
Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766
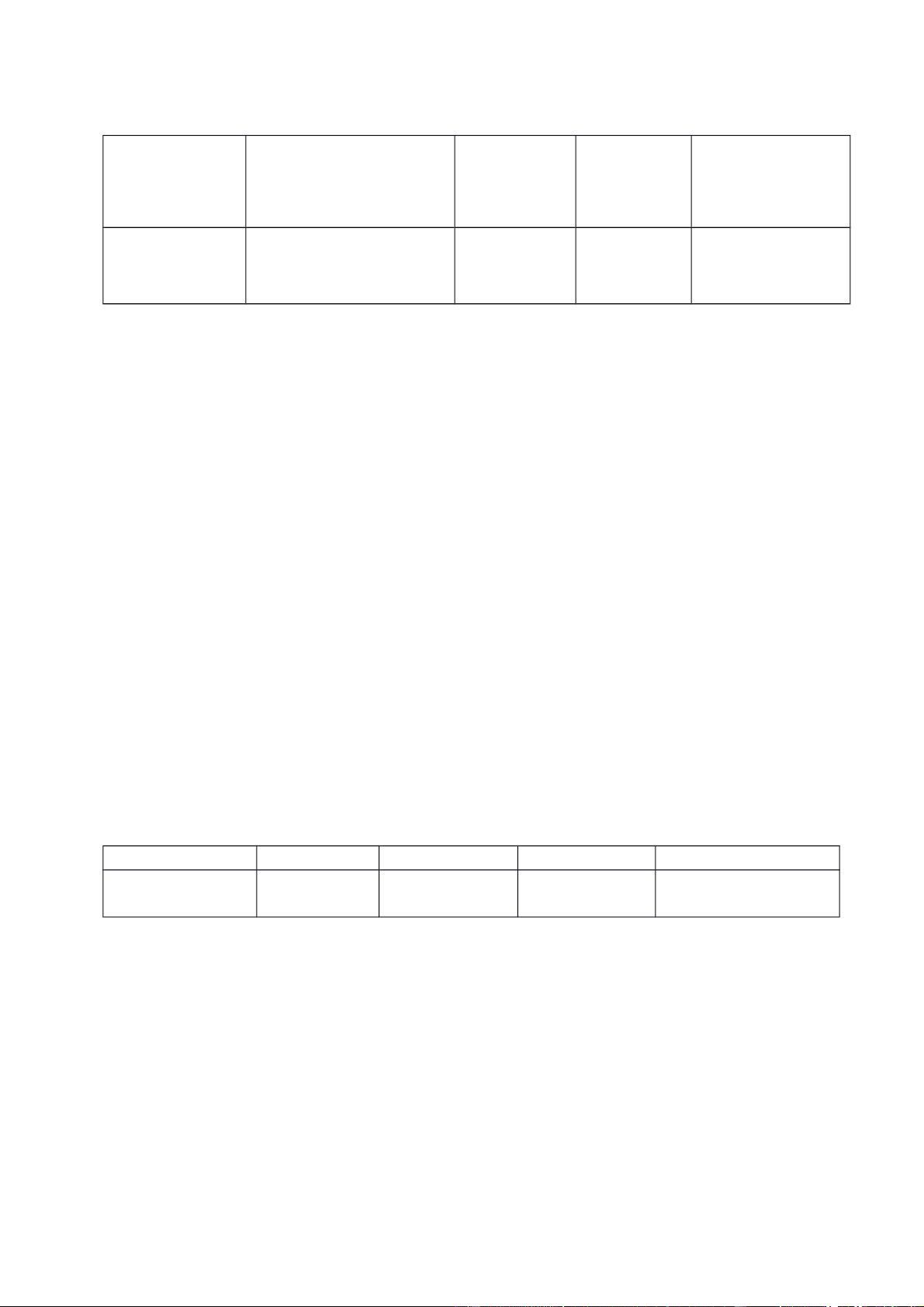
Choose one correct term for each of the following sentences/ definitions /phrases A. B. C. aplastic D. E. active exacerbations immunocompromised anemia bacteremia F. Kaposi G. hemophilia H. I. J. sarcoma hemoglobinopathy lymphadenopathy normocytic 1. periods of flare-up
2. any disorder due to abnormalities in the hemoglobin molecule
3. presence of bacteria in blood
4. associated with bone marrow failure
5. type of immunity where memory cells are formed
6. malignancy of connective tissue commonly associated with HIV
7. used to denote an erythrocyte that is normal in size
8. swollen or diseased lymph glands
9. term that denotes a weakened immune system 10. blood-clotting disorder PART 2 Do exercise A and B below.
