

Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 47205411 COURSE OUTLINE Course ID Course title Credits KT303DE01
Accounting Information System 03
To be applied to Semester 01 School year: 2014 – 2015 (From Semester 14.1A) under
Decision No. _______ /QĐ-BGH date __________
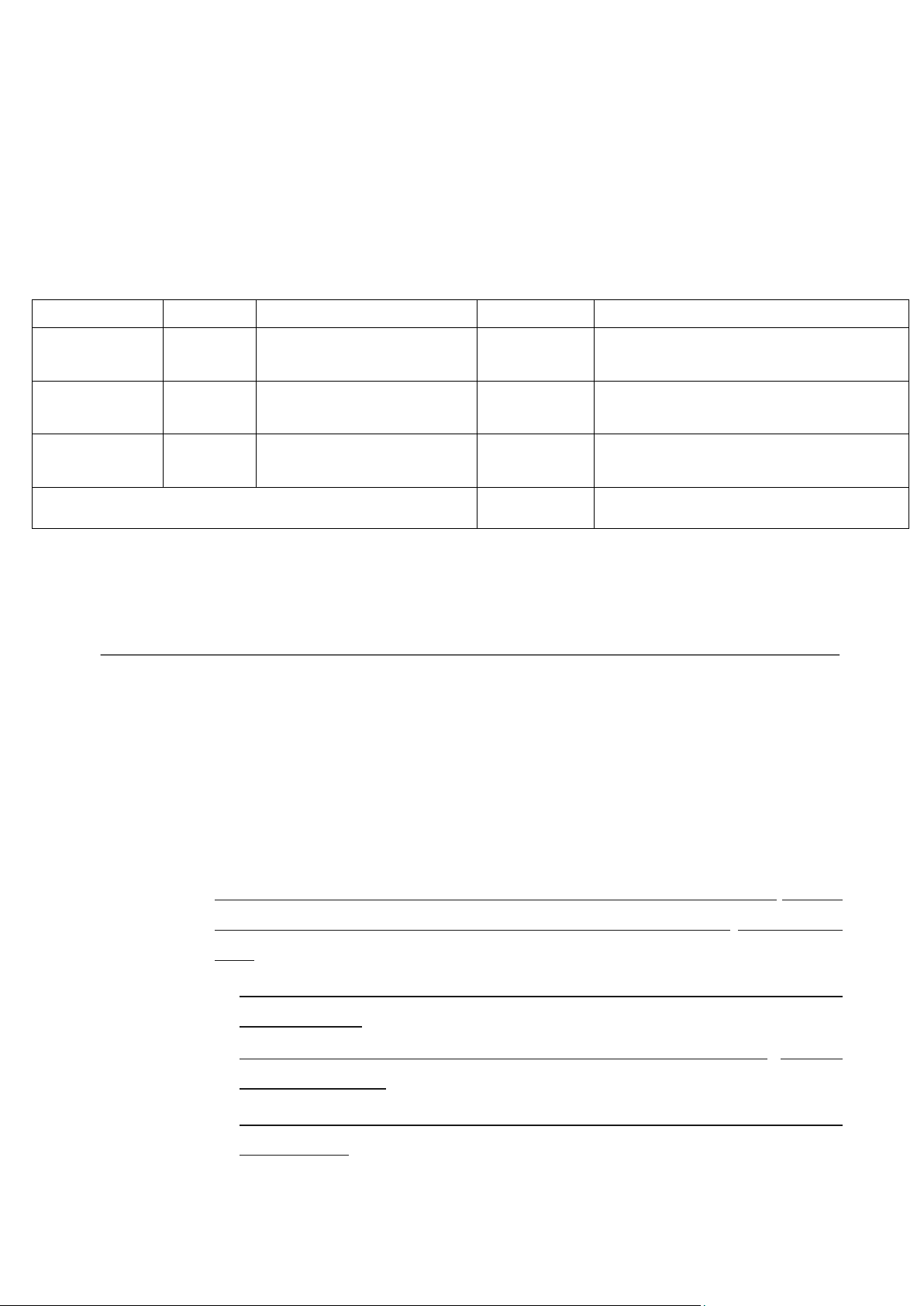
A. Course Specifications: Periods Periods in classrom Lecture/ Selfstudy Lecture Total periods* Activity
Lab room Fieldwork Seminar periods room (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) 45 45 0 90 45 0 0
B. Other related Subjects:
Other related Subjects Course ID Course title Prerequisites: 1. KT210DE01 Financial Accounting 1 2. AV203DV02 EIC 3 (EIC Int. 2) Co-requisites: 1. None Other requirements: 1. None
C. Course Description: 1/8 lOMoAR cPSD| 47205411
This course is intended to provide students with knowledge which they can apply in the
design and implementation of accounting information systems in a variety of organizations.
