
Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 CSC10009 – Computer System REVIEW # 1 DATA REPRESENTATION 4.0 fit@hcmus lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 ( Positional) Number Systems fit@hcmus
▪ General formular for unsigned integer with n digits in q - base system x n : MSB - 1 x 0: LSB (Most Si gnifican ) t Bit L
( ess Significan ) t Bit Value Exponential Form
Binary number system (base - 2) Octal number system (base - 8)
Decimal number system (base - 10)
Hexadecimal number system (base - 16) 2 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Sign Extension fit@hcmus
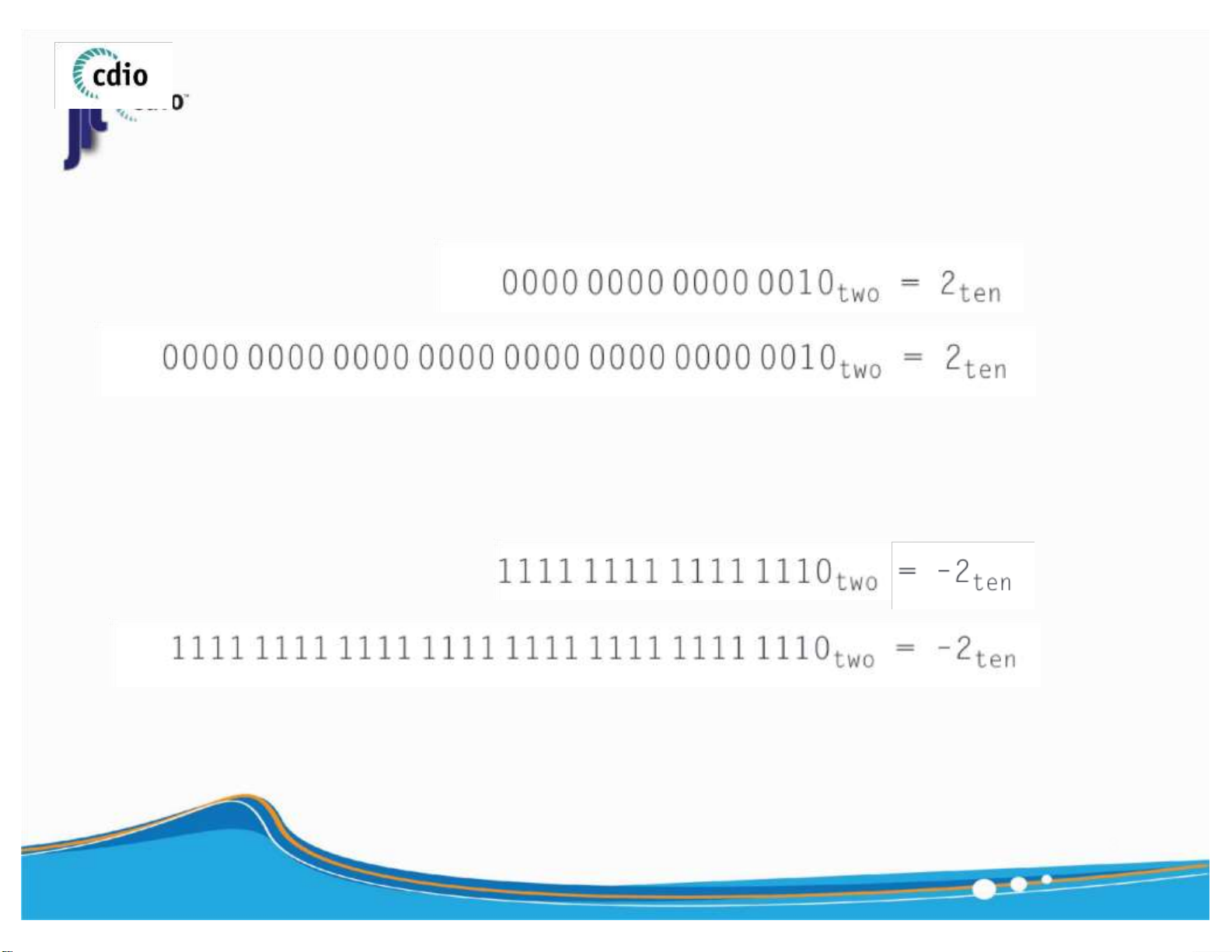
▪ Positive number 16 - bit to 32 - bit
▪ Negative number 16 - bit to 32 - bit 3 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Integer Representation fit@hcmus
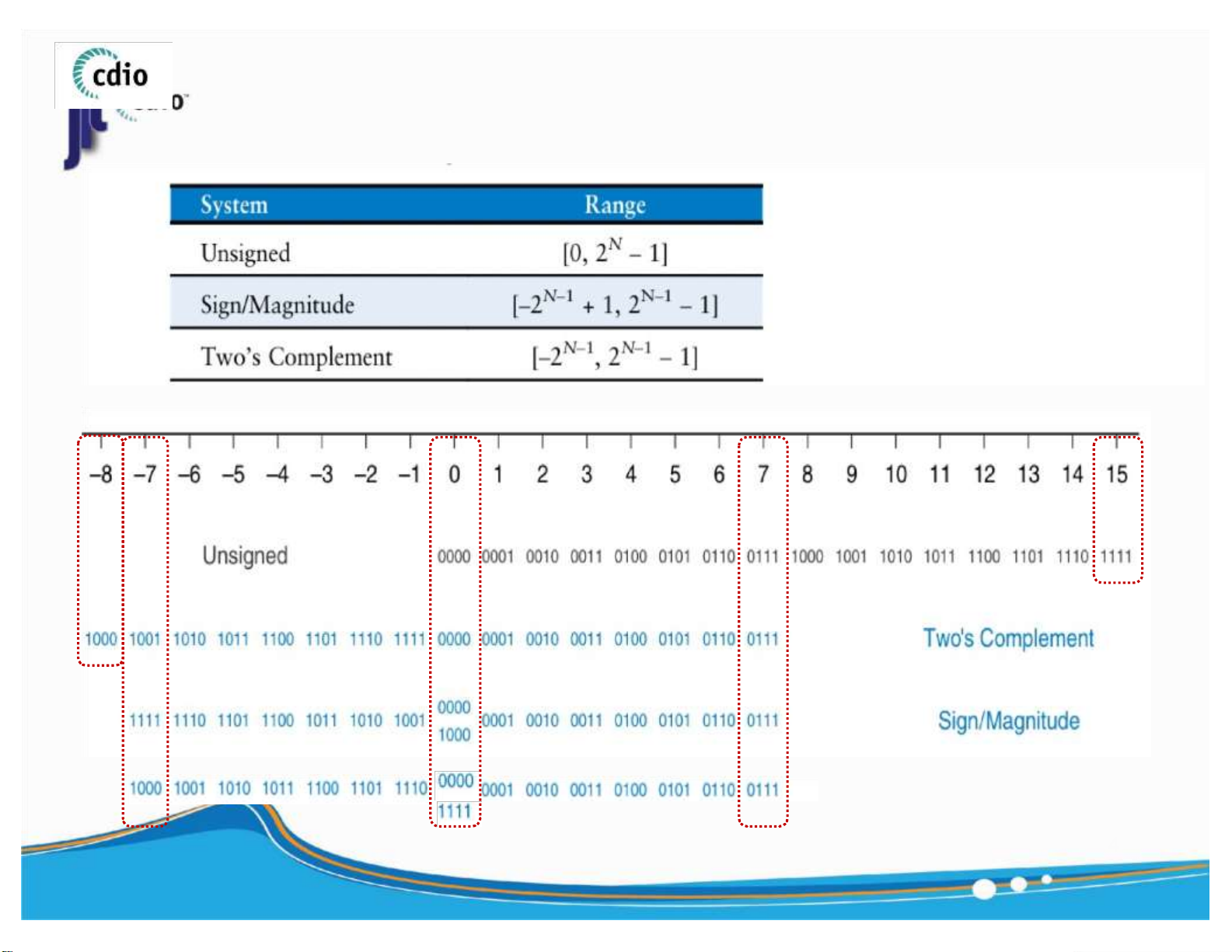
- 2 n - 1 - 2 n - 1 +1
2 n - 1 - 1
2 n - 1 One’s Complement 4 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Integer Representation (2) fit@hcmus
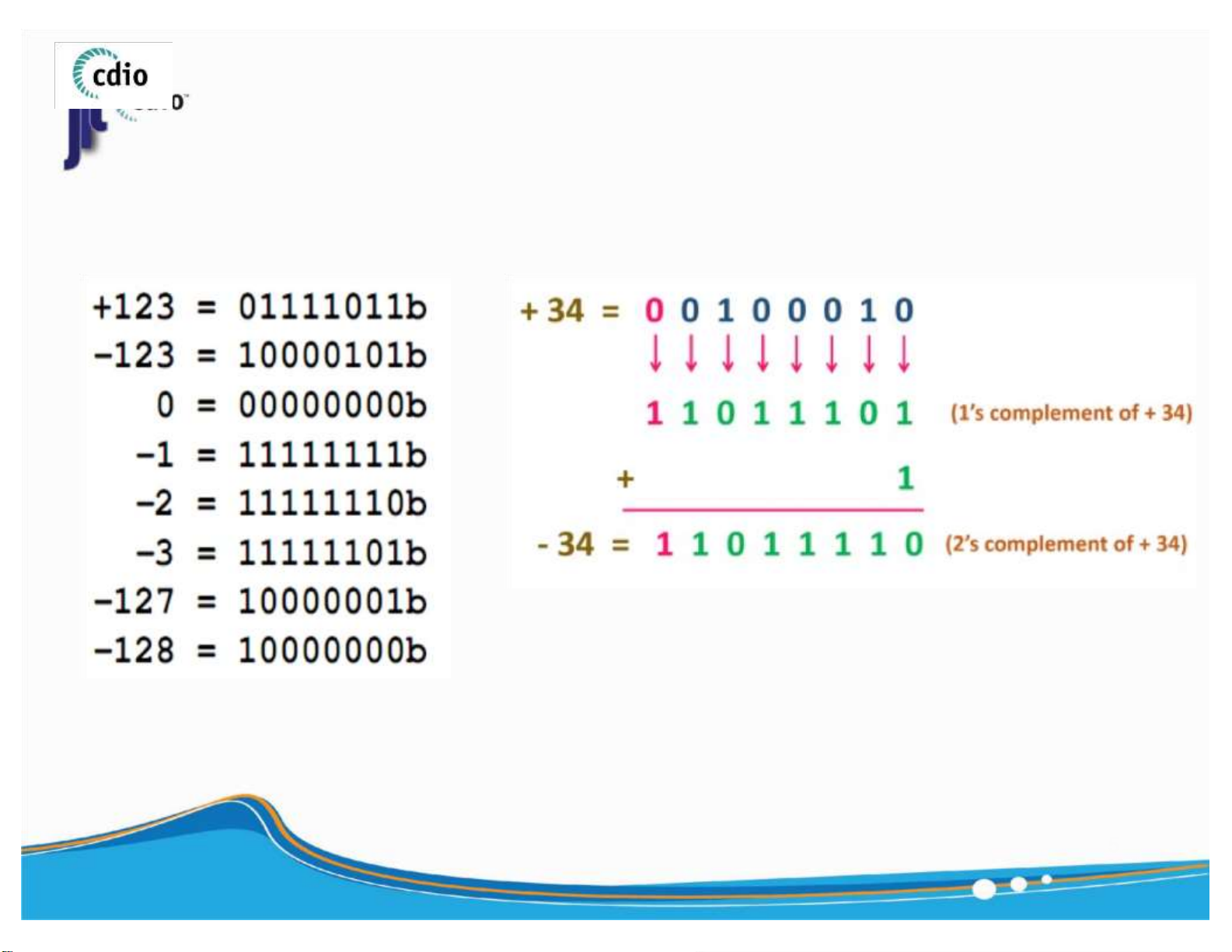
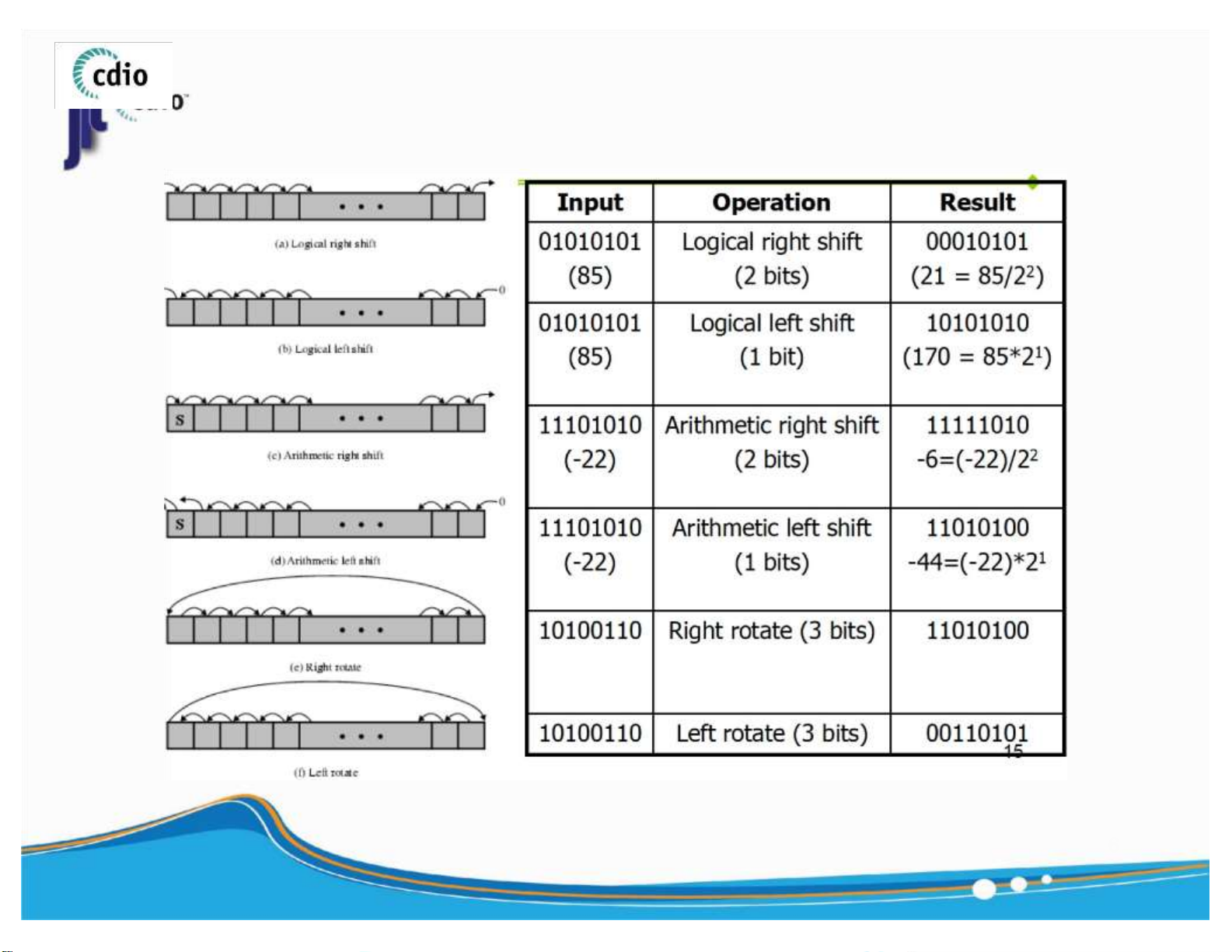
