Preview text:
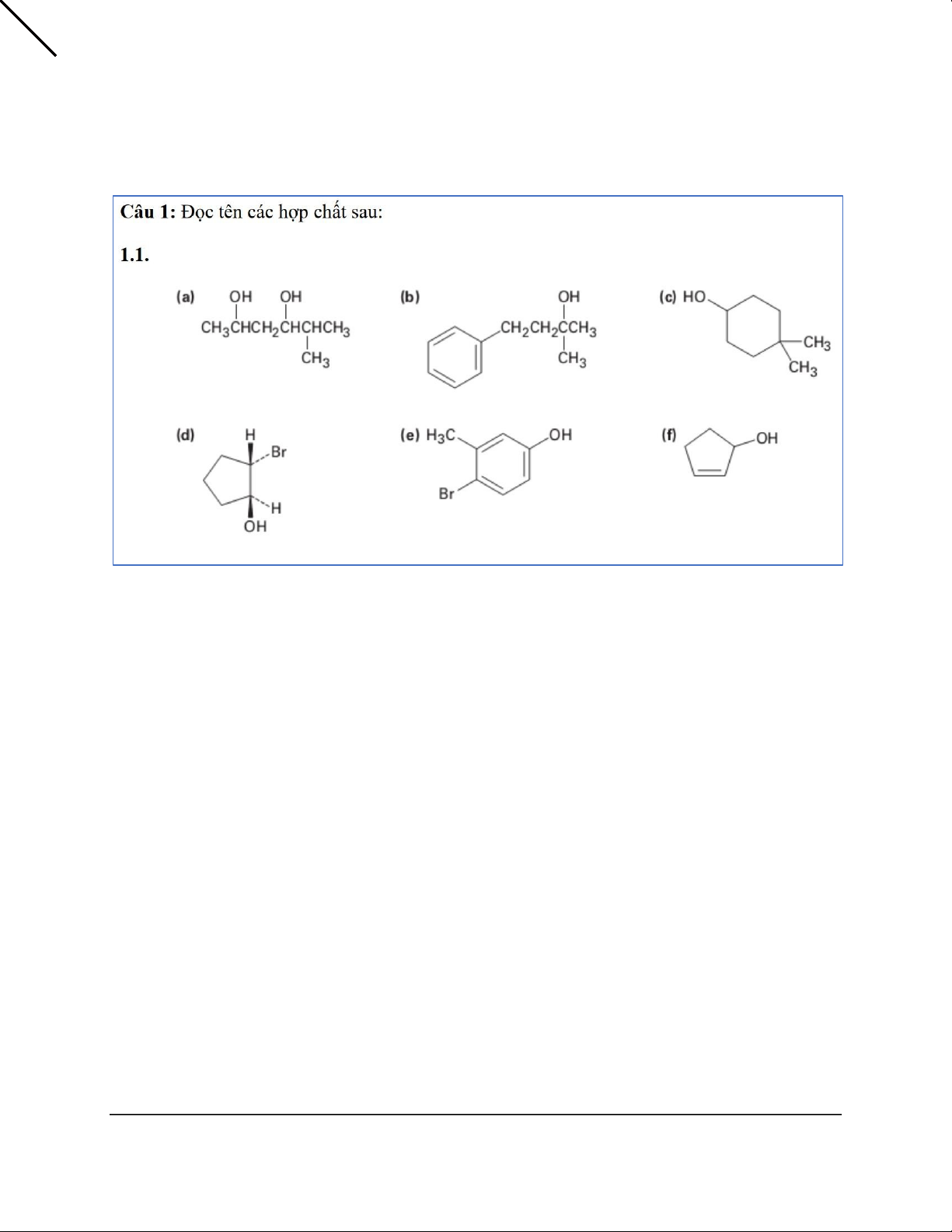
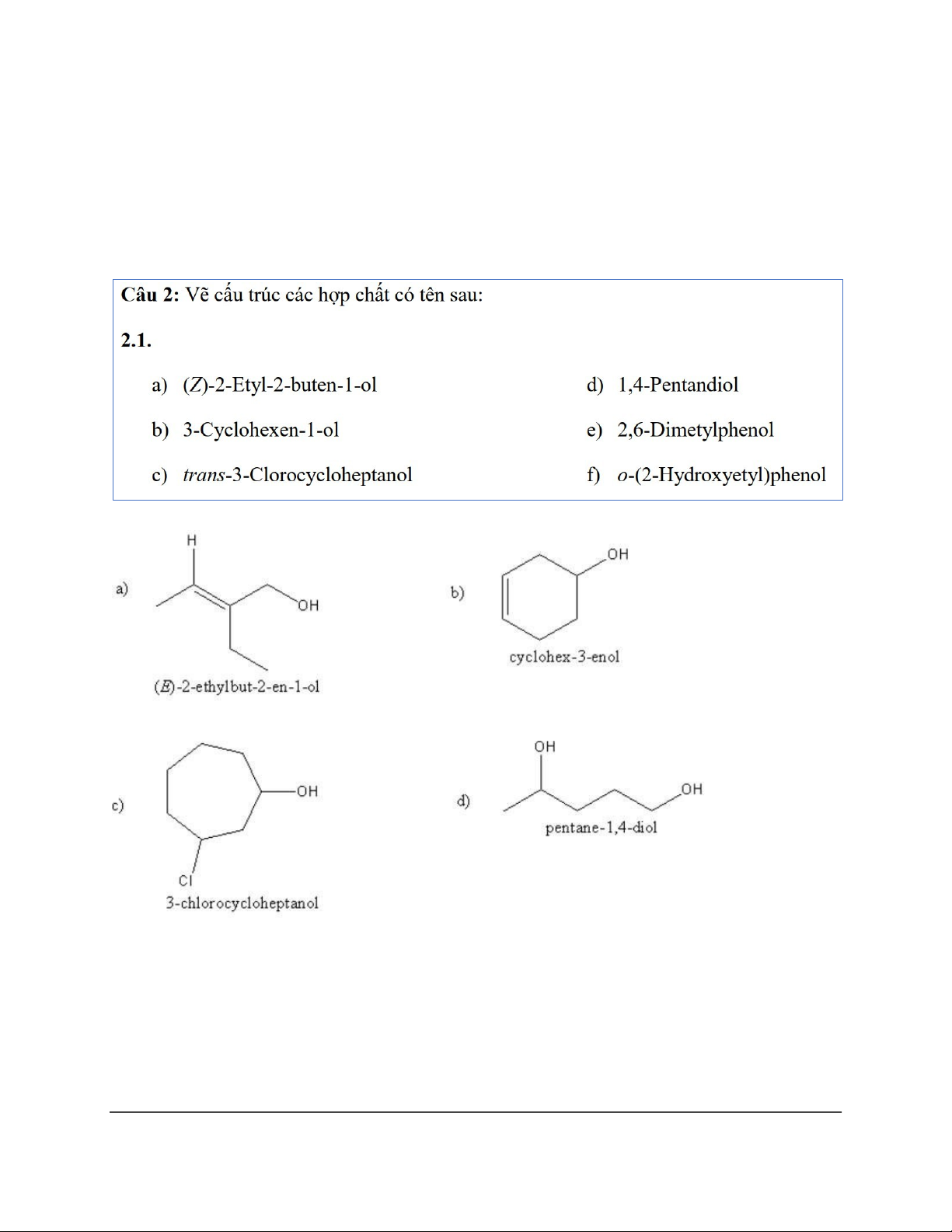
Chương 17 + 18 + 19: Dạng 1: Danh pháp a) 5-Methylhexan-2,4-diol
b) 2-Methyl-4-phenyl-butan-2-ol c) 4,4-Dimethylcyclohexanol
d) (1S,2S)-2-Bromocyclopentanol e) 4-Bromo-3-methylphenol f) Cyclopent-2-ene-1-ol 1 a) 2-Methyl-1,4-diol b) 3-Ethylhexan-2-ol
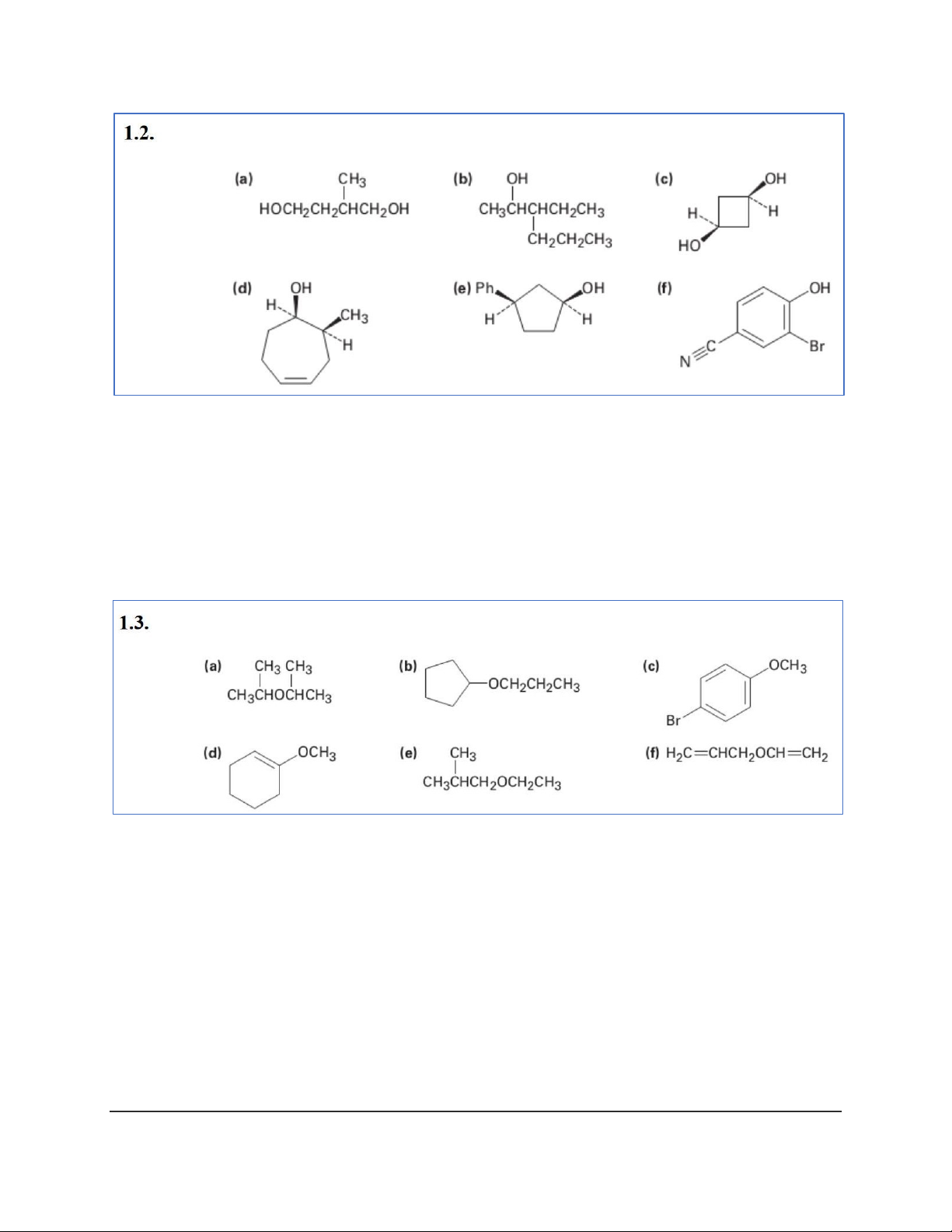
c) cis-Cyclobutan-1,3-diol
d) (1R,2S)-2-Methylcyclohept-4-ene-1-ol
