



Preview text:
Giảng viên : Hoàng Thị Minh Hằng (Ph. D)
Faculty of Law B209, Building B
Contact info : hanghtm@ftu.edu.vn; 0836863586 Overview
● Topic 1 : Theories of States and Law
● Topic 2 : Fundamentals of Civil Law in Vietnam
● Topic 3 : Fundamentals of Criminal Law of Vietnam
● Topic 4 : International Public Law
● Topic 5 : International Private Law
Mid-term (17/11/22) : Topic 1+2, Open book + in writing + in-class exam
Final test : Topic 2-5, Open book + in writing + In-class and take-home assignment
Grading Breakdown : Attendance (10%) + Mid-term (30%) + Final (60%)
Topic 1 : Theories of States and Law
Session 1 : Origin of States and Law
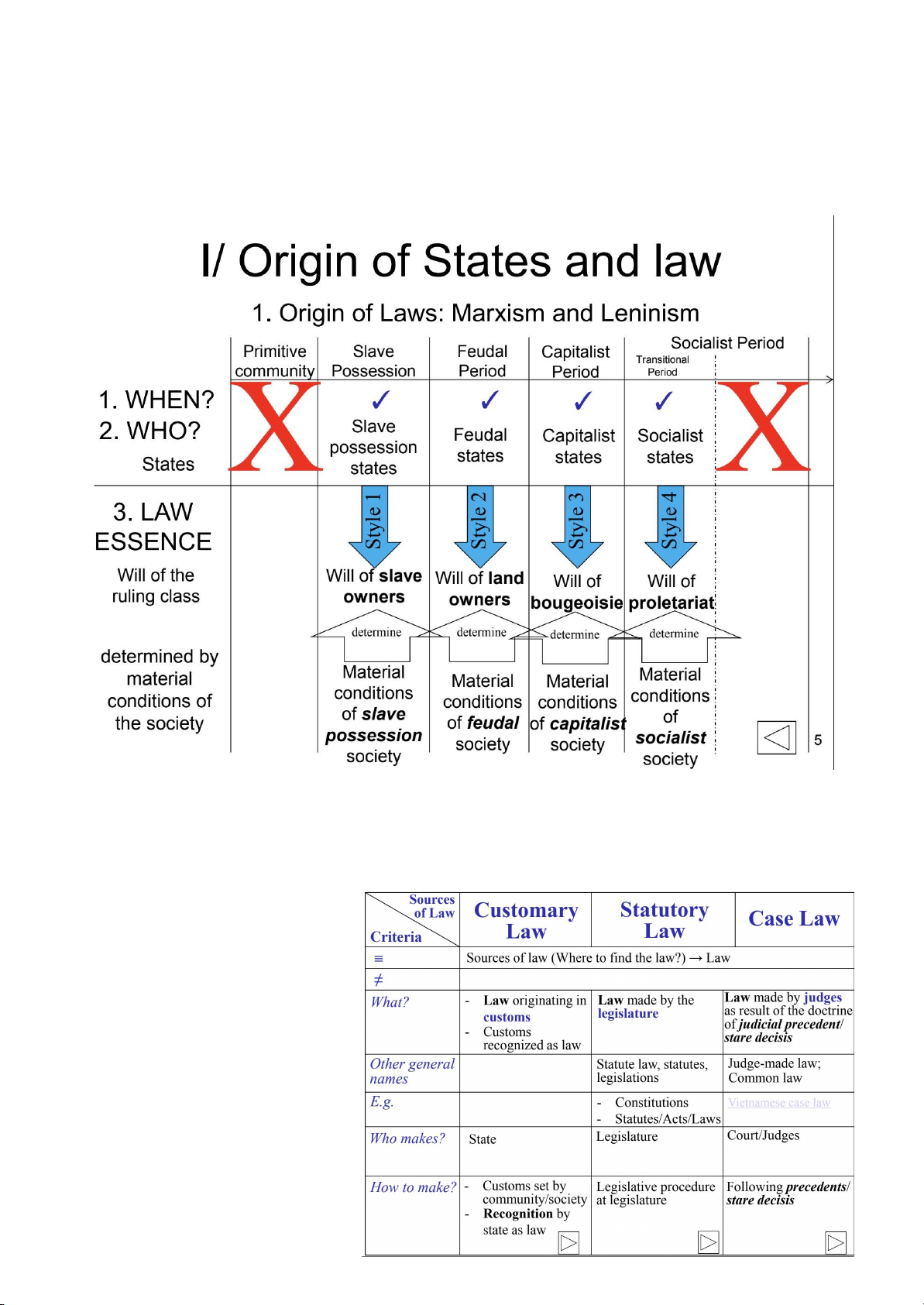
1. Origin of States : Marxism and Leninism
- Reasons of States Formation : 3 times of specializations
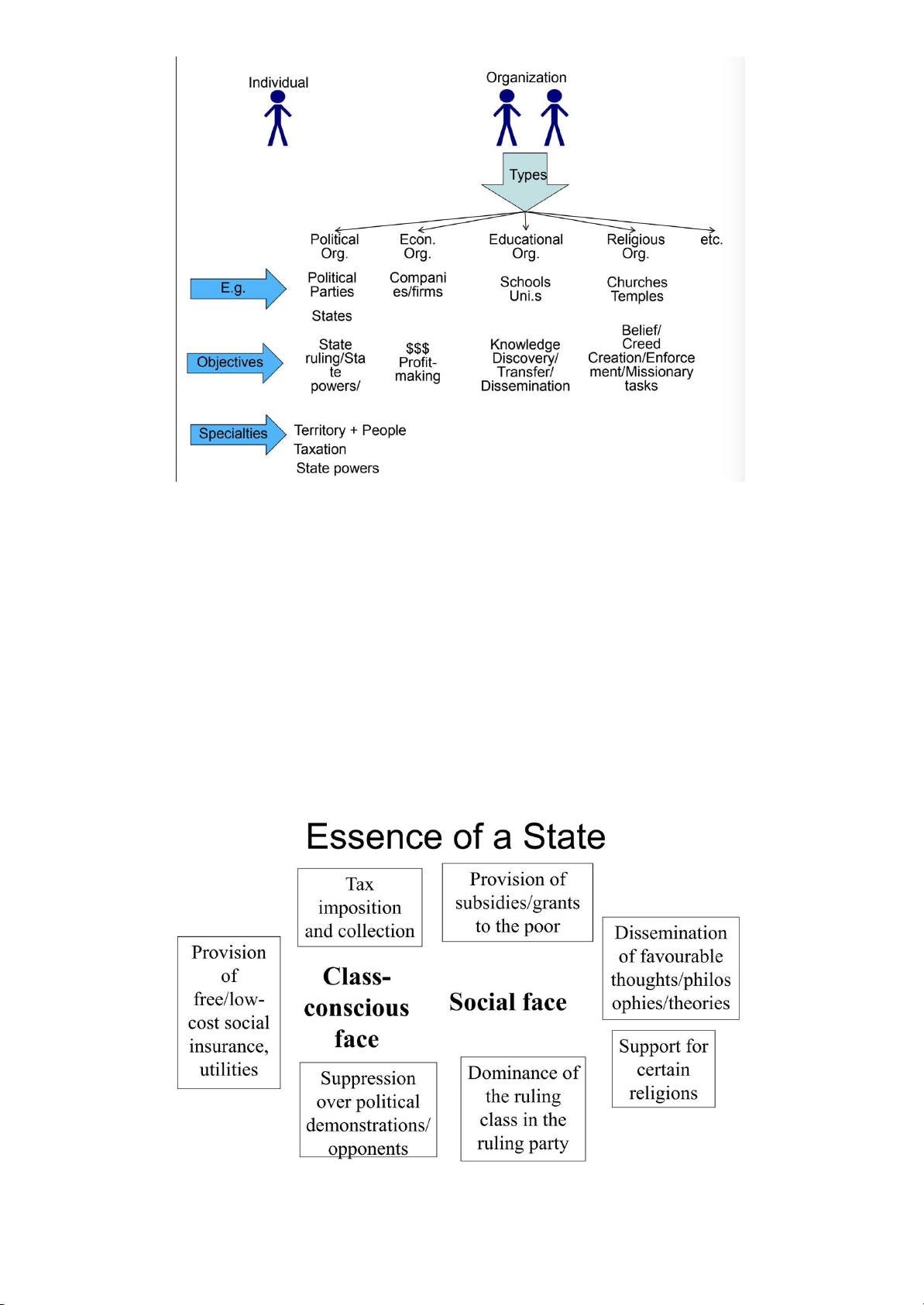
Primitive Community/ Classless society ⇒ Class society ⇒ States - Definition of State:
+ Special political organization
+ Protecting the rights and interests of the ruling class (bảo vệ quyền và lợi ích cho giai cấp thống trị)
+ Maintaining the stability of the society
+ Having enforcement power (tính cưỡng chế) - Powers of a state :
+ Legislative power (lập pháp) : power to make law (cal ed Legislature)
eg. National, Assembly, Parliament, Congress, National Diet…
+ Executive power (hành pháp) : power to administer law (cal ed Executive)
eg. Government, administration, cabinet, etc..
