








Preview text:
SỞ GIÁO DỤC VÀ ĐÀO TẠO
KỲ THI CHỌN ĐỘI TUYỂN HSG QUỐC GIA LỚP 12 TỈNH NINH BÌNH
NĂM HỌC 2011 - 2012
Môn: Tiếng Anh
ĐỀ THI CHÍNH THỨC Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút (không kể thời gian phát đề)
Đề thi gồm 4 phần, 11 trang Số phách Điểm bài thi
Họ và tên, chữ ký của giám khảo (Do Chủ tịch Hội
đồng chấm thi ghi)
Bằng số: ............................
Giám khảo số 1: ...............................................
Bằng chữ: ..........................
Giám khảo số 2: ............................................... PART A: LISTENING:
HƯỚNG DẪN THI NGHE HIỂU:
- Bài nghe gồm 3 phần, thí sinh được nghe 2 lần. Thí sinh được nghe lần lượt cả 3 phần lần 1, sau đó thí
sinh được nghe lại lần thứ 2. Mở đầu bài nghe có tín hiệu nhạc.
- Hướng dẫn làm bài chi tiết cho thí sinh bằng tiếng Anh đã có trong từng phần nghe.
Part 1: Listen to a conversation between two teaching assistants and choose the best answer for each question from 1 to 5.
1. What problem at the office are Cathy and Stan discussing?
A. There aren’t enough cabinets. B. There is too much noise.
C. Office supplies are taking up space.
D. Some teaching assistants don’t have desks.
2. Why do Jack’s students come to see him?
A. To chat with Jack socially. B. To get help in the course. C. To hand in assignments.
D. To practice giving interviews.
3. What does Stan suggest they do?
A. Give Jack a different office.
B. Complain to the department head.
C. Move the supplies to the storage room.
D. Try to get a room to use for meetings.
4. What does Cathy say about Stan’s suggestion?
A. They would have to get permission. B. Jack wouldn’t like it. C. She thinks it might work.
D. The other assistants should be consulted.
5. What are they going to do? A. Leave the office. B. Go to the storage room. C. Go to the meeting hall. D. Take out the cabinets. Your answers:
1. ………… 2. ………… 3. ………… 4. ………… 5. …………
Part 2: Listen to a passage and choose the best answer for each question from 6 to 10.
6. What have farmers realized about organic farming?
A. It is more costly than conventional farming.
B. It is more cost-effective than conventional farming.
C. It results in lower profits than conventional farming. - 1 -
7. In what way does organic farming benefit the environment?
A. It does not use chemicals.
B. It uses only synthetic materials.
C. It can be used to control produce.
8. What comment did the speaker make about the certification process?
A. Most farmers can pass it easily.
B. It involves a great deal of processing.
C. It involves quite strict standards.
9. Which concern do some people have about organic food? A. cost B. safety C. production methods
10. How does organic farming improve wildlife?
A. It results in a greater variety of species.
B. It reduces the amount of insects. C. It increases livestock. Your answers:
1. ………… 2. ………… 3. ………… 4. ………… 5. …………
Part 3: Listen to the messages on Jack Waterman’s office answerphone and answer each question
from 11 to 20 with NO MORE THAN 3 words.
11. Where is Mrs. Walterman?
....................................................
12. When will she phone her husband?
....................................................
13. Where is Shara Jones stuck in a traffic jam?
....................................................
14. When does she think she will arrive?
....................................................
15. Where will Dennis be this afternoon?
....................................................
16. What doesn’t Jack’s mother like?
....................................................
17. What does Terasa want to talk about?
....................................................
18. How long will she be away?
....................................................
19. Where is Jack’s son going tonight?
.................................................... 20. What does he want?
....................................................
PART B: LEXICO-GRAMMAR:
I/ Choose the word or phrase that best completes each sentence. Write your answer (A, B, C, or D)
in the numbered space.