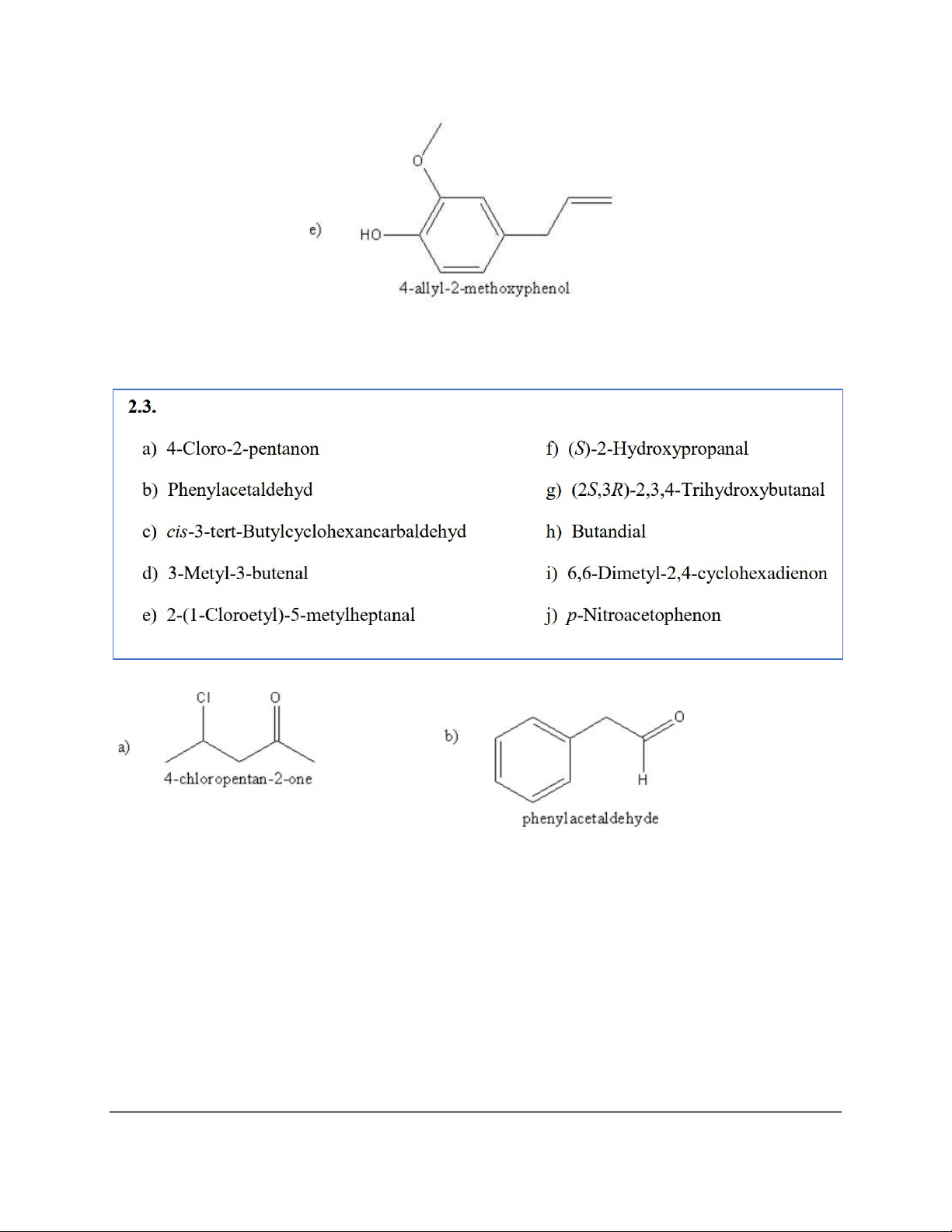
e) (1S,3R)-3-Phenylcyclopentanol f) 2-Bromo-4-cyanophenol a) Diisopropyl ether b) Cyclopentyl propyl ether
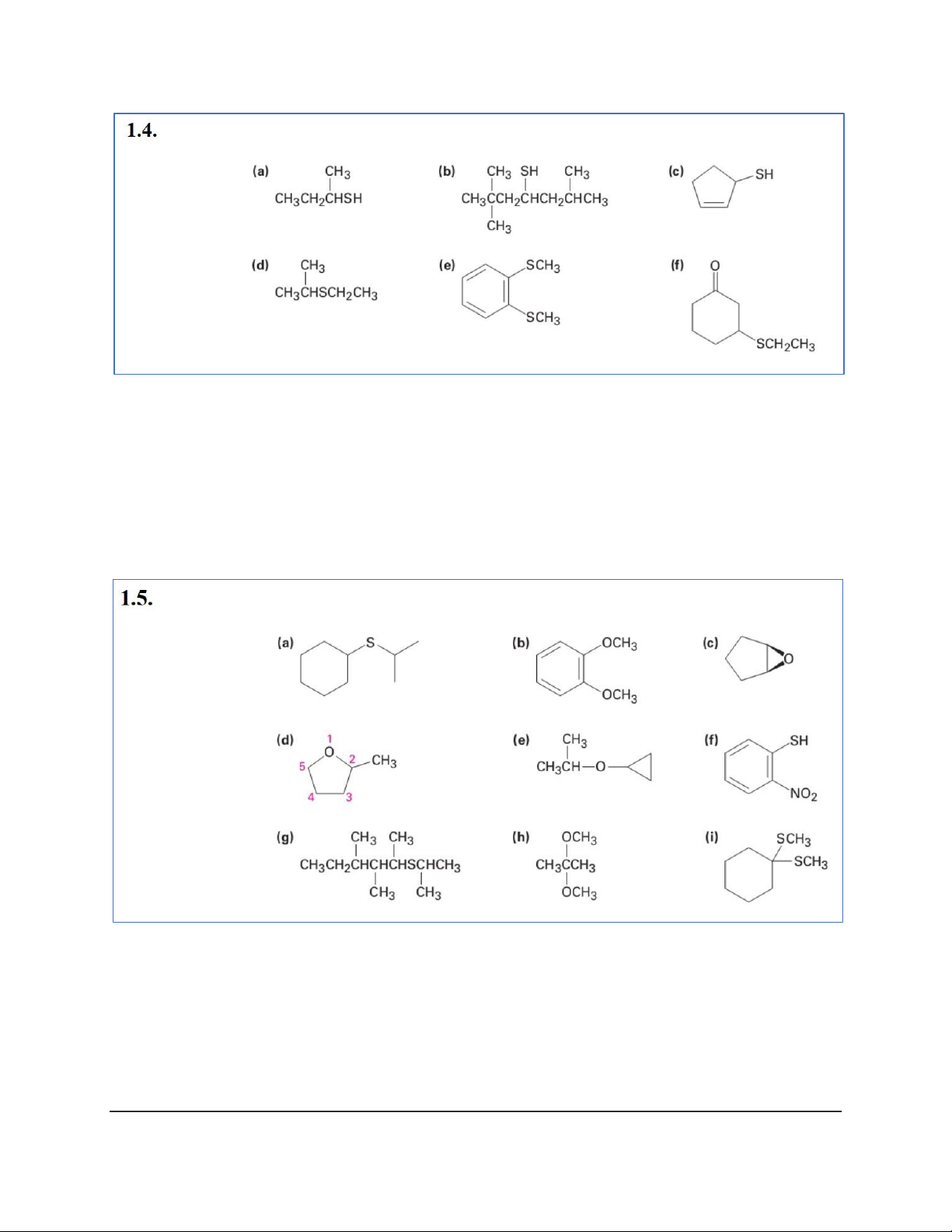
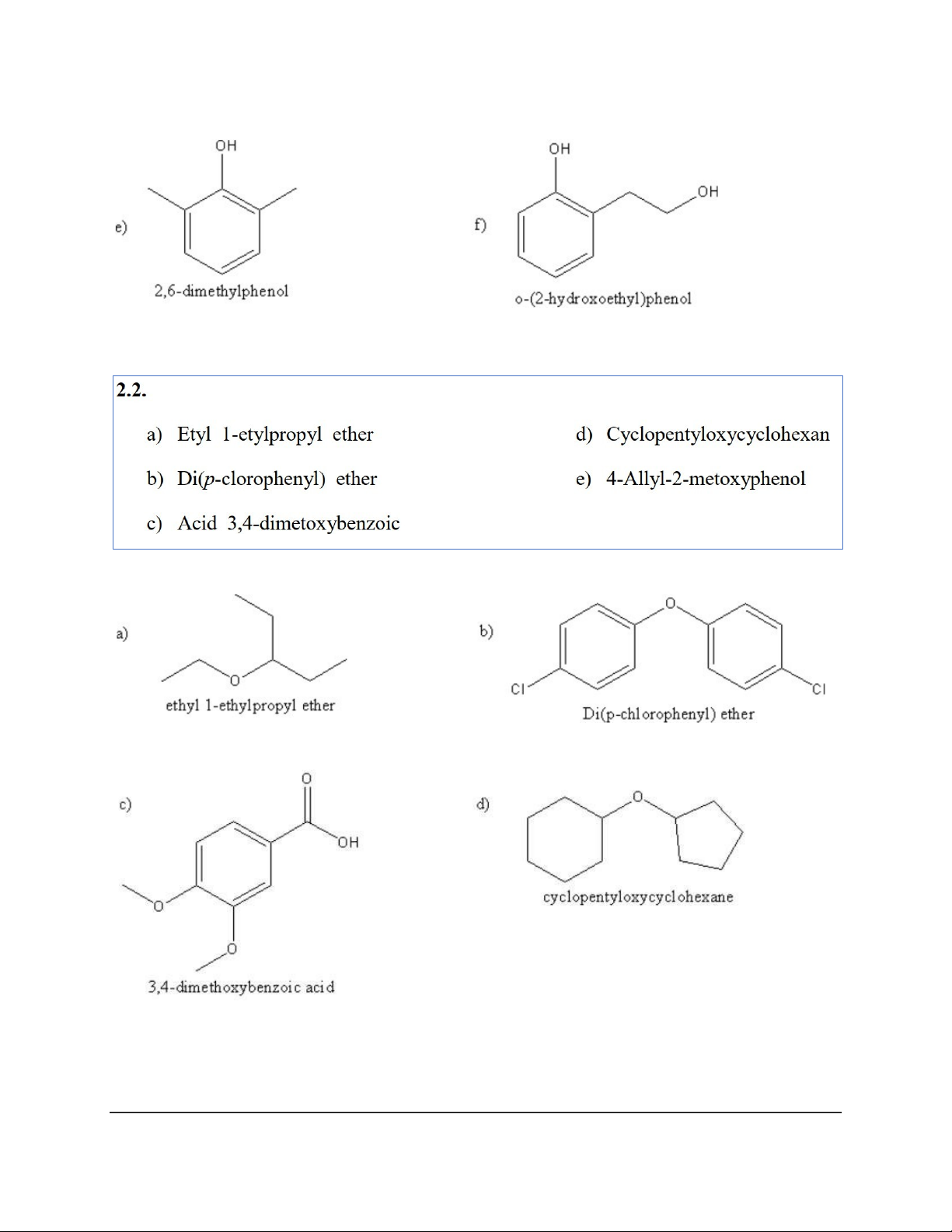
c) p-Bromomethoxybenzene d) 1-Methoxycyclohexene e) Ethyl isobutyl ether f) Allyl vinyl ether 2 a) Butan-2-thiol
b) 2,2,6-Trimethylheptane-4-thiol c) Cyclopent-2-enethiol d) Ethyl isopropyl sulfide e) 1,2-Dimethylthiolbenzene f) 3-Ethylthiolcyclohexanone
