




Preview text:
UNIT 8: PRODUCTION
Inventory(AmE & BrE) or a company's reserves of raw materials, parts, work
stock (BrE): hàng tồn kho in process, and finished products
any of piece or parts that make up a product or Component: thành phần machine
the (maximum) rate of output that can be achieved Capacity: dung tích from a production process
a collective word for all the buildings, Plant: cơ sở
machines,equipment,and other facilities used in the production process
the geographical situation of a factory or other Location: địa điểm facility
Supply Chain: chuỗi cung a network of organizations involved in producing ứng
and delivering goods or a service
buying products or processed materials from other Outsourcing: thuê ngoài
companies rather than manufacturing them Economies of scale: tính kinh tế theo quy mô
the cost savings arising from large-scale production
Lead time: thời gian hoàn the time needed ro perform an activity such as thiện
manufacturing a product or delivering it to a customer
A. The consequence of insufficient
D. The disadvantages of large capacity facilities
B. The consequences of excess
E. The advantages of having a large capacity inventory
C. The advantages of large facilities
F. The disadvantages of having a large inventory
1. A long lead time may allow competitors to enter the market. A,E
2. As production volume increases, you get economics of scale (the average per
unit produced decrease). C
3. Finding enough workers and coordinating material flows can become difficult. D
4. If lead time increases, some customers may go to other suppliers. E,A
5. Lost scales and market share are usually pernament. A
6. The working environment might get worse and industrial relations could deteriorate. D
7. There are costs of storage, handling, insurance, depreciation, the opportunity capital, and so on. F
8. You can be more flexible in product scheduling, and have longer lead times and
costs operation through larger production runs with fewer set – ups. E
9. There is always a risk of obsolescence, thelf, breakage, and so on. F
10. You can meet variation in product demand. E
11. You may be under – utilizing your workforce. B
12. You have protection against variation in raw material delivery time (due to
shortage strikes, lost orders, incorrect or defective shipments, etc). E
13. You may be forced to produced additional less profitable products. B
14. You can make advantage of quantity discounts in purchasing. E
15. You may have to reduce prices to stimulate demand. B, F Embedded: nhúng
firmly fixed in something or part of something Standards of living: tiêu
the quality of people's lives chuẩn sống Founder: sáng lâp
someone who establishes a company
Risk premium: phí bảo hiểm rủi ro
the potential cost of taking a chance Equity: công bằng
the value of a business activity
causing trouble and stopping something from Discruptive: gây rối continuing as usual
increasing or decreasing more and more quickly
Exponentially: nhanh chóng as time passes Procurement: tap vu the obtaining of supplies
the state of being successful and having a lot of Prosperity: sư phồn vinh money Stability: sư ổn đinh
the situation when something is not likely to change UNIT 9: LOGISTICS
a guess of what the size or amount of something Estimate: ước tính might be
a statement of what is expected to happen in the Forecase: dự đoán future Agile: nhanh nhẹn
able to move quickly and easily Accurate: độ chính xác
correct, exact and without any mistakes
designing and managing the flow of goods,
Logistics: quản lí cung ứng information and other resources Manual: thủ công done with the hands Lean: giảm chi phí, rút ngắn qui trình
using small quantities and avoiding any waste Replenish
to fill something up again
Pull strategy: Current demand
- Statisfied from (a small) inventory - Removed from stock
- Replacement are automatically ordered from reppliers.
Push strategy: Future demand - Lean production - Stockless production - Continuous flow manufacture - Agile manufacturing - Production lead time
Push strategies often incorporate safety stocks and safety leadtimes.
Replenishment strategy:
- Both production and suppliers are constantly reacting to the actual
cosumption of components, rather than planning ahead.
Just – In – Time (JIT):
- Production by Toyota in Japan in 1950s.
- The most common JIT systems is called Kanban
- A Japanese word approximately meaning “visual card”.