▪ Signed integer A of n - bit in 2 ’s Complement representation : 5 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Shift & Rotate fit@hcmus 6 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Shift & Rotate (2) fit@hcmus or 7 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Shift & Rotate (3) fit@hcmus
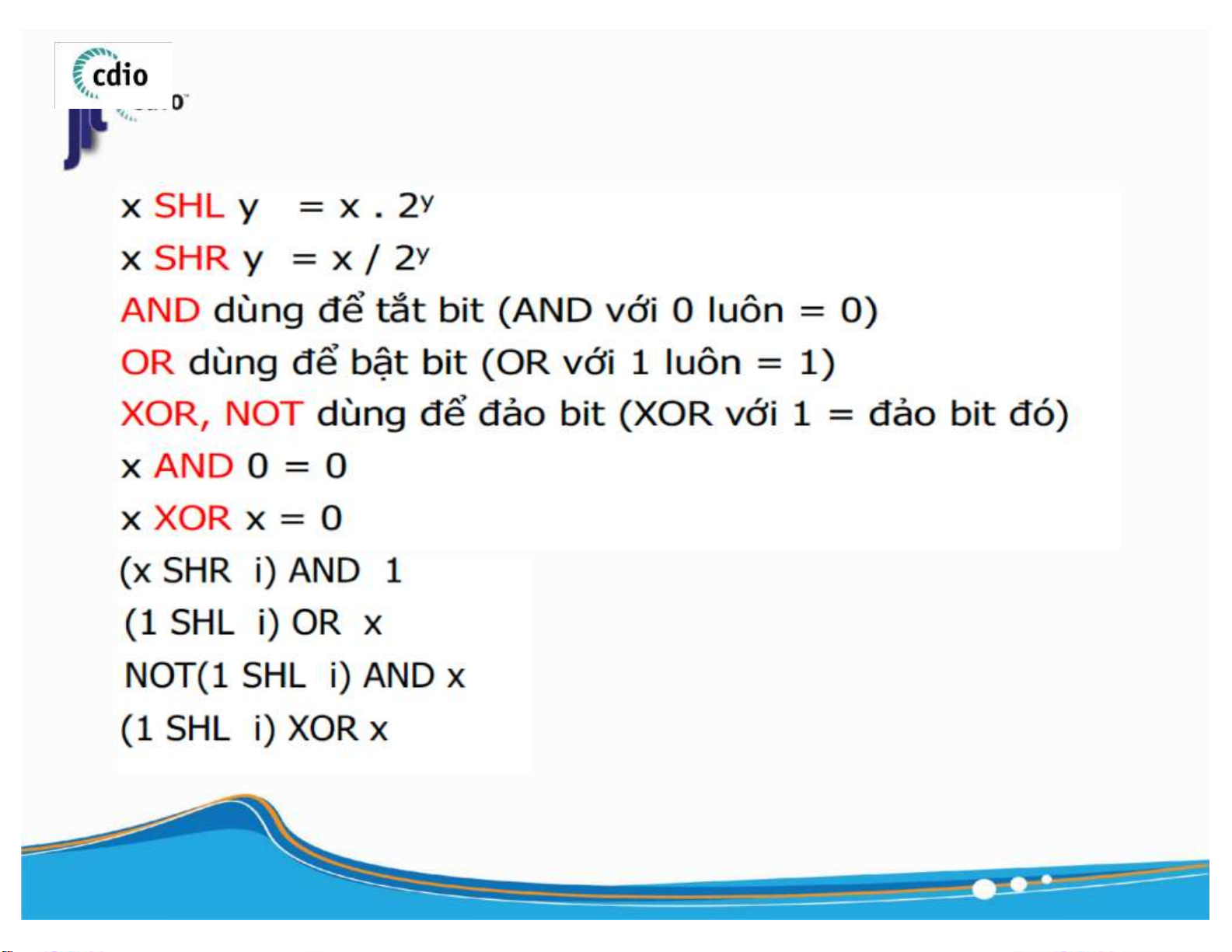
Clear a bit (AND with 0 is always 0)
Set a bit (OR with 1 is always 1)
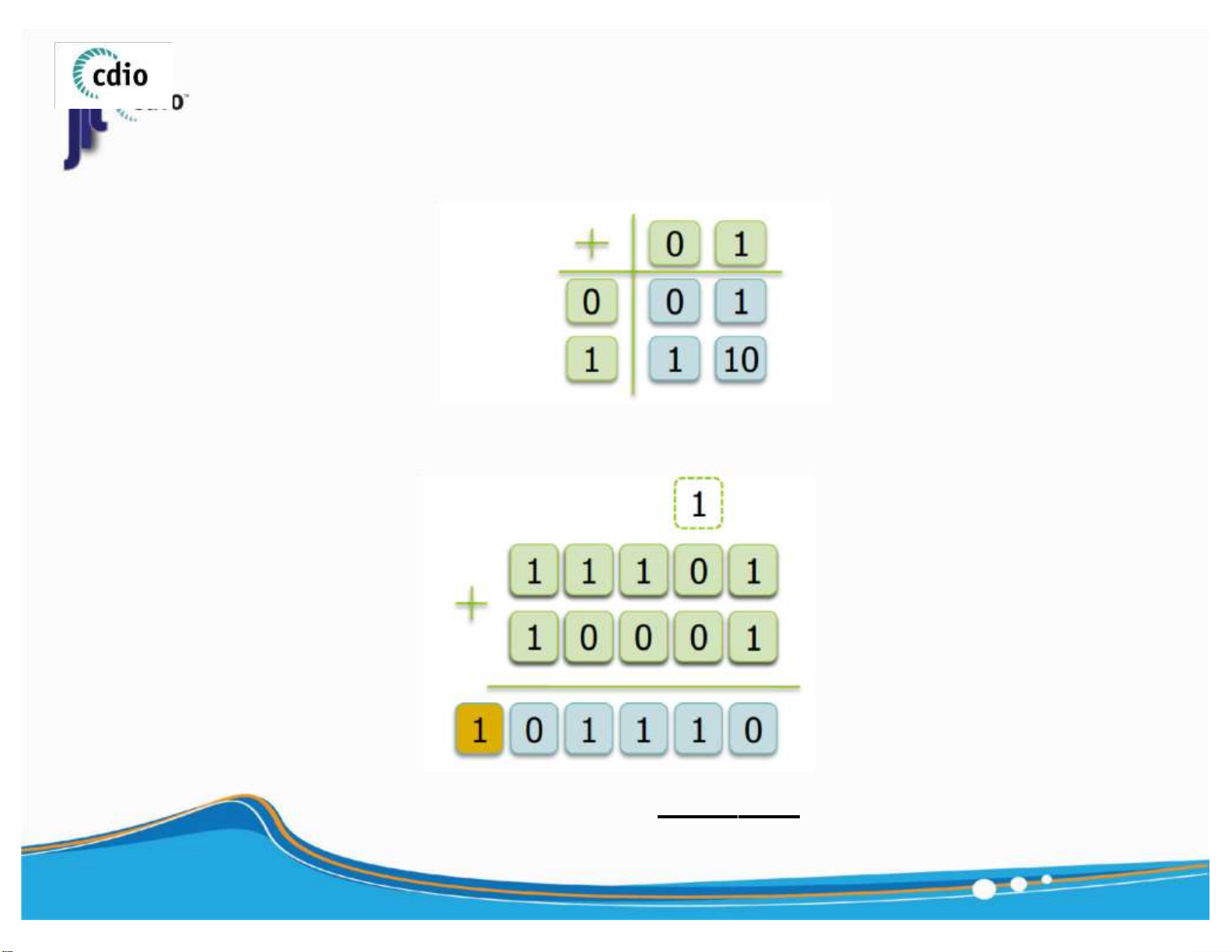
Flip a bit (XOR with 1 = flip that bit) : Get the value at bit i of x : Set bit i of x to 1 : Set bit i of x to 0 : Flip bit i of x 8 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Addition (Unsigned number) fit@hcmus ▪ General Rule
