







Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 40749825 Formal-english-Effectiveness
Advanced Grammar (Đại học Khoa học Xã hội và Nhân văn, Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh) lOMoAR cPSD| 40749825 Formal Informal language
- Wri 琀琀 en language
- Spoken language (dialect + accent)
- No contrac 琀椀 on (Không dùng thể rút gọn của từ) + don’t -> do not
+ I’d like -> I would like + I can’t -> I cannot
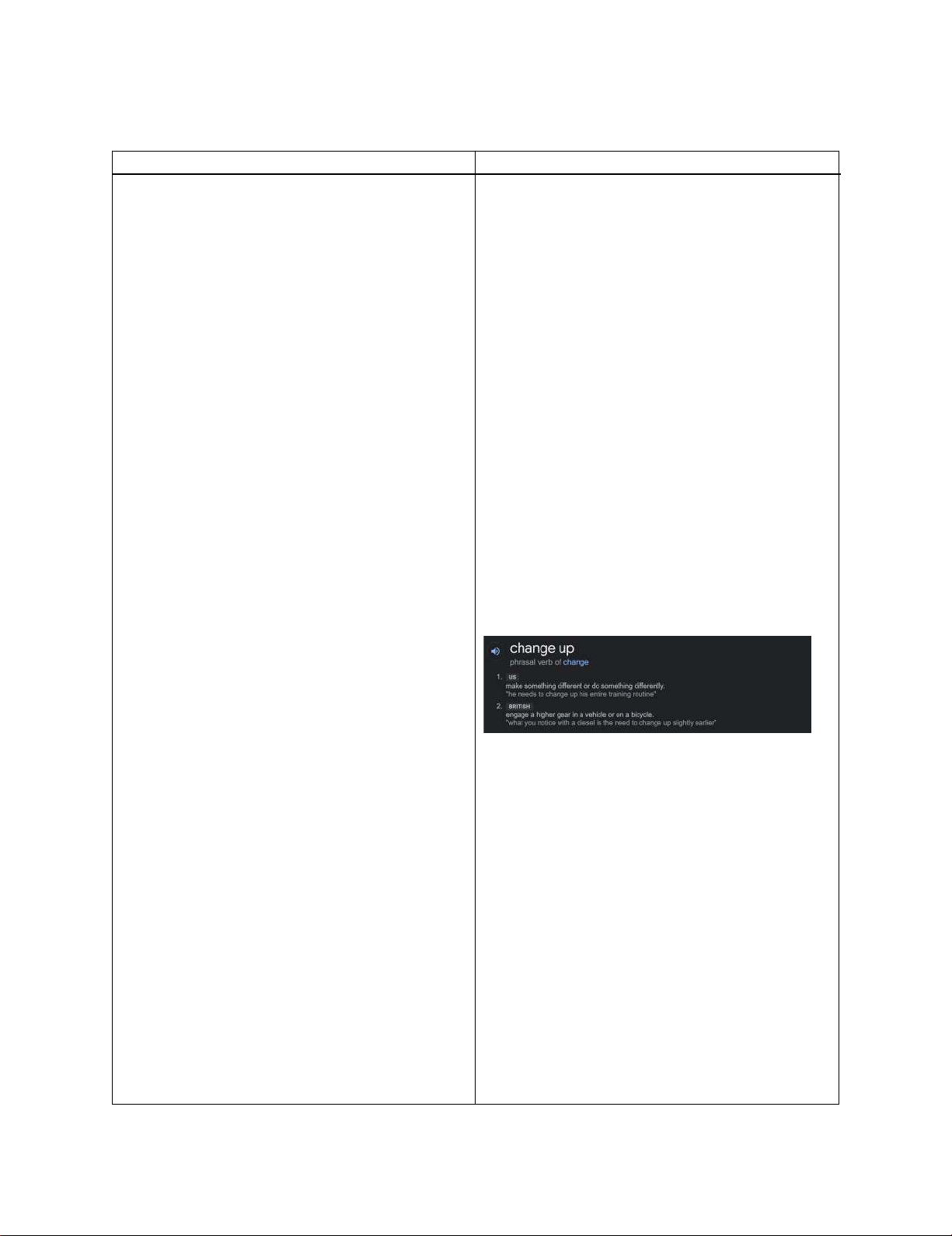
- Phrasal verbs (stylis 琀椀 cs)
- Academic/ one-word verbs
(Take in, mull over, take up, bring up, bring take in forth, etc.)
