






Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337 N. GREGORY MANKIW PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS Eight Edition CHAPTER The Theory of Consumer Choice Premium PowerPoint Slides by:
Modified by Hoang Anh Tuan V. AndreeaCHIRITESCU Eastern Illinois University 1 lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
Look for the answers to these questions:
How does the budget constraint represent the
choices a consumer can afford?
How do indifference curves represent the consumer s preferences?
What determines how a consumer divides her resources between two goods?
How does the theory of consumer choice
explain decisions such as how much a
consumer saves, or how much labor she supplies? lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337 Introduction People face tradeoffs.
Buying more of one good leaves less income to buy other goods
Working more hours means more income and
more consumption, but less leisure time
Reducing saving allows more consumption
today but reduces future consumption This
chapter explores how consumers make choices like these. The Budget Constraint: lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337 What the Consumer Can Afford Budget constraint:
The limit on the consumption bundles that a consumer can afford Example:
Hurley divides his income between two goods: fish and mangos.
A consumption bundle is a particular
combination of the goods, e.g., 40 fish & 300 mangos Active Learning 1 The budget constraint lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337 Hurley s income: $1200
Prices: PF = $4 per fish, PM = $1 per mango
A. If Hurley spends all his income on fish, how many fish does he buy?
B. If Hurley spends all his income on mangos, how many mangos does he buy?
C. If Hurley buys 100 fish, how many mangos can he buy?
D. Plot each of the bundles from parts A C on a graph
that measures fish on the horizontal axis and
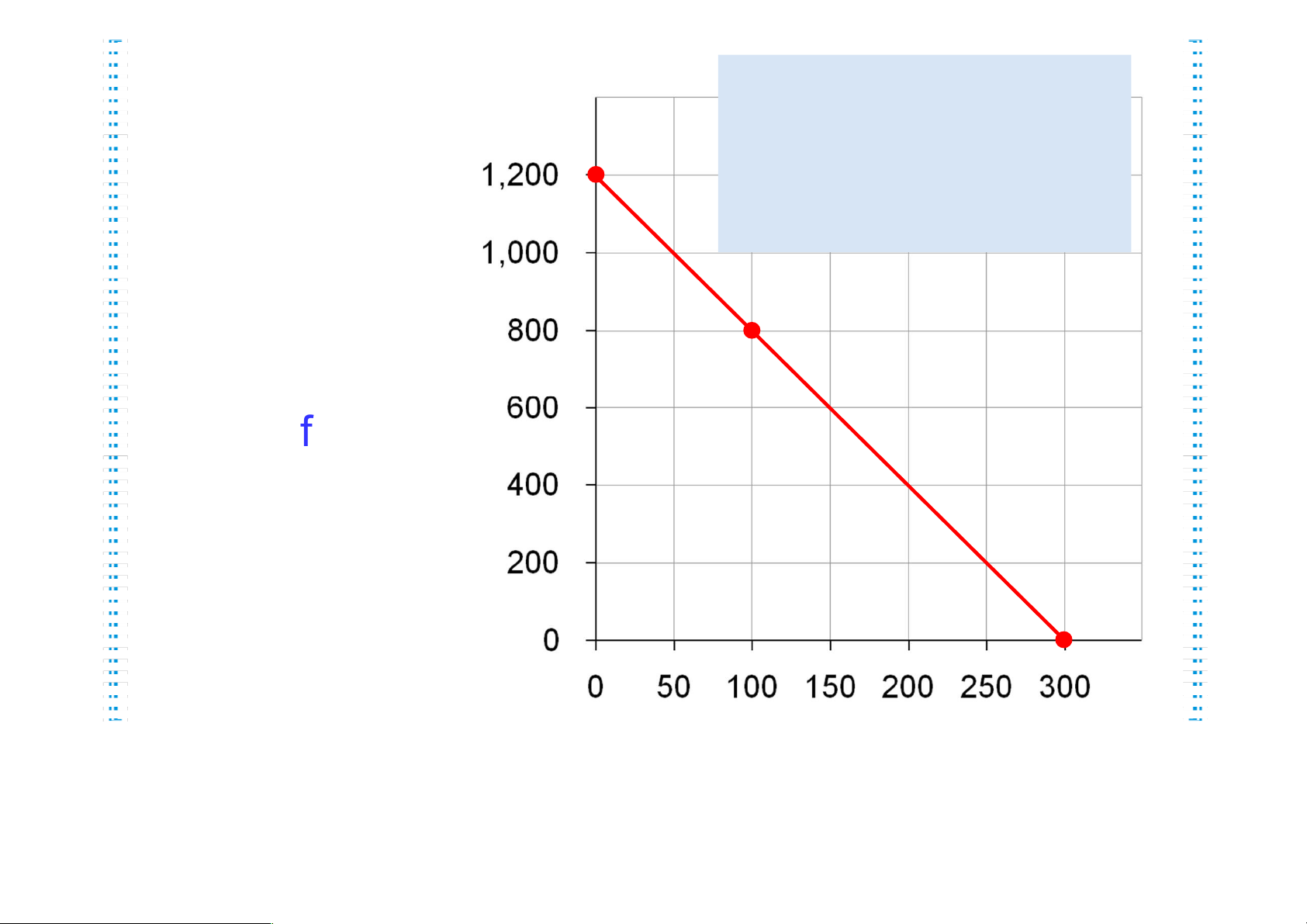
