



Preview text:
CHAPTER 1: MANAGING
- An organization is a deliberate collection of ppl brought together to accomplish some specific purpose
- 3 characteristics of organizations: distinct purpose, people, structured
- Nonmanagerial employees who work directly on a job or task and have no
responsibility for overseeing the work for others
- Managers – individuals in an organization who direct and oversee the activities of others
- Top managers – responsible for making decisions about the direction of the
organization and establishing policies that affect all organizational members.
- Middle managers – responsible for translating goals set by top managers into specific details
- First-line managers – responsible for directing the day-to-day activities of
nonmanagerial employees and/or team leaders
- Team leaders – responsible for leading and facilitating the acts for a work team
- Scientific management – one best way
- Supervisors and team leaders may both be considered first-line managers.
- (Team leaders -> first-line managers -> middle managers -> top managers)
- Management is the process of getting things done, effectively and efficiently, with and through other people
- ROWE – results only work environment
- EFFFICIENCY “DOING THINGS RIGHT” and getting the most output from the least amount of inputs
- EFFECTIVENESS “DOING THE RIGHT THINGS” by doing those work tasks
that help the organization reach it goals
- 4 management functions: planning, organizing, leading and controlling
+ planning: defining goals, establishing strategy, developing plan
+ organizing: determining needs what-how-who
+ leading: motivating, directing, selecting, resolving
+ controlling: monitoring, comparing, correcting
- Skill: + professional skill (employee) + leadership (employer) MINTZBERG'S VIEW
- 3 main roles: informational roles: monitor, disseminator and spokesperson
interpersonal roles: figurehead, leader and liaison
decisional roles: entrepreneur, disturbance-handler, resource- allocator and negotiator - SKILLS AND COMPETENCIES:
+ conceptual skills: analizing and dianosing complex situations
+ interpersonal skills: working well
+ technical skills: job-specific
+ political skills: power base, right connections
CHAPTER 2: MANAGERS DECISION MAKERS
- Decision-making process – 8 steps includes identifying a problems, selecting a
solutions, evaluating effectiveness of the solution
- Problem: a discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs
- 8 steps: identifine the problems identifine decision criteria (yeu to quyet dinh)
allocation of weights to criteria development of alternatives analysis of
alternatives selection of alternative
implementation of alternative
evaluation of decision effectiveness
- 3 approaches managers use to make decisions: rational model bounded
rationality intuition and managerial decision making
+ rational decision making: choices that consistent and value-maximizing within specified constraints
+ bounded rationality: limits of a manager’s ability
+ intituitive decision making: basic of experience anf accumulated judgment
- PROBLEM : + structured problems: straightforward, clear, familiar, easily defined
and comlete (progammed decision: using a routine approach)
+ unstructured problems: new, unsual, ambigious or incomplete
(nonprorammed decision: unique, using a custom-made solution)
- Procedure: series of interrelated, sequential steps used to respond to a structured prob)
- Rule: explicit statement that tells employees what can or not be done
- Policy: guideline for making decision
- Decision-making conditions – managers face: certainly, risk and uncertainly - ADVANTAGE OF GROUP DECISION: + more complete information
+ diversity of experiences and perspectives + more alternatives generated
+ increased acceptance of a solution + increased legitimacy
- DISADVANTAGE OF GROUP DECISION + time comsuming + minority domination + ambigious responsibility + pressures to conform
CHAPTER 6: Planning and goal setting
Planning involves: + defining the organization’s goal
+ establishing an overall strategy
+ developing a comprehensive hierachy to intergrate and coordinate
Planning provides direction to managers and nonmanagers alike
Informal planning: the planning takes place in smaller businesses
Formal planning: (1) defining specific goals covering a specific time period
(2) writing down goals and making them available to members
(3) using these goals to develop speccific plan – clearly define the path for organization
4 reasons for planning: 1. Set the standards to facilitate control 2. provide direction
3. Minimize waste and redundancy
4. Reduce the impact of change
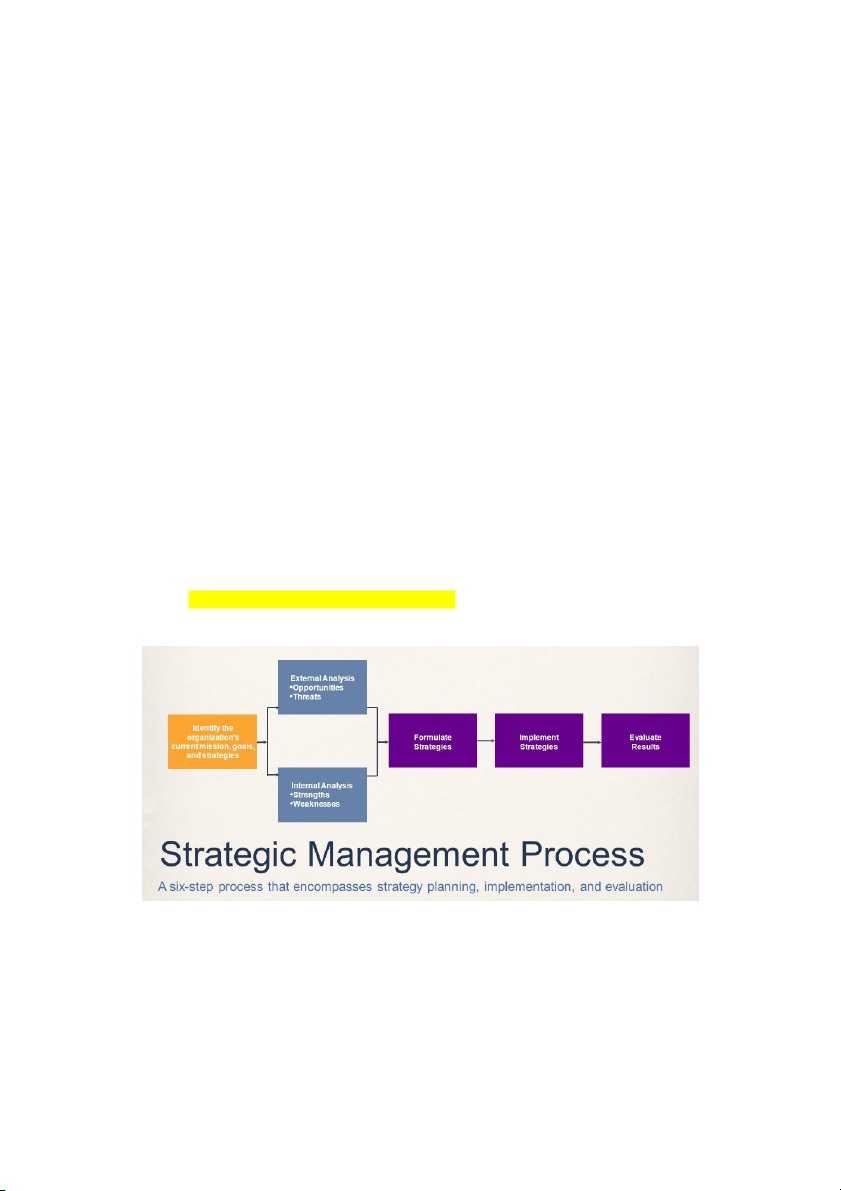
6 steps STRATEGY MANAGEMENT PROCESS
The combined external and internal analysis is SWOT analysis: SWOT + strength + weaknesses + opportunities + threads
MBO 4 ELEMENTS 1. Goal specificity
2. participative decision making 3. an explicit time period 4. performance feeback
increase employee performance and organizational productivity
3 CONTIGENCY FACTORS OF develop plan - Organizational level
- Degree of environmental incertainly - Length of future commitments
Four types of organizational structures are functional, multi-divisional, flat, and matrix structures
CHAPTER 7 STRUCTURING AND DESIGNING ORGANIZATIONS
Organizing + w needs to be done + how it will be done + who to do it
6 ELEMENTS OF ORGANIZE STRUCTURE 1. Work specialization 2. Departmentazation 3. Authority + responsible 4. Span of control
5. Centralization ver us decentralization 6. Formalization
CHAPTER 8 MANAGING HUMAN RESOURCE 8 important HRM activities 1. Recruitment 2. Downsizing 3. Selection 4. Orientation 5. Training 6. Performance appraise 7. Compensation 8. Benefits
After + establish an organization’s strategy It’s time to add ppl
+ design the organization structure
HRM process include : 1. Employment planning 2. recruitment and downsizing 3. selection
Emp planning = right number + right kinds of ppl
2 steps: assessing current HM + future HM needs
+ develop plan to meet those need
Human resource inventory: name, education,training, prior employment…
Job analysis: minimal knowledge, skills, ability of adequate performance
Job description: describe the job: what, how, why be done
Job specification: knowledge, skill, attitudes needed to the job
Recruitment: process of locating, identifying, and attracting capable applicants DOWNSIZING OPTIONS: 1. Firing permanent 2. Layoffs temporary
3. Attrition resignations or normal retirements
4. Transfers moving laterally or downward 5. Reduced workweeks 6. Early retirements 7. Job sharing
Major intent of any selection activity is to reduce the probability of making reject errors
or accept errors while increaseing the probability of making correct decisions
Performance-simulation test = selection devices based on actual job behaviors thử
nghiệm mô phỏng hiệu suất. 3 goals of orientation: reduce the initial anxiety
Familiarize new employee with the job
Facilitate the outsider – insider transition
Realistic job preview include both positive and negative information about the job and the company
CHAPTER 11: MOTIVATING AND REWARDING EMPLOYEES
Motivation refers to the process by which a person’s efforts are energized, directed, and
sustained toward attaining a goal
3 elements: energy, direction, persistence
MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS THEORY
Five basic categories of needs: physiological, safety, love, esteem, and self-actualization.
Lower-order needs satisfied - externally, higher-order needs – internally MCGREGOR’S THEORY X AND Y
Base on 2 assumptions about human nature
Theory X: negative – little ambition, dislike work, want to avoid responsibility, need to
be closely controlled to work effectively
Theory Y: positive – enjoy work, seek out, accept responsibility, exercise self-direction
To maximize motivation of employee use Theory Y HERZBERG’S 2 FACTORS THEORY
Intrinsic factors job satisfaction
concentrate on achievement & recognition
