



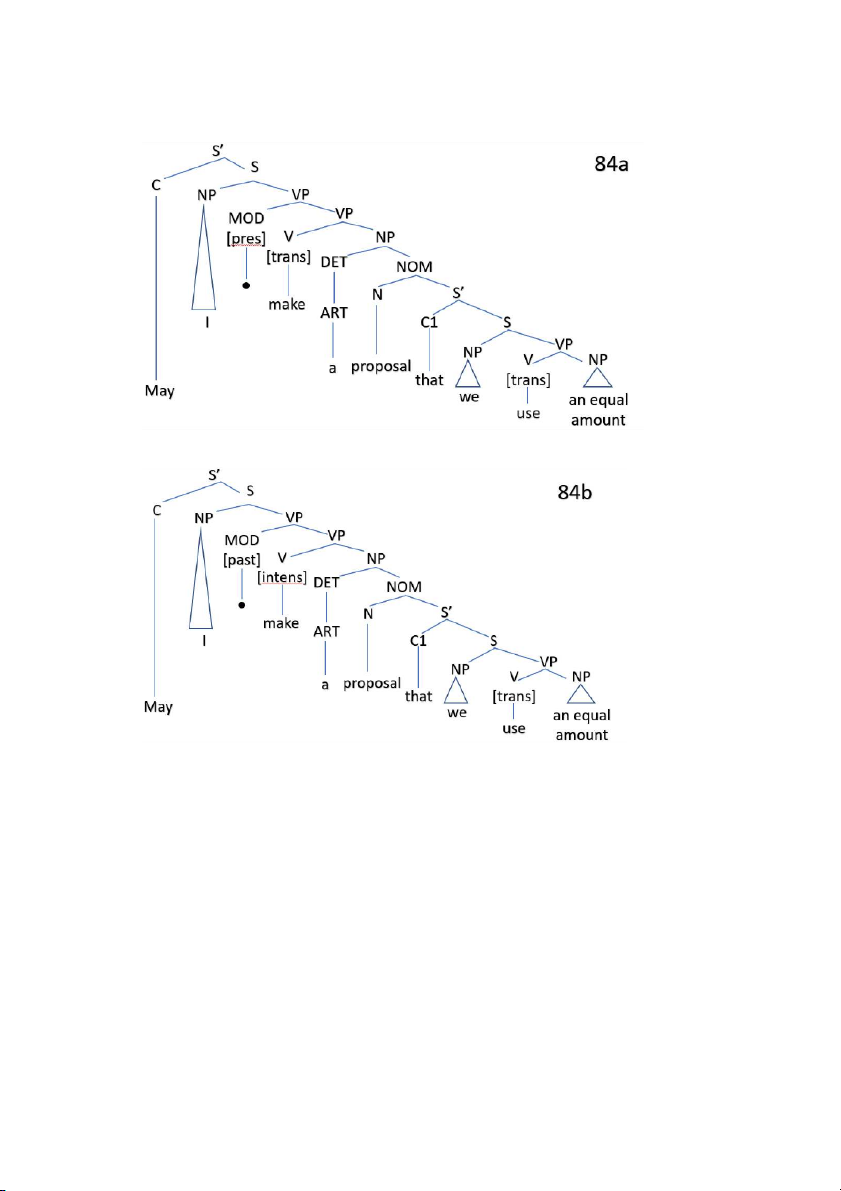
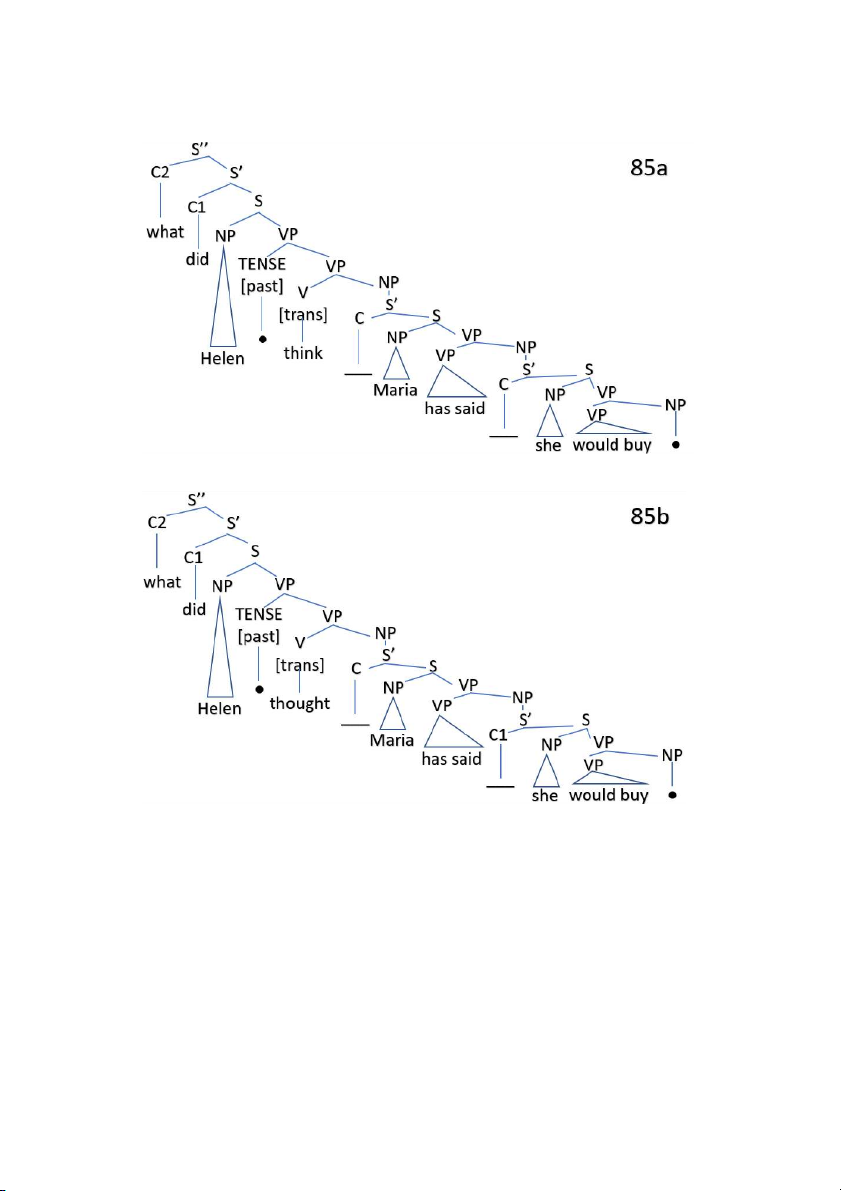








Preview text:
TRUE FALSE
1. When a head demands a further expression, that further (obligatory) x
expression is said to complement the head.
2. Within a PP, the relation between a preposition and the following NP is X a modifier-head relation.
3. Three things related to syntactic structure are: identifying linguistic X
expressions, analyzing categories, determining functions.
4. Plural count nouns and mass nouns can take the pre determiners. X
5. We need to distinguish between the category and function of a X
constituent because most categories of phrase have a variety of different functions.
6. The whole co-ordinate phrase and the elements that are co-ordinated in X
them have the different distribution but may be the same category.
7. A gap is created in the subject position left by the movement of the X subject to object position.
8. Disjunct adverbials provide some comment by the speaker about how X she feels through her sayings.
9. Participle movement provides a reliable test for distinguishing between X
ditransitive verbs and 2 complements.
10. The direct object position required by a transitive verb won’t be filled in X the passive.
11. In terms of the lexical verbs, we can identify clauses. X
12. As complements, noun-complement clauses are sisters to the head N X within NOM.
13. Not all WH-expressions appearing at the front of clauses are to be X
represented as occupying the higher C2 position.
14. That-clauses can sometimes function as complement to a P within PP X
15. An NP can function as either predicative or as direct object. X
16. Predicatives are used to attribute properties to the things or people X
referred to by other expressions. 17.
18. As the modifier of a complement NP, the non-restrictive relative clause X
must be represented as the sister of that NP within a higher VP.
19. The clause is said to ‘complement the noun’ because it’s in the same X
relation to the N within NP as clauses that complement the V in VP.