mangos on the vertical; connect the dots. Active Learning 1 Answers lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337 Quantity
D. Hurleys budget A. $1200/$4 constraint shows of Mangos = 300 fish B the bundles he can B. $1200/$1 afford. = 1200 C mangos C. 100 cost fish $400, $800 left buys 800 mangos A Quantity of Fish
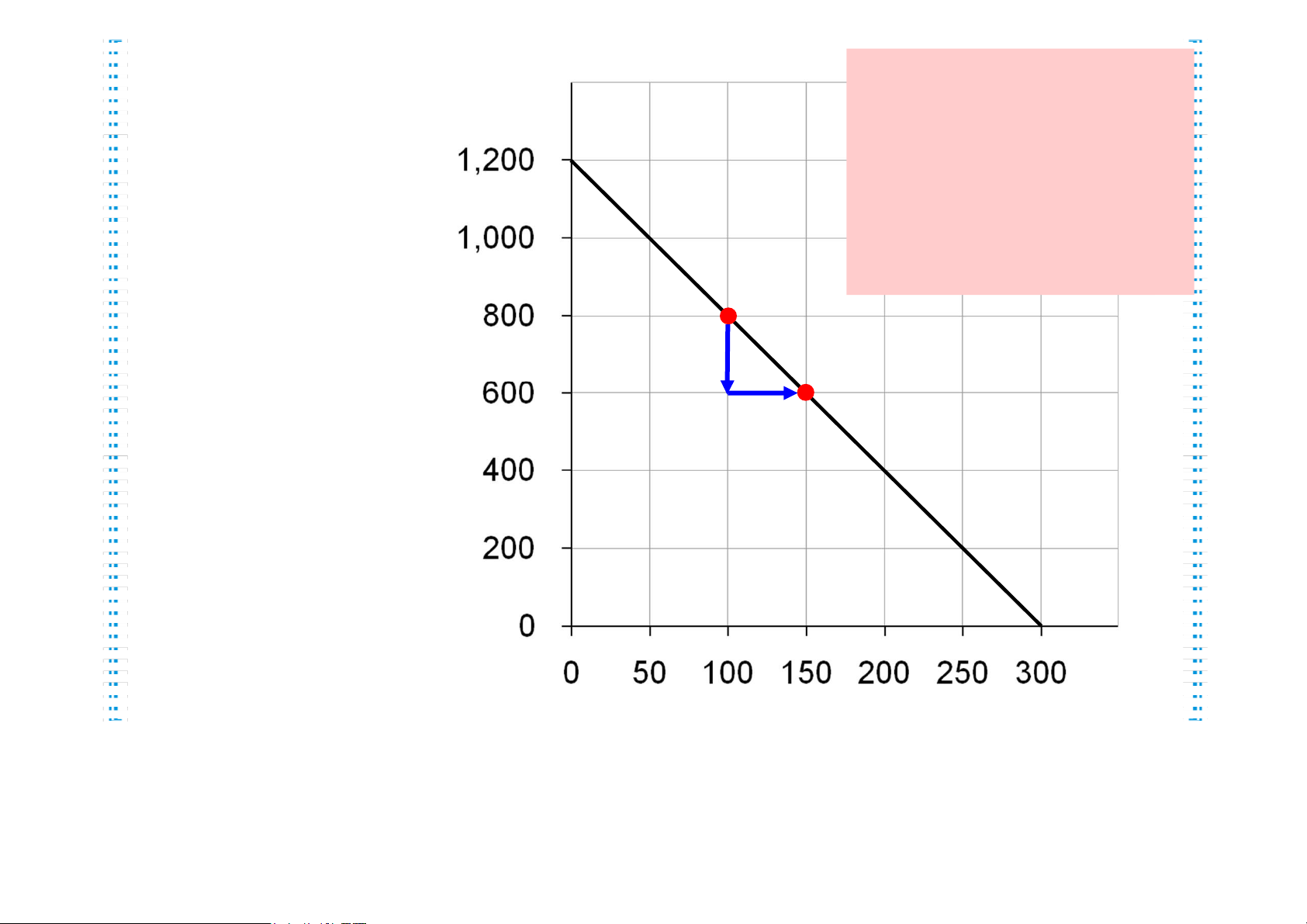
Active Learning 1 The Slope of the Budget Constraint lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337 Quantity The slope of the From C to D, of Mangos budget constraint rise = equals the relative 200 mangos price of the good on the X axis. run = C +50 fish D Slope = 4 Hurley must give up 4 mangos to get one fish. Quantity of Fish lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
Active Learning 2 The budget constraint, continued Initial problem: Hurley s income: $1200
Prices: PF = $4 per fish, PM = $1 per mango
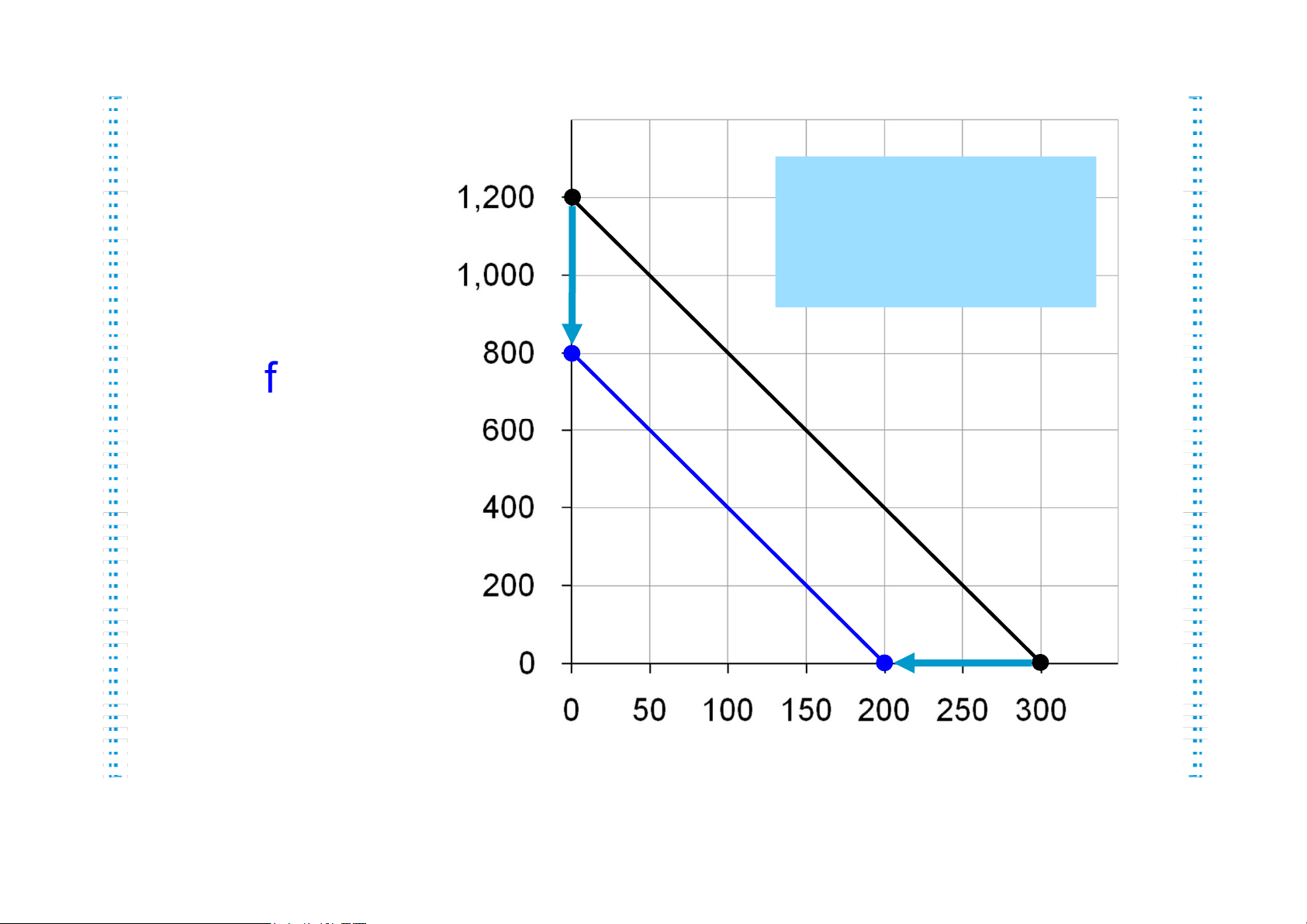
Show what happens to Hurley s budget constraint if: A. His income falls to $800.