Extrinsic factors job dissatisfaction
Ppl felt good – intrinsic factors – job content
Ppl were dissatisfied – extrinsic factors – job context
Hygience factors that eliminate job dissatifaction but don’t motivate: salary, status,…
Motivators factors that increase job satisfaction and motivation: achievement, recognition,… MCCLELLAND’S 3 NEEDS THEORY
nAch – drive to succeed, excel in relation to a set of standards nPow – make others behave
nAff (affiliation) – desire for friendly and close interpersonal relationships
Comtemporary theory 1. Goal setting 2. Equity 3. Expectancy
Goal-setting theory – specific goals increase performance, difficult goals, result in higher performance than do easy goals
Working toward a goal is a major source of job motivation
4 influences on goal-performance (contigencies): feedback, goal commitment, adequate
self-efficacy, national culture
Design the job by job characteristics model (JCM)
To motivate focus on the job content aspects 9the motivator)
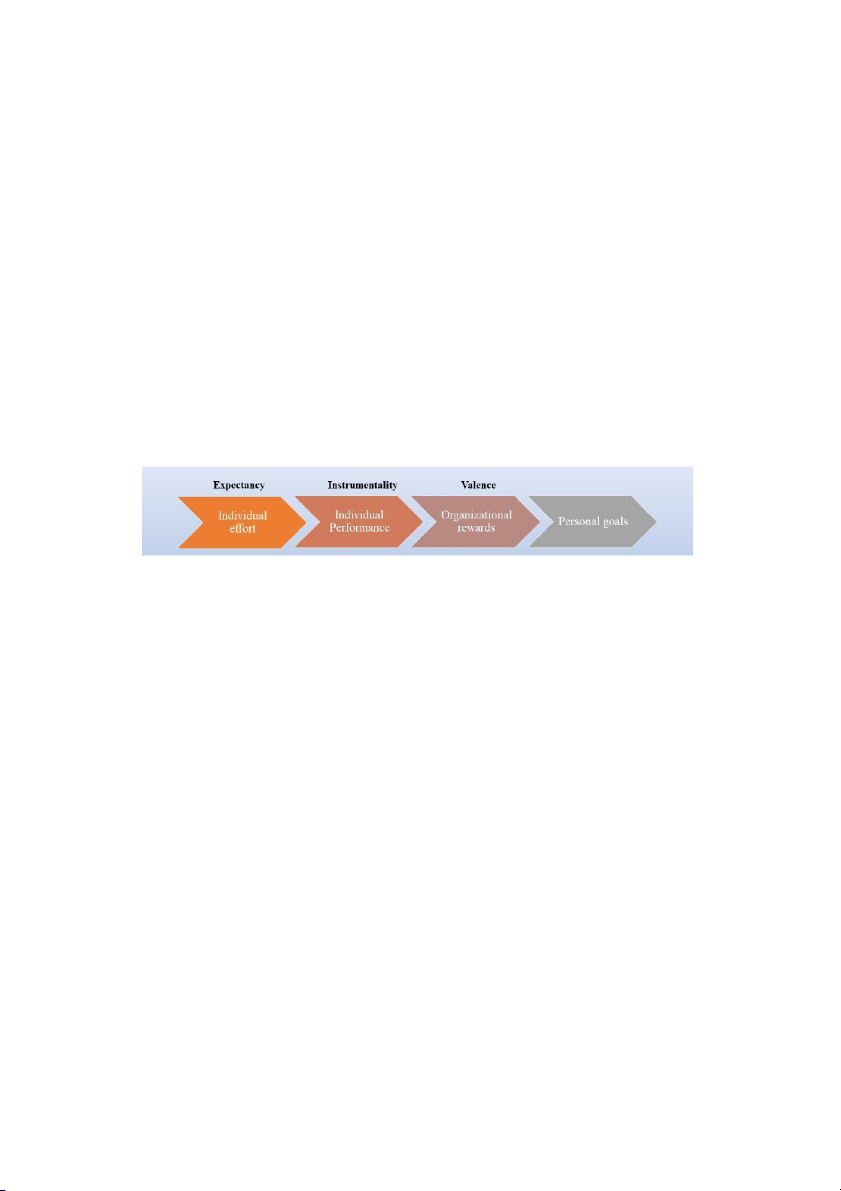
3 referant categories: persons, system, self EXPECTANCY MODEL
CHAPTER 14: CONTROLLING WORK AND ORGANIZATIONAL PROCESS
Control – monitoring activities to ensure that they’re being accomplished as planned and
correcting any significant deviation Control important is because:
1. It’s the only way to know whether goals are being met
2. It provides info + fb so managers feel comfortable enpowering employees
3. It helps protect an org + ít assets. Control process has 3 steps:
+ measuring actual performance
+ comparing actual performance against a standard
+ taking managerial action to correct deviations
Immediate corrective action that addresses problem at once to get performance back on track
Feedforward control that take place before a work activity be done
Concurrent control that take place whil a work activity is in process
Feedforward concurrent feedback
Feedback control takes place after the activity is done
2 advantages of feedback control:
+ give managers meaningful infor on how effective their planning efforts were
+ feedback can enhance motivation
“correct performance problems". Both formulating strategies and setting standards fall
primarily under the planning function, while structuring an organization is part of the organizing function
MBWA allows the manager to get a feel for the work area and the moods and attitudes of
the people who work there. (walking around) => personal contact
MBWA (management by walking around)
Controlling comes after planning, organizing, and leading in the management process, so it is the final step
The controlling function helps managers protect an organization's assets