a) Cyclohexyl isopropyl sulfide b) 1,2-Dimethoxybenzene
c) (1R,2S)-1,2-Epoxycyclopentane d) 2-Methyloxolane e) Cyclopropyl isopropyl ether f) 1-Mercapto-2-nitrobenzene 3
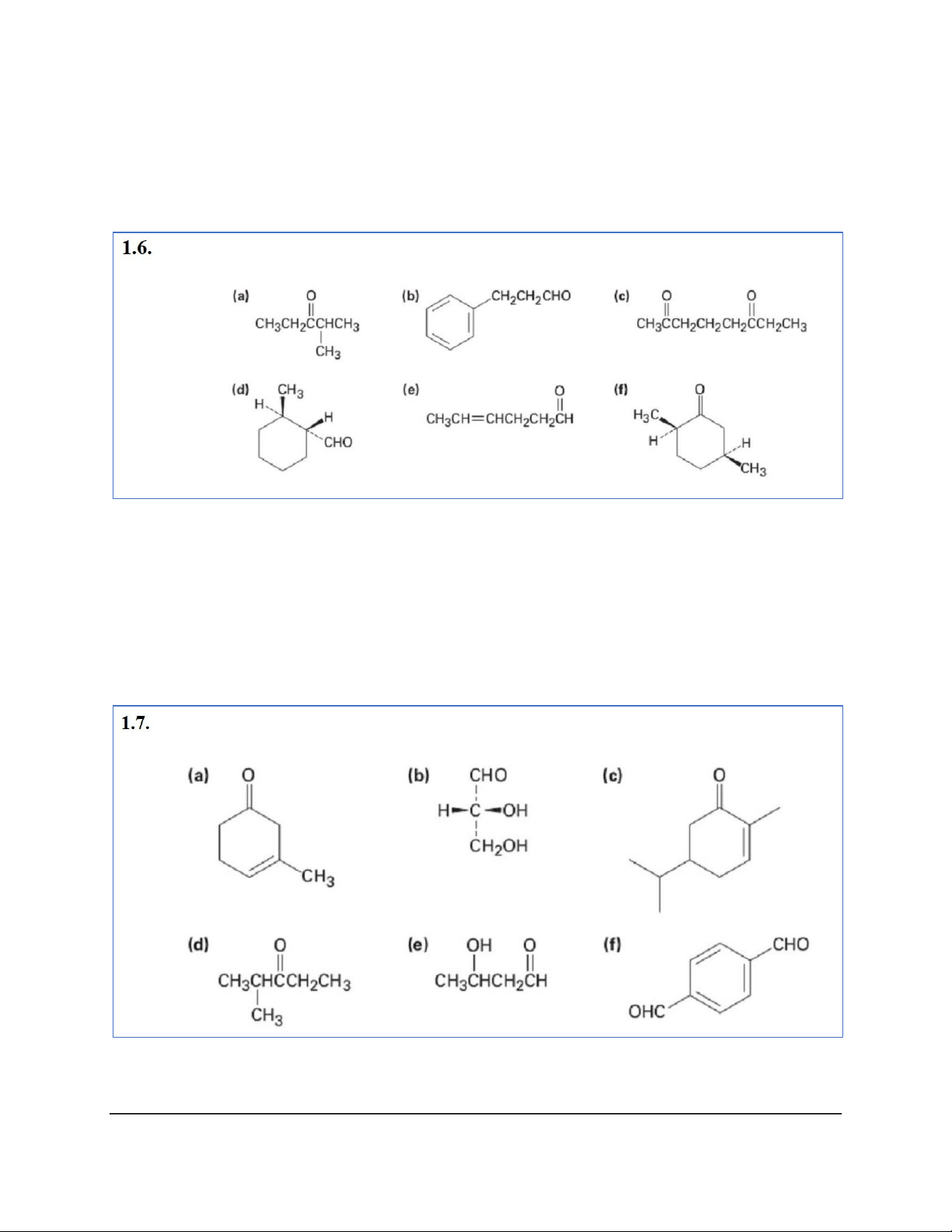
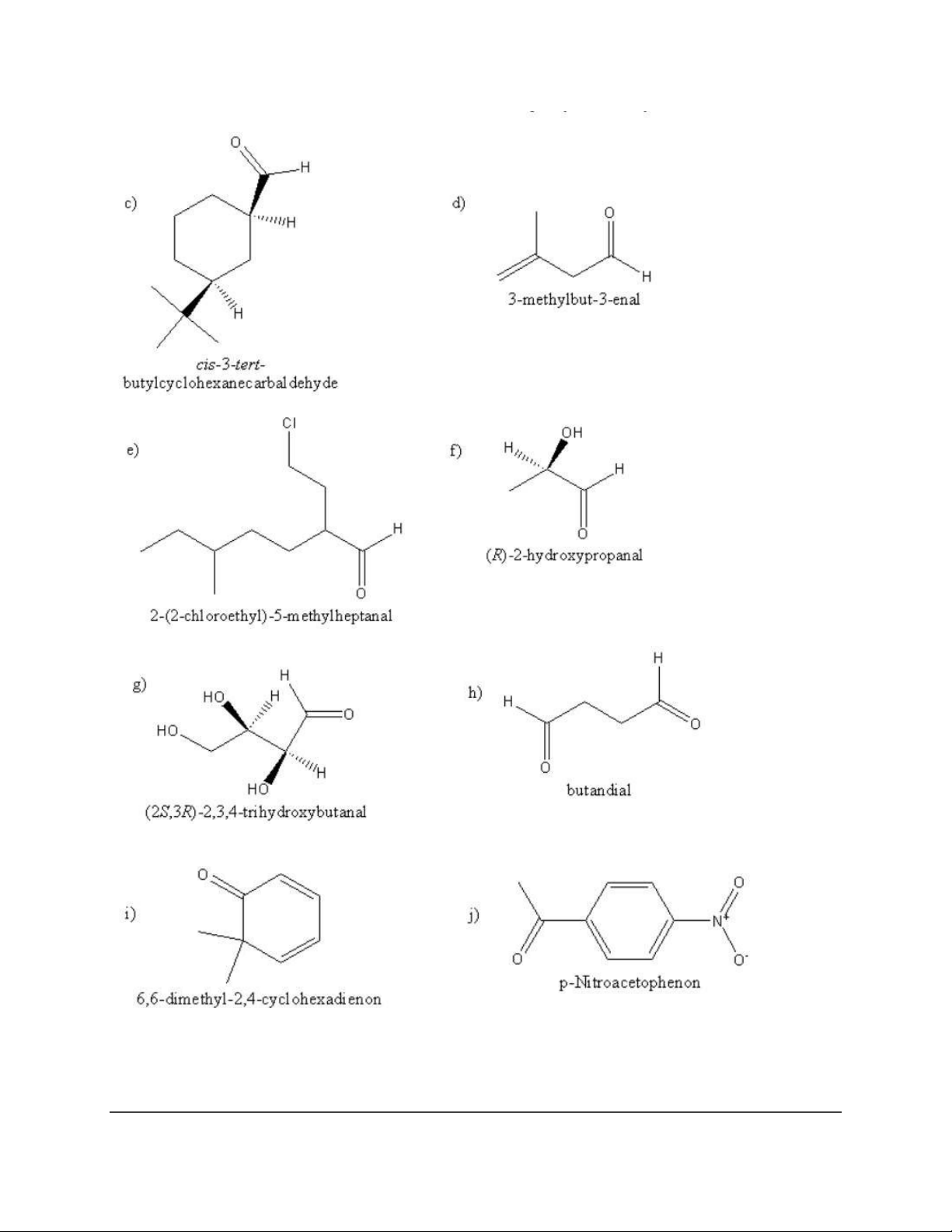
g) 2-(Isopropylthiol)-3,4-dimethylhexane h) 2,2-Dimethoxypropane i) 1,1-Dimethylthiocyclohexane a) 2-Methylpentane-3-one b) 3-Phenylpropanal c) Octane-2,6-dione