1. Sheila will inherit everything ________ her uncle’s death. A. on account of B. in spite of C. in the event of D. in place of
2. His poor handling of the business ________ on negligence. A. neared B. edged C. approached D. bordered
3. Down ________ for three days. A. the rain poured
B. poured the rain C. did the rain pour D. do the rain poor
4. Can I ________ your brains for a moment? I can’t do this crossword by myself. A. have B. pick C. mind D. use
5. The job wasn’t giving the ________ of the experience he wanted. A. width B. depth C. length D. breadth
6. I suppose I could ________ advertising. A. catch on B. get out of C. go in for D. work out
7. Whenever he watched detective films, his imagination ran ________ A. raging B. furious C. unchecked D. riot
8. She travelled the world in ________ of her dreams. A. pursuit B. finding C. chase D. trail - 2 -
9. The agency is ________ and not run for profit. A. charitable B. donated C. voluntary D. free
10. Mike, ________, will you switch off that television? A. once and for all B. now and then C. over and above D. from time to time Your answers:
1. ………… 2. ………… 3. ………… 4. ………… 5. …………
6. ………… 7. ………… 8. ………… 9. ………… 10. ………..
II/ The passage below contains 10 mistakes. Underline the mistakes and correct them in the space
provided in the column on the right. (0) has been done as an example.
Human and primates, the family of apes, gorillas, and chimpanzees, 0. Humans
among others, divide many common traits. 1. _________________
While primates are deemed the most intelligent of animals, most
researchers believed they lack the capacity to produce language. However, a 2. _________________
research project in the 1970s at University of Georgia showed promise that 3. _________________
chimpanzees have the ability to learn a certain language, just as human 4. _________________
children do. The project used several chimpanzees as test subjects in which
Lana, a female chimp was the study focus. 5. _________________
Though the primates lack the vocal constructions to make human 6. _________________
speech patterns, the researchers created a language called Yerkish, using 7. _________________
lexigraphy made up of symbols that represent sounds and words. 125
symbols were placed on a keyboard, which Lana was taught how to use the 8. _________________
board to communicate with the researchers. She successfully expressed her 9. _________________
thoughts by pressing different keys in succession. In some cases, she used up 10. ________________ to seven at times.
III/ Use the word given to form a word that fits in the space to complete the passage. LANGUAGE CHANCE
The phenomenon of language change probably attracts more public notice and more (1) ________
(disapprove) than any other linguistic issue. There is a widely held belief that change must mean
deterioration and decay. Older people observe the cause speech of the young and conclude that standards
have fallen (2) ________ (appreciate).
It is understandable that many people dislike change, but it is (3) ________ (wise) to condemn all
linguistic (4) ________ (modify). It is often felt that contemporary language illustrates the problem at its
worst, but this belief is shared by every generation.
There are indeed cases where linguistic change can lead to problems of unintelligibility and (5)
________ (ambiguous) and if change is too rapid there can be major communication problems. But as a
rule, the parts of language which are (6) ________ (go) change at any given time are relatively small in
comparison to the vast, unchanging areas of language. It is because change is so (7) ________ (frequent)
that it is so distinctive and (8) ________ (notice). Some degree of caution and concern is therefore always
desirable for the (9) ________ (maintain) of precision and (10) ________ (affect) communication but
there are no grounds for the extremely pessimistic attitudes so often encountered. Your answers:
1. ……………….…… 2. ……………….……
3. ……………….…… 4. ……………….…
5. ……………….…… 6. ……………….……
7. ……………….…… 8. ……………….… 9. ……………….…… 10. ……………….….. - 3 -
IV/ Complete each sentence with the correct form of one phrasal verb below. Write your answer in
the numbered space. Each phrasal verb is used once only. take up get through frown on crop up show off feel for fall through run out strive for devolve on
