



















Preview text:
FACTS ABOUT THE US
- Name: United States of America (the United S USA, US., America, the States)
(Name Origin: America is named after the Italian explorer, Amerigo Vespucci)
-Located in the Western Hemisphere on the Continent of North America
- Located in North America , the country is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and to the east by
the Atlantic Ocean . Along the northern border is Canada and the southern border is Mexico .
- 50 states , a federal district ( Washington D.C ) , 5 major self governing territories , and various
possessions ( in the Pacific ocean and Caribbean sea )
Alaska & Hawaii do not share a contiguous boundary with the country .
Alaska is located to the northwest corner of North America , sharing its border with Canada .
Hawaii island is in the Pacific ocean . The world's third largest country by total area Land Area 9,147,593
km2 Water Area 685,924 km2 Total Area 9,833,517 km2 -Population -329,886,493
-Population Density 32.95 / km2
-The 3rd most populous country
-Largest Cities : ( by population ) New York City , Los Angeles , Chicago , Houston , Phoenix , Philadelphia
-Religions : Protestant 52 % , Catholic 24 % , others
-Government Type : Constitutional Federal Republic
- National Day : July 4 ( 1776 declared independence from Great Britain ) -Flag
-National Emblem : The Bald Eagle
-Great Seal of the United States : ( Found on the back of the US one - dollar bill , specific documents ,
including foreign treaties and presidential proclamations )
-The flag of the United States features thirteen equal horizontal stripes of red ( top and bottom )
alternating with white ; there is a blue rectangle in the upper hoist side corner bearing 50 small , white ,
five - pointed stars arranged in nine offset horizontal rows of six stars ( top and bottom ) alternating with
rows of five stars ; the 50 stars represent the 50 states ; the 13 stripes the 13 original colonies .
-Why was the Bald Eager adopted as the National Emblem ?
Because it is a species unique to North America . It has become the living symbol of the USA's strength ,
freedom , spirit and pursuit of excellence . Its image and symbolism have played a significant role in
American architecture , art , folklore and music
-What monument is a symbol of American freedom known around the world ?
One of the most iconic and recognizable structures in the world , becoming a very literal representation
of the American ideals for immigrants coming to the U.S. throughout history
Give me your tired , your poor , Your huddied masses yearning to breathe free , The wretched refuse of
your teeming shore . Send these , the homeless . tempest - tossed to me , I lift my lamp beside the golden door ! POLITICS
-a federal republic and a representative democracy .
-a founding member of the United Nations , World Bank , International Monetary Fund , Organization of
American States ( OAS ) , NATO , and other international organizations . It is a permanent member of the
United Nations Security Council . ECONOMY
-A highly developed country , the United States is the world's largest economy by nominal GDP , the
second - largest by purchasing power parity , and accounts for approximately a quarter of global GDP . –
-The United States is the world's largest importer and the second - largest exporter of goods , by value .
-Although its population is 4 % of the world total , it holds 31 % of the total wealth in the world , the
largest share of global wealth concentrated in a single country
-It is the foremost military power in the world , making up a third of global military spending , and is a
leading political , cultural , and scientific force internationally . Introduction
• The United States of America has been a democracy for more than 200 years .
• Issues that were important in its early years remain so today :
■ big government versus small government
■ individual rights versus group rights
■ free markets versus controlled trade and
■ connection with the world versus focusing on internal affairs . Early America
-The most recent Ice Age was about 35,000 years ago . Much of the world's
water was frozen into big sheets of ice . A land bridge - as wide as 1,500
kilometers - joined Asia and North America . By 12,000 years ago , humans lived
throughout much of what now are the Americas .
-The first " Americans " crossed the land bridge from Asia . Historians believe
that they lived in what now is Alaska for thousands of years . They moved south
into today's mainland United States . They lived by the Pacific Ocean in the
Northwest , in the mountains and deserts of the Southwest , and along the
Mississippi River in the Midwest .
-By the time the first Europeans arrived , about two million native people lived in
what now is the United States . Discovery of the Americas.
-August 3 , 1492 - Christopher Columbus set out on his first voyage with three
ships and a crew of 90 to find a westward route to the east .
• October 12, 1492 - Christopher Columbus reported to be the 1st European to
set foot on the New World ( Dominican Republic ) .
-He thought he came to India , so he called the people there Indians ( West Indians ) Colonial Period 1700-1799
• The first permanent European settlement in North America was Spanish . It
was built in St. Augustine in Florida .
• May 14 , 1607 - First permanent English settlement in what's now the United
States was established at Jamestown , Virginia .
• 13 British colonies to the north later formed the United States . Virginia and
Massachusetts were the two earliest .
-Most people who came to the British colonies in the 1600s were English .
Others came from The Netherlands , Sweden , Germany , France , Scotland , and
Northern Ireland . By 1790 , there were 2.5 million people .
-People came for different reasons . Some left their homes to escape war .
Others seek political or religious freedom . Some had to work as servants to pay
back the cost of their trip before gaining their freedom . Some , like black
Africans , arrived as slaves .
• The relationships between settlers and Native Americans ( also called Indians )
were good and bad . In some areas , the two groups traded and were friendly .
In most cases , as the settlements grew bigger , the settlers forced the Indians to move .
The Road to Independence Revolutionary war ( 1775-1783 )
• Britain's 13 colonies grew in population and economic strength during the 1700s .
• Colonists were angry with the British rules and policies for taking away their
rights , restricting their way of life and local authority . ( no settling new land ,
illegal to print paper money . provide food and housing for the royal soldiers )
➔ Intolerable Acts and united to oppose . ( Boston Tea Party ) .
• Boston became a center of growing American discontent with British rule . The American Revolution
and the war for independence from Britain began in Boston on April 19,1775
• George Washington of Virginia became the commander - in - chief of the Continental army from the colonial forces .
• Questions : The people could remain unequal citizens under a king , or they could live in an
independent country with hopes of liberty and happiness .
• The Second Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence at Philadephia on July 4 ,
1776. The Fourth of July became Independence Day in the United States .
• Thomas Jefferson was the main writer of the Declaration of Independence
• American forces decisively defeated the British at Yorktown , Virginia , in 1781. The war ended when a
peace treaty was signed in Paris on April 15 , 1783. In this treaty , Britain and other nations recognized
the United States as an independent nation .
The declaration of independence All men are created equal
The Treaty of Paris in 1783 : Britain recognized American independence Forming a National Government
• The Treaty of Paris turned the 13 colonies into states , but the job of becoming one nation remained .
It was a nation of 13 countries .
• In May 1787 , 55 delegates met in Philadelphia to discuss the new national government . They
proposed the Constitution of United States , a constitution describing a new form of government based
on separate legislative, executive , and judicial authorities
• All 13 states ratified the Constitution by 1790.
- Geoge Washington became the first president of the United States on April 30, 1789.
Westward Expansion , and Regional Differences
• The U.S. doubled in size when it bought the Louisiana Territory from France in 1803 and Florida from Spain in 1819 .
