
































Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|36041561 CHAPTER 3 Managing Business Environment
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 Learning Outcomes
ü Contrast the actions of managers according to
the omnipotent and symbolic views.
ü Describe the external environment.
ü Describe the internal environment.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
3.1. The Managers’ View
ü Omnipotent View of Management - the view
that managers are directly responsible for an
organization’s success or failure.
ü Symbolic view of Management - the view that
much of an organization’s success or failure is
due to external forces outside managers’ control.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 What happens…
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Outside to industry to internal Non program decision Pest analysis
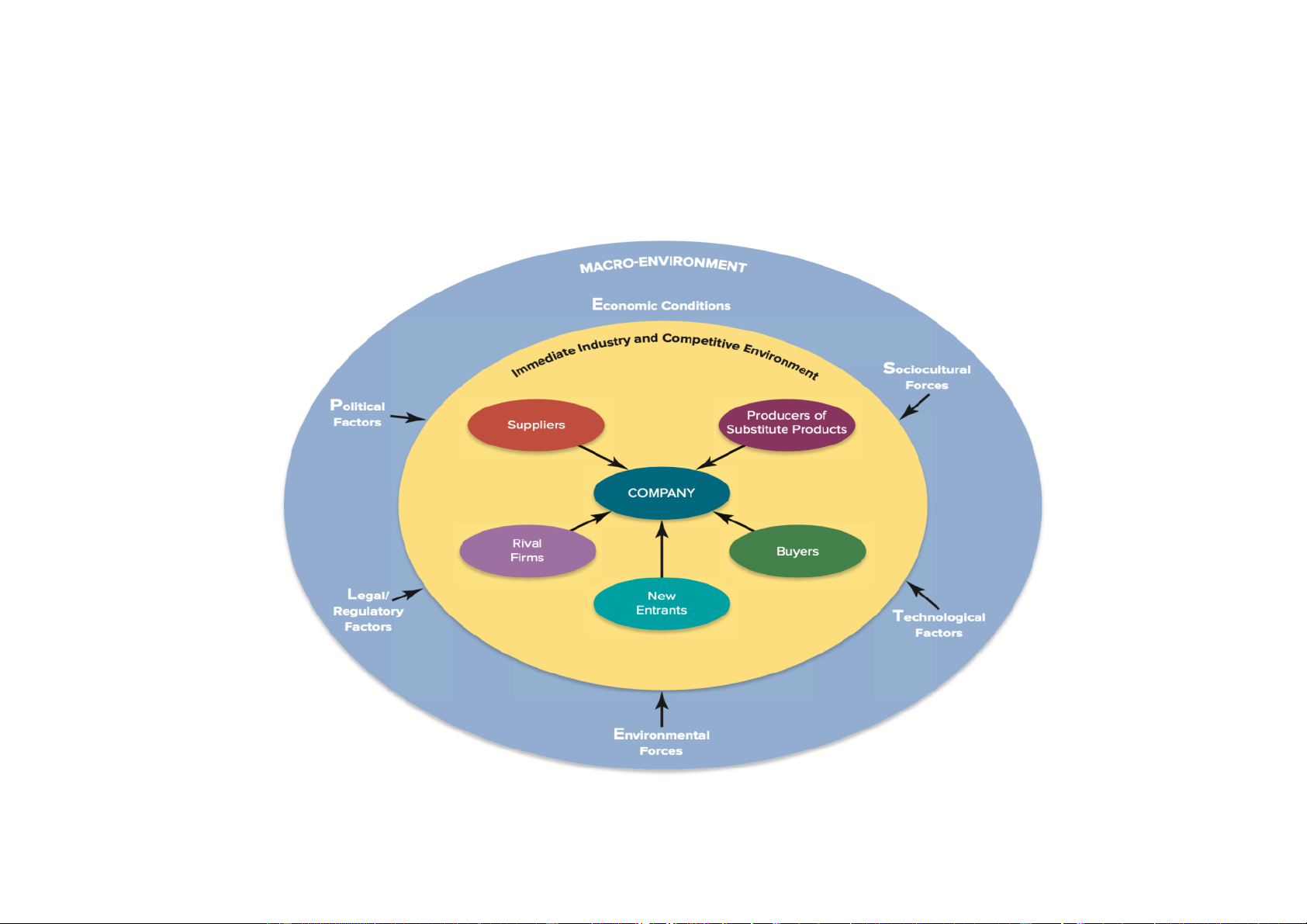
Exhibit 3-2 Components of External Environment
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
3.2. External Environment
A. The General Environment/Macro-Environment
vIs the broad environmental context in which a firm’s industry is situated.
vIncludes strategically relevant components over which
the firm has no direct control. ü General economic conditions
ü Immediate industry and competitive environment
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
3.2. External Environment
A. The General/Macro-Environment 3.2.1. Political-Legal
ü Government type and stability
ü Freedom of the press, rule of law and levels of bureaucracy and corruption
ü Regulation and de-regulation trends
ü Social and employment legislation
ü Tax policy, and trade and tariff controls
ü Environmental & consumer-protection legislation
ü Likely changes in the political environment
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
3.2. External Environment
A. The General Environment 3.2.2. Economic ü Stage of a business cycle
ü Current and projected economic growth, inflation and interest rates
ü Unemployment and supply of labor, labor costs
ü Levels of disposable income and income distribution ü Impact of globalization
ü Likely impact of technological or other changes on the economy
ü Likely changes in the economic environment
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
3.2. External Environment
A. The General Environment 3.2.3. Sociocutural sociaocultural
ü Cultural aspects, health consciousness, population growth rate, age distribution.
ü Organizational culture, attitudes to work, management style, staff attitudes.
ü Education, occupations, earning capacity, living standards. ü Ethical issues, diversity, immigration/emigration, ethnic/religious factors.
ü Media views, law changes affecting social factors, trends, advertisements, publicity.
ü Demographics: age, gender, race, family size.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
3.2. External Environment
A. The General Environment 3.2.4. Technological ü Maturity of technology, competing technological
developments, research funding, technology legislation. ü Information technology, internet, global and local communications.
ü Technology access, licensing, patents, potential innovation,
replacement technology/solutions, inventions, research,
intellectual property issues, advances in manufacturing. ü Transportation, energy uses/sources/fuels,
associated/dependent technologies, rates of obsolescence, waste removal/recycling.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
3.2. External Environment
A. The General Environment 3.2.5. Demographic ü Population growth rate ü Age distribution. ü Gender ü Race ü Family size.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
3.2. External Environment
A. The General Environment 3.2.6. Global
ü Economic recession/integration ü War, terrorism ü Tensions between countries ü Emerging Economies ü MNC expansions
ü Global advancements in technologies and telecommunications
ü Global Marketing & Distribution Channels
ü International Strategic Alliances
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 PESTEL Analysis
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Key aspects of PESTLE Analysis
ü Don’t just list environmental factors; derive implications for the industry
ü Focus on the key drivers of change
ü Focus is on future impact of environmental factors
ü Consider the combined effect of environmental factors
ü Environmental factors would be different from country to country
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 PESTLE and SWOT
v The PESTEL Analysis essentially provides the basis for
identifying many of the Opportunities and Threats for the SWOT Analysis.