1. I have been working very hard, I hope I will _________ my math exam.
2. He likes to _________ how well he speaks French.
3. They were sad because the plan _________ at the last minutes.
4. I do ________ you, honestly!
5. Sorry I am late. Something _________ at the office.
6. Most musicians spend their lives _________ perfection.
7. Clay-modelling _________ half the afternoon.
8. When the president is away, the work _________ the vice president.
9. Time was _________, so the committee had to make a snap decision.
10. Making private calls on the office phone is severely _________ in our department. Your answers:
1. ……………….…… 2. ……………….……
3. ……………….…… 4. ……………….…
5. ……………….…… 6. ……………….……
7. ……………….…… 8. ……………….… 9. ……………….…… 10. ……………….…..
V/ Fill in each gap of the following sentences with one preposition or particle. Write your answer in the numbered space.
1. Ben is a true adventurer. He has climbed this country's highest mountain, canoed _________ the
continent, and hiked through the Amazon jungle.
2. As I had put on weight, my dress was too tight so I had to let it ________ especially around the waist.
3. I'm sorry but Dr. Andrew sees patients _________ appointments only.
4. Breaking his leg a second time put his football career _________ jeopardy.
5. He spoke _________ such assurance that we couldn't but believe him.
6. You drove me _________ distraction with your silly question.
7. All visitors are requested to comply _________ the regulations.
8. This is the most peculiar letter. What do you make _________ it?
9. If you lead someone on, you put self –interest _________ truth.
10. They were all ears _________ the president’s speech. Your answers:
1. ……………….…… 2. ……………….……
3. ……………….…… 4. ……………….…
5. ……………….…… 6. ……………….……
7. ……………….…… 8. ……………….… 9. ……………….…… 10. ……………….…..
PART C: READING COMPREHENSION:
I/ Read the following passage and decide which answer (A, B, C, or D) best fits each gap. Write
your answer in the numbered space.
When faced with some new and possible bewildering technology change, most people
(1)________ in one of two ways. They either recoil (2) ________anything new, claiming that it is
unnecessary, or too complicated or that it (3)________ makes life less than human. Or they learn to adapt
to the new invention and (4)________ wonder how they could possibly have existed (5)________ it. Take
computers as example. For many of us, they still (6) ________ a threat to our freedom and give us a - 4 -
frightening (7)________ of a future in which all decisions will be (8)_______ by machines. This may be
because they seem (9)________, and difficult to understand. Ask most people what you can use a home
computer for, and you usually get vague answers about how ‘they give you information’. In fact, even
those of us who are (10)________ with computer and use them in our daily work, have little idea of how
they work. But it does not take long to learn how to operate a business programme, even if things
occasionally go wrong for no apparent (11)________. Presumably, much the same happened when
telephone and television became widespread. What seems to alarm most people is the (12)________ of
technology change, (13)________ than change itself. And the objections that are made to new technology
may (14)________ have a point to them, since change is not always an improvement. As we discover
during power cuts, there is a lot to be said for the oil lamp, the coal fire, and forms of entertainment, such
as books or board (15)________, which don’t have to be plugged into work. 1. A. react B. treat C. solve D. perform 2. A. of B. out of C. away from D. from 3. A. somewhere B. someplace C. someway D. somewhat 4. A. eventually B. possibly C. initially D. naturally 5. A. with B. without C. on D. for 6. A. show B. meet C. face D. represent 7. A. possibility B. sense C. idea D. prospect 8. A. invented B. changed C. taken D. done 9. A. unsteady B. unsure C. mysterious D. obvious 10. A. accustomed B. familiar C. used D. commonplace 11. A. reason B. cue C. excuse D. cause 12. A. rate B. swiftness C. speed D. tempo 13. A. more B. less C. rather D. other 14. A. badly B. better C. worse D. well 15. A. sports B. games C. plays D. shows Your answers:
1. ………… 2. ………… 3. ………… 4. ………… 5. …………
6. ………… 7. ………… 8. ………… 9. ………… 10. ………..
