






Preview text:
Giải bài tập SGK Tiếng Anh lớp 12 Unit 15 WOMEN IN SOCIETY
A. Reading (Trang SGK Tiếng Anh 12)
Before you read (Trước khi bạn đọc)
Work in pairs. Look at the pictures and answer the questions that follow. (Làm việc theo cặp. Nhìn vào
các bức tranh và trả lời các câu hỏi theo sau.)
1. How many roles does this woman have? (Người phụ nữ này đảm nhận bao nhiêu vai trò?)
=> This woman has two roles: a wife's role and a mother's role.
2. Is her life typical of a Vietnamese woman's life? Why/Why not? (Cuộc sống của cô ấy có phải là cuộc
sống điển hình của người phụ nữ Việt Nam không? Tại sao/Tại sao không?)
=> Yes, it is, because it's the Vietnamese traditional lifestyle and culture.
While you read (Trong khi bạn đọc)
Read the passage and do the tasks that follow. (Đọc đoạn văn và làm bài tập theo sau.) Hướng dẫn dịch:
Trong gần hết chiều dài lịch sử văn minh nhân loại, những quan niệm văn hóa lâu đời chỉ
cho phép phụ nữ đảm nhận một ít vai trò trong xã hội. Nhiều người cho rằng thiên chức
của người phụ nữ là làm vợ, làm mẹ. Những người này cho rằng phụ nữ thích hợp với việc
sinh con và trông nom nhà cửa hơn là tham gia vào đời sống kinh tế hay chính trị của xã
hội. Những nghi ngại chung về khả năng tư duy của người phụ nữ đã khiến cho nhiều xã
hội không cho nữ giới được học hành, tuyển dụng và nhiều quyền lợi chính trị và pháp lý.
Chính nam giới mới là người kiểm soát hầu hết việc làm và quyền lực trong xã hội.
Cuộc đấu tranh cho nữ quyền - quyền mang lại cho phụ nữ vị thế xã hội, kinh tế và chính
trị ngang bằng với nam giới - bắt đầu từ thế kỷ 18 trong một giai đoạn được gọi là Thời đại
Ánh sáng. Trong giai đoạn này, các triết gia chính trị ở châu Âu bắt đầu tranh luận rằng
mọi cá nhân, dù là nam hay nữ, sinh ra đã có quyền tự do và bình đẳng. Những nhà tư
tưởng tiên phong này chủ trương rằng phụ nữ không nên bị phân biệt đối xử vì lý do giới tính.
Ngày nay, mặc dù vị thế của phụ nữ ở mỗi quốc gia mỗi khác, phần lớn phụ nữ trên thế
giới đã được những quyền lợi pháp lý đáng kể. Trong số đó, quan trọng nhất là: cơ hội làm
việc và được trả lương ngang bằng với nam giới, quyền bầu cử và quyền được học hành tử tế.
Task 1. Give the Vietnamese equivalents to the following words and phrases. (Cho từ tiếng Việt tương
đương với những từ và cụm từ sau.) Gợi ý:
1. human civilization: nền văn
5. deep-seated cultural beliefs: quan niệm văn minh nhân loại hóa lâu đời
2. childbearing: việc sinh con
6. homemaking: việc chăm sóc gia đình
3. involvement: sự dấn thân, tham
7. intelleclual ability: khả năng trí thức/hiểu biết gia
4. Age of Enlightenment: Thời đại 8. equal work opportunity: cơ hội nghề nghiệp/ ánh sáng việc làm bình đẳng
Task 2. Choose the best option A, B, C or D to answer the following questions. (Chọn câu trả lời A, B,C
hoặc D đúng nhất để trả lời các câu hỏi sau.) Gợi ý: 1. C 2. D 3. C 4. B 5. A
Task 3. Choose the best title for the passage. (Chọn tiêu đề đúng nhất cho đoạn văn.)
A. Khả năng trí thức của phụ nữ
B. Thời kỳ ánh sáng
C. Quyền lợi của phụ nữ
D. Vai trò của phụ nữ trong Giáo dục Gợi ý: C. Women's Rights
After you read (Sau khi bạn đọc)
Work in pairs. Summarize the reading passage by writing ONE sentence for each paragraph. (Làm việc
theo cặp. Tóm tắt đoạn văn đọc bằng cách viết một câu cho mỗi đoạn văn.) Gợi ý: - Paragraph 1
In the past, women were limited to the natural roles: mother's and wife's because of
widespread doubt about their intellectual ability. - Paragraph 2
The struggle for women's rights began in the 18th century with European philosophers'
thoughts that women should not be discriminated on the basis of sex. - Paragraph 3
Women now enjoy significant legal rights such as equal work and pay rights, the right to
vote and to get formal education.