Quy trình sản xuất vân hành hàng hóa (Supply – chaining)
1. A Wal – Mart truck picks up merchandise at a supplier’s factory or warehouse.
2. The goods are unloaded at Wal – Mart’s distribution centre.
3. The boxes are placed on a small conveyor belt.
4. The small conveyor belt joins as a larger one. 5. A machine reads the on each box. barcodes
6. Eletric arms guide the boxes off the main conveyor belt onto another smaller one.
7. This belt leads to another bay where the boxes are loaded onto Wal-Mart trucks.
8. The products are delivered to the stores that ordered them. 9. A customer buys a product. 10.The cashier the product, which sends a scans
signal to the supplier to produce another one.
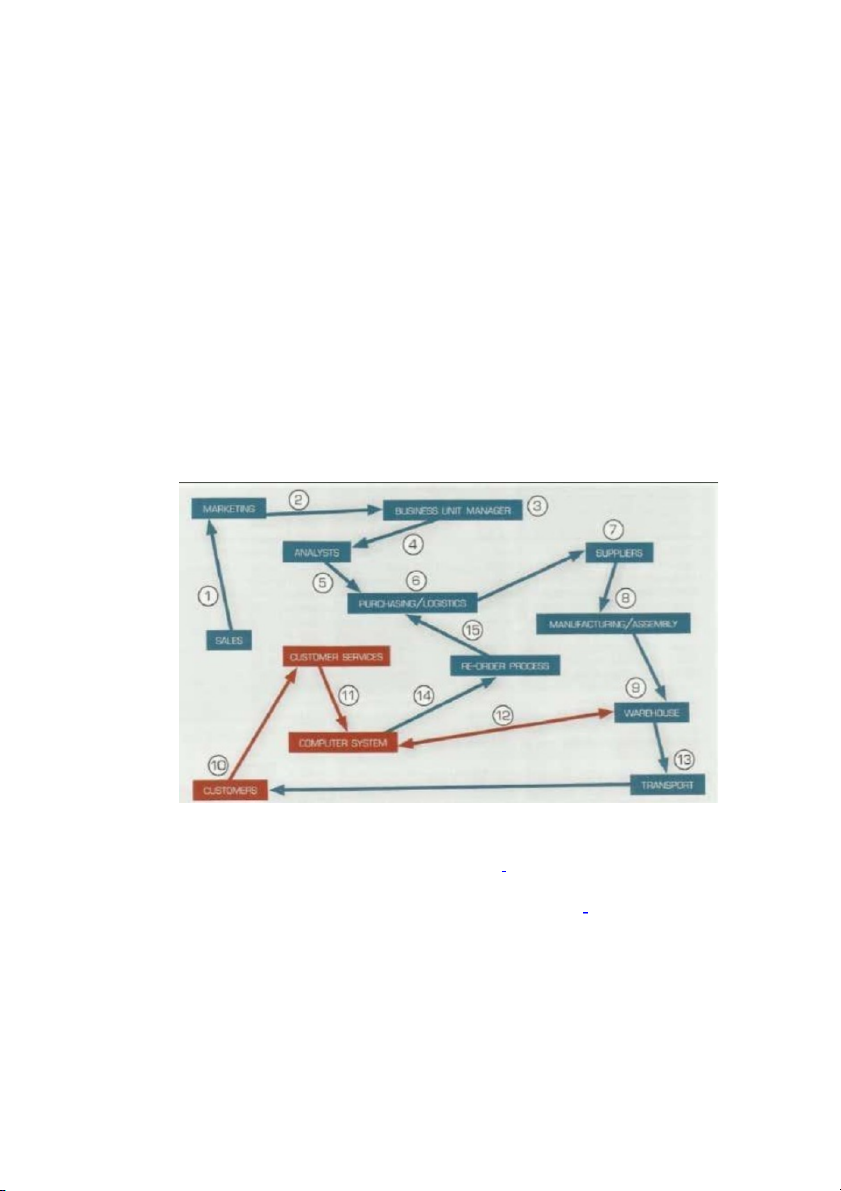
MANUFACTURING SUPPLY CHAIN WORK FLOW
1. The sales department identifies a need for a product, and tells the marketing department about it.
2. The marketing department researches the project, and forwards a detailed
business plan to the Business Unit Manager.