v Whereas, Strengths and Weaknesses are considered
INTERNAL to the organisation, Opportunities and Threats are EXTERNAL.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
3.2. External Environment
B. The Industry/Task Environment
ü To identify the main structural features of an industry
that influence competition and – therefore – profitability
=> understand how an industry structure drives the level
of competiton within the industry, which determines the level of its profitability
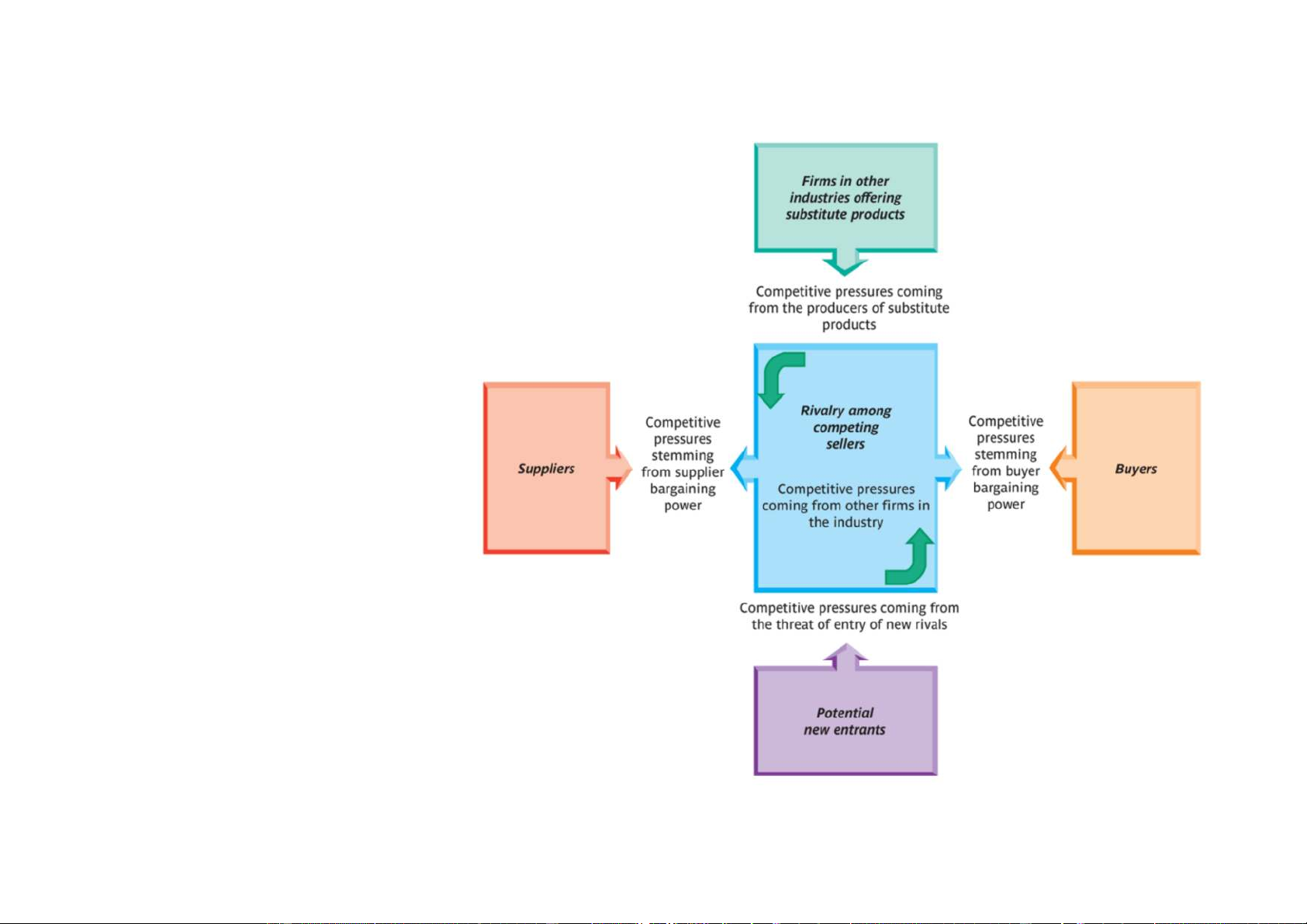
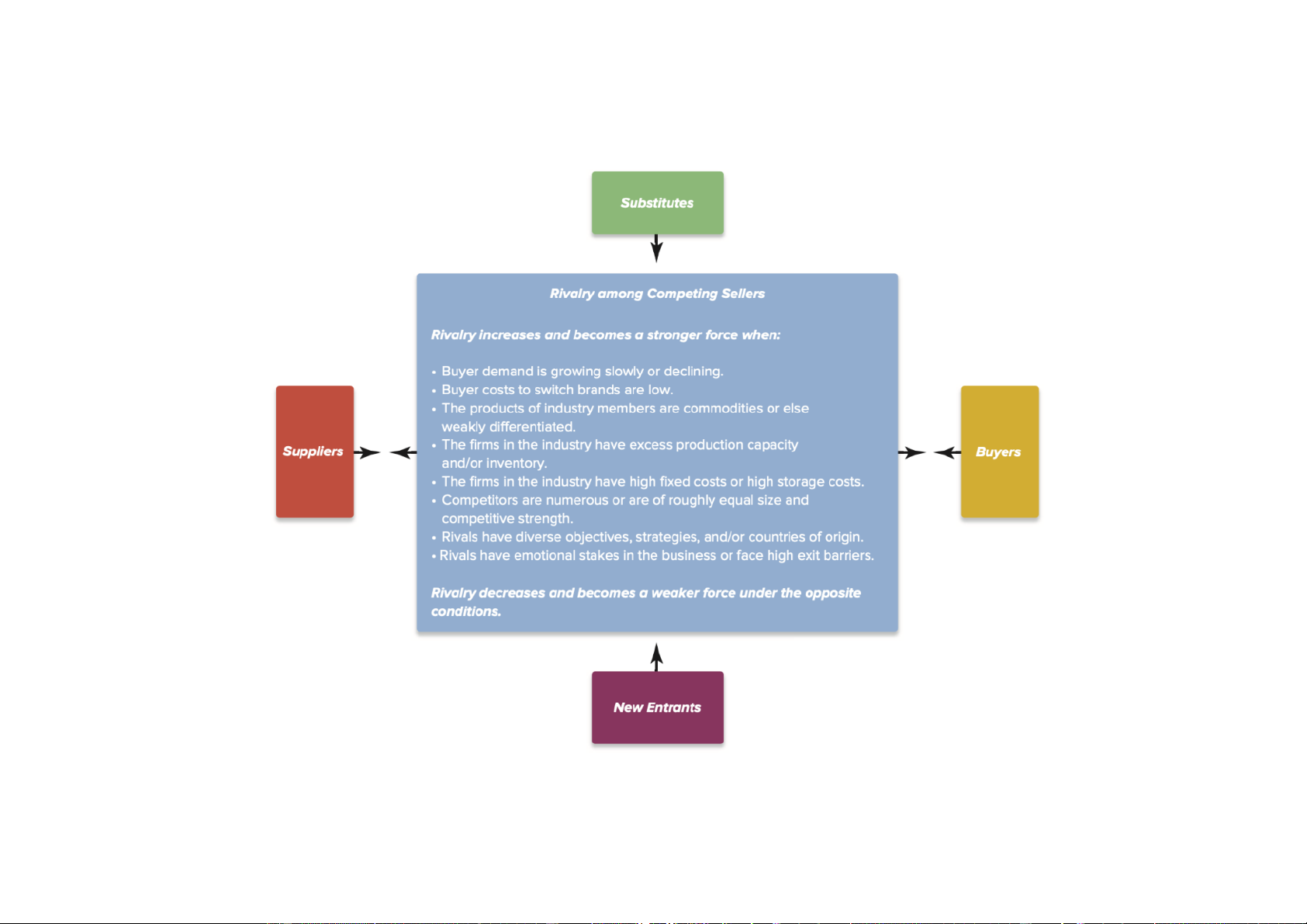
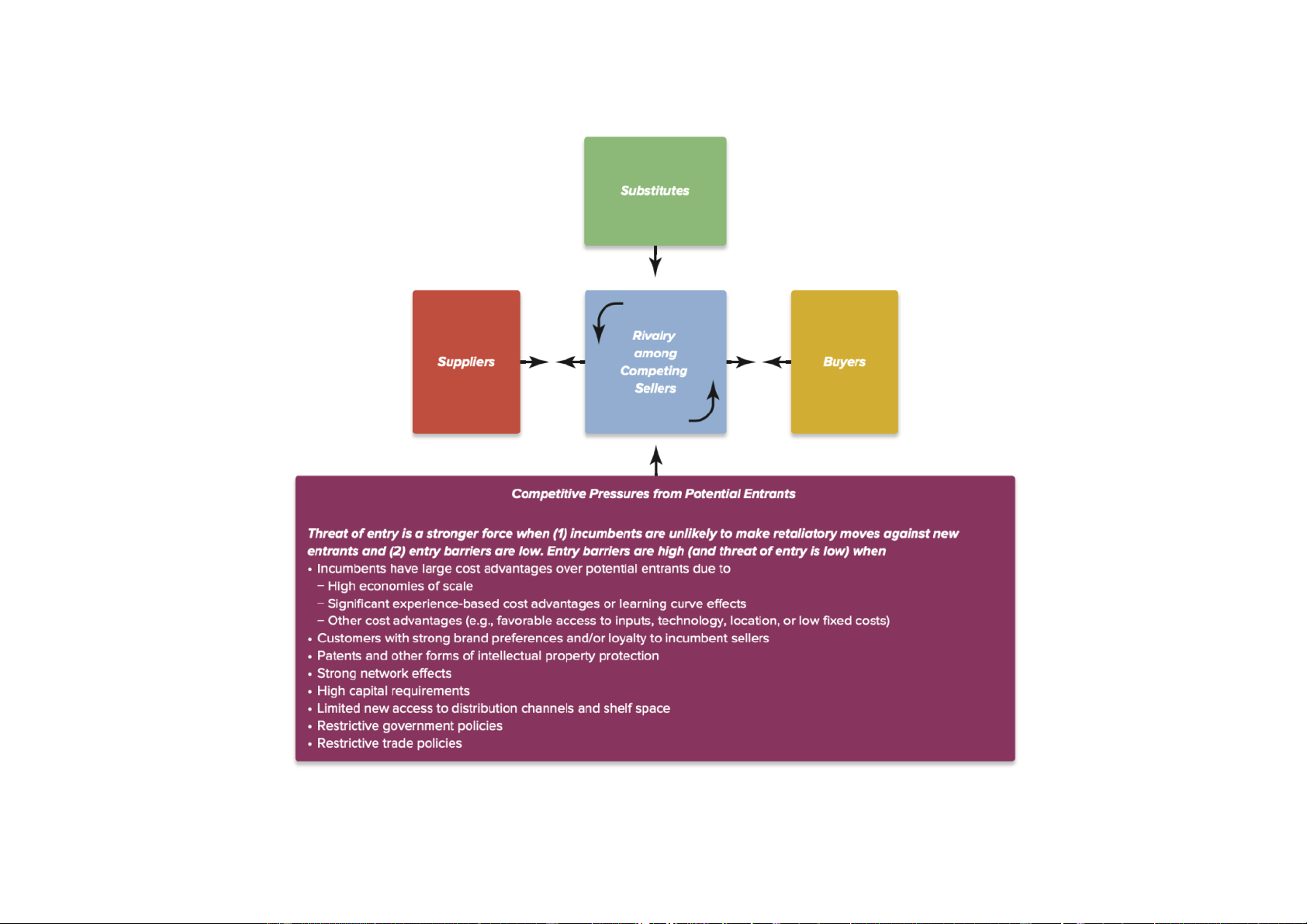