+ Judicial power (tư pháp) : Power to enforce law (cal ed Judiciary) eg. Court, Prosecution
- State protect the rights and interest of the ruling classes in politics, economy, social
rights and interests by State bodies (cơ quan nhà nước) + State powers
- Essence of a State (bản chất của nhà nước) : Session 2 : Origin of Law
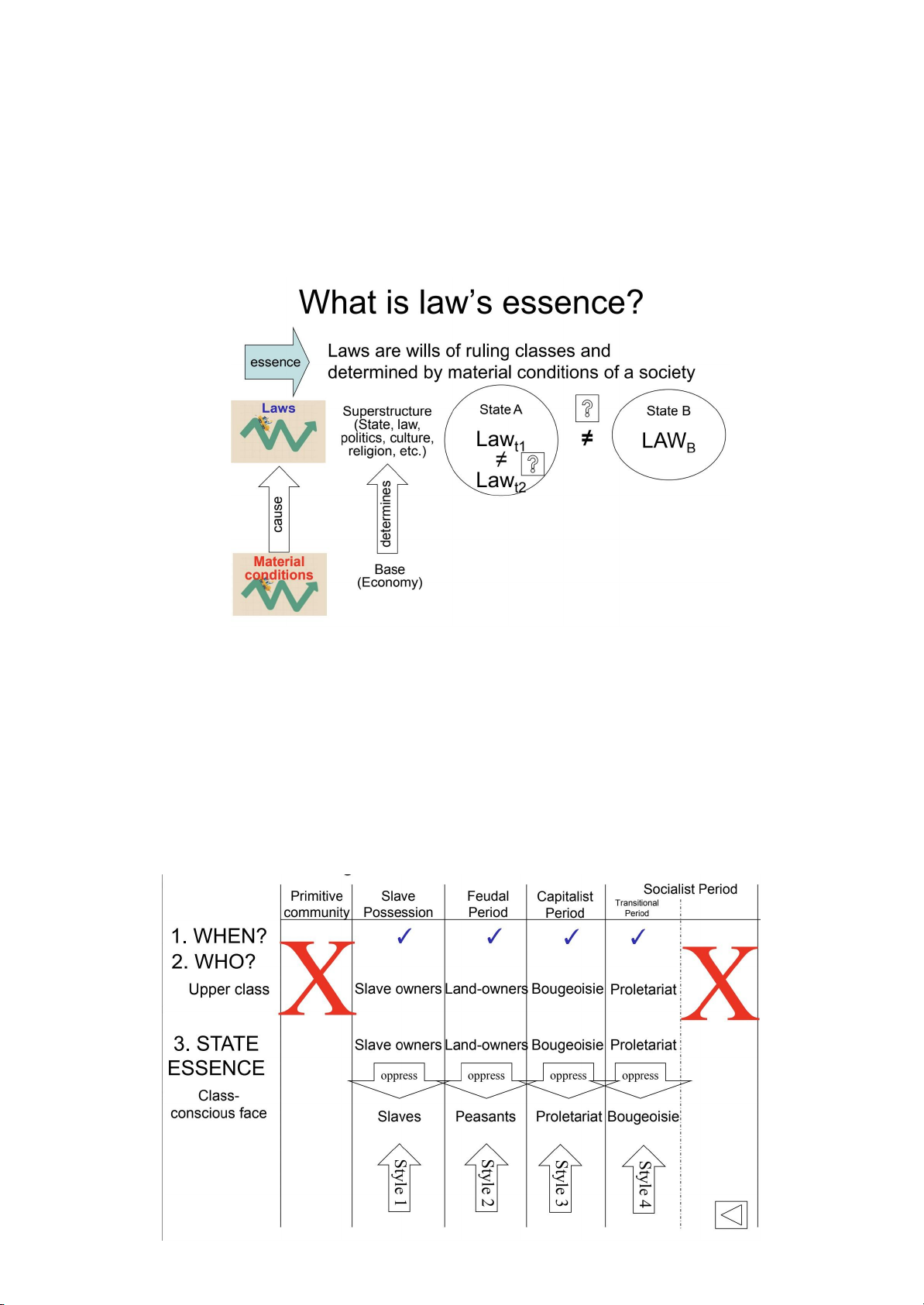
2. Origin of Law : Marxism and Leninism -
Primitive community : customs and usages ⇒ Class society ⇒ State ⇒ Law a) What is law? -
Laws : are legal y enforceable rules made by authorities within a society. Laws are wil s of
ruling classes and determined by material conditions of a society b) Essences of Law : - Laws are different from rules.