To achieve this, students must also gain an understanding of the broader management
information systems in use today.
This course focuses on 2 major components of accounting information systems: conceptual
models and physical implementation. Accounting systems are studied from an accounting
cycles perspective, emphasizing the nature and relevance of accounting internal controls
and the relationship of accounting systems to the functional areas of accounting. Using
contemporary information technology, students analyze, design, and implement accounting
systems along with relevant internal control structures.
Students will develop an understanding of the applications of information management to
accounting data. They will study systems theory and development, capabilities and
limitations of computer hardware and software, design and organization of data base
management systems, design and implementation of control systems, use of data
communications networks, and accounting systems in diverse organizations.
Students will gain an intermediate level knowledge of an accounting software package.
To sum-up, this course introduces students to the important concepts of Accounting
Information Systems (AIS). The course contents are divided into three main sections. The
first section introduces the basic concepts of AIS including its objectives, components and
subsystems. This section also introduces students to the techniques of documenting
accounting systems and database modeling tools. The second section discusses in depth the
common features of transaction processing systems such as purchase and accounts payable,
revenue and accounts receivable, manufacturing and inventory, human resource as well as
general ledger and reporting system. Integration of selected accounting software will also
take place at this stage to enable students apply the AIS concepts into practice. The final
section discusses the emerging issues in computer crimes, computer ethics and concept of
internal controls in organization. Application of internal controls concept into transaction
cycles is later discussed. As for the final topic, a special focus will be given to the concept
of E-business as an emerging trend of conducting business in the new era of information
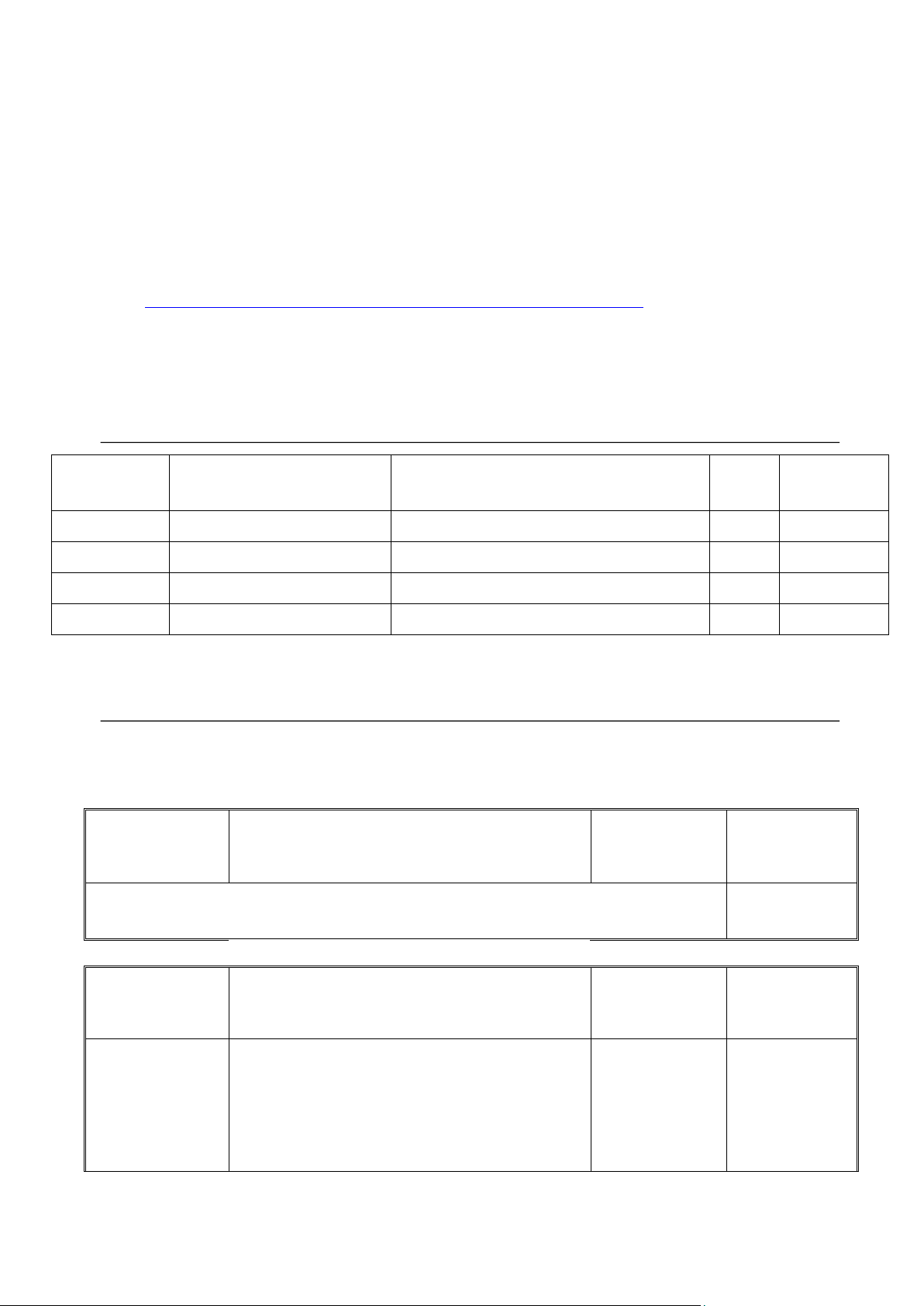
technology (IT). D. Course Objectives: 2/8 lOMoAR cPSD| 47205411 No. Course Objectives
Analyze data to provide insights about business operations and performance: 1.
Spreadsheets and database manager 2.
Design business processes and represent them with documentation tools.
Design and implement well-structured databases to enable business 3. processes.
Evaluate internal control in information systems and design controls to 4.
mitigate risks associated with information systems
Learn some basic accounting information system fundamentals relating to:
accounting cycles; tools for understanding, explaining, and designing
accounting systems; internal control concepts in both manual and 5.
computerized environments; and database concepts. These fundamentals are
important for understanding, developing, and working with all accounting
systems, from manual to computer-based.
accounting data analysis related to financial and managerial decisions using 6.
electronic spreadsheets and other analytical or statistical software 7.
an introduction to system design, analysis, implementation E. Learning Outcomes: No. Learning Outcomes 1.
Explain the basic concepts of AIS and its framework. 2.
Discuss the importance and functions of AIS in organizations.
Document a business process / system using system documentation 3.
techniques i.e. data flow diagrams and flow charts 4.
Discuss the elements and techniques of database modeling. 5.
Explain concepts of internal control and its components. 6.
Explain the common transaction cycles in business. 7.
Apply and integrate the AIS concepts in transaction cycles. 3/8 lOMoAR cPSD| 47205411
Demonstrate and use accounting software by applying AIS concepts and 8. elements.
F. Instructional Modes:
– This course was conducted in the class as lecture.
– Teaching in the class: 30 hours (2 hours per day) and learning in class room by face- to-face discussion.
– Hour for doing exercises: 15 hours (1 hour per day) and learning in class room.
– Students will be divided into some small groups to exchange, discuss, handle the
situation, do homework and declare taxes.
– Translation some exercise from Vietnam to English and solving them. This work is
helped the students knowing the academic terms in AIS.
– Do the seminar: comparison between Vietnamese system and system of foreign countries in the world.
Besides that, students in earlier terms advise doing the following to succeed in the course:
– Come to every class prepared to participate by having completed the assigned
activities. Avoid the temptation to procrastinate.
– Stay alert in class. Get every nuance about every learning activity. When you do not
understand something, ask immediately.
– Forget texting and surfing in class. Every text or surf you do in class represents
something you will miss that will bite you later.
– After class, redo the activities on your own to verify that you can do them without
assistance. There is no assistance on exams.
– Study the syllabus, schedule, and all the pages linked to them because they give good
guidance and answer many questions.
– Pay attention to the postings on the discussion board. Another student may have
answered your question or offered a valuable hint.
– Participate fully in team work to learn to do everything on the project. Exam
questions cover the whole project. G. Textbooks and teaching aids: 4/8 lOMoAR cPSD| 47205411 •
Required Textbooks and Materials:
– Marshall Romney, Paul Steinbart; Accounting information systems, 13th edition;
Pearson Education International; 2014
– Nancy, A. B., Mark, G. S & Carolyn, S. N (2014). Core Concepts of Accounting
Information System. 12th Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. •
Suggested Course Materials:
– Thieu Thi Tam, Nguyen Viet Hung and Pham Quang Huy (2007), ‘Accounting
information system’, Statistic publishing house.
– Heagy, Nash, Courtney; The design, selection, and implementation of accounting
information systems, 4th edition; DAME Publications, Inc; 1999
– Accounting information system, Faculty of Accounting and Auditing, UEH.
– Romney, M.B. & Steinbert, P.J.& Cushing, B.E. (2006), Accounting Information
Systems, 10th Edition, Prentice Hall, USA.
– Hall, A. J (2006), Accounting Information Systems, 4th Edition, South-Western Thomson Learning, USA.
– Gelinas, U. J., Sutton, S. G & Hunton, J. E. (2005). Accounting Information System,
6th Edition, South-Western Thomson Learning, USA.
– Wilkinson, W.J., Cerullo, J.M, Raval, M., Wong-On-Wing, B., (2000), Accounting
Information Systems: Essential Concepts and Applications, 4th Edition. Wiley. USA. • Teaching aids: – Projector and Micro
– Blackboard, chalk or pen for writing onto the board
– Internet Access: you will need convenient access to the Internet. While not all
assignments will be on-line, there will be submission requirements requiring
connection. Investigate as soon as possible getting connected or plan on using university resources.
H. Assessment Methods (Requirements for Completion of the Course): 1.
Description of learning outcomes assessment
Students who is seem to complete this course finished this subjects.
Accounting is an information support function, delivering products to a
variety of information customers. Specific topics include: 1) accounting’s 5/8 lOMoAR cPSD| 47205411
role and information customers, 2) the evolution of accounting information
systems, 3) understanding information technologies’ capabilities, 4)
analysis and design of accounting information systems using database
technology, 5) understanding organization risks and controls, and 6)other issues of importance. 2.