▪ Example ( 5 - bit, unsigned number ) 29 17
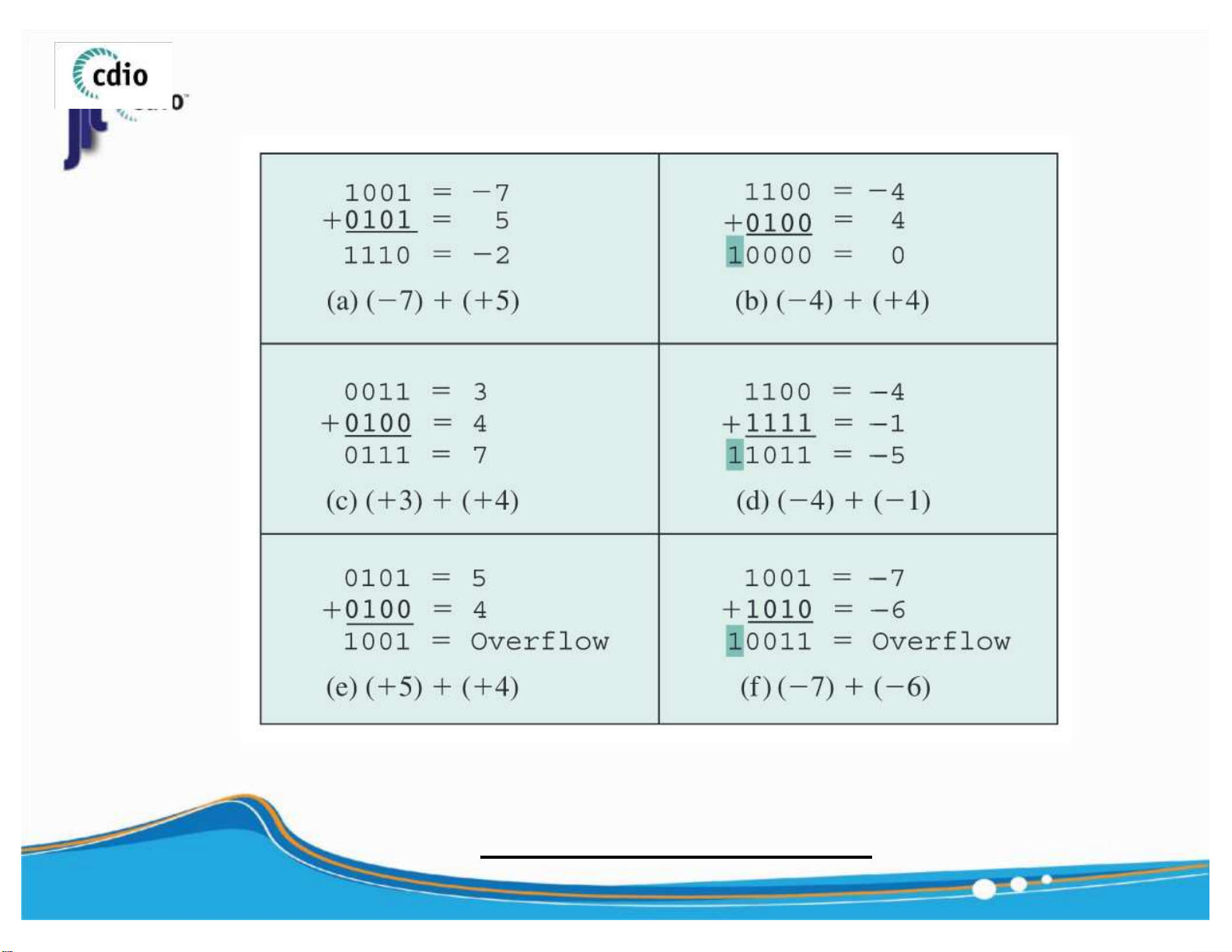
OVERFLOW: There is a carry - out bit from the 9 most significant bit (MSB). ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Addition (Signed number) fit@hcmus
OVERFLOW RULE : If two numbers are added, and they are both
positive or both negative, then overflow occurs if and only if
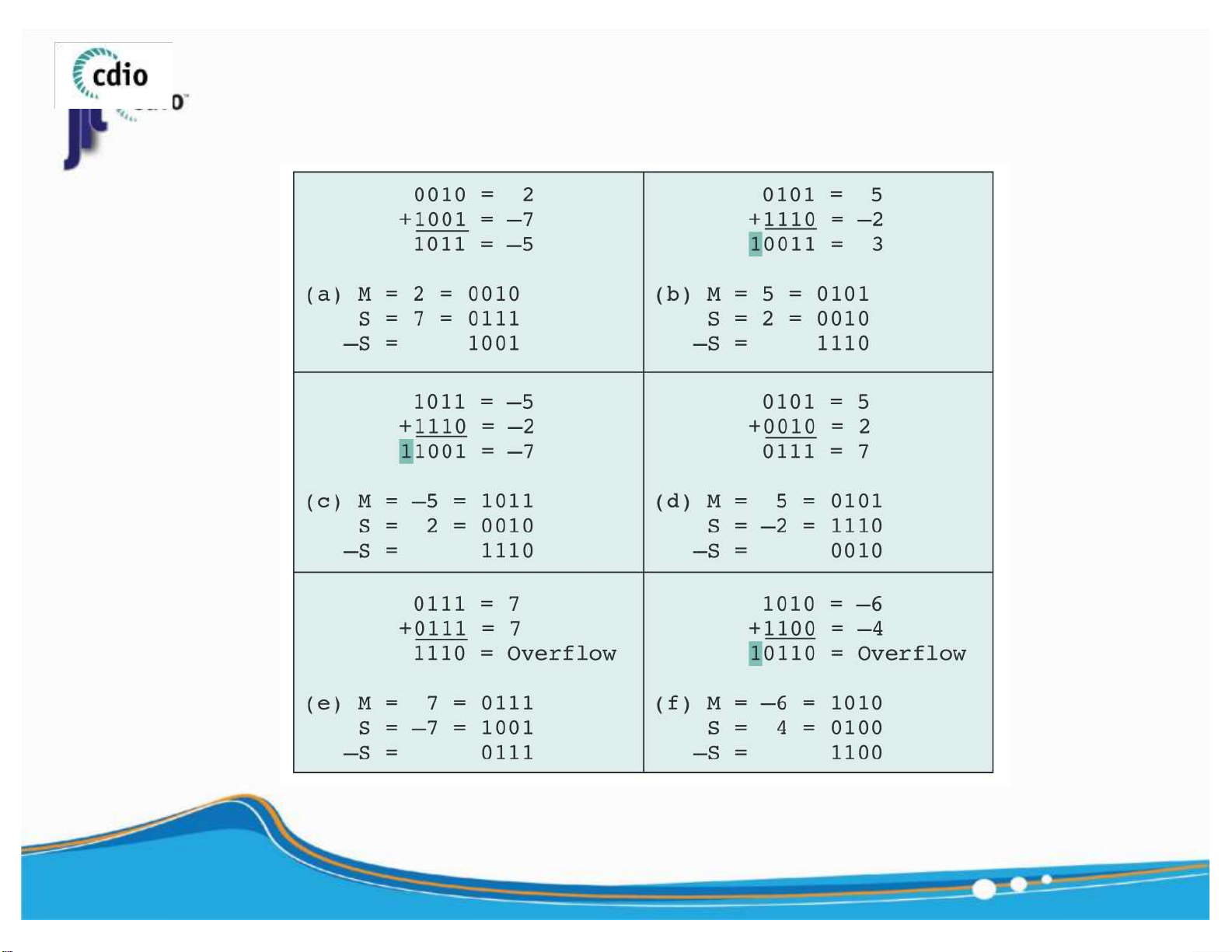
the result has the opposite sign . 10 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Subtraction (Signed number) fit@hcmus