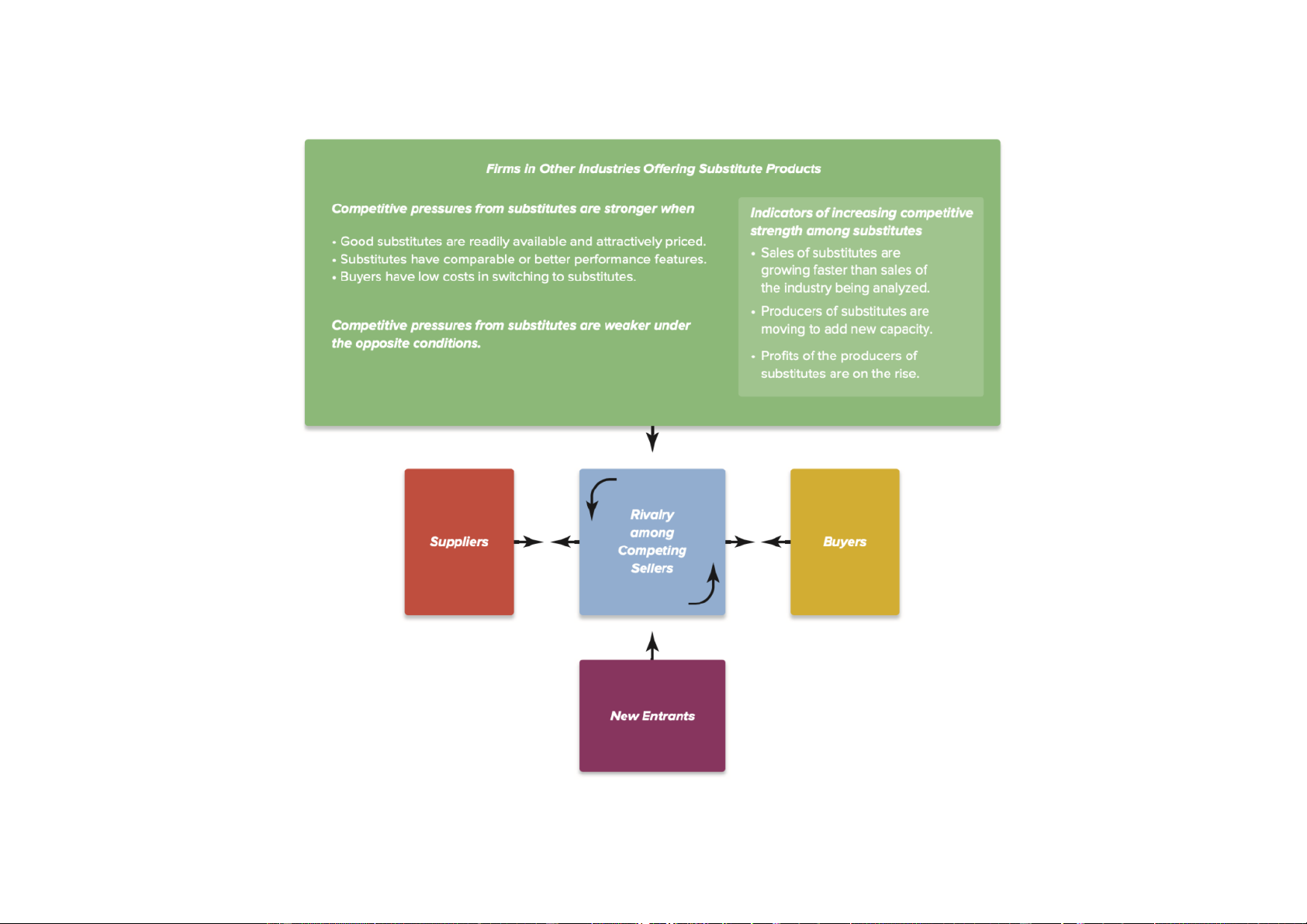
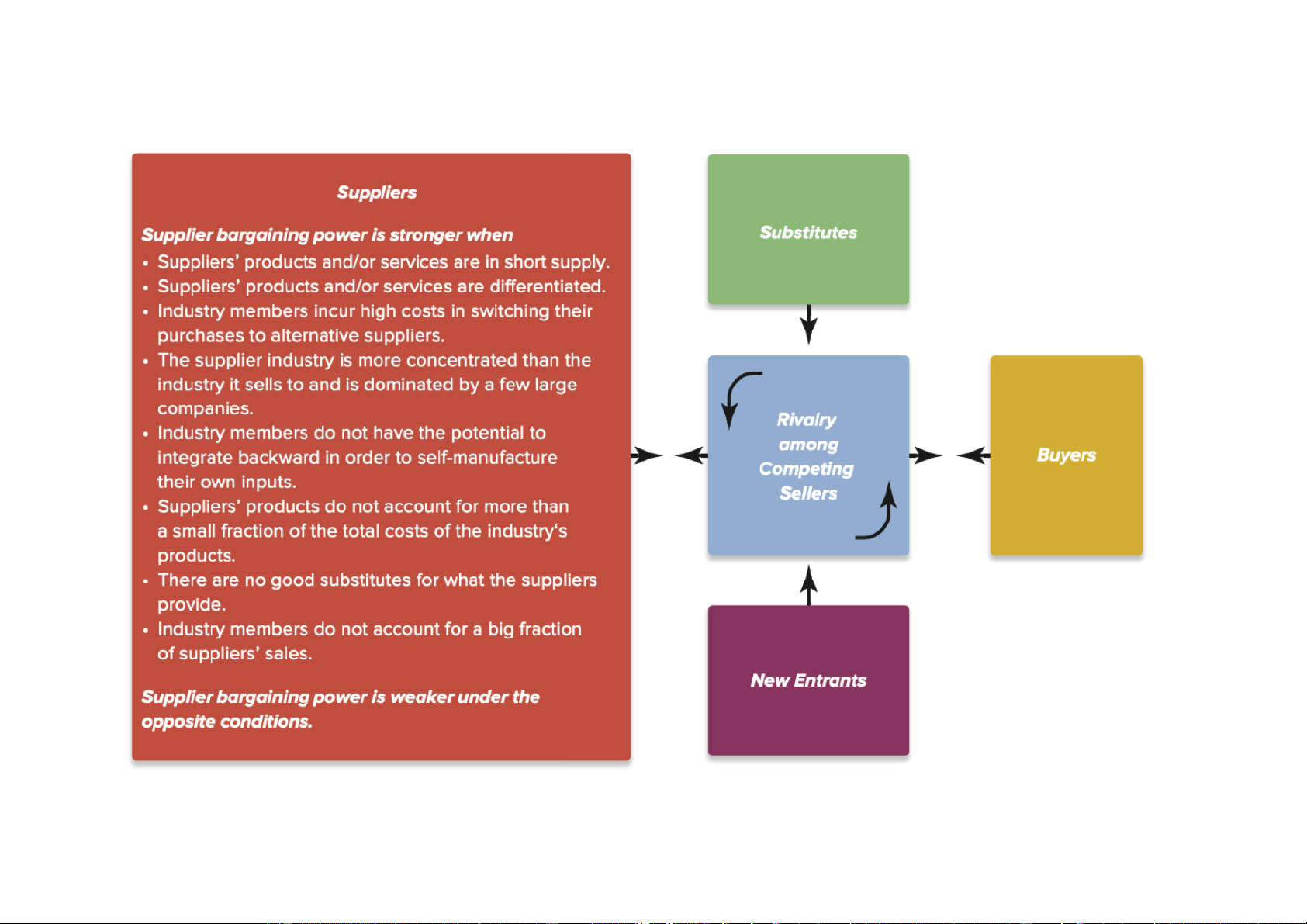
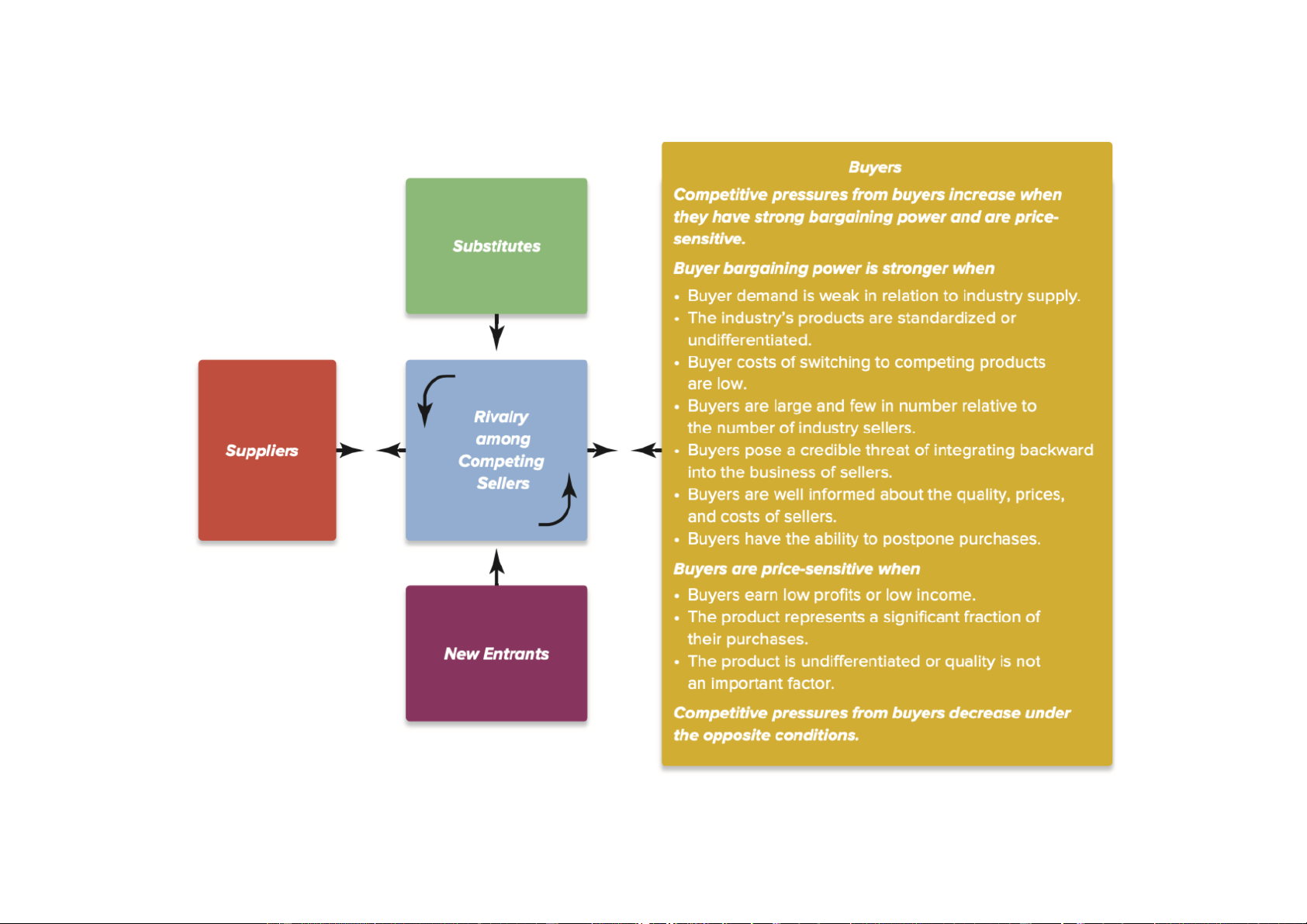
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 Exhibit 3-4 Industry environment Michael Porter’s five forces (1980)
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
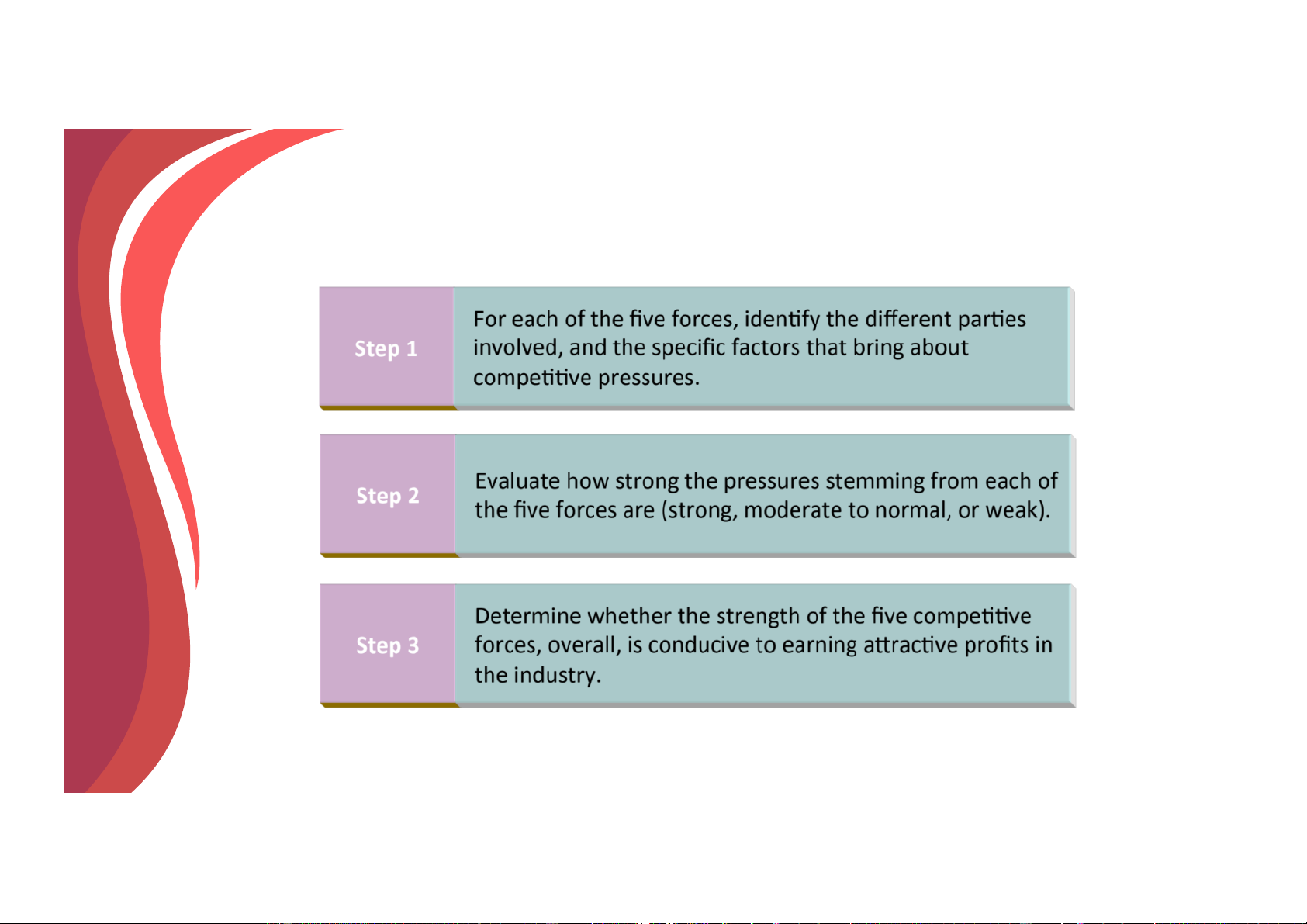
Using the Five-Forces model Analysis
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Switching cost : Cost to switch brand
Switch cost low: More competitive, easy change
Cola vs Pepsi: Product from cpmpetitor Sub:
exit barrier: hard to get out, same rival, competition, can be: Capital requirement, legislation