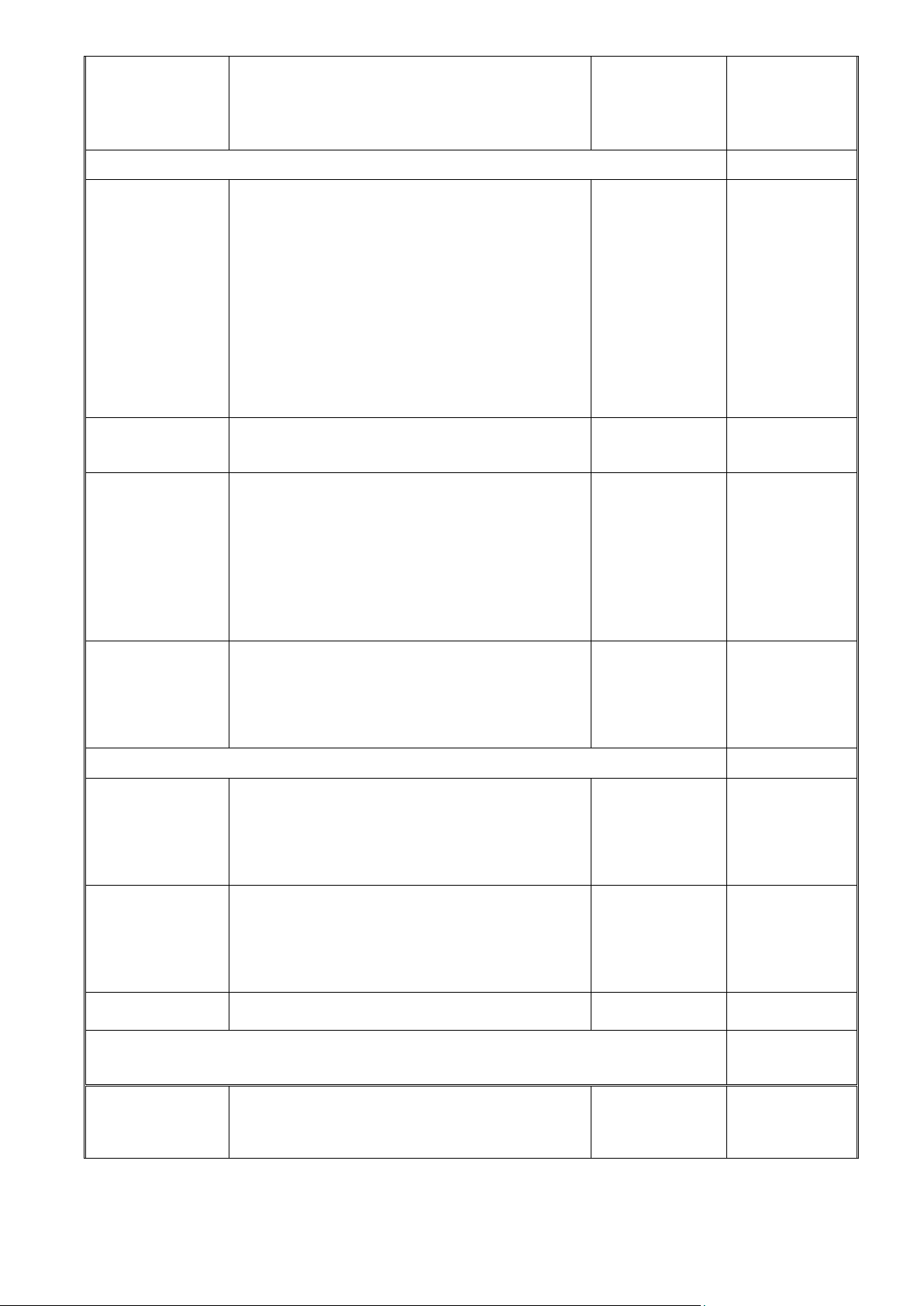
Summary of learning outcomes assessment
Components Duration
Assessment Forms Percentage Schedule Mini-Test 1 Hour Individual or group 20% Every week exercises Mid-term Test 60 mins Multiple choices and Week 8 30% Problem Final Test 90 mins Multiple choices and
Based on Education Department’s 50% Problem schedule Total 100%
Subordinate semester: test will be take place in class. I. Academic Integrity
Academic integrity is a fundamental value that affects the quality of teaching,
learning, and research at a university. To ensure the maintenance of academic
integrity at Hoa Sen University, students are required to:
• Work independently on individual assignments
Collaborating on individual assignments is considered cheating. • Avoid plagiarism
Plagiarism is an act of fraud that involves the use of ideas or words of another
person without proper attribution. Students will be accused of plagiarism if they:
i. Copy in their work one or more sentences from another person without proper citation.