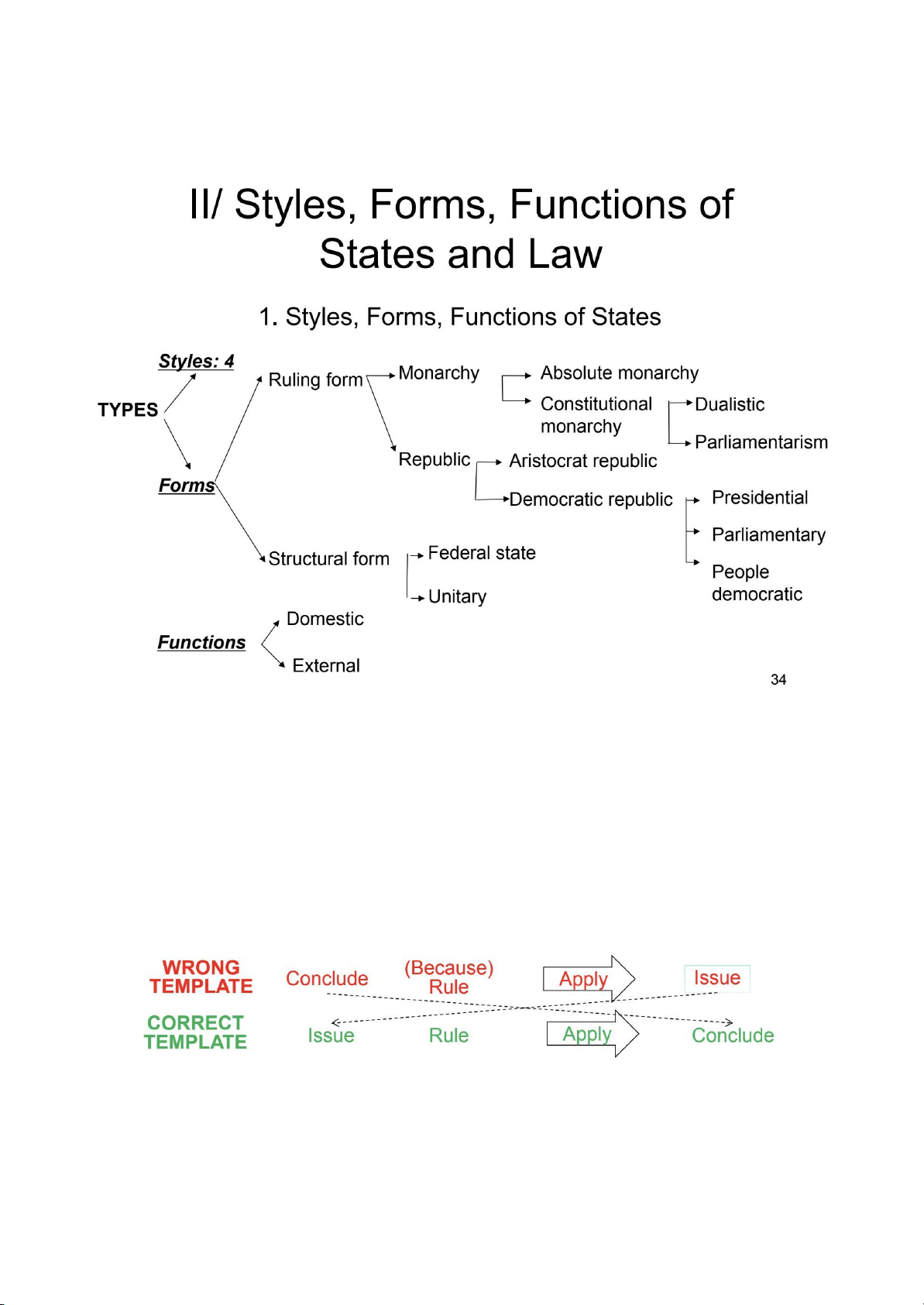
Session 3 : Styles, Forms and Functions of States 1. Style of States -
Denoting groups of states with the same class-conscious face (giai cấp xã hội) - Types :
+ Slave-possession style of states : chiếm hữu nô lệ
+ Feudal style of state : phong kiến
+ Capitalist style of states : Tư bản chủ nghĩa
+ Socialist style of states : xã hội chủ nghĩa 2. Forms of States : -
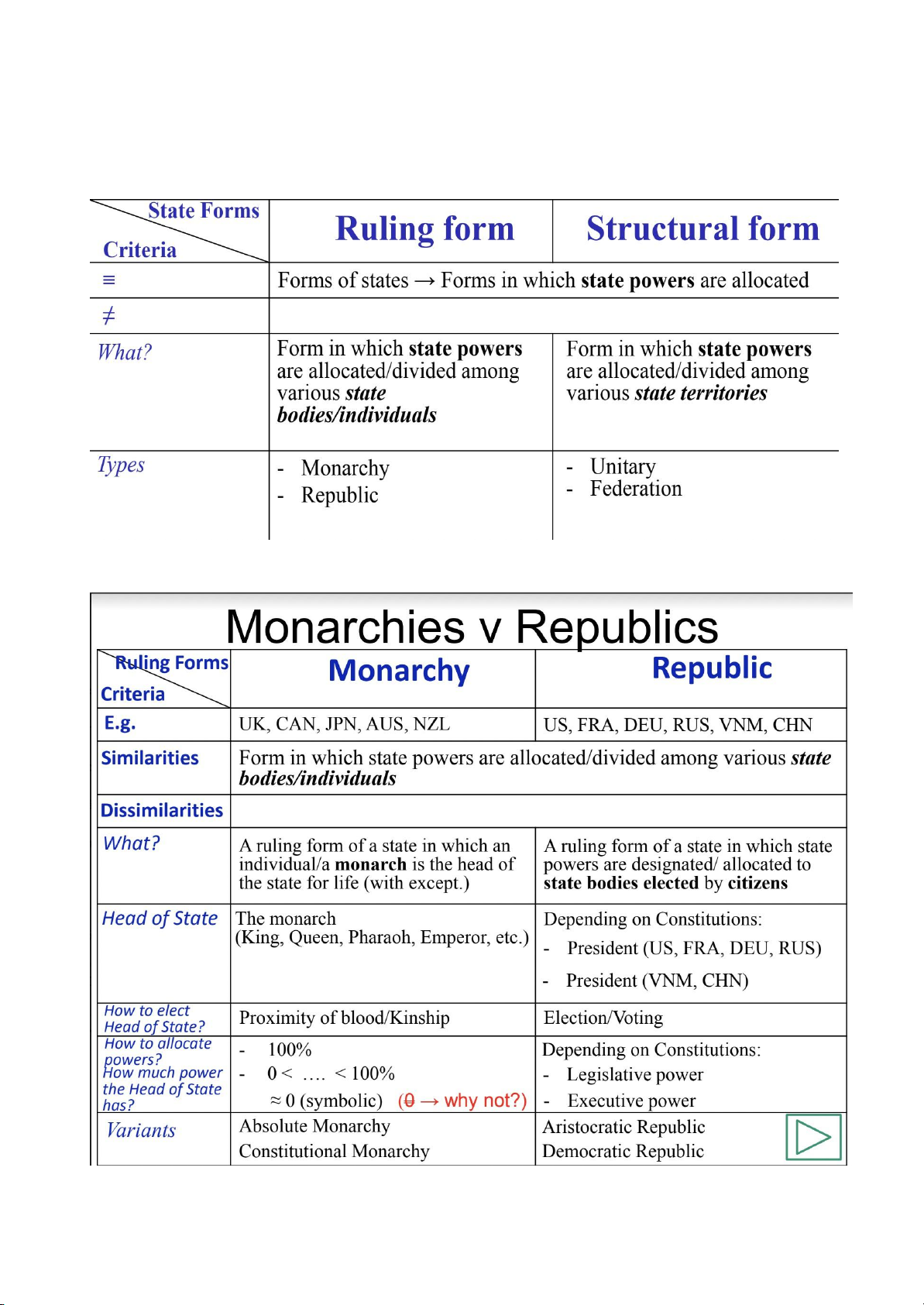
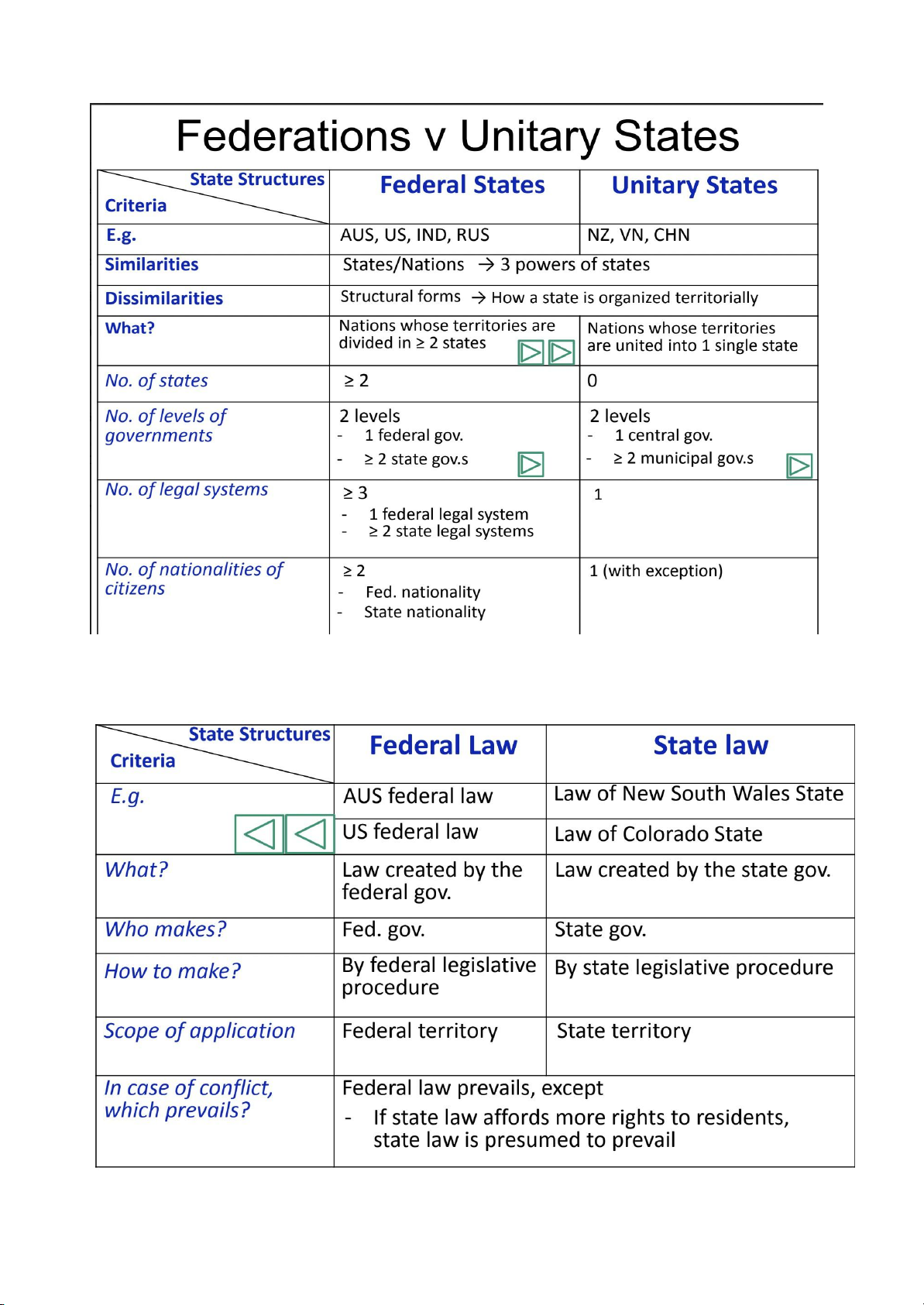
Forms in which states powers are al ocated/designated - Types – Ruling form – Structural form -
Nhà nước Quân chủ vs Chủ nghĩa : -
Nhà nước Liên bang và Thống nhất :
- Luật giữa Nhà nước Liên bang vs Nhà nước thống nhất : 3. Function of State :
● Internal Functions : Domestic (nội bộ)
● External Functions : External (đối ngoại) * CASE-SOLVING : IRAC model
– I (Issue): What is the issue/question?
– R (Rule): What is rule applicable to the issue/question?
– A (Application): Apply the Rule to the Issue
– C (Conclusion): Answer to the Issue/question?
Session 4 : Styles, Forms and Function of Law 1. Style of Laws : -
Denoting a group of laws of the same essence - 4 types :
+ Slave possession style of law (chủ nô)
+ Feudal style of law (phong kiến)
+ Capitalist style of law (tư bản)
+ Socialist style of Law (XHCN) -
Link between state styles and law styles :
+ The style of a state informs the style of its law
+ A state of a certain style has its law of the corresponding style 2. Forms of Law : -
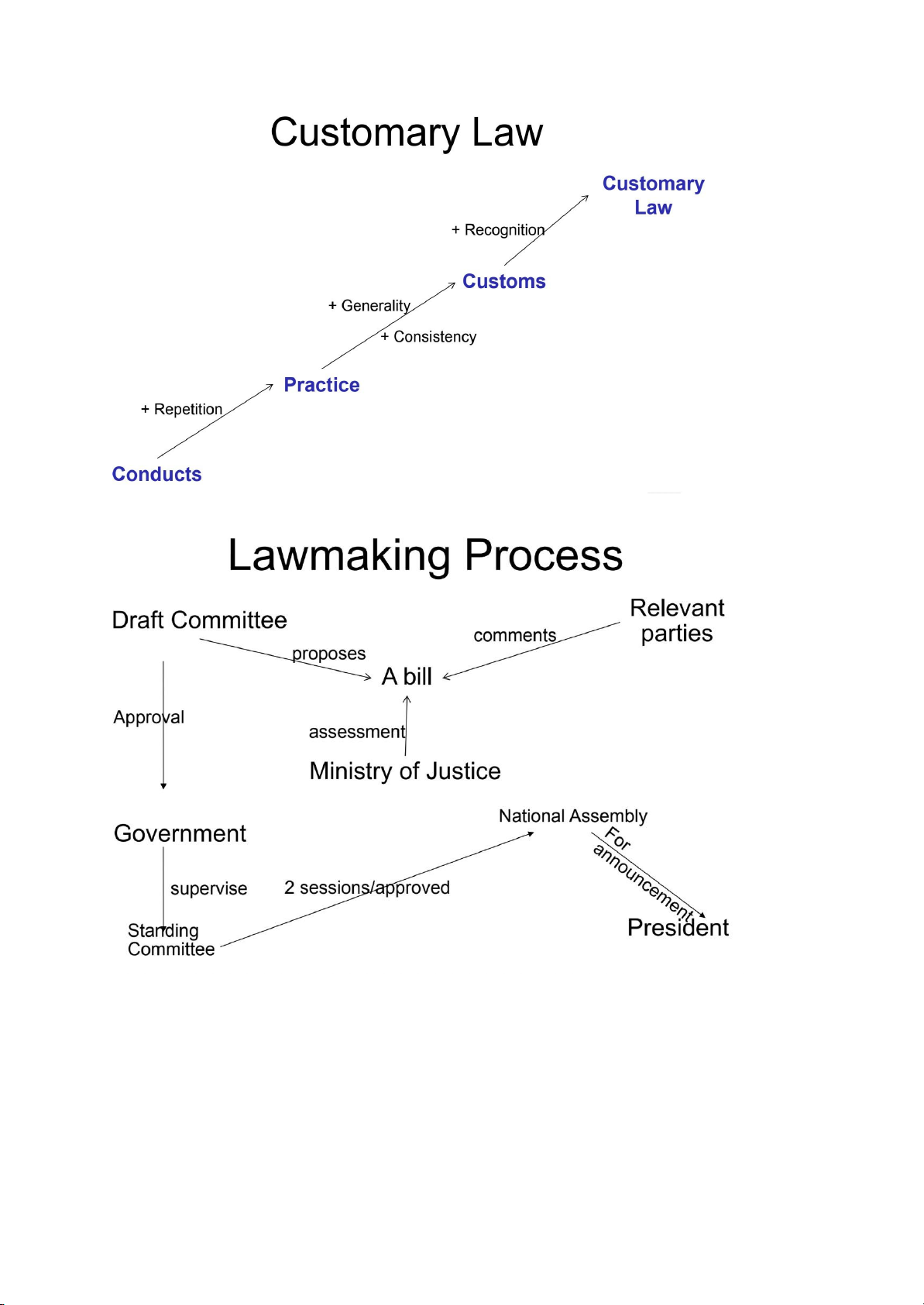
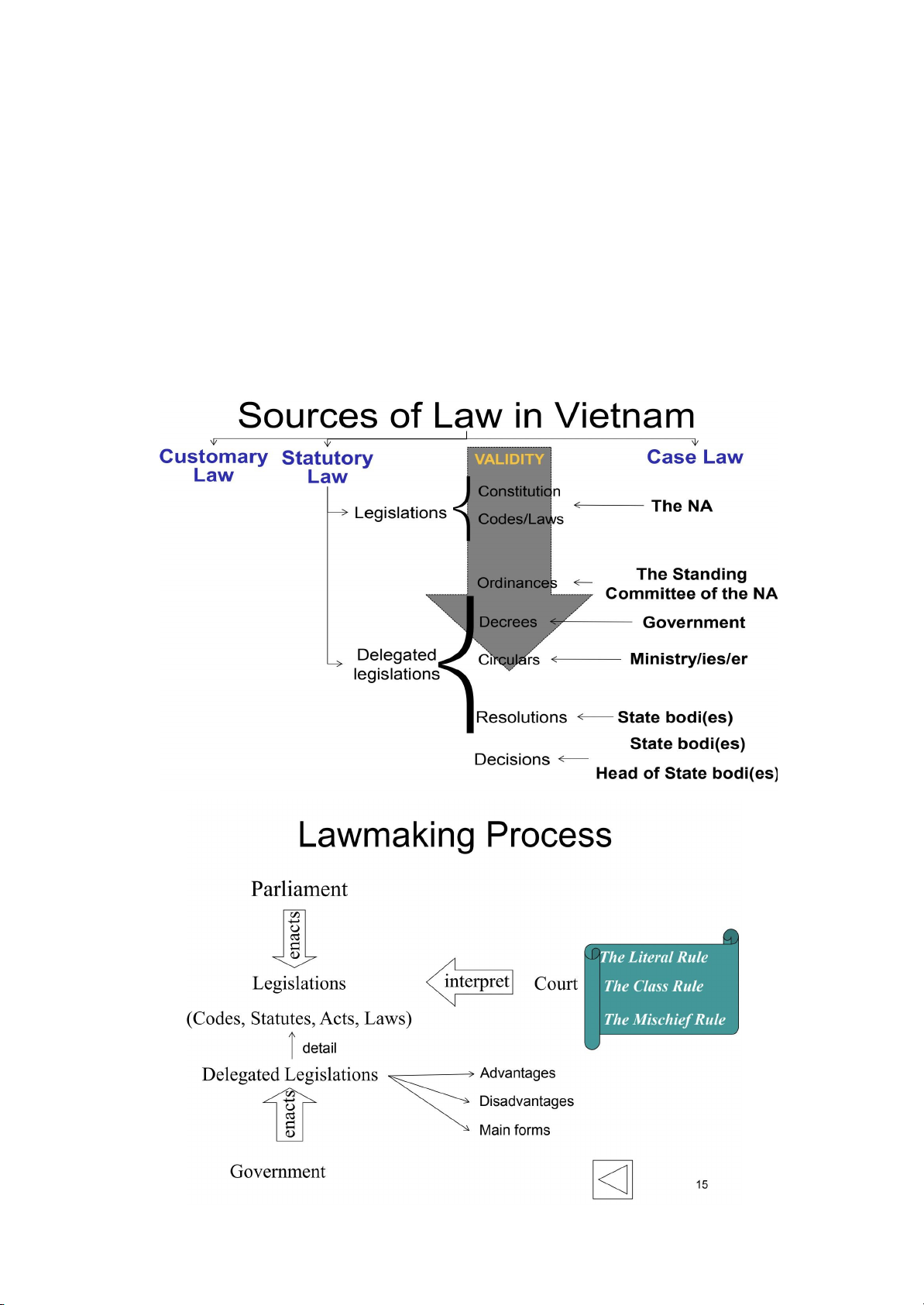
Answering the question of “Where to find the law” - So-cal ed “Source of law” - Types : + Customary law : luật tập quán/ tập quán pháp + Statutory law : luật thành văn/ văn bản quy phạm pháp luật + Case law : án lệ -
