1 394
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
LẦN THỨ XV – SƠN LA 2019
ĐỀ THI CHỌN HỌC SINH GIỎI
MÔN: TIẾNG ANH - KHỐI 10
Ngày thi: 27 tháng 7 năm 2019
Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề)
Tổng điểm bài thi Giám khảo
Số phách
(Do chủ tịch HĐ
chấm thi ghi)
Bằng số Bằng chữ
Giám khảo 1
(kí, ghi rõ họ tên)
Giám khảo 2
(kí, ghi rõ họ tên)
Lưu ý : Thí sinh làm bài trực tiếp trên tờ giấy thi. Cán bộ coi thi không giải thích gì thêm.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
-
PART I. LISTENING (50p)
HƯỚNG DẪN PHẦN THI NGHE HIỂU
Bài nghe gồm 4 phần; mỗi phần được nghe 2 lần, mỗi lần cách nhau 05 giây; mở đầu và kết thúc mỗi
phần nghe có tín hiệu. Thí sinh có 15 giây để đọc mỗi phần câu hỏi.
Mở đầu và kết thúc bài nghe có tín hiệu nhạc.
Mọi hướng dẫn cho thí sinh (bằng tiếng Anh) đã có trong bài nghe.
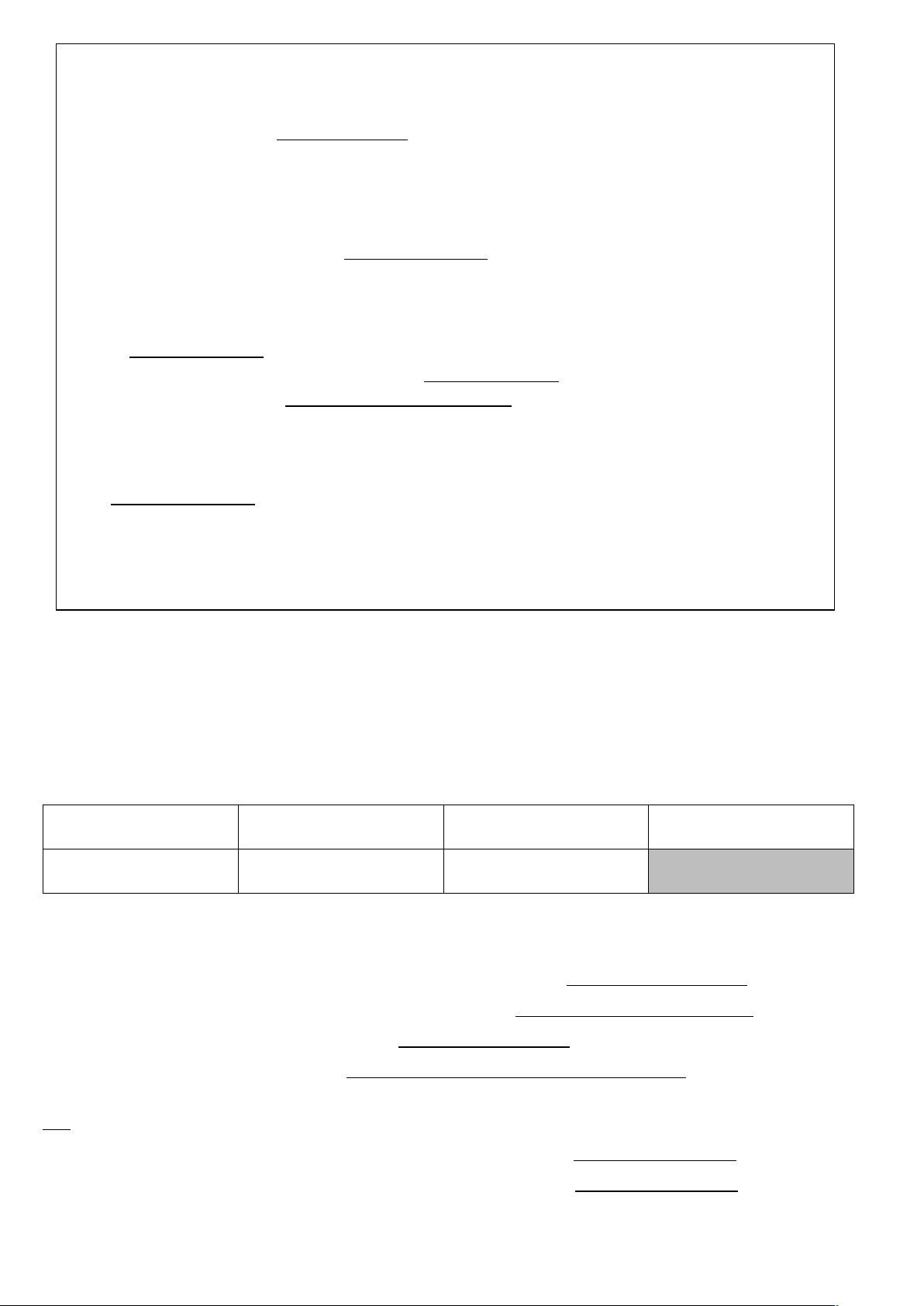
FAMILY EXCURSIONS
Travel on an old (1) .
Can take photos of the mountains that surround the lake
Farm visit
!"
#$!%
Cycling trips
"%&'
() $
*"!"$
&!+ ,-
".
/ !
2 394
Section 1. You will hear a man asking a woman the information about a family excursion. For questions
from 1 to 7, fill in each gap with NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER. (14p)
Write your answers here:
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7.
Section 2. Listen to the recording and complete each of the following gaps with NO MORE THAN THREE
WORDS AND/ OR A NUMBER (16p)
1. Unlike crowded jets, the Aircruise will allow passengers to travel in
2. The Aircruise can travel at low altitudes if there is something
3. Hydrogen fuels the airship and also provides for the people on board.
4. The Hindenburg airship disaster killed people.
5. Scientists are keen to develop transport options which are both
and environmentally friendly.
6. The luxury features on board include private apartments, a bar and a
7. Compared to airports, the Aircruise has the potential to land closer to

3 394
8. The concept is getting a lot of attention from a Korean company which makes
Write your answers here:
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7. 8.
Section 3. Listen to a teacher giving a lesson on the effects of tourism. For questions 1 – 5, decide whether
the statements are true (T) or false (F). (10p)
1. According to the teacher, tourism damages the things that tourists come to see.
2. Most people who visited Goa before 1986 were poor.
3. Local people welcomed the increase in tourism.
4. Local people benefit from all-inclusive holiday packages.
5. The removal of mangrove swamps increases the risk of coastal flooding.
Write your answers here:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Section 4. You will hear a radio interview with a ghost hunter called Carlene Belfort. For questions 1-5,
choose the best answer (A, B, C or D). (10 pts)
1 How did Carlene become a ghost hunter?
A. She wanted to contact her dead grandmother.
B. She grew up in a haunted house.
C. Her parents encouraged her.
D. She was often alone at home at night.
2. Who does Carlene mostly work for?
A. people who want reassurance
B. people who want to contact loved ones
C. people who want to find a ghost
D. people who call him
3. How does Carlene detect when ghosts are present?
A. She feels cold.
B. She gets evidence from her equipment.
C. She feels them touching her hair.
D. She sees the ghosts in photos.
4. What does Carlene think about people who don’t believe her?
A. She doesn’t understand why they think that.
B. She thinks they don’t have enough evidence.
C. She wants them to experience it for themselves.
D. She thinks most of them are scientists.
5. What does Carlene feel about her business?
4 394
A. She realizes she is taking advantage of customers.
B. She doesn’t think it is a business.
C. She wants to expand and make more money.
D. She feels she is providing a service.
Write your answers here:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
PART II: LEXICO - GRAMMAR (40p)
Section 1. Choose the word or phrase that best fits each blank in the following sentences. (20 p)
1. is imperative in your new job. The director disapproves of being late.
A. Having time B. Keeping time C. Being on time D. Taking time
2. Two students are talking about an upcoming test.
- Mary: “The sociology test seems to be very difficult. I am still not confident about my performance this
Friday. I’ve gone through all the materials, though!”
- Alexis: “ ”
A. You’ve read all the materials, it’s OK for you.
B. I have read all the chapters, but I have not studied the notes from the lectures.
C. That is correct! You are doing really well too, Mary!
D. I do not think that is your problem. It is probably a case of anxiety.
3. , the balcony chairs will be ruined in this weather.
A. Left uncovered B. Having left uncovered
C. Leaving uncovered D. Been left uncovered
4. Why do you have such a with model railways?
A. desire B. love C. fascination D. preference
5. Small companies may take their goods abroad for trade shows without paying foreign value-added
taxes by acquiring an ATA carnet.
A. a document calls B. a document called C. calls a document D. called a document.
6. She walked in _, as if nothing had happened.
A. as cool as a cucumber B. as clear as mud
C. as dead as a doornail D. as dry as a bone
7. Ever since we quarreled in the office, Janice and I have been enemies.
A. assured B. confirmed C. defined D. guaranteed
8. I can accept criticism in general, but George really it too far, so I had no other option but
to show my disapproval.
A. carried B. pushed C. put D. made
9. One of the organization’s aims is to information about the disease so that more people
know about its symptoms.
5 394
A. disentangle B. deride C. dwindle D. disseminate
10. Luckily, I a new pair of sunglasses as I found mine at the bottom of a bag.
A. needn’t have bought B. needed not to buy
C. didn’t need to buy D. hadn’t to buy
11. Take the doctor’s advice into consideration. He’s in earnest about the epidemic.
A. mortally B. fatally C. deadly D. gravely
12. Hotel rooms must be by 10 a.m., but luggage may be left with the porter.
A. vacated B. evacuated C. abandoned D. left
13. Mary: “Do you want to watch this or the
news?” Linda: “Oh, . It’s up to you.”
A. I agree B. I couldn’t agree more C. Don’t mention it D. I’m easy
14. It's difficult for a teacher to her students' interest for a whole semester.
A. sustain B. resist C. account for D. recognize
15. This cheese isn’t fit for eating. It’s all over after lying in the bin for so long.
A. rusty B. mouldy C. spoiled D. sour
16. We should all when advertisers attempt to use unfair practices.
A. make a stand B. make a deal C. make amends D. make a comeback
17. Katie O'Donovan, public policy manager at Google UK, said the company had shown its to
protecting children by developing its resources - such as an online safety course which has been taught
to 40,000 schoolchildren.
A. commitment B. enthusiasm C. interest D. keenness
18. The realization of our holiday plans has had to be because of my mother’s sudden illness.
A. prevented B. shelved C. expired D. lingered
19. The new situation has a lot of anger and dissatisfaction. Our duty now is to encounter it in
the most sensible way.
A. devised B. established C. originated D. provoked
20. Education should be a universal right and not a .
A. deliverance B. enlightenment C. privilege D. liberty
Write your answers here:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
11. 12. 13. 14. 15.
16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
Section 2. Fill each gap with the correct form of the words in brackets. (10 p)
1. It would be a decision to stop supporting the arts. (RUTH)

6 394
2. In the not-too-distant past farm, animals were able to live _ lives in what we would now term
'free- range' conditions. (NATURE)
3. Forests from an integral component of the are essential to the stabilization of global climate
and the management of water and land. (SPHERE)
4. Mr. Brown was the at the meeting. (CHAIR)
5. He was of making her acquaintance. (DESIRE)
6. As young women , they may perceive sex as an assertion of independence and gender
equality. (CULTURAL)
7. She is very efficient and polite to the customers. (FAIL)
8. She found him arrogant and . (DOMINATE)
9. An anonymous donated $2 million. (BENEFIT)
10. of course, I’m much better off than I used to be. (MONEY)
Write your answers here:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
7 394
Section 3. The passage below contains TEN mistakes. Identify the mistakes and provide the corrections
in the spaces below. (10 p)
Line
1 One of the most amazing marathon races in the world is the Marathon of the Sands. It takes places
2 every April in the Sahara Desert in the south of Morocco, a part of the world when temperatures can
3 reach fifty degrees centigrade. The standard length of the marathon is 42.5 kilometers but this one is
4 240 kilometers long and spends seven days to complete. It began in 1986 and now attracts about two
5 hundred runners, the majority of their ages range from seventeen to forty-seven. About half of them
6 come from France and the rest to all over the world. From Britain, it costs 2,500 pounds to enter,
7 this includes return air fares. The race is rapidly getting more and more popular despite, and perhaps
8 because of, the harsh conditions that runners must endure. They have to carry food and something
9 else they need for seven days in a rucksack weighing no more than twelve kilograms. In addition to
10 this, they are given a liter and a half of water every ten kilometers. Incredibly, near all the runners
11 finish the course. One man, Ibrahim EI Joual, took part in every race from 1986 to 2004. Runners
12 do suffer terrible physical hardships. Sometimes they lose toenails and skin peels on their foot.
13 However, doctors are always on hand to deal with minor injuries and to make sure that runners do
14 not push themselves too far.
15
Write your answers here:
Line
Mistakes Corrections
Line
Mistakes Corrections
1. 6.
2. 7.
3. 8.
4. 9.
5. 10.
PART III. READING (50p)
Section 1. Read the following passage and decide which answer (A, B, C, or D) best fits each gap. Write
your answer in corresponding numbered boxes. (10 p)
As time (1) , the power of newspapers seems to be on the increase. This is odd because in
the relatively (2) past people were predicting that the influence of the written word would
diminish in direct proportion to the rate of increase of the spoken word and moving image through TV and
video. The Internet, cable and satellite television, Tele text and multi-media computers in (3) other
home should surely have (4) _ for
newspapers by now, particularly alongside a perceptible resurgence in the audiences for news-carrying

8 394
radio stations. How have these organs survived, let alone flourished,
9 394
particularly on a Sunday? Why do people who have seen a football or tennis (5) live or on the
small screen rush the next day to read a potted version of it in four or five columns which surely cannot
mean more to the reader than that self-same viewer of the previous afternoon or evening? Why would
anyone who has seen a film and formed a (6) impression of it the following day read a review of the
aforesaid film in a newspaper? To see if he/ she is right? Isn’t that what friends are for? Don’t we have
colleagues for just that purpose – to see if our ideas on any (7) song, film or
programme tally with others? What is this product that (8) of not much more
than outrageous headlines, wayward comment, subjective editorials and hyperbolic sports pages still doing
in our lives? It seems for the time (9) to be leading a
charmed life. When it finally goes, though, many may come to mourn its (10) .
1. A. flies B. passes C. goes D. drags
2. A. latest B. distant C. immediate D. recent
3. A. all B. any C. every D. one
4. A. done B. gone C. stood D. set
5. A. player B. set C. match D. meeting
6. A. direct B. coloured C. bright D. vivid
7. A. given B. taken C. subjected D. written
8. A. comprises B. contains C. consists D. informs
9. A. out B. being C. given D. present
10. A. perishing B. dying C. falling D. passing
Write your answers here:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Section 2. Read the passage and fill in each gap with ONE suitable word. (10 p)
In British English this standard accent is known as R.P. or Received Pronunciation. This coupled
with the sort of English described in grammar books is the accepted (1)
. Its use, however, is
restricted (2)
geographically and socially; it is most (3)
used among the middle classes in the south of
England. Its speakers, (4)
, carry both a geographical and (5)
label, as do the speakers of all its
variants, although the more socially mobile someone is the more complex his accent becomes, and so the
more (6)
he is to label. Attitudes towards this vary, from the parents (7)
train their children not to speak
with a local (8)
so that “they will have a better chance in life”, to the liberal, trendy young manager
who adopts a local accent (9)
a form of inverted snobbery. But these stances are extreme, but,
nevertheless, the (10)
between language and social status is a potentially explosive subject in British
society.
Write your answers here:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.

10 394
Section 3: Read the following passage and complete the statements that follow by choosing A, B, C or D
to indicate your answer which you think fits best. (10 pts)

11 394
[1] Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution is known as one of the most important and controversial
scientific theories ever published. Darwin was an English scientist in the 19th century best known for his
book “On the Origin of Species.” In his book, Darwin postulated different species shared characteristics of
common ancestors, that they branched off from common ancestors as they evolved, and that new traits and
characteristics were a result of natural selection. The theory is based on the assumptions that life
developed from non-life and progressed and evolved in an indirect manner. Therefore, the Theory of
Evolution, while controversial, has shaped and influenced the modern scientific world's thinking on the
development of life itself. Darwin was born February 12, 1809 in England. Although initially entering
into medicine, Darwin chose to pursue his interest in natural science and embarked on a five-year journey
aboard the H.M.S. Beagle, a British sloop belonging to the Royal Navy. Because of his experience aboard
the Beagle, he laid the foundation for his Theory of Evolution while also establishing himself within the
scientific community. Specifically, Darwin's keen observation of the fossils and wildlife he saw during his
time on the Beagle served as the basis for the cornerstone of his theory: natural selection.
[2] Natural selection contributes to the basis of Darwin's Theory of Evolution. One of the core tenets of
Darwin's theory is that more offspring are always produced for a species than can possibly survive. Yet, no
two offspring are perfectly alike. As a result, through random mutation and genetic drift, over time offspring
develop new traits and characteristics. Over time beneficial traits and characteristics that promote survival
will be kept in the gene pool while those that harm survival will be selected against. Therefore, this natural
selection ensures that a species gradually improves itself over an extended duration of time. On the
other hand, as a species continues to 'improve' itself, it branches out to create entirely new species that are
no longer capable of reproducing together.
[3] Through natural selection, organisms could branch off of each other and evolve to the point where they
no longer belong to the same species. Consequently, simple organisms evolve into more complex and
different organisms as species break away from one another. Natural selection parallels selective breeding
employed by humans on domesticated animals for centuries. Namely, horse breeders will ensure that horses
with particular characteristics, such as speed and endurance, are allowed to produce offspring while horses
that do not share those above-average traits will not. Therefore, over several generations, the new
offspring will already be pre-disposed towards being excellent racing horses.
[4] Darwin's theory is that 'selective breeding' occurs in nature as 'natural selection' is the engine behind
evolution. Thus, the theory provides an excellent basis for understanding how organisms change over time.
Nevertheless, it is just a theory and elusively difficult to prove. One of the major holes in Darwin's theory
revolves around “irreducibly complex systems.” An irreducibly complex system is known as a system
where many different parts must all operate together. As a result, in the absence of one, the system as
a whole collapses. Consequently, as modern technology improves, science can identify these “irreducibly
complex systems” even at microscopic levels. These complex systems, if so inter -reliant, would be resistant
to Darwin's supposition of how evolution occurs. As Darwin himself admitted, “To suppose that the eye
with all its inimitable contrivance for adjusting the focus for different distances, for admitting different
amounts of light, and for the correction of spherical and chromatic aberration, could have been formed by
natural selection, seems, I free confess, absurd in the highest degree".
[5] In conclusion, “On the Origin of Species” is known as one of the most consequential books ever
published. Darwin's Theory of Evolution remains, to this day, a lightning rod for controversy. The theory
can be observed repeatedly, but never proven, and there are a plethora of instances that cast doubt on the
processes of natural selection and evolution. Darwin's conclusions were a result of keen observation
and training as a naturalist. Despite the controversy that swirls around his theory, Darwin remains one of the
most influential scientists and naturalists ever born due to his Theory of Evolution.

12 394
Questions:
1. The word 'postulated' in paragraph 1 is closest in meaning to…
A. disagreed B. proved C. opposed D. hypothesized
2. Which sentence is most similar to the following sentence from paragraph 1?
The theory is based on the assumptions that life developed from non-life and progressed and
evolved in an indirect manner.
A. The Theory of Evolution is founded on evidence that non-organic compounds are the basis of life,
developed in an unguided way.
B. Based on certain assumptions, we can prove that evolution occurs in all living and non-living entities.
C. According to Darwin, if we assume that life at its origin was created from nonorganic compounds
and developed in an unguided manner, his theory holds true.
D. Due to the controversy, it is hard to make assumptions about the Theory of Evolution.
3. According to paragraph 2, what are the causes for species developing new traits and characteristics?
A. medicine and longevity B. survival and selection
C. mutation and genetic drift D. tenets and theory
4. According to paragraph 3, what is natural selection most comparable to as a process?
A. branching trees B. selective breeding
C. irreducibly complex systems D. the human eye
5. What is the purpose of paragraph 3 in the passage?
A. To show the simple-to-complex nature of natural selection in context
B. To create doubt as to the validity of the theory
C. To contrast with the ideas presented in paragraph 2
D. To segue into the main point presented in paragraph 4
6. The word 'contrivance' in paragraph 4 is closest in meaning to:
A. organization B. retention C. absurdity D. systems
7. All of the following are mentioned in paragraph 4 as a viewpoint to state that natural selection is
difficult to prove EXCEPT …
A. The belief that the complexity of the human eye could have been formed by natural selection seems
highly unlikely.
B. The presence of irreducibly complex system contradicts how evolution occurs.
C. Modern technology has been used to prove that irreducibly complex systems exists.
D. Selective breeding is the major hole in the theory of natural selection.
8. Examine the four [█] in the selection below and indicate at which block the following sentence could
be inserted into the passage:
The five-year voyage proved to be a major turning point in his life.
⬛ [A] Darwin was born February 12, 1809 in England. █ [B] Although initially entering into medicine,
Darwin chose to pursue his interest in natural science and embarked on a five-year journey aboard the
H.M.S. Beagle, a British sloop belonging to the Royal Navy █ [C] Because of his experience aboard the
Beagle, he laid the foundation for his Theory of Evolution while also establishing himself within the
scientific community. █ [D]

13 394
A. [A] B. [B] C. [C] D. [D]

14 394
9. In paragraph 4, what was the author's purpose of including a quote that the belief that the complexity
of the human eye could have been formed by natural selection seems highly unlikely?
A. To provide evidence that irreducibly complex systems exists
B. To prove that the natural selection contradicts the basis of Darwin's Theory of Evolution
C. To support that the natural selection contributes to the basis of Darwin's Theory of Evolution
D. To support the claim that natural selection is just a theory and difficult to prove
10. These sentences express the most important ideas in the passage EXCEPT…
A. Natural selection explains how species change gradually over time.
B. The Theory of Evolution describes how species 'branch out' from a common ancestor.
C. Creationists strongly object to the premise of the Theory of Evolution
D. Both Darwin and “On the Origin of Species” are among the most influential things to happen to
naturalist science.
Write your answers here:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Section 4. Read the following passage and do the tasks that follow. (20p)
Flying tortoises
An airborne reintroduction programme has helped conservationists take significant steps to protect the
endangered Galapagos tortoise.
A
Forests of spiny cacti cover much of the uneven lava plains that separate the interior of the Galapagos island
of Isabela from the Pacific Ocean. With its five distinct volcanoes, the island resembles a lunar landscape.
Only the thick vegetation at the skirt of the often cloud-covered peak of Sierra Negra offers respite from the
barren terrain below.
This inhospitable environment is home to the giant Galapagos tortoise. Some time after the Galapagos’s
birth, around five million years ago, the islands were colonised by one or more tortoises from mainland
South America. As these ancestral tortoises settled on the individual islands, the different populations
adapted to their unique environments, giving rise to at least 14 different subspecies. Island life agreed with
them. In the absence of significant predators, they grew to become the largest and longest-living tortoises on
the planet, weighing more than 400 kilograms, occasionally exceeding 1.8 metres in length and living for
more than a century.
B
Before human arrival, the archipelago's tortoises numbered in the hundreds of thousands. From the 17th
century onwards, pirates took a few on board for food, but the arrival of whaling ships in the 1790s saw this
exploitation grow exponentially. Relatively immobile and capable of surviving for months without food or
water, the tortoises were taken on board these ships to act as food supplies during long ocean passages.
Sometimes, their bodies were processed into high- grade oil.
In total, an estimated 200,000 animals were taken from the archipelago before the 20th century. This
historical exploitation was then exacerbated when settlers came to the islands. They hunted the tortoises and
destroyed their habitat to clear land for agriculture. They also introduced alien species - ranging from cattle,
pigs, goats,

15 394
rats and dogs to plants and ants - that either prey on the eggs and young tortoises or damage or destroy their
habitat.
C
Today, only 11 of the original subspecies survive and of these, several are highly endangered. In 1989, work
began on a tortoise-breeding centre just outside the town of Puerto Villamil on Isabela, dedicated to
protecting the island’s tortoise populations. The centre’s captive-breeding programme proved to be
extremely successful, and it eventually had to deal with an overpopulation problem.
D
The problem was also a pressing one. Captive-bred tortoises can’t be reintroduced into the wild until they’re
at least five years old and weigh at least 4,5 kilograms, at which point their size and weight - and their
hardened shells - are sufficient to protect them from predators. But if people wait too long after that point,
the tortoises eventually become too large to transport.
E
For years, repatriation efforts were carried out in small numbers, with the tortoises carried on the backs of
men over weeks of long, treacherous hikes along narrow trails. But in November 2010, the environmentalist
and Galapagos National Park liaison officer Godfrey Merlin, a visiting private motor yacht captain and a
helicopter pilot gathered around a table in a small cafe in Puerto Ayora on the island of Santa Cruz to work
out more ambitious reintroduction. The aim was to use a helicopter to move 300 of the breeding centre’s
tortoises to various locations close to Sierra Negra.
F
This unprecedented effort was made possible by the owners of the 67-metre yacht White Cloud, who
provided the Galapagos National Park with free use of their helicopter and its experienced pilot, as well as
the logistical support of the yacht, its captain and crew. Originally an air ambulance, the yacht’s helicopter
has a rear double door and a large internal space that’s well suited for cargo, so a custom crate was designed
to hold up to 33 tortoises with a total weight of about 150 kilograms. This weight, together with that of the
fuel, pilot and four crew, approached the helicopter’s maximum payload, and there were times when it was
clearly right on the edge of the helicopter’s capabilities. During a period of three days, a group of volunteers
from the breeding centre worked around the clock to prepare the young tortoises for transport. Meanwhile,
park wardens, dropped off ahead of time in remote locations, cleared landing sites within the thick brush,
cacti and lava rocks.
G
Upon their release, the juvenile tortoises quickly spread out over their ancestral territory, investigating their
new surroundings and feeding on the vegetation. Eventually, one tiny tortoise came across a fully grown
giant who had been lumbering around the island for around a hundred years. The two stood side by side, a
powerful symbol of the regeneration of an ancient species.

16 394
For questions 1 – 5, choose correct heading for sections B – F from the list of headings below.
List of Headings
i
The importance of getting the timing right
ii
Young meets old
iii
Developments to the disadvantage of tortoise
populations
iv
Planning a bigger idea
v
Tortoises populate the islands
vi
Carrying out a carefully prepared operation
vii
Looking for a home for the islands’ tortoises
viii
The start of the conservation project
Example: Section A: v
1. Section B
2. Section C
3. Section D 4. Section E
5. Section F
For questions 6 –10, fill in each blank with ONE WORD from the passage.
The decline of the Galapagos tortoise
• Originally from mainland South America
• Numbers on Galapagos islands increased, due to lack of predators
• 17th century: small numbers taken onto ships used by (6.)
• 1790s: very large numbers taken onto whaling ships, kept for food and also used to produce (7.)
• Hunted by (8.) on islands
• Habitat destruction: for the establishment of agriculture and by various (9.)
not native to the islands, which also fed on baby tortoises and tortoises (10.)
.
Write your answers here:

17 394
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.

18 394
Section 5. Read the following passage and choose from people A-D. The people may be chosen more than
once. (10p)
A
Sundance by Teresa Wilson
Kerry:
I really don't know why this book is so popular. I mean, I suppose it is going to appeal to young girls who
want danger and romance, but I found this book really tedious. For a start, the characters were really
unconvincing. The author went out of her way to add lots of details about the characters, but I found these
details really pointless. I thought that some of the facts she presented about the main characters would
become significant in some way later in the novel, but they didn't. They were just worthless bits of
information. I also was disappointed that, although this book is meant to be about kids at high school, the
writer seems to have no recollection at all about what it's like to be 17. The main character thought and
acted like a 32-year old. It just wasn't believable. I'm not saying Teresa Wilson is a bad writer. She can
obviously string words together and come up with a story that is appealing to a large number of people, but
she lacks anything original. There is no flair. It just uses the same sort of language as you can see in many
other mediocre novels.
B
Wild Ways by Margery Emerson
Liz:
I have to say that I won't forget this book for a long time. I was hooked from the very first chapter. The
devastating story affected me so much that I don't know if I'll ever feel the same again. I was close to tears
on several occasions. I've got images in my brain now that I don't think will ever leave me. It's incredibly
well- researched and, although it is fiction, is based on shocking real-life events. I learned an awful lot about
things that went on that I never knew before. Margaret Emerson has a brilliant way with words and I really
felt real empathy towards the characters, although I was sometimes irritated by the choices they made.
However, the parallel story, the part that is set in the present, is not quite so good. I found myself just
flicking through that part so that I could get back to 1940s Paris.
C
Orchid by Henry Rathbone
Imogen:
This is a delightful novel full of wonderful imagery, a paints a remarkable picture of life in a distant time
and a far-away place. If you're looking to learn about Eastern culture in great detail, then this is probably not
the book for you, as the writer skims over most of the more complicated aspects of the country's etiquette.
The

19 394
historical aspects are also not covered in much depth. However, I wonder whether this was the writer's
intention. By doing this, he symbolise the superficiality of the girl's life. She, like the book, is beautiful and
eager to please, but remains too distant from us, the readers, to teach us much. Although I loved the book
and read it in one sitting, the ending was a bit of a disappointment. A story which involves so much turmoil,
in a place where the future is uncertain, should not have a happy-ever-after fairy-tale ending.
D
High Hills by Mary Holland
Hannah:
I read this book for a literature class. I know it's a classic, and I did try to like it, but I just didn't get into it. I
kept persevering, hoping that I'd start to enjoy it, but no such luck. The famous scene out on the moors was
definitely the best bit of the book, but even that I found ridiculous when it is clearly supposed to be
passionate. As I approached the end of the book, I figured there must be some kind of moral to the story,
something that I would learn from the experience of trudging through seven hundred long pages, but there
was nothing worthwhile. I don't know why the literary world sees this book as such a masterpiece. The
characters are portrayed as being intelligent, but they do such stupid things! And as for it being a love story
- marrying someone you don't love and then being abused by them - that doesn't spell love to me.
Which person read a book which...
1. was set in an Oriental country
2. had characters that the reader could sympathise with
3. is well-known and was written a long time ago
4. contained two stories
5. was historically accurate
6. made the reader cry
7. contained insignificant details
8. is written for teenagers
9. is classed as romantic fiction
10. has an attractive but shallow heroine
Write your answers here:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
PART IV: WRITING (50 points)
Section 1: Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means the same as the sentence
before it. (10 p)

20 394
1. I really enjoy getting thoroughly absorbed in this good book.
I am losing .
2. He’s partially deaf so he finds it difficult to communicate on the phone.
Were it .
3. Sally distrusts modern technology strongly.
Sally has .
4. If the weather is fine, we may go camping at the weekend.
Weather .
5. “There’s no point in writing it all out in longhand if you can use a typewriter, isn’t there?”
She dissuaded .
Section 2: Rewrite these sentences using the words in CAPITAL. You must not change the given words.
(10 p)
1. Do you think we can stew this kind of meat? (LEND)
Do ?
2. Normally, the money is released within about three months. (COURSE)
In .
3. We can’t possibly imagine how we are going to afford a new car. (REMOTEST)
We .
4. That medicine was very effective and I started to feel better immediately. (MAGIC)
That medicine
.
5. I’m sure Nancy is still presuming that the party starts at nine. (IMPRESSION)
I’m sure .
Section 3: Paragraph writing (30 p)
Recently, there have been an increasing number of school students choosing to take
standardized English examinations like TOEFL, IELTS or TOEIC.

