






Preview text:
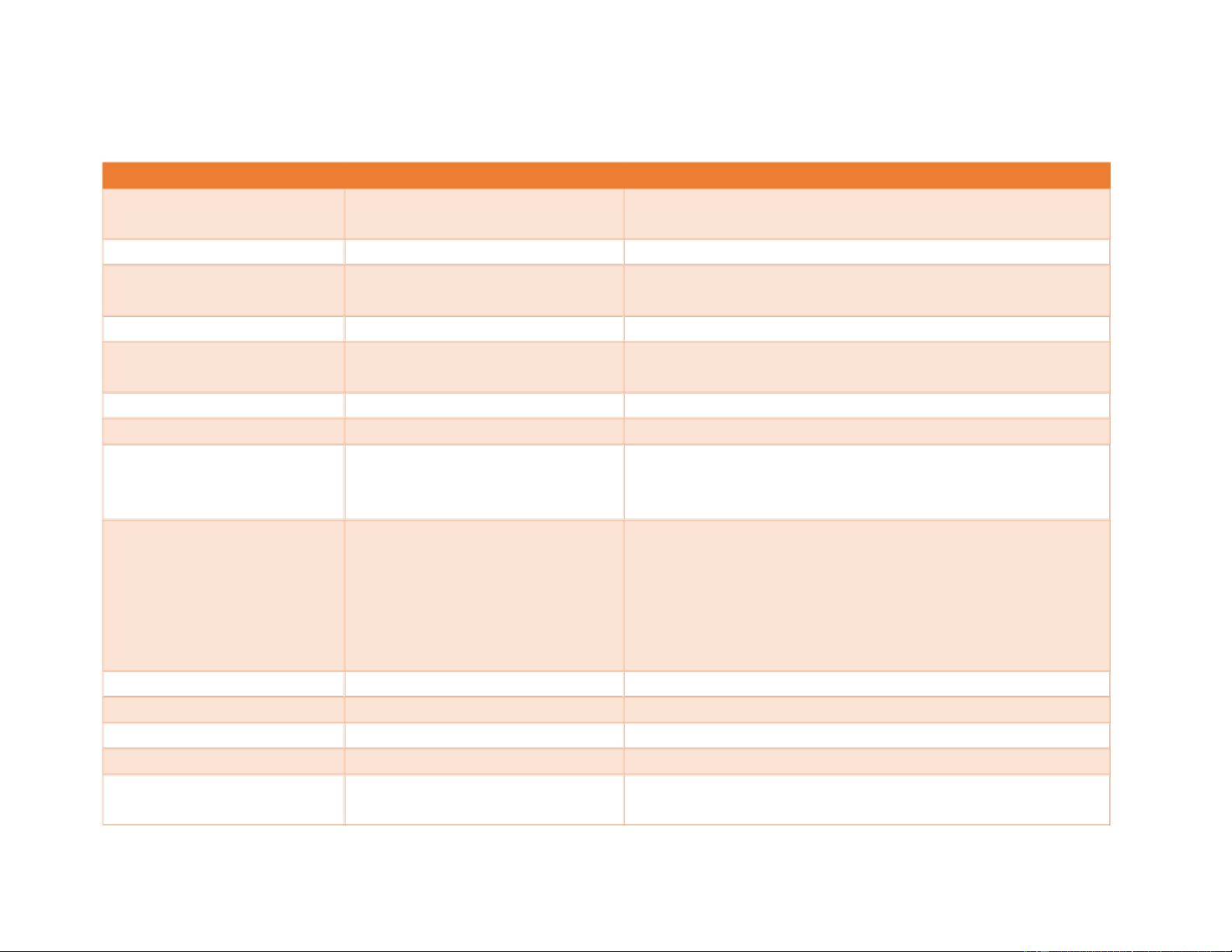
lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM A. VOCABULARY WORD PRONUNCIATION MEANING
Absorption ăb-SŎRP-shŭn Passage of materials through the walls of the small of
the wall of the small intestine into the bloodstream Achlorhydria ā-chlōr-HĪD-rē-ă
Amylase ĂM-ĭ-lās Enzyme (-ase) secreted by the pancreas and salivary
glands to digest starch (amyl/o) Anastomosis ă-năs-tō-MŌ-sĭs
Anus Ā-nŭs Terminal end or opening of the digestive tract to the outside of the body Appendectomy
ăp-ĕn-DĔK-tō-mĒ Sergical removal of the vermiform appendix Appendicitis ă-pĕn-dĭ-SĪ-tĭs
Inflammation of the vermiform appendix
Appendix ă-PĔN-dĭks Blind pouch hanging from the cecum (in the right
lower quadrant [RLQ]. It literally means hanging
( pend/o) onto (ap-, which is a form of ad -) Bile bīl
Digestive juice made in the liver and stored in the