d) (1R,2R)-2-Methylcyclohexanecarbaldehyde e) 4-Hexenal
f) (2R,5S)-2,5-Dimethylcyclohexanone a) 3-Methyl-3-cyclohexenone 4
b) (R)-2,3-dihydroxypropanal
c) 5-Isopropyl-2-methyl-2-cyclohexenone d) 2-Methyl-3-pentanone e) 3-Hydroxybutanal f) Benzene1,4-dicarbaldehyde 5 6 7 8
Dạng 2: So sánh nhiệt độ sôi
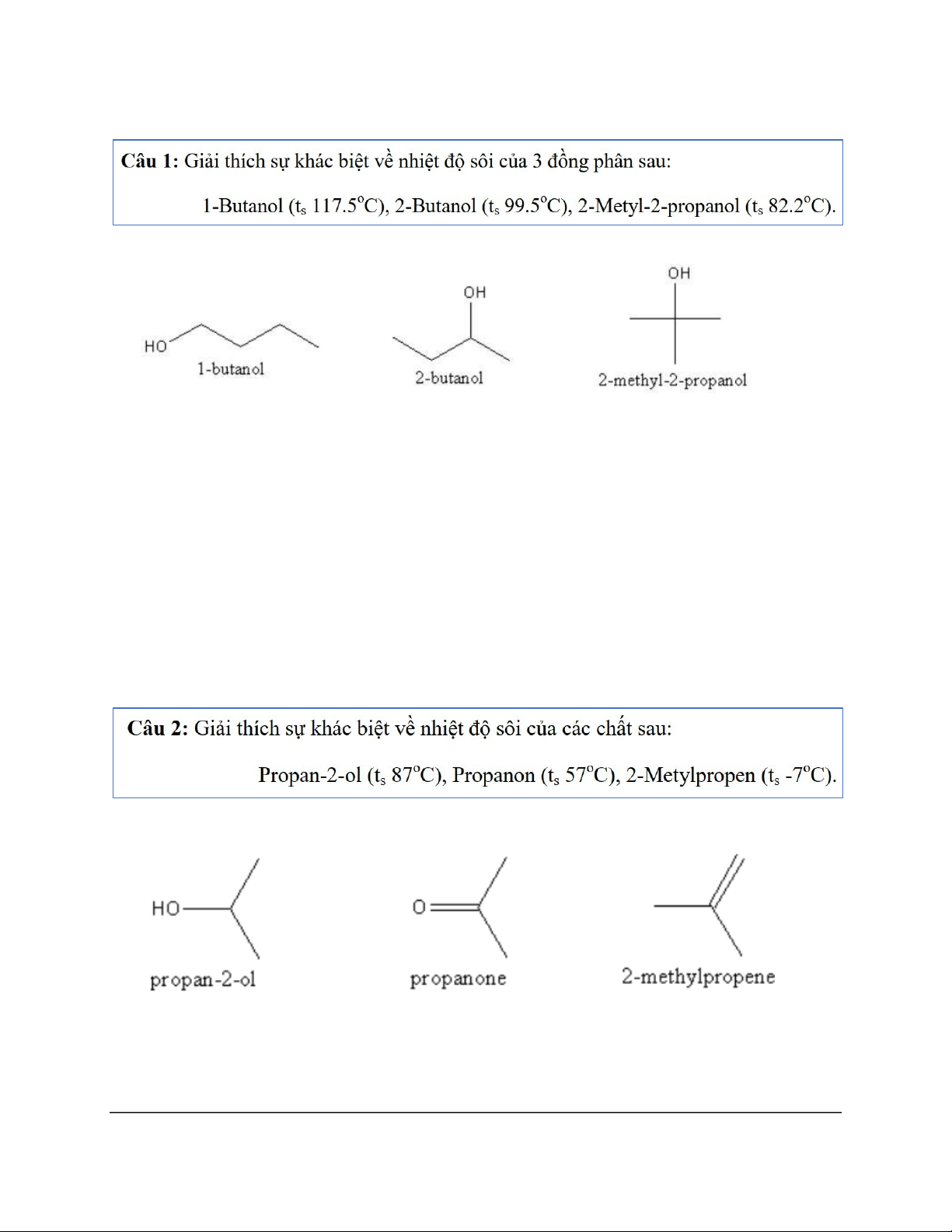
Cả 3 hợp chất trên đều có liên kết hydrogen liên phân tử, do đó, nhiệt độ sôi của cả 3 hợp chất