11. ……….. 12. ……….. 13. ……….. 14. ………. 15. ………..
II/ Read the following passage carefully and choose the best answer.
Composers today use a wider variety of sounds than ever before, including many that were once
considered undesirable noises. Composer Edgard Varese (1883-1965) called thus the "liberation of
sound...the right to make music with any and all sounds." Electronic music, for example-made with the aid
of computers, synthesizers, and electronic instruments-may include sounds that in the past would not have
been considered musical. Environmental sounds, such as thunder, and electronically generated hisses and
blips can be recorded, manipulated, and then incorporated into a musical composition. But composers also
draw novel sounds from voices and non-electronic instruments. Singers may be asked to scream, laugh,
groan, sneeze, or to sing phonetic sounds rather than words. Wind and string players may lap or scrape their instruments.
A brass or woodwind player may hum while playing, to produce two pitches at once, a pianist may
reach inside the piano to pluck a string and then run a metal blade along it. In the music of the Western
world, the greatest expansion and experimentation have involved percussion instruments, which
outnumber strings and winds in many recent compositions. Traditional percussion instruments are struck
with new types of beaters; and instruments that used to be couriered unconventional in Western music-
tom-toms, bongos, slapsticks, maracas-are widely used. - 5 -
In the search for novel sounds, increased use has been made in Western music of Microtones. Non-
Western music typically divides and interval between two pitches more finely than Western music does,
thereby producing a greater number of distinct tones, or micro tones, within the same interval. Composers
such as Krzysztof Penderecki create sound that borders on electronic noise through tone clusters-closely
spaced tones played together and heard as a mass, block, or band of sound. The directional aspect of
sound has taken on new importance as well Loudspeakers or groups of instruments may be placed at
opposite ends of the stage, in the balcony, or at the back and sides of the auditorium. Because standard
music notation makes no provision for many of these innovations, recent music scores may contain
graphlike diagrams, new note shapes and symbols, and novel ways of arranging notation on the page.
1. What does the passage mainly discuss?
A. The use of nontraditional sounds in contemporary music.
B. How sounds are produced electronically.
C. How standard musical notation has beer, adapted for nontraditional sounds.
D. Several composers who have experimented with the electronic production of sound.
2. The word "wider” in line 1 is closest in meaning to ________. A. more impressive B. more distinctive C. more controversial D. more extensive
3. The passage suggests that Edgard Varese is an example of a composer who ________.
A. criticized electronic music as too noiselike.
B. modified sonic of the electronic instruments he used in his music.
C. believed that any sound could be used in music.
D. wrote music with environmental themes.
4. The word "it" in line 11 refers to ________. A. piano B. string C. blade D. music
5. According to the passage, which of the following types of instruments has played a role in much of the
innovation in Western music? A. String B. Percussion C. Woodwind D. Brass
6. The word “unconventional” in line 14 could be best replaced by ________. A. nontraditional B. controversial C. illogical D. irregular
7. The word "thereby” in line 18 is closest in meaning to ________. A. in return for B. in spite of C. by the way D. by that means
8. According to the passage, Krzysztof Penderecki is known for which of the following practices?
A. Using tones that are clumped together.
B. Combining traditional and non-traditional instruments.
C. Seating musicians in unusual areas of an auditorium.
D. Playing Western music for non-Western audiences.
9. According to the passage, which of the followings would be considered traditional elements of Western music? A. Microtones B. Tom-toms and bongos C. Pianos D. Hisses