gallbladder. It breaks up (emulsifies) large fat
globules. Bile originally was called gall (Latin bilis,
meaning gall or anger), probably because it has a
bitter taste. It is composed of bile pigments (colored
materials), cholesterol, and bile salts. Biliary
BĬL-ē-ăr-ē Pertaining to the bile, bile ducts, or gallbladder Bilirubin bĭl-ĭ-ROO-bĭn
Pigment released by the liver in bile Bowel BŎW-ĕl Intestine Buccal mucosa
BŬK-ăl mū-KŌ-să The inner lining of the cheeks lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766 Canine teeth
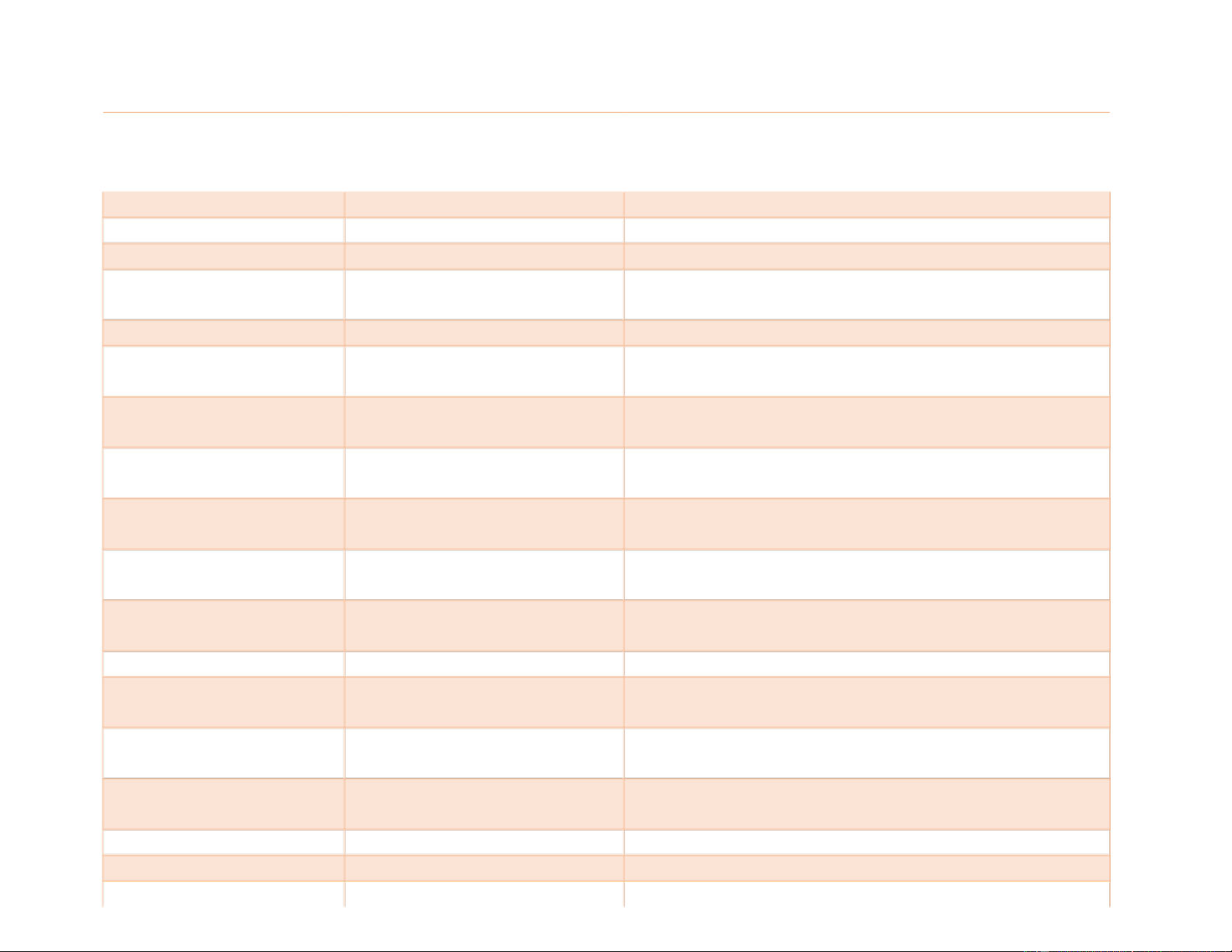
KĀ-nīn tēth The sharp, pointed teeth that sit next to the incisors and look like fangs. Cecal SĒ-kăl Pertaining to a cecum Cecum SĒ-kŭm
First part of the large intestine Celiac SĒ-lē-ăk Abdominal Cheilosis
kī-LŌ-sĭs A noninflammatory condition of the lips
characterized by chapping and fissuring.