OVERFLOW RULE : If two numbers are added, and they are both
positive or both negative, then overflow occurs if and only if the 11 result has the opposite sign. ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Multiplication (2) fit@hcmus
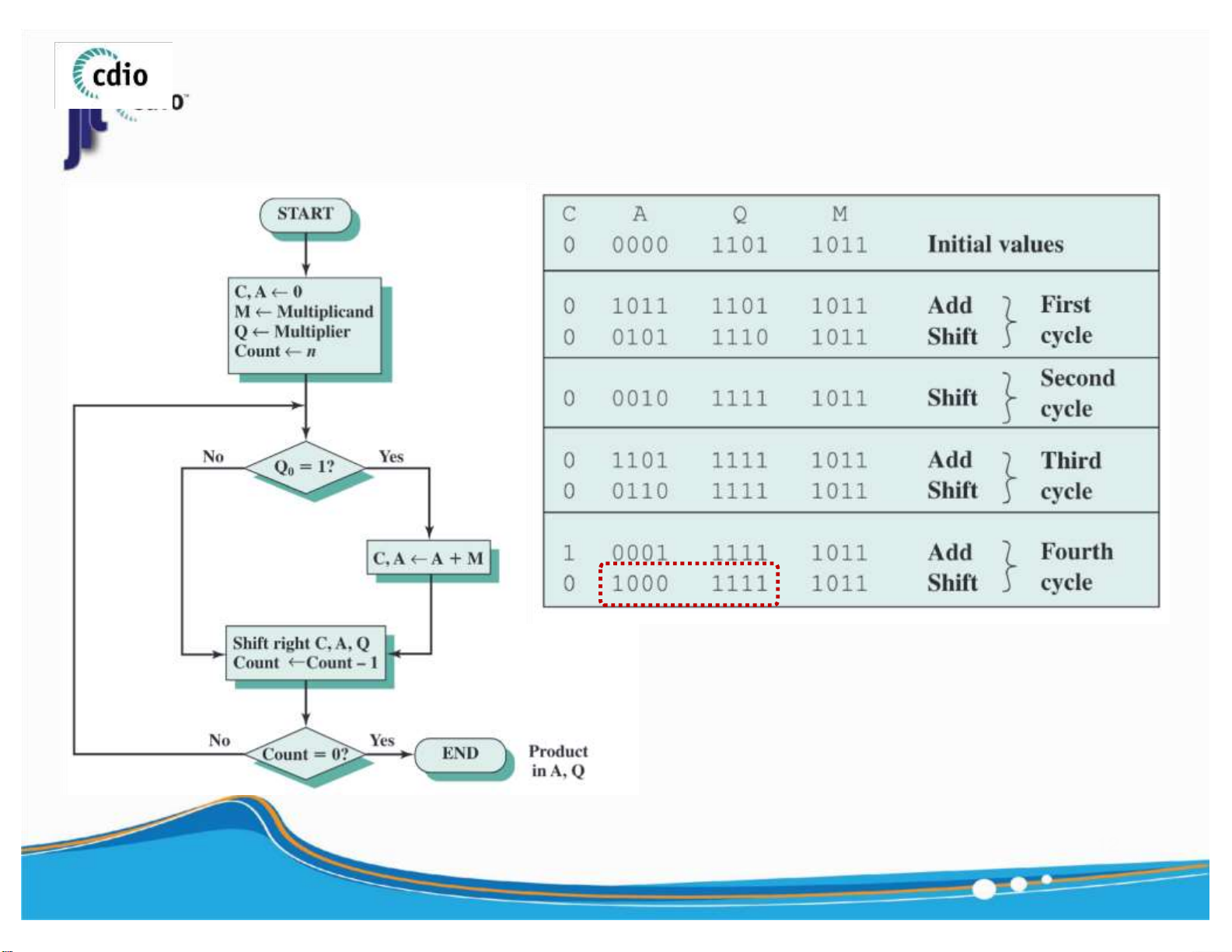
( Unsigned Number ) M ( 11 ) x Q ( 13 ) = ? 12 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Multiplication (3) fit@hcmus
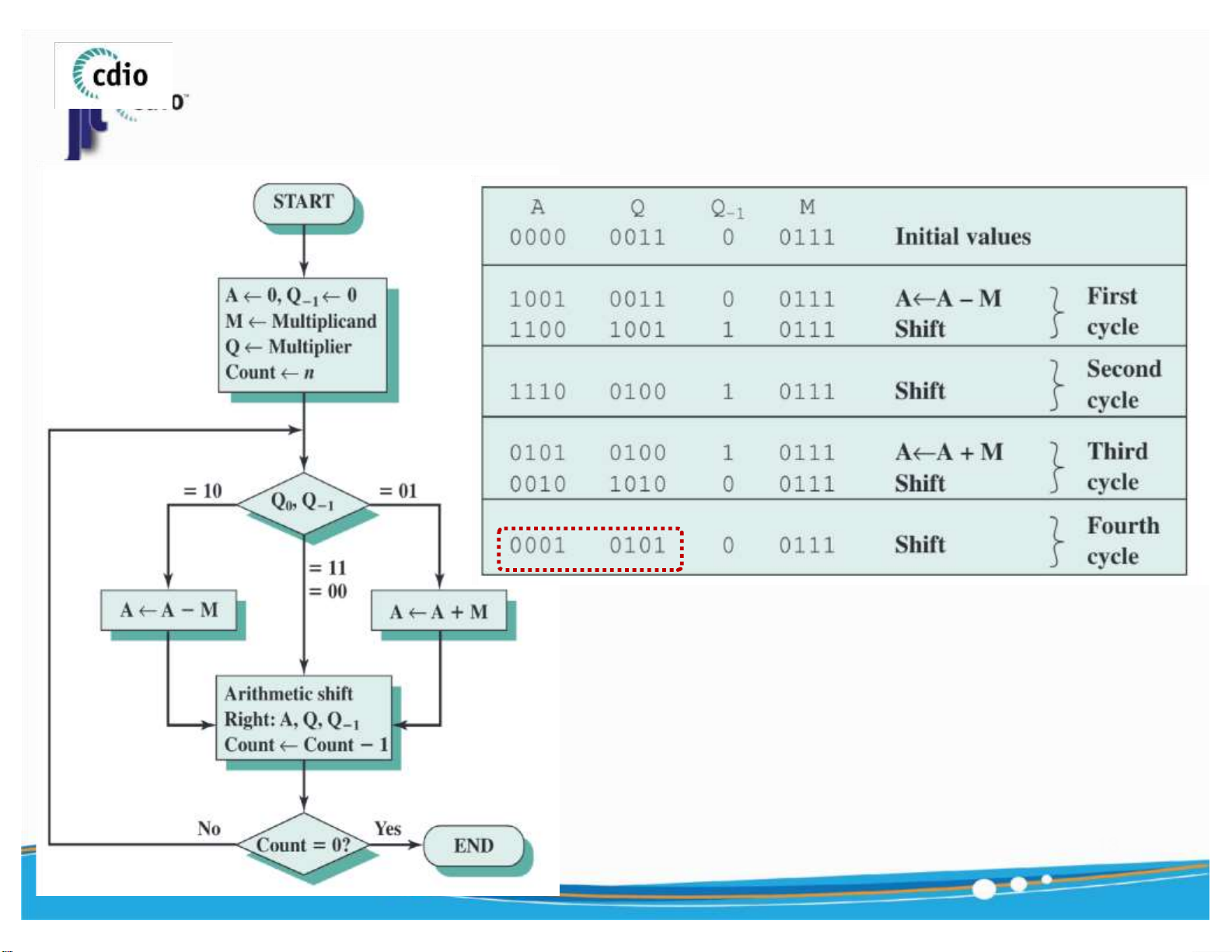
( Signed Number: Booth’s Algorithm ) M ( 7 ) x Q ( 3 ) = ? 13 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Division fit@hcmus