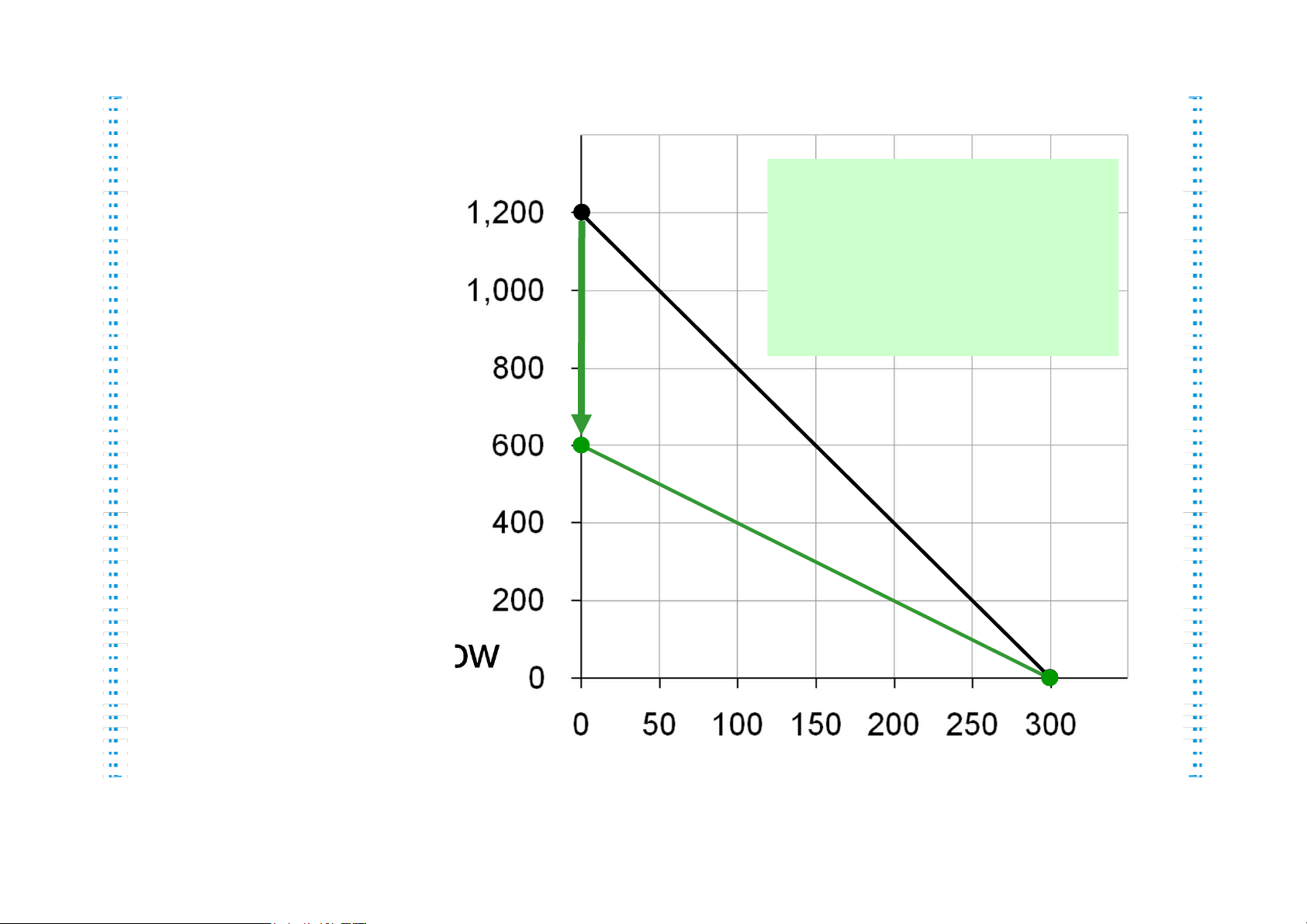
B. The price of mangos rises to PM = $2 per mango lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337 Active Learning 2 Answers, part A Now, Quantity of Mangos Hurley A fall in income can buy shifts the budget constraint down. $800/$4 = 200 fish or $800/$1 = 800 mangos or any combination in Quantity between. of Fish lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337 Active Learning 2 Answers, part B Hurley Quantity can still buy of Mangos An increase in the 300 fish. price of one good But now he pivots the budget constraint inward. can only buy $1200/$2 = 600 mangos. Notice: slope is smaller, relative price of fish is now only 2 mangos Quantity of Fish lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
Preferences: What the Consumer Wants
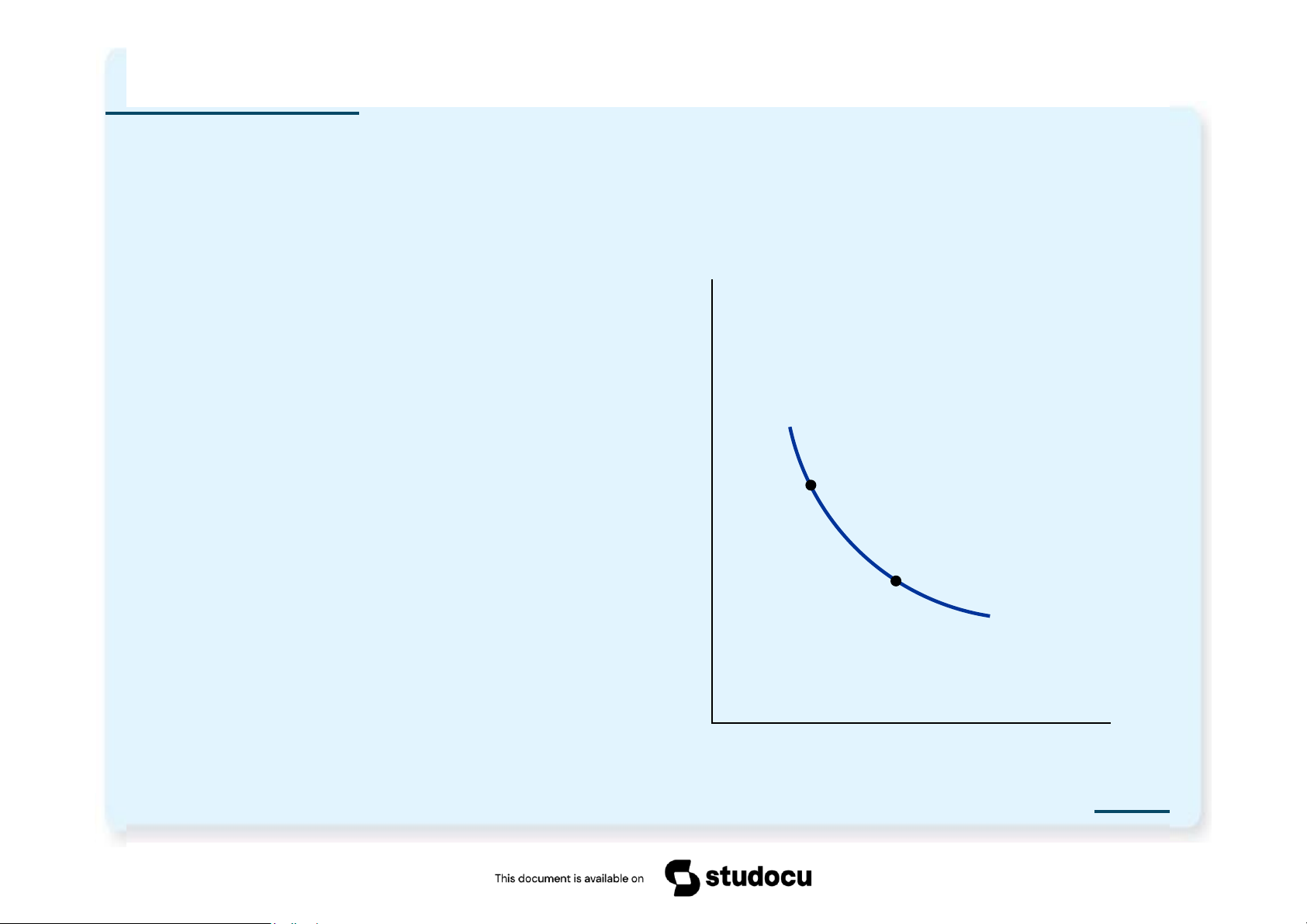
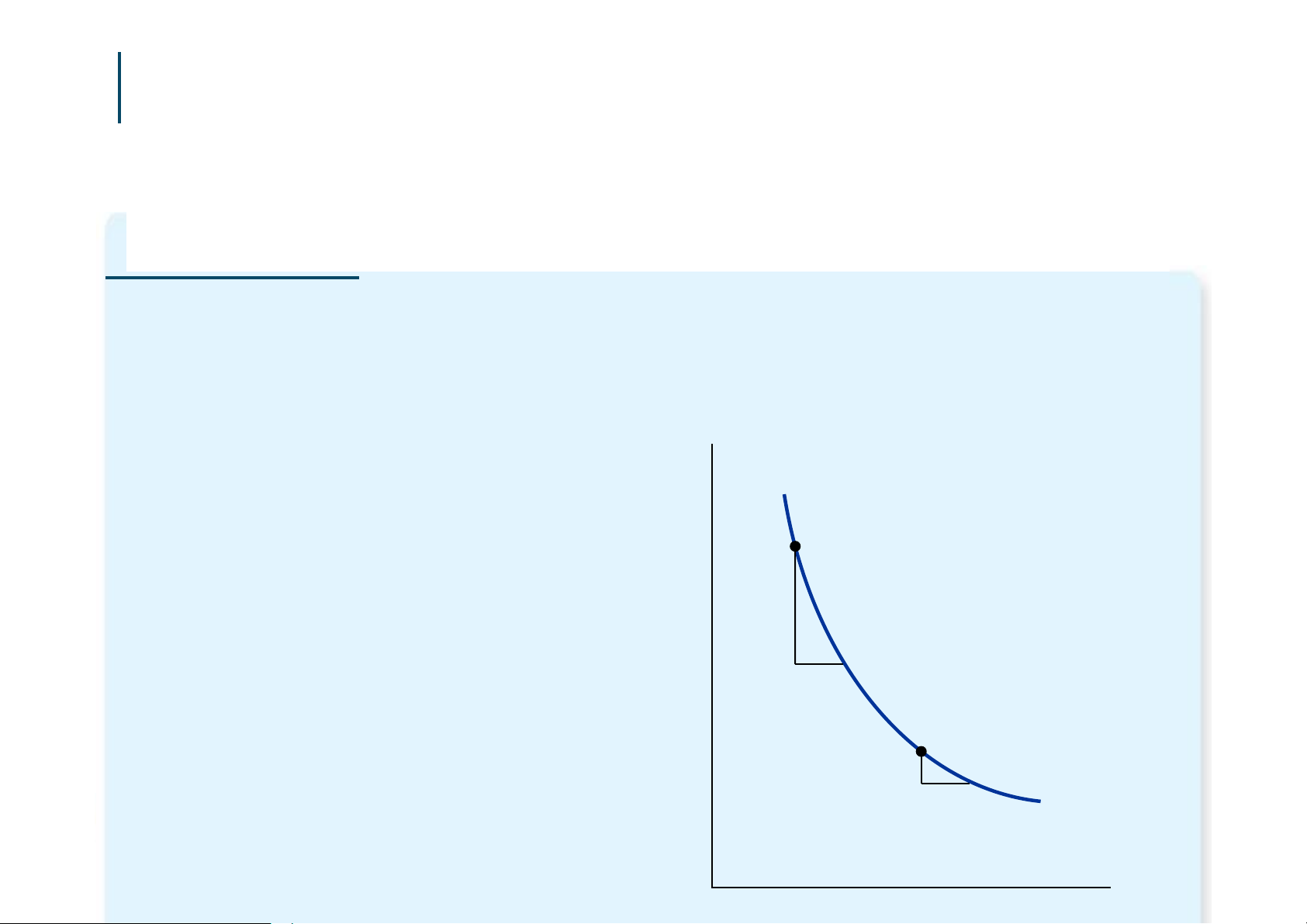
Indifference curve: Quantity One of Hurley s
shows consumption of Mangos indifference curves bundles that give the consumer the same level of satisfaction B
A, B, and all other
bundles on I1 make A Hurley equally happy: I1 of Fish
' 2018 Cengage Learningfi. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as
permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning 11
management system for classroom use.
Downloaded by June Lee (lenhungkttm@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
Four Properties of Indifference Curves he is indifferent between them. Quantity of Fish
' 2018 Cengage Learningfi. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use
as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning 12
management system for classroom use.
Downloaded by June Lee (lenhungkttm@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
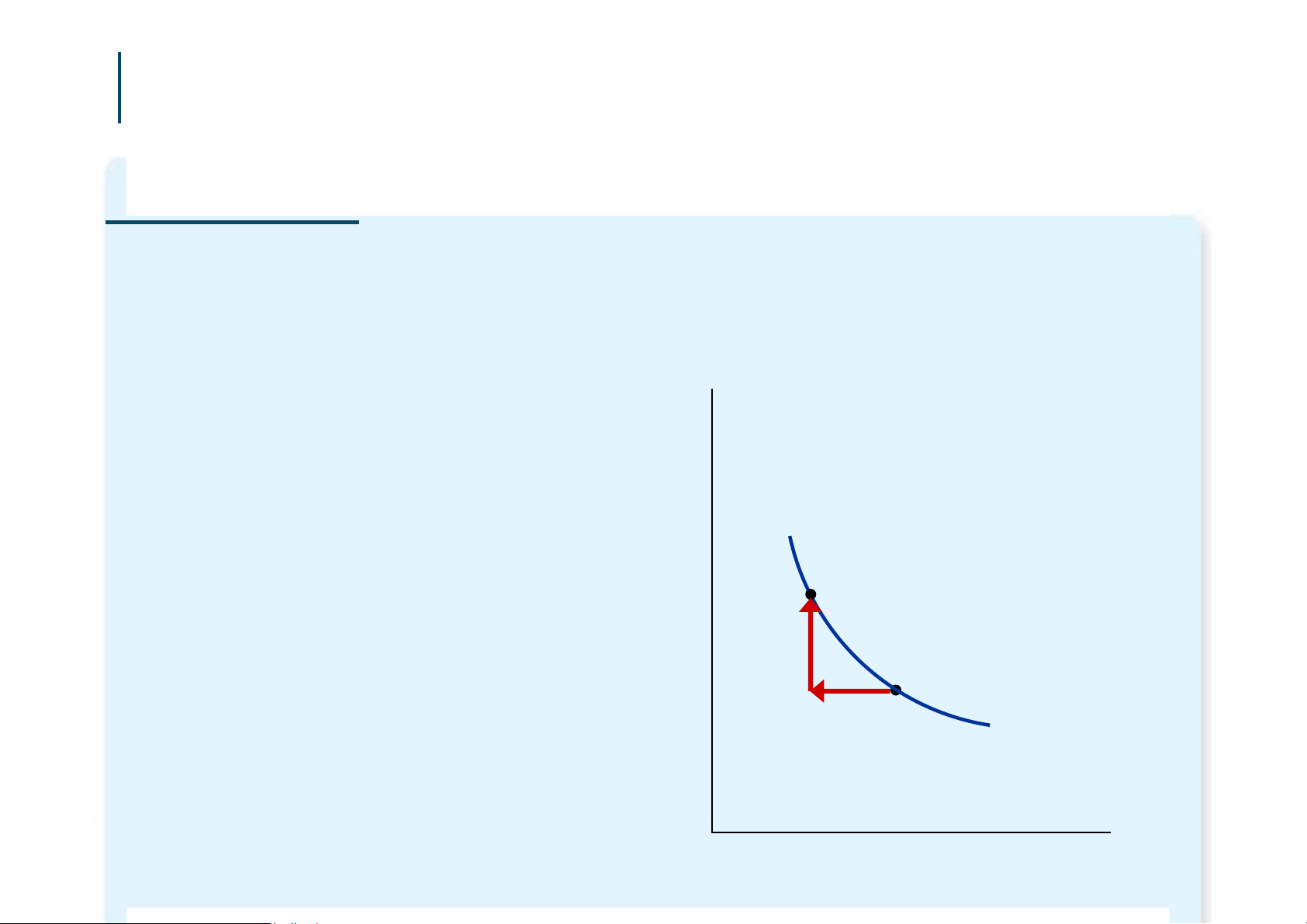
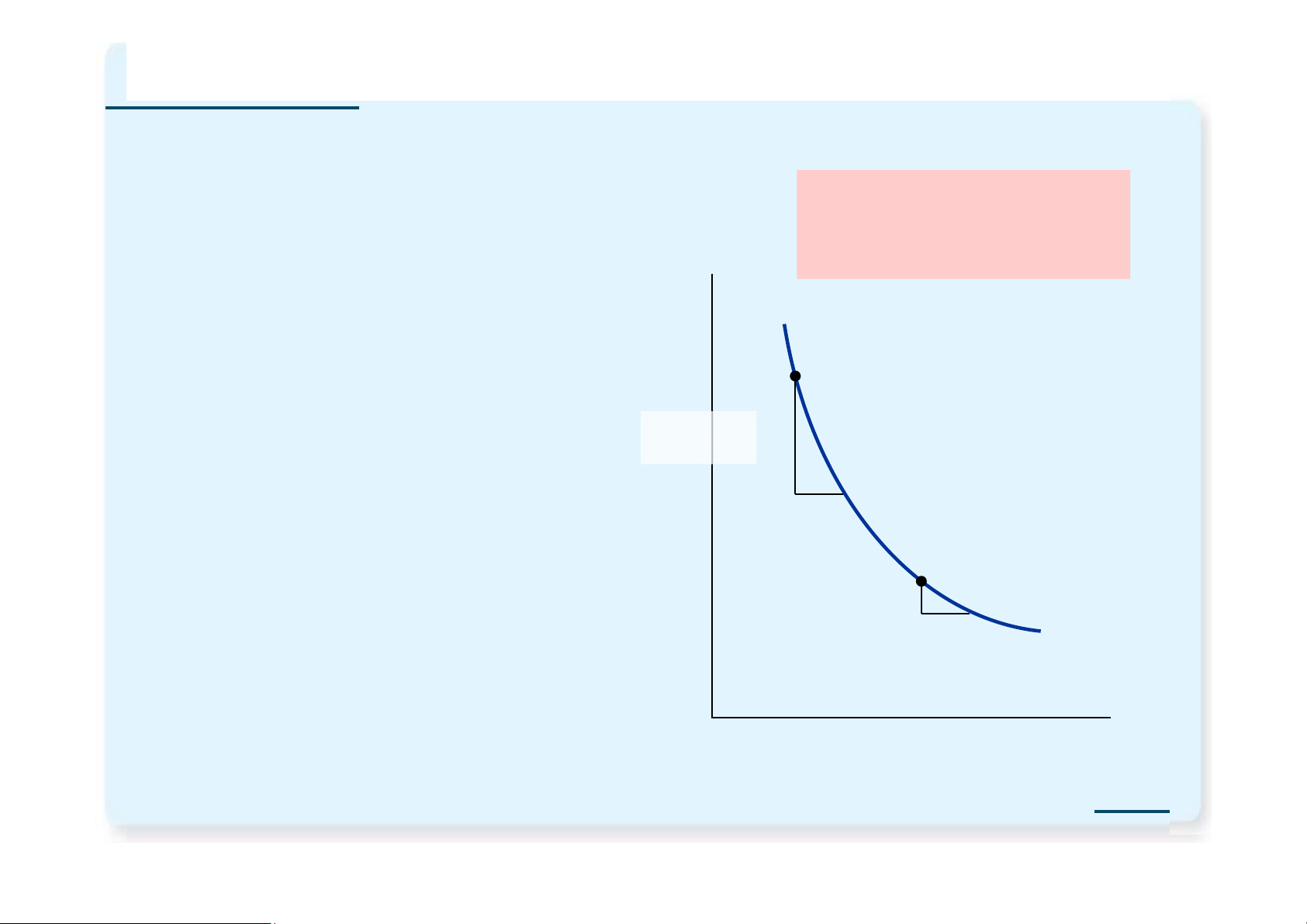
Four Properties of Indifference Curves
1. Indifference curves are downward- sloping. Quantity One of Hurleys of Mangos If the quantity of indifference curves fish is reduced, the quantity of mangos must be B increased to keep Hurley equally A happy. I 1 of Fish
' 2018 Cengage Learningfi. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as
permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning 13 Quantity
management system for classroom use.
Downloaded by June Lee (lenhungkttm@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
Four Properties of Indifference Curves of Fish
' 2018 Cengage Learningfi. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use
as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning 14
management system for classroom use.
Downloaded by June Lee (lenhungkttm@gmail.com)
2. Higher indifference curves are preferred lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
Four Properties of Indifference Curves
3. Indifference curves cannot cross. Suppose they did. Quantity Hurley s of Mangos indifference curves Hurley should prefer B
to C, since B has more of both goods.
Yet, Hurley is indifferent B between B and C:
He likes C as much as A C A (both are on I4). I1 I4 of Fish
' 2018 Cengage Learningfi. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use as
permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning 15
management system for classroom use.
Downloaded by June Lee (lenhungkttm@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
Four Properties of Indifference Curves
He likes A as much as B (both are on I1). Quantity of Fish
' 2018 Cengage Learningfi. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use
as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning 16
management system for classroom use.
Downloaded by June Lee (lenhungkttm@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
Four Properties of Indifference Curves
4. Indifference curves are bowed inward. Quantity of Mangos Hurley is willing to give up more A mangos for a fish if he has few fish (A) 6 than if he has many 1 (B). B of Fish 2
' 2018 Cengage Learningfi. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in w
hole or in part, except for use as
permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning 17 1 I 1
management system for classroom use.
Downloaded by June Lee (lenhungkttm@gmail.com) Quantity lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
The Marginal Rate of Substitution Marginal rate of
substitution (MRS): Quantity MRS = slope of the
rate at which a of Mangos indifference curve consumer is willing to
trade one good for another. A Hurley s
MRS is the MRS=6 amount of mangos he 1 would substitute for another B fish. MRS=2 1 I1 of Fish
' 2018 Cengage Learningfi. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use
as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning 18
management system for classroom use.
Downloaded by June Lee (lenhungkttm@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337 MRS falls as you move down along an indifference curve. Quantity
' 2018 Cengage Learningfi. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use
as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning 19
management system for classroom use.
Downloaded by June Lee (lenhungkttm@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 47882337
' 2018 Cengage Learningfi. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part, except for use
as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website or school-approved learning
20management system for classroom use.
One Extreme Case: Perfect Substitutes
Downloaded by June Lee (lenhungkttm@gmail.com)
Perfect substitutes: two goods with