Cholecystectomy kō-lĕ-sĭs-TĔK-tō-mē
Surgical removal of the gallbladder Choledocholithiasis
kō-lĕ-dō-kō-lĭ-THĪ-ă-sĭs The occurrence of
calculi (cholelithiasis) in the common bile duct.
Choledochojejunostom kō-lĕ-dō-kō-jĭ-jū-NŎS-tō-mē Surgical anastomosis of the common bile duct and y the jejunum Choledochotomy kō-lĕ-dō-KŎT-ō-mē Incision into the common bile
duct for exploration or removal of a calculus
Cholelithiasis kō-lē-lĭ-THĪ-ă-sĭs The presence or formation of gallstones; they may be
either in the gallbladder or in the common bile duct
Colon KŌ-lŏn Portion of the large intestine consisting of ascending,
transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments Colonic
kō-LŎN-ĭk 1.Pertaining to the colon; colic /2. colon hydrotherapy Colonoscopy
kō-lŏn-ŎS-kō-pē Examination by means of the colonoscope
Colostomy kŏ-LŎS-tō-mē An operation to divert 1 end of the colon (part of the
bowel) through an opening in the tummy. lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766 Common bile duct KŎM-ŏn bīl dŭkt Carries bile from the liver
and gallbladder to the duodenum. Also called the cholodochus
Defecation dĕf-ĕ-KĀ-shŭn Elimination of feces from the digestive tract through the anus
Deglutition dē-gloo-TĬSH-ŭn Swallowing
Dentibuccal dĕn-tĭ-BŬK-ăl
Pertaining to the teeth and check Dentin DĔN-tĭn
Primary material found in teeth. It is covered by the enamel in the crown and a
protective layer of cementum in the root Digestion
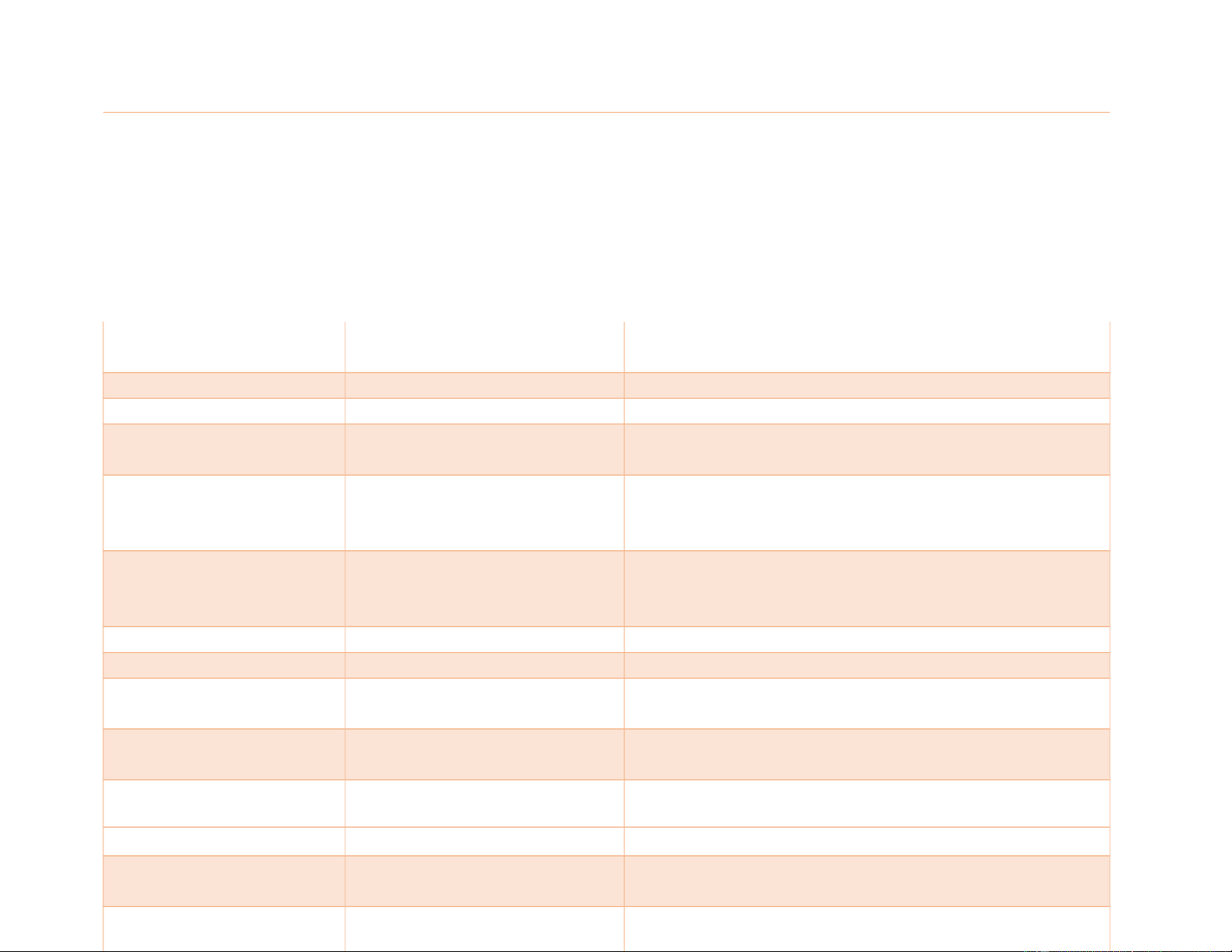
dī-JĔST-yŭn Breakdown of complex foods to simpler forms
Duodenal dū-ō-DĒ-năl or dū-ŎD-ĕ-năl
Of or relating to the duodenum Duodenum
dū-ō-DĒ-nŭm or dū-ŎD-ĕ- First part of the small intestine. Duo = 2, den = 10;
nŭm the duodenum measures 12 inches long
Elimination ē-lĭm-ĭ-NĀ-shŭn Act of removal of materials from the body; in the