• The US achieved large amount of territory as a result of winning the Mexican war in 1848 , extending
the western border to the Pacific Ocean .
• Land was claimed from Native Americans As the country grew , differences among the states became
more obvious . The differences began to create problems .
Conflict within the United States
• In 1850 , the United States was a large country , full of contrasts . New England and the Middle Atlantic
states were the centers of finance , trade , shipping , and manufacturing . Their products include
lumber , machinery , and textiles . Southern states had many farms that used slave labor to grow
tobacco , sugar , and cotton . The Middle Western states also had farms , but they were worked by free men .
• North vs South . Disagreement on government and slavery . North : anti slavery Civil War
• The American Civil War started in April 1861. The South claims the right to leave the United States ,
and form its own Confederacy .
• President Lincoln led the Northern states . He was determined to stop the rebellion and keep the
country united . May 6 , 1861 - President Abraham Lincoln declares a state of insurrection in the southern states
• In 1865 the Confederacy surrendered , bringing an end to the Civil war . Slavery was abolished
throughout the US . More Americans died in the Civil War than in any other U.S. conflict .
• President Abraham Lincoln was assassinated less than a week after the South surrendered . Growth and Transformation
• The United States changed after the Civil War . The frontier became less wild . Cities grew in size and
number . More factories , steel mills , and railroads were built .
• Immigrants arrived in the United States with dreams of better lives
• This was the age of inventions . Alexander Graham Bell developed the telephone . Thomas Edison
invented the light bulb . George Eastman made the moving picture , later called a movie .
• Railroad was built to help the expansion
• In 1914 , Germany , Austria - Hungary , and Turkey fought Britain , France , Italy , and Russia . Other
nations joined the conflict , and the war reached across the Atlantic Ocean to affect the United States .
• The British and German navies blocked American shipping . In 1915 , almost 130 Americans died
when a German submarine sank the British ocean liner Lusitania . President Woodrow Wilson
demanded an end to the German attacks . They stopped but started again in 1917 .
• The United States declared war . More than 1,750,000 U.S. soldiers helped to defeat Germany and
Austria Hungary . The war officially ended on November 11, 1918 , when a true was signed at Versailles in France . 1920s Prosperity .
• After the war the United States enjoyed a period of prosperity . Many families purchased their first
automobile , radio , and refrigerator . They went to the movies .
• Women finally won the right to vote in 1920 .
After nearly 100 years of related , demonstrations , and sit - ins , women of the United States were
officially granted the right to vote after the 19th Amendment was ratified on August 26, 1920 . Great depression 1929 - 1933
• The worst economic crisis to happen in the United States occurred when the stock market crashed in
October 1929 , resulting in the Great Depression . The New Deal and World War II
• President Roosevelt believed that democracy had failed in other countries because of unemployment
and insecurity . In the early 1930s , he proposed a " New Deal " to end the Great Depression
• The New Deal included many programs . Bank accounts were insured . New rules applied to the stock
market . Workers could form unions to protect their rights . Farmers received financial aid for certain
crops . The government hired people to plant trees , clean up waterways , and fix national parks . Skilled
workers helped build damage and bridges . The government provided flood control and electric power
for poor areas . The Social Security system helped the poor , disabled , and elderly . 1947-1991 THE COLD WAR
a period of merit tension between the Soviet Union and the United States and their respective allies , the
Eastern Bloc and the Western Bloc after World War II . There was no large scale fighting directly
between the two superpowers , but they each supported major regional conflicts based around the
ideological and protesting for global influence by the two powers.
• The United States remains neutral while Germany , Italy , and Japan attack other countries .
• The United States refused to sell oil to Japan
• On December 7, 1941 , Japan attacked the American fleet at Pearl Harbor , Hawaii . The United States
declared war on Japan . Because Germany and Italy were allies of Japan , they declared war on America.
• American industry focused on the war effort. Women built many of the 300,000 aircraft , 5,000 cargo
ships , and 86,000 tanks while the men became soldiers .
• President Harry S. Truman decided to use the atomic bomb on two Japanese cities- Hiroshima and
Nagasaki - to bring the war to an end without an invasion. World War II was finally over in August 1945 . World War II
• World War II officially begins in September 1939 after Germany invades Poland . The United States
didn't enter the war until after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941 .
• On August 6 and August 9, 1945, the United States dropped an atomic bomb on the Japanese cities of
Hiroshima and Nagasaki, effectively ending World War II. KOREA WAR & VIETNAM WAR
• After World War II , an agreement was reached to divide Korea Into two parts : a northern half to be
controlled by the Soviet Union and a southern half to be controlled by the United States .
• 1950-1953 us troops fought in the Korean War
• The Vietnam War was a nearly 20 - year battle ( November 1 , 1955 April 30 , 1975 ) . North Vietnam
won the war and Vietnam became a unified country . The Cold War
• The competition to the moon
• Richard Nixon and the policy of Vietnamization
• Demonstrations protested American involvement on American college campuses
• In July of 1969 astronaut Nail Armoto stepped out of Apollo 11 and on to the moon surface U.S. - CHINA TRADE WAR
• an ongoing economic conflict between China & the U.S.
• In July 2018 , US President Donald Trump followed through on months of threats to impose sweeping
tariffs on China for its unfair trade practices .
• back - and - forth negotiations , a tit - for - tat tariff war
Civil rights in the late 1950s
“If you can't fly , then run ,
if you can't run , then walk ,
if you can't walk , then crawl , but whatever you do ,
you have to keep moving forward .” -Martin Luther King Jr.
• Martin Luther King, Jr. , who had won the Nobel Peace Prize .
• From 1954-1968 , the African American Civil Rights movement took place , especially in the Southern
states . Fighting to put end to racial segregation and discrimination , the movement increased in the 1964 Civil Right Act.
America Cultural
Six Basic American Cultural Values
• One of the most interesting questions about the United States is what makes people " American " ?
With immigrants arriving from all over the world with vastly different cultural traditions , values , and
customs , what holds the country together ? And how did a nation of such diversity produce a
recognizable national identity ? " we all share a common set of values that make us American ... We are
by the rights we have ..... Our rights are our history , why the first European settlers came here and why
millions more have come here since ."
• Historically , the United States has been viewed as " the land of opportunity , " a place where
immigrants could have individual freedom , an equal chance for success , and the ability to have a better
standard of living . In order to have these benefits , however , they had to take care of themselves ,
compete with others , and work hard to fashion a new life . In time , their experiences led to the
development of the core American cultural values that still shape America today .
• The value system that has allowed the United States to assimilate millions of people from diverse
cultures all over the world and create a unique , enduring American identity . There are three pairs of
paid values consisting of three reasons / benefits why immigrants have come ( and still do ) to the United
States and three prices that are for these benefits . big will
RELATIONSHIP : BENEFITS & PRICES
• Individual freedom and self - reliance
• Equality of opportunity and competition
• Material wealth ( American dream ) and hard work
Individual Freedom and the price for that is Self - Reliance . We cannot be truly free if we cannot take
care of ourselves and be independent . Equality of Opportunity , and the price for that is Competition .
If everyone has an equal chance for success , then we have to compete . The American Dream , the
opportunity for a better life and a higher standard of living . The price for the American Dream has been Hard Work . RIGHTS & RESPONSIBILITIES
Americans believe that people have the right to individual freedom , equality of opportunity , and the
promise of material success, but these all require significant responsibility : self - , a willingness to compete , and hard work.
The relationship among these values - the rights and the responsibilities - creates the fabric of the
American society . It is this fabric that defines the American Dream - the belief that if people take
responsibility for their lives and work hard , they will have the individual freedom to pursue their
personal goals and a good opportunity to compete for success .
It is important to note that these six values are cultural values and not moral values , or even personal
ones . They are the foundation of our democratic nation . Rooted in the beliefs and visions of our
Founding Fathers and reinforced by historical experience , these cultural values are what distinguishes
our country from all others . They are what make us " Americans . "
American Core Beliefs and Values
There are certain ideals and values , rooted in the country's history , which many Americans share .
These are : FREEDOM , INDIVIDUALISM , PRAGMATISM , VOLUNTEERISM , MOBILITY , PATRIOTISM , PROGRESS , AMERICAN DREAM .
FREEDOM - Americans commonly regard their society as the freest and best in the world . Americans '
understanding of freedom is shaped by the Founding Fathers ' belief that all people are equal and that
the role of the government is to protect each person's basic " inalienable " rights . The U.S.
Constitution's Bill of Rights assures individual rights, including provisions for freedom of speech , press
and religion. No one single church dominates or controls in the US , there is a religious diversity .
INDIVIDUALISM - Americans ' notion of freedom focuses on the individual , and individualism has
strong philosophical roots in America . Thomas Jefferson believed that a free individual's identity should
be held sacred and that his or her dignity and integrity should not be violated . Individualism ,
understood not only as self reliance but also as economic self - sufficiency .
IDEALIZING WHAT IS PRACTICAL In America what works is what counts . Inventiveness was necessary for
survival . This " can - do " spirit is something Americans are proud of today . They like to think they are
natural - born do - it yourselfers SELF - HELP
VOLUNTEERISM - means people helping people through privately initiated , rather than government -
sponsored . Six out of ten Americans are members of a volunteer organization . Volunteerism reflects
Americans ' optimistic pride in their ability to work out practical solutions themselves . tivate to Sett
MOBILITY / Change In the American mind , change is seen as an indisputably good condition . Change is
strongly linked to development , improvement , progress , and growth . As a nation of immigrants ,
Americans have shared from the beginning the assumption that the practical solution to a problem is to
move elsewhere and make a fresh start . Mobility in America is not a sign of aim warmer but optimism
( hoping to secure a better job or enjoy a climate
PATRIOTISM - Americans develop relatively little attachment to place ( mobility ) In this century , national
pride has become generally stronger than regional pride . The prevalence of patriotic symbols : flags fly
in suburban neighborhoods , bumper stickers announce " I'm proud to be American " , the national
anthem is played at every sporting event
PROGRESS - directly associated with the idea of freedom is the ideal of progress . In this immigrant
society , progress is personally measured as family progress over generations . Many Americans can
boast that with each succeeding generation since their first arrived ancestors , the family's status has
improved . The attainment of the vision of one's birth is part of the American Dream . WHAT IS THE AMERICAN DREAM ?
"The American Dream is that dream of a land in which life should be better and richer and fuller for
everyone, with the opportunity for each according to ability or achievement.”
The U.S. Economy INTRODUCTION
• A highly developed country , the United States is the world's largest economy by nominal GDP , the
second - largest by purchasing power parity , and accounts for approximately a quarter of global GDP .
• The United States is the world's largest importer and the second - largest exporter of goods , by value .
• Although its population is 4 % of the world total , it holds 31 % of the total wealth in the world , the
largest share of global wealth concentrated in a single country
• It is the foremost military power in the world , making up a third of global military spending , and is a
leading political , cultural , and scientific force internationally . An Overview
The United States has a mixed economy with government playing an important role along with private
enterprise . That means it works as a free market economy in consumer goods and business services
and as a command economy in defense , retirement programs , some aspects of medical care , and other
areas . The U.S. Constitution created and now protects America's mixed economy .
Fast Facts About the U.S. Economy
There are a few key components of the U.S. economy . These different economic indicators help us
understand how the U.S. economy is doing .
• Gross domestic product ( GDP ) : $19.5 trillion ( annualized nominal rate for second quarter , or Q2 , 2020 )
• GDP growth rate : -31.7 % ( annualized rate for Q2 2020 )
• Real GDP per capita : $52,387 ( Q2 2020 )
• Gross national income : $21.6 trillion PPP dollars ( 2019 )
• Unemployment rate : 8.4 % for August 2020
• Minimum wage : $7.25 per hour
• Currency : United States Dollar
• Euro - to - dollar conversion : $1.18 as of August 20207
• Core inflation rate : 1.7 % year - over - year core rate for August 2020
• The U.S. economy remains the largest and most important in the world . The American dollar is still
the top reserve currency , making up 61.82 % of the world's reserves .
• With a total market capitalization of $30.44T ( trillion ) , the U.S. stock market is many times more
valuable than that of any other country .
• Your individual experience of the American economy depends on where you live . Some states like
California have enormous and dynamic economies , but others like Arkansas and Mississippi are lagging behind .
• There are significant problems looming on the horizon . The U.S. national debt is now over $22T , and
personal debt tops $70K in several states .
• The U.S. government collects $1.03T in taxes every year , but that's nowhere near enough money to
cover all of the government's expenditures .
Basic Ingredients of the U.S. Economy natural resources
• The United States is rich in mineral resources and fertile farm soil , and it is blessed with a moderate
climate . It also has extensive coastlines on both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans , as well as on the Gulf
of Mexico . Rivers flow from far within the continent , and the Great Lakes -- five large , inland lakes
along the U.S. border with Canada -- provide additional shipping access . These extensive waterways
have helped shape the country's economic growth over the years and helped bind America's 50
individual states together in a single economic unit.
• labor , which converts natural resources into goods .
+ The number of available workers and , more important , their productivity help determine the health
of an economy . While its history , the United States has experienced steady growth in the labor force ,
and that , in turn , has helped fuel almost constant economic expansion .
+ Today , Americans consider " human capital " a key to success in numerous modern , high - technology
industries . As a result , government leaders and business officials increasingly stress the importance of
education and training to develop workers with the kind of nimble minds and adaptable skills needed in
new industries such as computers and telecommunications . Entrepreneurship .
• An ability some people have to accept risks and combine factors of production in order to produce
goods and services . Entrepreneurs organize the various components necessary to operate a business .
• Entrepreneurship involves not only merely the organization and management of a business , but also
an individual's willingness to accept risks in order to make a profit .
• CEO don't have final control over the company and they do not make decisions that involve risking the company's resources IMPORTANT TERMS / INDICATORS
The best way to estimate the size of the U.S. economy is with gross domestic product , or GDP . GDP
measures everything produced in the United States , regardless of whether it was made by U.S. citizens
and companies or by foreigners
There are four components of GDP . Consumer spending is about 70% of the total . Business investment
includes manufacturing , real estate construction , and intellectual properties . Government spending
includes federal , state , and local expenditures . The fourth component is net exports , which includes
exports that add to the nation's economy , and imports , which subtract from it .
The U.S. has a trade deficit , which means it imports more than it exports . Its biggest export is also its
most significant import , and that's oil . U.S. budget deficit ?
-> The government spends more money than it takes in . 2. Does it matter ? -> Debtor , inflation ...
-> Affects national saving ... Inflation and Deflation
Short - term inflation happens when demand is greater than supply and prices go up . Once inflation
occurs , people begin to expect ever - higher prices . Consumers buy now before prices go up more in
the future . This increases demand and causes higher prices . Long term inflation generally happens
because of an increase in the money supply over time .
Deflation is the opposite of inflation . It occurs when prices fall , creating crashes in the stock or housing
markets , as well as other financial crises . It takes place during the contraction phase of the business cycle .
Characterristics of the American Economy
• Limited role of government • Freedom of enterprise • Freedom of choice • Profit incentive • Competition • Private property Limited Role of Government
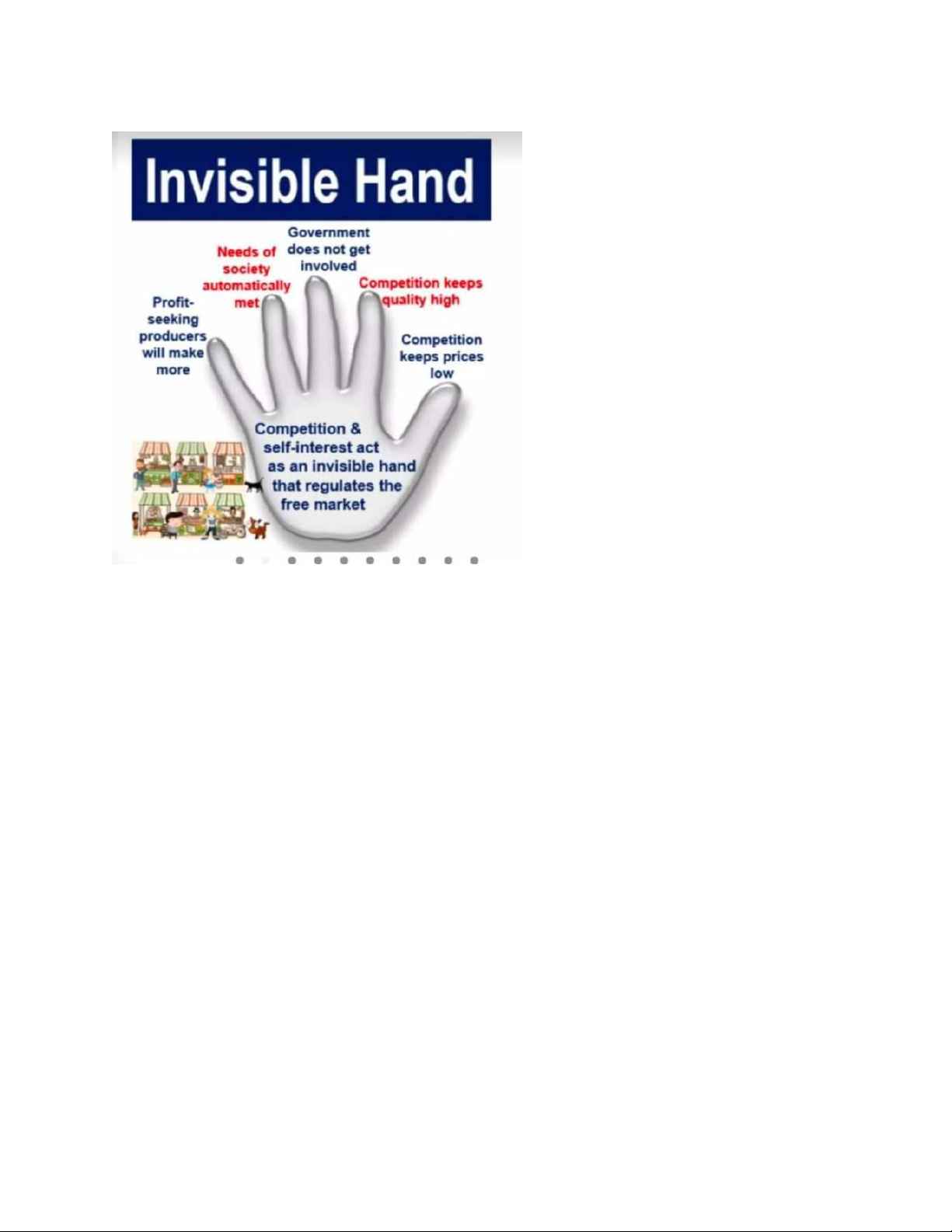
• Economist Adam Smith in 1776 describes a system in whi
ch the government has little to do with a
nation's economic activity . He said that individuals left on
their own would work for their own self
interest . In doing so , they would be guided as if by an " in
v isible hand " ( market force ) to use
resources efficiently and thus achieve the maximum good fo r society .
• Smith's version of the ideal economic system is called cap italism , another name for the market
system . Pure capitalism has also been called a laissez - fair e system . This French term means " let
[ people ] do [ as they choose ] / leave it alone . Freedom of Enterprise
• The American economy , besides being termed capitalist , is also known as a free - enterprise system .
This term emphasizes that individuals are free to own and control the factors of production .
• The American free enterprise system emphasizes private ownership . Private businesses produce most
goods and services , and almost two - thirds of the nation's total economic output goes to individuals for
personal use ( the remaining one - third is bought by government and business ) . The consumer role is
so great , in fact , that the nation is sometimes used as having a " consumer economy ."
• The government places certain legal restrictions on freedom of enterprise . ( For instance , just because
you know how to fix cars does not mean that you can set up an automobile repair business in your backyard.
Zoning regulations , child labor laws , hazardous waste disposal rules , and other regulations Amit free enterprise to
protect you and your neighbors . )
• Federal agencies regulate the quality of various foods and drugs , watch over the nation's money and
banking system , inspect workplaces for hazardous conditions , and guard damage to the environment .
• The federal government also uses tax revenues to provide social programs such as Social Security and
Medicare . State and local governments have expanded their roles in such areas as education , job
training , recreation , and care for the elderly . SHIFT ECONOMY
• The population and the labor force have significantly shifted away from farms to cities , from fields to
factories , and , above , to service industries . In today's economy , the providers of personal and public
services far outnumber producers of agricultural and manufactured goods . As the economy has grown
more complex , statistics also reveal over the last century a sharp long - term trend away from self -
employment towards working for others .
• Major products are machinery , automotive products , aircraft , chemical
• Since 1971 , the U.S. has imported more than exported .
• There is a shift in production from manufacturing to services
The Characteristics of American Business
• Businesses are directly / owned profit by private individuals / groups
• There are also organizations
• Public , owned institutions
• Nonprofit ( churches , charities etc )
How Business Competition Reinforces Other Values
• Business institutions are at the heart of American life
• Business is based on the ideal of competition which is the major source of progress and prosperity
• Thus competitive business institutions are reputable
• Competition protects freedom by preventing monopoly
• Quality of goods and services is guaranteed by competition
• Competition in business also promotes equality of opportunity •
Business competition is seen as an alternative to inherited privilege
• Business competition promotes hard work
• The harder working person is likely to " win " .
• However , many Americans distrust big business - putting profits before people
• Need for government regulation The Dream of Getting Rich
• Most wealthy Americans have achieved their wealth through successful business
• Often they started with very little
• Americans preferred business to farming because offered more opportunities to get rich
• Business is seen as benefiting the whole nation -through competition everyone can become rich
Two kinds of business heroes : They reflect American traditional values : Competition , hard work
, individual freedom , self opportunism , material wealth , equality of opportunity Entrepreneurs :
➔ are those who built great industries : steel , railroad , oil refining ...
➔ they start with almost nothing and end up with virtually everything .
➔ they are everyone's perfect heroes as they reflect the American dream in its purest meaning . Organization man / woman
• They run the businesses that are already established by others .
• With power and wealth , they are also models of success in the U.S. .
• But they don't have a strong hero image as entrepreneurs .
CEO's are not very popular - e.g. overpaid , self serving Many CEO's have abused the businesses they managed , and their employees
American Business in the Global Marketplace
• Until the 20th century , most American business took place in America
• Now , American business has become globalized
• The US is the largest market in the world ( a consumer society )
• The US is also a producer - but is finding it hard to compete with cheap foreign labor
The Changing American Workforce
• Traditionally, American business was dominated by white males
• Recently , more women have entered the workforce - now 50 %
• Few women are in senior positions ( 10-15 % ) although are equally qualified The Changing American
Workforce Traditionally , American business was dominated by white males .
• Women generally receive less pay
• Workers who want to succeed are under pressure to put work first and family second
• Women earn 78% of men's salary (on average)
• Minorities are also discriminated against
• New immigrants are changing the American workforce - less discrimination in future . Immigration Introduction
The United States prides itself on being a nation of immigrants , and the nation has a long history of
successfully , absorbing people from across the globe . The successful integration of immigrants and
their children contributes to economic vitality and to a vibrant and ever - changing culture . have offered
opportunities to immigrants and their children to better themselves and to be Americans fully
incorporated into the U.S. society , and in exchange immigrants have become Americans -embracing an
American identity and citizenship , protecting the United States through service in its military , fostering
technological innovation , harvesting its crops , and enriching everything from the nation's cuisine to its
universities , music , and art . Early days
• From its earliest days , America has been a nation of immigrants , starting with its original inhabitants ,
who crossed the land bridge connecting Asia and North America tens of thousands of years ago . They
were Native American ancestors.
• The United States experienced major waves of immigration during the colonial era , the first part of the
19th century and from the 1880s to 1920. Many immigrants came to America seeking greater economic
opportunity , while some , such as the Pilgrims in the early 1600s , arrived in search of religious freedom
, and immigrants who arrived against their will as enslaved people from West Africa .
• A larger share of immigrants came to America seeking economic opportunities . However , because
the price of passage was steep , an estimated one - half or more of the white Europeans who made the
voyage did so by becoming indentured servants . Although some people voluntarily indentured
themselves , others were kidnapped in European cities and forced into servitude in America .
Additional , thousands of English convicts were shipped across the Atlantic as indentured servants .
• Some of America's first settlers came in search of freedom to practice their faith . In 1620 , a group of
roughly 100 people later known as the Pilgrims fled religious persecution in Europe and arrived at
present - day Plymouth , Massachusetts , where they established a colony . They were soon followed by
a larger group seeking religious freedom , the Puritans , who established the Massachusetts Bay Colony .
By some estimates , 20,000 Puritans migrated to the region between 1630 and 1640 .
Immigration in the Mid - 19th Century .
• Another major wave of immigration occurred from around 1815 to 1865. The majority of these
newcomers hailed from Northern and Western Europe . Approximately one - third came from Ireland ,
which experienced a massive famished in the mid - 19th century . In the 1840s , almost half of America's
immigrants were from Ireland alone
• During the mid - 1800s , a significant number of Asian immigrants settled in the United States . Lured
by news of the California gold rush , some 25,000 Chinese had migrated there by the early 1850s .
• Also in the 19th century , the United States received some 5 million German immigrants . Many of
them journeyed to the present - day Midwest to buy farms or congregated in such cities as Milwaukee ,
St. Louis and Cincinnati . In the national of 2000, more Americans claim German ancestry than any other group .
• The influx of newcomers leads in anti immigrant sentiment among certain factions of America's native -
born , predominantly Anglo Saxon Protestant population . The new arrivals were often seen as
unwanted competition for jobs , while many Catholics - especially the Irish - experienced discrimination for their religious beliefs .
• Following the Civil War , the United States experienced a depression in the 1870s that contributed to a slowdown in immigration .
Ellis Island and Federal Immigration Regulation .
• Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 : The first significant pieces of federal legislation aimed at restricting
immigration which banned Chinese laborers from coming to America .
• To handle the ever - increasing influx of newcomers , in 1890 , President Benjamin Harrison ( 1833-
1901 ) designated Ellis Island , located in New York Harbor near the Statue of Liberty , as a federal
immigration station . More than 12 million immigrants entered the United States through Ellis Island
during its years of operation from 1892 to 1954 .
European Immigration : 1880-1920
• Between 1880 and 1920 , a time of rapid industrialization and urbanization , America received more
than 20 million immigrants . Beginning in the 1890s , the majority of arrivals were from Central , Eastern and Southern Europe .
In that decade alone , some 600,000 Italians migrated to America , and by 1920 more than 4 million had entered
the United States . Jews from Eastern Europe fleeing religious persecution also arrived in large numbers ; over 2
million entered the United States between 1880 and 1920 .
• The peak year for admission of new immigrants was 1907 , when approximately 1.3 million people
entered the country legally . Within a decade , the outbreak of World War I ( 1914-1918 ) caused a decline in immigration
• In 1917 , Congress enacted legislation requiring immigrants over 16 to pass a literacy test , and in the
early 1920s immigration quotas were established .
• The Immigration Act of 1924 created a quota system that restricted entry to 2 percent of the total
number of people of each nationality in America as of the 1890 national census - a system that favored
immigrants from Western Europe - and prohibited immigrants from Asia .
The Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965
• Immigration plummeted during the global depression of the 1930s and World War II ( 1939-1945 ) .
Between 1930 and 1950 , America's foreign - born population decreased from 14.2 to 10.3 million , or
from 11.6 to 6.9 percent of the total population , according to the U.S. Census Bureau .
• After the war , Congress passed special legislation enabling supporters from Europe and the Soviet
Union to enter the United States . Following the communist revolution in Cuba in 1959 , hundreds of
thousands of refugees from that island nation also gained admittance to the United States .
• In 1965 , Congress passed the Immigration and Nationality Act , which did away with quotas based on
nationality and allowed Americans to sponsors from their countries of origin . As a result of this act and
subsequent legislation , the nation experienced a shift in immigration patterns . Today, the majority of
U.S. immigrants come from Asia and Latin America rather than Europe . Refugees
• Refugees compose about one - tenth of the total annual immigration to the United States , though
some large refugee populations are very prominent . Since World War II , more refugees have found
homes in the U.S. than any other nation , and more than two million refugees have arrived in the U.S. since 1980 .
• Historically , the total number of refugees coming to the U.S. has fluctuated with global events and U.S. priorities .
• Since 1980 , 55 % of refugees have come from Asia , a far higher share than from Europe ( 28 % ) ,
Africa ( 13 % ) or Latin America ( 4 % ) .
• Refugee admissions into the U.S. have significantly decreased during Donald Trump's presidency .
• Trump's Policy Could Alter the Face of the American Immigrant
• New legal residents carry their own weight , without prejudice or favor . Yet the new rule for weeding
out those who might be a drain on taxpayers will certainly hardly disadvantage people from Latin
America , Africa and parts of Asia .
• More green cards will go to immigrants with a good education and a measure of self - sufficiency ;
fewer will be granted simply because someone has a family member in the United States . FACTS AND FIGURES
• One in seven U.S. residents are an immigrant
• In 2018, 44.7 million immigrants (foreign-born individuals) constitute 14 percent of the national population.
• The top countries of origin for immigrants were Mexico ( 25 percent of immigrants ) , India ( 6
percent ) , China ( 5 percent ) , the Philippines ( 4 percent ) , and El Salvador ( 3 percent ) .
• In 2018, 39.4 million people in the United States ( 12 percent of the country's population ) were native
- born Americans who had at least one immigrant parent.
• " More than any other nation on Earth , America has constantly drawn strength and spirit from wave
after wave of immigrants . In each generation , they have proved to be the most restless , the most
adventurous , the most innovative , the most industrious of people . Bearing different memories ,
honoring different heritages , they have all strengthened our economy , enrich our culture, renew our
promise of freedom and opportunity for all... " Bill Clinton
• “It says something about our country that people around the world are willing to leave their homes
and leave their families and risk everything to come to America. Their talent and hard work and love of
freedom have helped make America the leader of the world. And our generation will ensure that
America remains a beacon of liberty and the most hope fill society this world has ever known ." George W. Bush
U.S. Government and Politics BACKGROUND
• The Declaration of Independence 1776
• The American Constitution 1790 The Constitution outlines the structure of the national government
and specifies its powers and activities, and defines the relationship between the national government
and individual state governments.
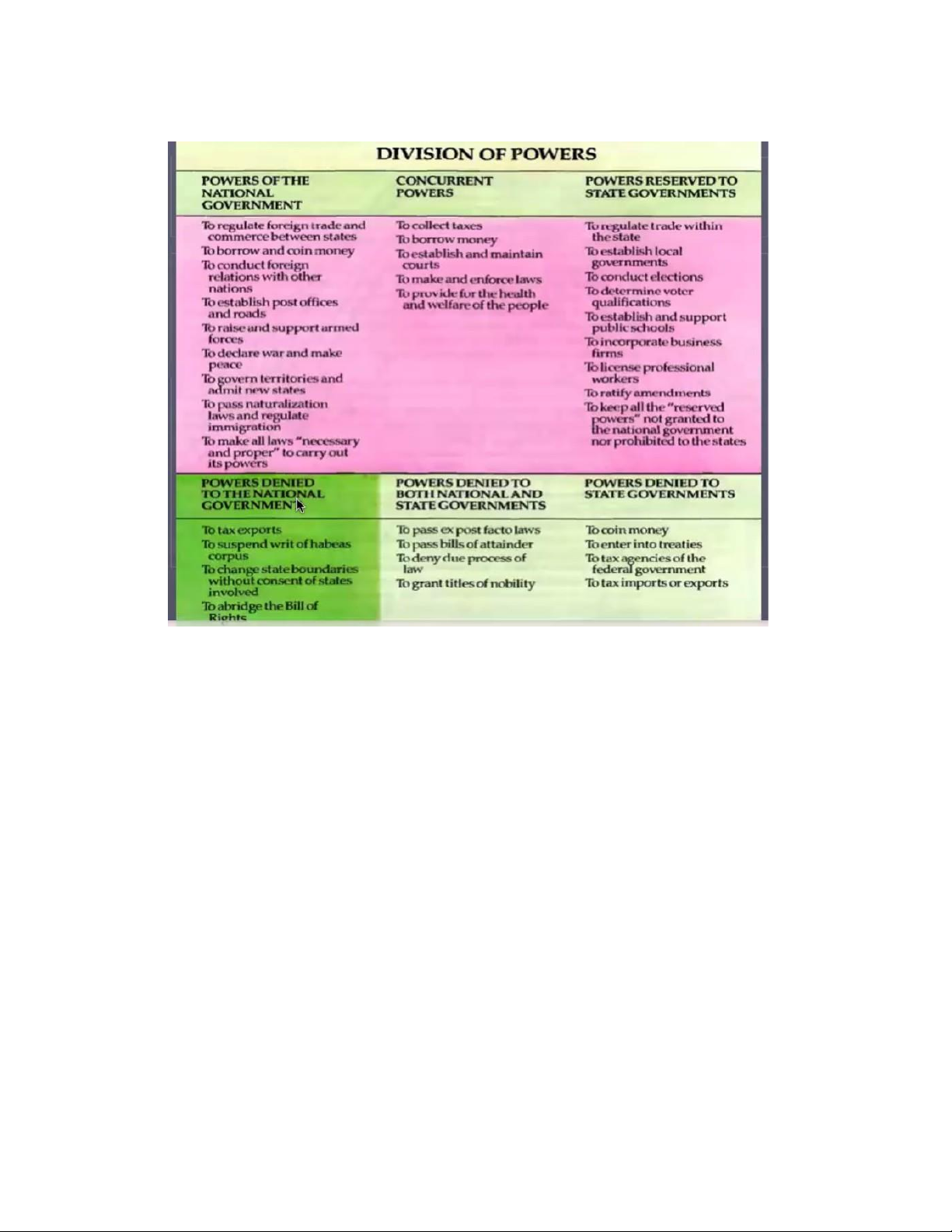
• Power is shared between the national and state (local) governments. Within each state are counties,
townships, cities and villages, each of which has its own elective government. Form of government
• The US = representative democracy ▪ These eat f
ures created by the Constitution to guard again tyranny : - ederal f organization of government - separ
ation of power among different branches system of checks and balance to r estrict the power of each branch State and Federal System
• Historically state and local government came first .
• The states have their own legislative , executive and judicial institutions
• State and local government control important areas like : - Highways - State income tax – -
Public schools and universities – -
Police and fire departments – -
Regulate business and supervise commercial affairs • The ederal F
system of government controls : -
Foreign policy , defense and monetary policy -
Areas that cannot be regulated locally and statewise : interstate commerce , inter state
crime , interstate environmental problems etc.
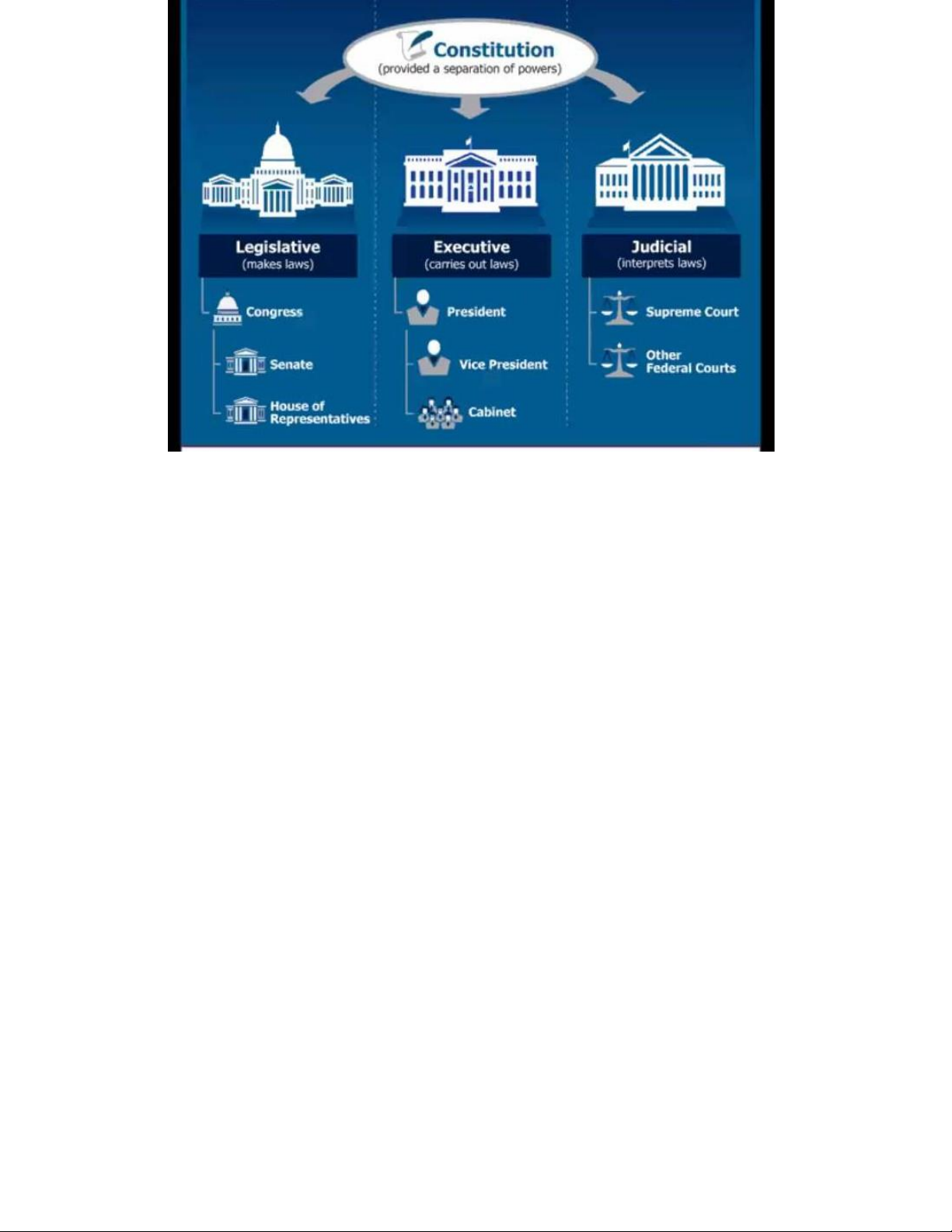
How the U.S. Government Is Organized .
• The Constitution of the United States into three branches to make sure no individual or group will have too much power :
> Legislative - Makes laws ( Congress , divide of the House of Representatives and Senate )
> Executive - Carries out laws ( president , vice president , Cabinet , most federal agencies )
> Judicial - Evaluate laws ( Supreme Court and other courts )
Legislative Branch of the U.S. Government
• The legislative branch drafts proposed laws, confirms or rejects presidential nominations for
heads of federal agencies , federal judges , and the Supreme Court , and has the authority to
declare war. This branch includes Congress (the Senate and House of Representatives) and
special agencies and offices that provide support services to Congress. American citizens have
the right to vote for Senators and through free , confidential ballots. CONGRESS
Congress is composed of two parts :
• Senate (Thượng Viện) - There are two Senators per state , totaling 100 Senators. A Senate term
is six years and there is no limit to the number of terms an individual can serve .
• House of Representatives (Hạ Viện) - There are 435 representatives , which are divided among
the 50 states in proportion to their total population. There are additional non voting delegates
who represent the District of Columbia and the territories. A Representative serves a two - year
term , and there is no limit to the number of terms an individual can serve.
Executive Branch of the U.S. Government
• The executive branch carries out and enforces laws . It includes the president , vice president ,
the Cabinet , executive departments , independent agencies , and other boards , commissions , and committees .
• American citizens have the right to vote for the president and vice president through free , confidential ballots .
Key roles of the executive branch
• President - The president leads the country . He or she is the head of state , leader of the
federal government , and O Commander in Chief of the United States armed forces . The
president serves a four - year term and can be dedicated no more than two times .
• Vice president - The vice president supports the president . If the president is unable to serve ,
the vice president becomes president . The vice president can be and serve an unlimited
number of four - year terms as vice president , even under a different president .
• The Cabinet - Cabinet members serve as advisors to the president . They include the vice
president , heads of executive departments , and other high - ranking government officials .
Cabinet members are nominated by the president and must be approved by a simple majority of
the Senate - 51 votes if all 100 Senators vote .
Power of president 5 major roles
• Chief executive : appoints secretaries of major departments making up cabinet and senior officials of agencies
• Head of state : represents the country
• Chief diplomat : appoints foreign ambassadors , makes treats with other nations .
• Commander in chief of military • Legislative leader
The president and law enforcement operate separacery unique feature
Judicial Branch of the U.S. Government
• The judicial branch interprets the meaning of laws , laws to individual cases , and determines
whether the president's laws of the Congress or actions of the violate the Constitution . It is
comprised of the Supreme Court and other federal courts . Judicial branch
• Function : to determine whether laws of the Congress or actions of the president violate the Constitution • Structure : - headed by the Supreme court -
under the Supreme court is state and federal courts -
Supreme court members : 9 members appointed by the president and serve for a life tim
• The Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States . The Justices of the Supreme
Court are nominated by the president and must be approved by the Senate .
• Nine members make up the Supreme Court - a Chief Justice and eight Associate Justices .
There must be a minimum or quorum of six Justices to decide a case .
• If there is an even number of Justices and a case results in a tie , the lower court's decision stands .
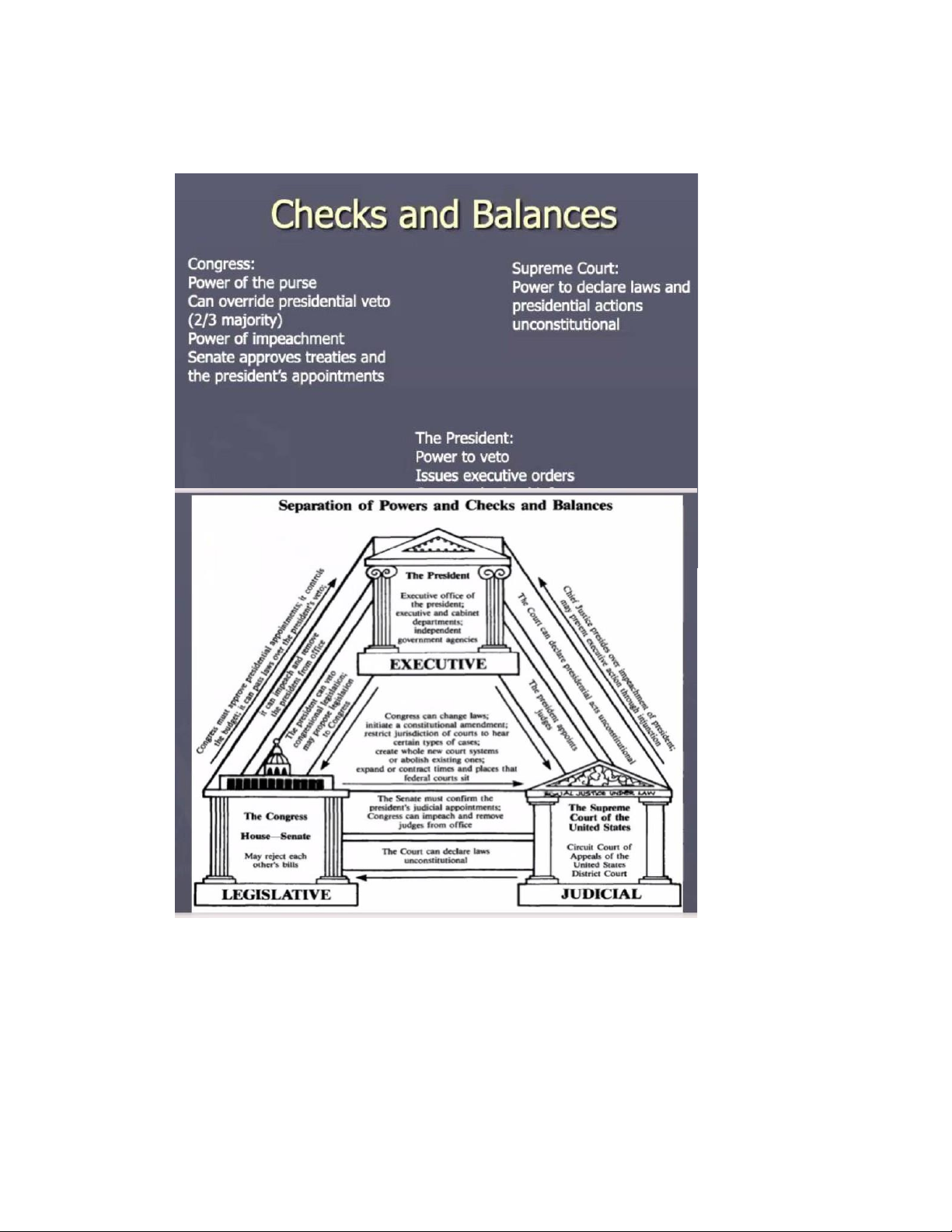
• There is no fixed term for Justices . They serve until their death , retirement , or removal in exceptional circumstances . Checks and balances
• Each branch checks and limits the power of the other branches through checks and balances system
• With this system , no branch has the superior power and the Constitution effectively ensures
that the Government power will not be usurped by a small powerful group of a few leaders .
THE SYSTEM OF CHECKS AND BALANCES
Each branch of government can change acts of the other branches :
✓ The president can veto legislation created by Congress and nominates he ads of federal agencies .
✓ Congress definitively or rejects the president's nominees and can remove the president from
office in exceptional circumstances .
✓ The Justices of the Supreme Court , who can overturn unconstitutional la ws , are nominated
by the president and confirmed by the Senate .
Two party system : Democrats and Republicans
• Characteristics of the two parties :
The two parties tend to be similar : both support the same political and economic goals ;
neither seeks to shake the foundation of US economy or social structure .
They propose diferent means of achieving similar goals :
+ democrats : believe that state and federal governments should provide economical and social help for needers
+ Republicans : think that social programs are too expensive ; tend to favor big businesses and
private enterprises , and want to limit the role of the government The role of the parties
• To organize the party's National Convention which decides who will be the candidate for
president and vice president .
• In the house of Representative and Senate , the major party will control the most powerful
committees , who decide what laws are made and how the administration spends its money . Minor parties
• Any party other than the two major parties can be called a third party
• No third party has ever achieved the control of the White House .
• In most cases , they have been assimilated or have just fade away
• Their most important role is to influence policy on one or more issues .
• Example : Socialist Labor party , American Independent party , Green parky ... Election system
• “ Winner take all ” system : only one candidate - the one with more votes is election to a
given office in one district .
• Indirect election : - the electoral college : Representatives of the people in presidential
elections . 270/538 electoral votes guarantee the Presidency
Elections and Political Parties
• Winner - take - all - election system • The Electoral College
• Two party system- both appealing to the middle of the political spectrum
• Balancing the ticket ( President and Vice president )
• Voting patterns : splitting the ticket
• Voting for individuals rather than party slate The Electoral College
• Representatives of the people in presidential elections
• 534 electors , corresponding to the numbers of Representatives and Senators
• 270 electoral votes guarantee the Presidency
• Each state votes as a single block ( minus Nebraska and Maine ) winner takes all
• Importance of Swing States and the big states Interest groups
• Are organized by people who want to influence public policy decision on special issues such
as the environment , social issues , peace ...
• Have the desire to sway public opinion and political policy through -
press , radio , and television -
letters , phone calls , hold public meetings and sponsorship of newspaper ads . -
Largest organization : Labor union , business group , farm group and professional group lobbyists
• A lobbyist is a lawyer or a former legislator , who -
Specializes the interest he or she represents -
Possesses an insider's view of the lawmaking process 50
• A lobbyist works for interest groups -
By keeping them informed about proposed legislation -
By talking to decision makers about their group's concerns