





Preview text:
Algebra Bases and coordinates Dr. Nguyen Tuan Long
MFE - Mathematics Faculty of Economics
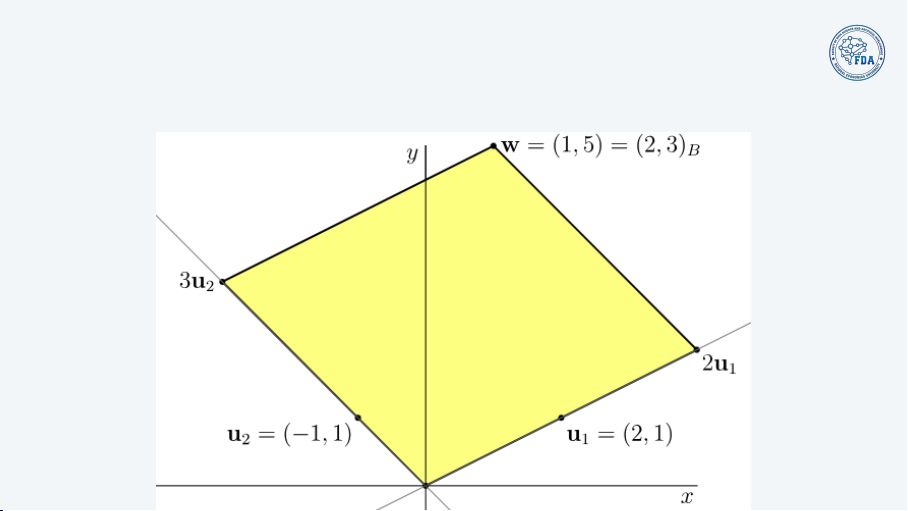
Coordinates with respect to a basis Definition
Let v ∈ Rn be a vector, and B = {x1, x2, . . . , xn} be a basic. Then v must be a linear
combination of {x1, x2, . . . , xn}. That is, there is exactly one choice of r1, r2, . . . , rn such that
v = r1x1 + r2x2 + . . . + rnxn.
We say that (r1, r2, . . . , rn) is the coordinates of v with respect to the basis B. Examples
The vector v, which has coordinates of (1, 2, 3) w.r.t the standard basis in R3, has
coordinates of (2, 1, 0) w.r.t the basis B = {(0, 1, 1), (1, 0, 1), (1, 1, 0)}. 2/7
Coordinates with respect to a basis 3/7
Linear combinations and matrices Property
Let B = {x1, x2, . . . , xn} be a basic of Rn, and v be a vector in Rn. Then the
coordinates (r1, r2, . . . , rn) of v w.r.t the basis B are given by r1 r 2 . .. = A−1v rn Examples
Find the coordinates of v = (2, 4, −1) w.r.t the basis B = {(−2, 0, 2), (4, 1, 0), (3, 2, 1)}? 4/7 Change of basis Property
Suppose that B1 and B2 are bases of Rn. Then there is a matrix C with the following
property: if v ∈ Rn and (r1, r2, . . . , rn) and (s1, s2, . . . , sn) are the coordinates of v with
respect to the bases B1 and B2, then s1 r1 s 2 r2 . . .
. = C .. . sn rn 5/7 Change of basis Property
Suppose that B1 = {x1, x2, . . . , xn} and B2 = {y1, y2, . . . , yn} are bases of Rn.
Additionally, let (c1j, c2j, . . . , cnj) be the coordinates of xj with respect to the basis B2,
that is, xj = c1jy1 + c2jy2 + . . . + cnjyn. Denote C = [cij]n×n. Then, for any vector v
which has the coordinates w.r.t the bases B1 and B2 of (r1, r2, . . . , rn) and
(s1, s2, . . . , sn), respectively. Then s1 r1 s 2 r2 . . .
. = C .. . sn rn 6/7
Linear combinations and matrices Examples
Let B1 = {x1, x2, x3} and B2 = {y1, y2, y3} be two bases of R3: 1 0 2 1 2 0 B 1 : x1 =
2 , x2 = 1 , x3 = 0 . B2 : y1 = 1 , y2 = 0 , y3 = 1 . 1 3 1 1 1 2 Tasks:
• Find the change-of-basis matrix C such that s = Cr, where r and s are the
coordinates of v in B1 and B2. 3
• Compute the coordinates of v = 4 in both B1 and B2. 5 7/7