10. In paragraph 3, the author mentions diagrams as an example of a new way to ________.
A. chart the history of innovation in musical notation.
B. explain the logic of standard musical notation.
C. design and develop electronic instruments.
D. indicate how particular sounds should be produced. Your answers:
1. ………… 2. ………… 3. ………… 4. ………… 5. …………
6. ………… 7. ………… 8. ………… 9. ………… 10. ……….. - 6 -
III/ Read the passage and do the following tasks:
Questions 1-5. Choose the most suitable heading for each paragraph. There are three headings that are not used. 1. Paragraph A 2. Paragraph B 3. Paragraph C 4. Paragraph D 5. Paragraph E List of headings I. Glacial continents
V. Glaciers through the years
II. Formation and growth of Glaciers VI. Types of Glaciers III. Glacial Movement
VII. Glacial Effects on Landscape
IV. Glaciers in the last Ice Age
VIII. Glaciers in National Parks GLACIERS
A. Besides the earth’s oceans, glacier ice is the largest source of water on earth. A glacier is a massive
stream or sheet of ice that moves underneath itself under the influence of gravity. Some glaciers travel
down mountains or valleys, while others spread across a large expanse of land. Heavily glaciated
regions such as Greenland and Antarctica are called continental glaciers. These two ice sheets
encompass more than 955 of the earth’s glacial ice. The Greenland ice sheet is almost 10,000 feet thick
in some areas, and the weight of this glacier is so heavy that much of the region has been depressed
below sea level. Smaller glaciers that occur at higher elevations are called alpine or valley glaciers.
Another way of classifying glaciers is in terms of their internal temperature. In temperate glaciers, the
ice within the glacier is near its melting point. Polar glaciers, in contrast, always maintain temperatures far below melting.
B. The majority of the earth’s glaciers are located near the poles, though glaciers exist on all continents,
including Africa and Oceania. The reason glaciers are generally formed in high alpine regions is that
they require cold temperature throughout the year, in these areas where there is little opportunity for
summer ablation (loss of mass), snow changes to compacted firn and then crystallized ice. During
periods in which melting and evaporation exceed the amount of snowfall, glaciers will retreat rather than
progress. While glaciers rely heavily on snowfall, other climatic conditions including freezing rain,
avalanches, and wind, contribute to their growth. One year of below average precipitation can stunt the
growth of a glacier tremendously. With the rare exception of surging glaciers, a common glacier flows
about 10 inches per day in the summer and 5 inches per day in the winter. The fastest glacial surge on
record occurred in 1953, when the Kutiah Glacier in Pakistan grew more than 12 kilometers in three months.
C. The weight and pressure of ice accumulation causes glacier movement. Glaciers move out from under
themselves, via plastic deformation and basal slippage. First, the internal flow of ice crystals begins to
spread outward and downward fro the thickened snow pack also known as the zone of accumulation.
Next, the ice along the ground surface begins to slip in the same direction. Seasonal thawing at the base
of the glacier helps to facilitate this slippage. The middle of a glacier moves faster than the sides and
bottom because there is no rock to cause friction. The upper part of a glacier rides on the ice below. As a
glacier moves it carves out a U-shaped valley to a riverbed, but with much steeper walls and flatter bottom.
D. Besides the extraordinary rivers of rice, glacial erosion creates other unique physical features in the
landscape such as horns, fjords, hanging valleys, and cirques. Most of these landforms don’t become
visible until after has receded. Many are created by moraines, which occur at the sides and front of a - 7 -
glacier. Moraines are formed when material is picked up along the way and deposited in a new location.
When many alpine glaciers occur on the same mountain, these moraines can create a horn. The matter
horn, in the Swiss Alps is one of the most famous horns. Fjords, which are very common in Norway, are
coastal valleys that fill with ocean water during a glacial retreat. Hanging valleys occur when two or
more glacial valleys intersect at varying elevations. It is common for waterfalls to connect the higher
and lower hanging valleys, such as in Yosemite National Park. A cirque is a large bowl-shaped valley
that forms at the front of a glacier. Cirques often have a lip on their down slope that is deep enough to
hold small lakes when the ice melts away
E. Glacier movement and shape shifting typically occur over hundreds of years. While presently about
10% of the earth land is covered with glaciers, it is believed that during the last Ice age glaciers covered
approximately 32% of the earth’s surface. In the past century, most glaciers have been retreating rather
flowing forward. It is unknown whether this glacial activity is due to human impact or natural causes,
but by studying glacier movement, and comparing climate and agricultural profiles over hundreds of
years, glaciologists can begin to understand environmental issues such as global warming
Question 6-10. Decide whether these statements are True (T), False (F) or Not Given (NG)