Ex: Banking: legislation: few bankruptcy
in this sector because wide effect, gov
will try to maintain, prevent from failing
=> Try to sale => Try to sell = campain, discount,... En ba high = low comp
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
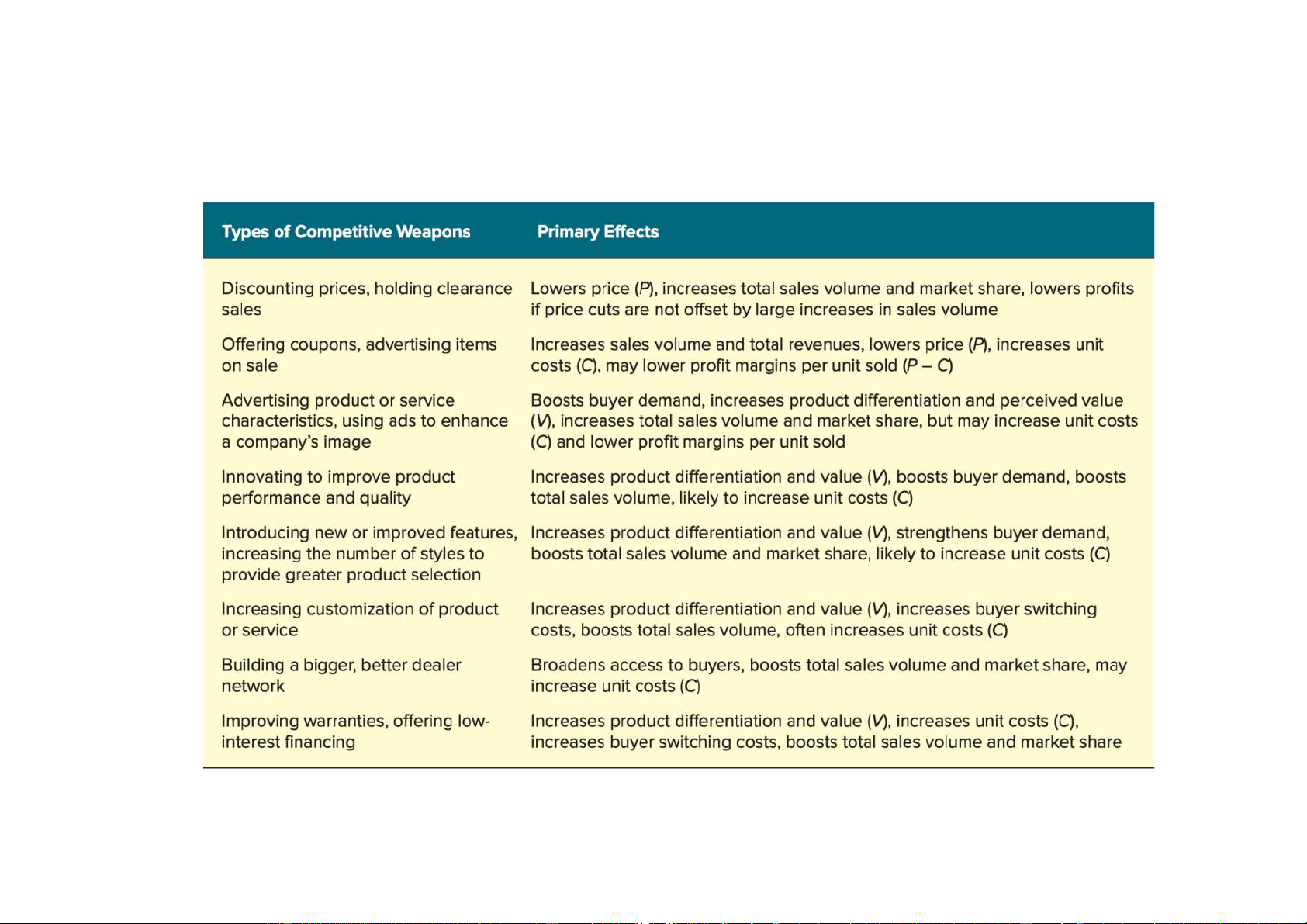
Common Weapons for Competing with Rivals
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 Forward/ backward integration
Tell how strong bargaining power,... etc
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 Conclude the whole pressure world bank, ims, statista,...