+ = understand = perceive = receive knowledge
Ex: The students bring up many topics in + = absorb class. + = digest
-> The students raise/ invoke many topics in class mull over
The teachers bring a chair up to eye level.
+ = contemplate = ruminate = muse
-> The teacher elevates a chair to eye level. bring up
+ imprecision in expression (meanings, + hint at = raise the issue colloquialism) + raise somebody bring forth + provide = supply
- Use gerund/ verbal nouns when possible - Proverbs and Idioms *Emphasis: ac 琀椀 on with 昀氀 ying colors
Ex: I play football quite o 昀琀 en with my friends rain cats and dogs
-> Playing football is my habit with friends. + colloquialism
-> the government enforces a bill. Idioma 琀椀 c language
-> the enforcing of a bill by the government /
allows students to wear uniform.
- Slangs (NOT FOR IELTS) - Academic words list Ex: ain’t = do not gonna = going to lOMoAR cPSD| 40749825 - Voice
+ passive should be used selec 琀
椀 vely *Emphasis: - ac 琀椀 on - receiver - unknown actor
Ex: Pollu 琀椀 on cannot be alleviated without stringent measures. My purse was stolen.
+ Ac 琀椀 ve should commonly be used *Emphasis: - ac 琀椀 on - actor
- First/second-person pronouns (I, you, we, us)
- Third-person pronouns (he, she, it, + biased
they) + impar 琀椀 ality
+ subjec 琀椀 ve
+ objec 琀椀 vity
Ex: You would have to spend numerous
hours on rec 琀椀 fying silly wri 琀椀 ng
Ex: Receiving a proper educa 琀椀 on
mistakes because you do not receive a
in formal wri 琀椀 ng prevents/ avoid
proper educa 琀椀 on in formal wri 琀椀
time wastage on rec 琀椀 fying regre 琀 ng.
琀 able mistakes in wri 琀琀 en
composi 琀椀 on. Line of thinking: + subjec 琀椀 ve language
+ emo 琀椀 ve/ absolute/ generalizing language Line of thinking:
Ex: All students => the majority of students + objec 琀椀 ve language + lacking evidence. + eviden 琀椀 ary Ex: + Reasoning
Extremely smart => rela 琀椀 vely
intelligent Totally disappointed => thoroughly/ deeply disappointed
completely corrupted => signi 昀 椀 cantly corrupted
Ex: Students must all wear the same
Ex: Students must all wear uniform, so they
types of clothing at school, so they will
will feel a sense of belonging/ community.
not feel hatred towards one another. lOMoAR cPSD| 40749825
II. E 昀昀 ec 琀椀 veness in wri 琀椀 ng: 1. Consistency:
+ Tone (Formal vs informal)
EX: I will punch you very hard, but physical assault will incur inevitable punishment by laws.
-> I will punch you very hard… => My inten 琀椀 on is to physically in 昀氀
ict severe pain on your body, but …
+ Voice (Ac 琀椀 ve vs passive)
Ex: The government had to develop a con 琀椀 ngency (n) plan for
the Covid-19 pandemic, yet the situa 琀椀 on cannot be improved due
to many people’s lack of social responsibility.
-> Con 琀椀 ngency plan for the Covid-19 pandemic had been
developed by the government, yet the situa 琀椀 on
-> The government had to develop a con 琀椀 ngency (n) plan for the
Covid-19 pandemic, yet the authori 琀椀 es cannot improve the situa 琀
椀 on due to many people’s lack of social responsibility.
+ mood (if you write a statement, please never write it along ques 琀椀
on, an order, a hypothesis, or a condi 琀椀 on).
Ex: The medical care for elderly should receive more funding; however,
is it s 琀椀 ll possible to so do? lOMoAR cPSD| 40749825
2. Do not overuse coordinator, subordinator,
conjunc 琀椀 ves, transi 琀椀 on signals. Ex”
=> When students enroll into courses at university, they believe that teachers have the sole
responsibility for their learning; nevertheless, many
educa 琀椀 onal experts disagree adamantly for two
reasons: the 昀 椀 rst being the risks behind
students’ overreliance on teachers, and the second being
students’ lack of engagement with knowledge.