Customary law : Tập quán pháp -
Quy trình làm luật : Law Making Process * CASE LAW : -
Judicial Precedent : Principles of consistency
+ Similar cases should be decided similarly/in the same way
+ Consistency = important feature of a good decision-making process
● A court’s decision is expected to be consistent (or at least not unjustify inconsistent) with previous decisions
● To provide opinion which parties and other can use to direct their future relations
● to decide cases in accordance with existing rules
+ Exceptions : when the solutions offered by a precedent not just due to ● Passage of time ● Changing circumstances -
Stare decisis : “to stand by a decision”/ “let a decision stand” 3. Functions of law - Regulation : tính quy định -
Prediction : tính báo trước -
Stabilization : tính ổn định
Session 5&6 : State and Law in Vietnam
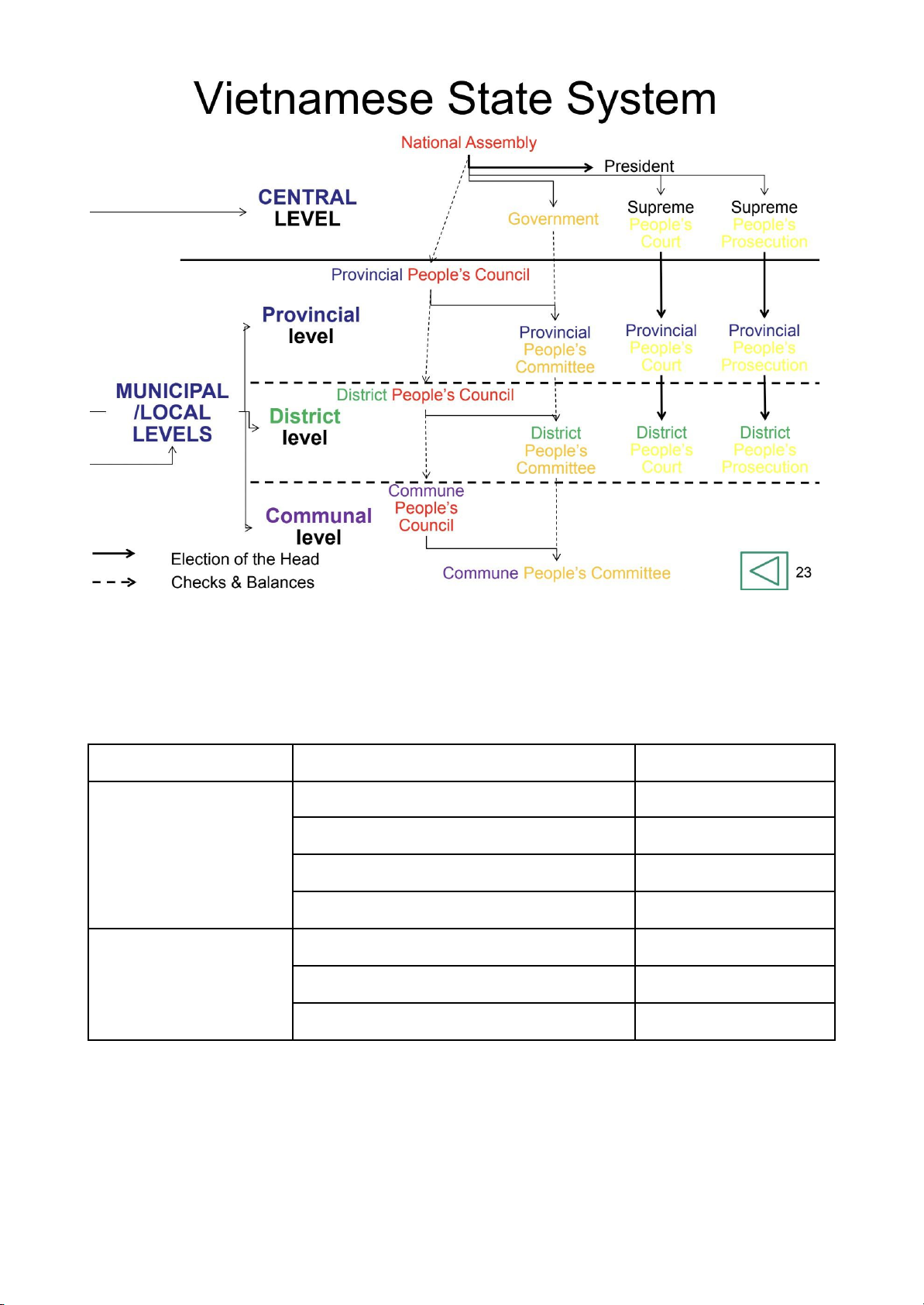
1. State in Vietnam : Style, Form and Function -
Vietnam : Socialist - Republic - Unitary State - Function : Internal + external Criteria Types VNM Style of State Slave possession style Feudal style Capitalist style Socialist style x Ruling form Monarchy Republic x Structural Form Unitary state x Federation 2. Law in Vietnam -
Vietnam : Socialist style - Form : Customary + Statutory + Case law -
Function : Regulation + Prediction + stabilization Criteria Types VNM Style of Law Slave possession style Feudal style Capitalist style Socialist style x Forms of Law Customary Law x Statutory Law x Case law x
* Statutory Law : Luật thành -
Legislation : văn bản luật ⇒ The National Assembly + Constitution : hiến pháp + Codes : bộ luật + Laws : luật
~ Unconstitution : vi hiến (vi phạm về hiến pháp) ⇒ vô hiệu -
Delegated legislation : văn bản dưới luật
+ Ordinance : pháp lệnh/lệnh ⇒ the Standing Committee of the NA (ban thường vụ quốc hội)
+ Decrees : nghị định ⇒ The government (Chính phủ)
+ Circulars : thông tư ⇒ Ministry/ies (Bộ/ban ngành)
+ Resolutions : nghị quyết ⇒ State bodies (Cơ quan nhà nước)
+ Decisions : quyết định ⇒ Head of the State bodies/ State bodies. (Cá nhân/tổ chức) E.g :
● Constitution of Vietnam 2013 : Luật hiến pháp Việt Nam 2013
● Civil Code of Vietnam 2015 : Luật dân sự Việt Nam 2015
● Law on Enterprises 2020 : Luật doanh nghiệp 2020
● Ordinance No.02/2020/UBTVQH14 : Pháp lệnh số No.02/2020/UBTVQH14
● Decree No. 92/2021/ND-CP : Nghị định No. 92/2021/ND-CP
● Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC : Thông tư 78/2021/TT-BTC (thông tư bộ tài chính)
● Resolution 68/NQ-CP : Nghị quyết 68/NQ-CP (nghị quyết chính phủ)
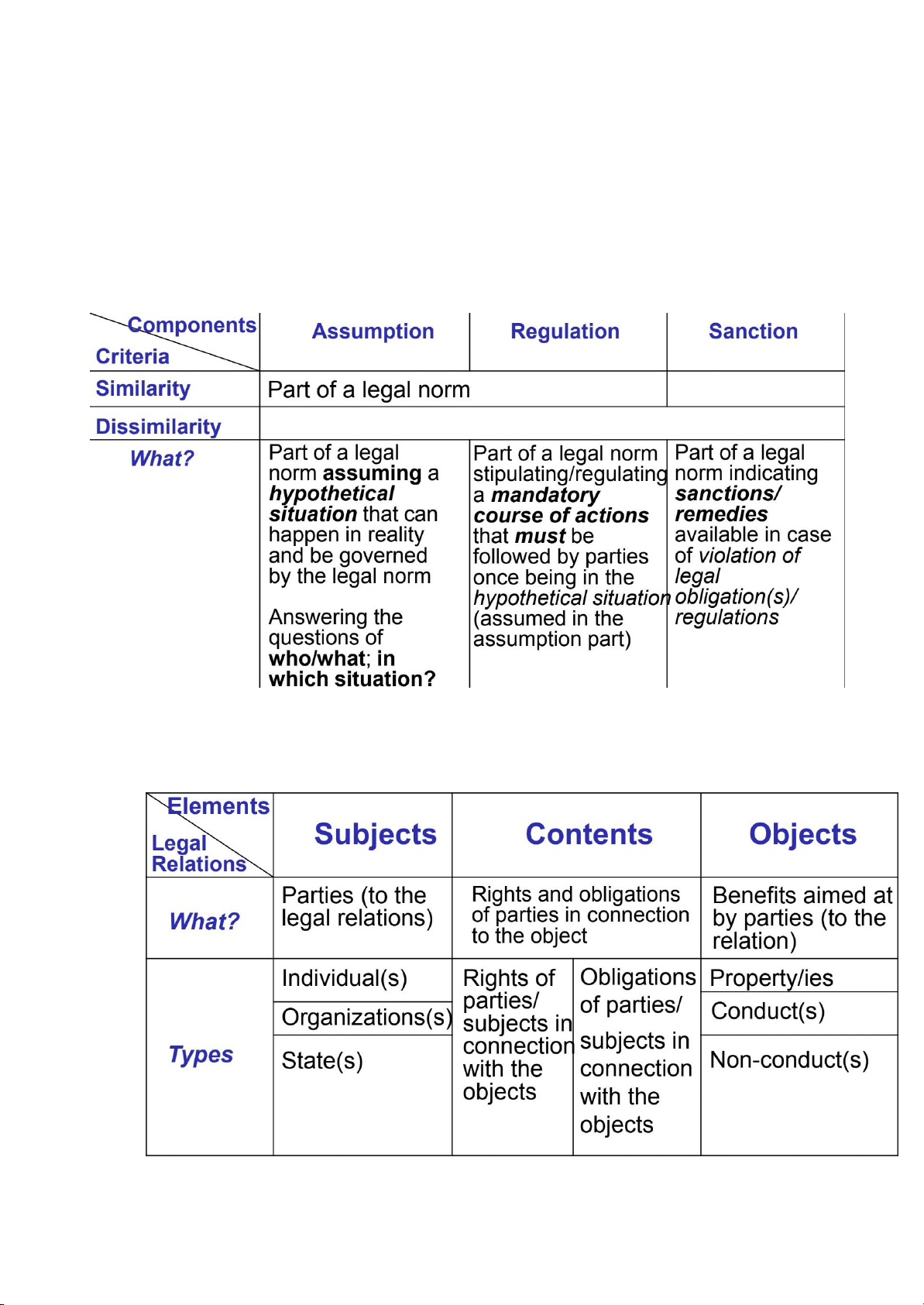
3. Legal norms (Quy phạm pháp luật) -
Smal est component/unit of legal system : đơn vị nhỏ nhất của hệ thống pháp luật -
Stated in the legislation : được công bố trong hiến pháp - Include :
+ Assumption : Giả định ⇒ ai/cái gì
+ Regulation : Quy định ⇒ theo luật
+ Sanction : Chế tài ⇒ hình phạt khi vi phạm pháp luật/regulation
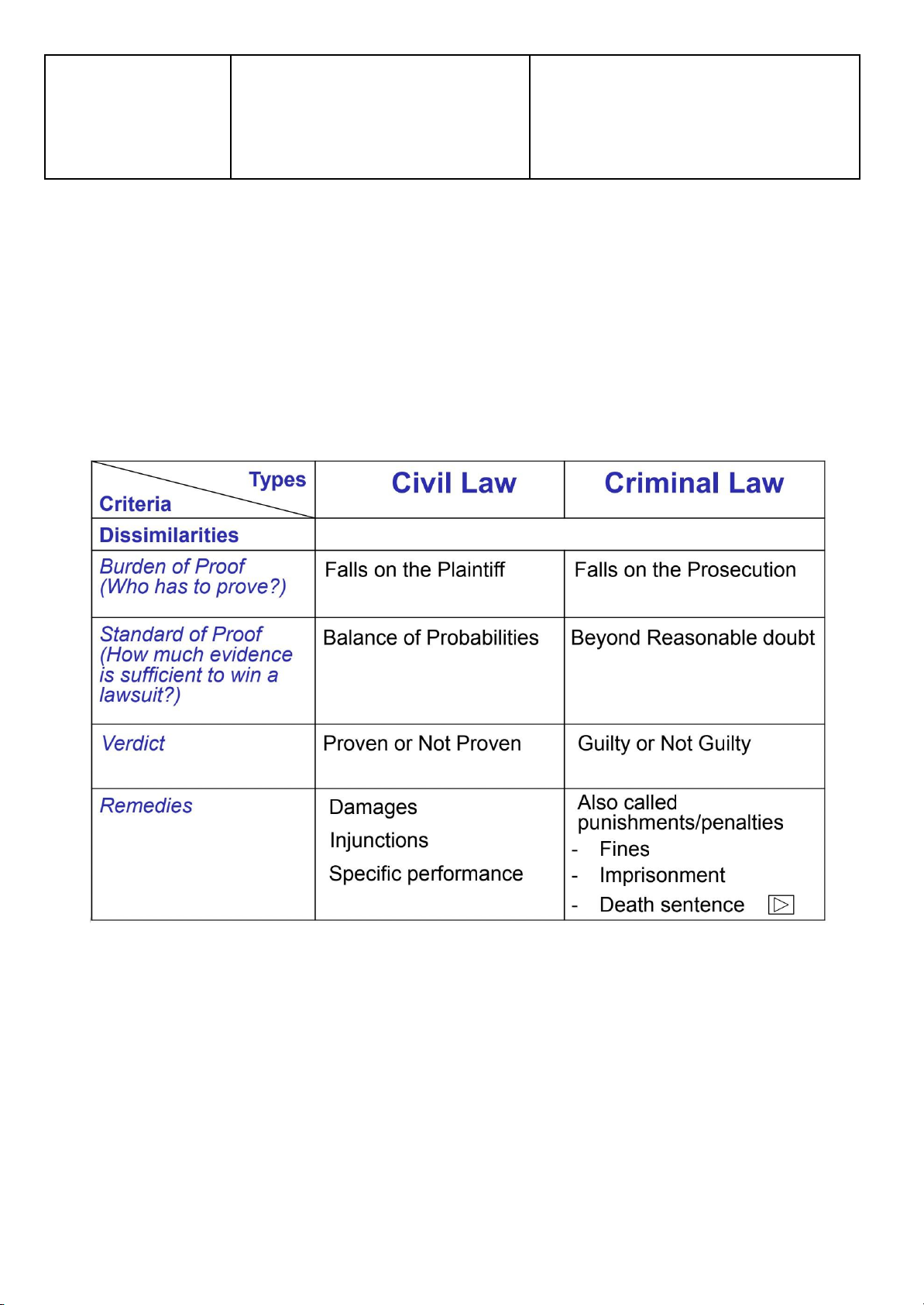
● Civil : Damages (if cause damage) + Restitution
● Criminals : Fines + imprisonment (limited/ unlimited) + death sentence
~ Phân biệt bằng assumption : Re ⇒ assumption ko sai, sanction ⇒ assumption sai * Shal = must
4. Legal Events (Sự kiện pháp lý) -
Social relations : friendship, courtship/mateship, kinship, col eagues… -
Legal relations have 3 elements : Subject (chủ thể), Content (nội dung), Object (khách thể) -
Subject : parties (to the legal relations) ⇒ 3 types : individual + organization + state -
Contents : rights and obligations of parties in connection to the object ⇒ 2 types : rights of
parties/ subjects in connection with the objects + obligations of parties/ subjects in connection with the objects -
Object (khách thể) : benefits aimed at by parties (to the relation) ⇒ 3 types : property + conduct + non-conduct E.g of legal events : Social relation How to establish how to modify How to terminate marital relations Marriage registration domestic divorce/death arrangements labor relations labor contract labor contract labor contract termination/ conclusion amendment death / bankruptcy / dissolution sales of goods entering into contract modification contract fulfil ment/ contracts contracts/ contractual termination conclusion -
Events of which the happening with legal relation (quan hệ pháp lý)
+ Establish and/or : bắt đầu + Modify and/or : thay đổi
+ Terminate legal relations : chấm dứt - Types :
+ Based on legal consequences : Dựa vào hệ quả pháp lý
● Legal events establishing legal relations
● Legal events modifying legal relations
● Legal events terminating legal relations
+ Based on the way in which a legal event occurs :
● Legal incidents : Legal events happening beyond intentions of parties to/subjects of legal relations
● Legal actions : Legal events happening on purpose of parties to/subjects of legal relations
● Other legal events : eg. Court decision. Session 7 : Types of Law I. Types of Law -
National Law and International Law : Luật quốc gia vs Luật quốc tế -
Substantive law and procedural law : Luật thực chứng - Public law and private law - Criminal vs Civil Law
1. National v. International Law National Law International Law Similarities
Law ⇒ definition of Law applies Dissimilarities - Name Domestic Law Law of the Nation Municipal Law - Makers Every single state >2 States
(National law ⇒ nation ⇒ state) (International law ~ International ~ Inter-national ~ among nation ~ among state - E.g National Law of Vietnam International Trade Law National Law of the US International Financial Law National Law of the UK International Investment Law National Law of Canada International Health Law National Law of AUS International Environment Law - Spatial scope of Within state territory Among states application
Exception : extra-territoriality - International Law : ● Inter-national law ● Inter- (prefix): between/among - Inter-continental - Inter-regional - Inter-action - Inter-national - Inter-link - Inter-net
2. Substantive v. Procedural Law : Luật nội dung v. Luật hình thức Types / Substantive law Procedural law Criteria Similarities
Law -> definition of Law applies Dissimilarities Subject-matters / Create, define and regulate:
Define the procedures/methods by contents - (Legal) rights and
which to obtain a remedy in a count - (Legal) obligations Example Law of sale contracts Rules of dispute settlement
(defining the right and obligations (eg: means of DS) of the buyer and the sel er)
“Where a sel er delivers property Statutory Limitations
in a quantity which is more than that agreed, the purchaser has
“The time-limit within which a request
the right to accept or not to accept may be made to a court to declare a the excess
civil transaction invalid (...) shal be -> Right of the buyer two years (...).
“A purchaser must pay ful price at Jurisdiction of Courts the agreed place and time” -> obligation of the buyer
3. Public law v. Private law : Types / Public law Private law Criteria Similarities
Law -> Definition of Law applies Dissimilarities Subject-matters / Regulation the organization of Regulating the relations among contents
government & with its relations persons and organizations Subjects / Parties - Public actors/STATE - Private actors to relations
- (private actors) (if relevant)
- State - Public actor (if relevant)
Public < — > public/private
Private < — > public/private Actor actor Actor actor Example - Constitutional law - Civil law - Administrative law - Commercial law - Criminal law - Family law - Property law - Law of succession - Labor law - Etc.
4. Civil law and Criminal Law Types / Civil law Criminal law Criteria Similarities
Law -> definition of Law applies Dissimilarities Subject-matters / Controls the actions between
Crime is an offence against the contents individuals and or business
society even though only one person organizations may suffer Aim Compensate a person who has Punish the criminal and suffered a loss by money is paid to the state, receiving money. This is not the victim known as damages Disputants At first-instance courts:
Prosecution/Prosecutor (công tố viên) - Plaintiff Accused (bị cáo) - Defendant/ Respondent - Cross - plaintiff (nguyên đơn chéo) - Cross - defendant (bị đơn chéo) At appeal courts: - Appel ant - Appel ee
- Legal Names of Disputing Parties : + Claimant : Nguyên đơn
● Who? the person who complains or brings an action asking the court for relief
● Also cal ed ‘the plaintiff’ + Defendant : Bị đơn
● Who? the person against whom a civil action is brought or who is
prosecuted for a criminal offence
● Also cal ed “respondent”
Exercise : Which of the above cases fal into ? Case Public Private Substantive Procedural Civil Criminal Law Law Law Law Law Law A claim for non- x x x payment of a debt worth $5000 A claim for personal x x injury from a motor accident for approximately $130 000 A dispute between a x x x citizen and the federal tax commissioner A constitutional x x x dispute between states in Australia A murder charge x x x Parties negotiate to x x x settle their disputes A court dismisses a x x x case for the lack of jurisdiction
Topic 2 : Civil Law in Vietnam
Session 8 : Overview of Civil Law in Vietnam
I. Objects of Regulation of Civil Law (Đối tượng điều chỉnh của quy định dân sự) Civil Relations (Art. 4.1) -
What? (Art. 1) RELATIONS established on the BASIS of ● Equality ● Freedom of wil ● Independence of property ● Self-responsibility - E.g. ● Civil Relations :
● Marriage and Family Relations : Hôn nhân gia đình
● Business and Trade Relations :
● Labour Relations : quan hệ lao động
● Inherent Relations : quan hệ thừa kế - Types of civil relations
● Property relations : Quan hệ tài sản
● Person (identity) relations : quan hệ nhân thân
* juridical person : pháp nhân (tổ chức/vật có quyền và nghĩa vụ với pháp luật)
Personal Identity Relation : further readings in page 25-39
Các giá trị nhân thân : (Không chuyển giao được)
Article 30. Right to declaration of birth and death : Quyền khai sinh và khai tử
Article 31. Right to nationality : Quốc tịch
Article 32. Rights of an individual with respect to his/her image : Quyền cá nhân với hình ảnh của mình
Article 33. Right to life, right to safety of life, health and body : Quyền được sống, được bảo vệ
Article 34. Right to protection of honor, dignity and prestige : Quyền được bảo vệ
danh dự, phẩm giá và uy tín
Article 35. Right to donate or receive human tissues and body organs and donate
corpses : Quyền được hiến và nhận bộ phận cơ thể, nội tạng và tử thi.
Article 36. Right to re-determine gender identity : Quyền tái xác định giới tính I . Methodology
• Equality : quyền bình đẳng
• Freedom of wil : quyền tự do ý chí
• Independence of property : Tự lập về tài sản
• Self-responsibility : Tự chịu trách nhiệm
I I. Principles : (Nguyên tắc) ● Principle of Equality
● Principle of Freedom and Voluntariness
● Principle of Goodwil and Honesty
● Principle of Non-violation of Interests (of the Nation, the Public and of other persons)
● Principle of Self-Liability (Art. 3, Civil Code 2015)
Tự do (Freedom) : thoát khỏi nguyên tắc của nhà nước
Tự nguyện (volunteer) : thoát khỏi nguyên tắc của mọi bên thứ 3 - Self-liability ● Liability - So cal ed “responsibility”
- HOW is (dis)similar to/from obligation?
- WHEN is it arising?/Being liable/responsible for what? ● Civil liability
- WHAT are types of civil : liability/responsibility/remedies in civil law? ● Specific performance ● Damages/Liquidated damages ● Cancel ation ● Restitution ● Injunction IV. Definition :
Civil law is a separate law branch in the Vietnam law system, a set of rules regulating
property relations and personal identity relations on the basis of equality, freedom of wil ,
independence of property and self- responsibility. → Objects of regulation → Types of civil relations → Methodology of civil law
V. Sources of Civil Law in Vietnam ● Customary Law ● Statutory Law - Legislations ● Constitution year of 2013 ● Civil Code year of 2015 ● Other laws - Delegated legislations ● Case Law
VI. Civil Code of Vietnam 2015 - 689 Articles - 6 Parts : – General Provisions
– Ownership Rights and Other Property-Related Rights – Obligations and Contracts – Inheritance
– Civil Relations Involving Foreign Elements