Ch ra competitive prssure, các yu t,... suy ra kt lun trong ngành, th trng,... có vl vs doanh ngip ko
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 Pestel analysis
3.2. External Environment
The External Environment Analysis (Macro-environment
+ Industry analysis) provides the basis for identifying
many of the Opportunities and Threats for the SWOT Analysis.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 SSwot
3.3 Internal Environment website, bctc
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 Strategic Capability
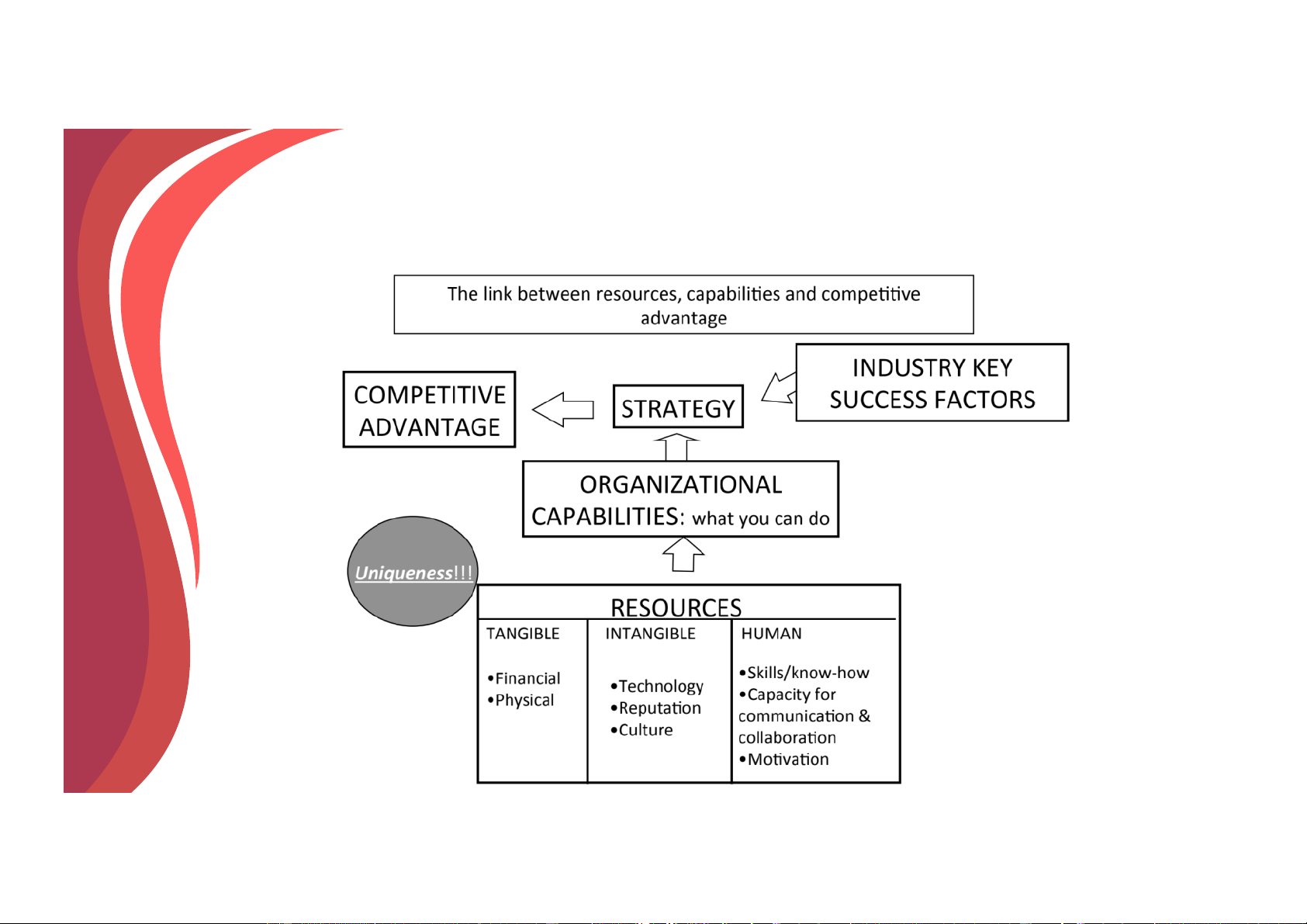
The Resource-Based View of Strategy (RBV)
ü “...The resource-based view emphasizes the
internal capabilities of the organisation in
formulating strategy to achieve a sustainable
competitive advantage.” A Henry, pp. 126
ü Strategic capability is based on the resources
available to the organisation and the competencies
it develops in order to make use of the resources
(Chief Advocates: Hamel & Prahalad(1990);
Rumelt(1991); Barney(1991); Grant(1991)).
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
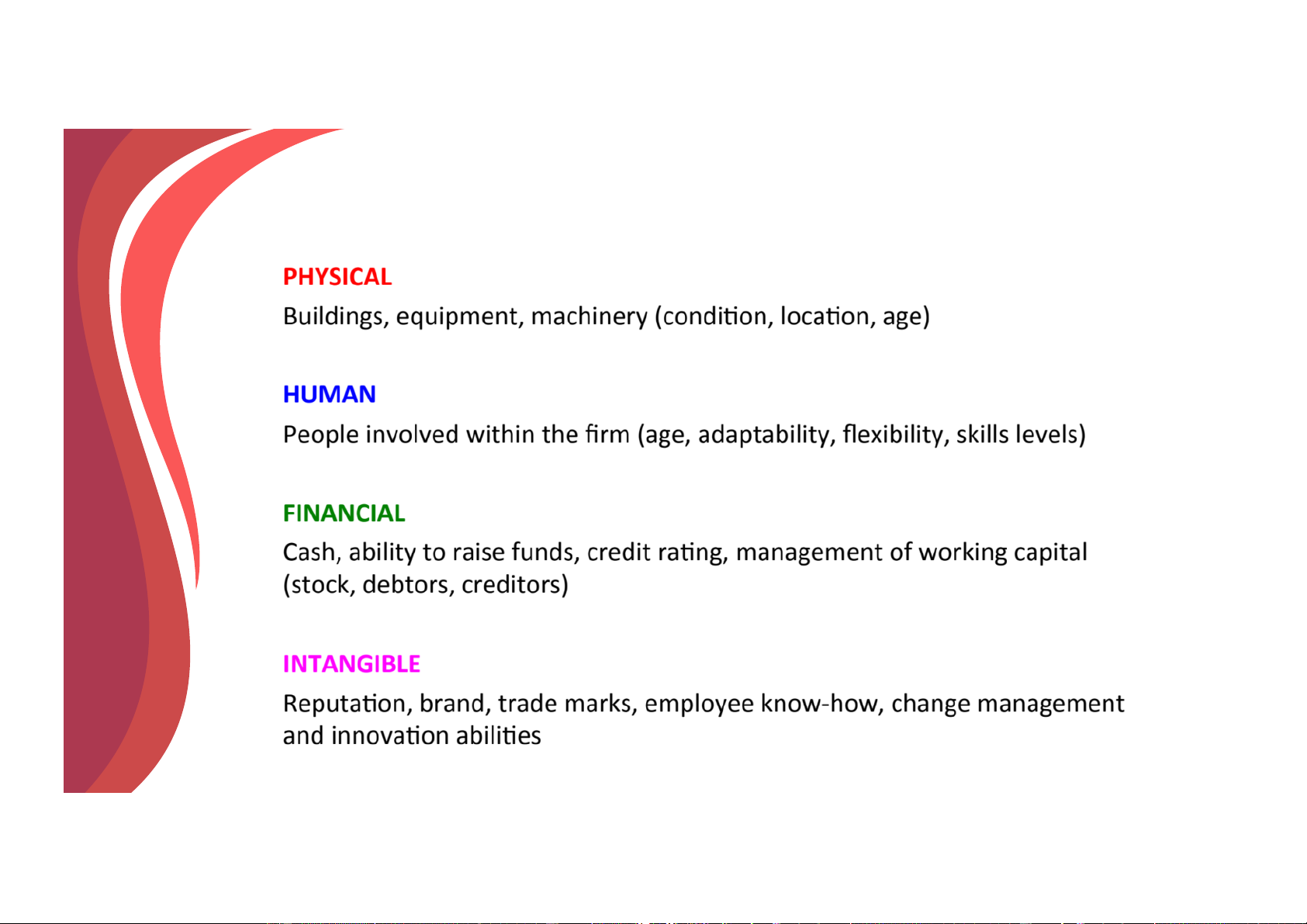
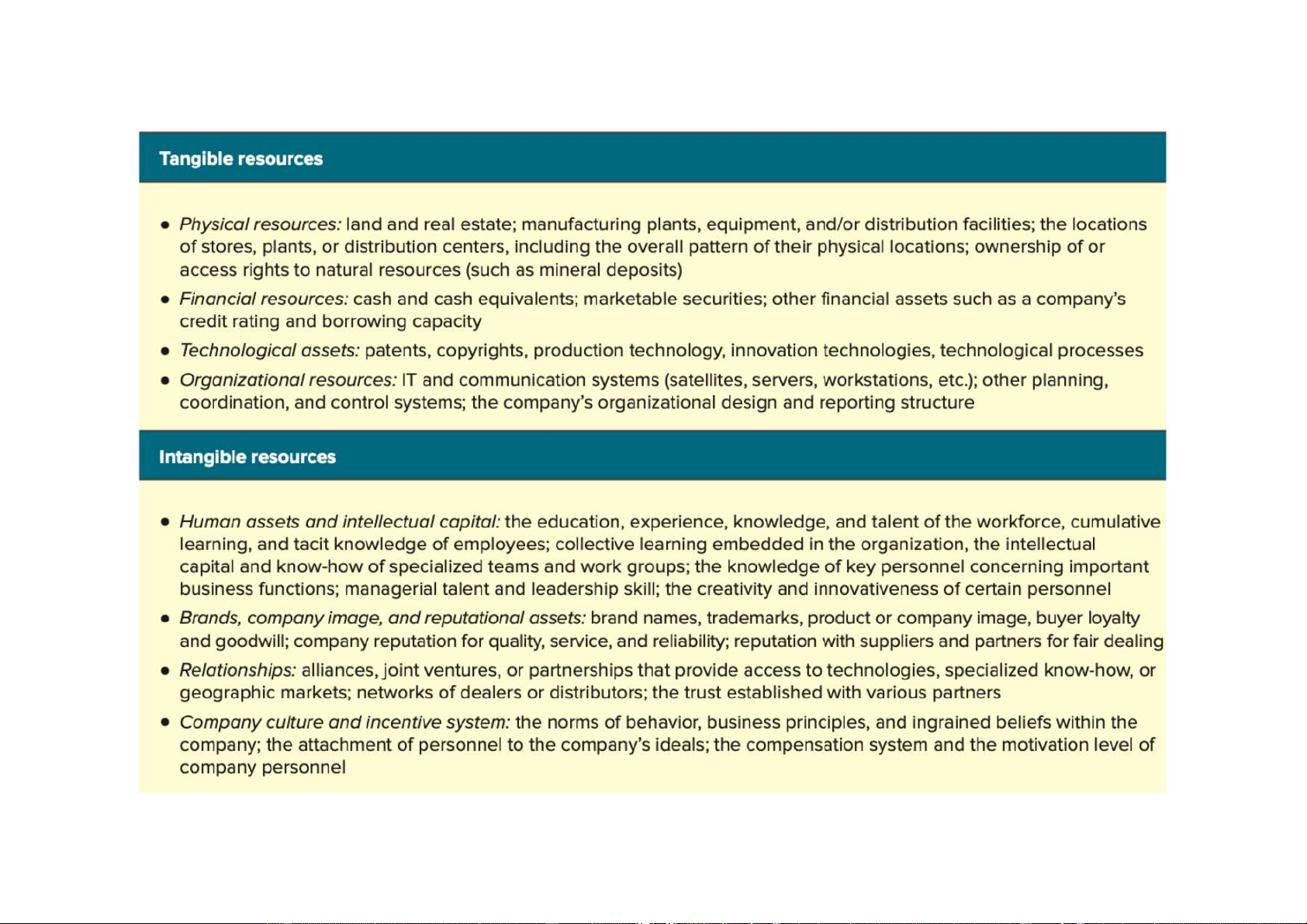
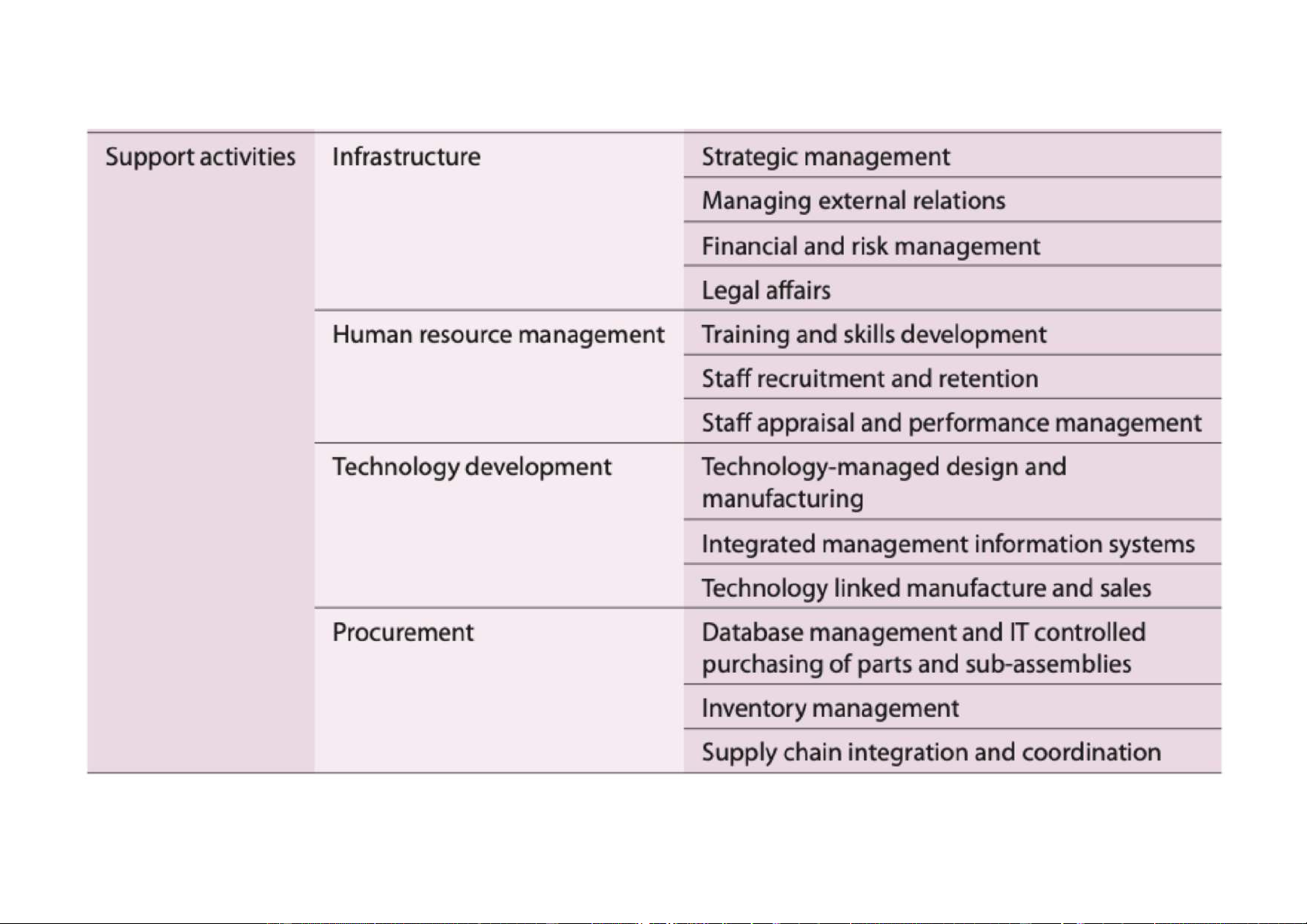
Definition of Resources and Capability v Resource
ü Is a productive input or competitive asset that is