When students enroll into courses at
university, they believe that teachers have the
sole responsibility for their learning. However,
many educa 琀椀 onal experts disagree
adamantly for two reasons: the risks behind
students’ overreliance on teachers and the
students’ lack of engagement with knowledge.
=> When students enroll into courses At
university, students believe that teachers have
the sole responsibility for their learning;
nevertheless, many educa 琀椀 onal experts
disagree adamantly (=vehemently= completely)
because of …. and … for two reasons: the 昀椀
rst being…, and the second being …. lOMoAR cPSD| 40749825
=> Many educa 琀椀 onal experts are adamantly
against university students' beliefs of teachers’ sole
responsibility for their learning is disagreed by many
educa 琀椀 onal experts due to 2 reasons: … and …
Be careful of misusing conjunc 琀椀 ons =>
incoherent. My house is very beau 琀椀 ful. My lovely abode
has three giant bathrooms and 2 wonderful
bedrooms (1). Therefore, many people love to visit
(2) my beau 琀椀 ful house. Moreover, my house
can also become a tranquil place for many
visitors. Those people love to be in a nice and
cozy accommoda 琀椀 on upon their short visit s.
(1) beau 琀椀 ful house because of bathrooms and bedrooms
(2) bathrooms + bedrooms => people love to visit (WHY??)
(3) Tranquil home (why beau 琀椀 ful house -> tranquil home???) Fall under the purview of lOMoAR cPSD| 40749825
3. Avoid clumping transi 琀椀 on signals, conjunc 琀椀 ve,
preposi 琀椀 onal phrase at the beginning of sentences:
Ex: First of all, in 1996, unfortunately, many labor
workers were sacked due to the economic crisis.
-> First of all, many labor workers were
unfortunately sacked due to the economic crisis in 1996.
4. Always try to maintain parallel structures
*** MUST use correla 琀椀 ves:
- not only … but also/ either … or/
whether… or/ neither… nor/ both … and.
5. Only use Dummy subject when necessary (it is/ there is)
**Only use Dummy subject to create emphasis in the
concluding statement (câu kết đoạn) and in the
evalua 琀椀 ve statement a 昀琀 er providing evidence.
6. Only use Passive voice when necessary. lOMoAR cPSD| 40749825
7. “as” is not good because it could mean “because” and “while”
8. “is when” and “is where” should not be used to give de 昀椀 ni 琀椀 on
Ex: A person becomes a good student is when he learns a lot.
-> A person becomes a good student because he learns a lot
9. Always complete comparison.
Ex: Developing countries struggle to achieve higher
GDP every year. Developed na 琀椀 ons, on the
other hand, have more resource to acquire high GDP.
-> Developing countries struggle to achieve higher GDP
than the previous period every year. Developed na 琀椀
ons, on the other hand, have more resource than
aforemen 琀椀 oned countries to acquire high GDP.
10. Always complete intensi 昀椀 er (so, such, too) -
(so …. That, such … that, too… to .
Ex: (Spoken) I am so 琀椀 red
(Wri 琀琀 en) I am so 琀椀 red that I fall asleep immediately.
(Wri 琀琀 en) I am too 琀椀 red to speak.
11. Reference of pronouns (including rela 琀椀 ve pronouns) must be clear.
I have to go to (preposi 琀椀 on) school and to do homework. lOMoAR cPSD| 40749825
12. Always try to reduce number of
clauses in one sentence to achieve clarity.
Students believe that they are not very academically driven
because they think that they are not smart enough.
-> Students believe that they are not very academically
driven due to/ because of their inferior intelligence.
-> Students believe that their lack of academic mo 琀
椀 va 琀椀 on stems from their inferior intelligence. Because = due to/ because of
by (the means of) = via = through Despite + N/ n phrase
Ex: Despite students’ tremendous/ immense e 昀昀 ort
to study for the university entrance exam, many of
them s 琀椀 ll face the reality of failure.
Even with immense e 昀昀 ort to study for the university
entrance exam, any of them s 琀椀 ll face the reality of failure.
With the looming prospect of a recession, many
households which belong to the middleclass face a
reality of cu 琀 ng back on many simple pleasures
including dining out regularly.
With the looming prospect of a recession, many
middle-class households must cut back on their budget
for many simple pleasures, such as dining out regularly One-sentence argument