đều rất cao. Tuy vậy, sự khác biệt ở nhiệt độ sôi nằm ở hình dạng phân tử: Phân tử có
dạng cầu (phân nhánh) có lực tương tác van der Waals yếu hơn so với các phân tử có
dạng dài (không phân nhánh) vì phân tử dạng hình cầu có bề mặt nhỏ dẫn tới khó tạo
liên kết liên phân tử hơn so với phân tử dạng dài.
Chính vì thế, nhiệt độ sôi của các hợp chất giảm dần:
1-butanol > 2-butanol > 2-methyl-2-propanol.
Trong 3 hợp chất trên, chỉ có propan-2-ol có khả năng tạo liên kết hydrogen liên phân tử
nên nhiệt độ sôi của hợp chất này là cao nhất. 9
Propanone có tương tác cảm ứng nên propanone có liên kết Van der Waals mạnh hơn 2-
Methylpropen. Do đó, propanone có nhiệt độ sôi cao hơn 2-Methylpropen. Dạng 3: So sánh tính acid
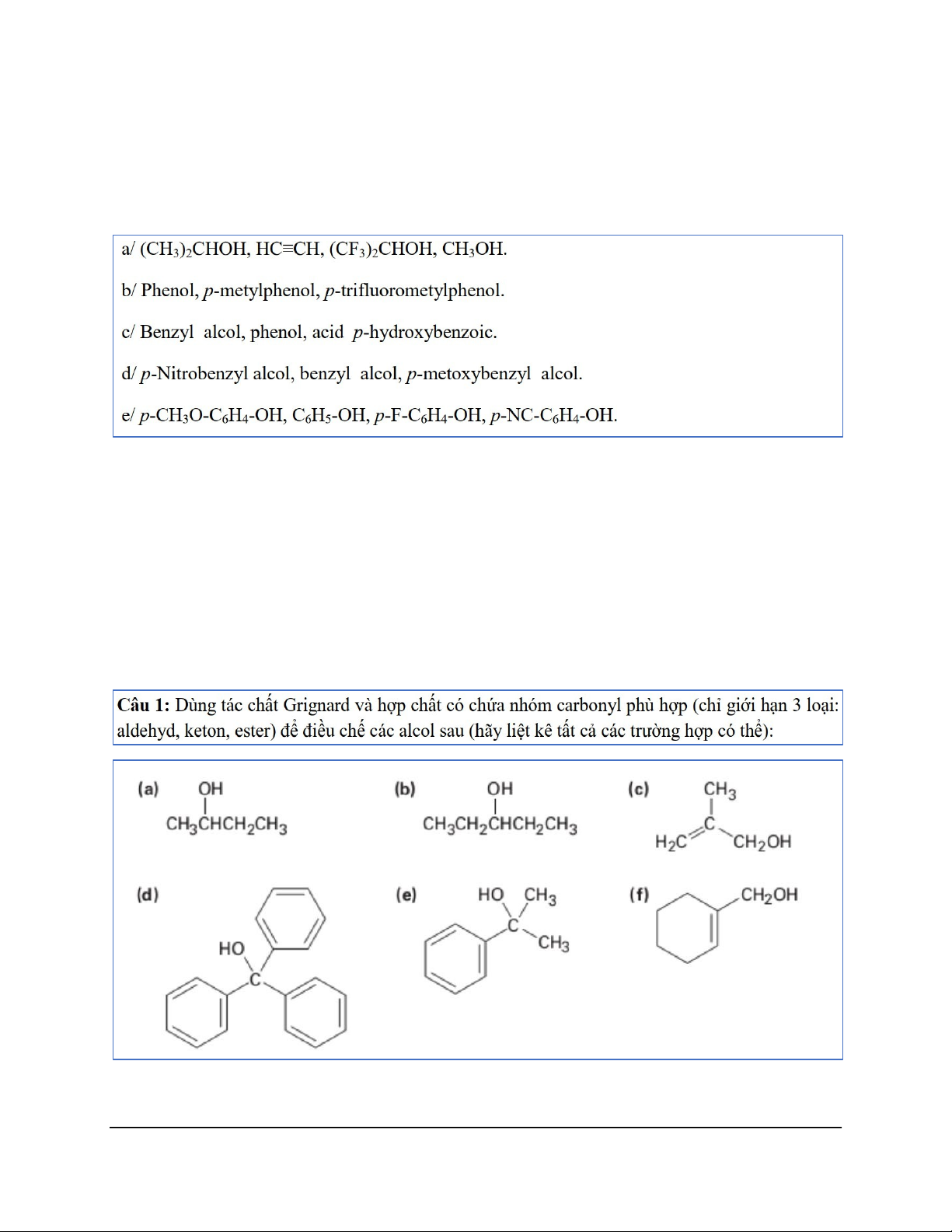
a) 𝐻𝐶 ≡ 𝐶𝐻 < (𝐶𝐻3)2𝐶𝐻𝑂𝐻 < 𝐶𝐻3𝑂𝐻 < (𝐶𝐹3)2𝐶𝐻𝑂𝐻
b) p-methylphenol < phenol < p-(trifluoromethyl)phenol
