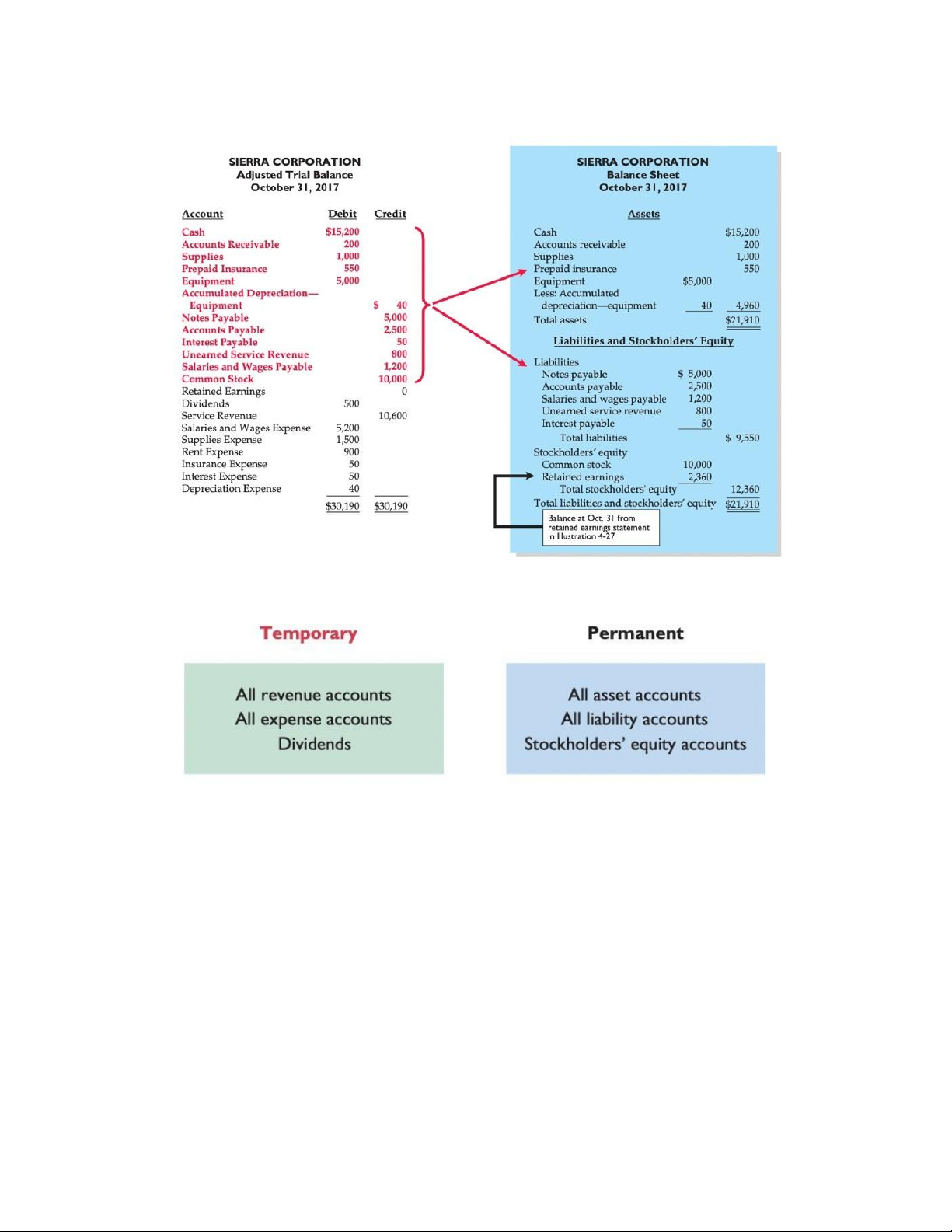
Preparing the adjusted trial balance: adjusted entries in different colors
Preparing financial statement: Quality of earnings: Closing the books:
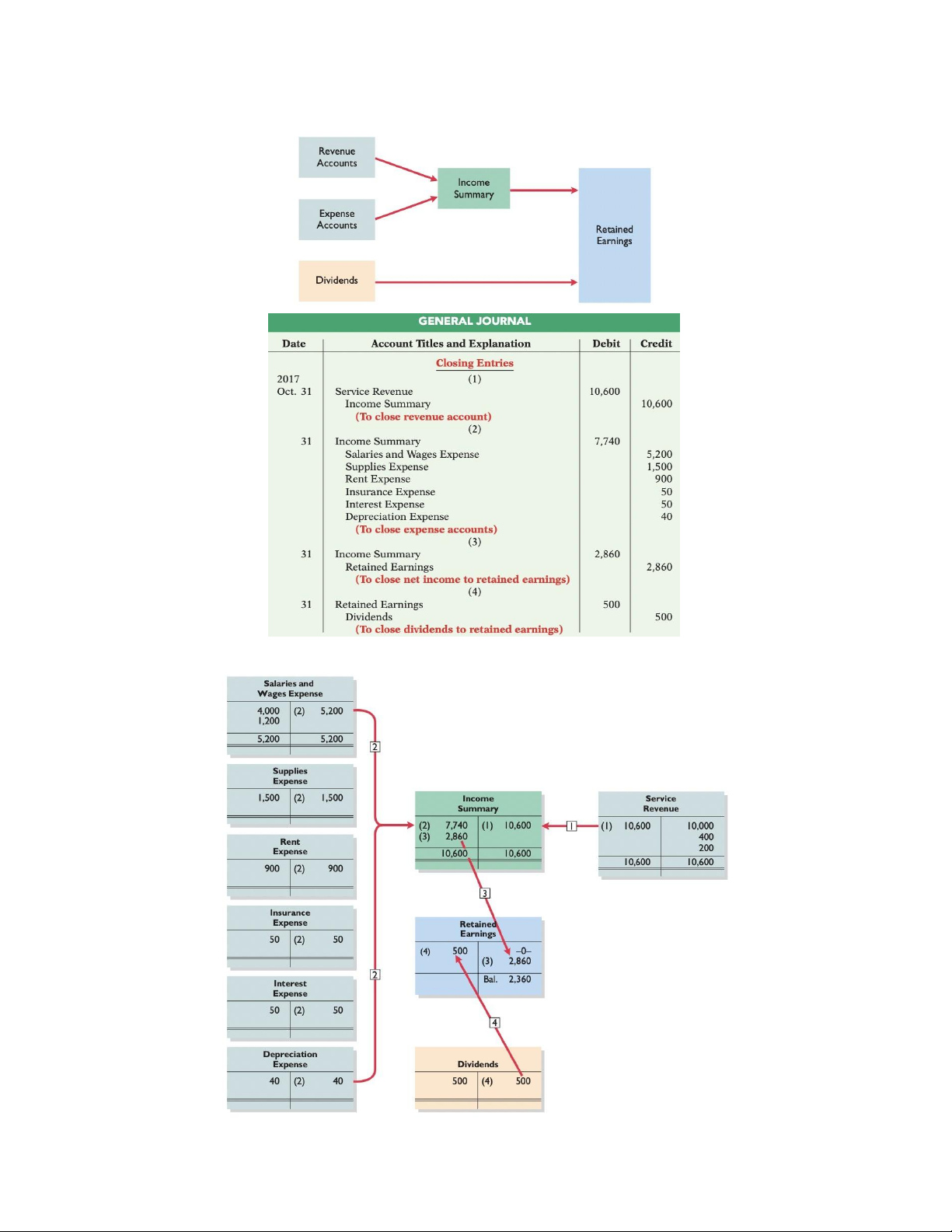
Prepare closing entries:
Preparing a Post-Closing trial balance:
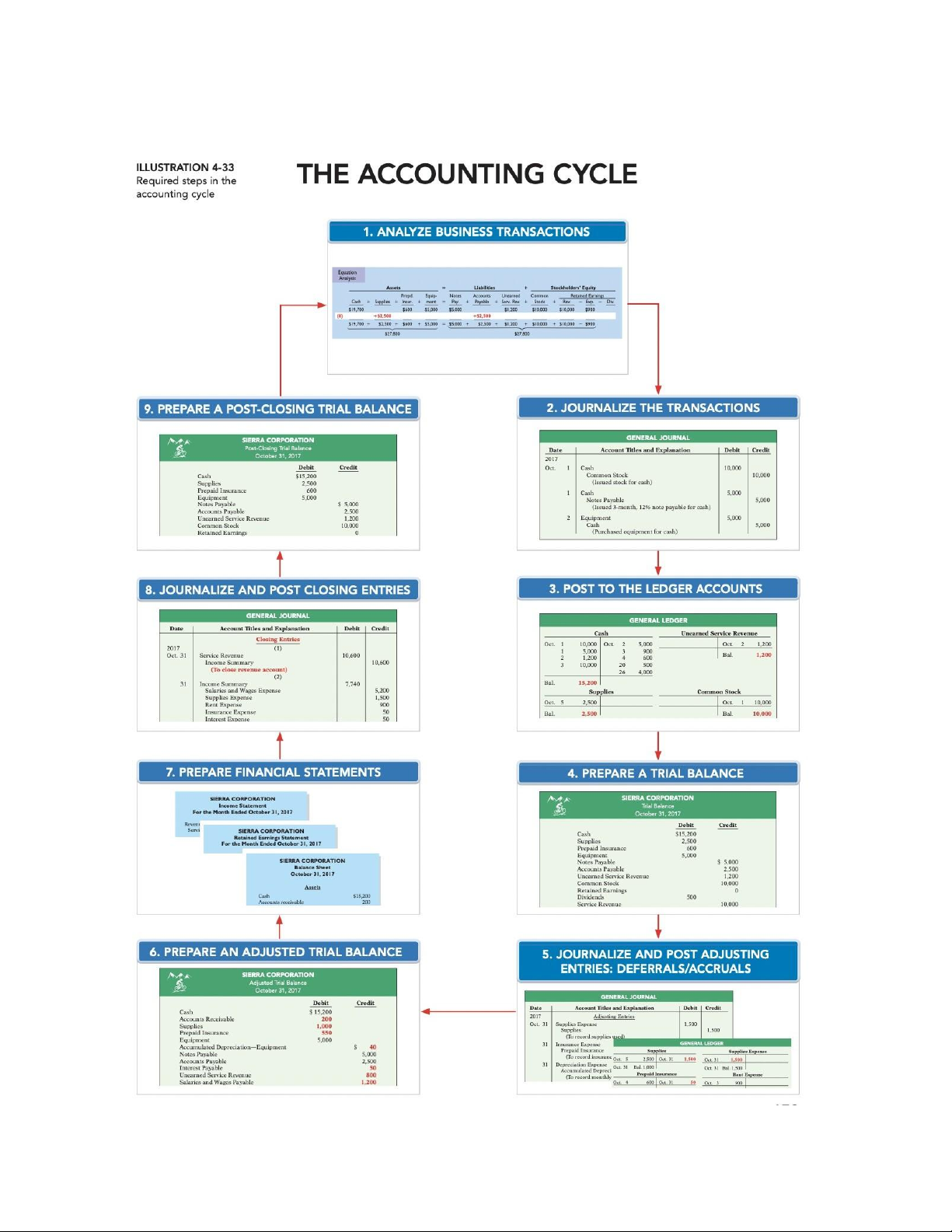
Summary of the accounting cycle:
Document Outline
- 1.Explain the accrual basis of accounting and the re
- 2.Prepare adjusting entries for deferrals:
- Summary of basic relationships:




