
















Preview text:
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING HOA SEN UNIVERSITY
FACULTY OF ECONOMICS & ADMINISTRATION ------------ FINAL REPORT TOPIC
MAIN MACRO FACTORS OF VIET NAM AFFECTING
THE VARIATION OF USD/VND EXCHANGE RATE IN
RECENT YEARS AND HOW DOES COVID-19 PANDEMIC EFFECTS ON IT ĐIỂM 9
LECTURER : LAM THANH PHI QUYNH
Subject: International Payment
Class’ ID: NT317DE01 - 0100 Semester: 2034 Students list:
1. TRẦN PHƯƠNG UYÊN 2199126 2. THÁI HUỲNH NHƯ 2194133 3. PHẠM THIÊN KIM 2192836
4. NGUYỄN NGỌC KHÁNH 2192575 5. TRẦM NGỌC LOAN 2196870 6. TRẦN CẨM TIÊN 2190949
7. PHẠM CỔ MINH VÂN 2191289
Ho Chi Minh city, August 2021 Hoa Sen University ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
First of all, our group would like to express our sincere thanks to lecturer Lam
Thanh Phi Quynh - who has been with us for the past 15 days studying . He has
conveyed extremely useful information in the subject as well as practical
knowledge so that we can apply it to our future work. Although in the process of
learning was affected by the Covid-19 pandemic, but whether the it is offline or
online, he has always been dedicated to instructing.
Besides, we also thank Hoa Sen University for constantly upgrading online
learning tools so that the process of study is more easily.
Finally, thank you to all members of group 6 for their serious cooperation and
high sense of responsibility in the process of completing this report. Your sincerely.
Final Report - International Payment Page | i Hoa Sen University TABLE OF CONTENTS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT...................................................................................i
LIST OF FIGURES...........................................................................................iii
INTRODUCTION..............................................................................................iv
ABSTRACT.........................................................................................................v
1. MACRO FACTORS IMPACTS ON EXCHANGE RATE...........................1
1.1. Inflation........................................................................................................1
1.1.1. Relationship between inflation and interest rates.................................1
1.1.2. The effects of inflation on the exchange rate.......................................2
1.1.3. Inflation in the 2000s in Vietnam.........................................................2
1.2. Relative Value..............................................................................................5
1.3. Interest rate Differential...............................................................................5
1.4. Relative income level...................................................................................6
1.4.1. Direct impact.......................................................................................6
1.4.2. Indirect impact.....................................................................................7
1.5. Government Intervention.............................................................................7
1.5.1. Direct Intervention...............................................................................9
1.5.2. Indirect Intervention..........................................................................10
1.5.3. Exchange rate adjustment policy of Vietnam.....................................10
1.6. Other factors...............................................................................................12
1.6.1. Psychological factors.........................................................................12
1.6.2. Investors’ expectations.......................................................................14
2. HOW COVID-19 PANDEMIC EFFECTS ON EXCHANGE RATE........14
2.1. The exchange rate of USD/VND before Covid-19.....................................14
2.2. Covid-19 effects on the exchange rate of USD/VND.................................15
2.3. Forecast and recommendations..................................................................18
CONCLUSION..................................................................................................20
REFERENCES..................................................................................................20
Final Report - International Payment Page | ii Hoa Sen University LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1 - Work assignment table........................................................................iv
Figure 2 - Factors affecting exchange rates..........................................................1
Figure 3 - Table of inflation and economic growth chart (1996-2007).................3
Figure 4 - Inflation data sheet...............................................................................3
Figure 5 - State Bank of Viet Nam (SBV)............................................................8
Figure 6 - Central rate (USD/VND) of Viet Nam 2019......................................15
Figure 7 - Table of exchange rate (USD/VND) in Viet Nam 2014-2020............16
Figure 8 - The exchange rate of USD/VND in 2020..........................................17
Final Report - International Payment Trang | iii Hoa Sen University INTRODUCTION Objectives
A brief system of information on exchange rates, get more information of
the macro-factors that effect on the exchange rate and how does the
Covid-19 pandemic impact on it.
Find out the exchange rate regime being applied in Vietnam and find out how
the bank updates the exchange rate on a daily basic.
Provide recommendations to limit risks from exchange rate fluctuations
Work assignment table Student’s ID Student’s full name Perform the work Completion rat 2192575 Nguyễn Ngọc Khánh
1.3. Interest rate Differential 100% 1.6. Other factors 2192836 Phạm Thiên Kim 100% Conclusion 2196870 Trầm Ngọc Loan 1.1. Inflation 100% 1.4. Relative income level 2194133 Thái Huỳnh Như 100% Conclusion 2191289 Phạm Cổ Minh Vân
2.2. Covid-19 effects on the exchange 100% rate of USD/VND
Final Report - International Payment Trang | iv Hoa Sen University
2.3. Forecast and recommendations 2199126 Trần Phương Uyên Abstract 100% 1.5. Government’s Roles 2190949 Trần Cẩm Tiên 1.2. Relative Value 100%
2.1. The exchange rate of USD/VND before Covid-19.
Figure 1 - Work assignment table ABSTRACT
An exchange rate is the value of one country's currency in terms of another
country's currency and is a value that fluctuates frequently and is difficult to
predict. It affects the economy and people's daily life because when the value of
the local currency increases, the price of goods will increase. Domestic goods are
expensive relative to foreign goods. Therefore, the exchange rate is a good tool
for creating favorable conditions, while maintaining the competitiveness of the economy.
For the above reasons, exchange rate policy can be considered as one of the most
important monetary policies of an open economy. On the other hand, currently,
USD is still considered the strongest currency in the world with nearly 80% of
transactions on the foreign exchange market using USD. In Vietnam, the USD
plays a similar role as it accounts for 60% of the foreign exchange reserves of the
State Bank (SBV) (Le Thi Tuan Nghia, Pham Thi Hoang Anh 2013), and is the
main currency used in import and export activities in Vietnam. Therefore, the
management and control of the USD exchange rate has been one of the focuses
of the State Bank towards the goal of long-term and stable growth.
Final Report - International Payment Trang | v Hoa Sen University
1. MACRO FACTORS IMPACTS ON EXCHANGE RATE
The exchange rate is the relative ratio of the currency of one country with another
country's currency (Chen, 2020). It is the price of one unit of this country's currency
expressed in units of another country's currency.
Figure 2 - Factors affecting exchange rates 1.1. Inflation
1.1.1. Relationship between inflation and interest rates
The inflation rate is highly monitored by central banks. They examine inflation to
direct their monetary policy and set their policy interest rates. Each central bank
generally sets itself an inflation threshold that it does not want to exceed and seeks
to avoid deflation (often synonymous with economic recession).
If inflation is moderate, the central bank sets its interest rates according to the level
of inflation and also according to the economic growth rate (GDP). Of course, many
other factors are also taken into account by central banks, but this is to simplify things.
Final Report - International Payment Page | 1 Hoa Sen University
Inflation therefore has an impact on the level of interest rates, but the opposite is also true.
1.1.2. The effects of inflation on the exchange rate
The level of inflation has a direct impact on the exchange rate between two currencies on several levels:
Purchasing power parity: Changes in purchasing power parity (and therefore
inflation) affect the exchange rate. If inflation is the same in both countries,
the exchange rate does not change. If it is higher in one country than in the
other, this is when inflation affects the exchange rate. The currency with the
higher inflation rate then loses value and depreciates, while the currency with
the lower inflation rate appreciates on the Forex market.
Interest rates: Too high inflation pushes interest rates up, which has the effect
of depreciating the currency (less remunerative) on Forex. On the other hand,
inflation that is too low (or deflation) pushes interest rates down, which has
the effect of appreciating the currency on the Forex market. However,
inflation has a much more frequent negative effect than a positive one. A
high rate of inflation is likely to have a negative impact on the exchange rate,
while low inflation is far from a guarantee of an increase in the exchange rate.
1.1.3. Inflation in the 2000s in Vietnam
Final Report - International Payment Page | 2 Hoa Sen University
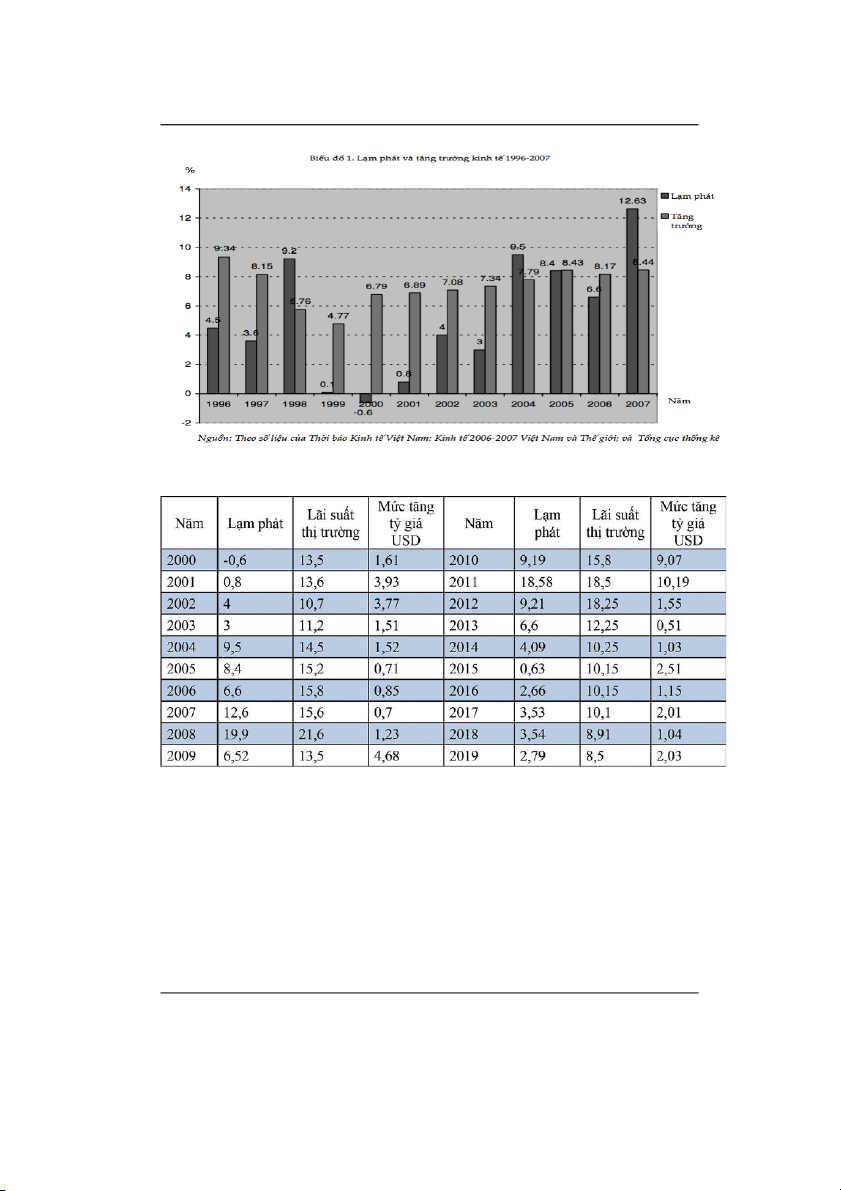
Figure 3 - Table of inflation and economic growth chart (1996-2007)
Figure 4 - Inflation data sheet
In the years 2000-2006, inflation was stable at single digit, interest rates were stable
at 13-15% per year. In the years 2007-2011, when inflation was at a high double-
digit rate, the interest rate increased from 18% to over 21%/year. Therefore, in the
period of 2000-2006. Applying the fixed anchor exchange rate mechanism, the
average inter-bank exchange rate announced by the SBV was kept around from
Final Report - International Payment Page | 3 Hoa Sen University
14,000 VND/USD to 16,000 VND/USD. In 2005, the SBV published the Ordinance
on Foreign Exchange and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) officially
recognized Vietnam to fully liberalize current transactions. In 2006, Vietnam's
foreign exchange market began to come under pressure from the process of
international economic integration. The amount of foreign currency poured into
Vietnam began to increase sharply. The World Bank and the IMF have warned the
SBV to increase the flexibility of the exchange rate in the context of increasing capital inflows into Vietnam.
The period 2007 to 2011. This is the period when the USD/VND exchange rate
fluctuates strongly. After Vietnam joined the WTO, the liberalization of the capital
account was expanded, leading to an increase in capital flows to Vietnam, which
greatly affected exchange rate fluctuations. Starting from April 2018, the amount of
loans in USD, the balance of payments due to the high trade deficit and the sharp
decrease of the total foreign exchange reserves created a strong demand for USD.
The State Bank continuously sold foreign currency to intervene when the official
exchange rate and the black market rate appeared with a large gap for a long time.
At the end of 2011, the SBV used many solutions to control and stabilize the market.
In the years 2012-2019, inflation dropped to a low level, averaging about 4%/year,
then the interest rate dropped significantly, averaging about 10%/year. Thus, in the
period 2000-2019, interest rates tend to move in a positive direction with inflation.
In the period from 2012 to 2019. The USD/VND exchange rate has been somewhat
more stable, the exchange rate management policy of the State Bank is more in line
with market movements. Monetary solutions of the State Bank have created positive
changes for the foreign currency market, the free market has almost stopped
working. The difference between the interbank exchange rate and the listed
exchange rate of commercial banks is narrowed (difference from 100 to 300
VND/USD), thereby reducing the psychology of holding foreign currency of organizations and individuals.
Final Report - International Payment Page | 4