c) benzyl alcohol < phenol < p-hydroxylbenzoic acid
d) p-methoxybenzyl alcohol < benzyl alcohol < p-nitrobenzyl alcohol
e) 𝑝 − CH3𝑂 − 𝐶6𝐻4 − 𝑂𝐻 < 𝐶6𝐻5𝑂𝐻 < 𝑝 − C6𝐻4 − 𝑂𝐻 < 𝑝 − nitrobenzyl alcohol
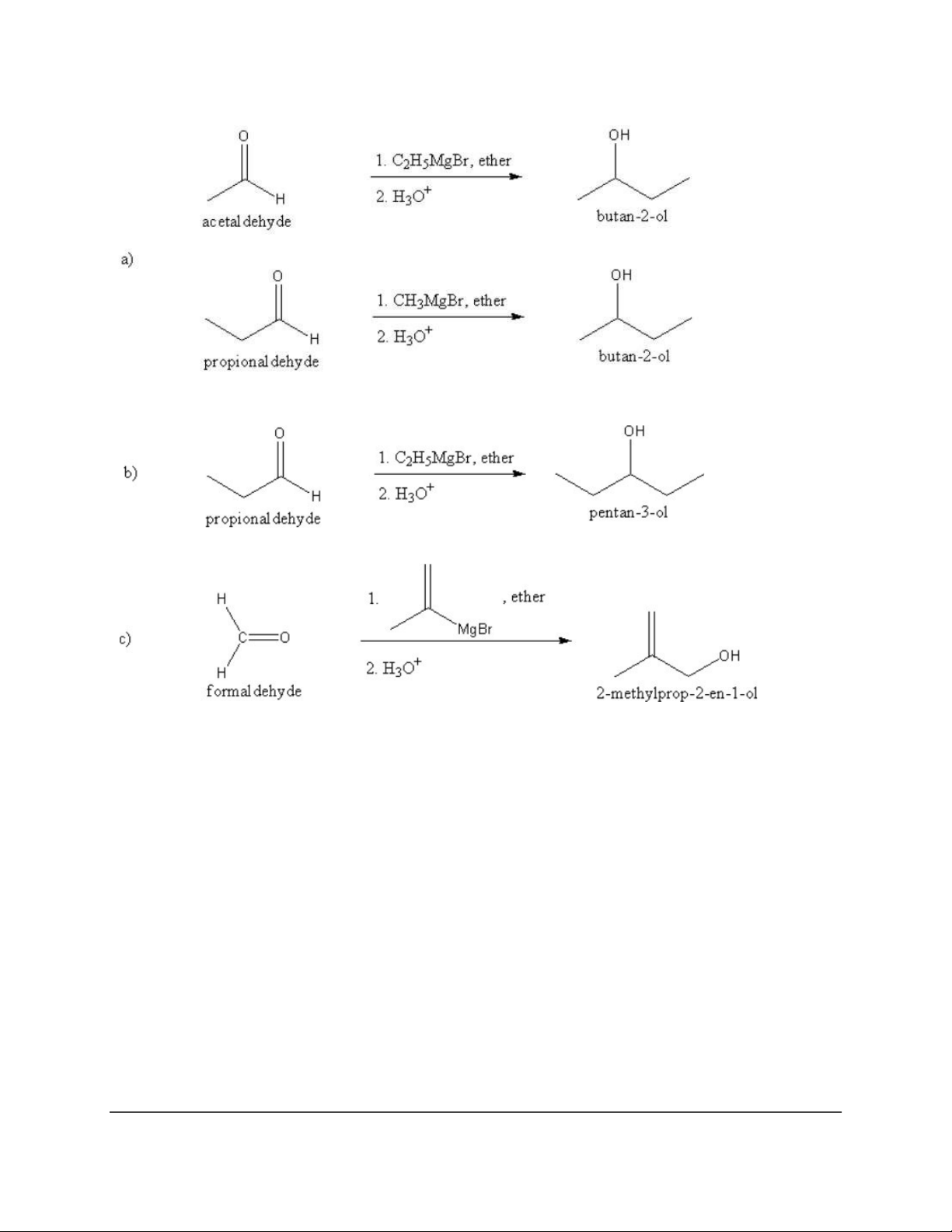
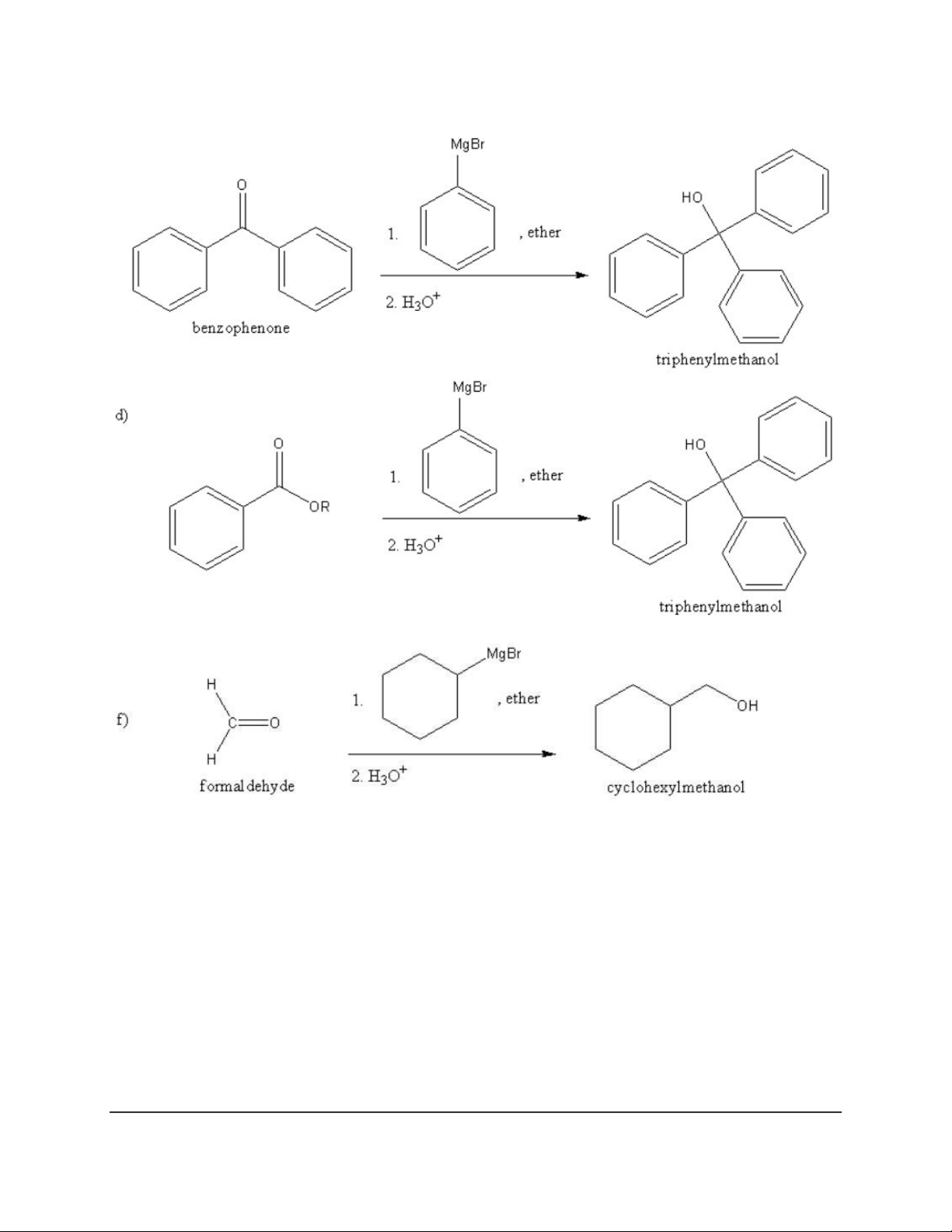
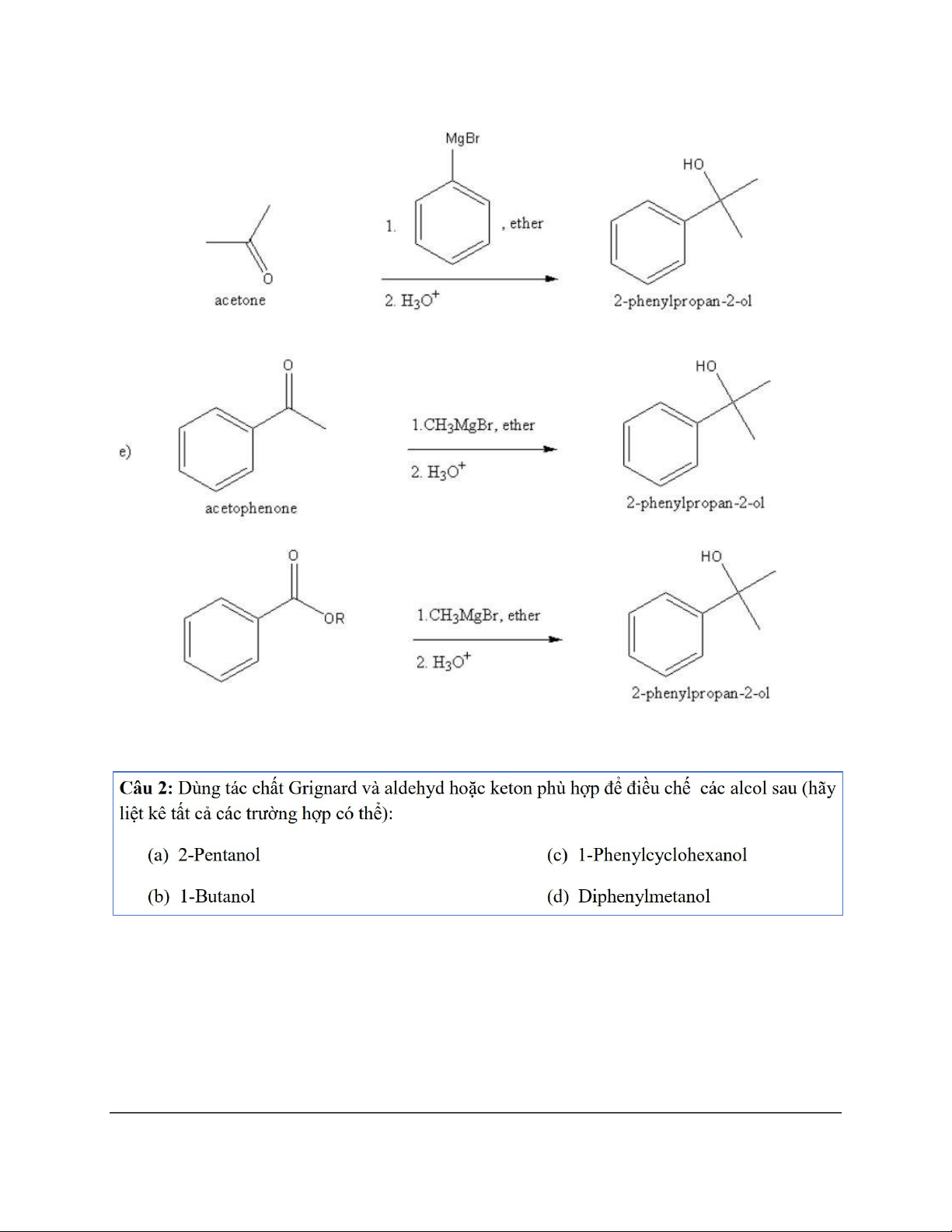
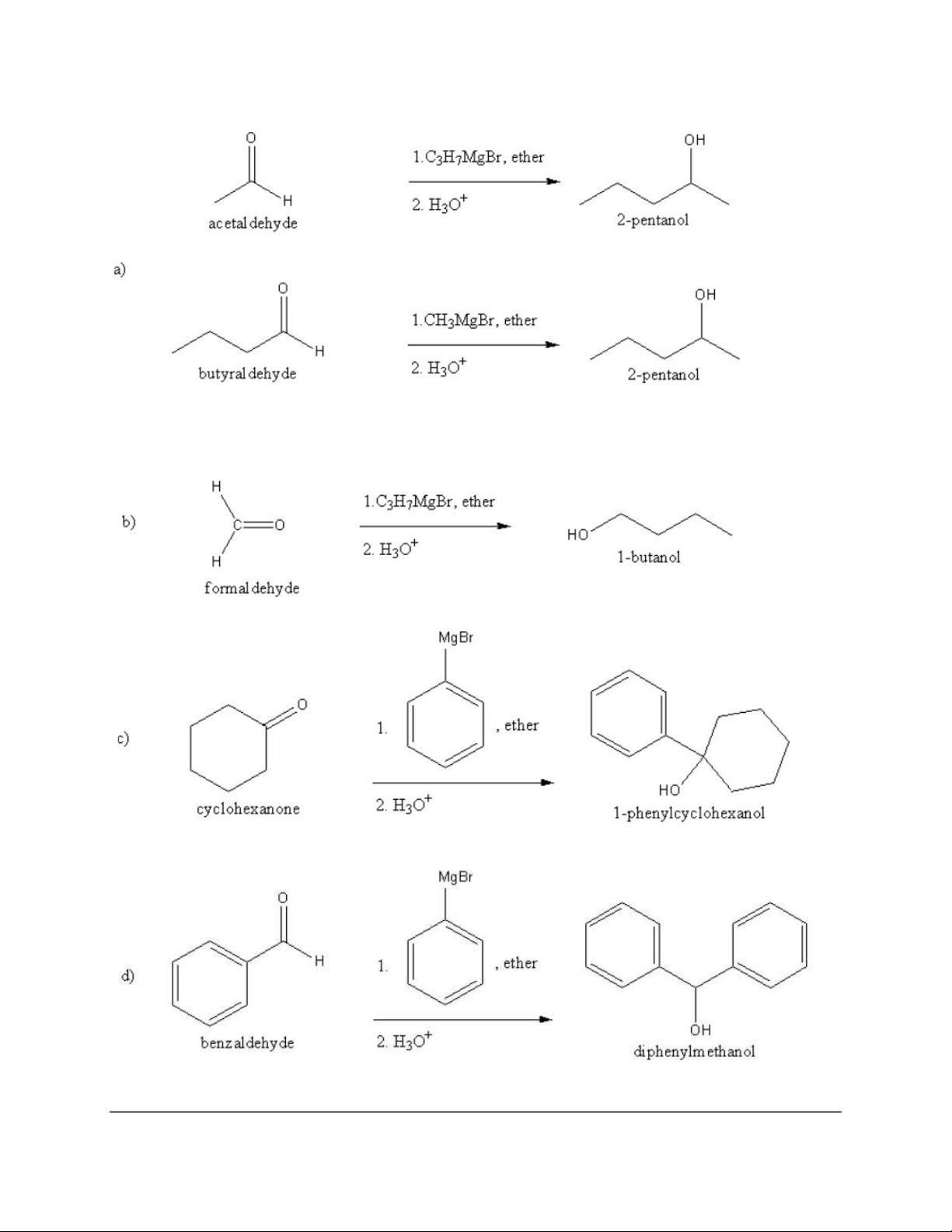
Dạng 4: Tác chất Grignard (RMgX) 10 11 12 13 14