6. Glaciers exist only near the north and south poles.
7. Glaciers are formed by a combination of snow and other weather conditions.
8. Glaciers normally move at a race of about 5 to 10 inches a day.
9. All parts of the glacier move at the same speed.
10. During the last ice age, average temperatures were much lower than they are now. Your answers:
1. ………… 2. ………… 3. ………… 4. ………… 5. …………
6. ………… 7. ………… 8. ………… 9. ………… 10. ………..
IV/ Fill in each blank with ONE suitable word. Write your answer in the numbered space provided below the passage.
Although the rise in the global temperature by 4 per cent predicted by many scientists may not
sound like much, it is the difference between (1)________ and the last Ice Age, when huge glaciers
(2)________ Europe and most of Britain. Nobody knows exactly what would happen in a warmer world,
(3)________ we do know some things. Heat a kettle and the water inside it expands. The temperature of
the world has climbed more than half a degree this century, and the oceans have risen by at (4)________ 10 cm.
But just as it takes several minutes for a kettle to begin (5)________, so it may have taken the
oceans thirty years to swell. This means that the global warming we are now (6)________ is a result only
of the carbon dioxide we have dumped into the atmosphere up to (7)________ 1960s. Since then, the use
of fossil (8)________ has increased rapidly. Scientists working for the United Nations and European
governments have (9)________ warning that what the Dutch and the people of the East Anglia will need
to do will be to build more extensive sea defences. Many of the world’s greater cities are at (10)________,
because they are located at sea level. Miami, (11)________ entirely built on a sandbank, could be swept
away. But the effects of (12)________ sea levels will be much worse for the developing countries. With a
metre rise in sea levels, 200 million people could become (13)________.
There are other fears too, (14)________ to a recent United Nations report. The plight of the hungry
in the northern Africa could (15)________, as rainfall in the Sahara and beyond is reduced by 20 per cent. Your answers:
1. ………… 2. ………… 3. ………… 4. ………… 5. …………
6. ………… 7. ………… 8. ………… 9. ………… 10. ………..
11. ……….. 12. ……….. 13. ……….. 14. ………. 15. ……….. - 8 - PART D: WRITING:
I/ Use the word(s) given in brackets and make any necessary additions to complete a new sentence
in such a way that it is as similar as possible in meaning to the original sentence. Do NOT change
the form of the given word(s). Look at the example. Example:
There was no conclusion at the end of the workshop. (conclude)
………………………...…………………………….
They did not conclude anything at the end of the workshop.