21 394
What are the causes of this trend?
Write a paragraph of 200 words to express your viewpoint.
Write your paragraph here:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………
PART I. LISTENING (50p)
Section 1. You will hear a man asking a woman about the information about a family excursion. For
questions from 1 to 7, fill in each gap with NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER. (14p)

22 394
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
LẦN THỨ XV – SƠN LA 2019
HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤM
ĐỀ THI CHỌN HỌC SINH GIỎI
MÔN: TIẾNG ANH - KHỐI 10
Ngày thi: 27 tháng 7 năm 2019
Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút (không kể thời gian giao
đề) HDC gồm có 4 trang
1. steamship 2. garden(s) 3. map 4. experience
5. Ratchesons 6. helmet 7. 267
Section 2. Listen to the recording and complete each of the following gaps with NO MORE THAN THREE
WORDS AND/ OR A NUMBER (16p)
1. comfort and style 2. interesting to see 3. power and water 4. 35
5. sustainable 6. glass floor 7. urban centres 8. electrical goods
Section 3. Listen to a teacher giving a lesson on the effects of tourism. For questions 1 – 5, decide whether
the statements are true (T) or false (F). (10p)
1. T 2. F 3. F 4. F 5. T
Section 4. You will hear a radio interview with a ghost hunter called Carlene Belfort. For questions 1-5,
choose the best answer (A, B, C or D). (10 pts)
1. B 2. A 3. B 4. C 5. D
PART II: LEXICO - GRAMMAR (40p)
Section 1. Choose the word or phrase that best fits each blank in the following sentences. (20 p)
1. C 2. D 3. A 4. C 5. B 6. A 7. B 8. A 9. D 10. C
11. C 12. A 13. D 14. A 15. B 16. A 17. A 18. B 19. D 20. C
Section 2. Fill each gap with the correct form of the words in brackets. (10 p)
1. ruthless
2. natural
3. biosphere
4. chairman
5. desirous
6. acculturate

23 394
7. unfailingly
8. domineering
9. benefactor
10. Moneywise
24 394
Section 3. The passage below contains TEN mistakes. Identify the mistakes and
provide the corrections in the spaces below. (10 p)
1. Line 1. places place
2. Line 2. when where
3. Line 4. spends takes
4. Line 5. their whose
5. Line 6. to from
6. Line 7. this which
7. Line 8. and or
8. Line 9. something anything
9. Line 11. near nearly
10. Line 13. foot feet
PART III. READING (50p)
Section 1. Read the following passage and decide which answer (A, B, C, or D) best fits
each gap. Write your answer in corresponding numbered boxes. (0) has been done as an
example. (10 p)
1. B 2. D 3. C 4. A 5. C
6. D 7. A 8. C 9. B 10. D
Section 2. Read the passage and fill in each gap with ONE suitable word. (10 p)
1. pronunciation 2. both 3. commonly 4. British 5. social
6. difficult
relation
7. who/that 8. accent 9. with 10. link/
Section 3: Read the following passage and complete the statements that follow by
circling A, B, C or D to indicate your answer which you think fits best. (10 pts)
1. D 2. C 3. C 4. B 5. A 6. D 7. D 8. C 9. D 10. C
Section 4. Read the following passage and do the tasks that follow. (10p)
1. Section B: iii 6. pirates
2. Section C: viii 7. oil
3. Section D: i 8. settlers
4. Section E: iv 9. species
5. Section F: vi 10. eggs
25 394
Section 5. Read the following passage and choose from people A-D. The people may be
chosen more than once. (10p)
1. C 2. B 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. B 7. A 8. A 9. D 10. C
PART IV: WRITING (50 points)
Section 1: Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means the same
as the sentence before it. (10 p)
1. I am losing myself in this good book.
2. Were it not for his partial deafness, he wouldn’t find it difficult to communicate on the phone.
3. Sally has a strong distrust of modern technology.
4. Weather permitting, we may go camping at the weekend.
5. She dissuaded me from writing it all out in longhand (and told me to use a typewriter).
Section 2: Rewrite these sentences using the words in CAPITAL. You must not change
the given words.
(10 p)
1. Do you think this kind of meat can lend itself to stewing?
2. In the normal course of events, the money is released within about three months.
3. We haven’t got / don’t have the remotest idea how we are going to afford a new car.
4. That medicine worked like magic and I started to feel better immediately.
5. I’m sure Nancy is still under the impressio n that the party starts at nine.
Section 3: Paragraph writing (30 p)
Recently, there have been an increasing number of school students choosing to
take standardized English examinations like TOEFL, IELTS or TOEIC.
What are the causes of this trend?
Write a paragraph of about 200 words to express your viewpoint.
Mô tả tiêu chí đánh giá Điểm tối đa
1. Bố cục
o Câu dẫn chủ đề mạch lạc
o Bố cục hợp lý rõ ràng, phù hợp với yêu cầu của đề bài
o Bố cục uyển chuyển từ mở bài đến kết luận
6

26 394
2. Phát triển ý
o Phát triển ý có trình tự logic
o Có dẫn chứng, ví dụ,… đủ để bảo vệ ý kiến của mình
6
3. Sử dụng ngôn từ
o Sử dụng ngôn từ phù hợp với nội dung
o Sử dụng ngôn từ đúng văn phong, thể loại
o Sử dụng từ nối cho các ý uyển chuyển
6
4. Nội dung
o Đủ thuyết phục người đọc
o Đủ dẫn chứng, ví dụ, lập luận
o Độ dài: Số từ không nhiều hoặc ít hơn quy định 10%
6
5. Ngữ pháp, dấu câu, chính tả
o Sử dụng đúng dấu câu
o Chính tả: Viết đúng chính tả
Lỗi chính tả gây hiểu lầm/ sai lệch ý sẽ bị tính một lỗi (trừ
1% điểm của bài viết)
Cùng một lỗi chính tả lặp lại chỉ tính một lỗi
o Sử dụng đúng thời, thể, cấu trúc câu đúng ngữ pháp. (Lỗi ngữ pháp
gây hiểu lầm/ sai lệch ý sẽ bị trừ 1% điểm của bài viết)
6
Tổng 30
THE END

27 394
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
LẦN THỨ XV - SƠN LA 2019
ĐỀ THI CHỌN HỌC SINH GIỎI
MÔN: TIẾNG ANH - KHỐI: 10
Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút (không kể thời gian giao
đề) Đề thi gồm có 13 trang
PART I. LISTENING (50p)
Section 1. You will hear a science student enquiring about English courses at a
University language center. For questions from 1 to 7, fill in each gap with NO
MORE THAN TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER. (14p) (ACHIEVE IELTS)
Courses Available
writing in first term
1. in second term
2. throughout the year
3.
Class sizes:
4.
during long vacation
maximum
Course costs often paid by the 5. _ Exams available in 6. _
_
Must enroll by 7.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7.
Section 2. Listen to the recording and complete each of the following sentences
with NO MORE THAN two words AND/ OR a number (16p) (FCE practice
tests)
Sky high
Gina dislike her first job as a (1)
The airline that Gina works for insists on at least (2) hours of flying experience from their
captains.
Gina says that because her husband is a travel writer he is tolerant of
her job. The " Notice to Pilots' provides information about any (3)
that are experiencing problems.
Gina says that if she has extra (4)_ she will need more
fuel for her flight.
Gina explains that many pilots she works with did a degree in (5) at university.
28 394
Gina says that all the (6) must be within
reach of the two pilots in the cockpit.
The pilots look at a (7) _ to check if anyone is
standing at the cockpit entrance.
Gina gets information from a (8) about any
small problem on the plane.
Gina says what she really appreciates is night flight.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7. 8.
Section 3: You will hear a man called Dan Pearman talking on the radio about
Pedal Power-a UK charity which sends bicycles to developing countries. Listen
and decide the following sentences True (T) or False (F). (10p)
1. In 1993 Dan Pearman went to Ecuador as part of his studies.
2. Dan’s neighbor was successful in business because he found it easy to
reach customers.
3. Dan says charities rely on getting enough bicycles to send regularly.
4. The town of Rivas has almost as many bikes as Amsterdam.
5. In August 2000, the charity was criticized in the British media.
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Section 4: You will hear two psychologists talking about modern childhood.
For questions 1 – 5, choose the answer (A, B, C, or D) which fits best according
to what you hear. (10 points)
1. What does Daniel imply about past images of childhood?
A. They are entirely fictional.
B. They all show the misfortunes of childhood.
C. They are diverse.
D. They represent the innocence of childhood.
2.
When
mentioning
the
children
throwing
bags
on
the
bus-stop,
Louise
is
_.
A. critical B. amused C. angry D. sarcastic
3. According to Daniel, .
A. children are failing to learn adequate social skills
B. children do not eat a balanced diet

29 394
C. children are becoming involved in political scandals
D. children are far more sociable than they used to be
4. Louise believes that .
A. parents are no longer interested in their children
B. children should study harder to pass school exams
C. modern life has a negative effect on children
D. most parents are emotionally unstable
5. Daniel implies that _ .
A. children would be happier if their parents taught them at home
B. machines are more of a menace to children than people are
C. teachers aren’t helping children to be competitive enough
D. most teenage problems stem from an unbalanced diet
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
PART 2. LEXICO-GRAMMAR ( 40 points)
Section 1 : Choose the best answer (A, B, C, or D) to each of the following
questions and write your answers in the corresponding numbered boxes.
1. When she puts her mind to it, she is always capable of sarcasm.
A. biting B. sharpening C. slicing D. striking
2. Fred has a of staying out of trouble at the office - he never gets involved.
A. trait B. ability C. skill D. knack
3. It is that the Minister of Justice should be accused of corruption
A. sarcastic B. sardonic C. ironic D. cynical
4. You can’t believe a word that woman says –she is a _ _liar.
A. committed B. compulsive C. impulsive D. devoted
5. The judge show that the murderer had shown a callous for human life.
A. disregard B. ignorance C. omission D. neglect
6. It was whether the operation would go ahead because so many staff
were on sick leave that week.
A. safe and sound B. touch-and-go C. pros and cons D. grin and bear
7. Anna’s friend knew the casting director, so she pulled a few to
arrange an audition.
A. ropes B. wires C. threads D. strings
8. The play is simply a vehicle for its stars and falls of having a decent plot.
A. fast B. short C. quick D. thin
9. Although he’s shy, it certainly hasn’t his career in any way.
30 394
A. restricted B. obstructed C. cramped D. impeded
10. She was caught cheating in the race. , she was disqualified.
A. Explicitly B. Accordingly C. Equally D. Fundamentally
11. Burglar alarms on cars and houses may act as a to the casual thief.
A. prevention B. precaution C. stopper D.
deterrent 12 The are against her winning a fourth consecutive gold medal.
A. chances B. bets C. prospects D. odds
13. Hardship and hard work are very much part and of student life.
A. package B. section C. province D. parcel
14. I’m sorry to have bothered you. I was under the that you wanted me to call you.
A. mistake B. miscalculation C. misconception D. misapprehension
15. we went swimming.
A. Being a hot day, B. It was a hot day, C. The day being hot, D. Due to a hot
day,
16. I’ve yet a person as Theo.
A. to meet as infuriating B. to have met such infuriating
C. been meeting as infuriating D. been meeting such infuriating
17. Sniffer dogs are able to locate survivors beneath the rubble with _ .
A. precision B. correctness C. meticulousness D. exactitude
18. The preparations for the Olympic Games are on according
to the committee in charge.
A. goal B. progress C. target D. aim
19. A number of mothers with young children are deterred from
undertaking paid work because they lack access to childcare.
A. substantial B. bleak C. thoughtless D. quaint
20. As I waited on the pavement, a black Mercedes beside me.
A. pulled up B. pulled down C. pulled off D. pulled through
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
Section 2. Fill each gap with the correct form of the words in brackets. (10p)
1. George gave the child a _of sweets. ( HAND)
2. Our class team has won five football match. ( SUCCEED)
3. The have discovered the laws of inheritance ( GENE)
4. Thousands of patients' lives have been made better
by the application of cloning genes. ( MEASURE)
5. His actions in destroying the tapes were _. ( DEFEND)
31 394
6. This margarine is full of - just look at the label! ( ADD)
7. That one kiss had left her with excitement.( BREATH)
8. She is employed by the president in an _ capacity.( ADVISE)
9. She was charged with bank records.( FALSE)
10. Nobody wants to make friends with a/ an _ person ( HEART)
Section 3. The passage below contains TEN mistakes. Underline the mistakes
and provide the corrections in the spaces below. (10p)
Line 1
Line 2
Line 3
Line 4
Line 5
Line 6
Line 7
Line 8
Line 9
Line 10
Line 11
Line 12
Line 13
Line 14
Line 15
Plastics are among the most ubiquitous materials in our economy,
our lives, and our environment. They are also among the most pervasive
and persistent pollution on Earth.
In recent years, stark images of beaches, waterways and wildlife
filling with plastic have spurred demands on action to address plastic
pollution. These calls are coupled with grown concern that plastic and its
toxic additives pose serious risks to human health at every stages of the
plastic lifecycle. Far more attention has been paid to the impacts of this
same lifecycle on the Earth’s climate. This is a dangerous oversight.
From catastrophic wildfires in California to searing heat waves and
record drought in India, the scale and growing severe of the climate crisis
are undeniable. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change warns
that humanity must limit warming below 1.5C or face far greater and
potential irreversible climate chaos. Achieving this, we must cut global
emissions 45% in 2030 and reach zero net emissions by 2050.
Answers
1. Line 6. Line
2. Line 7. Line
3. Line 8. Line
4. Line 9. Line
5. Line 10. Line
PART III. READING (60p)
I. Choose the words that best complete the sentences in the text. Write your
answers in the box provided (15 pts)

32 394
The knowledge and eloquence that people gain through travelling is usually
perceived as the best (2) _ _ in life. It is the inquisitive human nature that (3)
_ people to seek thrilling experiences and to set out on an
exploration trip. Those who travel frequently and to (5)
places benefit from establishing new relationships and acquire a better knowledge
about other cultures and lifestyles.
However, there is a (7) of truth in the assumption that people are prone to (8)
clichés and unfounded prejudices about other nations and their
characteristics. Sometimes, it is only the first-hand encounter that can help change
the (9) towards the so-called ‘inferior communities’. This direct contact with a different
civilization enables travelers to drop their baseless assumptions and get (11) with the real concept
of life in all four corners of the globe.
(12) question, travelling (13) friendship and makes it easier for
many individuals to acknowledge the true value of different traditions and customs.
Yet, it does not always mean enjoyment. It may also involve coming close with the
atrocities of real existence as well as becoming aware of the challenges and
hardships that other people have to struggle with. Hence, a true voyage is the one
with a good deal of experience to (15)
about, very often combined with exposure to abhorrent sights and
incredible ordeals. The learning to be complete, thus, requires an ability to observe
and analyze the surroundings, both their glamour and brutality.
1. A. completion B. fulfillment C. conclusion D. resolution
2. A. impels B. involves C. entails D. pursues
3. A. reverse B. averse C. diverse D. converse
4. A. speck B. grain C. scrap D. tip
5. A. persevering B. cherishing C. indulging D. persisting
6. A. prejudice B. manner C. outlook D. approach
7. A. informed B. realized C. acquainted D. defined
8. A. Apart B. Beyond C. Unfailing D. Beneath
9. A. facilitates B. affords C. elicits D. incites
10. A. commemorate B. reminisce C. resemble D. remind

33 394
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Section 2. Fill in each gap with one suitable word. Write your answer in
the box provided. (10 points)
QUEST – THE NEXT BIG THING?
How often do you go along to a gig and see (1) _ new? Well, Quest's
Friday night gig at the City Hall certainly caught my (2)_ . Having heard one or
two tracks online, I was (3) a group of about six musicians. Imagine my surprise
when just three young men walked on stage.
It was clear that the band already have a small but (4) following. A
group of fans in front of the small stage were singing (5) _ to at least half
of the songs. And it was easy to see why. Quest have a clever combination of
catchy (6) , an irresistible beat, and very much their
own sound. All three of the band members play with great energy and expertise (7) their age.
The only downside was when it came to the encores. They (8)_ up
repeating some of their material and giving us cover (9) of early rock classics.
A bit disappointing, but give them time and I'm sure they'll be writing a lot more.
I'm sure we'll be hearing a lot more from Quest. Check them out every Friday at the
City Hall until the end of the month. It's well (10) it.
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Secton 3. Read the following passage and choose the correct answer to each of
the following questions. Write your answers in the box provided. (10p)
Ethology is concerned with the study of adaptive, or survival, value of
behavior and its Evolutionary history. Ethological theory began to be applied to
research on children in the 1960’s but has become even more influential today. The
origins of ethology can be traced to the work of Darwin. Its modern foundations
were laid by two European zoologists, Konrad Lorenz and Niko Tinbergen.
Watching the behaviors diverse animal species in their natural habitats,
Lorenz, and Tinbergen observed behavior patterns that promote survival. The most
well-known of these is imprinting, the early following behavior of certain baby
birds that ensures that the young will stay close to their mother and be fed and
protected from danger. Imprinting takes place

34 394
during an early, restricted time period of development. If the mother goose is not
present during this time, but an object resembling her in important features is,
young goslings may imprint on it instead.
Observations of imprinting led to major concept that has been applied in
child Development” the critical period. It refers to a limited times span during
which the child is biologically prepared to acquire certain adaptive behaviors but
needs the support of suitably stimulating environment. Many researchers have
conducted studies to find out whether complex cognitive and social behaviors must
be learned during restricted time periods. For example, if children are deprived of
adequate food or physical and social stimulation during the early years of life, will
their intelligence be permanently impaired? If language is not mastered during the
preschool years, is the child’s capacity to acquire it reduced?
Inspired by observations of imprinting, in 1969 the British psychoanalyst John Bowl
by
applied ethological theory to the understanding of the relationship between an
infant and its parents. He argued that attachment behaviors of babies, such as
smiling, babbling , grasping, and crying, are built-in social signals that encourage
the parents to approach, care for, and interact with the baby. By keeping a parent
near, these behaviors help ensure that
the baby will be fed, protected from danger, and
provided with the stimulation and affection
necessary for healthy growth. The
development of attachment in human infants is a lengthy process involving changes
in psychological structures that lead to a deep affectional tie between parent and
baby.
1. What was Darwin’s contribution to ethology?
(A) Darwin improved on the original principles of ethology.
(B) Darwin was the professor who taught Lorenz and Tinbergen.
(C) Darwin’s work provided the basis for ethology.
(D) Darwin was the first person to apply ethological theory to children.
2. The word “diverse” is closest in meaning to
(A) small (B) varied (C) wild (D) particular
3. The word “ensures” is closest in meaning to
(A) guarantees (B) proves (C) teaches (D) assumes
4. According to the passage, if a mother goose is not present during the time period
when imprinting takes place, which of the following will most likely occur?
(A) The gosling will not imprint on any object.

35 394
(B) The gosling may not find a mate when it matures.
(C) The mother will later imprint on the gosling.
(D) The gosling may imprint on another object.
5. The word “it” refers to
(A) development (B) goose (C) time (D) object
6. The word “suitably” is closest in meaning to
(A) willingly (B) moderately (C) appropriately (D) emotionally
7. The author mentions all of the following as attachment behaviors of human
infants EXCEPT
(A) grasping (B) crying (C) eating (D) smiling
8. According to the passage, attachment behaviors of infants are intended to
(A) get the physical, emotional and social needs of the infant met
(B) allow the infant to become imprinted on objects that resemble the parent
(C) provide the infant with a means of self-stimulation
(D) prepare the infant to cope with separation
9. The phrase “affectional tie” is closest in meaning to
(A) cognitive development (B) emotional attachment
(C) psychological need (D) behavioral
change
10. It can be inferred from the passage that ethological theory assumes that
(A) to learn about human behavior only human subjects should be studied
(B) failure to imprint has no influence on intelligence
(C) the notion of critical periods applies only to animals
(D) there are similarities between animal and human behavior
Section 4. Read the following passage and do the tasks that follow.
(20p) A.
In the late 1890s, while travelling as an itinerant salesperson for the Crown Cork
and Seal Company, King C.Gillette observed how his corked bottle caps were
discarded immediately after opening. Nevertheless, his company turned a healthy
profit and there was immense business value. Gillette soon came to realise, in a
product that was used only a few times. Gillette had his own personal breakthrough
while struggling with a straight- bladed razor – a slow, fiddly, and potentially
dangerous instrument that required sharpening on a regular basis. A simple,
disposable blade that could be thrown away when it dulled would meet a real need
and generate strong profits, he correctly reasoned. After founding the American
Safety Razor Company in 1901, his sales leapt from 168 blades in 1903 to 123,648
blades only a year later.

36 394
B.
What King C. Gillette pioneered is far more than a convenient and affordable way
for men to shave, however, it is the business practice now known as “freebie
marketing” that has inspired many more companies over the years. Gillette’s
approach was contrary to the received wisdom of his era, which held that a single,
durable, high-quality and relatively expensive consumer item with a high profit
margin was the best foundation for a business. Freebie marketing involves two sets
of items: a master product that is purchased once, and a consumable product that is
frequently disposed of and repurchased on an ongoing basis. In this instance, the
master product is often sold with little to no profit margin and is sometimes oven
dispensed at a loss. As the consumables are purchased over months and years,
however, this can yield a much greater overall profit.
C.
Freebie marketing only works if the producer of the master item is also able to
maintain control over the creation and distribution of the consumables. If this does
not happen, then cheaper versions of the consumable items may be produced,
leaving the original company without a source of profit. The video game company
Atari, for example, initially sold its Atari 2600 consoles at
cost price while relying on game sales for profit. Several programmers left Atari,
however, and began a new company called Activision which produced cheaper
games of a similar quality. Suddenly, Atari was left with no way to make money.
Lawsuits to block Activision failed, and Atari survived only by adding licensing
measures to Its subsequent 5200 and 7800 consoles.
D.
In other instances, consumers sometimes find that uses for a master product
circumvent the need to purchase consumables. This phenomenon is well known to
have afflicted the producers of CueCat barcode readers. These were given away free
through Wired magazine with the intention that they would be used by customers to
scan barcodes next to advertisements in the publication and thus generate new
revenue flows. Users discovered, however, that the machines could be easily
modified and used for other purposes, such as building a personal database of book
and CD collections. As no licensing agreement was ever reached between Wired
and its magazine subscribers, CueCat were powerless to intervene, and after
company liquidation, the barcode readers soon became available in quantities over
500.000 for as little as US$0.30 each.
E.
Not all forms of freebie marketing are legal. One notable example of this is the use
of freebie marketing to “push” habit-forming goods in areas where there is
otherwise no market. For illegal substances, this is already restricted on the basis of
the product’s illegality, but the use of freebie marketing to promote legal goods
such as tobacco, alcohol,

37 394
and pharmaceuticals is also outlawed because the short-term gain to a small number
of commercial outlets is not deemed worth the social cost of widespread substance
abuse.
F.
Another practice that is prohibited under antitrust laws Is a form of freebie
marketing known as “tying”. This is when a seller makes the sale of one good
conditional on the acquisition of a second good. In these instances, the first good is
typically important and highly desirable, while the second is inferior and
undesirable. A music distributor who has the rights to an album that it is in high
demand, for example, might only allow stores to purchase copies of this album if
they also buy unpopular stock that does not sell very easily. Because this typically
relies on the manipulation of a natural monopoly on the part of the distributor, such
practices are widely understood to constitute anti-competitive behaviour. Choose
the correct headings for sections A-F from the list of headings below.
Write the correct number i-x in boxes 1-6 on the numbered spaces.
List of headings
i. No give-aways for addictive products
ii. Sales of razor blades increase astronomically
iii. Monopoly of consumables is vital for success
iv. Video gaming – a risky business
v. A novel method of dual marketing ruled out
vi. Freebie marketing restricted to legal goods
vii. Buyer ingenuity may lead to bankruptcy
viii. A marketing innovation
ix. A product innovation
x. More money to be made from high – quality products
1. Section A
3. Section C
5. Section E
2. Section B
4. Section D
6. Section F
Complete the summary below. Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from
the text for each answer. Write your answers in boxes 7-10 on the numbered
spaces.
Freebie
marketing
is
not
permitted
by
law
for
either
illegal
or
legal
(7)
products. This type of promotion of goods such as tobacco and
alcohol is not considered worth the (8) and has consequently been outlawed.
“Tying” is also prohibited. This is when the sale of an attractive

38 394
product is(9) on the purchase of another. It tends to occur when the
seller

39 394
takes advantage of a natural monopoly and is generally
considered to be(10)
Part 5. You are going to read a newspaper article about a young professional
footballer. For Questions 1-10, choose from the people (A-D).
Rising Star
Margaret Garelly goes to meet Duncan Williams, who plays for Chelsea
Football Club
A
It's my first time driving to Chelsea's training ground and I turn off slightly too
early at the London University playing fields. Had he accepted football's rejections
in his early teenage years, it is exactly the sort of ground Duncan Williams would
have found himself running around on at weekends. At his current age of 18, he
would have been a bright first-year undergraduate mixing his academic studies
with a bit of football, rugby and cricket, given his early talent in all these sports.
However, Duncan undoubtedly took the right path. Instead of studying, he is sitting
with his father Gavin in one of the interview rooms at Chelsea's training base
reflecting on Saturday's match against Manchester City. Such has been his rise to
fame that it is with some disbelief that you listen to him describing how his career
was nearly all over before it began.
B
Gavin, himself a fine footballer - a member of the national team in his time - and
now a professional coach, sent Duncan to three professional clubs as a 14 year-old,
but all three turned him down. 'I worked with him a lot when he was around 12,
and it was clear he has fantastic technique and skill. But then the other boys shot up
in height and he didn't. But I was still upset and surprised that no team seemed to
want him, that they couldn't see what he might develop into in time. When Chelsea
accepted him as a junior, it was made clear to him that this was more of a last
chance than a new beginning. They told him he had a lot of hard work to do and
wasn't part of their plans. Fortunately, that summer he just grew and grew, and got
much stronger as well.'
C
Duncan takes up the story: 'The first half of that season I played in the youth team.
I got lucky - the first-team manager came to watch us play QPR, and though we
lost 3-1, I had a really good game. I moved up to the first team after that
performance.' Gavin points out that it can be beneficial to be smaller and weaker
when you are developing - it forces you to learn how to keep the ball better, how to
use 'quick feet' to get out of tight spaces. 'A
40 394
couple of years ago, Duncan would run past an opponent as if he wasn't there but
then the other guy would close in on him. I used to say to him, ''Look, if you can do
that now, imagine what you'll be like when you're 17, 18 and you're big and quick
and they won't be able to get near you.'' If you're a smaller player, you have to use
your brain a lot more.'
D
Not every kid gets advice from an ex-England player over dinner, nor their own
private training sessions. Now Duncan is following in Gavin's footsteps. He has
joined a national scheme where young people like him give advice to ambitious
young teenagers who are hoping to become professionals. He is an old head on
young shoulders. Yet he's also like a young kid in his enthusiasm. And fame has
clearly not gone to his head; it would be hard to meet a more likeable, humble
young man. So will he get to play for the national team? 'One day I'd love to, but
when that is, is for somebody else to decide.'' The way he is playing, that won't be
long.
(Source: FCE Handbook. Reproduced with permission from
Cambridge English)
Which paragraph
1) states how surprised the writer was at Duncan's early difficulties?
2) says that Duncan sometimes seems more mature than he really is?
3) describes the frustration felt by Duncan's father?
4) says that Duncan is on course to reach a high point in his profession?
5) suggests that Duncan caught up with his team-mates in terms of
physical development?
6) explains how Duncan was a good all-round sportsperson?
7) gives an example of how Gavin reassured his son?
8) mentions Duncan's current club's low opinion of him at one time?
9) mentions a personal success despite a failure for the team?
10) explains how Duncan and his father are fulfilling a similar role?
Your answer:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
PART 1. Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means
exactly the same as the sentence printed before it. (10 points)
1. I am absolutely sure he took the money on purpose.
->He couldn’t .
2. Advanced technology cannot operate without special glass.
-> Were it .

41 394
3. People became aware of the damage to the zone layer when an enormous
hole was discovered over the South Pole.
-> It was the .
4. Mass tourism has been one of the causes of the environmental problems.
-> Mass tourism is .
5. I was strongly determined to complete my dissertation by the end of the month.
-
> I had
.
Part 2. Rewrite the following sentences with the given word. The given words
can’t be changed. (10 points)
1. Being her only niece, Ann is very precious to her. (APPLE)
Being her only niece .
2. The new musical has delighted theatre audiences throughout the country.
(STORM) The new musical has taken
3. The villagers prepared themselves to withstand the coming storm.
(BRACED) The villagers .
4. She told Arthur exactly what she thought of what he had done. ( TICKING
-OFF) She
5. Graham took back his words on noticing there were fresh strawberries on the menu.
(TUNE)
Graham sang .
Part 3: Write a paragraph about 150 words
What should be done to reduce plastic wastes in the world?
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
LẦN THỨ XV - SƠN LA 2019
ĐỀ ĐỀ XUẤT
HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤM
ĐỀ THI CHỌN HỌC SINH GIỎI
MÔN: TIẾNG ANH - KHỐI: 10
Ngày thi: 28 tháng 7 năm 2019
Hướng dẫn chấm gồm có 7 trang
A. LISTENING (50 points)
Section 1 (14 points - 2.0 points/correct
answer) (ACHIEVE IELTS)
1. listening 2. vocabulary and
grammar
3. general classes 4. 15
5. department 6. May 7. week five

42 394
Section 2 (16 points - 2.0 points/correct answer) (FCE practice tests)
1. teacher 2. 3,000/ three
thousand
3. airports 4. passengers
5. science 6. controls 7. monitor 8. report
Section 3 (5 points - 2.0 points/correct answer)
1. F 2.T 3. T 4. F 5. F
Section 4 (10 points - 2.0 points/correct answer) (FCE practice tests)
1. C 2.D 3. A 4. C 5. B
B. LEXICO- GRAMAR: 40
points Section 1: 20 points
1. A 2. D 3. C 4. B 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. B 9. D 10. B
11. D 12. D 13. D 14. D 15. C 16. A 17. A 18. C 19. A 20. A
Section 2: 10 points
1. handful 2. successive 3. geneticists 4. immeasurably 5. indefensible
6. additives 7. breathless 8. advisory 9. falsifying 10. hard- hearted
Section 3: 10 points
1. Line 3: pollution-> pollutants 6. Line 7: more - > less
2. Line 4: filling-> filled 7. Line 11: severe -> severity
3. Line 5: on -> for 8. Line 13: potential- potentially
4. Line 6: grown-> growing 9. Line 14: Achieving -> To achieve
5. Line 7: stages -> stage 10. Line 14: in -> by
C. READING
Section1: (10
points)
1. B 2. A 3. C 4. B 5. B
6. D 7. C 8. B 9. A 10. B
Section2: (10 points)
1. something 2. attention 3. expecting 4. loyal 5. along
6. lyrics 7. despite 8. ended 9. versions 10. worth

43 394
Section 3. Read the following passage and choose the correct answer to each of
the following questions. (10 points)
1.C 2.B 3. A 4. D 5. D
6. C 7. C 8. A 9. B 10. D
Section 4. Read the following passage and do the tasks that follow. (20 points)
1. ix 2. viii 3.iii 4. vii 5.i
6. V 7. habit-forming 8. social cost 9. conditional 10. anti-competitive
behaviour
Section 5. Read the following passage and do the tasks that follow. (10 points -
1.0 points/correct answer)
1. A 2. D 3. B 4. D 5. B
6. A 7. C 8. B 9. C 10. D
WRITING: 50 points
PART 1. (10 points)
1. He couldn’t (possibly) have taken the money by mistake/ chance/
accident/ coincidence.
2. Were it not for special glass advanced technology could not operate.
3. It was the discovery of an enormous hole over the South Pole that made people
aware of the damage to the ozone layer.
4. Mass tourism is partly responsible for/ to blame for the environmental problems.
5. I had a strong determination to complete my dissertation by the end of the month.
PART 2. (10 points)
1. Being her only niece, Ann is the apple of her eyes.
2. The new musical has taken theatre audiences by storm.
3. The villagers braced themselves for the coming storm.
4. She gave Arthur a ticking-off
5. Graham sang a different tune when noticing there were fresh strawberries on the menu.
Part 3: 30 points
TAPESCRIPT

44 394

45 394

46 394
Part 3
My name's Dan Pearman and Id like to talk about the work of Pedal Power, a small
charity based mainly in the UK. I'll be giving our contact details at the end, if
anyone would like to find out more about how to support us.
But first, how the charity began. I got the idea of exporting bicycles to developing
countries while I was in Ecuador. I went there in 1993 just after graduating from
university. After three years of studying, I wanted adventure. I loved travelling, so I
decided to join a voluntary organisation and was sent to Ecuador to carry out land
surveys. The project came to an end after five years and when I returned to the UK
in 1998, I started planning Pedal Power.
Where I lived in Ecuador was a very rural area. My neighbour had the only bicycle
in the
village, whereas everyone else walked everywhere. My neighbour's business was
unusually
successful, and for years I couldn't understand why. Then I realised
having a bike meant he could get where he wanted to go without much trouble.
Other local carpenters could only accept jobs in a three-kilometre radius, so no
matter how skilled they were, they could never do as many jobs as my neighbour.
At Pedal Power, we collect second-hand bikes in the UK and send -them to some of
the poorest regions in the world. When we distribute bikes overseas we don't give
them away for free. We'd like to, but long term that doesn't really help the local
economy. The demand for bikes is enormous, which makes them very expensive
locally. So we sell them for 5% of the normal price. But in order to continue
operating we need to have a constant supply of bikes which we send out every six

47 394
months.

48 394
One example of a town that's received bicycles from Pedal Power is Rivas. It was
the first place I sent a full container of bicycles to. Most people there now own a
bicycle. The local economy has developed so much, you wouldn't recognise it as
the same place. In fact, there are more bikes than on the streets of Amsterdam, if
you've ever been there.
But Pedal Power still needs your help. You may have read about some of our recent
problems in the British media. In August 2000, we simply ran out of money. We
had containers of bikes ready to send, but no money to pay the bills. It was a
terrible situation. We managed to ensure the bikes went out on time, but the other
problems carried on for several months.
Part 4:
Daniel: I hope this isn’t going to deteriorate into a “What is childhood?” discussion
– the one about solemn little miniature adults in old portraits and infants who toiled
from dawn to dusk in the fields, and poor unfortunates whipped within an inch of
their lives by sadistic schoolteachers. Or, alternatively, a debate about the
adventures of Huck Finn and the Famous Five, and apparent carefree innocence.
There have been many versions of childhood in fact and fiction, and I dare say
there’ll be many more.
Louise: Well, according to a recent newspaper report, childhood is dying. So
those cheeky little scamps I saw challenging each other to throw their school bags
on top of a bus-stop must have been a figment of my imagination. Or perhaps
they were making a political stand against the rigidities of the formal curriculum.
Who knows? Apparently a group of adults too. Academics and professionals have
put their signatures to a letter, subsequently championed by the Daily Telegraph
newspaper and the Tory Party, articulating the fall of childhood innocence. My
heart is with the sentiments of this campaign, but I worry that it loses sight of
practical wisdom.
Daniel: At birth, all children are distractible, impulsive, egocentric creatures, but
by the time they reach teenage years we expect them – as a result of their
experiences, environment and education – to have acquired a degree of self-control,
an ability to see other people’s points of view and the basic skills needed to enjoy
their life ahead. It’s the development from babyhood to adolescence that I
investigated for my book, Toxic Childhood, and my conclusion was that many
children in Britain today are indeed being robbed of the chance of a healthy
childhood. Many reach adolescence with poor attention

49 394
spans and self-control and a distinct lack of empathy for the people around them.
Their main and major basic skill is ticking boxes on tests, and this is scandalous.
Louise: As one of the richest, most highly developed nations in the world, we
really should be able to provide the sort of childhood that allows the next
generation to grow up happy, healthy, and civilised. Instead many of our children
have developed a taste for unhealthy food, a couch-potato lifestyle and have related
problems with sleeping.
An unacceptable number suffer from inadequate early emotional bonding, lack of
interaction with their parents and a high level of emotional instability. Rather than
stimulating, real-life experiences, children have TV and computer games at home
and a narrow test-and-target driven curriculum at school.
Moral guidance has suffered as societies have become increasingly confused, while
children are constantly exposed to manipulative advertising and the excesses of
celebrity culture. In a recent survey of children’s well-being among the countries of
the European Union, the UK came 21
st
out of 25. We should be ashamed of
ourselves.
Daniel: Yes, I believe we are robbing our children of something we could provide:
the conditions in which we grow up bright, balanced and well-behaved. Somehow
in the turmoil of rapid social, cultural, and technological change over the last 20
years or so, our society has lost sight of essential truths about child development
and education.
As a nation, we need to provide parents with information on children’s
developmental needs, including real food, real play, first-hand experience and
real-life interaction with the significant adults in their lives. Since parents are
terrified by media hysteria about “stranger danger” and the fevered imaginings of
the health and safety lobby, they also need information about the real dangers
from which children should be protected – for instance, TVs, and other
technological paraphernalia in their bedrooms.
As a profession, teachers should refuse to participate in the drive to accelerate
childhood with an ever-earlier start to formal education and a competitive winners-
and-losers approach to primary education. We should boycott the tests, targets and
league tables and do what we as professionals know is best for children. It’s time
we stopped robbing the next generation of their right to grow up healthy, happy and
whole.

50 394
SỞ GD&ĐT HÒA BÌNH
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN
HOÀNG VĂN THỤ
ĐỀ THI HỌC SINH GIỎI TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
LẦN THỨ:
MÔN: TIẾNG ANH LỚP 10
Ngày thi: Tháng 08 năm 2019
Thời gian: 180 phút (Không kể thời gian giao đề)
Đề thi gồm: 12 trang (Thí sinh viết câu trả lời vào bảng cho sẵn trong đề)
ĐỀ ĐỀ NGHỊ
LISTENING (50 pts)
There is a piece of music at the beginning and at the end of the listening part
There are three parts, each will be played twice
Before each part, students have 30 seconds to look at the questions
PART 1. Complete the form below (14pts)
Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND OR A NUMBER for each answer
PACK HAM’S SHIPPING AGENCY – customer quotation form
Example
Country of
destination:
Kenya
..........…..
Name: Jacob 1 …………
Address to be collected from: 2..................College, Downlands Rd
Town:
Bristol
Postcode: 3
………
Size of container:
Length: 1.5m
Width: 4 ………… Height: 5 …………

51 394
Contents: clothes
books
52 394
6 …………
Total estimated value: 7 £…………
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7.
PART 2. You will hear a radio programme about the history of roller skating and
complete the sentences. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND OR A NUMBER
for each answer. (16pts)
HISTORY OF ROLLER SKATING
The country where the first roller skates were probably made was Holland. In 1760, John
Merlin went to a ball in London playing a violin whilst on roller skates. Unfortunately,
John Merlin injured himself when he broke a (1) at the ball. In
Germany, roller skating was used in a ballet called (2) .
Plimpton's invention helped roller skaters to control the (3) of
their skates. The first team sport to be played on roller skates was (4) . In
Detroit in 1937, the first (5) in the sport took place. The use of plastics
meant that both the (6)
and of roller skates improved. The musical Starlight Express was seen
by as many as (7) in London. The speaker says that modern roller skates are now (8) than ever before.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7. 8.
PART 3. You will hear an introduction to a radio phone-in programme about modern
lifestyles. Listen and indicate true (T) or false (F) statements. (10pts)
1. Ron is a record-breaking athlete.
2. Ron thinks an accountant can lead a health and fulfilled life.
3. “Total Living” is believed to be good for athletes.
4. “Total Living” means that we should develop one aspect of our life to the full.
5. According to Ron Clarke, some current health trends are harming us.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
PART 4. Listen to the recording. (10pts)

53 394
You are going to hear two women talking about a holiday in France. Read the
sentences, and choose the best option: A, B, or C, to complete the statements about the
recording.
1. Paula's friend says that
A. she has been ill.
B. Paula doesn't look very well.
C. she's pleased to see Paula.
2. Before the trip, Paula
A. was enthusiastic about it.
B. wanted to go to the Lake District.
C. didn't tell anybody she was going.
3. Before Mark and Paula went to Paris,
A. Mark's boss didn't want him to go.
B. Paula arranged for somebody to look after the hamster.
C. Paula's sister promised to look after the children.
4. The journey across the Channel
A. was very smooth.
B. was unpleasant for Paula.
C. lasted eight hours.
5. The return trip from Paris was
A. disturbed by a flood.
B. an enjoyable experience.
C. earlier than planned.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
LEXICO – GRAMMAR (40 pts)
PART 1: Choose the best option to complete each of the following questions. (20 pts)
1. After several hours on the road they became to the fact that they would never
reach the hotel by nightfall.
A. dejected B. resigned C. depressed D. disillusioned
2. One of the organization’s aims is to information about the disease so that more
people know about its symptoms.
A. disentangle B. deride C. dwindle D. disseminate
3. Dealing with refusal from an employee is easier than dealing with false compliance.
A. an offset B. a remedial C. an agile D. an outright
4. Did you see Jonathan this morning? He looked like . It must have been quite a
party last night.
A. a wet blanket B. a dead duck C. a death warmed up D. a bear with a sore
head
5. In the of security, personnel must wear their identity badges at all time.
A. requirement B. demands C. assistance D. interests
54 394
6. I must my Spanish before I go to Seville.
A. make up for B. break out of C. brush up on D. cut out for
7. She has scrawled me a note in her familiar handwriting.
A. scratchy B. scruffy C. rusty D. sloppy
8. Education should be a universal right and not a
A. deliverance B. enlightenment C. privilege D. liberty
9. I know you're upset about breaking up with Tony but there are plenty more
A. horses in the stable B. cows in the field
C. tigers in the zoo D. fish in the sea
10. On Sunday, Vivian studied for seven hours
A. on end B. at once C. in full D. at length
11. Stephen really lost his when his dental appointment was cancelled again.
A. head B. voice C. calm D. rag
12. We were working overtime to cope with a sudden in demand.
A. boost B. impetus C. surge D. thrust
13. It was decided that the cost of the project would be so it was abandoned.
A. repressive B. prohibitive C. restrictive D. exclusive
14. She was determined to become wealthy and to that she started her own company.
A. view B. aim C. end D. object
15. He made a number of remarks about my cooking, which upset us.
A. slashing B. stabbing C. chopping D. cutting
16. She is afraid she is rather about the existence of the ghost.
A. skeptical B. partial C. adaptable D. incapable
17. I am sorry to have bothered you, I was under the that you wanted me to call you.
A. mistake B. miscalculation C. misconception D. misapprehension
18. Many children who get into trouble in their early teens go on to become offenders.
A. persistent B. insistent C. inverted D. innate
19. , Americans eat a light breakfast. They usually don’t eat a lot of food in the morning.
A. By and large B. Fair and square C. Ins and outs D. Odds and ends
20. If that boy doesn’t stop stealing, he will in jail.
A. end up B. bring about C. get round D. go by
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
PART 2. WORD FORM (10pts)
Complete the following passage with the correct forms of the bold words given in the bracket.
1. When we arrived at the hotel, we were amazed at the hospitality of the staff.
(COMPARE)
2. He is the bad manager in the factory and everyone is in attempt to him. (FAME)
3. The of an epidemic will be unavoidable unless measures are taken to prevent the
rural population from drinking the contaminated water. (BREAK)

55 394
4. Please keep the email short. makes everyone’s lives easier. (BRIEF)
5. With the help of the computer, checking information has become less . (LABOR)
6. You mustn’t leave your luggage for even a moment on the train. (ATTEND)
7. She looked in on the baby to check that it was all right. (PERIOD)
8. They were totally by the girl’s disappearance. (MYSTERY)
9. The talks were totally . We didn’t reach agreement on anything at all. (PRODUCT)
10. The boy was very violent and his parents found him . (MANAGE)
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
PART 3. ERROR CORRECTION (10pts)
There are 10 mistakes in the following passage. Write them down and give the
correct answers in the space provided. (10ps)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Of the many unexplained phenomenon which continue to puzzle scientists and laymen
like, the corn circles of Southern England remain one of the most mysterious. These
perfect- formed circles, which, when they see from the air appear to have been inscribed
with an enormous carving tool, seem to be a part of significant message; so far, however,
nobody managed to decipher it, and it is doubtful if anyone will ever be able to. But the
main question – how the circles came to be there – are just as far from being solved.
Although several people have come forward claiming to have made the circles ourselves,
scientists declare that it would be impossible for even a large group to create shapes of
such precision on so a large scale. These circles have become one of the strongest
arguments in support
of the existing of intelligent extra-terrestrial life forms.
Line mistakes Correction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
READING (60pts)
PART 1. Read the passage below and then choose the correct answer A, B, C or D. (10pts)
Until about 250 years ago, households did not take dirt as (1) as they do
now - it was a fact of life, and that was that. Cleaning often consisted of an annual (2)
called
'spring cleaning' when the furniture was moved aside, and all the linen products in the
house were cleaned. Carpets and rugs were taken outside, hung on ropes and had the dust

56 394
(3) out of
them - an exhausting and messy process. The industrial revolution brought about a major
change - as new

57 394
products became available to make homes cleaner, a corresponding interest in 'domestic
hygiene' appeared in households. This in turn led to the (4) of further
products, one of which was the vacuum cleaner. (5) has it that
when one of the first vacuum cleaners was demonstrated, a kindly scientist took the proud
inventor aside, and offered a bit of (6) that was to become (7) to the
future evolution of the product - 'make it suck, not blow'. The first vacuum cleaners
appeared in the 1860s in the United States. They were operated by hand pumps and were
almost as (8) as spring cleaning. It was only when electric motors had become
sufficiently advanced to become portable that vacuum cleaners became common
household items. Most of today's major (9)
_- including Electrolux and Hoover -
were born in the 1920s. The household
dirt
that
vacuum
cleaners
suck
up
is
mostly
dead
skin
cells
-
humans (10) millions of
cells every day. A much smaller proportion comes from dust and soil carried into the
house from outside.
1. A. importantly B. crucially C. considerately D. seriously
2. A. ritual B. result C. resolution D. scrub
3. A. cleaned B. taken C. beaten D. sucked
4. A. fabrication B. appearing C. recreation D. development
5. A. Story B. Epic C. Legend D. Tale
6. A. advise B. advice C. courage D. encouragement
7. A. standard B. crucial C. regular D. esteemed
8. A. laborious B. hard C. nefarious D. straining
9. A. brands B. marks C. makes D. trademarks
10. A. lose B. outgrow C. omit D. shed
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
PART 2. Read the text below and think of the word which best fits each space. Use only
one word in each space. (10pts)
Flamingos, those beautiful long-legged pink birds, rub the reddish pigments,
released in oil from a gland near their tail, into their feathers to bring (1) _ their vibrant
colour. The result, according to researchers studying the birds in Spain, (2) that
the birds seem to become far (3) likely to find themselves a mate. Scientists noticed
that, (4) they were arranging their feathers, many flamingos scraped their cheeks
across the gland before rubbing their face against their breast, back and neck (5)_
the aim of spreading the colour.
In a journal article, the experts explained that (6) so helped the birds
appear extra attractive to potential mates – not so (7) because of their eye-catching
colour, but because other flamingos could tell they had made an effort with their
appearance. One of the researchers says: “The rubbing is time-consuming. And the more
frequently the birds practice it, the pinker they become. “If the birds stop rubbing, their
colour fades in a few days because the pigments bleach quickly in the sunlight”
Rubbing the pigment into the feathers takes time and effort, and, as a results,
colorful feathers are a sign to the opposite sex that a flamingo is healthy and well-fed,

58 394
because it can afford to spend time on (8) it looks. “The behavior is more common in
female flamingos than in males,” the researchers said. They added that the brightest
coloured birds also took the best
59 394
breeding sites, (9) gives them a reproductive advantage (10)
their paler rivals.
Your answers
0 ) +
/ 1 2 3 0
PART 3. Read the following passage and choose the best answer. (10pts)
Large animals that inhabit the desert have evolved a number of adaptations for
reducing the effects of extreme heat. One adaptation is to be light in color, and to reflect
rather than absorb the Sun's rays. Desert mammals also depart from the normal
mammalian practice of maintaining a constant body temperature. Instead of trying to keep
down the body temperature deep inside the body, which would involve the expenditure of
water and energy, desert mammals allow their temperatures to rise to what would normally
be fever height, and temperatures as high as 46 degrees Celsius have been measured in
Grant's gazelles. The overheated body then cools down during the cold desert night, and
indeed the temperature may fall unusually low by dawn, as low as 34 degrees Celsius in
the camel. This is an advantage since the heat of the first few hours of daylight is absorbed
in warming up the body, and an excessive buildup of heat does not begin until well into
the day.
Another strategy of large desert animals is to tolerate the loss of body water to a point
that would be fatal for non-adapted animals. The camel can lose up to 30 percent of its
body weight as water without harm to itself, whereas human beings die after losing only
12 to 13 percent of their body weight. An equally important adaptation is the ability to
replenish this water loss at one drink. Desert animals can drink prodigious volumes in a
short time, and camels have been known to imbibe over 100 liters in a few minutes. A
very dehydrated person, on the other hand, cannot drink enough water to rehydrate at one
session, because the human stomach is not sufficiently big and because a too rapid dilution
of the body fluids causes death from water intoxication. The tolerance of water loss is of
obvious advantage in the desert, as animals do not have to remain near a water hole but
can obtain food from grazing sparse and far-flung pastures. Desert-adapted mammals have
the further ability to feed normally when extremely dehydrated, it is a common experience
in people that appetite is lost even under conditions of moderate thirst.
1. What is the main topic of the passage?
A. Weather variations in the desert. B. Adaptations of desert animals.
C. Diseased of desert animals. D. Human use of desert animals.
2. According to the passage, why is light coloring an advantage to large desert
animals?
A. It helps them hide from predators.
B. It does not absorb sunlight as much as dark colors.
C. It helps them see their young at night.
D. It keeps them cool at night.
3. The word "maintaining" is closest in meaning to .
A. measuring B. inheriting C. preserving D. delaying
4. The author uses of Grant's gazelle as an example of
A. an animal with a low average temperature

60 394
B. an animal that is not as well adapted as the camel
C. a desert animal that can withstand high body temperatures
List of headings
i. The reaction of the Inuit community to climate change
ii. Understanding of climate change remains limited
iii. Alternative sources of essential supplies
iv. Respect for Inuit opinion grows
v. A healthier choice of food
vi. A difficult landscape
vii. Negative effects on well-being
viii. Alarm caused by unprecedented events in the Arctic
ix. The benefits of an easier existence
61 394
D. a desert animal with a constant body temperature
5. When is the internal temperature of a large desert mammal lower?
A. Just before sunrise B. In the middle of the day
C. Just after sunset D. Just after drinking
6. The word "tolerate" is closest in meaning to _ .
A. endure B. replace C. compensate D. reduce
7. What causes water intoxication?
A. Drinking too much water very quickly. B. Drinking polluted water.
C. Bacteria in water. D. Lack of water.
8. Why does the author mention humans in the second paragraph?
A. To show how they use camels.
B. To contrast them to desert mammals.
C. To give instructions about desert survival.
D. To show how they have adapted to desert life.
9. The word "obtain" is closest in meaning to .
A. digest B. carry C. save D. get
10. Which of the following is NOT mentioned as an adaptation of large desert animals?
A. Variation in body temperatures. B. Eating while dehydrated.
C. Drinking water quickly. D. Being active at night.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
PART 4. (20pts)
Part V. Read the following passage. Choose the correct heading for paragraphs A-G
from the list of headings below. Write the correct number, i- ix, in blanks.
Paragraph A: viii
1. Paragraph B 2. Paragraph C 3. Paragraph D
4. Paragraph E 5. Paragraph F
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.

62 394
Climate Change and the Inuit
A. Unusual incidents are being reported across the Arctic. Inuit families going off on
snowmobiles to prepare their summer hunting camps have found themselves cut
off from home by a sea of mud, following early thaws. There are reports of igloos
losing their insulating properties as the snow drips and refreezes, of lakes draining
into the sea as permafrost melts, and sea ice breaking up earlier than usual,
carrying seals beyond the reach of hunters. Climate change may still be, a rather
abstract idea to most of us, but in the Arctic it is already having dramatic effects –
if summertime ice continues to shrink at its present rate, the Arctic Ocean could
soon become virtually ice-free in summer. The knock-on effects are likely to
include more warning, cloudier skies, increased precipitation and higher sea levels.
Scientists are increasingly keen to find out what’s going on because they consider
the Artic the ‘canary in the mine’ for global warming – a warning of what’s in
store for the rest of the world.
B. For the Inuit the problem is urgent. They live in precarious balance with one of the
toughest environments on earth. Climate change, whatever its causes, is a direct
threat to their way of life. Nobody knows the Artic as well as the locals, which is
why they are not content simply to stand back and let outside experts tell them
what’s happening. In Canada, where the Inuit people are jealously guarding their
hand-won autonomy in the country’s newest territory, Nunavut, they believe their
best hope of survival in this changing environment lies in combining their ancestral
knowledge with the best of modern science. This is a challenge in itself.
C. The Canadian Arctic is a vast, treeless polar desert that’s covered with snow for
most of the year. Venture into this terrain and you get some idea of the hardships
facing anyone who calls this home. Farming is out of the question and nature
offers meager pickings. Humans first settled in the Arctic a mere 4,500 years ago,
surviving by exploiting sea mammals and fish. The environment tested them to the
limits: sometimes the colonists were successful, sometimes they failed and
vanished. But around a thousand years ago, one group emerged that was uniquely
well adapted to cope with the Arctic environment. These Thule people moved in
from Alaska, bringing kayaks, sleds, dogs, pottery and iron tools. They are the
ancestors of today’s Inuit people.
D. Life for the descendants of the Thule people is still harsh. Nunavut is 1.9 million
square kilometers of rock and ice, and a handful of islands around the North Pole.
It’s currently home to 2,500 people, all but a handful of them indigenous Inuit.
Over the past 40 years, most have abandoned their nomadic ways and settled in the
territory’s 28 isolated communities, but they still rely on nature to provide food
and clothing.
Provisions available in local shops have to be flown into Nunavut on one of the
most costly air networks in the world, or brought by supply ship during the few
ice-free weeks of summer. It would cost a family around £ 7,000 a year to replace
meat they obtained themselves through hunting with imported meat. Economic
opportunities are scarce, and for many people state benefits are their only income.
E. While the Inuit may not actually starve if hunting and trapping are curtailed by
climate change, there has certainly been an impact on people’s health. Obesity,
heart disease and diabetes are beginning to appear in a people for whom these have
never before been problems. There has been a crisis of identity as the traditional

63 394
skills of hunting, trapping and preparing skins have begun to disappear. In
Nunavut‘s ‘igloo and email’ society, where

64 394
adults who were born in igloos have children who may never have been out on the
land, there‘s high incidence of depression.
F. With so much at stake, the Inuit are determined to play a key role in teasing out the
mysteries of climate change in the Arctic. Having survived there for centuries, they
believe their wealth of traditional knowledge is vital to the task. And Western
scientists are starting to draw on this wisdom, increasingly referred to as ‘Inuit
Qaujimajatuqangit’, or IQ. ‘In the early days scientists ignored us when they came
up here to study anything. They just figured these people don’t know very much so
we won’t ask them,’ says John Amagoalik, an Inuit leader and politician. ‘ But in
recent years IQ has had much more credibility and weight.’ In fact it is now a
requirement for anyone hoping to get permission to do research that they consult
the communities, who are helping to set the research agenda to reflect their most
important concerns. They can turn down applications from scientists they believe
will work against their interests, or research projects that will impinge too much on
their daily lives and traditional activities.
G. Some scientists doubt the value of traditional knowledge because the occupation of
the Arctic doesn’t go back far enough. Others, however, point out that the first
weather stations in the far north date back just 50 years. There are still huge gaps in
our environmental knowledge, and despite the scientific onslaught, many
predictions are no more than best guesses. IQ could help to bridge the gap and
resolve the tremendous uncertainty about how much of what we’re seeing is
natural capriciousness and how much is the consequence of human activity.
Questions 6-10: Choose no more than two words from paragraphs C and D to
complete their following summary.
If you visit the Canadian Arctic, you immediately appreciate the problems faced by
people for whom this is home. It would clearly be impossible for the people to engage in
farming as a means of supporting themselves. For thousands of years they have had to
rely on catching (6).....and fish as a means of sustenance. The harsh surroundings saw
many who
tried to settle there pushed to their limits, although some were successful. The Inuit people
were an example of the latter and for them the environment did not prove unmanageable.
For the present inhabitants, life continues to be a struggle. The territory of Nunavut
consists of little more than ice, rock and a few (7)… In recent years, many of them
have been obliged to give up
their (8)………………….lifestyle, but they continue to depend mainly on (9)…………………..
for their food and clothes. (10)......................produce is particularly expensive
Your answers
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
PART 5: You are going to read an article containing reviews of recently-published
books. For questions 1-10, choose from reviews (A-F). The reviews may be chosen
more than once. (10pts)
BOOK CORNER
A round-up of the latest fiction and non-fiction from Beth Young

65 394
A. Reading a new novelist is a bit like asking a stranger out on a date. You never
quite know if this is the start of a beautiful relationship. You check the blurbs, the
publicity photograph, and flick through the book to look for the two essentials:
entertainment and substance. Beginner’s

66 394
Greek by James Collins is certainly big on the latter, weighing in at 400-plus pages. And
the quotes on the back cover have the effect of a bunch of friends saying to you, ‘Go on,
you’ll get on brilliantly’. Early indications are that this blind date could lead to a deeper
relationship. Beginner’s Greek is described by The New York Times as a “great big sunny
lemon chiffon pie of a novel” about romantic love amongst the American middle classes.
It is indeed delicious.
B. In Manil Suri’s second outing The Age of Shiva we have a broad-sweeping,
epic novel with an unforgettable heroine so willful yet flawed that it calls to mind that
other famous leading lady, Scarlett O’Hara in Gone With the Wind. The story begins at a
firework party in Delhi where Meera falls disastrously in love. We follow her journey to
Bombay, marriage and obsessive motherhood, with occasional flashbacks to a childhood
that was marred by political turmoil. Mathematics professor, Suri, captures the fluidity of
the role of women with a beautiful kind of precision.
C. Devotees of playwright David Mamet, whose screen work includes Wag The
Dog and the award-winning Glengarry Glen Ross may be less than enamoured of Ira
Nadel’s new biography, David Mamet: A Life in the Theatre. It may seem churlish to
question the minutia of incidents that abound in this comprehensive tone, but whilst Nadel
is clearly striving for accuracy one feels there ought to have been more sifting, more
mining for the gold amongst the biographical trivia. In addition, Nadel’s tone is somewhat
dry and academic and seems at odds with the brilliance of David Mamet’s own writing.
That said, the book offers a sound introduction to the life and career of the man hailed as
one of America’s most outstanding writers.
D. Can any Mother help me? is the true story of a desperately lonely mother who,
in 1935, appealed to other women through the letters page of a women’s magazine.
Writing under a pseudonym, the woman known as Ubique (meaning ‘everywhere’) little
realised that she would be the trigger for the launch of a new and private magazine that
would last for the next fifty years. The Cooperative Correspondence Club was formed to
offer comfort and support to wives, often well-educated women, who craved stimulation
beyond the drudgery of family life. Jenna Bailey has done a superb job of organising and
editing this compendium, adding her own insightful commentary.
E. Subtitled, The Life and Times of Henry Howard, Earl of Surrey, Jessie Child’s
debut historical biography, Henry VIII's Last Victim, was the worthy winner of last year’s
Elizabeth Longford Prize. Henry Howard’s victim status is owing to the fact that he was
the final person to be executed by King Henry VIII, a mere nine days before the king
himself expired. Although killed ostensibly for treason, the Earl of Surrey’s only real
crime it seems was leading an unsuccessful army campaign in France. Only 29, he was
also a distinguished poet with a fine literary voice, a persona which refutes his reputation
as the spoilt son of the Duke of Norfolk.
F. This is the 25th outing for T. Keneally but he’s lost none of his writing powers.
The Widow and Her Hero take real life events during the Second World War as its
inspiration and builds a tale of love and intrigue. Grace looks back on her life to recall her
courtship with the hero of the title, the handsome Captain Leo Waterhouse. Leo is
tragically killed whilst on a secret mission but it is many years before Grace discovers the
facts about his death. Keneally made fans galore when Schindler’s Ark was published and
later made into the award-winning Steven Spielberg film, Schindler’s List. The Widow
and Her Hero will bring him even more fans.

67 394
In which section is the following mentioned?
68 394
1. A story in which someone is unaware of the impact of their action.
2. A description of the opening scene.
3. An author who exemplifies source material with their own analysis.
4. A humorous comparison with a real-life situation.
5. A character who finds out the truth about a situation.
6. A hint that the author’s future writing career will be positive.
7. A book that would be appreciated by people without much previous knowledge of the
subject.
8. A book which has already won critical acclaim.
9. A book which includes too much factual detail.
10. A mention of the profession of the author.
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
WRITING
PART 1. SENTENCE TRANSFORMATION
1. Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it is as similar as
possible in meaning to the sentence printed before it. (10pts)
1. I won’t go all that way to visit him again on any account!
On no account
2. I wasn’t surprised when they refused to pay me.
As I
3. We have credited the money to your current account at this bank.
We have placed
4. Your silly questions distracted me.
You drove
5. Edward eventually organised himself and started work.
Edward eventually got his
2. Rewrite the sentences below using the words in brackets without changing their original
form. (10pts)
1. I don’t think this record will ever be popular. (CATCH)
.............................................................................................

69 394

ĐÁP ÁN ĐỀ NGHỊ
70 394
2. Mike is never reluctant to make tough decisions as a manager. (SHRINKS)
............................................................................................
3. You can’t possibly expect me to have supper ready by eight o’clock. (QUESTION)
.............................................................................................
4. It is my opinion that there is no advantage in further discussion. (SEE)
.............................................................................................
5. Please excuse Jane’s poor typing: she’s only been learning for a month. (ALLOWANCES)
.............................................................................................
PART 2. PASSAGE WRITING (30 pts)
Creativity is considered an essential factor to spur development in all aspects of
life. In about 250 words, write a passage to suggest ways to promote creativity at school.
SỞ GD&ĐT HÒA BÌNH
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN
HOÀNG VĂN THỤ
ĐỀ THI HỌC SINH GIỎI TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
LẦN THỨ:
MÔN: TIẾNG ANH LỚP 10
Ngày thi: tháng 08 năm 2019
LISTENING
PART 1. Complete the form.
1. MKERE (Mkere) 2. Westall 3. BS8 9PU
4. 0.75 m/metre(s)/meter(s) (wide) / three(-)quarter(s) (of) (a) metre/meter (wide) /
¾ m (wide) / 75 cm(s) (wide)
5. 0.5 m/metre(s)/meter(s) (high/deep) / (a) half (a) metre/meter (high/deep) /
/ 50 cm(s) (high/deep)
6. (som
e) toys
7. 1,700
Words in brackets are optional - they are correct, but not necessary. Alternative answers are

71 394
separated by a slash (/).
PART 2. You will hear a radio programme about the history of roller skating and
complete the sentences.
1. (large) mirror 2. Winter Pleasures 3. Direction
4. (roller) hockey
order)
5. championships 6. design/performance (in either
7. eight million/8.000,000 people 8 lighter/safer (in either order)
PART 3
You will hear an introduction to a radio phone-in programme about modern lifestyles.
Listen and indicate true (T) or false (F) statements.
1. T 2. F 3. F 4. F 5. T
PART 4
1. C 2. A 3. B 4. B 5. C
LEXICO -
GRAMMAR PART 1
1.B 2.D 3.D 4.C 5.D 6.C 7.A 8.C 9.D 10.A
11.D 12.C 13.B 14.C 15.D 16.A 17.D 18.A 19.A 20.A
PART 2
1. incomparable 2. defame 3. outbreak 4. Brevity 5. laborious
6. unattended 7. periodically 8. mystified 9. unproductive 10. unmanageable
PART 3. There are TEN mistakes in this paragraph. Write them down & give the
correction. (10 ps)
Line mistakes correction
1 1. phenomenon phenomena
1 2. like alike
2 3. perfect-formed perfectly-formed
3 4. see are seen
4 5. significant message a significant message
4 6. managed has managed
6 7. are Is
7 8. ourselves themselves
8 9. so such
9 10. existing existence
REA
DIN
G
PAR
T 1

72 394
1. D 2. A 3. C 4. D 5. C 6. B 7. B 8. A 9. A 10. D
PART 2.
1. out 2. is 3. more 4.while/when/as 5. with
6. doing 7. much 8. how 9. which 10. over
PART 3. Read the passage and choose A, B, C, or D to indicate the correct answer
to each of the following questions (15ps)
1.B 2.B 3.C 4.C 5.A
6.A 7.A 8.B 9.D 10.D
PART 4. Choose the correct heading for paragraphs A-G from the list of headings
below. Write the correct number, i- ix, in blanks.
1. i 2. vi 3. iii 4. vii 5. iv
6.sea mammals 7. islands 8. nomadic 9. nature 10. Imported
PART 5
1.D 2.B 3.D 4.A 5.F
6.A 7.C 8.E 9.C 10.B
SECTION 4. WRITING
PART 1.
1. On no account will I go all that way to visit him again!
2. As I (had) expected, they refused to pay me.
3. We have placed the money to the credit of your current account at this bank.
4. You drove me to distraction with your silly questions.
5. Edward eventually got his act together and started work
II. Use the word given in bold and make any necessary additions to write a new sentence
in such a way that it is as similar as possible in meaning to the original sentence. Do not
change the form of the given word. (7.5p.)
1. I don’t think this record will ever catch on.
2. Mike never shrinks from making tough decisions as a manager.
3. It is out of the question (for me) to have/ get supper ready by eight
o’clock. There is no question of supper being ready by eight o’clock.
4. I do not/ cannot see any advantage/point/sense in further
discussion. I (can) see no advantage/point/sense in further
discussion.

73 394
As far as I can see, there is no advantage/point/sense in further
discussion. As I see it, there is no advantage/point/sense in further
discussion.
5. Please make allowances for Jane’s poor typing: she’s only been learning for a month.
Paragraph
writing
Marking
criteria:
1. Task response (7 points)
The writer clearly states their point of view (agree/disagree) and provides a well-
supported paragraph related to the topic.
2. Lexical resource (7 points)
- The writer uses synonyms and paraphrases flexibly.
- The writer uses topic-related vocabulary.
3. Coherence and cohesion (10 points)
- The paragraph has a topic sentence with controlling idea.
- The topic is well-developed with relevant supporting evidence, examples and facts.
- Ideas are well connected with suitable cohesive devices.
- The paragraph shows a certain organization pattern (for example: by
order of importance, etc.)
- The writer uses pronouns consistently and coherently, with third-person
pronouns (They, this, these, one/ones) gaining higher scores.
4. Grammatical range and accuracy (6 points)
- The writer uses a wide range of sentence structures (simple, compound
and complex)
- The writer uses verb tense and forms accurately.
- The writer shows good control of spelling and punctuation.
TAPESCRIPTS
Tapescript for Part 1 Listening.
You will hear a telephone conversation between a customer and an agent at a company
which ships large boxes overseas.
A Good morning Packham’s Shipping Agents. Can I help you?
B Oh yes, I’m ringing to make enquiries about sending a large box, a container,
back home to Kenya from the UK.
A Yes, of course. Would you like me to try and find some quotations for you?
B Yes, that’d be great. Thank you.

74 394
A Well first of all, I need a few details from you.
B Fine.
A Can I take your name?
B It’s Jacob Mkere.
A Can you spell your surname, please?
B Yes, it’s M-K-E-R-E.
A Is that ‘M’ for mother?
B Yes.
A Thank you, and you say that you will be sending the box to Kenya?
B That’s right.
A And where would you like the box picked up from?
B From college, if possible.
A Yes, of course. I’ll take down the address now.
B It’s Westall College.
A Is that W-E-S-T-A-L-L?
B Yes, ... college.
A Westall College. And where’s that
B It’s Downlands Road, in Bristol.
A Oh yes, I know it. And the postcode?
B It’s BS8 9PU.
A Right ... and I need to know the size.
B Yes, I’ve measured it carefully and it’s 1.5m long ...
A Right.
B 0.75m wide ...
A OK.
B And it’s 0.5m high or deep.
A Great. So I’ll calculate the volume in a moment and get some quotes for that. But
first can you tell me, you know, very generally, what will be in the box?
B Yes there’s mostly clothes.
A OK. [writing down]
B And there’s some books.
A OK. Good. Um ... Anything else?
B Yes, there’s also some toys.
A OK and what is the total value, do you think, of the contents?
B Well the main costs are the clothes and the books – they’ll be about £1500 but
then the toys are about another two hundred – so I’d put down £1700.
PART 2
You will hear a radio programme about the history of roller skating. For questions 9-18,
complete the sentences.
In today's programme, I'm going to be talking about roller skating: how the sport started
and how it has developed over the years. So who was the first person to come up with the
idea of attaching wheels to the feet in order to get about more quickly and easily?
Well, roller skates are not a new invention. In fact, roller skating developed out of the
much older activity of ice-skating, which has existed in Scandinavia and other northern
countries for

75 394
centuries. The actual inventor of the first roller skates is not known, but it's generally
thought that they originated in Holland in the early 1700s.
Roller skates first arrived in Britain in 1760 when the Belgian clockmaker John Merlin
wore some to a formal ball in London. Merlin was known as something of a mad inventor,
but he surprised everybody at the ball when he whizzed past them on wheels, playing the
violin at the same time. Unfortunately, Merlin did not manage to persuade people that
roller skating was a good idea. His skates had no brakes and he ended up crashing into a
large mirror. Merlin was quite seriously injured in the accident and, as a result, roller
skating did not immediately become popular in Britain.
In Germany, however, roller skates made a better impression. They were used in a ballet
with the name Winter Pleasures , which included a scene where the dancers skated on ice.
Because they couldn't produce the ice on stage, the organisers decided to use roller skates
instead.
After this, the sport gradually became more popular, but it was only thanks to technical
advances that it became safer. In 1863, an American named James Plimpton solved the
problem of controlling direction when skating by fitting them with rubber springs. His
design is widely regarded as the origin of the modern roller skate, although rubber toe
brakes, another important safety feature didn't come in until the 1870s.
The late nineteenth century saw the beginnings of events such as speed contests, artistic
displays and roller dancing as well as the first team sport on roller skates, roller hockey.
During the first decades of the twentieth century, hundreds of indoor and outdoor roller
skating rinks opened, especially in the USA, and the sport became really established as a
popular pastime. The first roller skating championships were held in Detroit in 1937.
The real development of the modern roller skate only began in the second half of the
twentieth century. From the 1950s onwards, the use of plastics led to improvements in the
design and performance of roller skates, and roller disco movies of the 1970s and 1980s
increased the popularity of the sport, with roller discos opening in many parts of the
world. Meanwhile, the stage musical Starlight Express, which features roller skating, ran
for seventeen years and was seen by eight million people.
The sport of roller skating has also been gaining a more serious following, especially in
southern Europe and South America. The biggest modern change to roller skates came in
1983 with the introduction of in-line skates, also known as rollerblades. Then during the
1990s, new materials, brakes and boot fastenings all combined to make skates both lighter
and safer than they had ever been in the past.
So why is roller skating so popular? I went to talk to some fans at a rink in Huddersfield
... PART 3
Good morning and welcome to our programm “Modern lifestyle”. Regular listeners will
remember the Health and Diet Programme we broadcast earlier in the year featuring Ron
Clark, an Australian accountant turned record breaking athlete.
Ron’s now Managing Director of the five successful Cannons Health Clubs in London and
he’s a firm believer in being positive about life. His philosophy is that in order to have a
healthy and fulfilled life (which he obviously felt being an accountant, even in Australia,
did not offer him!),

76 394
you have to enjoy everything you do. He advocates a healthy diet and exercise as a means
of supporting one’s work, family ans social life.
With this in mind, he devised the term “Total Living”. It certainly stood him in good
stead during his successful career as an athlete – and it’s an obvious feature of the health
clubs Ron runs in the city- but he believes it can help everybody. His latest venture’s a
book he’s just written, also entitled “Total Living”, which isn’t just another book of
physical exercises, but a guide to how physical exercise can augment a timetable already
filled with a pressurized job and hectic social life. As the term “Total Living” implies, we
should see our lives as a whole, not in the isolated compartments- and this means
integrating all the different aspects of our lives. Ron thinks that too often we don’t build
in time for what we need most – in this case, physical exercise!
You may think that combining work, play and exercise sounds daunting, but Ron also
argues very much against some current health trends; for example, assuring us that the
sun is beneficial for our health and not the danger to our health and longevity which the
anti- sun lobby would have us believe! And then, there’s dieting. How many of you can
honestly say you’ve never considered going on a diet? If you talk to Ron, he will insist
that slimming diets should be avoided at all costs.
Well, we’re fortunate to have Ron back in the studio with us today and he’s going to
answer some of your questions during the next half an hour or so but before ...
PART 4
Paula Hi Meg!
Meg Paula! It's great to see you! You look
fantastic! Paula Oh. do I? That's strange. I should
be looking awful. Meg Why? Have you been ill?
Paula No. Not that. It's just that trip to Paris. It was a nightmare'.
Meg Really? You must be joking! Don't tell me you didn't have a good time. When you
told me you were going I was green with envy.
Paula No wonder, I was so excited I just couldn't wait to go. Now I wish we'd gone to the
Lake District or even just stayed at home.
Meg But what was so bad about it? Paula Well, in the beginning everything looked all
right. Mark's boss gave him two weeks off without too much trouble, the children went to
stay with Mark's mother, and Sheila - you know, my younger sister-promised to come
over to our place to feed the hamster. So we packed our suitcases and set off.
Meg Sounds all right so far.
Paula Yes, but in Dover it turned out that the ferry terminal workers had gone on strike,
and we had to wait over eight hours before we could board a ferry.
Meg Oh no!
77 394
Paula And that was just the beginning. During the passage the weather turned stormy, and
I was terribly sea-sick all the way across the Channel.
Meg Oh, poor you!
Paula Yeah, it was horrid. Then, when we arrived in Calais, it was so late that we had to
look for somewhere to spend the night.
Meg Oh dear!
Paula Yes, but that's not all! On the way to Paris the next day we had a puncture, so Mark
had to change the tyre, the hotel where we'd booked a room turned out to be terribly noisy,
it was pouring with rain most of the time, and some of the galleries I wanted to visit were
closed.
Meg Oh no! So what did you do, then?
Paula Well, I ended up shopping for clothes. That's about the only thing I can't complain
about, but, obviously, it wasn't cheap, so Mark go t furious.
Meg No surprise there!
Paula Hmmm so in the end we decided to shorten our stay and left after just ten days. You
can imagine our return trip - I was unhappy. Mark was mad at me because of the money,
and," when we got home, the flat was flooded.
Meg Flooded?
Paula Yes, we couldn't believe it! When we were away, Sheila let the hamster out of the
cage for a while, and the horrid creature bit through the fridge cable. Of course, she didn't
even notice, but when we got back, there was water all over the kitchen floor and all the
food in the fridge had gone off.
Meg What a nightmare!
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN
TUYÊN QUANG
---------------
Đề thi gồm: 14 trang
ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG LẦN THỨ
XV MÔN: TIẾNG ANH. LỚP 10
Thời gian: 180 phút (Không kể thời gian giao đề)
PART I. LISTENING (50p)
Section 1. You will hear an interview to do a quesstionaire on the residency on
the north. For questions from 1 to 7, fill in each gap with NO MORE THAN
THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER. (14p)
North Residency Questionaire
Example
Age of the interview 19
Current occupation: 1.
Length of living in the North 9 years
Exact living area: 2.

78 394
Type of accommodation: A shared 3.
Private transport: On foot and by bike
Public transport: Take the 4. or a taxi.
Frequency of eating out 5.
Preferred exercises: Go swimming
Go to the gym
Go 6.
Part-time course: 7.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7.
Section 2. Listen to the recording and complete each of the following sentences
with NO MORE THAN two words AND/ OR a number (16p)
Janet can now do voluntary work because she is free of 1. . Most of Janet’s friends were 2.
by her decision to
volunteer.
Janet disagrees with people who say that she is 3. _ the people whe is
trying to help.
Janet advised on a project to improve 4. _ in a farming
community. The villagers had been dependent on 5. from charities to
survive.
The scheme aimed to make the villagers 6. _ in agricultural
production. Janet’s job was to help the villagers sell any 7. crops.
She believes that the 8. of the village have been changed dramatically
by the scheme.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7. 8.
Section 3. You are going to listen to Martin talking about his journey from
London to Avignon by car. Listen and decide if the following statements are True
(T) or False (F). Check (√) the appropriate boxes. You will hear the talk TWICE.
T F
1. The man claimed he invented the idea of wrapping cars with
advertisement.
2. People interested in having their cars wrapped must take a survey.

79 394
3. Ads on the Move will pay car owners over $300 a month to wrap their
car.