digestive system, the removal of indigestible materials as feces Emulsification ē-mŭl-sĭ-fĭ-KĀ-shŭn
Physical process of breaking up large fat globules
into smaller globules, thereby increasing the surface
area that enzymes can use to digest the fat Enamel
ē-NĂM-ĕl Hard, outermost layer a tooth Endodontist ĕn-dō-DŎN-tĭst
A dentist who specializes in endodontics
Enterocolitis ĕn-tĕr-ō-kō-LĪ-tĭs Inflammation involving both the small intestine and the colon Enteroenterostomy
ĕn-tĕr-ō-ĕn-tĕr-ŎS-tō-mē Surgical anastomosis between two segments of the intestine. lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766
Enzyme ĔN-zīm A protein molecule that catalyzes chemical reactions
of other substances without itself being destroyed or
altered upon completion of the reactions
Esophageal ĕ-sŏf-ă-JĒ-ăl Cancer that occurs in the esophagus – a long, hollow
tube that runs from your throat to your stomach.
Esophagus ĕ-SŎF-ă-gŭs Tube connecting the throat to the stomach. Eso –
means inward; phag/o means swallowing
Fatty acids FĂT-tē Ă-sĭdz
Substances produced when fats are digested. Fatty
acids are a category of lipids Facial FĀ-shŭl Of or on the face Feces FĒ-sēz Solid wastes; stool
Galbladder GAWL-blă-dĕr
Small sac under the liver; stores bile. Remember: gallbladder is one word
Gastrointeststinal tract
găs-trō-ĭn-TĔS-tĭn-ăl trăct A series of hollow
organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus. Gastrojejunostomy
găs-trō-jĕ-jū-NŎS-tō-mē 1.A gastroenterostomy
between the stomach and the jejunum/ 2. The anastomosis so created. Gastrostomy
găs-TRŎS-tō-mē 1, surgical creation of an artificial opening into the
stomach/2. The opening so established
Gingivitis jĭn-jĭ-VĪ-tĭs Inflammation of the gingivae; when it is associated
with bony changes, the condition is referred to as periodontitis.