3. The senior business managers make a decision on the project.
4. The plan is approved and passed to the analysts to prepare and implement the manufuring process.
5. The analysts pass details of raw material and components to purchasing.
6. The purchasing, logistics and transportation departments plan the purchase of
material and their delivery to the manufacturing.
7. Suppliers receive orders and despacted raw materials and components to the
manufacturing site on agreed dates.
8. The product is manufactured.
9. Finished goods are put into inventory in a warehouse awaiting orders
10.Customers place orders through customer services.
11.Customer services take orders and input them to the computer system.
12.The order is sent to the warehouse.
13.The transpor company collects the consignment and delivers it to the customer. UNIT 10: QUALITY Reworking: làm lại
changing or improving a product or service Warranties: bảo
guarantees: written promises to repair or replace products hiểm
that develop a fault (lỗi) Bountiful: nhiều
providing a large amount of good things Headaches: đau
things that cause difficulties đầu Regulation: quy định
official rules of the act of controlling something
Service: công tác to examine a machine and repair and faulty parts Scapping: phế liệu
getting rid of things which are no longer useful or wanted
TQM was developed by an American, W. Edwards Deming, in the 1940s.
TQM (today often ust called Quality Management) involves an attitude and a
corporate culture that are dedicated to providing customers with products and
services that satisfy their needs.
TQM requires all staff to be involved in the search for continuously
improving quality, in all the business’s activities – not just production or
customer service, but also in marketing, sales, purchasing, design,
engineering, R&D, finance, human resources, etc.
Produce workers should be empowered to stop production to solve problems,
as quality is more important than maximizing output or reducing costs. UNIT 11: PRODUCTS
places of business for selling goods to customers Outlets: cửa hàng (shops, stores, kiosks, etc.)
all the different products, brands, and items that a Product mix company sells
businesses that sell goods or merchandise(hàng Retailers: nhà bán lẻ hóa) to individual customers
a graphic image or symbol specifically created to Logo: thương hiệu
identify a company or a product
wrappers and containers used to enclose and Packaging: đóng góp protect a product
Brand recognition: nhận diện the extent (mức độ) to which consumers are aware thương hiệu
of a brand, and knows its name Shelves: kệ để đồ
surfaces in a store on which goods are displayed
the sales of a company expressed as (thể hiện) a Market share: thị phần
percentage of total sales in a given market Brand switchers: có xu
consumers who buy various competing products
hướng thay đổi thương hiệu rather than being loyal to a particular brand 1. PRODUCTS
- A product is anything that can be offered to a market that might satisfy a want or need. 2. BRANDING
- A brand is a name, or symbol, or a logo that distinguishes products and
services from competing offering, and makes consumers remember the company, product or service. 3. BRANDING STRATEGIES
- Some companies include their name in all their products (corporate
branding), e.g. Other companies do invidual brand and give each product its
own brand name, so the company name is less well – known than its brands 4. BRAND VALUE
- Which shows that the worth of a brand can be much greater than a
company’s physical assets. Brand value largely comes from customers
loyalty: the existence of customers who will continue to buy the products. UNIT 12: MARKETING
all the companies or individuals ("middleman") Distribution channel:
involved in moving goods or services from producers kênh phân phối to consumers
an intermediary that stores manufacturers' goods or
Wholesalers: người bán merchandise, and sells it to retailers and professional buôn buyers Market segmentation:
dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who phân khúc thị trường
have different requirements or buying habits
making a product (appear to be) different from
Product differentiation: similar products offered by other sellers, by product khác biệt hóa sản phẩm
differences, packaging, advertising, etc
possibilities of filling unsatisfied needs in sectors in
Market opportunities: cơ which a company can profitably produce goods or hội thị trường services
setting a high price for a new product, to make Market skimming: hớt
maximum revenue before competing products appear on váng thị trường the market
Sales representative: đại someone who contacts existing and potential customers, diện bán hàng
and tries to persuade them to buy goods or services Product features: tính
the attributes or characteristics of a product, such as năng sản phẩm
size, shape, quality, price, reliability, etc.