B. Speaking (Trang 165-166 SGK Tiếng Anh 12)
Task 1. Study the expressions and practise saying them aloud. (Học các các diễn đạt và luyện tập đọc to chung.) Hướng dẫn dịch: Cho ý kiến
Tôi nghĩ .../Tôi tin .../Theo ý tôi, .../Theo quan điểm
của tôi, .../Như tôi thấy, ... Hoàn toàn
Tôi hoàn toàn đồng ý./Tôi hoàn toàn đồng ý với đồng ý
bạn./ Tuyệt đối đồng ý!/ Đúng vậy! Đồng ý một
À, tôi hiểu ý bạn, nhưng .../Tôi không hoàn toàn phần
đồng ý/ Ở mức độ nào đó, đúng, nhưng ... Không đồng ý
Tôi không đồng ý./ E rằng tôi không đồng ý./Điều
đó sai./Điều đó không đúng. Hoàn toàn
Vô lí làm sao!/Phi lí sao ấy!/Tôi hoàn toàn không không đồng ý đồng ý.
Task 2. Work in groups. Read and respond to these statements. Begin ... . (Làm việc nhóm. Đọc và đáp
lại các phát biểu này. Bắt đầu lời đáp với một trong các cách diễn đạt ở Bài tập 1.) Gợi ý: A. → Absolutely!
B. → I'm afraid, I disagree. C. → What nonsense! D. → That's wrong. E. → That's right!
F. → That's not true. G. → I don't agree.
H. → I agree with you completely. I. → I quite agree!
Task 3. Work in groups. Discuss whether you agree or disagree with the following statement and give
explanations. (Làm việc nhóm. Thảo luận xem em đồng ý hay không đồng ý với phát biểu sau và đưa ra lời giải thích.)
Married woman should not go to work. (Phụ nữ có gia đình không nên đi làm.) Gợi ý:
A: From my point of view, married women should not go to work.
B: I completely disagree. I think if they stay at home, they gradually lose touch with social life.
C: And they are likely to waste, at some extent, education and knowledge they gained before marriage.
C. Listening (Trang 167-168 SGK Tiếng Anh 12)
Before you listen (Trước khi bạn nghe)
Work in pairs. Answer the following question. (Làm việc theo cặp. Trả lời câu hỏi sau.)
Is the life of a city woman easier than that of a village woman nowadays? What is your point of view?
Why? (Có phải ngày nay cuộc sống của phụ nữ thành phố thoải mái hơn cuộc sống của phụ nữ ở làng quê?
Quan điểm của bạn là gì? Tại sao?)
=> A city woman does housework is much easier thanks to modem labour-saving devices. But in some
other ways, the life of a city woman is more difficult and busier. I think ... . It is because of the high
standard of living that a city woman has to work much harder to make ends meet. Meanwhie the village
life is much simpler and not hasty. Most village women are content with their lot.
While you listen (Trong khi bạn nghe)
Task 1. Listen to the passage and choose the best answer A, B or C to complete each sentences. (Nghe
đoạn văn và chọ đáp án A, B, hoặc C đúng nhất để hoàn thành mỗi câu.) Gợi ý: 1. B 2. C 3. C 4. A 5. B
Task 2. Listen again then answer the following questions. (Nghe lại sau đó trả lời các câu hỏi sau.)
1. According to the passage, what percentage of all the world's jobs do women hold? (Theo đoạn văn,
phụ nữ làm bao nhiêu phần trăm công việc trên thế giới?) => It's 40 percent.
2. What do they earn for doing their domestic work? (Họ được gì khi làm việc nhà?)
=> They earn nothing for their domestic work.
3. How much food do women in developing countries produce? (Phụ nữ ở các quốc gia đang phát triển
sản xuất ra bao nhiêu thực phẩm?)
=> They produce more than half of the food.
4. How much farmwork do African women do? (Phụ nữ ở Châu Phi làm bao nhiêu việc đồng áng?)
=> They do 80 percent of farm work.
5. What time does a typical day for an African village woman begin? (Một ngày làm việc điển hình của
một phụ nữ làng quê Châu Phi bắt đầu lúc mấy giờ?)
=> She begins her day at 4.45 am.
6. What time does it finish? (Khi nào thì ngày làm việc kết thúc?) => It finishes at 9.30pm.
After you listen (Sau khi bạn nghe)
Work in pairs. Compare a typical day of an African village woman in the listening ... . (Làm việc theo cặp.
So sánh một ngày làm việc điển hình của một phụ nữ Châu Phi trong bài nghe với người phụ nữ trong gia
đình bạn (ví dụ, chị gái hoặc mẹ của bạn).) Gợi ý:
A: Let's compare a typical day of an African village woman with that of a woman in your family.