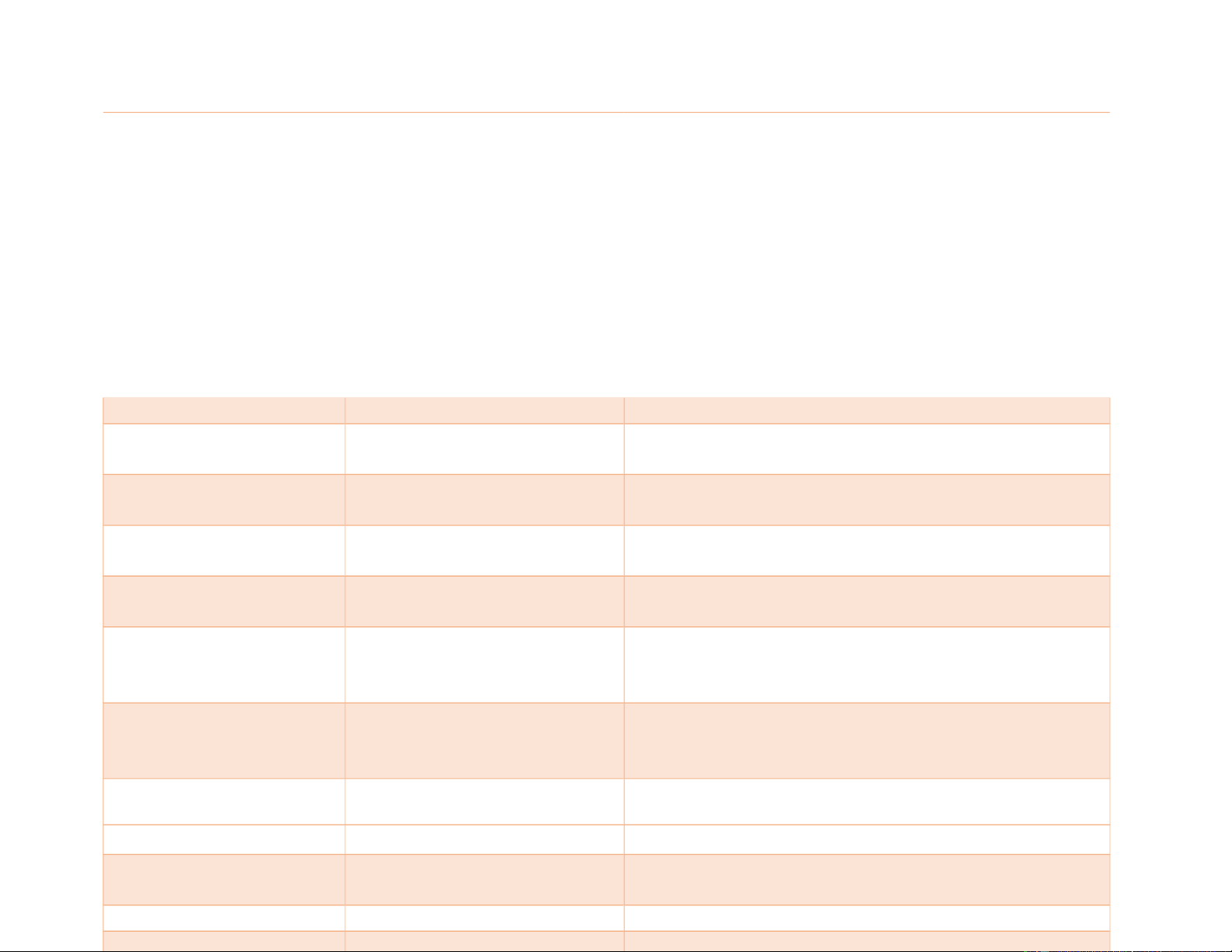
Gluconeogeneis gloo-kō-nē-ō-JĔN-ĕ-sĭs The formation of glucose from molecules that are not lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766
themselves carbohydrates, as from amino acids,
lactate, and the glycerol portion of fats
Glycogenolyis glī-kō-jĕ-NŎL-ĭ-sĭs The breakdown of glycogen to glucose by hydrolysis
(as in digestion or within lysosomes) or involving glycogen
Hepatoma hĕ-pă-TŌ-mă 1. A tumor of the liver 2. Hepatocellular carcinoma Hepatomegaly hĕ-pă-tō-MĔG-ă-lĒ Enlargement of the liver Hydrochloric acid
hī-drō-KLŎR-ĭk Ă-sĭd Substance produced by the
stomach; necessary for digestion of food Hyperbilirubinemia
hī-pĕr-bĭl-ĭ-roo-bĭ-NĒ-mē-ă Excessive bilirubin in
the blood, which may lead to jaundice
Hyperglycermia hī-pĕr-glī-SĒ-mē-ă 1. Accumulation and excretion of glycerol caused
by deficiency of glycerol kinase activit, an
Xlinked trait caused by mutation in the glycerol kinase gene.
