
Preview text:
THE PROCESS OF PLANT REPRODUCTION (SỰ SINH SẢN)
Topic: Seedlings grow from seeds Class: 5 Time: 35-40’ I. Aims 1. Knowledge
- Identify the structure of seeds including: shell, embryo, nutrients. - Know
the process of forming seedlings from seeds.
- Immediately recognize the functions and roles of each part: shell, embryo, nutrients. - Explain the growth of plants. 2. Skills
- Point on the picture, the real object is composed of particles
- Describe the germination process of seedlings - Planting plants with seeds 3. Attitude - Pay attention to the lesson
- Actively participate in exploring, discovering
- Building lessons, being confident - Interested in the lesson. II. Teaching aids
1. Teacher: Lesson plans, textbooks, some samples, video of seedling sprouting process 2.
Student: Textbooks, notebooks, beans (peanuts) have sprouted
III. Methods and techniques
1. Methods: Group disscussion, observation
2. Techniques: Brainstorming, mindmap IV. Vocabulary Words Pronounce Means seed /si d/ ː
the small hard part produced by a plant, from which a new plant can grow embryo / embriə ˈ / ʊ
a young plant in the very early stages of
development before birth, or before coming out of its seed nutrient / nju ˈ triənt/ ː
a substance that is needed to keep a living thing alive and to help it to grow process / prə ˈ s ʊ es/
a series of things that happen, especially ones that result in natural changes germination / d ˌ ʒɜːm ne ɪˈ ɪʃn/
the process by which a seed starts to grow V. Procedures Time Content Teacher’s activities Students’ activities 3-5’ Warm up Teacher asks questions + - 2-3 students answered - Objects: Review Name some insect previous knowledge pollinated flowers and learned. Describe the some wind pollinated reproduction of flowers. flowers that you know? + - Method: Question and What are the answer characteristics of color or fragrance of insect pollinated flowers and wind-pollinated flowers? - Call on students to comment - Students comment and - Teacher comments - supplement. finalize - Listen 10’
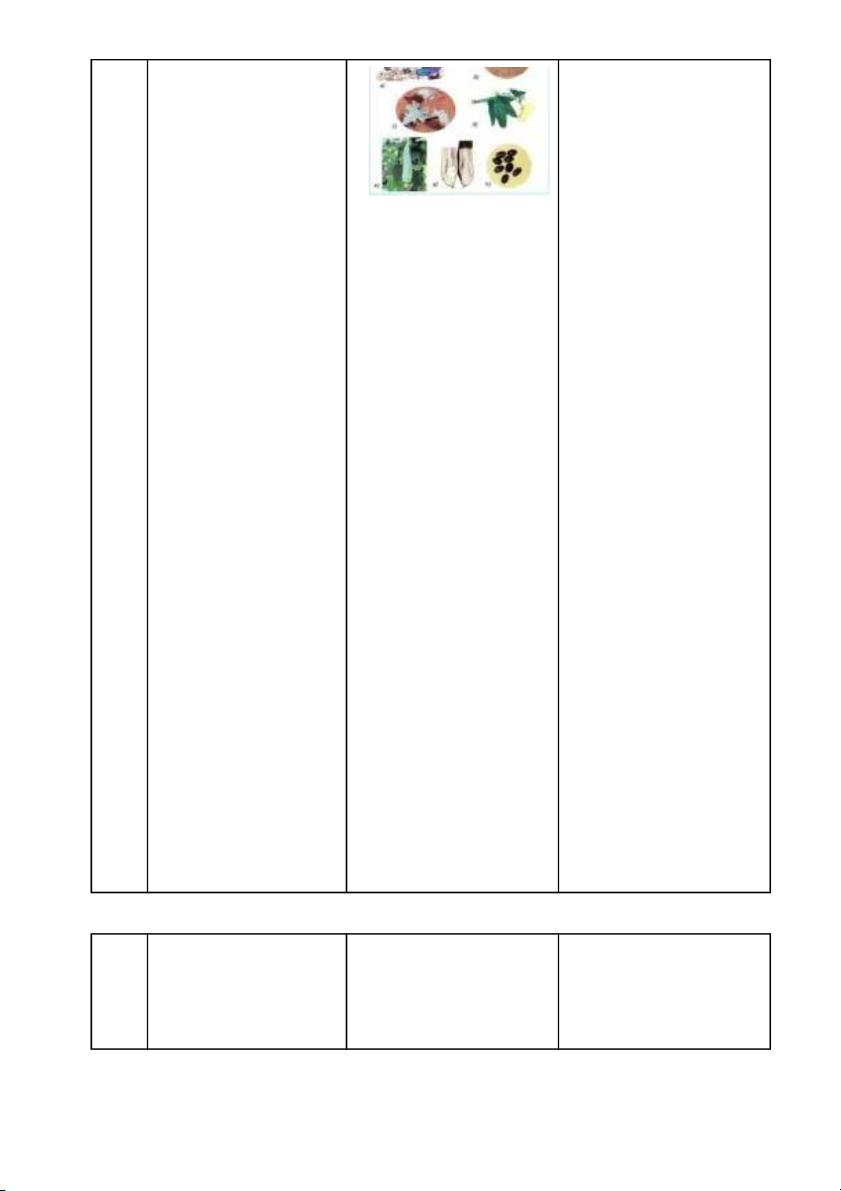
Activity 1: Learn seeds - Give the bean (peanut) - Listen - Objects: Observe and seedlings to the students to - Observe, listen describe the parts of a observe. seed; State the function - State the situation: Why of each part. do seedlings grow from - Methods: question and seeds; What's in the seed? answer group - Divide the class into 6 - Students work in groups discussion. groups, ask to observe the freshly soaked seeds the night before - Ask students to predict what the seeds have? – Draw a picture of a grain - Students draw pictures based on your own prediction - Ask representatives of - The group's the groups to present representative reports the - The teacher hangs the results sample picture and asks to - Students give their compare the student's opinions picture with the sample picture - Ask them to do a particle separation experiment, - Students perform the point out the parts of the experiment and report the seed they see and name results. that part Seeds consist of shell, - Call students to comment. embryo, and nutrients - Students comment and supplement - Teacher's final comment (when students can't come up with a scientific name, the teacher gives the correct name) - Students discuss and - Discuss in groups about report the results the roles and functions of + Shell: protect the seed + the parts of the particle. Embryo: is the part of a young plant that grows into a new plant - Call on students to + Nutrients: to feed the comment embryo - Teacher comments finalize. 8’ Activity 2: - Have students separate - Students discuss in Germination process germinated seeds. Point groups, report the results - Objects: to state the out the parts of the germ, Germs (embryos) include: role of the roots, shoots, name and state the + Sprouts: grow the roots and shoots; Describe the function and role of each of the plant to absorb process of sprouting. part nutrients to nourish the - Methods: question and - Teacher: show a picture plant answer group of germinated seeds (can + Stem: is the stem of the discussion, games. clearly see the components plant that later plays the of the sprout) and ask role of transporting and students to point to the storing water and picture and report the nutrients, helping the results of the discussion. plant to stand. + Sprouts: later are leaves, have an important role in the respiration and - Teacher comments. photosynthesis of plants - The teacher showed the - Students observe. students a video about the sprouting process. - The teacher hangs - Students represent pictures, and the text frame groups to answer has information about the sprouting process and asks students to arrange it in the correct order. - Divide the class into 2 groups, discuss and arrange on the board in the correct order - Teacher, student comments - Teacher closes. 12’ Activity 3: Practice - Show photo 7, ask - Students discuss in talking about the students to discuss in groups and the growth of the melon groups, fill in paper (6 representative of the plant groups) about the group presents the results - Objects: Describe the development process of of the discussion process of seed loofah from seeds. development. - Ask students to repeat the - Methods: Practice, process in front of the - Many students gave their question and answer class. -Teacher shows the opinions answers and explains the - Students follow development process of the melon tree. + Figure a: Melon seeds are sown in moist soil. + Figure b: After a few days, the cotyledons grow a lot, the cotyledons emerge from the ground with two cotyledons. + Figure c: The tree sprouts and grows many new leaves. + Figure d: Melon tree flowers and results + Picture e: The melon tree grows strongly, the fruit is large + Figure g: The old melon fruit has a lot of seeds inside. + Figure h: Old melon seeds used for planting. - Teacher asks the - Conditions for seed question: What are the germination are conditions for seeds to appropriate humidity and germinate? temperature (not too hot, not too cold) - The teacher records the conditions on the board - If many students give the same condition, the teacher will mark the number of times of agreement - Ask students to draw conditions from what the teacher has written - Final teacher (write the table): Conditions for seed germination are appropriate humidity and temperature (not too hot, not too cold) 5’ Activity 4: - The teacher let the
- Students participate in Consolidation-coaching students watch the video the game - Objects: Learn on tree care and asked the knowledge, know how to students to observe apply it in practice. carefully to prepare to play - Methods: Practice, the game. question and answer - Teacher gives the game: Divide the class into 2 groups. The student's task is to help the farmer perform the task of taking good care of the tree to have a bountiful harvest by adding conditions to each stage of the tree so that it can grow best. - Teacher summed up: from seeds, seedlings grow and start a new life. In order for that life to take place normally, it needs many conditions such as humidity, temperature, light. - Practice sowing seeds as required in the textbook.