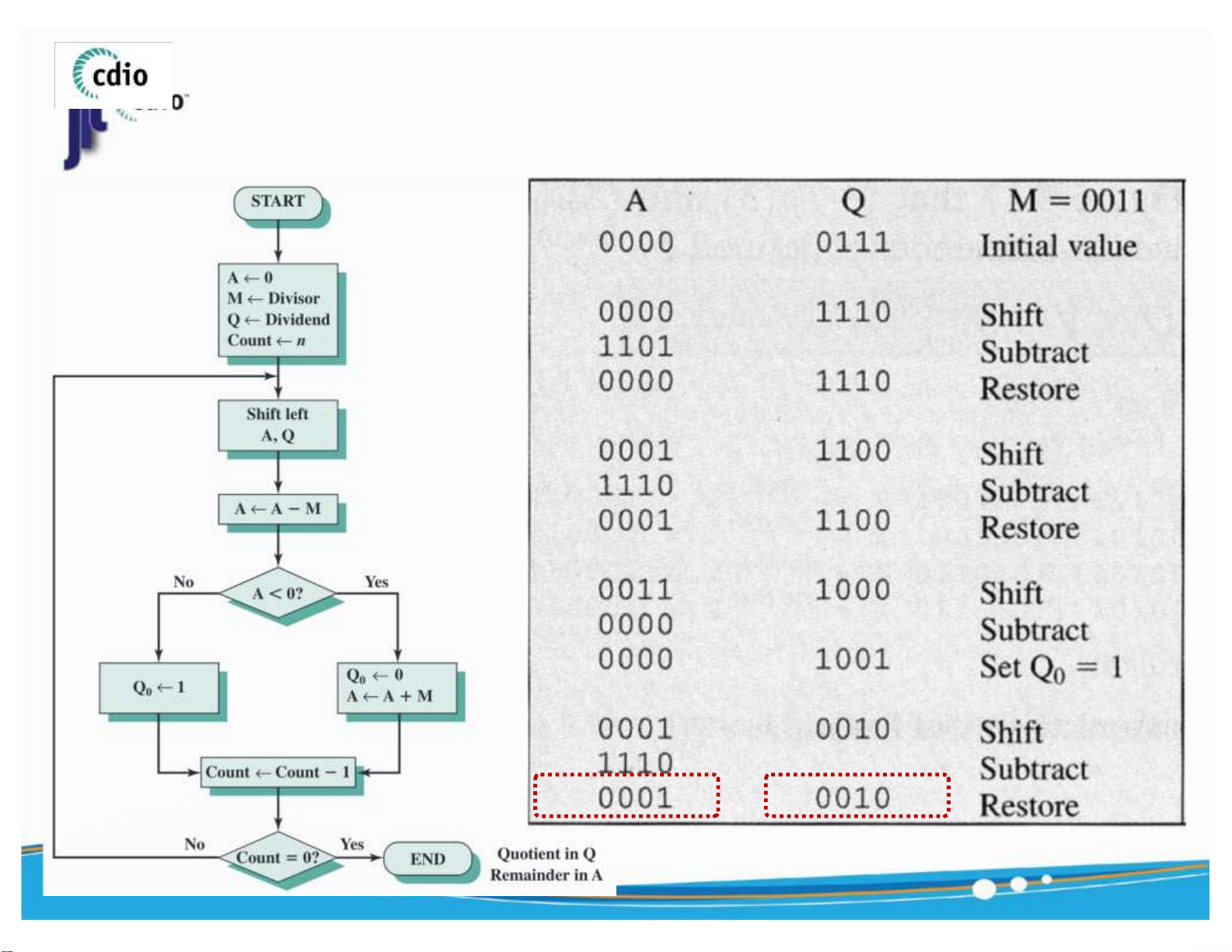
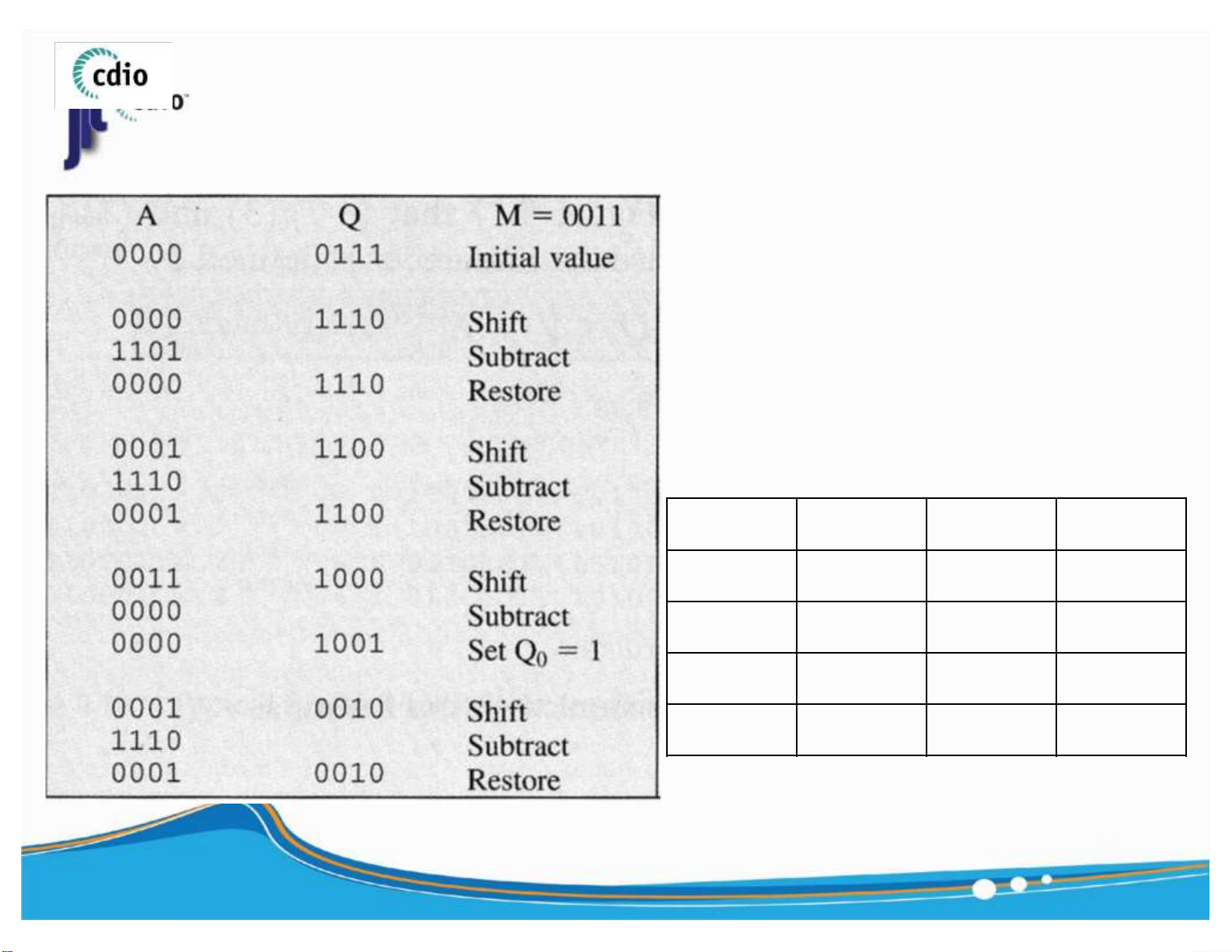
( Unsigned Number ) Q= 7 , M = 3 , Q/M=? R T 14 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Division (2) fit@hcmus
( Signed Number ) T = Q/M ; R = Q % M Q = 7 , M = 3 T = 2 , R = 1 Q = 7 , M = - 3 T = - 2 , R = 1 Q = - 7 , M = 3 T = - 2 , R = - 1 Q = - 7 , M = - 3 T = 2 , R = - 1 Q M T R >0 >0 >0 >0 >0 <0 <0 >0 <0 >0 <0 <0 <0 <0 >0 <0 15 ) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Fixed-point Numbers fit@hcmus ▪ Representation Integer part Fraction part