2. Excess of glycerol in the blood
Hypoglossal hī-pō-GLŎ-săl Sublingual Ileitis ĭl-ē-Ī-tĭs Inflammation of the ileum Ileocecal sphincter
ĭl-ē-ō-SĒ-kăl SFĬNK-tĕr A sphincter muscle
valve that separates the small intestine and the large intestine.
Ileostomy ĭl-ē-ŎS-tō-mē
Surgical creation of an opening into the ileum,
usually by establishing an ileal stoma on the abdominal wall. lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766 Ileum ĬL-ē-ŭm
Third part of the small intestine; from the Greek
eilos, meaning twisted. When the abdomen was
viewed at autopsy, the intestine appeared twisted, and
the ileum often was an area of obstruction Incisor ĭn-SĪ-zŏr
Any one of four front teeth in the dental arch Insulin ĬN-sŭ-lĭn
Hormone produced by the endocrine cells of the
pancreas. It transports sugar from the blood into cells
and stimulates glycogen formation by the liver
Jejunum jĕ-JOO-nŭm Second part of the small intestine. The Latin jejunus
means empty; this part of the intestine was always
empty when a body was examined after death Labial LĀ-bē-ăl
1. Pertaining to a lip or labium
2. In dental anatomy; pertaining to the tooth
surface that faces the lip; see under surface 3. bilabial
Laparoscopy lă-pă-RŎS-kō-pē Examination of the interior of the abdomen by means of a laparoscope. Lipase LĪ-pās
Pancreatic enzyme necessary to digest fats Lithogenesis
lĭth-ō-JĔN-ĕ-sĭs The formation of calculi
Liver LĬ-vĕr Large organ located in the RUQ of the abdomen. The
liver secretes bile; store sugar, iron, and vitamins;
produces blood proteins; destroys worn-out red blood
cells; and filters out toxins. The normal adult liver weghs about 2 ½ to 3 pounds lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766 Lower esophageal
LŌW-ĕr ĕ-sŏf-ă-JĒ-ăl Ring of muscles between the esophagus and the sphincter
(LES) SFĬNK-tĕr stomach. Also called cardiac sphincter
Mastication măs-tĭ-KĀ-shŭn Chewing
Mesentery MĔS-ĕn-tĕr-ē
A membranous flod attaching any of various organs
to the body wall, especially the folds of peritoneum
that attach the intestines to the abdominal wall
Molar teeth MŌ-lăr tēth Sixth, seventh, and eighth teeth from the middle on
either side of the dental arch. Premolar teeth are the
fourth and fifth teeth, before the molars
Oral ŎR-ăl 1. pertaining to the mouth; taken through or applied in the mouth. 2. Lingual Orthodontist
ŏr-thō-DŎN-tĭst A dentist who specializes in orthodontics Palate PĂL-ăt
Roof of the mouth. The hard palate lies anterior to
the soft palate and is supported by the upper jawbone
(maxilla). The soft palate is the posterior fleshy part
between the mouth and the throat
Palaropharyngoplasty păl-ă-tō-fă-RĬNG-gō-plăs-tē
A trimming back of excess palatal and pharyngeal
tissue, done in order to widen the airway and relieve
obstructive sleep apnea or server snoring. Palatoplasty
PĂL-ă-tō-plăs-tē Plastic reconstruction of the palate, including cleft palate operations. Pancreas
PĂN-krē-ăs Organ under the stomach; produces insulin (for lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766
transport of sugar into cells) and enzymes (for digestion of foods)
Pancreatitis păn-krē-ă-TĪ-tĭs Inflammation of the pancreas, which may be acute or
chronic, asymptomatic or symptomatic, and is often
complicated by autodigestion of pancreatic tissue by its own enzymes Papillae pă-PĬL-ē
Small elevation on the tongue. A papilla is a nipple- like elevation
Parenteral pă-RĔN-tĕr-ăl
Of, pertaining to, or derived from the parents Parotid gland
pă-RŎT-ĭd glănd Salivary gland within the cheek, just anterior to the
ear. Note the literal meaning of parotid (par- =near; ot/o = ear) Perianal
pĕ-rē-Ā-năl Near or around the anus Periodontist
pĕr-ē-ō-DŎN-tĭst A dentist who specializes in periodontics
Peritonitis pĕr-ĭ-tō-NĪ-tĭs
Inflammatory reaction of the tissues surrounding a
tooth (periodontium), usually resulting from the
extenstion of gingival inflammation into the periodontium
Peristalsis pĕr-ĭ-STĂL-sĭs
Rhythmic contractons of the tubular organs. In the
gastrointestinal tract, peristalsis moves the contents
through at different rates: stomach, 0.5 to 2 hours;
small intestine, 2 to 6 hours; and colon, 6 to 72 hours.