owned or controlled by a company (e.g., a fleet of oil tankers). v Capability
ü Is the capacity of a firm to perform some activity
proficiently (e.g., superior skills in marketing). It is a
“firm’s capacity to deploy resources for a desired end result”.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 Resources
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 40
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 SBU: Strategic business unit
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
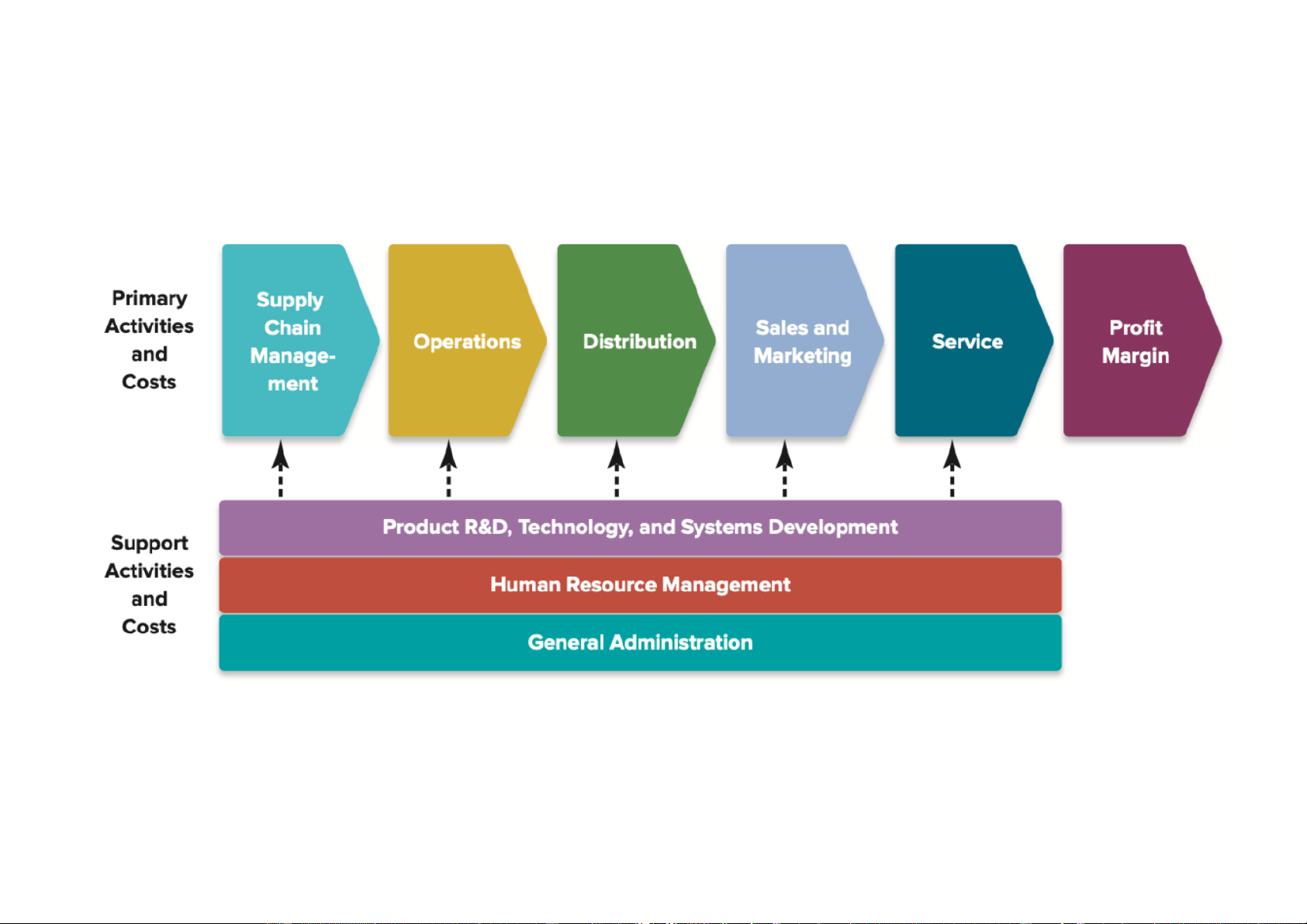
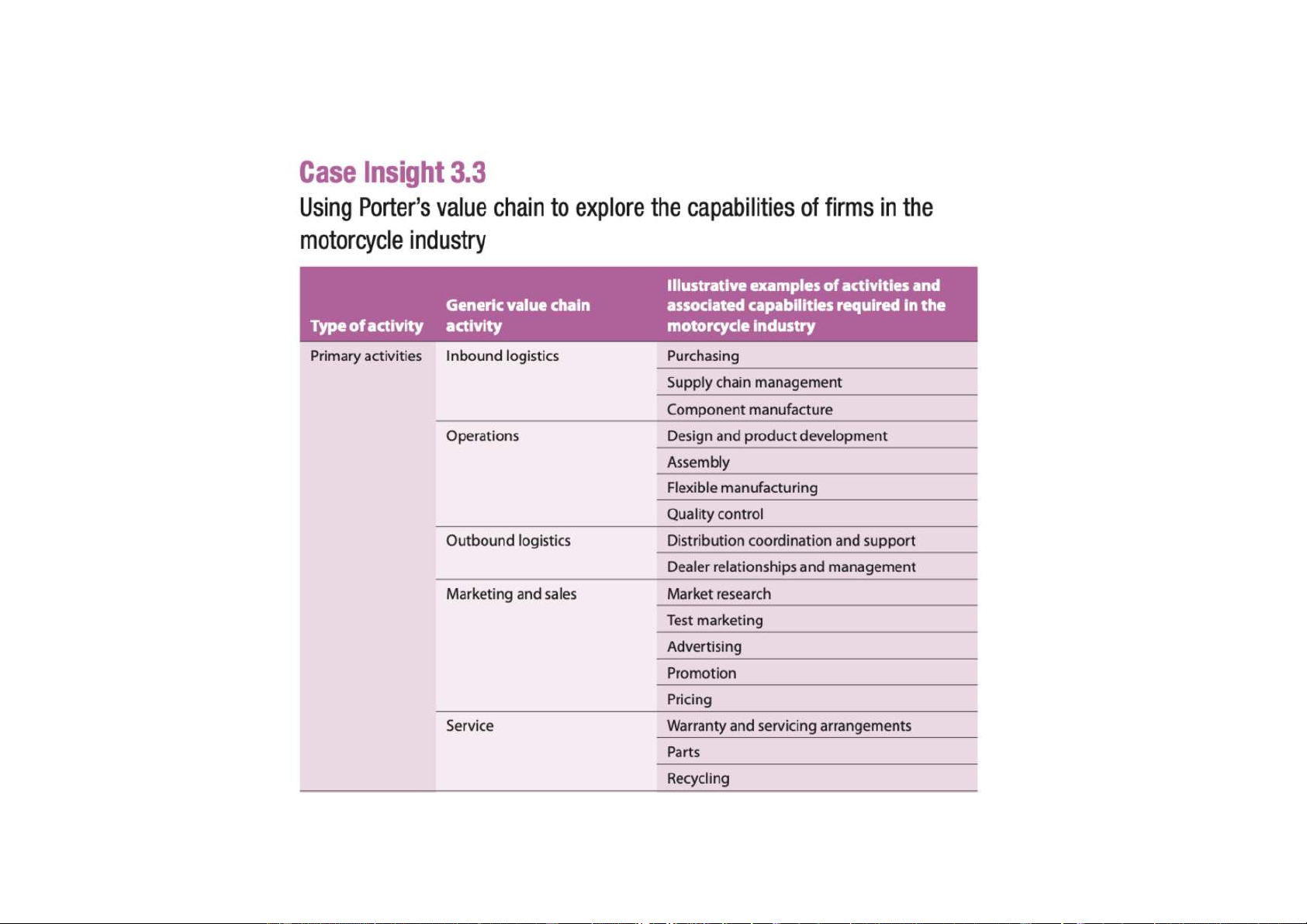
Source: Based on the discussion in Michael E. Porter, Competitive Advantage (New York: Free Press, 1985), pp. 37–43. Phân tích cty dch v
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Source: Based on the discussion in Michael E. Porter, Competitive Advantage (New York: Free Press, 1985), pp. 37–43.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 44
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 45
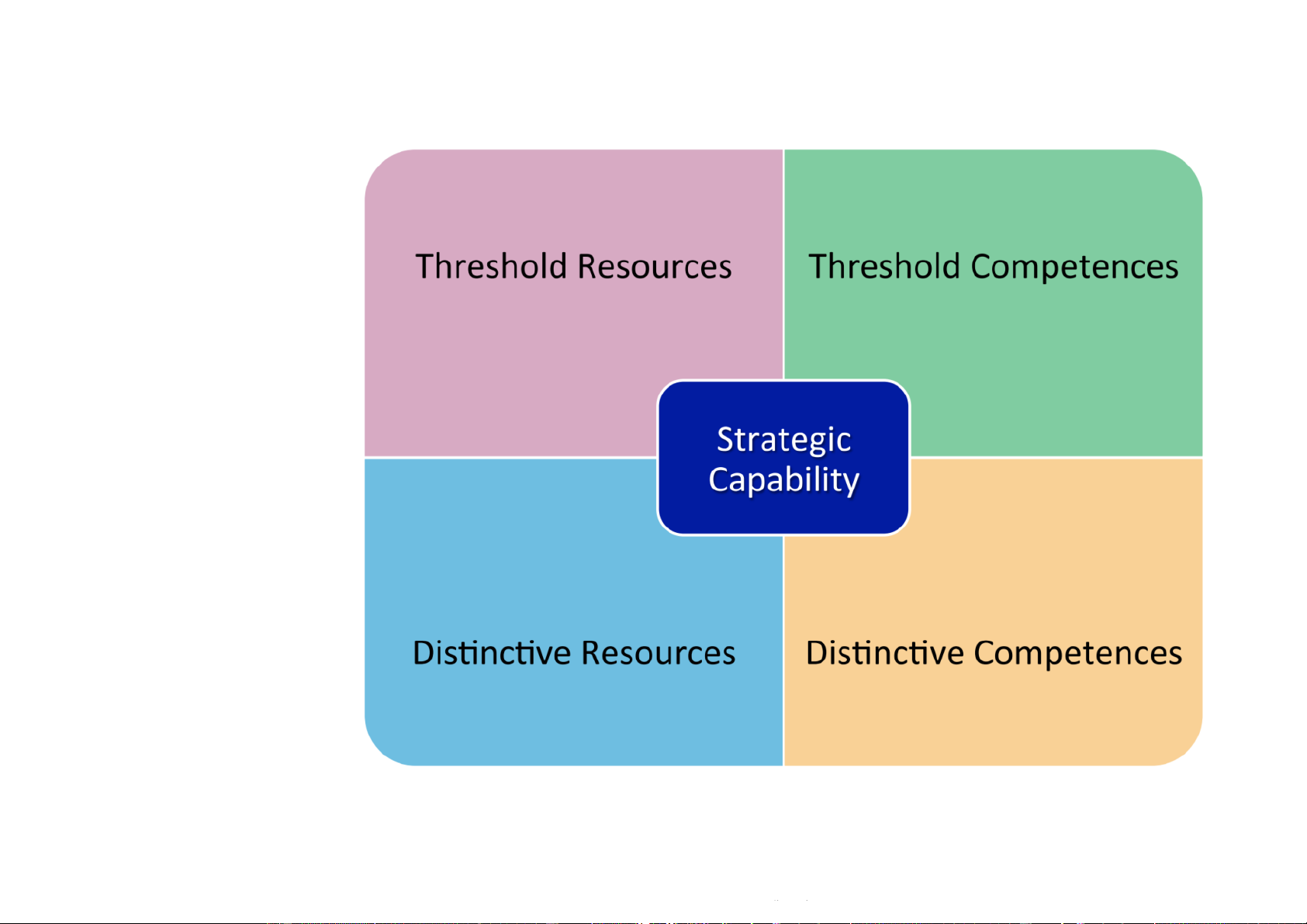
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 threshold: minimum standard threshold resources: Tài sn ngng ti thiu The Competency framework
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561 Resources
v THRESHOLD RESOURCES – “needed to play”
Those resources that an organisation needs to have in order
to meet the minimum requirements of its customers
ü For example, an airline needs more than a fleet of planes, it
will also need all the supporting structure, including landing and fly-over rights
v DISTINCTIVE RESOURCES – “needed to win”
“...those resources that criPcally underpin competitive
advantage and that others cannot easily imitate or obtain.”
ü For example, a strong brand name or reputation 47
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
VRIO/ VRIN framework: evaluate : ko có trong chng trình Competencies
v THRESHOLD COMPETENCIES – “needed to play”
Those minimum competences an organisation requires in
order to ensure that resources are deployed efficiently
enough to meet minimum customer requirements
ü For example, an airline will need to ensure its operations
conform to minimum safety standards
v DISTINCTIVE (CORE) COMPETENCIES - “needed to win”
“...the linked set of skills, activities and resources that,
together, deliver customer value, differentiate a business
from its competitors and, potentially, can be extended or developed .”
ü For example, a high level of marketing expertise 48
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
3.3 Internal Environment
ü Organizational culture
ü A system of shared meanings and common beliefs held
by organizational members that determines, in a large
degree, how they act towards each other.