ii. Rephrase, paraphrase, or translate another person’s ideas or words without proper attribution.
iii. Reuse their own assignments, in whole or in part, and submit them for another class. 6/8 lOMoAR cPSD| 47205411
• Work responsibly within a working group
In cooperative group assignments, all students are required to stay on task and
contribute equally to the projects. Group reports should clearly state the
contribution of each group member.
Any acts of academic dishonesty will result in a grade of zero for the task at hand and/or
immediate failure of the course, depending on the seriousness of the fraud.
Please consult Hoa Sen University’s Policy on Plagiarism at
http://thuvien.hoasen.edu.vn/chinh-sach-phong-tranh-dao-van. To ensure the
maintenance of academic integrity, the university asks that students report cases of academic
dishonesty to the teacher and/or the Dean. The names of those students will be kept
anonymous. J. Teaching Staff:
Email, Phone number, Office Office No. Professor’s name Position location hours 1 Pham Quang Huy pqh.huy@gmail.com - - 2
Phung Thai Minh Trang trang.phungthaiminh@hoasen.edu.vn - - 3 4
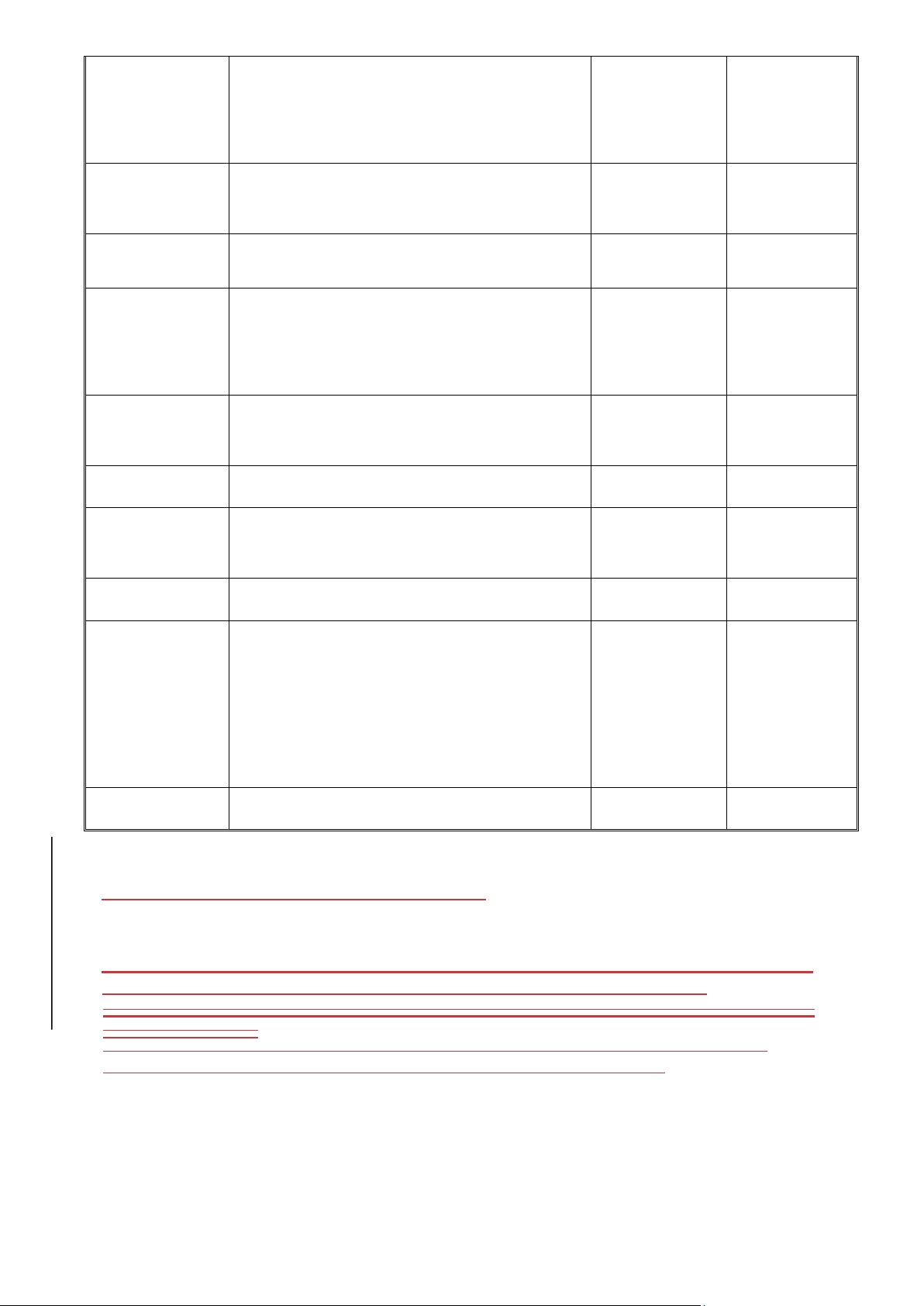
K. Outline of Topics to be covered (Learning Schedule):
Main semester: Once per week
Subordinate semester: Twice per week Week/ Topics References Homework Meeting /Assignment
Chapter 1: Accounting Information
System: an overview Week/ Topics References Homework Meeting /Assignment 1. – What is AIS?
– Characteristics of Useful information.
– The impact of AIS on corporate strategy and culture. 7/8 lOMoAR cPSD| 47205411
2. – The role of The AIS in the Value Chain and Supply Chain.
– The AIS and Corporate Strategy.
Chapter 2: Overview Business Processes
3. – Information Needs and Business Activities
– Business Cycle. Transaction Processing: The Data Processing Cycle.