Peri – means surrounding – stalsis is constriction
Pharyngeal făr-ăn-JĒ-ăl or fă-RĬN-jē-ăl
Made by making the muscles in the pharynx tighter lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766
so that air cannot flow freely Pharynx
FĂR-ĭnks Throat, the common passageway for food from the
mouth and for air from the nose
Portal vein PŎR-tăl vān Large vein bringing blood to the liver from the intestines Postprandial
pōst-PRĂN-dē-ăl After a meal Premolar teeth
prē-MŌ-lăr tēth Transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth
Proctologist prŏk-TŎL-ō-jĭst A specialist in proctology Protease
PRŌ-tē-āse Enzyme that digests protein
Pulp pŭlp Soft tissue within a tooth, containing nerves and blood vessels
Pyloric sphincter pī-LŎR-ĭk SFĬNK-tĕr
Ring of muscle at the end of the stomach, near the
duodenum. From the Greek pyloros, meaning
gatekeeper. It is normally closed, but opens when a
wave of peristalsis passes over it Pyloroplasty
pī-LŎR-ō-plăs-tē Incision of the pylorus and reconstruction of the
channel through it, such as to relieve obstruction or acceler Pylorus
pī-LŎR-ŭs Distal region of the stomach, opening to the duodenum
Rectocele RĔK-tō-sēl Hernial protrusion of part of the rectum into the vagina
Rectum RĔK-tŭm Last section of the large intestine, connecting the end of the colon and the anus lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766 Rugae ROO-gē
Ridges on the hard palate and the wall of the stomach Saliva să-LĪ-vă Digestive
juice produced by salivary glands. Saliva
contains the enzyme amylase, which begins the digestion of starch to sugar Salivary glands SĂL-ĭ-vār-ē glăndz
Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands
Sialadenitis sī-ăl-ă-dĕ-NĪ-tĭs
Inflammation of a salivary duct Sialolith
sī-ĂL-ō-lĭth A calcareous concretion or calculus in the salivary
ducts or glands, involving most commonly the
submaxillary gland and its duct, less frequently the
parotid and sublingual glands and their ducts, and
seldom the minor salivary glands
Sigmoid colon SĬG-moyd KŌ-lŏn Fourth and last, S-shaped segment of the codon, just
before the rectum; empties into the rectum Sigmoidoscopy sĭg-moyd-ŎS-kō-pē Inspection of the sigmoid colon through a sigmoidoscope
Sphincter SFĬNK-tĕr Circular ring of muscle that contricts a passage or closes a natural opening
Steatorrhea stē-ă-tō-RĒ-ă
Excessive amounts of fats in the feces, as in malabsorption syndromes Stomach
STŎM-ak Muscular organ that receives food from the esophagus
Stomatitis stō-mă-TĪ-tĭs
Inflammation of the oral mucosa, due to local or
systemic factors, which may involve the buccal and
labial mucosa, palate, tongue, floor of the mouth, and the gingivae lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766
Sublingual sŭb-LĬNG-wăl
Beneath the tongue; called also hypoglossal and subglossal
Submandibular sŭb-măn-DĬB-ū-lăr Inferior to the mandible Triglycerides trī-GLĬ-sĕ-rīdz
A compound consisting of three molecules of fatty
acid esterified to glycerol; it is a neutral fat
synthesized from carbohydrates for storage in animal
adipose cells. On enzymatic hydrolysis, it releases free fatty acids in the blood Uvula Ū-vū-lă a pendent, fleshy mass lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766 Uvulectomy
ū-vū-LĔK-tō-mē excision of the uvula Villi
VĬL-ī genitive and plural of villus B. EXERSISE I.
Practice using combining form to create medical terms. Your repertoire of word parts should be
sufficient now to accomplish this task. Create the term, and then provide its meaning.
Remember, you may have to change some of the word parts slightly to create a new term. 1. Jejun/o stoma col/o Term: jejunocolostomy
Meaning: the surgical formation of passage between the jejunum and the colon 2. Ectomy pylor/o Term: pylorectomy
Meaning: surgical removal of the pylorus 3. Col/o itis enter/o Term: enterocolitis
Meaning: inflammation of the intestines 4. Duoden/ al gastro Term: gastroduodenal
Meaning: pertaining to the stomach and the duodenum
5. Itis enter/o gastr/o Term: gastroenteritis
Meaning: inflammation of the stomach and the intestines 6. Pathy colon/o Term: colonopathy
Meaning: any disease of colon 7. Scope sigmoid/o Term: sigmoiddoscope
Meaning: a tube-like device that it used to visualize
the sigmoid colon and the rectum. 8. Sigmoid rect/o Term: rectosigmoid
Meaning: pertaining to both the rectum and the sigmoid stomach 9. Ectomy gastr/ Term: gastrectomy
Meaning: surgical removal of all or part of the stomach 10. An/o rect/o -al Term: anorectal
Meaning: pertaining to both the anus and the rectum II.