ü “The way we do things around here.”: Values, symbols, rituals, myths, and practices ü Implications: v Culture is a perception. v Culture is shared. v Culture is descriptive.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
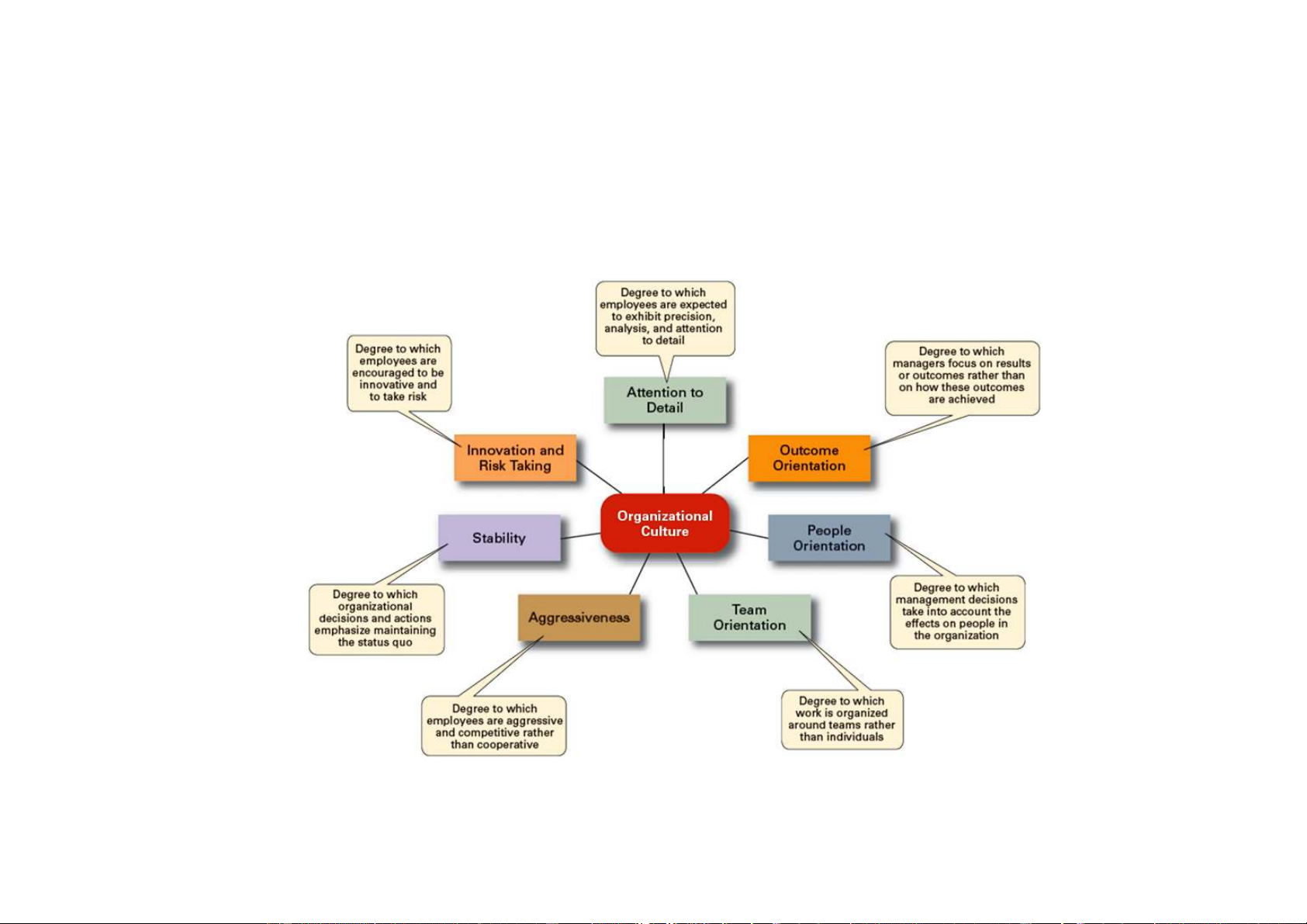
Exhibit 3-5 Organizational Culture
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
How Culture Affects Managers
Cultural Constraints on Managers
Ø Whatever managerial actions the organization
recognizes as proper or improper on its behalf
Ø Whatever organizational activities the organization values and encourages
Ø The overall strength or weakness of the organizational culture
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Exhibit 3–6 Managerial Decisions Affected by Culture • Planning
• The degree of risk that plans should contain
• Whether plans should be developed by individuals or teams
• The degree of environmental scanning in which management will engage • Organizing
• How much autonomy should be designed into employees’ jobs
• Whether tasks should be done by individuals or in teams
• The degree to which department managers interact with each other
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Exhibit 3–6 Managerial Decisions Affected by Culture • Leading
• The degree to which managers are concerned with increasing employee job satisfaction
• What leadership styles are appropriate
• Whether all disagreements—even constructive ones—should be eliminated • Controlling
• Whether to impose external controls or to allow employees to control their own actions
• What criteria should be emphasized in employee performance evaluations
• What repercussions will occur from exceeding one’s budget
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Organization Culture Issues v Creating an Ethical Culture
vCreating an Innovative Culture ü High in risk tolerance ü Challenge and involvement ü Low to moderate ü Freedom aggressiveness ü Trust and openness ü Focus on means as well ü Idea time as outcomes ü Playfulness/humor ü Conflict resolution ü Debates ü Risk-taking
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Exhibit 3–7 Creating a More Ethical Culture
• Be a visible role model.
• Communicate ethical expectations.
• Provide ethics training.
• Visibly reward ethical acts and punish unethical ones.
• Provide protective mechanisms so employees
can discuss ethical dilemmas and report
unethical behavior without fear.
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
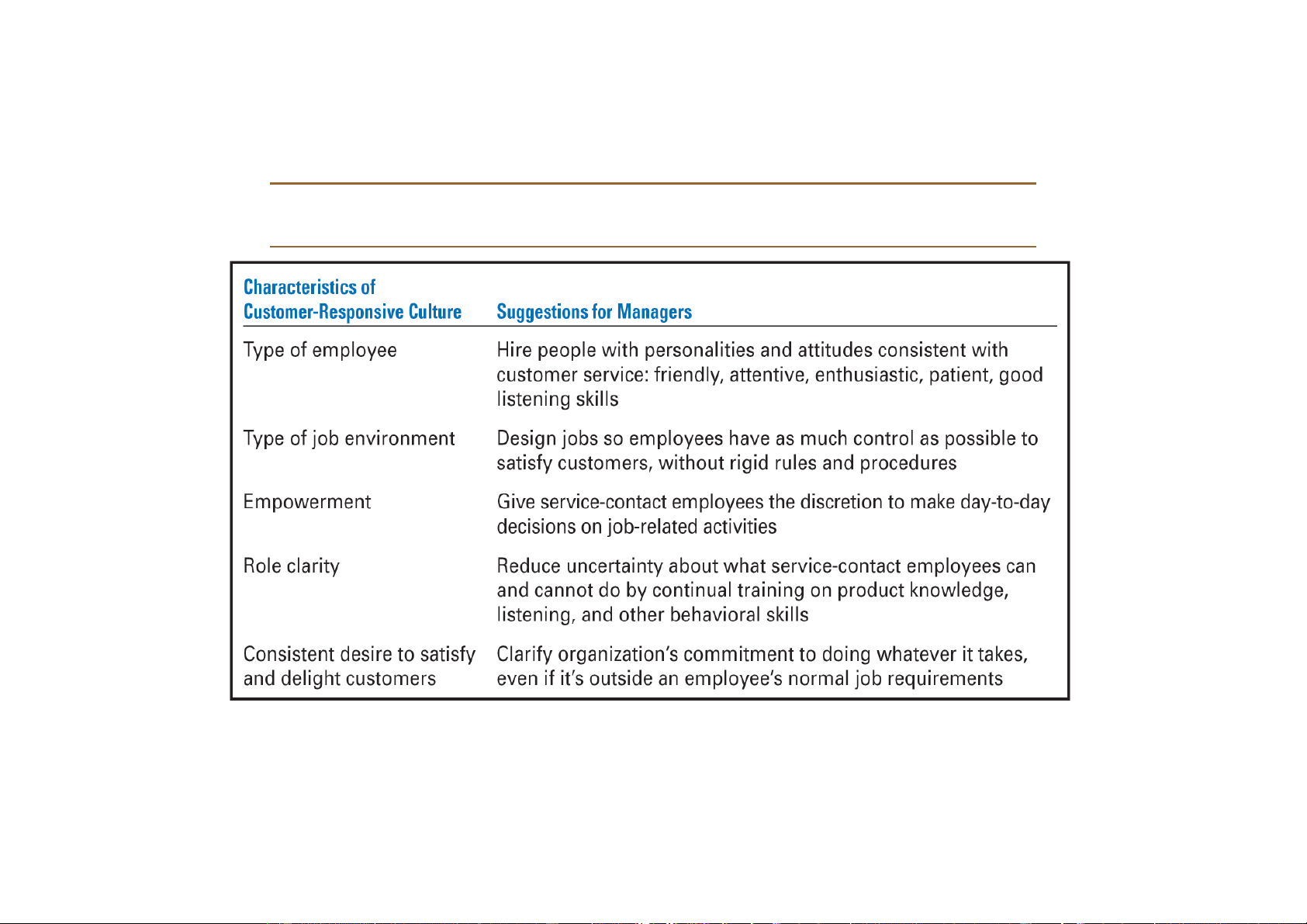
Organization Culture Issues
v Creating a Customer-Responsive Culture
ü Hiring the right type of employees (those with a strong interest in serving customers)
ü Having few rigid rules, procedures, and regulations
ü Using widespread empowerment of employees
ü Having good listening skills in relating to customers’ messages
ü Providing role clarity to employees to reduce
ambiguity and conflict and increase job satisfaction
ü Having conscientious, caring employees willing to take initiative
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|36041561
Exhibit 3–8 Creating a Customer-Responsive Culture
Downloaded by Nga T??ng (ngahuong55@gmail.com)


