


Preview text:
Unit 5 Lớp 11: Listening trang 57 - Global Success Bài 1
Black carbon and global temperature
(Cacbon đen và nhiệt độ toàn cầu)
Work in pairs. Match the words with their meanings.
(Làm việc theo cặp. Nối các từ với ý nghĩa của chúng.)
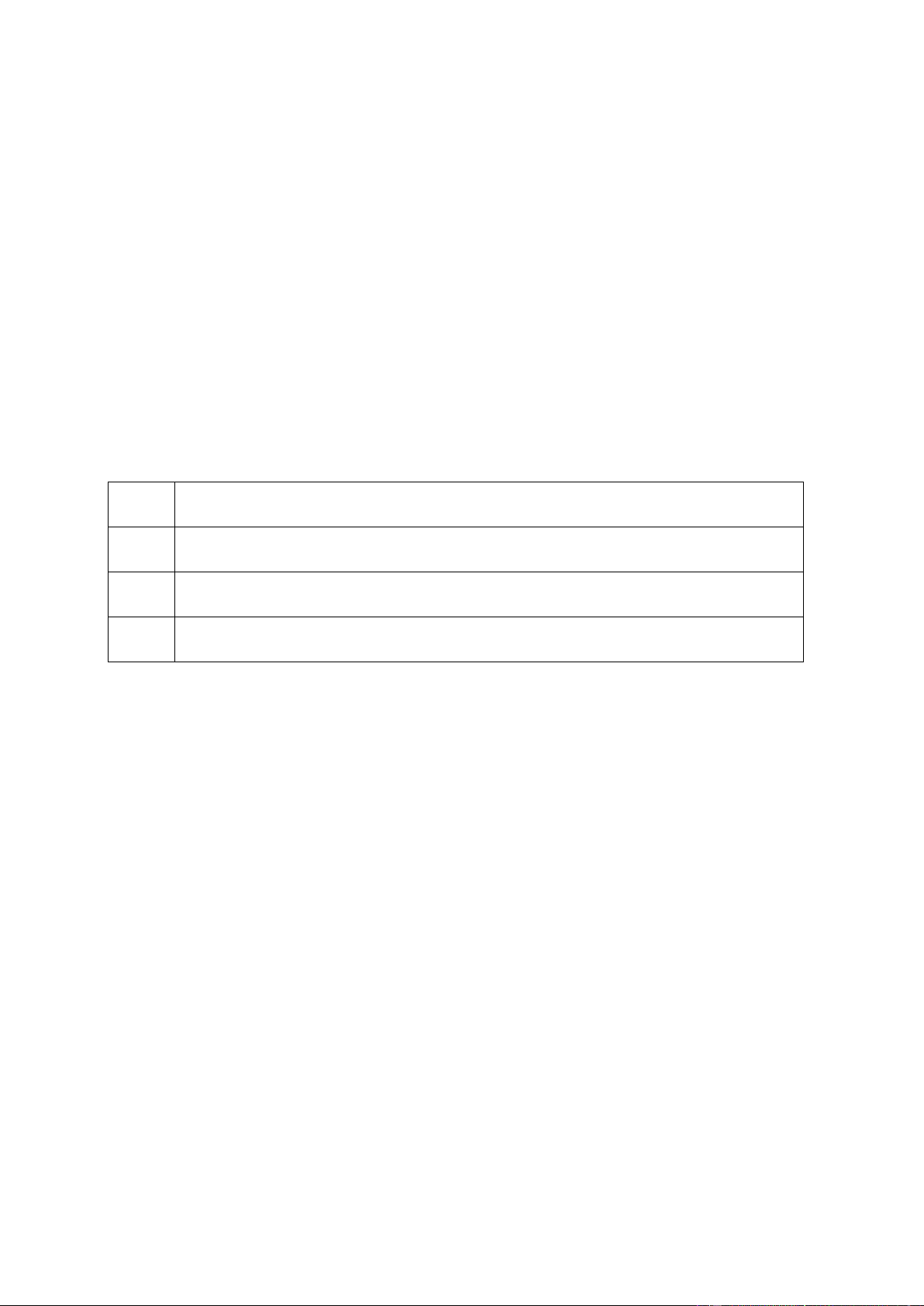
1. soot a. to make or become liquid by heating
2. melt b. the upper layer or the earth in which trees and plants grow
3. crop c. tiny pieces of black dust that are produced when wood, coal, etc. is burnt
4. soil d. a plant such as rice or fruit, grown by farmers and used as food Gợi ý đáp án 1. c 2. a 3. d 4. b Bài 2
Listen to a talk and choose the main idea.
(Nghe một bài nói và chọn ý chính.)
A. Farmers produce the largest amount of soot.
(Nông dân sản xuất lượng bồ hóng lớn nhất.)
B. Black carbon contributes to burning crop waste and wildfires.
(Cacbon đen góp phần đốt chất thải cây trồng và cháy rừng.)
C. Black carbon emissions come from several sources and affect the earth’s temperature.
(Khí thải cacbon đen đến từ nhiều nguồn và ảnh hưởng đến nhiệt độ trái đất.) Gợi ý đáp án Đang cập nhật! Bài 3
Listen to the talk again. Choose the correct answers A, B, or C.
(Nghe nói chuyện một lần nữa. Chọn câu trả lời đúng A, B hoặc C.)
1. The world’s biggest source of soot is ____________.
A. burning forests (cháy rừng)
B. burning crop waste (đốt chất thải cây trồng)
C. killing living things in the soil (làm chết các sinh vật sống trong đất)
2. Black carbon only stays in the atmosphere for a few ____________.
A. hours (giờ)
B. days or weeks (ngày hoặc tuần) C. months (tháng)
3. Black carbon speeds up _______________.
A. the release of sunlight into the air (giải phóng ánh sáng mặt trời vào không khí)
B. burning of crop waste (đốt chất thải cây trồng)
C. ice melting (băng tan)
4. The next part of the talk will probably be about ______________.
(Phần tiếp theo của bài nói có thể sẽ là về ____________.)
A. ways to reduce black carbon emissions (cách để giảm lượng khí thải carbon đen)
B. heat-trapping gases (khí giữ nhiệt)
C. other heat-trapping pollutants (các chất ô nhiễm giữ nhiệt khác) Gợi ý đáp án 1. B 2. C 3. C 4. A Bài 4
Work in groups and answer the questions.
(Làm việc theo nhóm và trả lời câu hỏi.)
Is black carbon found in your city or neighbourhood? If so, where does it come from?
(Carbon đen có được tìm thấy trong thành phố hoặc vùng lân cận của bạn không?
Nếu vậy, nó đến từ đâu?) Gợi ý đáp án
Black carbon is a common air pollutant found in many urban areas around the world.
Black carbon primarily comes from the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels,
biomass, and biofuels. Sources of black carbon emissions can include transportation
(e.g., cars, trucks, buses), industrial processes, and residential cooking and heating (e.g., wood-burning stoves).
In urban areas, the most significant sources of black carbon emissions are typically
transportation and residential heating. In developing countries, biomass burning for
cooking and heating can also be a significant source of black carbon emissions.
It is important to note that black carbon is not only a local pollutant but also a global
one. It can travel long distances through the atmosphere and contribute to climate
change by absorbing sunlight and warming the atmosphere.