EXERCISE A: Complete the passage with the following suitable words.
A. ligaments B. jelly-like C. eyeball D. crystalline E. muscle F. controls G. H. cornea
I. transparent J. lacrimal glands composed
The eyes are the organs of the sight. The (1), which is spherical in shape, is located in
the bony eye socket or orbit. The protective organs of the eyes are eyebrows, eyelids,
eyelashes, and (2). They protect the eyes from water, dust, microorganisms and other
foreign bodies. The eyelid protects the front part of the eye keeping it clean and moist
by blinking. This is the opening and shutting of the eye throughout the day. Blinking is
both voluntary, meaning it can be controlled, and involuntary, meaning it sometimes
happens automatically. When the eyelid blinks automatically, it is a reflex. This reflex
occurs when the eyes need to adjust to bright light, or when they are needed to shut
quickly for protection. The eyelids keep dirt and other substances from entering a person's eyes.
The outer part of the eye is (3) of three layers of tissues - the sclera, choroid and retina.
The outside layer is the sclera, a protective coating, commonly called 'the white of the lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766
eye'. It covers about five-sixths of the surface of the eye. The central anterior part of the
sclera, the cornea, is (4) and forms the so-called window of the eye. The front surface
of the sclera is covered with conjunctiva. The middle layer of the coating of the eye is
the choroid, a vascular layer lining the posterior three-fifths of the eyeball. The choroid
is continuous with the ciliary body and with the iris, which lies at the front of the eye.
The innermost layer is the light-sensitive retina.
The (5) is a tough, five-layered membrane through which light is admitted to the interior
of the eye. Behind the cornea is a chamber filled with clear, watery fluid, the aqueous
humor which separates the cornea from the crystalline lens. The lens itself is a flattened
sphere constructed of a large number of transparent fibers arranged in layers. It is
connected by (6) to a ring-like muscle, called the ciliary muscle, which surrounds it.
The ciliary muscle and its surrounding tissues form the ciliary body. This (7), by
flattening the lens or making it more nearly spherical, changes its focal length.
The pigmented iris hangs behind the cornea in front of the lens, and has a circular
opening in its center known as the pupil. There are muscles attached to the iris that
change its shape, which (8) the amount of light going through the pupil. This muscle
contracts or relaxes, making the pupil larger or smaller, to control the amount of light
admitted to the eye. When the light is dim, the iris contracts, the pupil dilates and
more light can enter the eye. In bright light, the iris relaxes, narrowing the pupil and
less light enters the eye. Behind the iris is the (9) lens which can change its shape and
focuses, in this way, the light on the retina. The posterior chamber is located behind
the lens. It is filled with a (10) body, called vitreous humor, which keeps the eyeball in its spherical shape.
EXERCISE B. Answer the following questions in complete sentences.
1. What are the protecting structures of the eye?
………………………………………………………………………………..
2. What are the three layers of the eye wall?
………………………………………………………………………………..
3. How many chambers is the eye divided into? What are they
………………………………………………………………………………..
4. What are these chambers filled with?
………………………………………………………………………………..
5. How does the iris regulate the size of the pupil?
………………………………………………………………………………..
PART3 .Write a referral letter for a case from these notes To Dr Ahmed
C/o a rash , several parts, 3/12.
Aslo bilateral intermittent nasal blockage, itchy noses and eyes
Given antibiotics – rash decresed Not related allergy (carpet) lOMoAR cPSD| 46836766 Piriton helps the rask
Spent many years in Africa, volunteer in his 20. African connection? PART 4 Câu 1
A lot of water is necessary for the chemical reduction of food into its end products. Food
is moved along the length of the intestines by the rhythmic contraction of the muscle
walls. This is called peristalsis. What is left of the food, after some has been absorbed
by the small intestines, moves through the large intestines where water is reabsorbed
into the body. The material that cannot be used by the body is excreted from the rectum
through the anus as feces or waste. Câu 2
Eating disorders constitute some of the major medical health problems in the western
world. Sufferers share symptoms such as a distorted view of one’s own body shape and
weight, and extreme disturbances in their eating behaviour, which may present a serious
health threat. Anorexia nervosa is one of the most common disorders associated with
restricted food intake or bingeing, as well as distress or excessive concern about body shape or weight.