Identify the term or prefix that indicates each direction or location.
1. Across transverse
Downloaded by Tr?n Lan Anh (lananh1406@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766 2. Upward ascending 3. Downward descending
4. Within or toward the middle intra-
5. Occurring behind retro- III.
Match each word with its definition or description. 1. Hepatitis rupture of the liver 2. Hepatogastric inflammation of the liver and kidneys
3. Hepatocystic poisonous to the liver 4. Hepatonephritis
referring to the stomach and the liver 5. Hepatorrhexis inflammation of the liver
6. Hepatotoxicpertaining to the gallbladder and the liver
IV. Break down each term into its component parts. Define each part, and then define the term. 1. Cholecystitis
Meaning: chole (gall or bile) + cyst (vessel or bladder) + -itis
( inflammation): inflammation of the gallbladder. 2. Choleccystopathy
Meaning: chole (gall or bile) + cysto (vessel or bladder) +
graph (writing or record) + -y (condition or state): disease of the gallbladder. 3. Cholangiography
Meaning: cholangio (bile vessels or ducts) + graph (writing or
record) + -y (condition or state) = an x-ray or radiograph of the bile ducts 4. Cholangioma
Meaning: cholangio (bile vessels or ducts) + -oma (tumor) = cancer of the bile ducts. V. BUILD MEDICAL WORD
Use esopha/o (esophagus) to build words that mean:
Downloaded by Tr?n Lan Anh (lananh1406@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766
1. Pain in the esophagus
esophagodynia or esophagalgia
2. Spasm of the esophagus esophagospasm
3. Stricture or narrowing of the esophagus esophagostenosis
Use gastr/o (stomach) to build words that mean:
4. Inflammation of the stomach gastritis 5. Pain in the stomach
gastrodynia or gastralagia
6. Disease of the stomach gastropathy
Use duoden/o (duodenum), jejun/o (jekunum), or ile/o (ileum) to build words that mean:
7. Excision of all or part of the jejunum jejunectomy
8. Relating to the duodenum duodenal
9. Inflammation of the ileum ileitis
10. Pertaining to the jejunum and ileum jejunoileal
Use enter/o (usually small intestine) to build words that mean:
11. Inflammation of the small intestine enteritis
12. Disease of the small intestine enteropathy
13. Inflammation of the small intestine and colon entercolitis Use col/o (colon) to build words that means:
14. Inflammation of the colon colitis
15. Pertaining to the colon and rectum colorectal
16. Prolapse or downward displacement of the colon coloptosis
17. Disease of the colon colorpathy
Use proct/o (anus, rectum) or rect/o (rectum) to build words that mean:
18. Narrowing or constriction of the rectum proctosenosis or rectostenosis
19. Hemiaton of the rectum
rectocele or proctocele
20. Paralysis of the anus (anal muscles)
proctoplegia or proctoparalysis Downloaded by Tr?n Lan Anh (lananh1406@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766
Use chol/e (bile, gall) to build words that mean:
21. Inflammation of the gallbladder cholecystitis
22. Abnormal condition of a gallstone
cholelithiasis Use hepat/o (liver) or pancreas) to build words that mean 23. Tumor of the liver hepatoma
24. Enlargement of the liver hepatomegaly
25. Inflammation of the pancreas pancreatitis
VI. MATCH THE FOLLOWING TERMS WITH THE DENFINITIONS IN THE NUMBERED LIST.
Anorexia dysphagia hematemesis
Cachexia dyspnea lesion
Cirrhosis fecalith melena
Dyspepsia halitosis obstipation
1. Vomiting blood hematemesis
2. Difficulty swallowing or inability to swallow dysphagia 3. Fecal concretion fecalith 4. “bad” breath halitosis 5. Loss of appetite anorexia 6. Poor digestion dyspepsia
7. Degenerative liver disease cirrhosis
8. State of ill health, malnutrition, and wasting cachexia
9. Intractable constipation obstipation 10. Open sore lesion
Downloaded by Tr?n Lan Anh (lananh1406@gmail.com)