80 394
4
. The cost of advertising on billboards is going up.
5. The woman is interested in having her car wrapped.
Section 4: You will hear part of a radio interview in which David Evans, a chef in
a British school, is talking about his work. Choose the answer (А, В, C or D)
which fits best according to what you hear. (10p)
1.What was the students’s initial reaction to the food they were served?
A. They didn’t like being the subjects of an experiment.
B. They would rather have eaten traditional British food.
C. They were not sure whether it was good or bad.
D. They felt that it was an adventure for them.
2. According to David, why do some students have difficulty in accepting the
“restaurant system”?
A. They are uncomfortable eating meals with adults.
B. They are not used to having meals with others.
C. They don’t like talking about food.
D. It takes too long to be served their food.
3. What main role do the staff play in the school restaurant?
A. They check that students are eating their meals.
B. They learn about the students’ home lives.
C. They deal with students’ complaints about the food.
D. They help students learn about a balanced diet.
4. In David’s view, which of his previous jobs prepared him best for his work as a
school chef?
A. teacher B. manager C. waiter D. cook
5. Why does David think that his approach could be difficult to introduce on other schools?
A. Many students are resistant to change.
B. Not all students see healthy eating as important.
C. Other schools don’t see healthy eating as a priority.
D. Parents would be unwilling to accept it.
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
PART II. LEXICO - GRAMMAR (40p)
Section 1. Choose the word or phrase that best fits each blank in the following
sentences. (20p)
1. Simon has a very strong of duty so he will always carry out his promises.
A. sense B. idea C. mind D. thought
81 394
2. I slept badly last night and am feeling particularly this morning.
A.
far-
reaching B. slow-witted C. off-hand D. top-heavy
3. My older brother is extremely fond of astronomy, he seems to a lot of
pleasure from observing the stars.
A. possess B. seize C. reach D. derive
4. I’m sorry to _ to your conversation but there’s an urgent message for you.
A. come in B. bump in C. butt in D. pop in
5. I’m not keen on control of the project to a relative newcomer.
A. undertaking B. charging C. entrusting D. allowing
6. She went under as a waitress to write an article on tipping.
A. cover B. act C. pose D. mask
7. Even at that early state the school felt that she a good chance of
passing her exams.
A. possessed B. stood C. gained D. took
8. His speech _ little or no relation to the topic given.
A. gave B. reflected C. bore D. was
9. He in me on the understanding that I wouldn’t tell anyone else.
A. intimated B. confessed C. disclosed D. confided
10. We intend to _ with the old system as soon as we have developed a
better one.
A. do up B. do away C. do in D. do down
11. There is a huge amount of associated with children’s TV nowadays.
A. produce B. manufacturing C. merchandising D. sales
12. As the order to abandon the ship was given, hundreds of people _
into the icy water.
A. plunged B. emerged C. drowned D. submerged
13. Not once did I see him a finger to help in the home.
A. shift B. move C. click D. lift
14. The engineers won’t be able to repair the telephone system until they can
the cause of the fault.
A. separate B. isolate C. estimate D. concentrate
15. He was writer because he persuaded many people to see the truth
of his ideas.
A. an exceptionally B. a prolific C. an unlimited D. an influential
16. They are happily married although, of course, they argue _.
A. most times B. from day to day C. every now and then D.
on the occasion
17. It is physically impossible for any human being to such extreme
cold for long.
82 394
A. endure B. persist C. withhold D. last
18. Terry is an old of mine. We split up nine years ago but we’ve stayed friends.
A. fire B. flame C. spark D. blaze
19. You know how I worry about you driving at night. Call me when you arrive to
set my mind .
A. easy B. at peace C. calm D. at rest
20. I slept badly last night and I am feeling particularly _ this morning.
A.
far-
reaching B. off-hand C. slow-witted D. top-heavy
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
11. 12. 13. 14. 15.
16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
Section 2. Fill each gap with the correct form of the words in brackets. (10p)
1. Be careful. You may be _ to put all your eggs in one basket. (ADVICE)
2. The cancellation of the ccase resulted from the in court of the
defendant resulted in. (APPEAR)
3. I’ve never met such a strong girl. Her energy seems . (EXHAUST)
4. It is very diffcult to find Mrs. Pie’s shop, for it was from all others
in the street. (DISTINGUISH)
5. Students hate their classmates who get treatment form their
teachers. (PREFER)
6. The educational program we are launching is to teenage girls
in rural areas. (POWER)
7. Doesn’t she know that her good result will make her parents _
proud of her? (MEASURE)
8. A list of events for the autumn is being prepared. (COME)
9. Most people who work feel that they are (PAY)
10.She was the only visitor _ into the sick room. (ADMISSION)
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Section 3. The passage below contains TEN mistakes. Underline the mistakes
and provide the corrections in the spaces below. (10p)
Crime preventing is as crucial in the workplace as it is in the home or neighbourhood.
Reducing crime is as much a part of good management as prompt delivery, good staff relations,
and other
Line 1
Line 2

83 394
acceptable management functions. Losses from shops through shoplifting are extremely high
and utimately, those losses are payment for by all of us in high prices. There are many
opportunities for shopkeepers themselves to reduce shoplifting. As with all types of criminal,
prevention is better than cure. The best deterrent is the present of staff properly trained in how
to identify potential shoplifters. There are also many secure devices now available. Video
camera surveillance is a popular system, even with quite small retailers. In clothes shopping,
magnetic tag marking systems that set off an alarm if they are taken out of the shop have
proved their worthless. However, there are many simpler measures that retailers should
consider. Better lighting and ceiling-hung mirrors can help staff to watch all parts of the
display area. Similarly, simply arrangement shelves and display units to allow clear fields of
visible is a good deterrent
Line 3
Line 4
Line 5
Line 6
Line 7
Line 8
Line 9
Line 10
Line 11
Line 12
Your answers:
1. 6.
2. 7.
3. 8.
4. 9.
5. 10.
PART III. READING (60p)
Section 1. Read the following passage and decide which answer (A, B, C, or D)
best fits each gap. Write your answer in corresponding numbered boxes. (10p)
Homestay
When studying a foreign language abroad, a large majority of students
choose “homestay” accommodation, living with a host family while they (1)
classes in a nearby language school. Very (2)
, however, once lessons have
finished, students speak their mother tongue with other class members of the same
nationality. On a Homestay Language International study trip, we ensure total
immersion in the target language environment by arranging accommodation and
one-to-one tuition in your teacher’s home, (3)
you are surrounded by the
language during every moment of your (4)
.
As you are the (5)
_ student, you can learn at your own pace, and lessons
are tailor-made to (6)
_ your individual interests and objectives. You will also
have the chance to (7)
fully in your host teacher’s family and social life,
including trips to places of interest in the local area. All of our teachers have a
university degree and a relevant teaching qualification, and most hav spent time
abroad so understand the needs and concerns of their student guests.
Homestay Language International offers a wide (8)
of general or
business courses for young and old alike, with a choice of over 80 (9)
throughout
the world. Whether it’s English in New Zealand, French in Canada or German in
Austria you can

84 394
(10) a warm welcome in a relaxed home environment and an unforgettable
study experience.
1.A. assist B. present C. attend D. go
2. A. more B. often C. much D. well
3. A. because of B. in case C. in order D. so that
4. A. halt B. pause C. stop D. stay
5. A. only B. alone C. unique D. lonely
6. A. agree B. adapt C. suit D. adjust
7. A. enjoy B. involve C. participate D. include
8. A. sort B. kind C. type D. range
9. A. terminals B. destinations C. stations D. destinies
10. A. expect B. wait C. reach D. hope
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Section 2. Read the passage and fill in each gap with ONE suitable word. (10p
)
FUNCTIONAL
FOODS
In the 21
st
century food will do more than just feed you. A new range of
products appearing (1)
shelves in shops and supermarkets is designed to give
you specific health benefits. The demands of modern life make these foods very
attractive. Not only do they provide proven ways to improve health, but they are
also very attractive (2) _
a quick and convenient way of making sure we enjoy a
healthy diet.
In some countries it is already possible to buy crisps that make you feel (3)
depressed, chewing gum that increases your brain power and tea that helps you (4)
over the tiredness associated with long-distance air travel. (5)
_ the future,
experts promise biscuits that will keep your heart healthy, and a hot chocolate drink
to give you strong bones.
Despite the fact that these “functional” foods cannot replace a balanced diet
and regular exercise they can help the body perform at (6)
best a lot of the time.
At present, these foods are more expensive than other foods, but that is due to the
ingredients they (7) _
of and the way they are made. All the foods contain
probiotics (8)
increase the number of “good” bacteria in your stomach, helping
to keep your digestive system healthy.
There may even (9)
a functional food to protect eyesight, so keep an
eye out as you never know (10)
you might be eating tomorrow.
Your answers:

85 394
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Section 3. Read the following passage and choose the correct answer to each
of the following questions. Write your answers in the box provided. (10p)
Population ecology is the science that measures changes in population size and
composition and identities the causes of these fluctuations. Population ecology is
not concerned solely with the human population. In ecological terms, a
population consists of the individuals of one species that simultaneously occupy the
same general area, rely on the same resources, and are affected by similar
environmental factors. The characteristics of a population are shaped by its size and
by the interactions among individuals and between individuals and their
environment.
Population size is a balance between factors that increase numbers and factors that
decrease numbers. Some factors that increase populations are favorable light and
temperature, adequate food supply, suitable habitat, ability to compete for
resources, and ability to adapt to environmental change. Factors that decrease
populations are insufficient or excessive light and temperature, inadequate food
supply, unsuitable or destroyed habitat, too many competitors for resources, and
inability to adapt to environmental change.
Another important characteristic of any population is its density. Population density
is the number of individuals per unit, such as the number of maple trees per square
kilometer in a county. Ecologists can rarely determine population size by actually
counting all individuals within geographical boundaries. Instead, they often use a
variety of sampling techniques to estimate densities and total population sizes. For
example, they might estimate the number of black bears in a national park by
counting individuals in a few sample plots representative of the whole park. In
some cases, they estimate population size through indirect indicators, such as the
number of nests or burrows, or signs such as tracks or droppings.
Another important population characteristic, dispersion, is the pattern of spacing
among individuals within the population’s geographical boundaries. Various
species are distributed in their habitats in different ways to take better advantages of
food supplies and shelter, and to avoid predators or find prey. Within a population’s
range, densities may vary greatly because not all areas provide equally suitable
habitat, and also because individuals space themselves in relation to other members
of the population.
Three possible patterns of dispersion are clumped, uniform, and random. A
clumped dispersion pattern means that individuals are gathered in patches
throughout their habitat. Clumping often results from the irregular distribution of
resources needed for survival and reproduction. For example, fallen trees keep the
forest floor moist, and many forest insects are clumped under logs where the
humidity is to their liking. Clumping may also be associated with mating, safety, or

86 394
other social behavior. Crane flies, for example, swarm in great numbers, a behavior
that increase mating chances, and some fish swim in large schools so they are less
likely to be eaten by predators.

87 394
A uniform or evenly spaced distribution results from direct interactions among
individuals in the population. For example, regular spacing of plants may result
from shading and competition for water. In animal populations, uniform
distribution is usually caused completion for some resource or by social
interactions that set up individual territories for feeding, breeding, or resting.
Random spacing occurs in the absence of strong attraction or repulsion among
individuals in a population. Overall, random patterns are rare in nature, with most
populations showing a tendency toward either clumped or uniform distribution.
Populations change in size, structure, and distribution as they respond to changes in
environmental conditions. Four main variables- births, deaths, immigration, and
emigration- determine the rate of change in the size of the population over time. A
change in the birth rate or death is the major way that most populations respond to
changes in resource availability. Members of some animal species can avoid or
reduce the effects of environmental stress by emigrating from one are and
immigrating to another with more favorable environmental conditions, thus altering
the population’s dispersion.
1.Which sentence best expresses the essential information in the highlighted
sentence in paragraph 1?
A. Any species of life can be studied in population ecology.
B. Population ecologists care about the future of humanity
C. The growth of the human population is a major concern.
D. Population ecology does not consider humans worthy of study.
2. According to the passage, which factors might cause the population of a
species to decrease in size?
A. A favorable amount of light and water
B. An ability to hide from or defend against predators
C. A large number of other species competing for food
D. A greater number of births than deaths
3. Which of the following is an indirect indicator of a population’s density?
A. The distribution of food in a given area
B. The number of nests in a given area
C. The number of births in a given period of time
D. The number of individuals counted in a given area
4. The distribution pattern of individuals within a population’s geographical
boundaries is known as_ _
A. population ecology B. population density
C. population change D. population dispersion
5. The word range in paragraph 4 is closest in meaning to .
A. territory B. control C. history D. shelter
6. The word their in paragraph 5 refers to .

88 394
A. resources B. trees C. insects D. logs

89 394
7. All of the following are given as reasons for clumping EXCEPT .
A. uneven resource distribution B. territorial disputes
C. mating behavior D. safety from predators
8. The phrase set up in paragraph 6 is closest in meaning to .
A. forbid B. establish C. increase D. conceal
9. Which of the following situations would be most likely to result in a uniform
dispersion pattern?
A. Birds compete for a place to build their nests.
B. Fish swim in large schools to avoid predators.
C. Whales develop strong bonds among relatives.
D. Elephants form a circle to protect their young.
10. Why does the author mention immigration and emigration in paragraph 8?
A. To identify factors affecting population dispersion
B. To give examples of territorial behavior in animals
C. To show that population balance themselves over time
D. To explain why animals populations are uniformly dispersed
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Section 4. Read the following passage and do the tasks that follow. (20p)
What is Personality?
A
We are all familiar with the idea that different people have different personalities,
but what does this actually mean? It implies that different people behave in
different ways, but it must be more than that. After all, different people find
themselves in different circumstances, and much of their behavior follows from this
fact. However, our common experience reveals that different people respond in
quite remarkably different ways even when facced with roughly the same
circumstances. Alan might be happy to live alone in a quiet and orderly cottage, go
out once a week, and stay in the same job for thirty years, whilst Beth likes nothing
better than exotic travel and being surrounded by vivacious friends and loud music.
B
In cases like these, we feel that it cannot be just the situation which is
producing the differences in behaviour. Something about the way the person is
“wired up” seems to be at work, determining how they react to situations, and more
than that, the kind of situations
they get themselves into in the first place. This is why
personality seems to become stronger
as we get older; when we are young, our
situation reflects external factors such as the social and family environment we
were born into. As we grow older, we are more and more

90 394
affected by the consequences of our own choices (doing jobs that we were drawn
to, surrounded by people like us whom we have sought out). Thus, personality
differences that might have been very slight at birth become dramatic in later
adulthood.
C
Personality, then, seems to be the set of enduring and stable dispositions that
characterizze a person. These dispositions come partly from the expression of
inherent features of the nervous system, and partly from learning. Researchers
sometimes distinguish between temperament, which refers exclusively to
characteristics that are inborn or directly caused by biological factors, and
personality, which also includes social and cultural learning. Nervousness, for
example, might be a factor of temperament, but religious piety is an aspect of
personality.
D
The discovery that temperamental differences are real is one of the major
findings of contemporary psychology. It could easily have been the case that there
were no intrinsic differences between people in temperament, so that given the
same learning history, the same dilemmas, they would all respond in much the
same way. Yet we now know that this is not the case.
E
Personality measures turn out to be good predictors of your health, how
happy you typically are- even your taste in paintings. Personality is a much better
predictor of these things than social class or age. The origin of these differences is
in part innate. That is to say, when people are adopted at birth and brought up by
new families, their personalities are more similar to those of their blood relatives
than to the ones they grew up with.
F
Personality differences tend to manifest themselves through the quick, gut-
feeling, intuitive and emotional systems of the human mind. The slower, rational
deliberate system show less variation in output from person to person. Deliberate
rational strategies can be used to override intuitive patterns of response, and this is
how people wishing to change their personalities or feelings have to go about it. As
human beings, we have the unique ability to look in at our personality from the
outside and decide what we want to do with it.
G
So what are the major ways personalities can differ? The dominant approach
is to think of the space of possible personalities as being defined by a number of
dimensions. Each person can be given a location in the space by their scores on all
the different dimensions. Virtually all theories agree on two of the main
dimensions, neuroticism (or negative emotionality) and extroversion (or positive
emotionality). However, they differ on how many additional ones they recognize.
Among the most influential proposals are openness, conscientiousness and

91 394
agreeableness. In the next section I will examine these five dimensions.
92 394
For questions 1 – 5, choose correct heading for sections B – F from the list of
headings below.
List of Headings
i
ii
iii
iv
v
vi
vii
viii
ix
x
A degree of control
Where research has been carried out into the effects of family on personality
Categorising personality features according to their origin
A variety of reactions in similar situations
A link between personality and aspects of our lives that aren’t chosen
A possible theory that cannot be true
Measuring personality
Potentially harmful effects of emotions
How our lives can reinforce our personalities
Differences between men’s and women’s personalities
Example: Section A: iv, Section G:
vii
1. Section B
3. Section D
5. Section F
2. Section C
4. Section E
For quesions 6 – 10, write in the corresponding numbered boxes.
YES if the statement agrees with the claims of the writer
NO if the statement contradicts the claims of the writer
NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
6. Alan and Beth illustrate constrating behavior in similar situations.
7. As we grow older, we become more able to analyse our personalities.
8. Nervousness is an example of a learned characteristic.
9. The discovery of differences in temperament has changed the course of
psychological research.
10. The rational behavior of different people shows greater similarity than their
emotional behavior.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Section 5. You are going to rea an article in which four writers talk about the
first book they wrote. For questions 1-10, choose from the people (A-D). The
writers may be chosen more than once. (10p)
Which writer
A. Harry Holden

93 394
I remember my first book very clearly; I suppose evevry writer does. But I also remember

94 394
it because I’ve changed so much since then. It was a biography of the Duke of
Wellington, which I’d been asked to write by a friend of mine, a publisher, who
knew I was very interested in the subject. I’d had no experience of writing but I
have to say the book was actually quite good. In fact, I was awarded the General
Haig Memorial Prize for the book the year it was published, I was completely
exhausted. I’d been working on it more or less full time for five years. So since
then, I’ve concentrated on detective stories. They’re far easier!
B. Marcia Onslow
My first book was quite successful, although to be completely frank, looking back,
I think I was very lucky. I attended a creative writing course at university, intending
to concentrate on short stories for magazines, which is quite a lucrative market. As
a project in my final year, I was asked to write a long work of fiction, and I decided
to write a love story set in America during the California gold rush. Anyway, I’d
been advised to establish a strict schedule, so I would write ten pages every
morning and correct them every evening. Then I left university, started writing
stories for publication, and more or less forgot about the book for about ten years,
until my publisher suggested I might try writing a novel. So I just handed it to her,
all finished, and she published it right away!
C. Maria Delangelo
When I wrote the first draft of my first novel, Chasing William, it wasn’t much like
the version that was eventually published; my editor told me I would have to make
some changes to the hero, William, because he wasn’t interesting enough.
Naturally, I was pretty offended at the time, but I’m glad to say I had the good
sense to listen to my editor, who was completely right. The problem was that I had
based the whole story on the real adventures of my uncle, William Hargreaves,
simply describing my uncle’s character. When you write a work of fiction, you
have to make the main character intriguing, but describing a real person isn’t
always the best way to do that. Funnily enough, in the short stories I’d published
previously I never tried to use real people. I’m glad my editor talked me out of
doing it in the novel.
D. John Hopkins
I learnt a few important lessons from my first book, one of which is that you have
to leave certain things to the publisher. For instance, the editor gave me a lot of
advice about how to structure my book, a study of the Industrial Revolution. I was
a bit hesistant in the beginning, but then I decided to follow his advice and I
haven’t regretted it. It was the same with the artistic work on the cover, which I
really hated at first. But in the end the book was very successful, and I suppose the
design must have been right. The other lesson I learnt was about working methods.
I’m quite an impetuous person, and I don’t like being tied down to fixed ways of
doing things. I discovered I had to be strict about how long I would work for and
not write any more than that, even though it meant I spent half a year writing it.
Otherwise I’d have been completely exhausted and never actually finished it!
95 394
Your answers
took six months to write the book? 1. _
was upset at something their editor said?
2. _
did not like part of the book design?
3. _
had written the book years before it was published? 4. _
has never written that type of book since then? 5. _
produced a certain amount of writing each day?
6. _
revised the manuscript because the main character was boring? 7. _
wrote for a set amount of time each day? 8. _
wrote short stories before the first book? 9. _
won something for the first book?
10.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
PART IV. WRITING (50 points)
Section 1: Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means the
same as the sentence before it. (10p)
1. One advantage of living in the city is the range of clothes shops.
One point
in .
2. We have credited the money to your current account at this
bank.. We have placed
.
3. You may be disqualified if you don’t obey the
regulations. Failure
.
4. The police’s prejudice against foreigners could not be recorded in the
official files. The fact that
_.
5. As people grow older, they become more and more
forgetful. The
.

96 394
Section 2: Rewrite these sentences using the words in CAPITAL. You must not
change the given words. (10p)

97 394
1. We did not think that canceling the order was a good idea .
(INADVISABLE)
We thought .
2. We will ultimately all feel the effects of
pollution. (END)
In us all.
3. He finally accepted the situation, although he was
concerned. (TERMS)
Despite
his .
4. Being inexperienced was a disadvantage to her when she applied for
promotion . (COUNTED)
Her when she
applied for promotion.
5. This medicine will relieve the pain, but it will not cure everything.
(MIRACLES)
This medicine bring
some pain relief.
Section 3: Paragraph writing (30p)
Nowadays, there is a trend that reports of media focus on problems and
emergencies rather than positive developments. Do you think it is harmful to
individuals and to society?
You should write a paragraph of 150-180 words to express your viewpoint.

98 394
----THE END----
Người ra đề: Nguyễn Ngọc Hà - 093.664.949
HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤM MÔN TIẾNG ANH LỚP 10
PART I. LISTENING (50p) 2.0 points/correct answer
Section 1. You will hear an interview to do a quesstionaire on the residency on the
north. For questions from 1 to 7, fill in each gap with NO MORE THAN THREE
WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER. (14p)
1. salesman 2. Spring Park 3. apartment 4. train
5. once a month 6. sailing 7. Japanese
99 394
Section 2. Listen to the recording and complete each of the following sentences with
NO MORE THAN two words AND/ OR a number (16p)
1. commitments 2. impressed 3. patronising 4. irrigation
5. handouts 6. self-sufficient 7. surplus 8. prospects
Section 3. You are going to listen to a conversation about certain type of advertising .
Listen and decide if the following statements are True (T) or False (F). Check (√) the
appropriate boxes. You will hear the talk TWICE.
1. F 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. F
Section 4: You will hear part of a radio interview in which David Evans, a chef in a
British school, is talking about his work. Choose the answer (А, В, C or D) which fits
best according to what you hear. (10p)
1. C 2. B 3. D 4. B 5. A
PART II. LEXICO - GRAMMAR (40p) 1.0 points/correct answer
Section 1. Choose the word or phrase that best fits each blank in the following
sentences. (20p)
1.A 2. B 3. D 4. C 5. C
6. A 7. B 8. C 9. D 10. C
11. C 12. A 13. D 14. B 15. D
16. C 17. A 18. B 19. D 20. C
Section 2. Fill each gap with the correct form of the words in brackets. (10p)
1. ill-advised 2. non-appearance 3. inexhaustible 4. indistinguishable 5. preferential
6. empower 7. immesuarably 8. forthcoming 9. underpaid 10. admitted
Section 3. The passage below contains TEN mistakes. Underline the mistakes and
provide the corrections in the spaces below. (10p)
1. preventing->prevention 6. secure -> security
2. acceptable-> accepted 7. shopping -> shops
3. payment -> paid 8. worthless -> worth
4. criminal -> crime 9. arrangement -> arranging
5. present - > presence 10. visible ->vision/visibility
PART III. READING (60p)
Section 1. Read the following passage and decide which answer (A, B, C, or D) best fits
each gap. Write your answer in corresponding numbered boxes. (10p)
1.0 points/correct answer
1. C 2. B 3. D 4. D 5. A
6. C 7. C 8. D 9. B 10. A

100
394
Section 2. Read the passage and fill in each gap with ONE suitable word. (10p)
1.0 points/correct answer
1. on 2. as 3. less 4. get 5. in
6. its 7. consist 8. which/that 9. be 10. what
Section 3. Read the following passage and choose the correct answer to each of the
following questions. Write your answers in the box provided. (10p)
1.0 points/correct answer
1.A 2. C 3. B 4. D 5. A
6. C 7. B 8. B 9. A 10. A
Section 4. Read the following passage and do the tasks that follow. (20p)
2.0 points/correct answer
1. ix 2. iii 3. vi 4. v 5. i
6. YES 7. NOT GIVEN 8. NO 9. NOT GIVNE 10. YES
Section 5. You are going to rea an article in which four writers talk about the first book
they wrote. For questions 1-10, choose from the people (A-D). The writers may be
chosen more than once. (10p)
1.0 points/correct answer
1. D 2. C 3. D 4. B 5. A
6. B 7. C 8. D 9. C 10. A
PART IV. WRITING (50 points)
Section 1: Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means the same
as the sentence before it. (10p)
2.0 points/correct answer
1. One point in favor of living in the city is the range of clothes shops.
2. We have placed the money to the credit of your current account at this bank.
3. Failure to obey the regulations may cause your disqualification.
4. The fact that the policemen were prejudiced against foreigners could not be recorded
in the official files.
5. The older people grow, the more forgetful they become.
Section 2: Rewrite these sentences using the words in CAPITAL. You must not change
the given words. (10p)
2.0 points/correct answer
1. It was ( would be) inadvisable to cancel the order.
2. In the end, pollution will affect us all.
3. Despite his concern, he finally came to terms with the situation.
101
394
4. Her lack of experience/ inexperience counted against her when she applied for promotion.
5. This medicine will not work/perform miracles, but it will bring some pain relief.
Section 3: Paragraph writing (30p)
Nowadays, there is a trend that reports of media focus on problems and emergencies
rather than positive developments. Do you think it is harmful to individuals and to
society?
You should write a paragraph of 150-180 words to express your viewpoint.
Mô tả tiêu chí đánh giá Điểm tối đa
1. Bố cục
o Câu dẫn chủ đề mạch lạc
o Bố cục hợp lý rõ ràng, phù hợp với yêu cầu của đề bài
o Bố cục uyển chuyển từ mở bài đến kết luận
6
2. Phát triển ý
o Phát triển ý có trình tự logic
o Có dẫn chứng, ví dụ,… đủ để bảo vệ ý kiến của mình
6
3. Sử dụng ngôn từ
o Sử dụng ngôn từ phù hợp với nội dung
o Sử dụng ngôn từ đúng văn phong, thể loại
o Sử dụng từ nối cho các ý uyển chuyển
6
4. Nội dung
o Đủ thuyết phục người đọc
o Đủ dẫn chứng, ví dụ, lập luận
o Độ dài: Số từ không nhiều hoặc ít hơn quy định 10%
6
5. Ngữ pháp, dấu câu, chính tả
o Sử dụng đúng dấu câu
o Chính tả: Viết đúng chính tả
Lỗi chính tả gây hiểu lầm/ sai lệch ý sẽ bị tính một lỗi (trừ
1% điểm của bài viết)
Cùng một lỗi chính tả lặp lại chỉ tính một lỗi
o Sử dụng đúng thời, thể, cấu trúc câu đúng ngữ pháp. (Lỗi ngữ pháp
gây hiểu lầm/ sai lệch ý sẽ bị trừ 1% điểm của bài viết)
6
Tổng
30
Section 1

102
394

103
394
Section 2
Earlier this year I fulfilled a lifelong ambition of mine by working for three months
as a volunteer in an African country. I’m in my late 50s now and I don’t have the
commitments that have previously held me back. I’ve worked in marketing for much of
my life, and I wanted to use the skills I have to help out in a small way.
I applied to do voluntary work a couple of years ago, but it wasn’t until about a
year later that a suitable scheme came up and I was asked to go. The reaction of my
friends to the news was

104
394
interesting. Many were impressed, I think, and a lot said that given the opportunity they’d
like to do something similar- although I must say that not all of them were so keen when I
told them later about how basic the conditions were. But a few clearly disapproved of
what was doing. They argued that I was patronising Africans by intervening and telling
them how to run their lives. But I saw it rather differently. Ideally, development schemes
should be set up by the communities themselves. But sometimes local people don’t yet
have the necessary skills to make them effective, and need some kind of outside, expert
support. And that’s where I came in.
The scheme I worked on was based in a village of about 200 people in Tanzania. It
involved building concrete tanks to capture water during the wet season with the aim of
reducing the problem of drought during the rest of the year. With better irrigation would
come more reliable crops, so that eventually the villagers would become self-sufficient.
There had been a severe drought in the area for the previous three or four years. The whole
region was on the brink of starvation and handouts from charities were the only thing that
kept people alive. The scheme had been underway for less than a year when I arrived, and
my brief was to suggest ways in which the villagers could market any agricultural
production that was surplus to their own requirements- any food that they didn’t need
themselves. I’v heard now that the village is making money from its crops and it’s built a
primary school and had a smal health centre. It’s very gratifying to know that the scheme
has completely transformed its prospects, and the village is now well on its way to
becoming a thriving community.
Sect
ion
3 A:
wo
ma
n B:
Ma
n
A: Sir… excuse me…yes, you I’m sorry but…
B: Me? Can I help you?
A: Yes, if you don’t mind… I have to ask you about the ad on your car.
B: No, problem, everyone is curious about it. I’m hapy to tell you about it. You see, I’m
not just one of the folks who are paid to have the ad on their car, I work for the agency
that places them. Interested? I might convince you to let us put an ad on your car.
A: Yes, you might. And then again, you might not. But I am curious. How did they ever
come up with this idea? It seems so innovative… and yet when you think about it, it seems
silly that we haven’t seen ads on cars for years.
B: I wish I could say I was the one who first had the idea, but I wasn’t. In fact, there are a
number of companies who wrap cars with advetisements, and each one has a story about
how its founder was the first to get the idea. All the stories are a variation on the same
theme, though, and they go something like this. A guy is stuck in traffic, staring at a car-
in some versions it is a pick-up… you know, with the big “Toyota” or “Food” name

105
394
written on the back – and the guys thinks to himself, “Hey, that is great advertising! I can’t
get “Ford” out of my head. I spend twenty hours a week or more in my car staring at
brands like that. And the crazy thing is, that the driver of that

106
394
car is basically paying Ford- or Chevrolet, or Toyota, or Dodge, or what ever- thousands
of dollars for the privilege of doing the adversising for the company.” And then it hits the
guy- you know, like the apple falling on Newton’s head- the company ought to pay the
driver! Not the other ay around. Anyway, that is the story, and then some entrepreneur put
it into action, and a couple of companies were born.
A: Wow, that is some story. So what is the name of your company… “Ads on Wheels”?
“Drivertisements”? “Autotisement”?
B: Ours is a bit less creative… “Ads on the Move”
A: Well, that says it all.
B: Here’s how it works. If you are a car owner interested in getting wrapped…
A: Wrapped?
B: That’s what we call it when we wrap an advertisement around your car. So if a person
is interested, we ask them to answer a survey.
A: A survey? Why?
B: Well, we need to know where that car is likely to be… how often it is on the road…
information like that, so we can match it up to an appropriate sponsor. If there is a match
between the car and the advertiser, we pay the driver between 200 and 300 dollars a
month to display the ad.
A: Wow! That would really come in handy.
B: Now, you sound interested.
A: I’m just curious.. what are some of the advantages to an advertiser? I mean, why
choose this over, say… a traditional roadside billboard?
B: Well, first of all… you pass a billboard once or twice and you read the ad… but
sometimes you follow a car for hours! That’s the number-one advantage of this kind of
advertising. But there are other reasons, too. For instance, there are a limited number of
billboards, and their prices are increasing. Plus, some cities have restricted the
construction of new outdoor adverstisements, so they are more difficult to get. Some
cities, like Scottdale, Arizona, and two whole states- Hawaii and Maine- have banned
outdoor advertising altogether.
A: I didn’t know.
B: So, do you know everything you need to know? Are you interested in going the next
step and applying to have your car wrapped?
A: I have to be honest with you…I don’t drive. I was waiting for the bus.
B: That’s okay, I…

107
394
Section 4
Interviewer: Today I’m talking to David Evans, who’s a school chef at Academy School
in Wales. Now, David, this is a new school, isn’t it? And it takes a rather unusual
approach to school meals.
David: That’s right. When the school opened about this time last year the new Principal
proposed that school dinners should be compulsory. Some people thought she’s be crazy
to go ahead with the plan, but she was determined to. Obviously this was quite a risky
experiment. Students aren’t allowed to bring sandwiches or fizzy drinks. And each day
there are only two options available one vegetarian. We try to introduce a wide range of
styles of cooking. Naturally, at first, students were a little dubious about the food. Most
had only eaten what you might call “traditional” British food, so think it was quite
adventurous for them to try what they saw us unusual, the kinds of food they normally
wouldn’t have the opportunity to eat at home, or wouldn’t want to.
Interviewer: And rather having a typical school canteen with individual students lining
up to collect food from the kitchen, you have a different arrangement.
David: Yes, we have our restaurant system. We get everybody seated at about 12.30 on
tables of six and then one student from each table collects the food from the kitchen and
serves it the the others. It’s slow, but we deliberately encouragw students to sit and talk
around the table, including about the food they’re eating. There’s still some resistance to
this, particularly as a lot of our students come from homes where fast food and ready
meals are what’s normally eaten, and family members eat at different times. They don’t
have the habits of conversation over a meal or discussions of food. But we see this as part
of our mission, to give them basic social skills so they can operate in an adult world.
Interviewer: And what about the staff here? What’s their part in this?
David: Staff are expected to eat in the restaurant and sit with students, but they’re not
there to control things. They’re there to talk to students about the food they’re eating and
in this way they learn about nutrition and how important it is to get the right amounts, and
that having too much carbohydrate or fat isn’t a good thing. Of course, it’s not all food
talk. And unexpected benefits is that the teachers learn more about students outside the
classroom. At first there were grumbles from teachers about being forced to eat with
students rather than sitting with other members of staff, but now I think they prefer to.
Interviewer: And you always try to cook with fresh ingredients.
David: Yes, that’s right. Although we offer international dishes, both for nutritional
reasons and because of environmental concerns, pretty much all of the produce we use is
locally sourced. We’ve also got a small herb garden behind the science block. Students
can help with this if they’re willing to. So as well as having fresh food, we’re reducing the
environmental problemss associated with transporting food over long distances. We put up
a map in the restaurant to show where food has come from. It’s not always possible to get
local produce, of course, but we do what we can.
Interviewer: Now what about you personally, David? How did you come to take on the
post of school chef here?

108
394
SỞ GD & ĐT CAO BẰNG
TRƯỜNG THPT
CHUYÊN
ĐỀ THI ĐỀ NGHỊ
THAM DỰ TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
NĂM 2019
ĐỀ THI MÔN: TIẾNG ANH – LỚP 10
Thời gian: 180 phút (Không kể thời gian giao đề)
(Đề thi gồm 18 trang)
David: Well, I’ve had a varied career. I’ve been a waiter and a chef in a London
restaurant, I’ve run two smal companies, and I went on to train as a teacher. I taught
domestic science in a secondary school for ten years before taking on this job. I’ve found
that probably the most important part of the job is to listen to what the students say about
the food. I spend a lot of time in the restaurant. I go and talk to the students. They’ll
always give me an honest opinion on whether or not they’ve enjoyed something. The time
I spent in management has helped me most with this. You need to listen to what people are
saying to get the best out of them and make the right decisions.
Interviewer: And do you think the approach to food you’ve eaten here could be adopted
in any school?
David: No, I don’t think all schools would be able to. We’re lucky in that we’re a new
school and we set it up the ethos that learning about healthy eating is an important life
skill, and students and their parents accept that, although sometimes rather unwillingly. It
could be difficult to introduce this into an established school where, for example, chips
and burgers are a regular feature of school dinners. Introducing a radical change when
students are used to doing things in a certain way can be difficult. But any school could
take some steps to make students aware of the importance of healthy eating. I’d certainly
advise them to. Over time I think we’ll see most schools moving in this direction.
A. LISTENING (50 pts)
Part 1: You will hear a conversation between a Scottish student called
John and a Finish student called Pirkko about the Tampere Student
Games in Finland. For
questions 1-5, complete the notes below. Write NO
MORE THAN THREE WORDS
AND/OR A NUMBER for each answer in
the corresponding numbered boxes. (10 pts)
109
394
Tampere Student Games
- Dates of the games: (1)
- Cost of taking part (2) euros per day each
- Entry fee includes competition entrance, meals and (3)
- Hotel (4) has a special rate during the games
- Hotel is close to (5)
- Website address: www.sellgames.com
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Part 2. Listen and complete the sentences below. Write no more than three
words for each answer. (20 pts)
1. Governments have been mistaken to.......................slums.
2. There is often a lack of......................concerning housing projects.
3. Housing policies which are based on principles of....................are particularly
effective.
4. Some...........................should always be provided by governments.
5. Migrants will only..........................in housing if they feel secure.
6. Governments often underestimate the importance of.......................to housing
projects.
7. The availability of ..................... is the starting point for successful
housing development.
8. Urbanisation can have a positive effect on the...........................of individuals.
9. The population size of cities enables a range of............................to occur.
10. City living tends to raise the level of......................................to occur.
110
394
Part 3. You will hear an extract from a radio programme and decide
whether the statements are true or false. (10 pts)
1.Mrs Kent is worried about the weather in the near future.
2. According to Tom Sheridan, people don’t talk about the weather any more.
3. Paul Spenser does the production of a cookery programme.
4. Jane thinks that students should be given free books.
5. An elderly listener doesn’t think young people should have to pay in the discos.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Part 4: You will hear a radio discussion about children who invent
imaginary friends. Choose the answer (A, B, C or D) which fits best
according to what you hear. Write your answers in the corresponding
numbered boxes. (10 points)
1. In the incident that Liz describes,
A. her daughter asked her to stop the car.
B. she had to interrupt the journey twice.
C. she got angry with her daughter.
D. her daughter wanted to get out of the car.
2. What does the presenter say about the latest research into imaginary friends?
A. It contradicts other research on the subject.
B. It shows that the number of children who have them is increasing.
C. It indicates that negative attitudes towards them are wrong.
D. It focuses on the effect they have on parents.
3. How did Liz feel when her daughter had an imaginary friend?
A. always confident that it was only a temporary situation
B. occasionally worried about the friend’s importance to her daughter
C. slightly confused as to how she should respond sometimes

111
394
D. highly impressed by her daughter’s inventiveness
4. Karen says that one reason why children have imaginary friends is that
A. they are having serious problems with their real friends.
B. they can tell imaginary friends what to do.
C. they want something that they cannot be given.
D. they want something that other children haven’t got.
5. Karen says that the teenager who had invented a superhero is an example of
A. a very untypical teenager.
B. a problem that imaginary friends can cause.
C. something she had not expected to discover.
D. how children change as they get older.
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
B. LEXICO - GRAMMAR (40pts)
Part 1. Choose the word or phrase that best fits each blank in the following
sentences. (20pts)
1. The police say they have some important clues the murderer.
A. on B. about C. to D. in
2. Camels have either one hump or two humps. The Arabian camel has one
hump. The Bactrian camel, has two humps.
A. nevertheless B. however C. therefore D. otherwise
3. I’ll be with all of you in hour.
A. a quarter of an B. one quarter of an C. a quarter of one D. a quarter of
4. any other politician would have given way to this sort of pressure years ago.
A. Really B. Practically C. Actually D. Utterly
5. Private printing was simply a means he could increase his income.
A. whereupon B. whereby C. wherewithal D. whereabout
6. Buying shares in this company is as safe as . There’s no way you
can lose your money.

112
394
A. houses B. a bank C. gold bars D. a vault
7. I’m sorry to have bothered you. I was under the that you wanted me
to call you.
A. mistake B. miscalculation
C. misconception D. misapprehension
8. When he examined the gun, the detective’s suspicion turned into .
A. certainty B. confirmation C. reality D. conclusion
9. The management are making to increase the company’s efficiency.
A. measures B. steps C. moves D. deeds
10. Tim: “Will you come for a walk with me?” Mary: “ ”.
A. No, I won’t, thanks B. No, I shan’t, thanks
C. No, I’d prefer not, thanks D. No, I’d prefer
not to, thank you
11. Kate: “It seems to me that spring is the most beautiful time of the
year.” Tony: “ ! It’s really lovely!”
A. You’re exactly right B. You could be right
C. You are wrong D. I couldn’t agree less
12. She said that she would be punctual for the opening speech, she were late?
A. but what if B. how about C. and what about D. so if
13. In a money-oriented society, the average individual cares little about solving
problem.
A. any other B. any other’s
C. anyone else’s D. anyone’s else
14. Would you please leave us details of your address forwarding any
of your mail to come?
A. for the purpose of B. as a consequence of
C. for the sake of D. by means of
15. of the Chairman, the Executive Director will be responsible for
chairing the meeting.
A. For the absence B. On the absence
C. In the absence D. To the absence
16. we went swimming.
A. Being a hot day, B. It was a hot day,
C. The day being hot, D. Due to a hot day,
17. The web of the common house spider is an ingenious trap that catches
small insects.

113
394
A. simple B. useful C. fragile D. clever
18. For most male spiders courtship is a perilous procedure, for they may be
eaten by females.
A. complicated B. peculiar C. dangerous D. ordinary
19. These two essays are word word the same.
A. for B. from C. with D. in
20. “What time is it your watch?”
A. at B. with C. by D. from
1.
………….......
2.
………….......
3.
………….......
4.
………….......
5.
………….......
6.
………….......
7.
………….......
8.
………….......
9.
………….......
10.
.…………......
11.
.…………......
12.
.…………......
13.
.…………......
14.
.…………......
15.
.…………......
16.
.…………......
.
17.
.…………......
.
18.
.…………......
.
19.
.…………......
.
20.
.…………......
.
Part 2. The passage below contains 10 mistakes. IDENTIFY and
CORRECT them. Write your answers in the space provided in the
column. (10pts)
LINE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Leonardo Dicaprio is one of the hotter young film stars around at the
moment. His face has been on the covers of all the top movies and young
magazines over the last few months and he has been the subject of
countless articles, rumours and showbiz gossip. Leonardo doesn’t like
reading about him because “I read things about me that I’ve never said in
my life and never did”.
Leonardo Dicaprio was born in Los Angeles on 11 November, 1974. He’s
a Scorpio. His full name is Leonardo Wilhelm Dicaprio. His mother is
Germany and his father Italian-American. They called him Leonardo
because when his mother was still pregnant, he started kicking while she
was stood in front of a painting by Leonardo De Vinci. His friends call
him
114
394
12
13
14
15
16
17
Leo. He has a scar from when he was stinging by a Portuguese man-of-
war.
His parents separated before he was born, so his mother moved to a poor
neighborhood of Hollywood there Leo grew up. At school he was very
good at imitating people, especially Michael Jackson. This made him very
popularly. His childhood hero was Poseidon, the Greek god of the sea.
After appearance in TV commercials and episodes of Roseanne, he played
the cast of Roseanne, the TV sitcom starring Kirk Cameron. Leonard
played the part of Luke, a homeless boy. Lately, he played the part of Jim
Carroll in The Basketball Diaries. But he has really become famous since
he acted
in the film Titanic.
Your answers: Ex: Line 1: hotter =>hottest
LINE MISTAKE CORRECTION LINE MISTAKE CORRECTION
Part 3. Write the correct FORM of each bracketed word in the numbered
spaces provided. (10pts)
appropriate great improvisation compel intensely
essence direct instrument fuse intelligent
When jazz began to lose its reputation as “low-down” music and to
gain well- deserved acclaim among (1), musicians began to feature many
instruments previously considered (2) for jazz. Whereas before 1950s, jazz
musicians played only eight basic (3) in strict tempo, in this decade, they
started to (4) on the flute, Electric organ, piccolo, accordion, cello, and even
bagpipes, with the rhythm section

115
394
composed for strings or piano. Big bands no longer dominated jazz, and most
changes emerged from small combos.
Jazz continued to move in new (5) during the 1960s. And in the 1970s,
musicians blended jazz and rock music into (6) jazz which combined the
melodies and the improvisations of jazz with the rhythmic qualities of rock
‘n’ roll. The form of jazz music was (7) affected by electric instruments and
electronic implements to (8), distort, or amplify their sounds. However, the
young musician of the time felt (9) to include a steady, swinging rhythm
which they saw a permanent and (10) element in great jazz.
1.
………….......
.
2.
………….......
.
3.
………….......
.
4.
………….......
.
5.
………….......
.
6.
………….......
7.
………….......
8.
………….......
9.
…………......
10.
.…………......
C. READING COMPREHENSION (60pts)
Part 1: Read the passage below and decide which answer (A, B, C or D)
best fits each gap. Write your answer in the numbered boxes. (10 pts)
In Europe, Midsummer Night's Eve, also known as St John's Eve,
occurs on June 23
rd
. It originates from the pagan celebrations of the summer
solstice which were held on June 21
st
. On that night throughout Europe
bonfires were lit along hillsides to (1) the shortest night of the
year. It must have looked as if some kind of violent insurrection was taking
place down the coast of Scotland and England, but these signal fires in fact
had a very important purpose. Bones of farm animals (2) the previous
autumn were burned and, when the fires had
(3)
, the remaining ash was put to good use: it was spread on the
fields to enrich the land and ensure a good harvest. The word 'bonfire' is
(4)
from 'bone fire'.
In Brazil too St John's Eve means bonfires and fireworks. Another
quaint tradition involves the (5) of small paper
hot-air balloons, although they are prohibited by law in the cities because of
the fire (6) . Bonfires mark the beginning of spring
rather than the summer in Sweden and are lit on the last night

116
394
of April. In the Swedish Midsummer's Eve (7) , held on June 24th, a
large pole, decorated with flowers and leaves, is placed in the ground.
Thistles also have a significant role in the celebration of Midsummer's
Night in Europe. In the past they were thought to (8) witches. The pretty,
prickly plant was nailed over barn doors and used in wreaths, the circular
shape being a symbol of the turning of the seasons. Wheels laced with straw
and soaked in pitch were lit from the bonfires and then rolled down hills.
There is less risk of fire in a (9) tradition to many Slavic
countries. Young women and girls float little baskets of flowers and lighted
candles down streams. Local boys swim out to (10) a basket, find the
girl it belongs to and claim a dance at the town's Midsummer's Eve Party.
1. A. celebrate B. honour C. commemorate D. commiserate
2. A. revised B. assassinated C. slaughtered D. sacrificed
3. A. doused B. extinguished C. smothered D. gone out
4. A. derived B. developed C. evolved D. decayed
5. A. landing B. launching C. propelling D. ejecting
6. A. certainty B. peril C. jeopardy D. hazard
7. A. tradition B. custom C. ceremony D. practice
8. A. deflect B. ward off C. attract D. avert
9. A. unique B. common C. mutual D. prevalent
10. A. salvage B. rescue C. set free D. liberate
Part 2. Read the following text and fill in the blank with ONE suitable
word. Write your answers in corresponding numbered boxes. (10 pts)
The origin of language
The truth (0).
is
nobody really knows how the language first
began. Did we all start talking at around the same time 1. of the manner
in which our brains had begun to develop?
Although there is a lack of clear evidence, people have come up with various
theories about the origins of language. One recent theory is that human
beings have evolved in 2. a way that we are programmed for language
from the moment of birth.
117
394
In 3. words, language came about as a result of an evolutionary
change in our brains at some stage.
Language 4. well be programmed into the brain but, 5. this, people still need
stimulus from others around them. From studies, we know that 6.
children are isolated 7. human contact and have not
learnt to construct sentences before they are ten, it is doubtful they will ever
do 8. . This research shows, if 9. else, that language is a social
activity, not something invented 10. isolation.
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Part 3. Read the passage and choose the best answer to each of the
questions. (10 pts)
How I found my true voice
As an interpreter, Suzanne Glass could speak only for others – but the work
provided terrific material for her first novel.
‘No, no, no! You’ve got to get away from this or you’re going to lose
it.’ The voice reverberating in my head was my own. I was at an international
conference. My throat was killing me and my headphones were pinching. I
had just been interpreting a speaker whose last words had been: ‘We
must take very seriously the standardization of the length of cucumbers and
the size of tomatoes.’ You can’t afford to have your own thoughts when
you’re interpreting simultaneously, so, of course, I missed the speaker’s
next sentence and lost his train of thought. Sitting in a darkened booth at the
back of a huge conference hall, I was thrown. Fortunately, my colleague
grabbed my microphone and took over.
This high-output work was not quite the dream profession I had hoped for.
Although I had fun with it in the beginning – occasionally being among the
first to hear of medical and political breakthroughs would be exciting for
any 25-year-old
–I realized that this was a job in which I would never be able to find my own
voice. I had always known that words would be my life in one form or
another. My mother

118
394
thought she’d given birth to an alien when I began to talk at the age of seven
months. That momentous day, she had placed my playpen in the hallway and
gone into the bedroom. In imitation of the words she had repeated to me
again and again, I apparently called out towards the bedroom door: ‘I see
you. I see you.’ I was already in training for a career as a professional parrot.
But how mistaken I was to think that international interpreting would be
glamorous. The speaker rarely stops to think that there’s someone at the
back of the room, listening to his words, absorbing their meaning, and
converting them into another language at the same time. Often I was
confronted with a droner, a whisperer or a mumbler through my headphones.
The mumblers were the worst. Most of the time, an interpreter is thought of
as a machine – a funnel, a conduit, which, I suppose, is precisely what we are.
Sometimes, when those we are translating for hear us cough or sneeze, or
turn round and look at us behind the smoky glass of the booth, I think they’re
surprised to see that we’re actually alive.
Ironically, part of the secret of interpreting is non-verbal communication.
You have to sense when your partner is tired, and offer to take over. At the
same time, you have to be careful not to cut him short and hog the
microphone. Interpreters can be a bit like actors: they like to show off. You
do develop friendships when you’re working in such close proximity, but
there’s a huge amount of competitiveness among interpreters. They check on
each other and sometimes even count each other’s mistranslations.
Translating other people’s ideas prevented me from feeling involved and
creative as an interpreter. Actually, you can’t be a creative interpreter. It’s a
contradiction in terms. Sometimes, when I disagreed with a speaker, I
wanted to rip off my headphones, jump up and run out of the booth,
shouting: ‘Rubbish. Rubbish. You’re talking a lot of nonsense, and this is
what I think about it.’ Instead, I had to sit there and regurgitate opinions in
violent contradiction with my own. Sometimes, I’d get my revenge by
playing games with the speaker’s tone of voice. If he was being serious, I’d
make him sound jocular. If he was being light-hearted, I’d make him sound
earnest.
Eventually, I wanted to find a career where my own words would matter
and where my own voice would be heard. So, to redress the balance, I
decided to write a novel. While I was writing it, I did go back and interpret
at a few conferences to get inside the head of Dominique, my main
character. At first, I was a little rusty and a couple of the delegates turned
round to glare at me, but after twenty

119
394
minutes, I was back into it, playing that old game of mental gymnastics.
Interpreting is like learning to turn somersaults: you never forget how to do
it. But for me, sitting in the booth had a ghost-like quality to it – as though I
had gone back into a past life
- a life that belonged to the time before I found my own voice.
1. In the first paragraph, the writer says she discovered that_ .
A. there were some subjects she had no interest in dealing with.
B. the standard of her work as an interpreter was getting lower.
C. her mind was wandering when she should have been doing her job.
D. she could no longer understand subjects she had previously covered.
2. What does the writer say about being an interpreter in the second paragraph ?
A. It was the kind of job her parents had always expected her to do.
B. It turned out to be more challenging than she had anticipated.
C. It was what she had wanted to be ever since she was a small child.
D. It gave her access to important information before other people.
3. What does the writer say about speakers she interpreted for ?
A. Some of them had a tendency to get irritated with interpreters.
B. She particularly disliked those she struggled to hear properly.
C. They usually had the wrong idea about the function of interpreters.
D. Some of them made little attempt to use their own language correctly.
4. The writer says that relationships between interpreters .
A. can make it difficult for interpreters to do their jobs well.
B. are affected by interpreters’ desires to prove how good they are.
C. usually start well but end in arguments.
D. are based on secret resentments.
5. The writer says that when she disagreed with speakers, she
would sometimes .
A. mistranslate small parts of what they said.
B. make it clear from her tone of voice that she did not agree.
C. exaggerate their point of view.
D. give the impression that they did not really mean what they said.
6. The writer says that when she returned to interpreting, .
A. she did not start off very well.
B. she briefly wished she had not given it up.
C. she thought that two of the delegates recognized her.
D. she changed her ideas about the main character in her novel.

120
394
7. What is the writer’s main point in the article as a whole ?
A. It is not always a good idea to go into a profession because it
looks glamorous.
B. Most interpreters eventually become disillusioned with the work.
C. Being an interpreter did not allow her to satisfy her need to be creative.
D. Most interpreters would actually like to do something more creative.
8. Which is the closest in meaning to momentous in ‘That momentous day’?
A. unimportant B. historic C. momentary D. hard
9. Which is the closest in meaning to ‘to glare’?
A. to glower B. to caress C. despise D. wonder
10. Which is the closest in meaning to ‘simultaneously’?
A. all again B. all at once C. once and for all
D. once too often
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Part 4. Read the following passage and do the tasks that follow. (20 pts)
THE PROBLEM OF SCARCE RESOURCES
Section A
The problem of how health-care resources should be allocated or
apportioned, so that they are distributed in both the most just and most
efficient way, is not a new one. Every health system in an economically
developed society is faced with the need to decide (either formally or
informally) what proportion of the community’s total resources should be
spent on health-care; how resources are to be apportioned; what diseases and
disabilities and which forms of treatment are to be given priority; which
members of the community are to be given special consideration in respect of
their health needs; and which forms of treatment are the most cost-effective.
Section B

121 394
What is new is that, from the 1950s onwards, there have been certain general
changes in outlook about the finitude of resources as a whole and of health-
care resources in particular, as well as more specific changes regarding the
clientele of health-care resources and the cost to the community of those
resources. Thus, in the 1950s and 1960s, there emerged an awareness in
Western societies that resources for the provision of fossil fuel energy were
finite and exhaustible and that the capacity of nature or the environment to
sustain economic development and population was also finite. In other words,
we became aware of the obvious fact that there were ‘limits to growth’. The
new consciousness that there were also severe limits to health-care resources
was part of this general revelation of the obvious. Looking back, it now
seems quite incredible that in the national health systems that emerged in
many countries in the years immediately after the 1939-45 World War, it was
assumed without question that all the basic health needs of any community
could be satisfied, at least in principle; the ‘invisible hand’ of economic
progress would provide.
Section C
However, at exactly the same time as this new realization of the finite
character of health-care resources was sinking in, an awareness of a contrary
kind was developing in Western societies: that people have a basic right to
health-care as a necessary condition of a proper human life. Like education,
political and legal processes and institutions, public order, communication,
transport and money supply, health-care came to be seen as one of the
fundamental social facilities necessary for people to exercise their other rights
as autonomous human beings. People are not in a position to exercise
personal liberty and to be self-determining if they are poverty-stricken, or
deprived of basic education, or do not live within a context of law and order.
In the same way, basic health-care is a condition of the exercise of autonomy.
Section D

122 394
Although the language of ‘rights’ sometimes leads to confusion, by the late
1970s it was recognized in most societies that people have a right to health-
care (though there has been considerable resistance in the United Sates to the
idea that there is a formal right to health-care). It is also accepted that this
right generates an obligation or duty for the state to ensure that adequate
health-care resources are provided out of the public purse. The state has no
obligation to provide a health-care system itself, but to ensure that such a
system is provided. Put another way, basic health-care is now recognized as a
‘public good’, rather than a ‘private good’ that one is expected to buy for
oneself. As the 1976 declaration of the World Health Organisation put it:
‘The enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of health is one of the
fundamental rights of every human being without distinction of race, religion,
political belief, economic or social condition’. As has just been remarked, in
a liberal society basic health is seen as one of the indispensable conditions for
the exercise of personal autonomy.
Section E
Just at the time when it became obvious that health-care resources could not
possibly meet the demands being made upon them, people were demanding
that their fundamental right to health-care be satisfied by the state. The
second set of more specific changes that have led to the present concern
about the distribution of health- care resources stems from the dramatic rise
in health costs in most OECD countries, accompanied by large-scale
demographic and social changes which have meant, to take one example, that
elderly people are now major (and relatively very expensive) consumers of
health-care resources. Thus in OECD countries as a whole, health costs
increased from 3.8% of GDP in 1960 to 7% of GDP in 1980, and it has been
predicted that the proportion of health costs to GDP will continue to increase.
(In the US the current figure is about 12% of GDP, and in Australia about
7.8% of GDP.)

123 394
As a consequence, during the 1980s a kind of doomsday scenario (analogous
to similar doomsday extrapolations about energy needs and fossil fuels or
about population increases) was projected by health administrators,
economists and politicians. In this scenario, ever-rising health costs were
matched against static or declining resources.
Notes:
- OECD: Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development
- GDP: Gross Domestic Products
Questions 1-5: (10pts)
Choose the correct heading for the five sections A-E of the Reading Passage
from the list of headings below.
List of Headings
i The connection between health-care and other human rights
ii The development of market-based health systems.
iii The role of the state in health-care
iv A problem shared by every economically
developed country
v The impact of recent change
vi The views of the medical establishment
vii The end of an illusion
viii Sustainable economic development
1. Section A: ……………
2. Section B: ……………
3. Section C: ……………
4. Section D: ……………
5. Section E: ……………

124 394
Questions 6-10: (10 pts)
Do the following statements agree with the view of the writer in the Reading
Passage?
Write
YES if the statement agrees with the views of the writer
NO if the statement contradicts the views of the writer
NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
6Personal liberty and independence have never been regarded as
directly linked to health-care.
7Health-care came to be seen as a right at about the same time that the
limits of health-care resources became evident.
8In OECD countries population changes have had an impact on
health-care costs in recent years.
9OECD governments have consistently underestimated the level of
health-care provision needed.
10In most economically developed countries the elderly will to make
special provision for their health-care in the future.
Section 5. You are going to read four different opinions from leading
scientists about the future of fuel. For questions 1-10, choose from the
writers A-D. The writers may be chosen more than once. (10 pts)
A. Howard Bloom, Author
Even though most people are convinced that peak oil has already passed, to
me, peak oil is just a hypothesis. There is a theory that carbon molecules can
be found in interstellar gas clouds, comets and in space ice, and if this is the
case, our planet could ooze oil for ever. And even if we stay earthbound,
those who say we have raped the planet of all its resources are wrong. There's
a huge stock of raw materials we haven't yet learned to use. There are
bacteria two miles beneath our feet which

125 394
can turn solid granite into food. If bacteria can do it, surely we creatures with
brains can do it better. As far as the near future of energy is concerned, I
believe the most promising alternative fuels are biofuels, such as ethanol. It's
an alcohol made from waste products such as the bark of trees, woodchips,
and other 'waste materials'. And that's not the only waste that can create
energy. My friend in the biomass industry is perfecting an energy-generation
plant which can run on human waste. We produce that in vast quantities, and
it's already gathered in centralised locations.
B. Michael Lardelli, Lecturer in Genetics at The University of Adelaide
Nothing exists on this planet without energy. It enables flowers and people to
grow and we need it to mine minerals, extract oil or cut wood and then to
process these into finished goods. So the most fundamental definition of
money is as a mechanism to allow the exchange and allocation of different
forms of energy. Recently, people have been using more energy than ever
before. Until 2005 it was possible to expand our energy use to meet this
demand. However, since 2005 oil supply has been in decline, and at the
same time, and as a direct result of this, the world's economy has been unable
to expand, leading to global recession. With the world's energy and the
profitability of energy production in decline at the same time, the net
energy available to support activities other than energy procurement will
decrease. We could increase energy production by diverting a large
proportion of our remaining oil energy into building nuclear power stations
and investing in renewable forms of energy. However, this is very unlikely to
happen in democratic nations, because it would require huge, voluntary
reductions in living standards. Consequently, the world economy will
continue to contract as oil production declines. With energy in decline, it will
be impossible for everyone in the world to become wealthier. One person's
increased wealth can only come at the expense of another person's worsened
poverty.
C. Jeroen van der Veer, chief executive of Royal Dutch Shell

126 394
People are understandably worried about a future of growing energy
shortages, rising prices and international conflict for supplies. These fears are
not without foundation. With continued economic growth, the world's energy
needs could increase by 50% in the next 25 years. However, I do not believe
that the world is running out of energy. Fossil fuels will be able to meet
growing demand for a long time in the future. Taking unconventional
resources into account, we are not even close to peak oil. The priority for oil
companies is to improve efficiency, by increasing the amount of oil recovered
from reservoirs. At present, just over a third is recovered. We can also
improve the technology to control reservoir processes and improve oil flow.
However, these projects are costly, complex and technically demanding, and
they depend on experienced people, so it is essential to encourage young
people to take up a technical career in the energy industry. Meanwhile,
alternative forms of energy need to be made economically viable.
International energy companies have the capability, the experience and the
commercial drive to work towards solving the energy problem so they will
play a key role. But it is not as simple as merely making scientific advances
and developing new tools; the challenge is to deliver the technology to people
worldwide. Companies will need to share knowledge and use their ideas
effectively.
D. Craig Severance, blogger
What will it take to end our oil addiction? It's time we moved on to
something else. Not only are world oil supplies running out, but what oil is
still left is proving very dirty to obtain. The Deepwater Horizon oil spill
occurred precisely because the easy- to-obtain oil is already tapped. If we
don't kick oil now, we will see more disasters as oil companies move to the
Arctic offshore and clear more forests. The cheap petroleum is gone; from
now on, we will pay steadily more and more for our oil - not just in dollars,
but in the biological systems that sustain life on this planet. The only solution
is to get on with what we will have to do anyway - end our dependence

127 394
on it! There are many instances in which oil need not be used at all. Heat and
electricity can be produced in a multitude of other ways, such as solar power
or natural gas. The biggest challenge is the oil that is used in transportation.
That doesn't mean the transportation of goods worldwide, it's the day-to-day
moving around of people. It means we have to change what we drive. The
good news is that it's possible. There are a wide range of fuel efficient cars on
offer, and the number of all-electric plug-in cars is set to increase. For long
distance travel and freight, the solution to this is to look to rail. An electrified
railway would not be reliant upon oil, but could be powered by solar,
geothermal, hydro, and wind sources. There is a long way to go, but actions
we take now to kick our oil addiction can help us adapt to a world of
shrinking oil supplies.
Which writer:
believes that from now on, less oil is available
believes there are ways to obtain energy that we have not yet discovered
believes that people need to be attracted to working in the energy industry
sees a great potential in natural fuels
believes that future oil recovery will lead to more environmental disasters
believes the fuel crisis will cause the poor to become poorer
believes that better technology can help to maintain oil production levels
believes there may be sources of oil outside our planet
thinks that oil companies are responsible for developing other types of
energy
recognises that inventions that can help to prevent an energy crisis are
already available
1. …………..
2. …………..
3. …………..
4. …………..
5. …………..
6. …………..
7. …………..
8. …………..
9. …………..
10. …………
D. WRITING (40 pts)

128 394
Part 1. Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means
the same as the one printed before it. Write your answers in the space
provided. (10 points)
1. They believe that Oliver failed his exam because he was nervous.
--> Oliver’s failure
2. The inhabitants were far worse-off twenty years ago than they are now.
--> The inhabitants are nowhere
3. If you don't know the art market, there's a risk you will spend a lot of
money on rubbish.
--> If you don't know the art market, you are
4. Whatever the methods used to obtain the result, drugs were definitely not
involved.
->There was no question
5. Those terrapins which survive their first year may live to be twenty.
-> Should
Part 2. Rewrite the sentences below in such a way that their meanings stay
the same. You must use the words in capital without changing their
forms. Write your answers in the space provided (5 points)
6. Every student will get good marks to express their gratitude towards
teachers. (lengths)
7 I am determined to become a teacher of
maths. (heart)
129 394
8 Some of the patients taken to the hospital have got an infectious
disease. (diagnosed)
9 This contract is as important and confidential as
that one. (equally)
10 He has called the meeting in order to raise money for the latest
storm. (purpose)
Part 3: Write an paragraph of about 200 words on the following topic. (30
pts) “Is online education as effective as traditional on-campus
schooling?”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………
A. LISTENING
(50pts) Part 1: 5 x
0.2 = 10 pts
1. 20-23 May 2. 18 3. floor space 4. Hermica 5. University of Technology
130 394
SỞ GD & ĐT CAO BẰNG
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN
HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤM ĐỀ THI ĐỀ NGHỊ
THAM DỰ TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG NĂM
2019
ĐỀ THI MÔN: TIẾNG ANH – LỚP 10
(Hướng dẫn chấm gồm 09 trang)
Part 2. Listen and complete the sentences below. Write no more than
three words for each answer. 10 x 0.2 = 20 pts
1. demolish 2. real consultation 3. self-help 4. services
5. invest money 6. community values 7. employment 8. freedom
9. specialist activities 10. Understanding
Part 3. You will hear an extract from a radio programme and decide
whether the statements are true or false. ( 5 x 0.2 = 10 pts)
1.F 2. T 3. T 4. F 5. F
Part 4. You will hear a radio discussion about children who invent
imaginary friends. Choose the answer (A, B, C or D) which fits best
according to what you hear. Write your answers in the corresponding
numbered boxes. ( 5 x 0.2 = 10 pts)
1. B 2. C 3. A 4. C 5. C
B. LEXICO - GRAMMAR (50pts)
Part 1. Choose the word or phrase that best fits each blank in the
following sentences. ( 20 x 1 = 20pts)
1. C 2. B 3. A 4. B 5. B
6. A 7. D 8. A 9. C 10. D
11. A 12. A 13. C 14. A 15. C
16. C 17. D 18. C 19. A 20. C
Part 2. The passage below contains 10 mistakes. IDENTIFY and CORRECT them.
Write your answers in the space provided in the column.

131 394

132 394
(10 x 1 = 10pts)
Line Mistake Correction Line Mistake Correction
2 young youth 10 stinging stung
4 him himself 11 there where
5 did done 13 popularly popular
7 Germany German 14 appearance appearing
9 stood standing 16 Lately Later
Part 3. Complete each sentence with a suitable preposition or particle.
Write your answers in the numbered spaces provided. ( 10 x 1 = 10pts)
1. through 2. on 3. back 4. out 5. to
6. with 7. to 8. with 9. on 10. aside
Part 4. Write the correct FORM of each bracketed word in the numbered
spaces provided. (10 x 1 = 10pts)
1.
intellectuals
2.
inappropriate
3.
instruments
4.
improvise
5.
directions
6. fusion 7. greatly 8. intensify 9.
compelled
10. essential
C. READING COMPREHENSION (50pts)
Part 1: Read the passage below and decide which answer (A, B, C or D)
best fits each gap. Write your answer in the numbered boxes. ( 10 x 1 = 10
pts)
1. A 2. C 3. D 4. A 5. B
6. D 7. C 8. B 9. B 10. B
Part 2. Read the following text and fill in the blank with ONE suitable
word. Write your answers in corresponding numbered boxes. (10 x 1 =
10pts)

133 394
1. because 2. such 3. other 4. could/may/might 5. despite
6.
if/when/whenever
7. from 8. so 9. nothing/little 10. in
Part 3: Read the passage and choose the correct answer (10X1 = 10pts)
1. C 2. D 3. B 4. B 5. D
6. A 7. C 8. B 9. A 10. B
Part 4. Read the following passage and do the tasks that follow. ( 1 x 10 =10 pts)
1. iv 2. viii 3. i 4. iii 5. v
6. N 7. Y 8. Y 9. NG 10. NG
Part 5. You are going to read four different opinions from leading
scientists about the future of fuel. For questions 1-10, choose from the
writers A-D. The writers may be chosen more than once. (10 x 1 = 10 pts)
1. B 2. A 3. C 4. A 5. D 6. B 7. C 8. A 9. C 10. D
D. WRITING (40 points)
Part 1. Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means
the same as the one printed before it. Write your answers in the space
provided. (10 points)
1. Oliver’s failure in his exam was put down to the fact that he was
nervous. Or / Oliver’s failure in his exam is believed to have resulted
from his nerve.
2. The inhabitants are nowhere near as badly-off as they were twenty years ago.
3. If you don't know the art market, you are in danger of spending a lot of
money on rubbish
4. There was no question of drugs being involved, whatever the methods
used to obtain the result

134 394
5. Should terrapins survive their first year, they may live to be twenty.
Part II. Rewrite the sentences below in such a way that their meanings stay
the same. You must use the words in capital without changing their
forms. Write your answers in the space provided (5 points)
6. Every student will go to any lengths to express ….
7. My heart is set on becoming a teacher of
maths. I have set my heart on
becoming…
8. An infectious diseases has been diagnosed in this hospital.
9. Both contracts are equally important and confidential.
10. His purpose in calling the meeting is to raise…
He has called the meeting for the purpose of raising…
TAPE SCRIPTS
Section 1
John: Hello, Pirkko. I’m phoning to let you know that my college basketball
team are very keen to come over to Finland to take part in the Tampere
Student Games. Pirkko: Well, that’s great. We’re hoping to make it a really
special event this year, as it’s the 80th anniversary of Finnish Student Sport!
John: Fantastic! We’re all looking forward to coming. Let me just check -
the games start on May 19th, right?
Pirkko: Oh, that was the provisional plan when you first contacted me, that
they’d run from the 19th to the 23rd. But we’ve cut the programme by a day,
so now it’ll begin on the 20
th
, still ending on the 23
rd
(1). There’s going to
be an opening ceremony on the first evening.
John: We don’t want to miss that, do we! And how much is the entry fee for
the Games?
Pirkko: This year it's gone up from 16 to 18 euros (2) a day per person. I’m
afraid, but you get a lot for that.

135 394
John: How do you mean?
Pirkko: Well, of course it covers the competition entrance, but you also get
three meals a day and even floor space (3) if you want it - we can’t manage
beds for everyone!
John: Sounds a bit basic to me. Can you recommend a hotel?
Pirkko: Well, Tampere is quite a big city, so there are a lot of hotels. The
Homeland would be convenient if you come by train, or maybe you’d prefer
the Hermica, as it’s offering a reduced rate for participants in the games. It’s
spelt H-E-R-M-I-C-A (4). Its a very nice hotel.
John: And where is it exactly?
Pirkko: Well, that’s the other good thing from your point of view, it’s in the
Hervanta district of Tampere, near the University of Technology (5)
John: And why is that good for us?
Pirkko: Because all the basketball matches are taking place near there.
John: Oh, I see
Pirkko: Look, why don’t you give the website address, and then you can
look up the programme and find anything else you need to know.
John: Good idea. So, what is it?
Pirkko: OK, it’s www dot sellgames – that’s S-E-doublei-G-A-M-E-S dot com
John: Brilliant! I’ll have a look now. Thanks, Pirkko.
Pirkko: See you soon, then. Bye, John.
Sect
ion
2.
Lect
urer
:
Now, a key issue in the ability of cities to grow is the question of housing.
However, quality is as important as quantity here. But that isn't to say
that this is easy to guarantee, and the development, or at least the spread
, of
many modern cities is marked by the sprawl of slum or shanty town
housing.
Governments are, of course, keen to address this, but the tendency to
demolish (1) them has often proved disastrous, as it doesn't solve the
problem, unless satisfactory replacements are ready for the inhabitants.
What I'm saying is that suitable housing projects have to be l ined
up to accommodate these otherwise displaced people. And suitable is the

136 394
key
word

137 394
here. All too frequently, there isn't real
consultation
(2),
only token
gestures. If the residents aren't fully involved, they are unlikely to find the
resulting development appropriate to their needs. People need to feel
reasonably independent, and strategies for providing accommodation
schemes work much better if an approach rooted in self-help (3) is applied.
People value things more when they have been part of bringing them into
being. At the same time, residents can't do everything for themselves, or not
well enough anyway, and so governments need to accept that a number of
services (4) will always have to be laid on. These would include electricity
and water and so on. From the other side, residents need to feel able to
commit. Migrants are essential to the growth of cities, bringing
rapid
increases
in population, skills and income. But they need to have a sense of security, of
long-term commitment to the city if they are to invest money (5) in building or
buying
houses.
Developing this sense of commitment isn't straightforward, and it takes
time. It's complex and involves several factors. People need to feel they
belong and, unfortunately, too many governments fail to appreciate that
community values (6) are a crucial component of that. Sadly, there are too
many housing schemes which don't work – people drift away, or the whole
place becomes crimeridden. It's easy to be wise after the event, but it is
worrying that a lot of housing is put up without analysis having been carried
out to examine how much employment (7) is going to be available for people.
But I don't want to labour the negatives too hard. Such difficulties as there
are challenges, and challenges that can be, and often are, overcome. And
cities are, I believe, a good thing.
Urbanisation – the process of developing cities and the societies that
comprise them – may not be everyone's dream, but is has a huge impact on the
economy and also benefits each and every person's freedom (8). Furthermore,
the sheer volume of people means that work can be differently distributed. In
villages, people need to be multi-skilled in order to be autonomous, but in
cities you can see the evolution of a variety of specialist activities (9) and
this means people live in a more sophisticated way. It's not only tangible
phenomena – there are all sorts of other, equally important benefits, too.
Residing in cities brings us face to face with many different ways of thinking
or going about things, and this increases our degree of understanding (10)
– something which is hard to measure in scientific terms, but which surely
makes better people of us all. Right, well, now I'd like to turn our attention to
...

138 394
Section 3.
A = Jim Adams R = Reader PS = Paul Spenser
JA: Hi, this is “Say it like it is”, the programme in which your comments
about what’s been on Radio One for the last week are read. And for today ...
Well, we had many listeners writing in about last Tuesday’s science
programme which is based on weather this time. John Holmes from Oxford
says:
R: Your “Climate changes” turned out to be quite an interesting programme.
Professor Jones’ theory that we’re slowly going towards another Ice Age was
quite astounding. I was taught that the earth was moving nearer the sun!
JA: You could be right. But I don’t think that it will happen in our lifetime.
Mrs Kent from Brighton talks about weather problems which could
affect us in the near future (1).
R: Some experts may tell us what the weather may be like in the next century
but I’m more concerned about the present day situation. I think that tax
money and scientific studies should try to focus on short-term weather
forecasts and try to make them more precise and accurate.
JA: Many listeners have the same point of view. On the other hand, Tom
Sheridan from Manchester has a different opinion.
R: I hear that experiments are being made to change the weather in Britain.
But, who wants it? Nobody would like a set weather pattern. All those
conversations about the weather would disappear (2).
JA: We’d find something else to talk about. I’m sure. Food, for example. It
seems to be a favourite of our readers judging from the letters we receive ...
R: Dear Jim, I’m writing in objection to the Cookery Series on
Wednesdays. JA: Tim Saunders, from Coventry writes;
R: Most men already know how to do things like making toast so our time
shouldn’t be wasted by such programmes.
JA: Tim would like more challenging cooking tips. We’ve got the producer
of our cookery show here today, Mr. Paul Spenser (3). What about more
difficult cookery on your show?
PS: I can relate to what Mr. Saunders is saying. Up to now we’ve been doing
basic things to help beginners but we’ll be moving on to more difficult
recipes in the next

139 394
few weeks. I hope that the programme will be more interesting for Mr.
Saunders in the future.
JA: I hope so! To finish off we have a few letters referring to the rumours that
lending libraries won’t be free to the public anymore. Jane from
Bournemouth has a few things to say about this.
R: For
students
like
me,
books
are
too
expensive
to
buy
and
we
depend
on libraries for our books! 20p is too much to pay for every book
we take out (4). JA: Don’t worry Jane. It’s only a rumour so far. And our last
letter comes from one of the elderly in our community.
R: The
elderly
have
to
pay
for
their
needs
so
why
shouldn’t
others
pay
for theirs? They pay in pubs and discos, why not at libraries (5).
JA: Well, that’s all for today. More for you to think about. If there’s something
you’d like to comment on write to Jim Adams, “Say It Like It Is” Radio One.
Section 4:
You will hear a radio discussion about children who invent imaginary friends.
Presenter: Today we’re talking about children and their tendency to have
imaginary friends. Liz McManus has a daughter called Caitlin, who’s eight
now. When she was three, she had an imaginary friend called Tytner. Liz, tell
us about Caitlin and Tytner. Mother: Well, I’ll give you an example. One
day I was driving Caitlin and Greg, her baby brother, home, when she
solemnly informed me that Tytner was hitting the baby. So I said: ‘You tell
Tytner that if he does that again, he’ll be walking home.’ Fifteen seconds
later cam the inevitable news: ‘He’s just done it again, Mummy.’ So I found
myself in the embarrassing position of having to pull over, open the back
door and say to this imaginary little boy. ‘Tytner, out, now!’ And of course,
as we drove off, Caitlin started crying because her friend was standing on the
pavement all alone. I had to turn back and go through the rigmarole of pulling
over and opening the door to pick him up again.
Presenter: Wow, that’s some story! But in fact Caitlin is no different from
many children and her invented, make-believe friend is far from unusual. As
many as 65% of children have had an imaginary friend at some point in their
lives. The latest research suggests that invisible friends, far from being a
cause for concern, should be welcomed by parents because they can help
children to be more creative, confident and articulate, and have more
advanced communication skills. It is thought that these findings will help
reverse misconceptions about children with imaginary

140 394
friends and that they will come to be seen as having an advantage, rather than
a problem that needs to be worried about. Did it worry you, Liz?
Mother: I know it does lots of parents but I never fretted about it, I think I
was just amused. I’d be reading to her and I’d say, ‘Is Tytner around?’ and
she’d say, ‘Yes, he’s just sitting at the end of the bed.’ He became the centre
of her life. She’d have tea parties with him, and he’d go to bed with her. She
was shy and this was her answer. I knew she would grow out of it.
Presenter: Now Liz is one of 15 people taking part in a study of imaginary
friends at the Institute of Education in London, run by Karen Majors, an
education psychologist and lecturer at the institute. Karen, should parents
worry about it?
Expert: Well, parents sometimes think, ‘Is this healthy and how long should
it go on for?’ But it is a normal phenomenon for normal children. And it’s
very healthy. Presenter: Why do children invent imaginary friends?
Expert: I think that children create pretend friends for many reasons; as safe,
trustworthy best friends at a time when they are just starting to make real
friends; as someone to confide in; and as someone to play with. Sometimes it
is about wish fulfilment; children who cannot have a pet, for example, will
invent one. I interviewed one little girl, aged six, who had a pony called
Minty for several years. It went to school with her and the teachers knew all
about it. It was a really strong relationship.
Presenter: Presumably, when they get older, children no longer have these
imaginary friends, Karen?
Expert: Well, my most surprising finding is that children don’t always stop
having these made-up playmates when they start school. The imaginary
friends often stay with them through their teenage years, providing comfort
and escape – although in secret. One teenager I talked to had invented a
superhero to help him through tricky patchers. When things hadn’t gone well
at school, he would come home and play with the superhero, for whom
everything always went well.
Presenter: How should parents treat these invisible people, Karen?
SECTION 1. LISTENING (50 points)
Part 1. Listen to a conversation and complete the notes below. Write NO MORE THAN
THREE WORDS or A NUMBER. (14 pts)

Type of event: example
Event Details
Dragon Boat Race
Race details
Day and date: (1) Place: Brighton Marina
Registration time: (2)
Sponsorship
aim to raise over (3) as a team and get a free t-shirt
free Prize Draw for trip to Hongkong
Team details
must have crew of 20 and elect a (4)
under 18s need to have (5) to enter
need to hire (6)
advised to bring extra (7)
must choose a name for the team.
141 394
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
LẦN THỨ XX
ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN CHU VĂN AN TỈNH LẠNG
SƠN
ĐỀ THI CHỌN HỌC SINH GIỎI
MÔN: TIẾNG ANH – KHỐI 10
(Đề thi có 13 trang)
(IELTS Practice Tests Plus 1, p91)
Part 2. (16 pts)
You will hear an interview with a woman called Juliet Mills, who talks about
drinking and alcohol. For each question, complete the sentence with a word or short
phrase.
Juliet Mills says we started drinking alcohol (1) ago.
Juliet says alcohol helps people relax and become more sociable and (2) . Every year, several
thousand British people die from (3) .
Alcohol produces a feeling of well-being because it provides a rush of (4) . The effects become
noticeable as soon
as alcohol in
your bloodstream gets to your (5)
.
Occasional drinking is unlikely to cause permanent (6) .
Since alcohol affects the immune system, (7) are less protected
against various infections.
142 394
Alcohol is a leading cause of (8) in Britain.
(FCE Listening and Speaking Skills 1, p28)
Part 3. You will hear an interview with a woman called Jennie Thorpe, who is a trapeze
artist in a circus. For each question, decide whether the information is true (T) or false
(F). (10 pts)
Answer
1. Jennie got her present job when her manager saw her performing at a gymnastics
competition.
2. Jennie says it’s unlikely to earn a living as a trapeze artist after a certain age.
3. Jennie finds having to get up early every day the most difficult thing to get used to.
4. In Jennie’s opinion, circus skills have helped some school students by making them
physically stronger.
5. Jennie wants to do a training course next.
(FCE Practice Tests Plus, 2008, p122)
Part 4. You will hear an interview with Dr Peter Ludwig about sugar in our diet.
For each question, choose the best answer A, B, C or D. (10 pts)
1. Dr Ludwig is surprised that parents
A. buy the sweet food sold at Hershey Park.
B. use sugary snacks as part of their children’s diet.
C. see sugary snacks as a special treat.
D. rely on sugar snacks for nutritions
2. The number of cases of obesity and diabetes is increasing
A. by 23% a year B. by 25% a year C. quite slowly D. very quickly
3. Food companies in France and Germany _
A. have reduced the amount of sugar in their products.
B. use an unnecessary amount of sugar.
C. use sugar to make their food crisp and textured.
D. use sugar as an essential ingredient.
4. In 19th century, British factory workers were given sugar
A. because their work was long and tiring.
B. as a quick, cheap form of medicine.
C. because many of them were very young children.
D. because it was much more important than fish and chips.
5. Dr Ludwig thinks that parents should
A. watch their children’s behaviour more carefully.
B. stop giving their chidren extra sugar for a week or two.

143 394
C. try to find ways to make their children feel better.
D. give their children foods without sugar to improve their behaviour.
(FCE Listening and Speaking Skills 2, p22)
SECTION 2. LEXICO-GRAMMAR
Part 1. For question 1-20, read the following sentences and then decide which word
A, B, C or D best fits each space. Circle the correct answer.
1. For a team to be successful, all members have to _ their weight.
A. take B. make C. get D. pull
2. You really
will
have to be able to down a job for more than
six
we
e
ks.
A. keep B. turn C. take D. hold
3. It took him a long time to come to with the fact that he was homeless.
A. terms B. acceptance C. tabs D. agreement
4. Simon has a very strong of duty so he will always carry out his promises.
A. sense B. idea C. mind D. thought
5. The birth of their first child caused a lot of in Angela Ken’s lives.
A. uproar B. upheaval C. outcry D. overthrow
6. The interviewer’s warm smile soon put Jill at her .
A. comfort B. leisure C. rest D. ease
7. No how long it takes, I will keep trying to find an answer.
A. way B. matter C. worry D. mind
8. I to think how you’re going to cope all by yourself with two babies.
A. fear B. avoid C. dread D. worry
9. However at the last training session there was a very poor .
A. turn-up B. turnover C. turnout D. turn-off
10. The old lady on going to court to give evidence.
A. demanded B. urged C. begged D. insisted
11. We all know that you are guilty so why don’t you up?
A. give B. turn C. own D. say
12. How could we have been so gullible- it was all a _ of lies.
A. pack B. heap C. bunch D. pile
13. They were caught because their sudden wealth gave the away.
A. fact B. game C. idea D. match
14. Kate Tim that he had an appointment after lunch.
A. remembered B. recalled C. reminded D. recollected
15. Police are trying to the stolen goods.
A. trace B. track C. shadow D. stalk
16. I am my brother is.
A. nowhere like ambitious as B. nothing near as ambitious as

144 394
C. nothing as ambitious like D. nowhere near as ambitious as
17. are considered humorous is mainly due to his characters’ use of slang.
A. That Myan’s stories B. Myan’s stories, which
B. Myan’s stories D. Because Myan’s stories
18. After a six-year relationship, Martha and Billy have decided to .
A. break the bank B. turn the page C. tie the knot D. make the grade
19. After the accident, there was considerable doubt exactly what had happened.
A. in the question of B. as to C. in the shape of D. for
20. Most discounts have been dramatically in the final days of our
clearance sale from 15% to 5%.
A. declined B. diminished C. slashed D. taken down
Part 2. For question 1-10, use the word in capitals at the end of the sentence to form
one word that fits in the space. There is an example at the beginning (0).
0. We really must look for staff who have good qualification . QUALIFY
1. is much more effective than
aggression. ASSERT
2. The singer’s lifestyle attracts the attention of
the press. CONVENTION
3. When she passed 30, Sue became
increasingly DESPAIR
4. The unresponsive audience made the lecturer
somewhat HEAR
for a baby.
.What a shame.
5. My brother’s a comedian who specializes in doing of famous
people. PERSON
6. Michael Spencer’s book is likely to be a huge success. COME
7. Some now have their own nursery facilities for staff with
children. WORK
8. He won’t get angry with you- he has a very calm . TEMPER
9. Sam was very grateful to his parents for their
generosity. ADOPT
10. The subtle photography and music make the film very . ATMOSPHERE
Part 3. The passage below contains 10 mistakes. Identify and correct the mistakes.
Write your answers in the answer box below. Line (0) has been done for you as an
example. (10 points)

145 394
Line THE EIGHTH WONDER OF THE WORLD
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
The Thames Barrier is a major part of the flood defending scheme for protecting
London against rise water levels. The defenses also include raised river embankments
and additional flood gates at strategic points, including the Barking Barrier. The
unique structure that are the Barrier spans the 520-metre wide Woolwich reach and
consist of 10 separate movable gates, each pivoting and supported between concrete
structures which house the operating machinery. When raising, the four main gates
each stands as high as a five-storey building and as wide as the opening of Tower
Bridge. Each weights 3700 tonnes. During the first twelve years of operation, the
Barrier has closed twenty-nine times to protect London.
View the Barrier from the comfortable cafeteria. Picnic at the riverside embankment.
Enjoy beautiful views from the riverside walk. Visit the shop stocks a large selection
of souvenirs, books and Barrier information.
There is a children play area suitable for 4-to-12-year olds, located adjacent near the
riverside walk. A visit to the spectacular Thames Barrier is a memorable experience.
Source: FCE successful practice tests
Your answers
e.g. Line 0: defending defence
Line Mistake Correction Line Mistake Correction
146 394
SECTION 3. READING
Part 1. Choose which answer best fits each gap. (10 points)
FRIENDSREUNITED.CO.UK
Have you ever looked into what happened to your old friends? Friends Reunited is
a
website
which
puts
old
school
and
college
friends
back
in
(1)
with one another. It
was (2)
by a husband and wife team when the wife, Julie Pankhurst, decided she wanted to track
(3) some of her own school friends. The website now has over five million (4) and is one of
the most popular websites in the UK. You pay a small (5) to join, and then add
your name and email address to a list. This list is (6) by school and year,
so it is easy to find people.
Thousands of reunions have now (7) place across the UK and the idea
has spread to many other countries. So if you join Friends Reunited, you can find the
person who was your best friend when you were eight, even if he or she's now living on
the other side of the world! There may even be some surprises (8) for
you! You might (9) _ that the quiet boy who everyone used to
tease in school has now become a professor of Physics, and the tall shy girl has now
become a top fashion model with her picture in Vogue magazine. Or, (10) , you
might find that no one you knew has changed much at all!
1. A. connection B. association C. meeting D. touch
2. A. set up B. made out C. put on D. got off
3. A. for B. down C. in D. out
4. A. players B. holders C. users D. consumers
5. A. price B. fare C. expense D. fee
6. A. organized B. demonstrated C. managed D. controlled
7. A. made B. taken C. given D. done
8. A. in store B. on order C. in place D. en route
9. A. investigate B. identify C. discover D. invent
10. A. in particular B. in effect C. on the whole D. on the other hand
(FCE-Use of English)
Part 2. This following reading passage has nine paragraphs, A-I. (10 points)
List of Headings
i A fresh and important long-term goal
ii Charging for roads and improving other transport
methods iii
Changes affecting the distances goods may
be transported iv Taking all the steps necessary to
change transport patterns

147 394

148 394
v The environmental costs of road
transport vi The escalating cost of
rail transport
vii The need to achieve transport
rebalance viii The rapid growth of
private transport ix Plans to develop
major road networks
x Restricting road use through charging policies
alone xi Transport trends in countries
awaiting EU admission
Example: Answer:
Paragraph F vii
What have been the trends and what are the prospects for European transport systems?
It is difficult to conceive of vigorous economic growth without an efficient
transport system. Although modern information technologies can reduce the demand for
physical transport by facilitating teleworking and teleservices, the requirement for
transport continues to increase. There are two key factors behind this trend. For passenger
transport, the determining factor is the spectacular growth in car use. The number of cars
on European Union (EU) roads saw an increase of three million cars each year from 1990
to 2010, and in the next decade the EU will see a further substantial increase in its fleet.
As far as goods transport is concerned, growth is due to a large extent to changes in
the European economy and its system of production. In the last 20 years, as internal
frontiers have been abolished, the EU has moved from a ”stock” economy to a ”flow”
economy. This phenomenon has been emphasised by the relocation of some industries,
particularly those which are labour intensive, to reduce production costs, even though the
production site is hundreds or even thousands of kilometres away from the final assembly
plant or away from users.
The strong economic growth expected in countries which are candidates for entry
to the EU will also increase transport flows, in particular road haulage traffic. In 1998,
some of these countries already exported more than twice their 1990 volumes and
imported more than five times their 1990 volumes. And although many candidate
countries inherited a transport system which encourages rail, the distribution between
modes has tipped sharply in favour of road transport since the 1990s. Between 1990 and
1998, road haulage increased by 19,4%, while during the same period rail haulage
decreased by 43,5%, although – and this could benefit the enlarged EU – it is still on
average at a much higher level than in existing member states.
However, a new imperative-sustainable development – offers an opportunity for
adapting the EU's common transport policy. This objective, agreed by the Gothenburg
European Council, has to be achieved by integrating environmental considerations into
Community policies, and shifting the balance between modes of transport lies at the heart
of its strategy. The ambitious objective can only be fully achieved by 2020, but
proposed measures are nonetheless a first

149 394
essential step towards a sustainable transport system which will ideally be in place in 30
years‟ time, that is by 2040.
In 1998, energy consumption in the transport sector was to blame for 28% of
emissions of CO2 , the leading greenhouse gas. According to the latest estimates, if
nothing is done to reverse the traffic growth trend, CO2 emissions from transport can be
expected to increase by around 50% to 1,113 billion tonnes by 2020,compared with the
739 billion tonnes recorded in 1990. Once again, road transport is the main culprit since it
alone accounts for 84% of the CO2 emissions attributable to transport. Using alternative
fuels and improving energy efficiency is thus both an ecological necessity and a
technological challenge.
At the same time greater efforts must be made to achieve a modal shift. Such a
change cannot be achieved overnight, all the less so after over half a century of constant
deterioration in favour of road. This has reached such a pitch that today rail freight
services are facing marginalisation, with just 8% of market share, and with international
goods trains struggling along at an average speed of 18km/h. Three possible options have
emerged.
The first approach would consist of focusing on road transport solely through
pricing. This option would not be accompanied by complementary measures in the other
modes of transport. In the short term it might curb the growth in road transport through the
better loading ratio of goods vehicles and occupancy rates of passenger vehicles expected
as a result of the increase in the price of transport. However, the lack of measures
available to revitalise other modes of transport would make it impossible for more
sustainable modes of transport to take up the baton.
The second approach also concentrates on road transport pricing but is
accompanied by measures to increase the efficiency of the other modes (better quality of
services, logistics, technology). However, this approach does not include investment in
new infrastructure, nor does it guarantee better regional cohesion. It could help to achieve
greater uncoupling than the first approach, but road transport would keep the lion’s share
of the market and continue to concentrate on saturated arteries, despite being the most
polluting of the modes. It is therefore not enough to guarantee the necessary shift of the
balance.
The third approach, which is not new, comprises a series of measures ranging from
pricing to revitalising alternative modes of transport and targeting investment in the trans-
European network. This integrated approach would allow the market shares of the other
modes to return to their 1998 levels and thus make a shift of balance. It is far more
ambitious than it looks, bearing in mind the historical imbalance in favour of roads for the
last fifty years, but would achieve a marked break in the link between road transport
growth and economic growth, without placing restrictions on the mobility of people and
goods.
Questions 1 – 5:
Choose the correct heading for paragraphs A-E from the list of headings below.
1. Paragraph A
2. Paragraph B

150 394
3. Paragraph C
4. Paragraph D
5. Paragraph E
Questions 6 – 10
Do the following statements agree with the information given in the reading
Passage? In boxes 6-10, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the
information FALSE if the statement
contradicts the information NOT GIVEN if
there is no information on this
6. The need for transport is growing, despite technological developments.
7. To reduce production costs, some industries have been moved closer to their
relevant consumers.
8. Cars are prohibitively expensive in some EU candidate countries.
9. The Gothenburg European Council was set up 30 years ago.
10. By the end of this decade, CO2 emissions from transport are predicted to
reach 739 billion tonnes.
(IELTS 10- Test 2 – Reading Passage 2, p 22)
Part 3. Read the following passage extracted from www.asiatravel.com and select the
best answer to each question below. (10 points)
Culture Shock is not something that people generally get on a holiday but as soon
as your boss calls you into the office and says "Hi John, we value you so much we want
you to head our Hong Kong operations!" you really need to start thinking about the
implications and how you are going to avoid this condition. It is not so much as a life
threatening disease, but it can lead to some very serious problems if you do not take a few
precautions.
Culture shock is definitely a serious condition that needs to be watched, and
checked upon. I personally have suffered from it on numerous occasions and sleep
deprivation, mood swings, and depression are all in there.
Travelling to a new
destination
with
unusual
habits
and
traditions
can
be
a very traumatic experience. A little research before you leave will help
tremendously but the most important thing is to actually leave with an open mind. A lot of
people fly off without any research and expect things to be done in exactly the same way
and at the same speed as they were at home. Well this just isn't going to happen. And it is
very important to try to understand the culture religion and people of the country that you
are travelling to.
The culture shock selection of books are a very good starting place, but one that
you will not really understand fully until you are actually in the country mingling with the
locals. One interesting point of this can be found in the book Culture Shock Thailand. Thai
people are among the nicest people in the world but it is a very different world from,
let's say, the UK. The book

151 394
explains a good deal about Thai culture and traditions and it explains how Thais smile
their way out of an embarrassing situation and look down on those that don't. The book
then puts this into a couple of different examples to try to ensure that the reader
understands. One such example is that if you are walking down the street and someone
throws dirty water over you from a doorway, you should smile at the person that did this,
showing your forgiveness. This should help clear the air and the person will most likely go
out of their way to help you clean up. Imagine this happening in London! Thais shy away
from confrontation, and this is one of the many aspects that make them such a happy and
kind nation.
If as an expatriate you are moving to a country with severe Culture Shock such as
perhaps Cambodia, or Vietnam, then even more research would be needed. Nowadays you
can possibly do a lot more research than ever with the growth of the internet. You can see
pictures of pretty much every destination in the world and even read restaurant, hotel and
bar reviews without having even left your office. It is also advisable to stay away from a
lot of the other expats especially before you leave and while after you arrive in the
destination. A lot of expats can be very negative about a country, even though they
continue to stay there and this is not something that you need when you have just travelled
half way around the world. Instead, leave with an open mind and make your own
judgments about the place after you have started to understand it a little.
One of the biggest causes, though, of Culture Shock is language. It will make an
enormous amount of difference to you if you learn a little or as much as possible of the
local language before you leave. Take up classes and practice it as much as you can; if you
are studying Thai, eat out at Thai restaurants and try to practice your Thai. This small step
will make your life a lot simpler and will also give you immediate respect when you arrive
in the foreign country, not to mention open many new doors. If you show an interest in the
other person’s language and culture they will show an interest in you.
If you are being relocated by your company, try to find out a little about the living
conditions in that country and the package that the company offers you. Will they supply
you with hotel accommodation or will you be straight into an apartment or house? Are you
given a housing allowance and allowed to choose the accommodation yourself? Will the
company pay the deposits that the landlord requires? Will you have maids? What about a
car? How many return trips will you have a year to your home country? Will they be in
economy or business class? What about your family rights - the wife - the husband - the
children? How long is the posting for? Will the company pay for repatriation due to
illness, or unemployment? Do they have limits to the amount of furniture that you can
send over but most importantly bring back? Will they cover these charges? Do they have
any restrictions as to how you send these things? Do they offer you insurance that is
suitable for the country that you are travelling to?
When you arrive it is important to fit in, get a feel for the place, the smells and the
sounds. I would suggest just walking for a day or two experiencing the mystique of the
new land you have just discovered. After a while when you are feeling a little more at
home join a club, and make friends socially outside of your regular work patterns, and try
to meet and befriend as many locals

A. fantasticB. upsettingC. unavoidableD. resembling
152 394
a you can, so that you will really get a deeper understanding of where you and most
probably appreciate the differences in culture a lot more.
Culture Shock basically comes from a lack of understanding and built up anxiety,
and can be caused by the most minute things, building up. One time in Hong Kong a
colleague seemed to be literally screaming at the waitress in Cantonese, I was very
anxious and asked what was wrong, my colleague looked very confused as to why I was
asking the question and she simply replied that she was ordering some water!
All in all every expat has had his or her bad days, and there are times you just want
to get on a plane and fly back, however these days are minimal compared to the fun, and
amazing discoveries that you will make. Once you are bitten by the spirit and feeling of
adventure you are about to embark on, you will have more difficulty believe it or not,
returning "home" than you imagined especially the longer you stay away.
1. What is the main idea of the reading passage?
A. Travelling abroad has some specific negative effects on your feelings due to
culture shock.
B. It is believed that every expat is certain to encounter culture shock during the
overseas trip.
C. There are always some things one can do to get over anger and confusion when
traveling abroad.
D. There is no point in worrying about culture shock in other countries since it is
not as serious as people thought.
2. It can be inferred from the third paragraph that .
A. people’s expectation that the destination country will bear the similarity to their
home one is useless
B. Most of the countries have unusual habits as one characteristic to help
building up culture shock.
C. More research should be carried out before the trip so as to avoid understanding
unusual habits in a new country.
D. People should be open-minded since what they are going to experience will not
have much difference to that in their country.
3. Which of the following can best replace the word “traumatic” in the third paragraph?
4. According to the passage, what should people do when Thais cause some annoyance to them?
A. Buy a book called Culture Shock Thailand to learn more about the trouble.
B. Try to talk to them about the problem in order to clear the air.
C.Clean up yourself and continue to walk down the street so as not to have any
trouble with them.
D. Give them a smile and be tolerant of the situation.

153 394
5. What does the writer advise people to do when they arrive in a new country?
A. People should arrange a short trip a few days earlier in order to get
accustomed to restaurants, hotels and bars in the new place.
B. It’s best not to talk to people who arrived there since they may give
irrelevant and negative comments.
C. People should make their own judgements right before the trip.
D.People should understand the new place a little by staying away from expats
because of their negative points.
6. What does the word “it” in the sixth paragraph refer to?
A. culture shock B. difference C. classes D.
language 7. It can be inferred from the seventh paragraph that .
A. Shelters should be first considered when people have plans to travel to a country.
B. Being aware of the situation in which you live and other services is essential for
people’s abroad relocation.
C. As soon as people are relocated by their company, they should ask themselves
some necessary questions in order to prepare for culture shock.
D. People should look down on the offers from the company for the relocation
since all questions have already been dealt with.
8. Which of the following phrases can best replace the word “fit in” in the eighth paragraph?
A. become involved B. feel the similarity \
C. control feelings D. see the point
9. What can be inferred from the writer’s experience in the restaurant with his colleague
during the trip in Hong Kong?
A. He felt very annoyed about his colleague.
B. The waitress in the restaurant was shocked at her colleague’s screaming.
C. A lack of understanding is a cause to culture shock.
D. His anxiety was built up during the trip.
10. In the last paragraph, what does the writer mean by saying “you will have more
difficulty believe it or not, returning "home" than you imagined especially the longer
you stay away”?
A. Once people underwent culture shock, they would find it hard to leave the
destination country due to its extreme annoyance.
B. People would like to stay longer to understand more about the culture shock
since they think it is more interesting than annoying.
C. Culture shock is inevitable and may cause people to want to return home since
the longer people stay the more trouble they have.
D. The difficulty in returning home will make people stay longer in the destination
country than you expected.

154 394
Part 4. For questions 1-10, read the text below and think of the word which best
fits each space. use only one word in each space. (10 points)
Men and women are often considered to be completely at odds with each other, in
terms of their attitudes and behaviour. Not so when they are in love, new research has
discovered. As far as their hormone levels are (1) , when men and women are in love,
they are more similar to each other than at any other time. It has (2) been known that love can (3)
havoc with hormone levels.
For example the hormone cortisol, which is known for its calming effect on the
body, dips dramatically when one person is attracted to (4) putting the love-struck on a
par with sufferers of obsessive compulsive disorder.
But a new study has found that the hormone testosterone, commonly associated
with male aggression, also falls when he is in love. In women, it's quite the (5)
Testosterone levels, which (6) to be lower
among females, rise towards (7) of the male.
Donatella Marazziti of the University of Pisa, Italy, (8) this down to
nature attempting to eliminate the differences between the sexes. By doing so, they can
concentrate fully on reproduction. This suggestion seems to be supported by the fact that
(9) couples in a
long (10) relationship, nor participants in the study who were single at the time of
the experiment, exhibited such changes.
Part 5. The article is about people who stayed in tree houses. Choose from the
people (A- D) to answer the questions. The people may be chosen more than once.
(10 points)
Which person Question Answer
says they probably would not stay in a tree house again? 1
was sometimes keen to get back to the tree house? 2
was glad there was protection from insects? 3
enjoyed the view from the tree house? 4
did not have to walk up to the house? 5
took part in water sports? 6
liked the fact that local people benefit from the tree houses? 7
immediately accepted an unexpected offer? 8
spent a lot of time walking? 9
was pleasantly surprised by the local food? 10
Holidays in a tree house
A
Primary-school teacher Anisha Kapoor went to the Green Magic Nature Resort in Kerala,
south-west India. “It wasn’t my first experience of tree house living,” she says, “but it was
certainly the
best.
I
was
pleased
to
see
that
in
a
region
where
there
aren’t
many
jobs,
the
houses
are entirely built and maintained by workers from the area, using traditional techniques and

155 394
local materials. For instance, the lifts up to the front doors are made of cane grown in nearby
fields. They work fine, by the way, and I was glad there was no stairs to climb – the houses
are 25 metres up! That’s good, though, because at the height there’s often a cool breeze
blowing through the branches. For power there’s solar energy and the taps in the kitchen and
bathroom are supplied by pollution-free natural springs in the nearby hills. There’s even a
pretty good shower.
B Ever since TV researcher Whitney Martin worked on a programme about tree houses, she’d
dreamt about staying in one. So when her neighbours happened to mention they had just
such a place in Alaska, and asked whether she’d like to spend a fortnight there in July, she
said “yes” without a moment’s hesitation. “I couldn’t believe it when I saw it,” she says, “it
had everything: even hot running water and cable TV. Though I rarely watched that because
I was out most of the time. Just a few steps from the house there were trails that seemed to
go on forever through the forests to some really fantastic rivers and lakes. And of course that
far north the days are really long summer, so I could keep going until very late. I hardly ever
felt cold, though, and on those occasions when I did, I had a nice warm place of my own to
look forward to. The only disadvantage of being there at that time of the year was the huge
number of mosquitoes. I must have been bitten a hundred times.”
C
Australian technician Richie O’Hara was a guest at the Hinchinbrook Island Wilderness
Lodge, on an island off the north coast of tropical Queensland. “The wooden tree house was
quite comfortable,” he says, “and they had all the advertised facilities such as running water
and a fridge. Actually, I hadn’t fully read the brochure, so when I arrived, I was surprised to
find an internet connection in the house and I wished I’d brought my computer with me.
Still, I found plenty of healthy things to do, like canoeing and diving, and in the evening I
could sit in the living room looking out above the rainforest to the Pacific beyond. That was
great. After a week or so, though, I was a little tired of the climb to and from the house, so I
doubt whether I’d repeat the tree-top experience. But I’m sure kids would love it – it’s just a
pity I didn’t go there when I was about ten!”
D
Medical student Kirsty Hammond spent a week in Tanzania’s Lake Manyara National Park,
at the Lake Manyara Tree Lodge. “As we approach it,” she says, “we glimpsed the buildings
up among the branches, with the Great Rift Valley in the background. It was a wonderful
sight. The houses were comfortable, too, with running water, a well-equipped bathroom and,
fortunately, large mosquito nets above the beds – I’m very aware of the dangers if they bite
you. I also liked the fact that almost everything was above ground, even the restaurant. To be
honest, I’d had my doubts about some of the traditional meals I’d seen people eating, but
once
I tasted them, I realized how good they were. The only problem there was the high night-time
156 394
temperature: although my bedroom had an overhead fan, I didn’t sleep very well. But
generally I had a great time. There’s some fantastic wildlife around, including tree-
climbing lions –
though perhaps luckily I didn’t actually see any of those.”
SECTION 3. WRITING
Part 1. For questions 1-5, complete the second sentence so that it has a similar
meaning to the first sentence, using the word given. Do not change the word given.
(10 points)
1. I fully intended to find out who is responsible for the graffiti. INTENTION
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…….
2. Absolute secrecy was crucial to the success of the
mission. SUCCESS
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…….
3. He would never agree to sell his business, even if he received a very
temping offer. OFFER
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…….
4. Something must be done quickly to solve the problem of
homelessness. ACTION
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…….
5. Philip’s inability to make decisions dates from his
accident. UNABLE
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…….
Part 2. For questions 1-5, complete the second sentence so that it has a similar
meaning to the first sentence. (10 points)
1. Apparently, the restaurant in town has been bought out by someone else.
I hear the restaurant in town is
.......................................................................................................

157 394
2. Sarah cried her eyes out immediately she was told she'd failed her driving test.
Sarah
broke.....................................................................................................................................
3. The Government recently said our problems are the fault of the worldwide
economic slowdown.
The Government have
placed.........................................................................................................
4. You led me to believe the job was mine if I wanted it.
I was
left........................................................................................................................................
.
5. He would never have guessed that at the age of 17 he would be playing for his country.
Little...............................................................................................................................................
......
Part 3. Write a paragraph. (30 points)
Write a paragraph of at least 200 words about the folloing topic:
Learning to play team sport is an important part of a child’s education.
Do you agree or disagree?
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own knowledge
T
or experience.
SECTION 1. LISTENING (50 points)
Part 1. (14 points)
Items Correct answers Points
1 Sun(day) 2
nd
July 2
2 9.30 (am) 2
3 £1,000/one/a thousand pounds 2
4 (team) captain 2
5 parents’ permission 2
6 (20/twenty) life jackets 2
7 clothes/clothing/set of clothes 2
RẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
LẦN THỨ XX
HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤM
ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT
ĐỀ THI CHỌN HỌC SINH GIỎI
MÔN: TIẾNG ANH – KHỐI 10
(Hướng dẫn chấm gồm có 5 trang)

158 394
Part 2. (16 points)
Items Correct answers Points Items Correct answers Points
1 thousands of years 2 5 brain 2
2 cheerful 2 6 damage 2
3 alcohol abuse 2 7 heavy drinkers 2
4 energy 2 8 heart disease 2
Part 3. (10 points)
Items Correct answers Points Items Correct answers Points
1
F
2 4
F
2
2 T 2 5 T 2
3
F
2
Part 4. (10 points)
Items Correct answers Points Items Correct answers Points
1 B 2 4
A
2
2
D
2 5 B 2
3
A
2
SECTION 2. LEXICO-GRAMMAR (40/200)
Part 1. (20 points)
Items Correct answers Points Items Correct answers Points
1
D
1 11 C 1
2
D
1 12
A
1
3
A
1 13 B 1
4
A
1 14 C 1
5 B 1 15
A
1

159 394
6
D
1 16
D
1
7 B 1 17
A
1
8 C 1 18 C 1
9 C 1 19 B 1
10
D
1 20 C 1
Part 2. (10 points)
Items Correct answers Points Items Correct answers Points
1 ASSERTIVENESS 1 6 UPCOMING 1
2 UNCONVENTIONAL 1 7 WORKPLACES 1
3 DESPERATE 1 8 TEMPRAMENT 1
4 DISHEARTENED 1 9 ADOPTIVE 1
5 IMPERSONATION 1 10 ATMOSPHERIC 1
Part 3. (10 points)
Lines Mistake Correction Points
1 rise rising 1
3 are is 1
4 consist consists 1
5 raising raised 1
9 at on 1
7 weights weighs 1
8 has closed has been closed 1
10 shop stocks shop which/that stocks 1
12 children children’s 1
12 adjacent near adjacent to 1
SECTION 3. READING (60/200)
160 394
Part 1. (10 points)
Items Correct answers Points Items Correct answers Points
1
D
1 6
A
1
2
A
1 7 B 1
3 B 1 8
A
1
4 C 1 9 C 1
5
D
1 10
D
1
Part 2. (20 points)
Items Correct answers Points Items Correct answers Points
1 Paragraph A viii 2 6 TRUE 2
2 Paragraph B iii 2 7 FALSE 2
3 Paragraph C
xi 2 8 NOT GIVEN 2
4 Paragraph D i 2 9 NOT GIVEN 2
5 Paragraph E v 2 10 FALSE 2
Part 3. (10 points)
Items Correct answers Points Items Correct answers Points
1 B 1 6
D
1
2
A
1 7 B 1
3 B 1 8
A
1
4
D
1 9 C 1
5 B 1 10 B 1
Part 4. (10 points)
Items Correct answers Points Items Correct answers Points
1 concerned 1 6 tend 1
2 long 1 7 those 1
3 play 1 8 puts 1
4 another 1 9 neither 1
5 reverse 1 10 terms 1
Part 5. (10 points)
Items Correct answers Points Items Correct answers Points
1 C 1 6 C 1
2 B 1 7
A
1
3
D
1 8 B 1
4 C 1 9 B 1

161 394
5
A
1 10
D
1
SECTION 4. WRITING (50/200)
Part 1. (10 points)
Items Correct answers Points
1 I had every intention of finding out who is responsible for the graffiti. 2
2 Without absolute secrecy the mission wouldn’t have been a success. 2
3 However tempting the offer was he would never agree to sell his business. 2
4 Urgent action must be taken to solve the problem of homelessness. 2
5 Phillip has been unable to make decisions ever since his accident. 2
Part 2. (10 points)
Items Correct answers Points
1 I hear the restaurant in town is under new management 2
2 Sarah broke down in tears as soon as she heard she'd failed her driving
test.
2
3 The Government have placed the blame on the worldwide economic
slowdown for our problems.
2
4 I was left with the impression that the job was mine if I wanted it. 2
5 Little did he guess/know/ realize that at the age of 17 he would be
playing for his country.
2
Part 3. (30 points)
Mô tả tiêu chí đánh giá Điểm tối đa
1. Bố cục
o Câu dẫn chủ đề mạch lạc
o Bố cục hợp lý rõ ràng, phù hợp với yêu cầu của đề bài
o Bố cục uyển chuyển từ mở bài đến kết luận
6
2. Phát triển ý
o Phát triển ý có trình tự logic
o Có dẫn chứng, ví dụ,… đủ để bảo vệ ý kiến của mình
6

162 394
3. Sử dụng ngôn từ
o Sử dụng ngôn từ phù hợp với nội dung
o Sử dụng ngôn từ đúng văn phong, thể loại
o Sử dụng từ nối cho các ý uyển chuyển
6
4. Nội dung
o Đủ thuyết phục người đọc
o Đủ dẫn chứng, ví dụ, lập luận
o Độ dài: Số từ không nhiều hoặc ít hơn quy định 10%
6
5. Ngữ pháp, dấu câu, chính tả
o Sử dụng đúng dấu câu
o Chính tả: Viết đúng chính tả
Lỗi chính tả gây hiểu lầm/ sai lệch ý sẽ bị tính một lỗi (trừ
1% điểm của bài viết)
Cùng một lỗi chính tả lặp lại chỉ tính một lỗi
o Sử dụng đúng thời, thể, cấu trúc câu đúng ngữ pháp. (Lỗi ngữ pháp
gây hiểu lầm/ sai lệch ý sẽ bị trừ 1% điểm của bài viết)
6
Tổng
30
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG LẦN THỨ
XV TRƯỜNG PT VÙNG CAO VIỆT
BẮC
ĐỀ THI MÔN TIẾNG ANH - KHỐI 10
(Đề này có 17 trang)
ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT
-------------------
PART I. LISTENING
Question 1: Listen to an interview between a young woman who has
applied for a position with a company and the personnel officer of the company.
As you listen, fill in the form below with NO MORE THAN THREE
WORDS/NUMBER. You will hear this piece twice. (14 points)
Name of applicant (1)...............................................
University attended (2)...............................................
Subject English
Year of graduation (3)...............................................
Work experience:
Last position
Years
a secondary school teacher
(4)...............................................