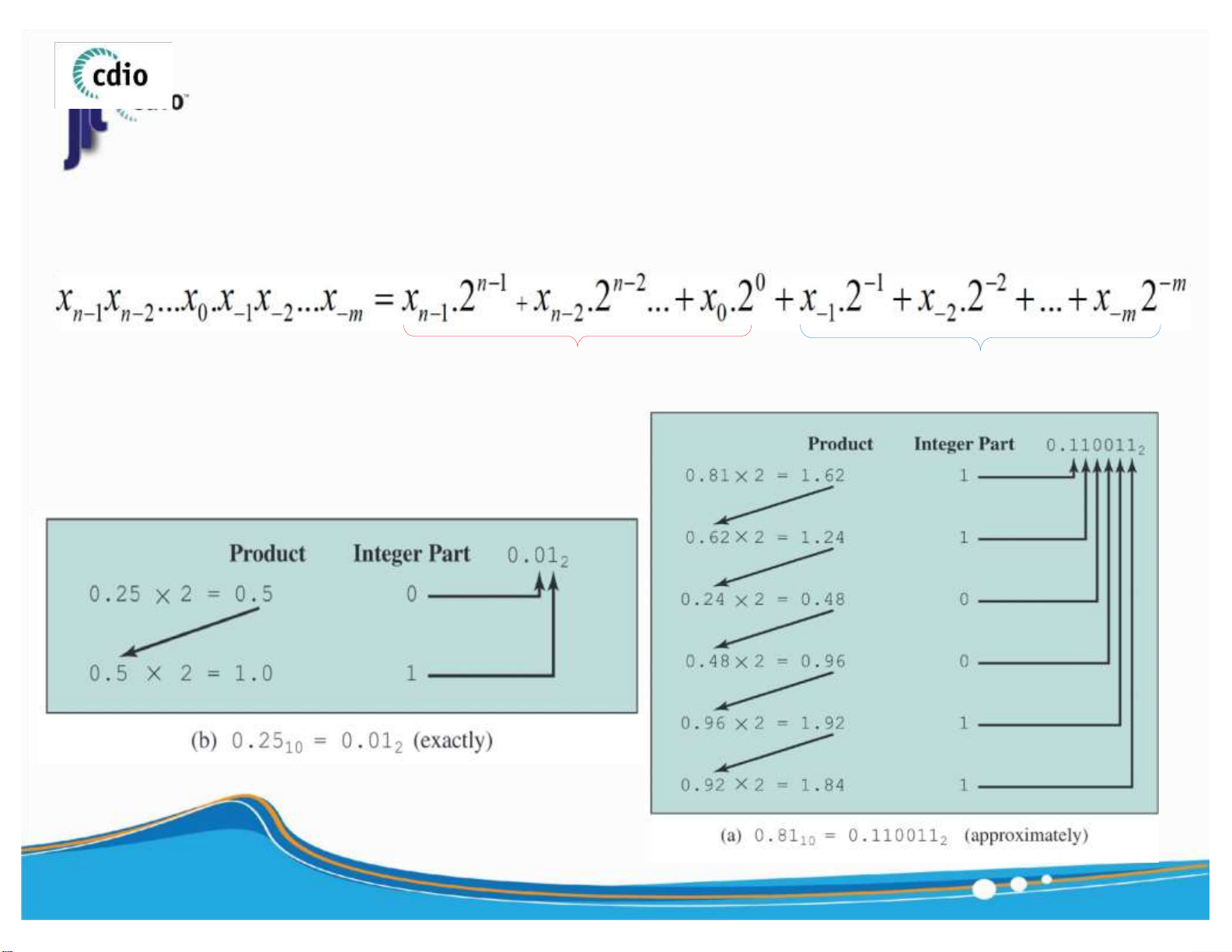
▪ Convert decimal binary 17
Downloaded by Bao Han (hanbao3006@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Fixed-point Numbers (2) fit@hcmus Integer part Fraction part 123.375 10 = 0111 1011 . 0110 0000 2 13.625 10 = 0000 1101 . 101 2 18
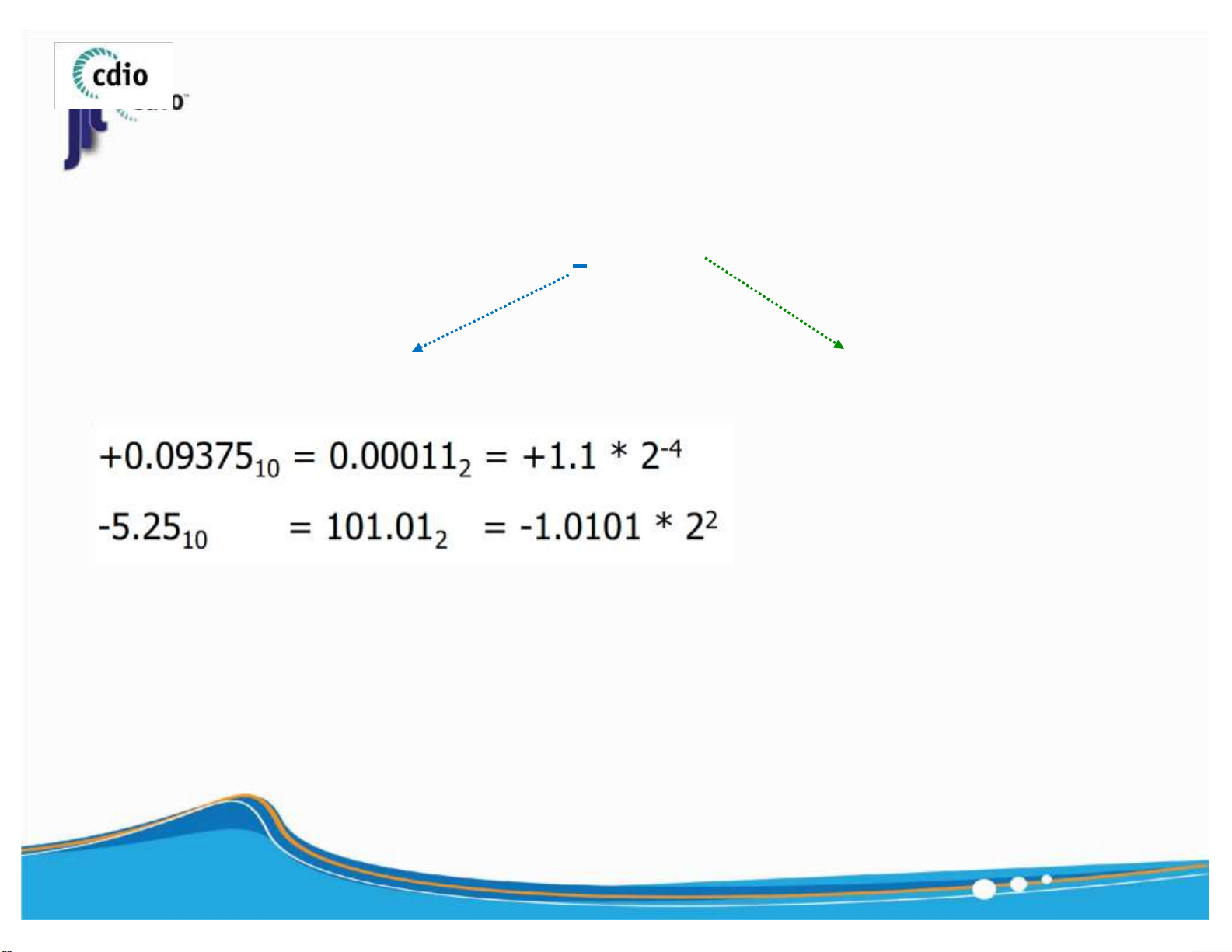
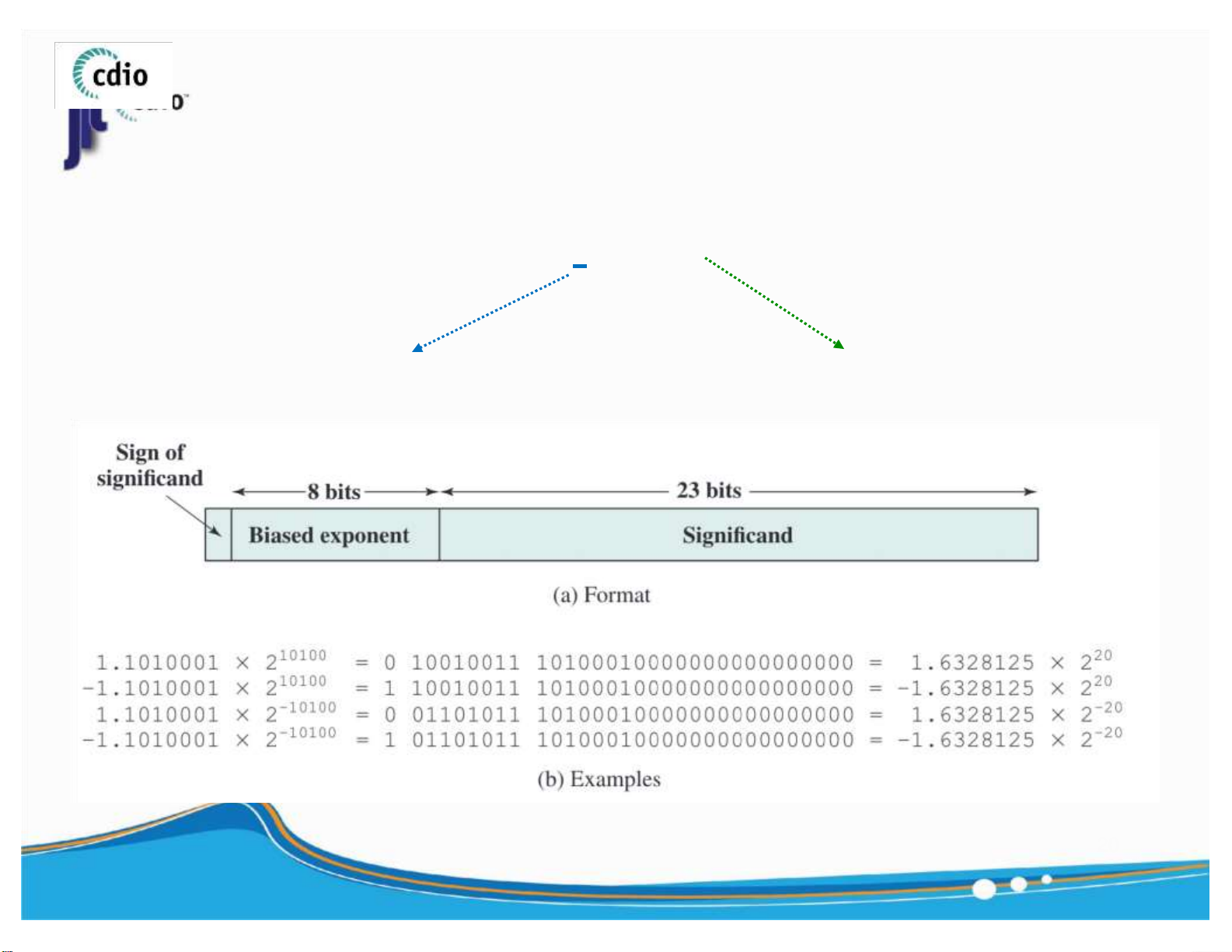
Downloaded by Bao Han (hanbao3006@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Normalized Float Number fit@hcmus ± E . 1 F * 2 Significand (Fraction) Exponent 19