20. The distinction between sister-of-N and sister-of-NOM is now a X
linguistically significant distinction within NP. SYNTAX - EXERCISES
21. ……………. represent structure by marking which sequences of words in a sentence are its constituent phrases Phrase markers Phrase diagram Phrase structure
22. . In a phrase marker, a sequence of elements is represented as a ……………… if there is a
node that dominates all those elements and no others. Phrase Clause Constituent
23. These are various kinds of evidence for constituents, except: Omission Addition to a single word Question test
24. Constituents always have their functions in respect of their …………… constituents. Mother Sister Daughter
25. The ………….. of a phrase is the element that the phrase is centred on. Head Constituent Function
26. In the structure of a phrase, modifiers are optional; the head is the obligatory element. Obligatory / optional Optional / obligatory Obligatory / obligatory
27. When a head demands a further expression, that further (obligatory) expression is said to ……………. the head. Modify Complement Depend on
28. It is the category of the head word that determines the category of the …………. as a whole. Phrase Constituent Modifier
29. ……………..adjectives do not accept the -er/-est inflection, or modification by degree adverb. Gradable Non-gradable Degree
30. The verb that follows a ………. auxiliary always appears in its basic stem form. Modal Primary Ordinary
31. The perfect auxiliary ‘have’ provides a way of referring to ………time independently of ………. tense Past / past Past / present Present / past
32. the ordering of the verbs is absolutely fixed: ……. before …… before …… before …… before Lexical V. MOD / PERF / PROG / PASS MOD / PASS / PROG / PERF MOD / PROG / PERF / PASS
33. A full VP ……….. contain a lexical verb and it ……………. contain auxiliary verbs. Must / may May / must Must / must
34. An ………… verb is one that does not require any further constituent as a sister in the VP. Intransitive Transitive Intensive
35. ……………. are usually the recipients or beneficiaries of the action. (PAGE 70) Indirect objects Direct objects Object Predicatives
36. Each auxiliary verb is the head of its VP and takes a VP………….. (PAGE 122) Complement Modifier Adverbial
37. In passive sentences, a gap created in the object position left by the movement of the object
to subject position is called …….. Blob Ellipsis Extraposed
38. Much, many, few, and little are ………….. Quantifying adjectives Quantifiers Pre-determiners
39. In a sequence of modifiers that includes a noun modifier, e.g. ‘some expensive roof
maintenance’, noun modifiers always appear ………. (PAGE 148) Last Before determiners After post-modifiers
40. a sister-of-N in an NP functions as a(n) ……… in the NP and a sister-of-NOM functions as a(n) ………. in NP. Complement / adjunct Adjunct / complement Complement / complement
41. The clause that is not subordinate to any other clause is the ………….. Main clause Subordinate clause Extraposed clause
42. The complementiser position – ‘C’ – is defined as: ………..of S-bar (S′) and …….. of a following S. Daughter / sister Sister / daughter Sister / Daughter
43. In addition to functioning (like that) as a marker of clausal subordination, whether indicates
that the subordinate clause is a(n)……………. Interrogative clause Affirmative clause Negative clause
44. A characteristic of clausal subjects is that they can be ……….. from under the subject NP
node to the end of the sentence, leaving behind the empty pronoun it. (PAGE 177) Extraposed Ellipted Modified
45. The clause is said to ‘complement the noun’ because it’s in the ………. to the N within NP as
clauses that complement the V in VP. (PAGE 183) same relation same position same function
46. The inclusion of a WH - word in a main clause has the effect of making it into a question –
more specifically, a …………. WH – question Yes / No question Tag question
47. Relative clauses function as …………. (PAGE 204) Modifiers Complements Adverbials
48. The difference between restrictives and non-restrictives lies in the way they relate to the
……. …….. within the overall NP. (PAGE 208) Head noun Modifier Complement
49. As the modifier of a complete NP, the non-restrictive relative clause must be represented as
the …………. of that NP within a higher NP (PAGE 210) Sister Daughter Mother
50. Which underlined string in the following sentences is NOT the constituent of its sentence?
John considered doing his homework with his friends.
In the machine the gremlin could be heard juggling with ball-bearings.
Maria simply gazed at the bollard she had just demolished.
51. Which of the following strings is a well-formed phrase?
The singers that Mary met in the festival and the celebrities
Rather quickly and inconsistence
Obviously fascinating and to New York City
52. Which underlined complement NP is complementing an intensive verb as predicative
Max turned a subtle shade of green. Max turned another card.
Tarzan felt a tap on his shoulder.
53. Identify the major function of the underlined word / phrase in the sentence: I like my coffee as hot as you can make it. Indirect object Direct object Object Predicative
54. Identify the category of the verb in the sentence:
“The sedan-chair proved very useful.” Intensive verb Transitive verb Intransitive verb
55. Identify the category of the verb in the sentence:
“Someone stole my contact-lenses.” Intensive verb Transitive verb Intransitive verb
56. Identify the function of the boldfaced word / phrase in the sentence:
“It sounds like a really good film.” Subject predicative Direct object Object predicative
Choose the correct phrase marker of the following sentences: 57. a 58. a 59. a 60. a 61. a