– Computer-Based Storage Concepts.
– Batch and On- Line Processing.
– Forms of Information Output.
Chapter 3: System Development and
Documentation Techniques 4. - Systems Development and Documentation Techniques. - Data Flow Diagrams (DFD). - Subdividing the DFD. - Flowcharts Symbols. 5. - Document Flowcharts. - System Flowcharts. - Program Flowcharts.
Chap. 4: Internal Control System 6. - Introduction - Why have to control? - Internal Control Systems 7. - Types of Controls - Control Activities - Evaluating Controls
8. Mid term test
Chapter 5: The Revenue Cycle: Sales and
Cash Collections Week/ Topics References Homework Meeting /Assignment 8/8 lOMoAR cPSD| 47205411
9. - Revenue Cycle: Business Activities.
- Information Processing Procedures. - Control Objectives. 10. - Threats and procedures.
- Revenue Cycle Information Needs.
Chapter 6: Expenditure Cycle: Business Activities
11. - Information Processing Procedures. - Control Objectives. - Input and Output 12. - Threats and Procedures.
- Expenditure Cycle Information Needs.
Chapter 7: The Production Cycle
13. - Production Cycle Activities.
- Information Processing Activities
Chapter 8: Human Resources Cycle
14. - Information Processing Procedures. - Control Objectives. - Input and Output Chapter 9: Accounting software
evaluation and design reports
15. General Review – Revision – Q&A Notice:
One session may be reserved for a guest speaker.
Lecturer can arrange one - day field trip for students to visit specific companies instead of
one in-class session and inform Education Department one week in advance.
Lecturer can arrange one - day field trip for students to visit specific companies instead of one in-class session.
Subject is designed with the participant of guest speaker who will share reality from
experience or students will be attended the seminar during the subjects 9/8