1. From the educational point of view his childhood years had been well spent. (terms)
…………………………………………………………………………
2. He's very good at tennis and he's also a very good footballer. (addition)
…………………………………………………………………………
3. Why does everything seem to be difficult to me? (only)
…………………………………………………………………………
4. If you work without a break, you are more likely to make an error. (prone)
…………………………………………………………………………
5. We agreed that each of us would do the washing - up on alternate days. (turns)
…………………………………………………………………………
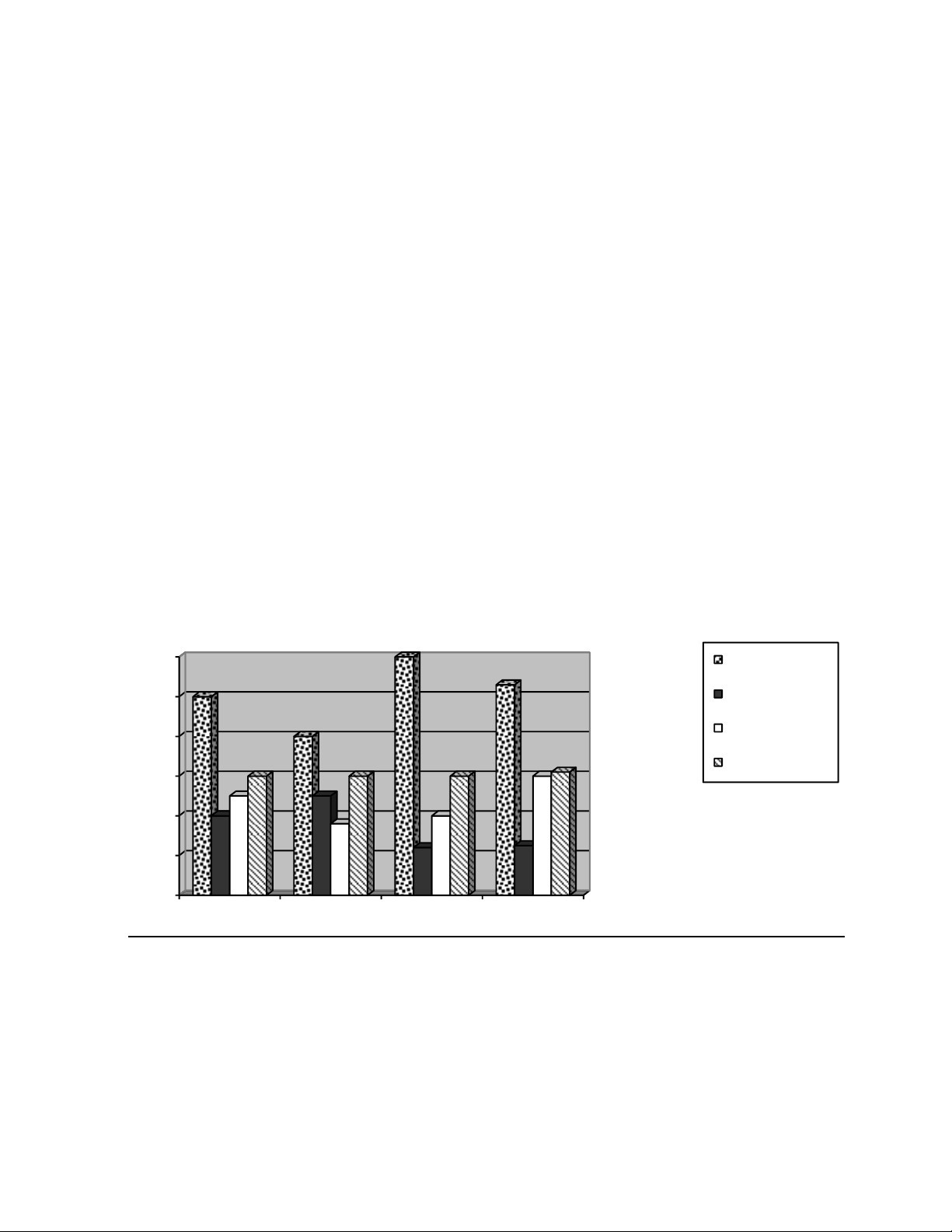
II/ The chart below shows the results of a survey on various home activities among young people
aged 11 to 16 in four countries. Write a report (of at least 150 words) describing the information in
the chart. You may add comments and reasons to your report.
Home activities among young people 60 Computer Games 50 Reading Board Games 40 Watching TV 30 20 10 % 0 England Scotland Ireland Wales
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. - 9 -
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
III/ In about 300 words, write an essay that ends with the remark “Not everything learned is
contained in books and knowledge gained from experience sometimes contrasts with knowledge gained
from books”. In your opinion which source is more important? Give reasons and examples to
support your position. You may continue your writing on the back page if you need more space.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. - 10 -
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. THE END - 11 -