B: Well, first I see the African village woman works more hours than my mother: nearly 17 hours.
A: What about the nature of work?
B: You mean hard work or light work? A: That's it.
B: OK. Both hard and more. From the passage, I see an African village woman does nearly all domestic
work. My mother only does the cooking and the washing - up. All other housework has been done by
machine. She doesn't have to find firewood and water. My mother's work day is much easier.
A: So I he life of African village women is really difficult.
B: It's undoubted that with development program of the UN, African village women's life will get much improved. A: I hope so, too.
Tapescript - Nội dung bài nghe
D. Writing (Trang 168-169 SGK Tiếng Anh 12)
Describing a chart (Miêu tả biểu đồ)
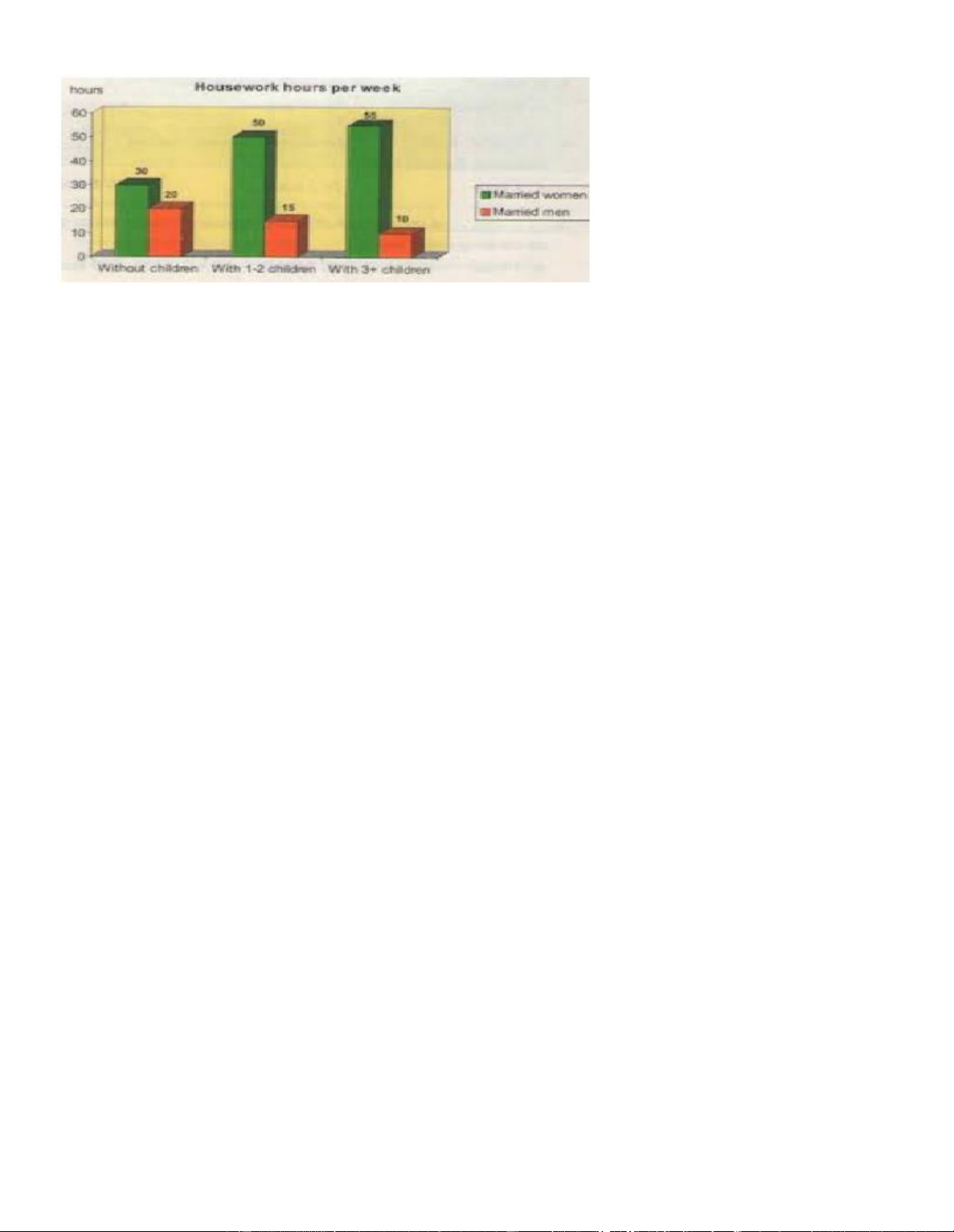
Task 1. Work in pairs. The chart below shows the average hours of housework per week by people ... .