163 394
Salary
Previous work
Years
(5)...............................................
(6)...............................................
1990-
1992
New job’s salary (7)...............................................
Benefit of the job Four hours per week at full pay to attend
college courses
Question 2. GAP FILLING (16 points)
Listen to the recording. Complete the notes below by writing no more than three
words in the space provide.
The Mystery Personality
has played for (8)………………..
is a (9)…………….
John Tebbit’s group
aimed at young people (10)………………
connected with sports which involve some (11)………………
after appeal many people offered their services as (12)………………..
received many offers (13)……………….free (14)……………….
Some donations over (15)…………………
Your answers
8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
13. 14. 15.
Question 3: You are going to listen to a report from a local TV news program
about
the
island
of
Samsø
in
Denmark
and
decide
whether
the
following
statements
are
True
(T) or False (F) (10 points)
Your answers

164 394
T F
1. The major source of power on Samsø is oil.
2. Samsø produces more electricity than it needs.
3. Americans on average produce more carbon dioxide than Dutch
citizens.
4. The furnace is used for both heating and making fertilizer.
5. Farmers on Samsø have lost money by changing to
environmentally-friendly
practices.
Question 4. You are going to hear an account of choirgirl Laura –Jane Foley’s
experiences in Faking it. As you listen, choose the best answer to each question.
(10 points)
1.How did Laura-Jane and the program-makers first make contact?
A. The program-makers emailed lots of choir singers, including Laura-Jane.
B. Laura-Jane phoned the TV company.
C. The program-makers went to see her choir.
2. Laura-Jane was amazed that
A. the program-makers were interested in a Cambridge student.
B. so many people from the TV company went to see her.
C. the program-makers started filming so soon.
3. According to Laura-Jane, why were arguments with Harry inevitable?
A. Harry leads a real rock singer’s lifestyle.
B. Harry and Laura-Jane both have strong opinion.
C. They only had four weeks for all the training.
4. In what sense was Laura-Jane’s training a failure?
A. She didn’t really change her style or attitude.
B. She didn’t enjoy the whole experience of becoming a rock singer.
C. She didn’t make the judges believe that she was a real rock singer.
5. One positive result of the experience is that it made Laura-Jane:

165 394
A. change her views on life
B. become a more confident person
C. change her opinion of rock singers
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
B. LEXICO-GRAMMAR (20 points)
Question 1. Choose the word or phrase (A, B, C, or D) which best completes
each sentence
1.There is a strong movement supporting the abolition of the death .
A. penalty B. punishment C. discipline D. condemnation
2. The study adds to a growing _ _ of evidence that links a lack of
sleep with weight gain.
A. body B. form C. hulk D. soul
3. It is probable that they are the original bindings of the manuscript.
A. widely B. highly C. utterly D. bitterly
4. The show was _ bit as good as I expected.
A. every B. so C. very D. much
5. The similarities between all three crimes were such that they could not be _ down to chance.
A. put B. laid C. set D. taken
6. She doesn't mind working overtime because she gets paid _ .
A. by the hour B. all the hour C. at the hour D. in the hour
7. People often complain that children nowadays don't seem to respect their .
A. elderly B. elders C. aged D. age
8. All statistical analysis must allow for a of error.
A. margin B. border C. frontier D. boundary
9. It's time to take a rough against obesity.
A. stance B. measure C. legislation D. angle

166 394
10. The world's first boot camp for teenagers addicted to the Internet may be the
of things to come.
A. draft B. formula C. character D. shape
11. We believe that the government has a duty ……… its pledges.
A. bear out B. standby C. go back D. count on
12. Don’t forget to buy a packet of..............Peas
A. chilled B. frozen C. frosted D. chilly
13. He was so mean that he couldn’t bear to..............the smallest sum of money for the
charity appeal.
A. pay off B. part with C. give in D. let out
14. A huge crowd...............in the pouring rain to cheer the president.
A. turned out B. held up C. saw off D. dropped in
15. We hadn’t................for such heavy traffic, and we were delayed.
A. expected B. bargained C. calculated D. supposed
16. Beyond all....................., it was Alice who gave away our secrets
A. fail B. conclusion C. dispute D. contradiction
17. The book says that the revolution was ………….off by the assassination of the
state governor.
A. launched B. cropped C. triggered D. prompted.
18. The hijackers have demanded a …………….to be paid for releasing the
civilian hostages from the plane
A. currency B. revenue C. deposit D. ransom
19. Just.................these proofs for me as I’m in a hurry.
A. run into B. run off C. run over D. run out
20. She resigned..................No one forced her to do so.
A. for her own sake B. of her own accord
C. with a will D. on purpose
Your answers:

167 394
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
Question 2. Give the correct form of the words in the brackets (10 points)
1. They are waiting for the doctor’s................................(diagnose)
2. There was a heavy …………yesterday afternoon which completely ruined the
church Garden Party. (pour)
3. His contribution to medical science was outstanding laying the
foundations for research by the scientists who would follow in his
(foot)..................
4. Cigarettes, coffee and alcohol and other (addict).....................are known to have an
adverse influence upon human health.
5. Marie Curie's life offers us a profound and fascinating (sight).............into the changing
world of women in science and academia
6. Be careful! That’s a........................poison. (dead)
7. The talks were totally ………… We didn’t reach agreement on anything. (product)
8. The boy was very violent and his parents found him ………… (manage)
9. Tax exemption only applies to those with.............................status. (resident)
10.books have been written on the subject. (number)
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Part 3: There are ten mistakes in the text below. Underline the mistakes and
correct them in the space provided. (10 points)
Although speech is the most advance form of communication, there are
many ways of communication without using speech. Signals, signs, symbols and
gestures may be find in every known culture. The basic function of a signal is to
impinging on the environment in such way that it attracts attention as the dots and
the dashes of a telegraph circuit. Coding to refer to speech, the potential for
communication is very great. Less
168 394
adaptable to the codification of words, signs also contain meaning in and of
themselves. A stop sign or a barber pole conveys meaning quickly and
conveniently. Symbols are more difficult to describe than signals and signs because
of its relationship with the receiver's cultural perceptions. In some cultures,
applauding in a theatre provides performances with an auditory symbol of approval.
Gestures such as waving and handshaking also communicate some certain cultural
message. Although signals, signs, symbols and gestures are very useful, they do
have a major disadvantage. They usually do not allow ideas to share without the
sender being directly adjacent to the receiver.
Your answers:
1. 6.
2. 7.
3. 8.
4. 9.
5. 10.
PART III: READING (60 points)
Question 1. Read the following passage and choose one of four options A, B, C,
or D to answer each question. (10 points)
It was once believed that being overweight was healthy, but nowadays few people
subscribe to this viewpoint. While many people are fighting the battle to reduce
weight, studies are being conducted concerning the appetite and how it is controlled
by both emotional and biochemical factors. Some of the conclusions of these
studies may give insights into how to deal with weight problems. For example,
when several hundred people were asked about their eating habits in times of stress,
44 percent said they reacted to stressful situations by eating. Further investigations
with both humans and animals indicated that it is not food which relieves tension
but rather the act of chewing.

169 394
A test in which subjects were blindfolded showed that obese people have a
keener sense of taste and crave more flavorful food than non-obese people. When
deprived of the variety and intensity of tastes, obese people are not satisfied and
consequently eat more to fulfill this need. Blood samples taken from people after
they were shown a picture of food revealed that overweight people reacted with an
increase in blood insulin, a chemical associated with appetite. This did not happen
to average-weight people.
In another experiment, results showed that certain people have a specific,
biologically induced hunger for carbohydrates. Eating carbohydrates raise the level
of serotonin, a neurotransmitter in the brain. Enough serotonin produces a sense of
satiation, and hunger for carbohydrates subsides.
Exercise has been recommended as an important part of a weight-loss program.
However, it has been found that mild exercise, such as using the stairs instead of
the elevator, is better in the long run than taking on a strenuous program, such as
jogging, which many people find difficult to continue over long periods of time and
which also increases appetite.
(Adapted from Cambridge Preparation for the TOEFL Test by Jolene Gear)
1. “Subscribe to” in paragraph 1 is closest in meaning to _.
A. disagree with B. agree with C. object to D. like
2. The word” crave” in bold in paragraph 2, can best be replaced with .
A. devour B. absorb C. season D. desire
3. It can be inferred from the passage that .
A. overweight people are tense
B. thin people don’t eat when under stress
C. weight watchers should chew on something inedible when tense
D. 56 percent of the population isn’t overweight
4. It can be inferred from the passage that .
A. thin people don’t enjoy food

170 394
B. a variety of foods and strong flavors satisfy heavy people
C. overweight people have an abnormal sense of taste
D. deprivation of food makes people fat
5. According to the passage, insulin .
A. increases in the bloodstream when people eat large amounts of food
B. can be used to lessen the appetite
C. causes a chemical reaction when food is seen
D. levels don’t change in average-weight people who see food
6. It can be inferred that for certain people _ .
A. eating carbohydrates eliminates hunger
B. carbohydrates biologically induce hunger
C. carbohydrates don’t satisfy a hungry person
D. carbohydrates subside when serotonin is produced
7. What can be said about serotonin?
A. It is a chemical that increases the appetite
B. Only certain people produce it in their brains
C. It tells the brain when a person is full
D. It neurotransmits carbohydrates to the brain
8. The word ‘mild’ in the last paragraph can best be replaced with .
A. important B. hard C. heavy D. light
9. In order to lose weight, it would be a good idea for heavy people to .
A. jog 3 miles daily and chew on carrot sticks
B. walk up stairs and look at pictures of food
C. eat plenty of chewy carbohydrates
D. avoid stressful situations and eat spicy foods
10. Which one of the following exercises might be best for an overweight person to
engage in daily?
A. 10-mile bicycle rides B. cross- country skiing
171 394
C. a long swim D. an evening walk
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Question 2: Read the passage and fill in each blank with ONE suitable word. (10 points)
The British are widely (1) to be a very polite nation, and in (2)
respects this is true. An Italian journalist once commented of the British that they need (3)
fewer than four “thank yous” merely to buy a bus ticket. The first, from the bus
conductor means, “I’m here.”. The second accompanies the handing over of the
money. The third, again from the conductor, (4)
“Here is your ticket.”, and then
the passenger utters a final one as he accepts the tickets. Such transactions in most
(5)
parts of the world are usually conducted in total silence. In sharp contrast to
this excessive politeness
with strangers, the British are strangely lacking (6)
interaction. The exhortation “Good appetite”, uttered in so
(7)
ritual phrases for social
_ other languages to
fellow-diners before a meal, does not exist in English. The nearest equivalent –
Enjoy your dinner! – is said only by people who will not be pataking of the meal in
question. What’s more, the British (8)
happiness to their friends or
acquaintances only at the start of a new year and at (9)
such as birthdays, (10)
the Greeks routinely wish all and sundry a “good week” or a “good month”.
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Question 3. Read the following passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your

172 394
answer sheet to indicate the correct word for each of the blanks. (10 points)
You will make the interview process easier for the employer if you prepare
relevant information about yourself. Think about how you want to present your
(43)_
, experiences, education, work style, skills, and goals. Be prepared to
supplement all your answers with examples that support the statements you make.
It is also a good idea to review your resume with a critical eye and (44)
areas
that an employer might see as limitations or want further information. Think about
how you can answer difficult' questions (45)
_ and positively, while keeping
each answer brief.
An interview gives the employer a (46) to get to know you. While
you do want to market yourself to the employer, answer each question with an
honest (47) . Never say anything
negative about past experiences, employers, or courses and professors. Always
think of something positive about an experience and talk about that.
You should also be (48)
. If you are genuinely interested (49)
the job, let the
interviewer know that.
One of the best ways to show you are keen on a job is to demonstrate that
you have researched the organization prior to the interview. You can also (50)
interest by asking questions about the job, the organization, and its services and
products. The best way to impress an employer is to ask questions that build upon
your interview discussion. This shows you are interested and (51)
close
attention to the interviewer. It is a good idea to prepare a few questions in advance,
but an insightful comment based on your conversation can make an even stronger
statement. At the (52)
of an interview, it is appropriate for you to ask when you
may expect to hear; from the employer.
1. A. pressures B. strengths C. practices D. promotions
2.
A. hide B. limit C. express D. identify
3.
A. accurately B. rightly C. hardly D. sharply
4.
A. change B. practice C. way D. chance
5. A. ability B. response C. expression D. respect
6.
A. enthusiast B. enthusiasm C. enthusiastic D. enthusiastically
7.
A. for B. on C. with D. in
8.
A. appear B. show C. conceal D. cover
9.
A. spend B. pay C .choose D. During
173 394
10.
A. end B.close C.finish D. socialize
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Question 4:
1. Reading the Passage, there are five paragraphs, A-E. Choose the correct
heading for paragraphs A-E from the list of headings below. Write the
appropriate numbers (I-VI) in boxes 1 – 5 on your answer box. (10 points)
TELESCOPE TO DETECT ET ON HIS MOBILE
A
Astronomers are planning to build the world’s largest telescope – a machine so
powerful it could detect radio signals from a planet up to 50 light years, or 13.5
billion years from Earth. The giant radio – telescope is called the Square Kilometer
Array (SKA) and will consist of 3,000 separate radio dishes and other antennae all
linked together in to one huge machine. It will generate 100 times more data than
all the information Currently on the Internet and will need the world’s most
powerful supercomputer to analyse the information it collects.
B
The SKA will work in the similar way to other large radio telescopes such as
Australia’s CSLR Parkes radio telescope, also known as ‘’The Disk’ . The
telescope gets its name from the bowl-shaped reflector called a ‘dish’ that is used to
collect radio waves from space. The refectory focuses the waves onto an antenna
that changes them into electric

174 394
signals. From the antenna, the signals are transmitted down into the control room at
the base of the telescope and are picked up by a radio receiver. This receiver makes
the signals stronger. The signals are then analysed by a computer at another
location and the information is used to draw a picture of the source of the radio
waves.
C
Compared to ‘The Dish’, however, SKA will be thousands of times more sensitive.
This sensitivity is because of its size, the larger the dish, or the more dishes there
are, the more powerful the radio signal can be, allowing unknown areas of the
universe to be discovered. ‘We know that the universe is incrediblyvast , containing
hundreds of billions of stars’ said Richard Schillzzi, director of the SKA project.
‘However, at present we carl only see a fraction of what is out there. The SKA will
enable us to explore some of its furthest reaches.’ Scientists hope to find alien life
intelligent enough to invent radio. The SKA will be able to detect a mobile phone
system within 50 light years of Earth, but will also probably be able to scan star
systems which are much further away, because any advanced life form would have
powerful radio emitters such as radar and radio stations.
D
But looking for the evidence of extra-terrestrial life is just one of many tasks for
the SKA. Scientists also hope that the telescope will help them to understand how
the first stars and planets were formed, during a period of time called ‘first light.’
‘The SKA is a bit like a time machine,’ said Phil Diamond, head of the astronomy
and space science division of CSIRO the Australian Government’s research arm.
‘It will gather radiation emitted more than 13 billion years ago, , allowing us to get
a picture of what the universe looked like then. By choosing the type of radiation
we look at, we can get similar pictures of the universe from any other era we
choose – so we can watch how it evolved.
E
More than 20 countries will share the estimated 1.4 billion pounds cost of the
project for the telescope. Two potential sites have been chosen, one in Western
Australia and the other in South Africa. Both are in the southern hemisphere
because this will give the instrument a direct line of sight into the heart of the
Milky Way. The SKA must be built

175 394
on a site completely free of radio interference – with the host country promising it
will prevent the construction of any mobile phone, radio or TV masts for up to 50
years. This means it will have to be built mainly in a desert-either in the outback of
Western Australia or the Karoo of South Africa.
List of headings
i Budgeting for the construction of SKA
ii Discovering the secret origins of the universe
iii Abilities of advanced life forms
iv Potential to see further than before
v Methods of mapping the location of the planets
vi Plans for the world’s largest telescope
vii Location considerations for SKA
viii The collection and analysis of radio waves
Your answers:
Paragraph Answer
1. Paragraph A
2. Paragraph B
3. Paragraph C
4. Paragraph D
5. Paragraph E
2. Question 5-10: Do the following statements agree with the information
given in the Reading Passage? (10 points)

176 394
TRUE if the statement agrees with the
information FALSE if the statement contradicts
the information NOT GIVEN if there’s no
information on this
6. The SKA will be made from many parts.
7. The SKA will be the world’s most powerful telescope.
8. About one third of the universe has been discovered.
9. Scientists hope to get in touch with aliens by mobile phone.
10. Governments have decided where the SKA will be built.
Your answers:
Question 5:
You are going to read a newspaper article about four people having written
travel books. Choose from the people (A-D). The people may be chosen
more than once. Mark your answers on the answer box. (10 points)

177 394
On the road
A. Eleanor Young
Young has written a book about a journey which took seven months. Beginning in
Beijing, she headed west out of China and then south to Kashmir. The 20 years of
her life until then had been varied – she had been a correspondent for a French
weekly, she had sailed in the Olympics and skied internationally, but her main love
was travelling. She had made a similar journey in Central Asia and had a minor
success with the resulting book. When she writes she thinks of her audience as one
family member or one good friend. She writes what was seen and felt, the way it
turned up on the road – her descriptions on the camel journey are mixed with
discussions about politicians and images of a girl with her hair in a hundred plaits.
B. Fiona Dalton
When Dalton visited the bottom tip of Chile and saw the edge of the ice-field, she
decided to cross Antarctica. She tried not to be discouraged by others who had
done it. ‘The men who had skied across alone didn’t know how to deal with the
idea of someone happy to take a plane some of the way, but I wanted to do the trip
my own way.’ She spent seven months crossing the continent, pitching tents on the
sea ice. Dalton says that as a woman, her reasons for exploration are different from
those of men. ‘Men have done it to show they can win. I may go to see what the
environment can teach me, or to feel the air and see what it looks like. Or just sit
around and appreciate the scenery.’ She is a writer who explores the world in order
to write. She says, “It also suits me to get away. I love to free myself from the bills
and the bank manager. Antarctica is perfect for that. ‘It was, however, the most
testing environment she has ever experienced – it could be ‘a
full-time job just surviving’.
C. Ruth Moore
On her first trip, aged 24, Moore hitch-hiked through Nigeria, canoed down the
Congo and rode horseback across Cameroon. What started as a year-long trip
turned into a three- and-a-half-year journey. ‘The emptiness that lay ahead was
wonderful – days waiting to be filled.’ She was raised in the African bush and her
mother and grandmother had grown

178 394
up in China. ‘I don’t where I belong. My family thought it was totally normal that I
had a large view of the world.’ She dismisses fear. ‘Wild animals will look for an
escape route rather than attack,’ she says. Amongst other things, Moore has devised
her own cure for homesickness. ‘You can always improvise something. I felt
homesick for eggs for breakfast while floating down the river, so I had eggs –
crocodile eggs – and felt much better.’ Moore does believe that a woman’s
approach is different. She rarely undertakes journeys with an ultimate aim, goal or
destination – she decides as she goes along, often with the flip of a coin.
D. Sally Wade
Wade is probably more of an ex-explorer – her last journey has put her off. Wade
was born in Queensland, Australia. She was sent to boarding school, then just
wandered about
– studying music, biology and later Japanese. At 25, Wade bought a couple of
camels and rode them over 2,000 kilometrers across the Australia outback. Her
account became a best-seller. ‘I never intended to write about it – it was a private
thing. I wanted to get to know aboriginal culture and the desert. It was a glorious
trip. I went by camel because I was broke and couldn’t afford a vehicle.’ Then in
1992 she joined a group of Rabari in India. Wade’s account of that Indian journey
with them tells of failure. ‘The two trips were not comparable.’ She tried to live a
Rabari existence – except that she could always leave. She remained an outsider.
On which writer is the following stated?
1. She does not make decisions in advance
2. She used to be a journalist
3. She has given up travelling
4. She writes in an informal way
5. She travels with the intention of putting her experiences into print
Which writer says
6. She took no notice of other people’s opinions when planning one trip?

179 394
7. On one trip, just staying alive took up most of her time?
8. She takes pleasure in her surroundings?
9. She chose her method of transport because of lack of funds?
10. She is confident of finding solutions to problems?
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
PART IV: WRITING (50 points)
Question 1: Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means
exactly the same as the sentence printed before it using the given words.
(10points)
1. He suddenly thought that he might have
misunderstood her. It crossed
……………………………………………………
2. She doesn’t know why they are attracted to spending all day on the
beach She can’t see
…………………………………………………………………
3. The house is very beautiful. Its gate was painted blue.
The house, the ……………………………………………………
4. Do you think Sally will be able to come to us for
Christmas? Is there any............................................................?
5. You may be disqualified if you don’t obey the
regulations. Failure to
……………………………………………………
Question 2: Rewrite the following sentences, using the word given in brackets. You
must not alter the word in any way. (10 points)
1. A government official leaked the story to the world press. (WIND)
…………………………………………………………………………………………
180 394
2. There is a risk that the black rhino will become extinct. (THREATENED)
…………………………………………………………………………………………
3. After the scandal, he was asked to resign. (HAND)
…………………………………………………………………………………………
4. He offers them more money to encourage them to do the job quickly. (INCENTIVE)
…………………………………………………………………………………………
5. Please don’t tell anyone about this for the time being. (SOONER)
…………………………………………………………………………………………
Question 3: Write a composition (about 200 – 250 words) on the following
topic: (30 points)
Nowadays environmental problems are too big to be managed by individual
persons or individual countries. In other words, it is an international problem. To
what extent do you agree or disagree?
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG LẦN THỨ
XV TRƯỜNG PT VÙNG CAO VIỆT
BẮC
-------------------
HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤMĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT MÔN
TIẾNG ANH - KHỐI 10
PART I- LISTENING
Question 1. (14 points)
1. Shirley Sutto 2. Leeds University 3. 1990 4. 1992-1993
5. £500 a month 6. shop assistant 7. £600 a month
Question 2. (16 points)
8. his national team 9. a famous
footballer
10. up to 11. expense
12. volunteers 13. to use facilities 14. of charge 15. 5,000 pounds

181 394
Question 3. (10 points)
1. F 2. T 3. T 4. T 5. F
Question 4. (10 points)
1.A 2.C 3. B 4. C 5. B
B. LEXICO-
GRAMMAR
Question 1. (20
points)
1.A 2.A 3.B 4.A 5.A 6.A 7.B 8.A 9.A 10.D
11. B 12. B 13. B 14. A 15. B 16. C 17. C 18. D 19. C 20. B
Question 2 (10 points)
1.diagnosis 2. Pourdown 3. Footsteps 4. Addictions 5. insight
6. deadly 7. unproductive 8. unmanageable 9. non-resident 10. Innumerable
Question 3. (10 points)
1. advance => advanced 6. coding => coded
2. find => found 7. its => their
3. impinging => impinge 8. performances => performers
4. way => a way 9. message => messages
5. as => like 10. to share => to be shared

182 394
PART III – READING
Question 1. Read the following passage and choose one of four options A, B, C,
or D to answer each question. (10 points)
1. B 2. D 3. C 4. B 5. D
6. A 7. C 8. D 9. D 10. D
Question 2: Read the passage and fill in each blank with ONE suitable word. (10 points)
1. considered 2. some 3. no 4. means 5. other
6. in 7. many 8. wish 9. celebrations 10. while
Question 3.
Read the following passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer
sheet to indicate the correct word for each of the blanks . ( 10 points)
1. B 2. D 3. A 4. D 5. B
6. C 7. D 8. B 9. B 10. A
Question 4:
1. Reading the Passage, there are five paragraphs, A-E. Choose the correct
heading for paragraphs A-E from the list of headings below. Write the
appropriate numbers (I-VI) in boxes 1 – 5 on your answer sheet. (10 points)

183 394
Paragraph Answer
1. Paragraph A vi
2. Paragraph B viii
3. Paragraph C iv
4. Paragraph D ii
5. Paragraph E vii
2. Question 5-10: Do the following statements agree with the information given
in the Reading Passage? (10 points)
6. TRUE 7. TRUE 8. NOT GIVEN 9. FALSE 10. FALSE
Question 5:
You are going to read a newspaper article about four people having written travel
books. Choose from the people (A-D). The people may be chosen more than once.
(10 points)
1. C 2. A 3. D 4. A 5. B
6. B 7. B 8. B 9. D 10. C
PART IV: WRITING (50 points)
Question 1: Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means
exactly the same as the sentence printed before it using the given words. (10pts)
1. He suddenly thought that he might have misunderstood her.
2. She can’t see the attraction of spending all day on the beach

184 394
3. The house, the gate of which was painted blue, is very beautiful.
4. Is there any possibility that Sally will come to us for Christmas?
5. Failure to obey the regulations may lead to (result in) disqualification.
Question 2: Rewrite the following sentences, using the word given in brackets.
You must not alter the word in any way. (10 points)
1. The world press got wind of the story from a government official
2. The black rhino is threatened with extinction.
3. After the scandal, he was asked to hand in his resignation.
4. He offers them more money as an incentive to do the job quickly
5. I would sooner you didn’t let anyone know about this for the time being.
Question 3. Paragraph writing: The mark given to these parts is based on the
following criteria (30 points)
- Effectively address the topic and task (35% of total mark)
- Be well- organised, well developed with appropriate explaination,
display unity and Coherence (30% of total mark)
- Good use and control of grammatical structures, display consistence facility
in the use of language, appropriate word choice (30% of total mark)
- Good punctuation and no spelling mistakes (5% of total mark)
Typescri
pts
Part
1:
A: I wonder if you’d mind telling me your full name, please, Miss
Sutton. B: Shirley Sutton.
A: How do you spell
Sutton? B: S-U-T-T-O-
N
A: Thank you. Now let me see. Uhmm, you studied English at college,
didn’t you? B: Yes, that’s right. I was at Leeds University.
A: When was that?

185 394
B: In 1990.
A: So you graduated about 4 years
ago. B: That’s right.
A: And could you tell me what kind of work experience you’ve had?
B: My last position was as a teacher at Smithfield Secondary School in
Leeds. A: When was that exactly?
B: From 1992 to 1993.
A: uhuh
B: Before that I work for K Mart as a shop assistant. That was from 1990 to 1992.
And I’ve been doing freelance work for the last few months.
A: Well, Ms. Sutton, your qualifications for the job are excellent. Could you tell me
what kind of salary you are expecting?
B: Well, in my last job I was making five hundred pounds a month. I understand
that this job position has a starting salary of around five hundred a month.
A: That’s right.
B: That would be fine with me.
A: And is there anything you’d like to ask about the job?
B: Yes, I’d like to know if the company provides opportunities for further
education. A: Yes. Our employees are allowed to take up to four hours a week at
full pay to attend college courses.
B: That’s very generous.
A: Is there anything you’d like to
know? B: No, not at this time.
A: Well, I’ve enjoyed meeting and talking with you. We’ll call you within the
week. B: Thank you. I appreciate the time you’ve given me. Bye.
A: Goodbye.
Part 2.

186 394
Listen to the recording. Complete the notes below by writing no more than three
words in the space provided
PRESENTER: And now for our Mystery Personality of the week and your chance
to win one of our fabulous prizes. Last week’s competition generated a huge
response and the first five answers pulled out of the bag will receive 100 pounds
worth of sports clothes vouchers. And if you didn’t win last week, here’s another
chance. And this week’s prize is even bigger. We’re giving ten prize of 250
pounds worth of book, music and clothes vouchers to mark the first anniversary of
the show on the air, so get your pen ready to take down the address details. Just
write the name of the person you think is our Mystery Personality and send it to
Mystery Draw at the address Marcia will give you in just a second. The address
will be repeated at the end of the show for those of you who didn’t get it. And so
it’s over to Marcia who will tell you a few tantalizing details about our mystery
person this week. MARCIA: Thanks, Mike. Well here goes. Our mystery person
this week is a very well- known footballer who plays for a famous club, and has
also played for his national team. He is very talented and enormously popular,
especially for the part he played in a famous footballing victory. And two clues: He
hasn’t got a famous wife and e speaks French. If you think you knows who it is,
then pop the answer on a postcard and send it to Mystery Draw, PO Box 5510.
PRESENTER: Thank you, Marcia. Get those porcards in and make this a bumper
anniversity draw. Now, if you remember, last week on the show we talked to the
organizer of a new group set up to help young people up to the age of 20 to get
involved in activities like orse-riding, tennis, scuba diving, cycling or any form of
sport which involves some kind of expense. John Tebbit, the organizer rang us to
say that the response to is appeal on the show was staggering. A large number of
people both young and old have offered their survices free as volunteers. The whole
things have been overwhelming. John said they also had numerous offers of help
throughout the country to use acidities free of charge. As if that was not enough,
they have received many donations, including several rather large gifts of more
than 5000 pounds! On behalf of John Tebbit and also those who will benefit from
the generous to the trust, I would like to say thank you.

187 394
This week we are going to talk to a very unusual athlete indeed. Patrick, who is 20
years of ages, has been wheelchair-bound for the past five years after a motorcycle
accident left him paralysed from the waist down. This has not stopped this young
man from getting out and about. He’s an inspiration to all of us. Patrick has
excelled in archery, beating the best in the field; so much so that he has won
sponsorship from leading sport manufactures which has now enabled him to devote
more time to perfecting his skills. So, I would like to introduce you to Patrick who
is going to tell us what this sponsorship means to him.
Part 3:
Reporter: Good evening, and thanks for tuning in. This is News 12 at 6. I’m
Christine Bagley. Our top story tonight takes us to a small island off the coast of
Denmark. A team of scientists and researchers from the University of Virginia in
Charlottesville has been visiting the island of Samsø. Samsø has become famous as
the most environmentally- friendly place in the world…
Dr. Franklin: I’m standing here on the beautiful island of Samsø, about 12 miles
from the Danish mainland in the North Sea. I’m surrounded by wind turbines and
some very excited scientists. This is simply amazing! We don’t have any
alternative power project on this scale in the United States. This place is years
ahead of us.
Reporter: That’s Dr. Albert Franklin of the University of Virginia. He’s here
along with a group of researchers from the university to learn from Samsø’s
success in becoming the “greenest place on earth.” These wind turbines harness the
immense power of the weather in this windy, remote island. The wind turns these
huge windmills behind me, and the motion generates electricity. In fact, the
turbines create so much electricity that they supply not only the 4,200 residents of
Samsø, but the mainland of Denmark, too. By selling electricity to Denmark’s
power grid, the islanders claim to be carbon negative. Here’s Dr. Franklin again.
Dr. Franklin: Carbon dioxide, or CO2, is a natural gas. However, human activity
is releasing more and more CO2 into the environment than ever before. Too much
CO2 is bad because it’s a greenhouse gas. That means carbon dioxide is
responsible for global warming. CO2 is emitted from power stations that burn coal
and oil to make electricity,

188 394
cars, planes, fertilizers, and even some types of food production. It is possible to
reduce the amount of CO2 you put into the atmosphere—by planting trees, or
using renewable energy, for example. These are called offsets. If a country makes
more CO2 than it offsets, it’s called carbon positive. If it offsets more than it
produces, it’s called carbon negative. Reporter: And Samsø is the most carbon
negative area of its size anywhere on the planet. Here are some numbers. Each
American is responsible for about 20 tons of carbon dioxide every year. That’s the
highest figure of any nation. Each Dane produces about 13 tons. Samsø is 140
percent carbon-negative, which means that each resident actually takes out carbon
from the atmosphere. They calculate this by adding up all the green energy they
produce and subtracting the few carbon costs they have from cars and other
forms of transportation.
Dr. Franklin: Look at this system here. This is the way humans can live in
harmony with nature.
Reporter: Dr. Franklin has brought me to the central furnace. That’s basically a
very large oven which burns straw to heat the homes of Samsø.
Dr. Franklin: Straw is just dried plants, and those plants take CO2 out of the
atmosphere. So, straw is carbon-neutral. Now, if you burn straw at a very high
temperature, it pollutes very little, and it can heat the houses. But it gets better.
After the straw is burned, you are left with a gray dust called ash. This ash is a great
fertilizer, so farmers spread it on their fields. That way, they don’t need to buy
fertilizer—the process of making fertilizer from oil releases CO2, of course. The
ash fertilizer helps the plants grow, and the plants make straw and we’re back to the
furnace. A fully renewable, carbon-neutral cycle of energy production!
Reporter: It’s cold and windy—it’s always windy here, it seems—but everyone’s
excited about carbon on this island. Samsø made this remarkable change to
renewable energy as a result of a competition. In 1997, the Danish government held
a competition to find an island with the best plan to become carbon neutral by
2008. Samsø won the competition, and the rest is history (with a little financial help
from the government and the European Union, of course). But environmentalism
has also been good business. The Danish government buys

189 394
Samsø’s wind-generated electricity at such a good price that the farmers who
swapped crops for turbines are already making a profit. And that’s not counting the
money the islanders save from not buying gasoline, which is 2 to 3 times more
expensive than in the
U.S. Did we mention biodiesel?
Dr. Franklin:
Biodiesel! Here’s another case where one environmentally-friendly
idea creates a whole chain of green consequences. Take canola, for example. That’s
a plant that grows easily here, and also in the U.S. If you press the canola seeds,
you get canola oil, which you can use as biodiesel—so, no gasoline-based diesel.
But after you press the canola seeds, you have a green mash. You can then give this
to your cows, which means you don’t have to buy feed—feed is imported, which
means transportation carbon costs. Your cows produce organic milk and cheese, so
you can live off the land.
Reporter: This is what environmentalists call self-sufficiency: Samsø can
survive by producing its own energy and food. It doesn’t need a lot of imports,
and fewer imports mean less transportation which damages the environment by
producing carbon dioxide. This all helps Samsø’s carbon budget, which makes Dr.
Franklin and the other Americans here very jealous. On the island on Samsø,
Denmark, I’m Christine Bagley for News 12. Part 4.
Laura-Jane Foley, a twenty-year old student at Cambridge University who sang in the
university choir, took part in Series 5 of the TV program, Faking it. Along with
many other members of classical choirs around the country, Laura-Jane received an
email about Faking it! She thought it sounded really exciting, so she phoned the
number in the email. She did not really think that they’d be interested in her. But
then, to her surprise, members of the TV company went to see her, and soon after
that, they were filming. From Laura-Jane’s point of view, the whole thing happened
amazingly quickly!
Twenty-year old Laura was a student at Cambridge University. She had
never even been to a rock concert in her life, so it was going to need a huge
transformation to make her into a convincing rock singer. The program-makers
decided that her new identity would be called LJ (the initials of her real name Laura
Jane) and that she would be the lead singer of a band called Rehab.