the extent to which supply or demand (the quantity
Price elasticity: co giãn produced or bought) of a product responds to change giá of price Market penetration: sự
the strategy of setting a low price to try to sell a large thâm nhập thị trường
volume and increase market share The product life cycle 1. Introduce Stage 2. Growth stage 3. Maturity stage 4. Decline Stage Sales:
A. The sales volume is low and customers have to be persuade to try the
product. Introduce Stage
B. A Public awareness about the product increases and sales volume rises
significantly. Growth stage
C. Sales volume peaks. Maturity stage
D. Sales volume begins to go down. Decline Stage Costs:
E. Costs are high. Introduce Stage
F. Costs are reduced due to economics of scales, so profitability increases. Growth stage
G. The product’s features may have to changed so that it differs from
competing brands, which involves new cots. Maturity stage
H. Either costs are too high compared to sales, so the product is discontinued,
or the company continues to offer the product to loyal customers, while
reducing costs to a minimum. Decline Stage Price:
I. The company can choose between high skim pricing to recover development
costs, or low penetration pricing to build market share rapily, if there are
already competitors. Introduce Stage
J. The price can remain unchanged because demand is increasing but
competitors aren’t usually yet well established. Growth stage
K. Prices may have to be reduced because competitors are established in the
market, but companies try to defend their market share while also
maximizing profit. Maturity stage
L. The price is either maintained, or greatly reduced to liquidate stock if the
product is discontinued. Decline Stage Promotion:
M. Promotion is aimed at educating potential consumers (innovators and early
adopters) about the products, and building product awareness. Introduce Stage
N. Promotion is aimed at a much broader audience (the majority of the
product’s users). Growth stage
O. Promotion emphasizes product differentiation. Maturity stage
P. At this stage, there is virtually no promotion. Decline Stage UNIT 13: ADVERTISING advertising agency: công ty quảng cáo
companies that design advertising for clients
advertising campain: chiến dịch the advertising of a particular product or service quảng cáo
during a particular period of time brief: ngắn gọn
the statement of objectives that a client works out with an advertising agency
target customers: khách hàng
a defined set of customers whose needs a mục tiêu company plans to satisfy the amount of
advertising budget: ngân sách
money a company plans to spend in quảng cáo
developing its advertising and buying media time or space
media plan: kế hoạch truyền
the choice of where to advertise in order to reach thông the right people comparative-parity method: phương pháp so sánh ngang
choosing to spend the same amount on advertising giá as one's competitors
free sample: mẫu vật miễn phí
a small amount of a product is given to customers
to encourage them to try it
free advertising, when satisfied
word-of-mouth: câu của miệng customers
recommend products to their friends
viral marketing: tiếp thị lan
trying to get consumers to forward an online truyền
marketing message to other people
1. What are the two functions of adverting?
- To inform consumers about products and services, and to persuade them to buy it.
2. What is the role of advertising agencies?
- To create advertisements and develop a media plan.
3. What three different methods of determining advertising spending are mentioned?
- Spend a fixed percentage of current scales
- Revenue spending as much as competitors
- Increasing current spending in order to increase sales.
4. What does the text describe as disadvantages of traditional advertising?
- It is expensive, it doen’t always reach the target customer, and it isn’t always
welcome as it interupts people when they are trying to do something else.
5. What ways of using the Internet to advertise are mentioned?
- Blog, online forums, commenting on blogs and social networking sites, podcasts, viral videos.