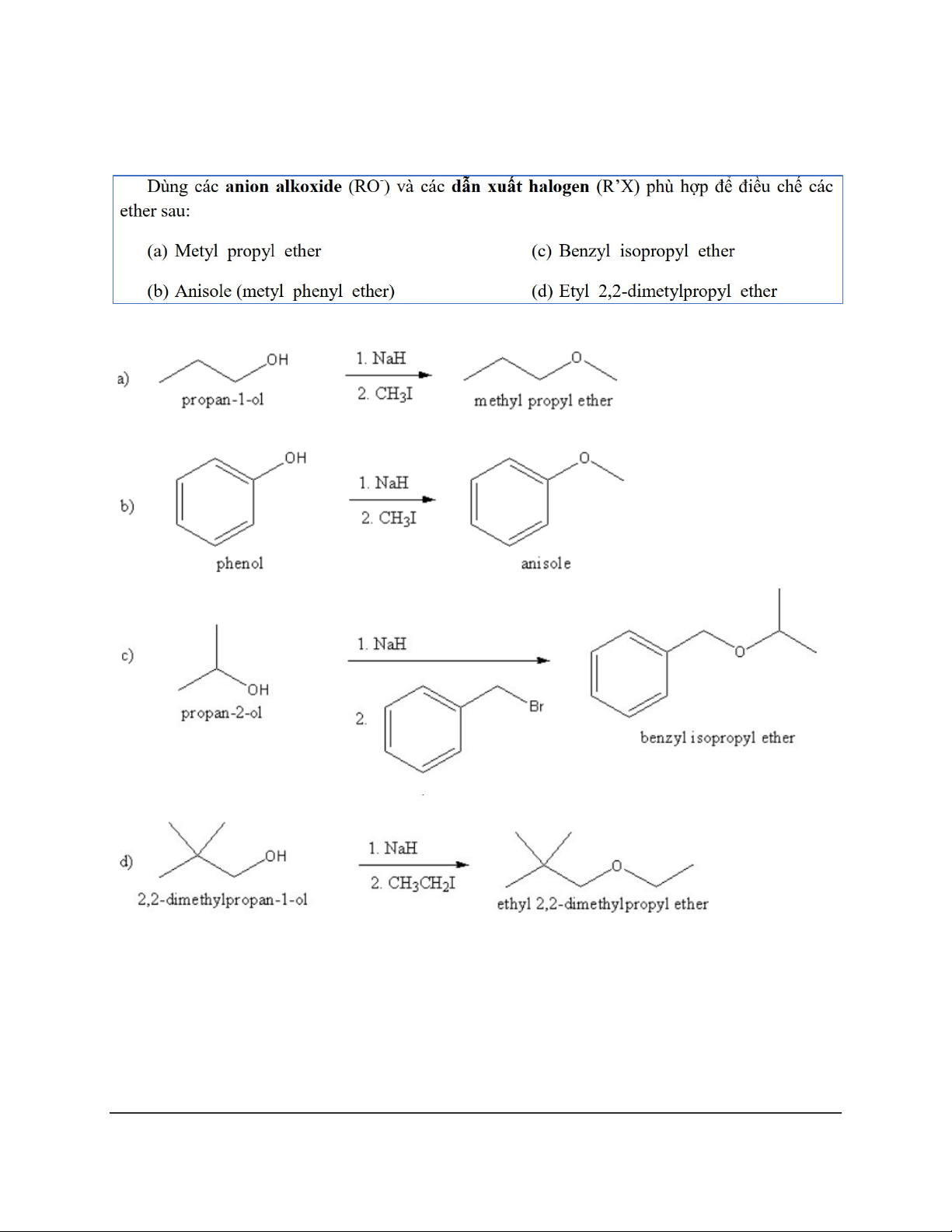
Dạng 5: Tổng hợp ether theo phương pháp Wil iamson 15
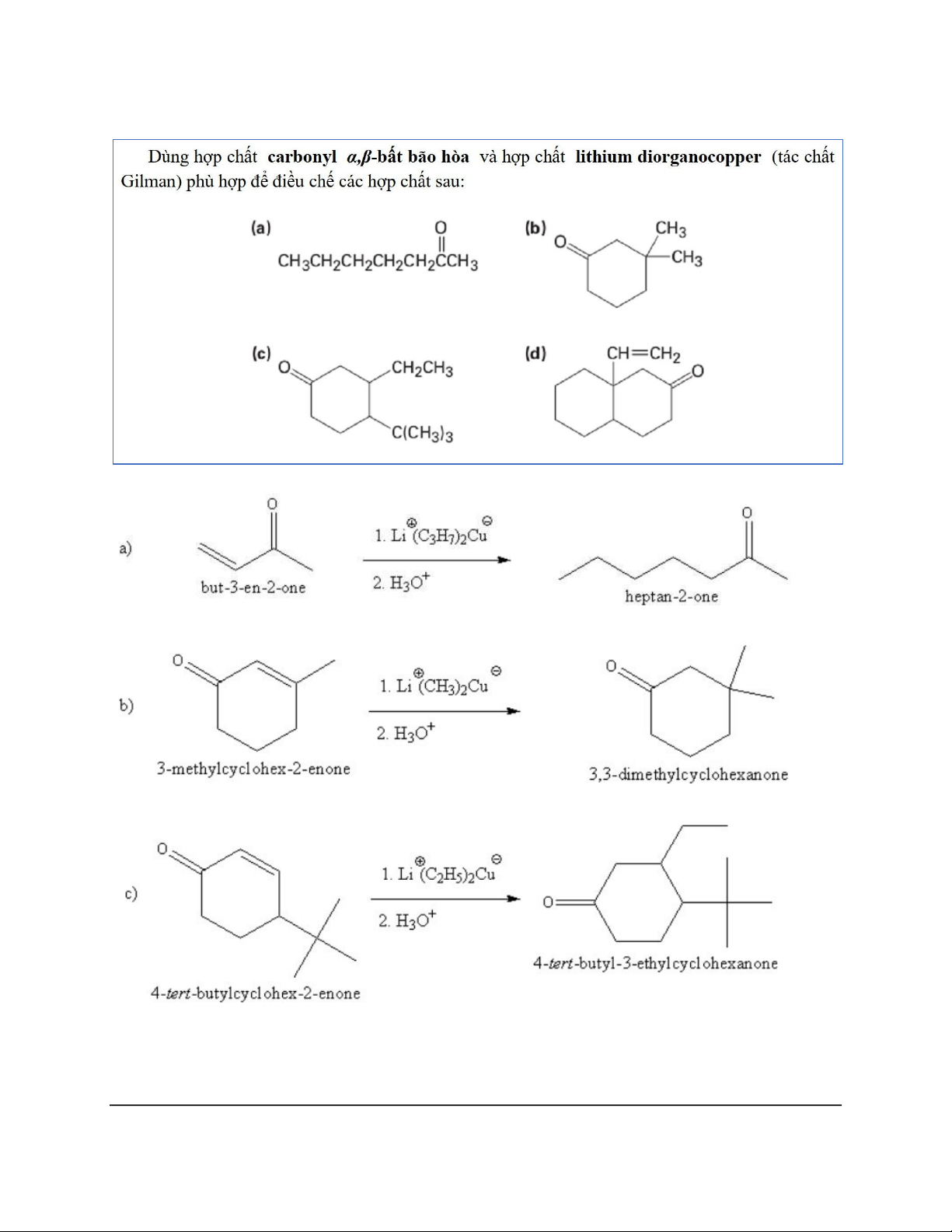
Dạng 6: Tác chất Gilman (𝑅2𝐶𝑢𝐿𝑖) 16
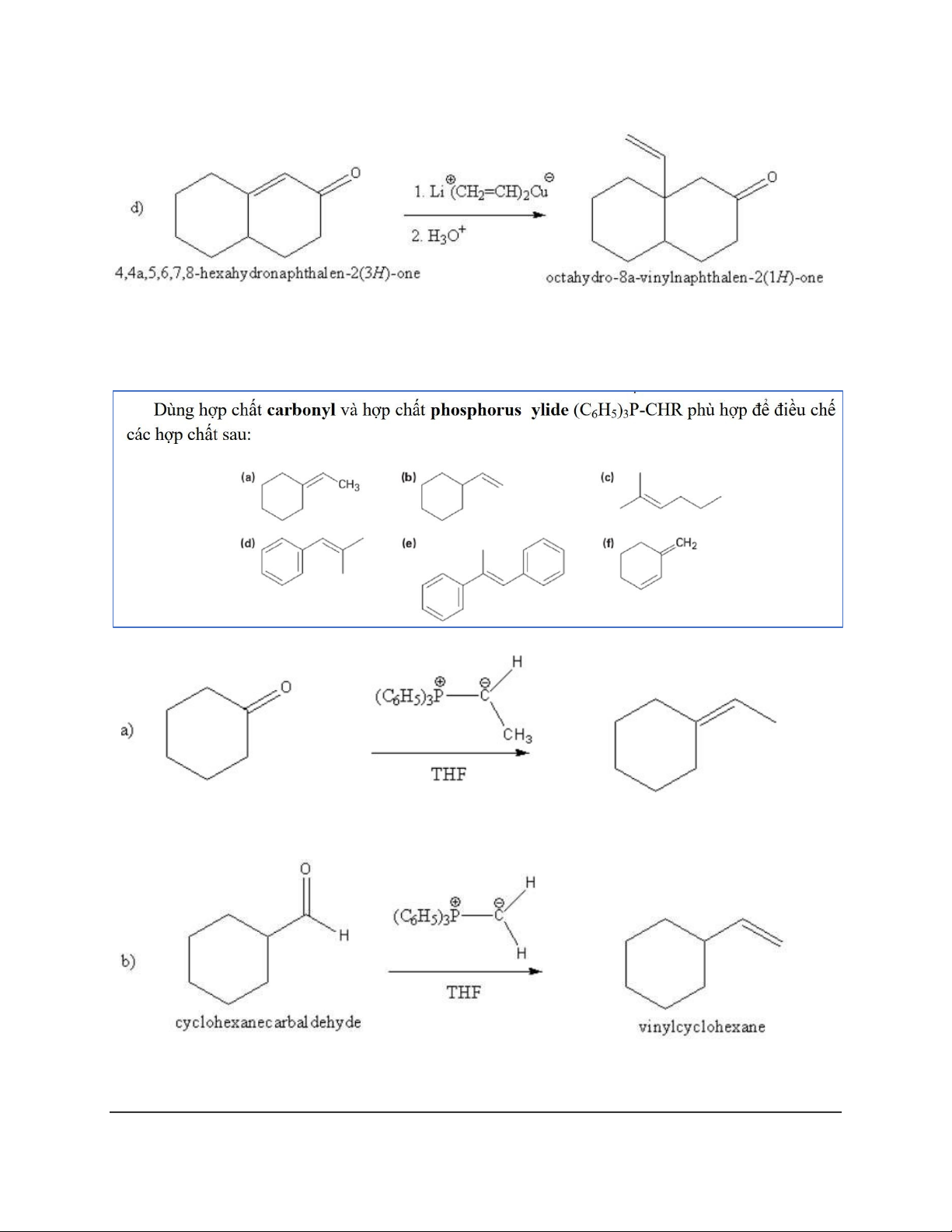
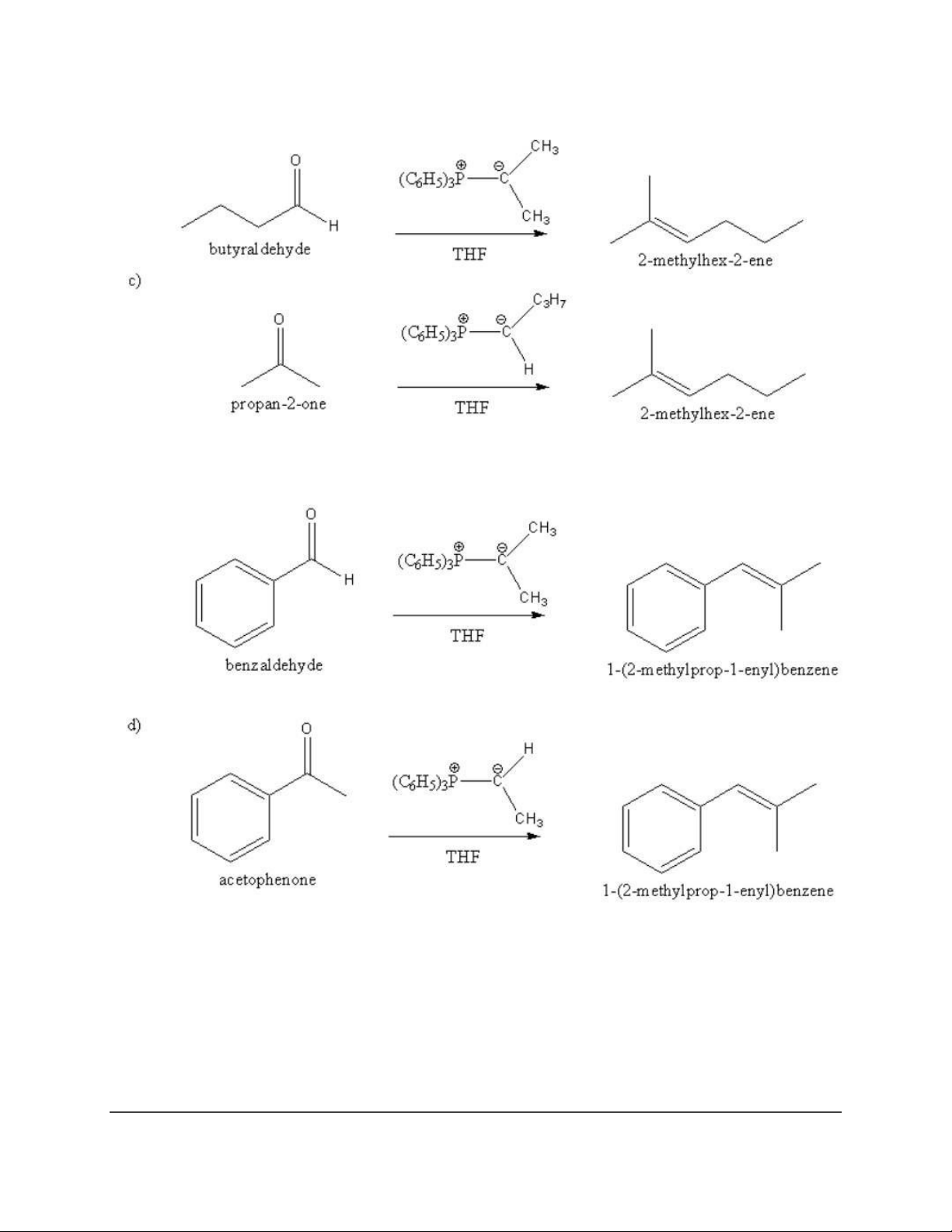
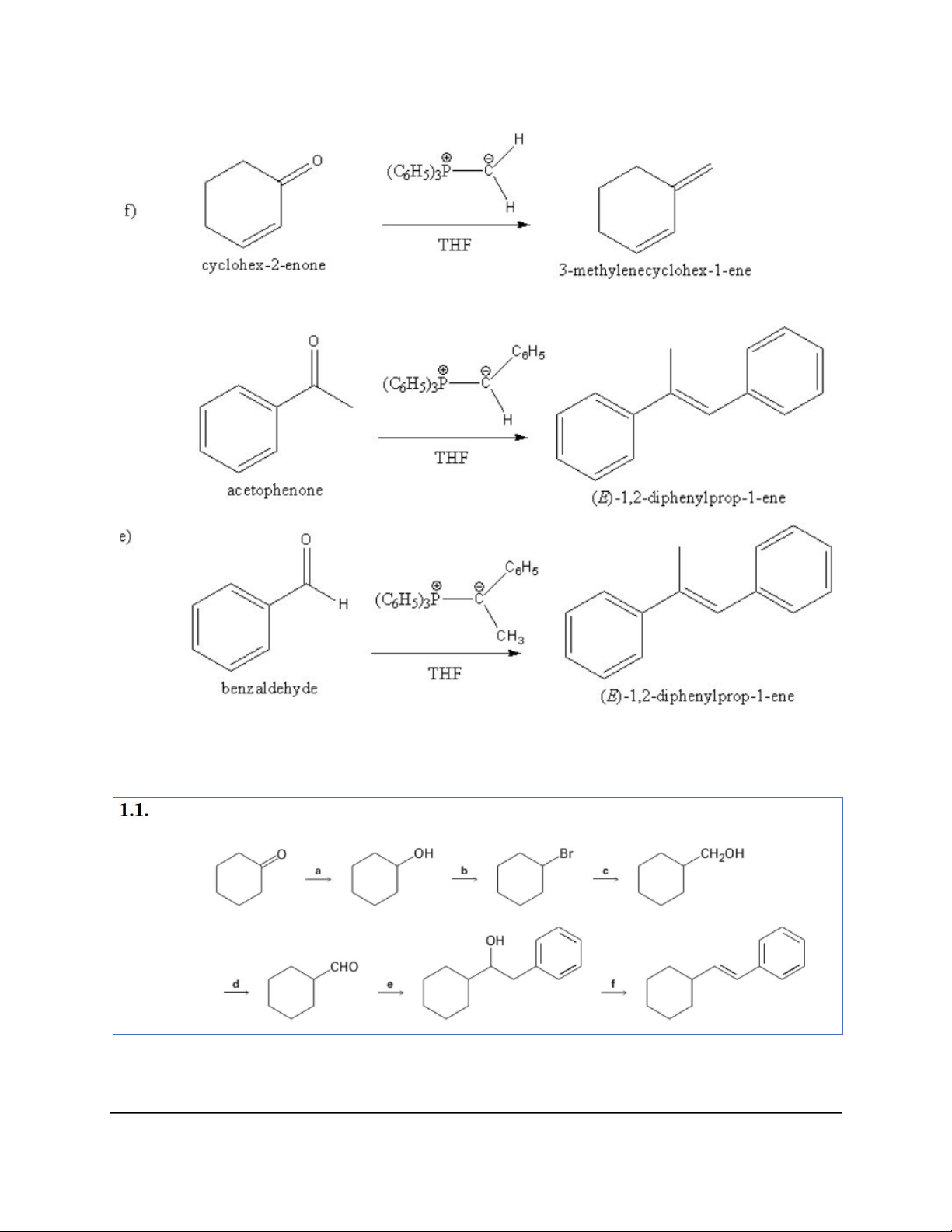
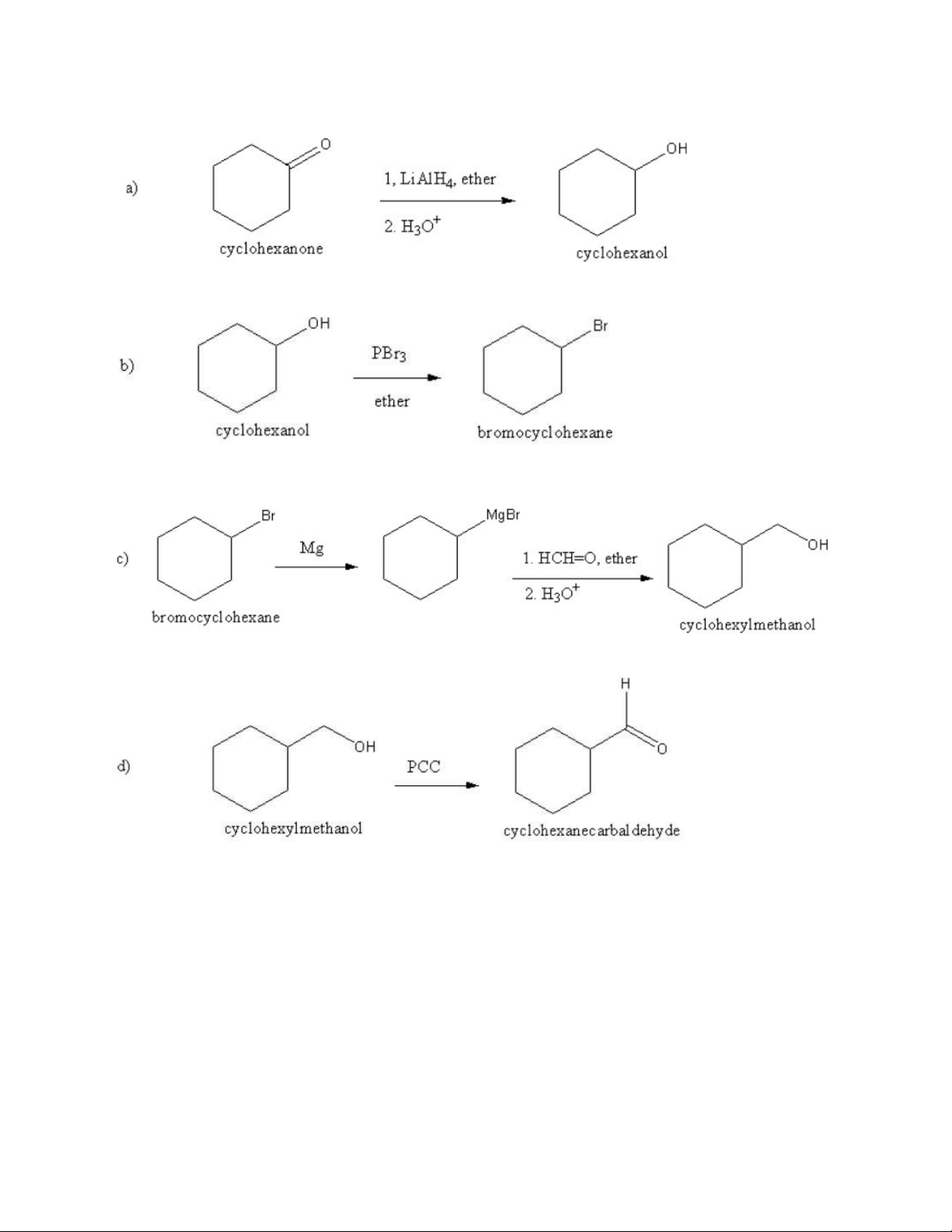
Dạng 7: Phản ứng Wittig (điều chế alken có số nhóm thế nhỏ hơn hoặc bằng 3) 17 18 Dạng 8: Chuỗi phản ứng 19