(Làm việc theo cặp. Biểu đồ dưới đây thể hiện số giờ làm việc nhà trung bình mỗi tuần của những người có
giới tính và tình trạng hôn nhân khác nhau ở Fantasia. Nhìn vào biểu đồ sau đó trả lời các câu hỏi theo sau.)
1. Who, in general, does more housework? (Nói chung thì ai làm nhiều việc nhà hơn?)
=> In general, married women do more housework than men.
2. Do married women have to do more or less housework when they have more children? (Phụ nữ đã có
gia đình phải làm nhiều hay ít việc nhà hơn khi họ có con?)
=> They have to do more housework when they have more children.
3. Do married men have to do more or less housework when they have more children? (Đàn ông đã có
gia đình phải làm nhiều hay ít việc nhà hơn khi họ có con?)
=> Married men have to do less housework when they have more children.
4. How many hours do married men and women without children spend on their housework per week?
(Đàn ông và phụ nữ đã lập gia đình mà chưa có con thì dành bao nhiêu thời gian để làm việc nhà mỗi tuần?)
=> Married men and women without children spend 20 and 30 hours on their housework per week respectively.
5. How much time does it take men and women with one or two children to do their housework every
week? (Đàn ông và phụ nữ với một hoặc hai đứa con thì dành bao nhiêu thời gian để làm việc nhà mỗi tuần?)
=> It takes men and women with one or two children 15 and 50 hours respectively to do their housework every week.
6. What are the numbers of weekly housework hours that men and women with three or more children
do respectively? (Số giờ làm việc nhà mỗi tuần tương ứng của đàn ông và phụ nữ với ba hoặc nhiều trẻ hơn?) => They are 10 and 55.
7. What do you think should be done to reduce the unequal distribution of housework hours per week
between married men and women? (Bạn nghĩ điều gì cần nên được thực hiện để giảm sự phân phối việc
nhà không cân bằng giữa đàn ông và phụ nữ đã có gia đình?)
=> Married men should spend more time sharing the housework with their wives.
Task 2. Write a report describing the information shown in the column chart in Task 1. Begin your
report with: (Viết một bản báo cáo mô tả thông tin đã cho trong biểu đồ cột ở Bài tập 1. Bắt đầu bản báo
cáo của bạn với:) Gợi ý: Bản báo cáo 1:
The column chart illustrates the average hours of housework per week done by married
women in comparison with married men.
In households where there are no children, women are reported to work some 30 hours per
week in housework. Men's contribution to this work averages a considerably lower 18 hours.
When children enter the household, however, the inequality becomes even more
pronounced. In families of 1 - 2 children, men maintain approximately the same number of
hours of housework as in childless households, but the number of hours women work in
the home rise to 52 per week, much of which, no doubts, is due to childcare responsibilities.
Interestingly, when there are three or more children in the household, men are found to
work even fewer hours around the house than before the appearance of the third child.
Whereas women's unpaid hours rise to approximately 56 per week, the corresponding
figure for men, 16, actually represents a decrease.
The chart suggests that if women are to gain social equality, they should first be liberated
from familial responsibilities. This can only be done if men lend a more helpful hand to
women in doing domestic chores. Bản báo cáo 2:
The column chart illustrates the average hours of housework per week done by married
women in comparison with married men.
As seen in the chart, there is the distinctive difference in the average hours of housework
in households. In childless families, the gap of housework hours per week between men
and women is not largely. Women do some 30 hours per week, meanwhile men's
contribution in housework is about 20 hours.
In families of one or two children, however, the number of men's housework hours
decreases to 15 hours, but women's number of housework rises even to 50. Undoubtedly
the cause of this rise is due to childcare.
And amazingly in households with three or more children, the inequality becomes more
distinct. Men work fewer hours than about 10 hours, but women's housework hours rise to 55 per week.
The chart shows that the inequality in housework between husband and wife should be
resolved. It is important that women should be liberated from the unreasonable burden of
familial responsibilities. And to get the target, men should do their share of housemaking.
E. Language Focus (Trang 169-170-171 SGK Tiếng Anh 12) Grammar
Exercise 1. Choose one of the following verbs (in the correct form) + the correct preposition to complete
the sentences. (Chọn một trong các động từ sau (trong dạng đúng) + giới từ đúng để hoàn thành các câu.) Gợi ý: 1. glance at 2. invited to 3. listen to 4. throw ... at 5. starting at 6. speaking to 7. wrote to 8. point ... at
Exercise 2. Fill in each of the blanks with an appropriate preposition if necessary. (Điền vào mỗi chỗ
trống với một giới từ thích hợp nếu cần thiết.) Gợi ý: 1. for 2. for 3. to 4. for 5. about 6. _No_ 7. about 8. for 9. for 10. for