Downloaded by Bao Han (hanbao3006@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Normalized Float Number (2) fit@hcmus ± E . 1 F * 2 Significand (Fraction) Exponent 20
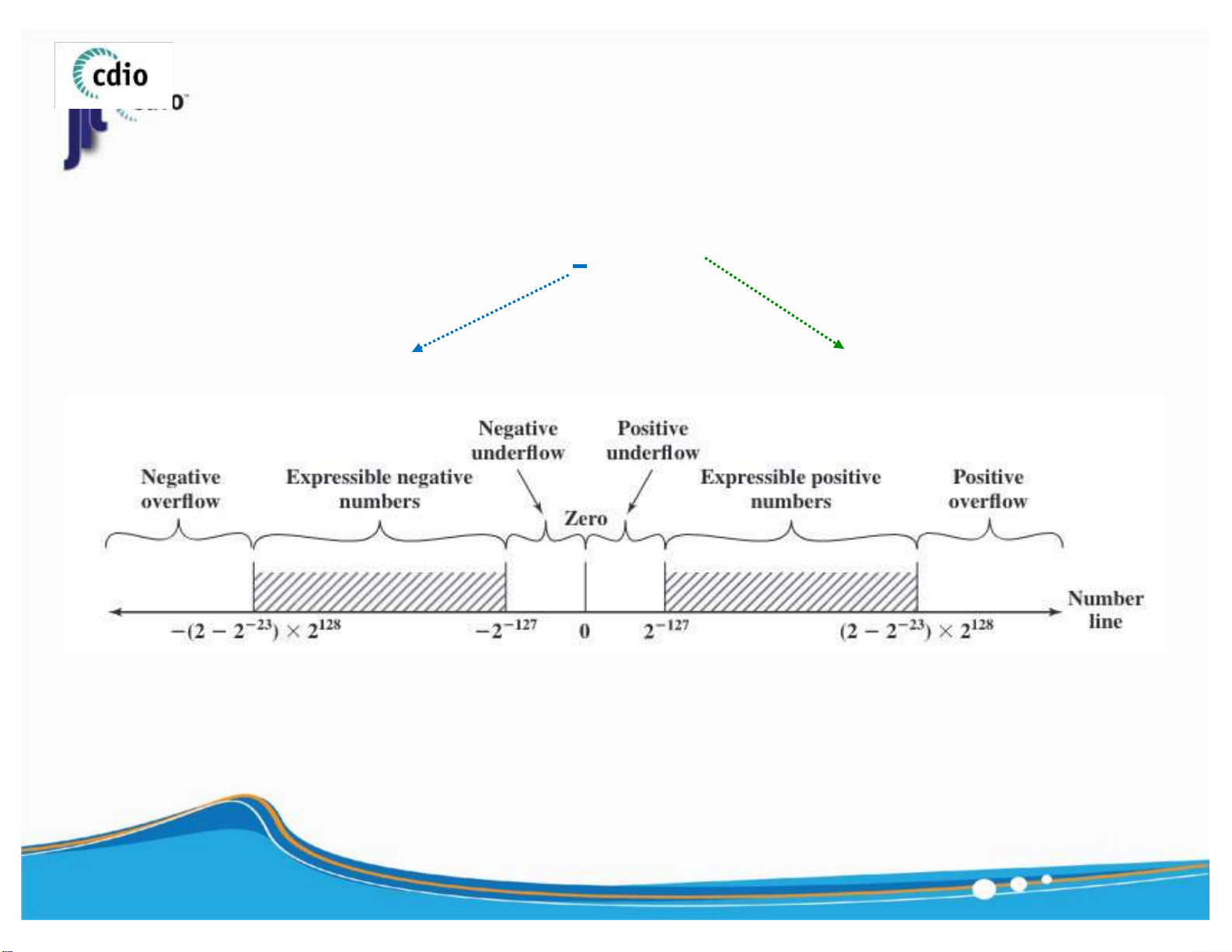
Downloaded by Bao Han (hanbao3006@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 59994889 4.0 Overflow vs. Underflow fit@hcmus ± E . 1 F * 2 Significand (Fraction) Exponent
Overflow : A positive exponent becomes too large to fit in the exponent field.
Underflow : A negative exponent becomes too large to fit in the exponent field. 21
Downloaded by Bao Han (hanbao3006@gmail.com)