190 394
In order to learn the skills and attitude necessary in just four weeks, Laura
Jane went to live with a girl called Harry, a real rock singer who enjoys living a
rock singer’s lifestyle. But the two girls found it difficult to get along- they were
just too different. For Laura- Jane, this was the worst part of the whole experience.
She explained that she and Harry were both strong individuals with strong opinions
and so big disagreements were inevitable. For example, when Harry decided that
Laura Jane needed a new, shorter hairstyle, Laura Jane refused. From Harry’s point
of view, Laura-Jane just wasn’t trying. In fact, Harry couldn’t understand why
Laura-Jane had agreed to take part in the program at all if she wasn’t prepared to
make changes-she suspected that Laura-Jane just wanted to be in TV.
As part of her training, Harry took Laura-Jane to rock concerts. For
example, on the second day of the four-week training period, they went to see
American rock star Marilyn Manson. Laura-Jane confessed that she hadn’t really
enjoyed the experience at all. She complained that everyone had been dancing
around, banging into each other. She’s found the whole evening dangerous and
crazy.
Nikki Lambourne, a singer who has performed with world famous bands
such as The Who, was employed to help Laura-Jane change and develop her style
of singing. Laura-Jane got on with Nikki much better than with Harry, and she also
liked the boys in her fake band, Rehab. She commented that they looked like
punks, but were nice and really intelligent. It reminded her that your opinion of
someone can’t be based on what they look like. Unfortunately, because of the
problems with her preparation and in particular her bad relationship with Harry,
Laura-Jane was not successful in fooling the judges at the end of the program. After
they had heard three different rock bands, two with genuine female rock singers
and the other with Laura-Jane, they correctly identified Laura –Jane as the “fake”.
So in that sense, her training was a failure. And she admits that, although it was an
amazing experience, she would not want to do it again. The rock world just didn’t
appeal to her, although she claims to have bought her first rock CD since the
program!
Laura says that the whole experience of taking part in Faking it has made
her more confident. However, it has not changed her views on life-and it certainly
has not made her

191 394
more rebellious. She is still a respectable, classical music loving girl who sings in a
choir- she’s definitely not a rock chick!.
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG LẦN THỨ XV
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN LÊ QUÝ ĐÔN - ĐIỆN BIÊN
ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT
Môn: Tiếng Anh khối 10
PART I: LISTENING
Listen 1. Complete the notes below. Write NO MORE THAN THREE
WORDS AND/ OR A NUMBER for each answer.
Fitness centre
Example Answer
Current class aerobics
Facilities: Body building equipment
Keep – fit studio
1.
Special course: 2.
Refreshments after
exercising:
3. shop
4. and oil-free
5. food
Membership scheme
Super
Time: At any time (both weekdays and weekend)
Charge: 6. for the annual subscription fee
Under super
Time: Monday to Sunday (except 7. )
Charge: £ 500.00 for the annual subscription fee

192 394
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7.
Listen 2. You will hear a wildlife photographer called Leanna Marson
talking about her work. Answer the following questions using NO
MORE THAN TWO WORDS OR A NUMBER for each answer.
1. Leanna describes she experiences when she takes a good
wildlife photograph as .
2. She feels that photography is not simply about .
3. Leanna says her work involves
.
an animal's
4. She considers it a(n) to be able to take
pictures of wildlife.
5. She says that she needed to be on one particular occasion.
6. On a recent trip, Leanna was away for .
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6.
Listen 3. For questions 1-5, listen to a short talk and decide the
statements are True (T) or False (F).
T F
1. At the beginning of the conversation about traveling overseas,
the man felt relaxed.
2. You could bargain over the price with shopkeepers to get the
best deal.
3. People stared at him out of a distrust of foreigners.
193 394
4. The people seem to pass through traffic as if unaffected by
everything around them.
5. Some countries share some similar characteristics that bind
them together.
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Listen 4. You will hear part of a radio interview in which a travel writer,
Owen Grifiths, is talking about his career. For questions 1 - 5, choose the
best answer which fits best according to what you hear.
1. Why does Owen feel well suited to a career as a travel writer?
A. He believes ha has the desire and determination to succeed
B. He finds it easy to adjust to living in different places
C. He feels he has both the right character and skills
D. He doesn't feel ready to settle down in one place
2. Why did Owen work for a newspaper after leaving university?
A. to gain writing experience
B. to follow in his mother's footsteps
C. to finance his novel writing
D. to please his parents
3. Why was Owen's first travel piece published?
A. The paper had been planning a piece on that region
B. He was the only writer able to meet the deadline
C. It solved a problem for his boss
D. His boss wanted to reward him
194 394
4. According to Owen, what quality must a travel piece possess?
A. It needs a balance between information and opinion
B. It has to appeal to all readers of the newspaper
C. It should be constructed like a short story
D. It must convey the writer's enthusiasm for the place
5. What criticism does Owen make of his own writing?
A. He sometimes struggles to produce original pieces
B. He often ands up leaving out the best part of his journeys
C. He believes his ideas could be better organized
D. He sometimes writes to please himself more than his teachers.
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
PART II: LEXICO – GRAMMAR
A. Choose the correct answer A, B, C, D to each of the following questions.
1. The boxer hit his opponent so hard that he was for ten minutes.
A. asleep B. knocked about C. unconscious D. stopped
2. Because of an unfortunate your order was not dispatched by
the date requested.
A. hindrance B. oversight
C. negligence D. transgression
3. The death in the earthquake has been put at over one thousand.
A. damage B. toll C. rate D. loss
4. Don’t be
true, it probably
is.
by false advertisements. If something looks too good to be
A. put off B. given up C. taken in D. put down
5. By next Saturday you with us for 6 months.

195 394

196 394
A. will have stayed B. will stay C. have stayed
D. are staying
6. The child sat in the middle of the floor and refused to move.
A. distinctively B. decisively C. flatly D. totally
7. The manager told his assistant to the mistake immediately.
A. rectify B. maltreat C. sanction D. banish
8. After a six-year relationship, Martha and Billy have decided to .
A. break the bank B. turn the page C. tie the knot D. make the
grade
9. Not until the seventeenth century to measure the speed of light.
A. anyone did even attempt B. did anyone even attempt
C. even did anyone attempt D. did even attempt anyone
10. The director retired early ill health.
A. on behalf of B. ahead of C. on account of D. in front
of
11. Little did I imagine The Amazing Race would entail long-winded
journeys and ups and downs .
A. aplenty B. inexhaustibly C. profusely D. superabundant
12. It stands to reason that a touch of humor and optimism can work
.
A. on all cylinders B. spectacles
C. wonders D. your fingers to the bone
13. I admit that I am late for the conference, but by of
excuse let me explain: my plane was delayed for 6 hours in Hanoi.
A. courtesy B. dint C. means D. way
14. A lot of criticism and scorn has been heaped his opinions.
197 394
A. above B. beyond C. on D. up
15. At first, she was dumbfounded to hear that he wanted to
break up, and then came the stirrings of auto-hypnotic perturbation.
A. exceedingly B. out-and-out C. somewhat D. utterly
16. What stands out from The Voice Kids is that many young children are
with natural talent for music.
A. bestowed B. conferred C. endowed D. vouchsafed
17. With the economic situation looming large, many families find it
difficult to rear their .
A. descendant B. lineage C. offspring D. successor
18. Researchers have made a(n) plea for more sponsorship
so that they can continue their project.
A. compassionate B. dispassionate C. encompassed D. impassioned
19. That Mary is an liar: you must take what she says with a small
grain of salt.
A. incorrigible B. incurable C. irredeemable D. irremediable
20. Unanswered, the demands for nuclear deterrents have fears
of civil war.
A. flashed up B. prognosticated C. sidetracked D. stoked up
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
B. Fill in the bracket with the correct form of the words
198 394
1. Many teachers expressed serious about the
new tests.
GIVE
2. The price of property in the city is PROHIBIT
3. is an economic theory which states that a
progressively greater level of consumption is beneficial to
the
consumers.
CONSUME
4. If your credit card debt is mounting and yet you can't stop
spending, you could be a _
SHOP
5. The number of people suffering from shopping addiction has
the number of drug and drink addicts
combined.
TAKE
6. He gained for being difficult to work with as
an actor.
NOTORIOUS
7. The Transformer is quite intriguing. It is one of
the best movies of the year.
DOUBT
8. Her hip has been for quite a while, and she'll
probably need surgery on it.
TROUBLE
9. Her latest novel is a thriller, set some time in
the late 21st century.
FUTURE
10. The new policy only serves to the
inadequacy of help for the homeless.
ACCENT
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
C. There are ten mistakes in the following passage. Find and correct them.
199 394
Line 1
Line 2
Line 3
Line 4
Line 5
Line 6
Line 7
Line 8
Line 9
Line 10
Line 11
Line 12
Line 13
Line 14
Line 15
Line 16
Skiing is one of the most popular sports in the world. According to
recent estimation, about one hundred millions of people ski regularly
or occasionally.
Sliding across the snow on skis is also one of the most ancient
methods of transport known to the man. It has demonstrated that men
were already travelling across the snow by means of primitive skis
before the invention of the wheel. In the Asiatic region of Altai and in
Scandinavia, for example , the remains of skis have been found which
dated back to 4,000 BC. Further evidence is supplied by ancient cave
paintings which depict people skiing, and a Norway saga which tells
the story of an invasion of its territory 8,000 years ago by a tribe of
skiers who came from the north.
Nowadays, skiing, apart from a sport, has become a big industry
and a notable feature of leisure culture. Ski resorts and all the activity
that they generate is the main source of wealth in many mountain
regions, which were previously remote and accessible. And far from
its once elitist image, skiing is now enjoyed by an increasingly
broader
spectra of society.
Mistakes Correction
1. ……………………..…. Line: …..
2. …………………..……. Line: …..
3. …………………..……. Line: …..
4. …………………..……. Line: …..
5. …………………..……. Line: …..
6. …………………..……. Line: …..

200 394
7. …………………..……. Line: …..
8. …………………..……. Line: …..
9. …………………..……. Line: …..
10. …………………....…. Line: …..
PART III: READING
A. Choose the best answer from A, B, C or D to fill in the gaps in the
following passage.
A POWERFUL INFLUENCE
There can be no doubt at all that the Internet has made a huge difference to
our lives. Parents worry that their children spend too much time browsing the
Internet or playing computer games, hardly (1) …….. doing anything else in
their spare time. Naturally, parents are (2) ……. to find out why the Internet
is so attractive, and they want to know if it can be harmful for their children.
Should parents worry if their children are spending that much time (3)
………… their computers.
Obviously, if children are bent over their
computers for hours, (4)…......................................................................................in
some game , instead of doing their homework, then something is wrong.
Parents and children could decide how much use the child should (5)… of
the Internet,
and the child should give his or her (6)………….. that it don’t interfere with
homework. If the child is not (7)……….… to this arrangement, parents can
take more drastic steps. Dealing with a child’s use of the Internet is not much
different from
negotiating
any
other
sort
of
bargain
about
behavior. Any parents who is seriously alarmed about a child’s behavior
should make an appointment to discuss the matter with a teacher. Spending
time in front of a computer screen does not (8) affect a child’s
performance at school. Even
if a child is (9)……..…. crazy about using the Internet, he or she is probably
just (10)….......through a phase, and in a few months there will have
something else
to worry about!
201 394
1. A. always B. rarely C. never D. ever
2. A. worried B. concerned C. curious D. hopeful
3. A. staring at B. glancing at C. looking D. watching
4. A. supposed B. occupied C. interested D. absorbed
5. A. do B. have C. make D. create
6. A. word B. promise C. vow D. claim
7. A. holding B. sticking C. following D. accepting
8. A. possibly B. necessarily C. probably D. consequently
9. A. absolutely B. more C. quite D. a lot
10. A. going
Answers:
B. passing C. travelling D. walking
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
B. Read the text below and think of the word which best fits each gap.
Use only ONE word in each gap.
WHAT ARE YOU DOING TO DO WITH YOUR LIFE?
At some time or another, each and every young person must provide
themselves with the necessary skills - "What can I do with my life". It seems
easy to
(1)....................the big question down into a few smaller ones. For example, "Where
do I want to live?" "How much time can I (2).....................myself over to achieving
my goals? or "What kind of qualifications will I need to acquire? But two of
paramount (3) …………… are "What are my interests?" and "What are my
strengths?"
When you start to make (4) ………….. for interests and strengths, it
makes sense to consider the (5) …………… first. After all, a successful
career is best measured in how satisfying you find (6) …………….. , and
it's easer to develop

202 394
strengths and skills than to actually have to force yourself (7).........................loving
what you're supposed to do.
You're probably thought a lot about what you like and don't like, and
what kinds of
jobs
would
(8)
…………….
your
interest.
But
the
more
clearly
you
(9)
…………….out those interests, the closer you'll be to (10)...........................smart
career choices.
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
READING PASSAGE 1
C. Read the passage and choose the best option A, B, C or D to
answer the following questions
The Underground Railroad
Slavery was legal for over 200 years in some parts of North America,
particularly the southern states of the United States, where the plantation
system of agriculture depended on the labor of slaves, most of whom came
from Africa. Slaves had no rights or freedoms because they were thought of
as property. From the time of its origin, slavery had opponents. The
abolitionist movement began in the 1600s when the Quakers in Pennsylvania
objected to slavery on moral grounds and wanted to abolish the institution.
In 1793, Canada passed a law abolishing slavery and declared that any
escaped slaves who came to Canada would be free citizens. Slavery was
already illegal in most northern states; however, slaves captured there by
slave hunters could be returned to slavery in the South. Canada refused to
return runaway slaves or to allow American slave hunters into the country. It
is estimated that more than 30,000 runaway slaves immigrated to Canada and
settled in the Great Lakes region between 1830 and 1865.

203 394
The American antislavery movement was at the height of its activity during
the 1800s, when abolitionists developed the Underground Railroad, a loosely
organized system whereby runaway slaves were passed from safe house to
safe house as they fled northwards to free states or Canada. The term was
first used in the 1830s and came from an Ohio clergyman who said, “They
who took passage on it disappeared from public view as if they had really
gone to ground”. Because the Underground Railroad was so secret, few
records exist that would reveal the true number of people who travelled it to
freedom. The most active routes on the railroad were in Ohia, Indiana, and
western Pennsylvania.
Runaway slaves usually traveled alone or in small groups. Most were young
men between the ages of 16 and 35. (A) The fugitives hid in wagons under
loads of hay or potatoes, or in furniture and boxes in steamers and on rafts.
(B) They traveled on foot through swamps and woods, moving only a few
miles each night, using the North Star as a compass. Sometimes they moved
in broad daylight. (C) Boys disguised themselves as girls, and girls dressed as
boys. In one well-known incident, twenty-eight slaves escaped by walking in
a funeral procession from Kentucky to Ohio. (D)
The railroad developed its own language. The trains were the large farm
wagons that could conceal and carry a number of people. The tracks were the
backcountry roads that were used to elude the slave hunters. The stations
were the homes and hiding places where the slaves were fed and cared for as
they moved north. The agents were the people who planned the escaped
routes. The “conductors” were the fearless men and women who led the
slaves toward freedom. The “passengers” were the slaves who dared to run
away and break for liberty. Passengers paid no fare and conductors received
no pay.
The most daring conductor was Harriet Tubman, a former slave who
dedicated her life to helping other runaways. Tubman made 19 trips into the
South to guide 300

204 394
relatives, friends and strangers to freedom. She was wanted dead or alive in
the South, but she was never captured and never lost a passenger. A
determined worker, she carried a gun for protection and a supply of drugs to
quiet the crying babies in her rescue parties.
A number of white people joined the effort, including Indiana banker Levi
Coffin and his wife Catherine, who hid runaways in their home, a “station”
conveniently located on three main escape routes to Canada. People could be
hidden there for several weeks, recovering their strength and waiting until it
was safe to continue on their journey. Levi Coffin was called the “president
of the Underground Railroad” because he helped as many as 3,000 slaves to
escape.
The people who worked on the railroad were breaking the law. Although the
escape network was never as successful or as well organized as Southerners
thought, the few thousand slaves who made their way to freedom in this way
each year had a symbolic significance out of proportion to their actual
numbers. The Underground Railroad continued operating until slavery in the
United States was finally abolished in 1865.
1. Why did thousands of runaways slaves immigrate to Canada?
A. They preferred the climate of the Great Lakes region.
B. Working conditions for slaves were better in Canada.
C. Canada had no laws restricting immigration.
D. Former slaves could live as free citizens in
Canada.
2. The phrase “the term” in paragraph 3 refers to
A. Antislavery movement C. Underground Railroad
B. Abolitionist D. free state
3. The word “fugitives” in paragraph 4 is closest in meaning to
A. Leaders B. old men C. runaways D. brave ones

205 394
4. All of the following are mentioned as methods of escape on the
Underground Railroad EXCEPT
A. Hiding in a hay wagon C. riding in a railcar
B. Wearing a disguise D. walking in a procession
5. The author discusses the language of the Underground Railroad in
paragraph 5 in order to
A. Trace the history of American English words
B. Illustrate the secret nature of the escape network
C. Point out that some words have more than one meaning.
D. Compare the Underground Railroad to other railways.
6. The word “elude” in paragraph 5 is closest in meaning to
A. avoid B. follow C. find D. assist
7. Which of the following statements is true about passengers on the
Underground Railroad?
A. Their destination was in the northern states or Canada.
B. They were not allowed to make stops during the journey.
C. Their babies were disguised to look like baggage.
D. They paid the conductors at the end of the journey.
8. Why was Harriet Tubman wanted dead or alive in the South?
A. She was a criminal who carried a gun and sold drugs.
B. She refused to return the runaway slaves that she captured.
C. She was an escaped slave who led others to freedom
D. She became the president of the Underground Railroad.
9. It can be inferred from paragraph 8 that the author most likely believes
which of the following about the Underground Railroad?
A. The people who worked on the railroad should have been arrested.
B. The railroad was unsuccessful because it could not help every slave.

206 394
C. Southerners did not know about the railroad until after it closed.
D. The railroad represented a psychological victory for abolitionists.
10. Where would the following sentence best fitted into paragraph 4?
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
Women and children also escaped, but they were more easily captured.
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
READING PASSAGE 2
D. Read the following passage and do as required.
A. The need for a satisfactory education is more important than ever
before. Nowadays, without a qualification from a reputable school or
university, the odds of landing that plum job advertised in the paper are
considerably shortened. Moreover, one’s present level of education could fall
well short of future career requirements.
B. It is no secret that competition is the driving force behind the need
to obtain increasingly higher qualifications. In the majority of cases, the urge
to upgrade is no longer the result of an insatiable thirst for knowledge. The
pressure is coming from within the workplace to compete with ever more
qualified job applicants, and in many occupations one must now battle with
colleagues in the reshuffle for the position one already holds.
C. Striving to become better educated is hardly a new concept.
Wealthy parents have always been willing to spend the vast amount of extra
money necessary to send their children to schools with a perceived
educational edge. Working adults have long attended night schools and
refresher courses. Competition for employment has been around since the
curse of working for a living began. Is the present situation so very different
to that of the past?

207 394
D. The difference now is that the push is universal and from without as
well as within. A student at a comprehensive school receive low grades is no
longer as easily accepted by his or her peers as was once the case. Similarly,
in the workplace, unless employees are engaged in part-time study, they may
be frowned upon by their employers and peers and have difficulty even
standing still. In fact, in these cases, the expectation is for careers to go
backwards and earning capacity to take an appreciable nosedive.
E. At first glance, the situation would seem to be laudable; a positive
response to the exhortations of politicians for us all to raise our intellectual
standards and help improve the level of intelligence within the community.
Yet there are serious ramifications according to at least one educational
psychologist. Dr. Brenda Gatsby has caused some controversy in academic
circles by suggesting that a bias towards what he terms “paper excellence”
might cause more problems than it is supposed to solve. Gatsby raises a
number of issues that affect the individual as well as society in general.
F. Firstly, he believes the extra workload involved in resulting I
abnormally high stress levels in both students at comprehensive schools and
adults studying after working hours. Secondly, skills which might be more
relevant to the undertaking of a sought-after job are being overlooked by
employers not interviewing candidates without qualifications on paper. These
two areas of concern for the individual are causing physical as well as
emotional stress.
Questions 1-5: Match the headings to the paragraphs in the passage.
The first paragraph has been done for you.
Eg: Paragraph A - iii
1. Paragraph B
2. Paragraph C
3. Paragraph D
4. Paragraph E
5. Paragraph F

208 394
i. The struggle for better education results in parents sending children to
costlier schools
ii. Doubts as to whether competition is a modern phenomenon.
iii. The value of education in securing employment.
iv. Questions raised concerning the over-emphasis placed on
paper qualifications.
v. Causes of concern for the individual
vi. Comprehensive school students no longer receive low grades.
vii. Competition in the workplace increasing the need for higher qualifications.
viii. Pressure to perform well at school and continue study while working.
Answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Questions 6-10: Following is a summary of a part of the passage. Fill in
the gaps with NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS from the passage.
Dr. Gatsby, an educational psychologist, has suggested that there are
problems affecting the individual and society when the workplace is biased
towards hiring personnel only on the basis of their (6) .
He claims that an over-emphasis placed on (7) is causing stress in
students at school and in working adults studying part-time. Also, more
practical skills might be overlooked by employers hiring applicants for
jobs. However, the most (8)
consequence of this preference for ever more
highly qualified applicants, apart from a possible drop in
university (9)
is that those who are unable to afford a
higher level of education are disadvantaged. (10) have not met
with universal acceptance.
Answers:
Future-Friendly Awards
Four local community groups run by volunteers have been nominated to win a
cash prize.
Who do you think should win?
209 394
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
READING PASSAGE 3
E. You are going to read an article about groups run by volunteers in their local
community. For questions 1-10, choose from the groups (A-D). The
groups may be
chosen more than once .
Which of the groups
1. has a name that might give people a wrong idea of its activities?
2. wants to respond to feedback from users of a service it provides?
3. has put the results of its work on show to the public?
4. has found it hard to finance its activities?
5. offers advice to beginners in an activity?
6. provides a pick-up service for its users?
7. plans to start selling things to make money?
8. would use the prize money to publicize its activities?
9. noticed that something that was still useful was going to waste?
10. provides a service for people all over the country?

210 394
A. CycleStreets
You're keen to get on your bike, but you're not so keen on bumping
over poor roads, sweating up hills or riding between all the large trucks
on the main roads. Where can you go? The answer is to ask
www.cyclestreets.net, a journey-planning website for cyclists. 'We aim to
give newcomers the confidence to start cycling - with all its
environmental and health benefits - and to improve routes for those who
already cycle,' says spokesperson Martin Lucas-Smith. The not-for-profit
group is based in Cambridge, but routes are available in all regions
nationwide. Cyclists can get involved, too, by contributing photographs
and reporting obstructions or other issues. 'We've done years of unpaid
work and winning this award would help us make some major
improvements, which the cyclists who contact us have been asking for,'
says Martin.
B. Sefton Green Gym
If you visit Sefton Green Gym in Liverpool, don't go expecting to see
weights or rowing machines - this 'gym' just has rows of lovingly
tended organic fruit and vegetables. The gym was set up to help local
people improve their skills, make new friends and enjoy the health
benefits of gardening. Members range from young people with learning
difficulties to elderly people with health problems. 'My dad went
along after a serious illness to get fit and make new friends, ' says Joanne
Woods . 'He's worked hard to raise funds but with limited success, and
the gym faces closure if we don't get any more.' The award would help the
gym to expand by installing eco-friendly solar heating, as well as
advertising for new members and extending its links with the community.
C. The Project Group

211 394
The Project Group, from the small town of Oswestry, helps people with
health problems and learning disabilities to build their self-esteem through
creativity. This year, the group has focused on using recycled materials,
including making vases from waste paper and pictures from recycled
glass. Last year, it helped stage an exhibition of sculptures entirely
created from rubbish such as cri sp packets, plastic bags and odd shoes.
It has also created posters for the local Wildlife Trust, and helped other
community groups. 'The whole organization is user-led, and our artwork
can now be admired in many public buildings and spaces in our region,'
says spokeswoman Jo Davis. 'We also hope to use the award to
develop a retail range of
recycled products to help fund our activities.'
D. Clean stream Carpets
Every year, an astonishing three-and-a-half million carpet tiles are thrown
away in South Wales and south-west England. Recognizing that many
tiles could be reused, a group of volunteers formed Clean stream Carpets
to collect and supply them at affordable prices to local organizations
and community groups
. Volunteers collect and grade tiles before selling them from Clean
stream's premises near Rhondda. Satisfied customers range from local
schools to a community furniture bank in Bedfordshire, and the tiles have
even been used to build refuges for endangered animals such as great
crested newts. 'Our unique selling point is the guarantee that the product
is diverted from landfill,' says one volunteer. 'Winning the award would
give us encouragement to explore other ways of using other recycled
material.'
PART IV: WRITING

212 394
A. Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means the
same as the sentence before it.
1. The boy was about to cry when he was reprimanded by his
mother. The boy was
on…………………………………………………………………
…….
2. In terms of economy, Vietnam has been developing very quickly over the
last 20 years.
When it ……………………………………………..…..…………………………..
3. He is very good at cooking
spaghetti. He is a dab
……………………………………………….……………….………….
4. The students’ rebellious behaviors should have been severely
punishment. The students deserved
…………………………………………………….………….
5. There’s no one available in this moment to take her
class. There’s no one
………………………………………………….…………………….
B. For each of the sentences below, write a new sentence as similar as
possible in meaning to the original sentence, but using the word given.
This word must not be altered in any way.
1. Don’t you regret not learning to swim? (DON’T.............SWIM ?)
……………………………………………………………..……………………
2. I can’t often afford to spend my holiday abroad. (SELDOM)
……………………………………………………………..………………………
3. The two young men introduced a virus into the computer system. (ALLEGED)
……………………………………………………………..………………………

213 394
4. I would like to express my thanks for everything you have
done for me. (I …SAY … THANKFUL.…)
……………………………………………………………..………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………..…
………………
5. Since the company’s methods were exposed in a newspaper, people
have lost their good opinion of it. (DISREPUTE)
……………………………………………………………..………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
…..…………
C. WRITING PARAGRAPH
Write a paragraph of about 200 words on the following topic:
On June 1
st
, 2019, in the first enrollment, secondary school of the
University of Foreign Languages (National University of Hanoi) recruited
only 100 indicators, but more than 3,000 registration documents. Why did too
many parents want their children to study at this school?
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG LẦN THỨ XV
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN LÊ QUÝ ĐÔN - ĐIỆN BIÊN
ĐÁP ÁN ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT
Môn: Tiếng Anh khối 10
PART I. LISTENING
Listen 1. (14 points )
1.
Badminton
court
2. Judo
(classes)
3. (a) diet 4. caffeine 5. low -
calorie
6. £ 700.00 7. Fridays
214 394
Listen 2. (16 points)
1. the
emotion/
magical
2. (the)
technical
elements
3. predicting/
movements
4. privilege 5. (very)
trusting
6. 7 months
Listen 3. (10 points)
1. T 2. T 3. T 4. T 5. F
Listen 4. (10 points)
1. B 2. C 3. C 4. A 5. A
PART II: LEXICO – GRAMMAR
A. (20 points)
1. C 2. B 3. B 4. C 5. A 6. C 7. A 8. C 9. B 10. C
11. A 12. C 13. D 14. C 15. D 16. C 17. C 18. D 19. A 20. D
B. (10 points)
1. misgivings 2. prohibitive 3.
consumerism
4. shopaholic 5. overtaken
6. notoriety 7. undoubtedly 8. troublesome 9. futuristic 10. accentuate
C. (10 points)
Mistakes Correction
1. estimation - Line: 2 estimates
2. millions of - Line: 2 million
3. the man - Line: 5 man
4. has - Line: 5 has been
5. dated - Line: 8 date

215 394
6. Norway - Line: 10 Norwegian
7. a sport - Line: 12 being a sport
8. is - Line: 14 are
9. accessible - Line: 15 inaccessible
10. spectra - Line: 16 spectrum
PART III: READING
A. (10 points)
1. D 2. C 3. A 4. D 5. C
6. A 7. A 8. B 9. A 10. A
B. (10 points)
1. break 2. give 3. importance 4. allowance(s)
5. former/
first
6. it 7. into 8. hold 9. set 10. making
C. (10 points)
1. D 2. C 3. C 4. B 5. B
6. A 7. A 8. C 9. D 10. A
D. (20 points)
1. vii 2. ii 3. viii 4. iv 5. v
6.
qualification
paper
7. academic
success
8. undesirable 9. standards
10. Gatsby’s
view
E. (10 points)
1. B 2. A 3. C 4. B 5. A
216 394
6. D 7. C 8. B 9. D 10. A
PART IV: WRITING
A. (10 points)
1. The boy was on the point of crying when he was reprimanded
by his mother.
2. When it comes to economy, Vietnam has been developing very
quickly over the last 20 years.
3. He is a dab hand at cooking spaghetti.
4. The students deserved severe punishment for their rebellious behaviors.
5. There’s no one available at such short notice to take her class.
B. (10 points)
1. Don't (you wish you had learnt) swim?
2. I' m seldom able to afford to spend my holiday abroad.
3. The two young men are alleged to have introduced a virus
into the computer system.
4. I ('d like to) say (how) thankful (I am for everything you have done for
me.)
5. Since the company’s methods were exposed in a newspaper, it has fallen
into dispute.
C. (30 points)
1. Organization: (5 points)
+ Three parts (topic sentence, supporting sentences, concluding sentence)
+ Topic sentence: consists of topic and controlling idea.
+ Concluding sentence: summarizes the main supporting ideas / restates the
topic sentence and gives personal opinion.

217 394
2. Content, coherence and cohesion: (15 points)
+ Supporting sentences: support directly the main idea stated in the topic
sentence and provide logical, persuasive examples.
+ Use of transition signals appropriately.
3. Language use and accuracy: (10 points)
+ Variety of structures, expressions and good use of vocabulary
+ No spelling or grammar mistakes.
!"#$!%&
!"#!$%&'
()'*+,-.%/(%0*,
'()*&+,
!
"#$%&'(')*+,*+))-'.,./',0(1)23&4
-./0123415678912/3-55:3.1
!"#
#$ %!&'(
)
# ! * !
+,!
!-#
.
!
# /
218 394
-9.:52;1.
%' <' =' >'
*' ?' @'
5%!!%%
&&6&%7!& %
'(')*+,,./'!28&4
0 !!12 .%
0 !. $
"0 ! $ $ .!!
&0 3!.$! 4
)0 5. $! 4!
+0 6.! %!
-0 # !.$! 7! 0
80 #.$%
! .%0
-9.:52;1.2
%' <' =' >'
*' ?' @' A'
9!!%:%!
%!2*4 242;&4
0 ! * *.!! !
! 0
0 5 0
"0 9 *.!!%!$
$!! 0
&0 !:! !0
)0 ! %%: 0
%' <' =' >' *'
3:!<#
%= >?@ (:>A#
2,#1742;&4
0 ; !!.!! $0
10 $! . %!0
30 !! !0
0 .! !. .%
219 394
0 .!. 7 !. 0
0 ; !!$ !! ! $0
10 ! ! 30! !!
0! 0 !! 0
"0 ; ! ! .
0
10 !..%.!$ 0 30 0
0! 0 0 $ 0
&0 6!.;%!$! <
10 $ 30!.!
0!. 0!
!
)0 ;! !!! .0
10 30$ !.9
0!! 0 ! =
%' <' =' >' *'
'(#)*&+,
16/3-5%' 0--21/01;-.4-.+0.:21/0:/B12/C3/21:60BD:5E35/01F-DD-;35G
215/15612')<&+,
0 ! !$!% ! 0
10 .! 30. 0. 0.
0 4 $ !.!!! 0
10 30 0 0 %
"0 >! ! ?5 *6 ' 0
10 !! 30! !! 0! 0!
&0 >.!*$>4 =! !0
10!! 30
0 !% 0!
)0 5!.!$! $ 0
10 30 0 0
+0 !: $ !% !!7! 0
10 30 0! 0
-0 1.! $%! $$ 7 0
10 30 0 0
80 !!!!*0
10.% 30.%
0.% 0.%

220 394
@0 >!. !! !7!. $
! 0
10 4!30 !4! 0 4! 0!4
A0 !!!%!!0
10 ! 30 0 0 !
0 B%*$. !! .! 0
10 30 ! 0 0
0 3C4
!<D;!C D0
10 E *> !% 300>.
0,%0!. 0E *> !
"0 E!!.!F!4 !
.!0!! !. !!4
10 $% 30 0 0%
&0 1.$$ !!!4 $ 0
10 ! 30!% 0 0
)0 ! !0
10! 30 0! 0!
+0 ! 4% $% 0
10 30$
0!( 0!
-0 > $ <>4! .$ 0
10! 30% 0 0
80 !:$. 4! !!.0
10 .! 30! 0! 0$!
@0 !7 *!. !!!! .0
101!!! 301!$ 0,! 0>!
A0 !. .$ 0
10! 30! 0 0
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
%%' %<' %=' %>' %*'
%?' %@' %A' %H' <&'
16/3-5<'I3DD1:60G:+;3/0/016-..16/F-.J-F/01;-.4235B.:6E1/2')%&+,
0 ;!. $ $ 0I(
0 ! ..!!$ 0(
"0 #! !! !! 0KK
&0 %.!F%!0;! 0K
)0 1$% G ..!! 0(

221 394
+0 $! !$ ! 0I(K,
-0 3! G!! 0> !G%
$!0(I(
80 6! H!*.4!!
$ !! 0(
@0 ;!!!!.! !$ 0 ),
A0 .! ! ! : .* G $
(0L(,
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
16/3-5='01+:22:G1B1D-;6-5/:352(J32/:E12'541.D351/01J32/:E12:54
+.-M341/016-..16/3-5235/012+:612B1D-;')%&+,
! !$*
%!!0>.
$ $ ! 7* !.*
! !!0I ! !!
$.!!!
! ! $
006#7* *!
$ !$ !!
7 ! $: 4'! !
.! ! ! 7
$! !01 !$$
! ! $*! $:
$ $ !! !.
$!. 01
! ! !! $!
** $0,
! ! ! $
$.$! 0,*
!.* !
!!!$!0
B
B
B"
B&
B)
B+
B-
B8
B@
BA
B
B
B"
B&
B)
(N:J+D1!
A0 BJK
222 394
3512 32/:E1:546-..16/3-5 351 32/:E1:546-..16/3-5
%' ?'
<' @'
=' A'
>' H'
*' %&'
'(K)?&+,
16/3-5%'1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:54416341;0360:52;1.)OOO-.K,B12/C3/2
1:60G:+'P.3/17-9.:52;1.356-..12+-5435G59JB1.14B-N12')&,0:2B1154-51:2
:51N:J+D1')%&+,
12345,'3'3)3) 6,323'%)3 7& ! 7,%)5)83'-
B*!!$I*7 !!!A
0;!.*!7% % 0 !
. 1/*.! B* ! ! *
.!! (
. *.!.!! 0
1*>"!$ . *$>.
$! >!!.&0 ;*>. ! !$
.
!.!) 0
B ;*! *. !$*.!I1
;10> %%+ $.!4 .%
* .! * $% 0 $ .!
! - !. 0 , 7 !* !
!*:!!$$=$
0>
8 0! ! !@ !.
*!.*$!!>!!!!=!*!.
. $ !.06 A
!7 *$>%.>4$B0
0 10 307 0 0%
0 10 30! 0 0
"0 10 30 0 0. !
&0 10 30$ 0 0
)0 10 30 0! 0%
+0 10$ 30 . 0 0$
-0 107 30. 0 ! 0.!!
80 10! 30 07 0
@0 10 30 0 0
A010 30 0 0
223 394
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
16/3-5<'1:4/01+:22:G1:54C3DD351:60G:+;3/0(293/:BD1;-.4')%&+,
; ! A
-F
.! ! #
06 .! !$
$!.! 4$!0> ! L
!.! !!$. ! !
! * .! ! .0 E .! .!
. !"
$!! *$ ..$0;!
! !!0
, ! $.! :&!.
$! . . ) 0 ; .
+
.!0
B*!.*.0,.!.!- $$
.% !! 018 !!.
!$$! $* @$* ! . !
! $0 > . = $
. .! A
! .% 0
-9.:52;1.2!
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
16/3-5='1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:5460--21/016-..16/:52;1./-1:60-F/01
F-DD-;35GQ912/3-52'P.3/17-9.:52;1.235/01B-N+.-M3414')%&+,
2$ . ! $ !* ! !
F4 * $ A)A* . 0 F $ %
7 0! $ . .
! !. 0#$ !$!66'
66'* ! * .!! .%$ $ ! ! 1
5 ; * ! : !
%!0
3A)A*$"A&A!.! !
*.! $ !!.
! !. .! ! 0
. . $ $7 $ $
*%. ! 0!.
*$ ! !!*!4
$$ %0!! %%! 0

224 394
C!. 0>!! *! !*
!.$ $ . D*0I%B *!
! !* $ ! 0'
$ ! ! . !
!!0C>% 7!. .!D*! 0
2$. $!$ * ! *
.!! !!! !06 !
! $$+ : $$.0+
"08 $AA0
0B !4 7. .!$
. ! . 0 C>!%!. !!
!!. *M! N*D
0B 0C! %!$ *!!
! % ! .! !0D
!!*.!!.$ .* !$50
5 66' F ! !
0 ' * *$$. 0C5$.
.!$ ! %!!
! !!.% .! .*D! 0;
!!! ! =! *
! ! F .!! $ 0
: ! .. . $ ) @A $ AA*
.!! %! 0
CF! $ $
!* !% B F% $! 6 F. I !
6 I
!.!*D505 *! . .$0 !
. . $ ! $ $ .
0505 !%$!F .
. 7$0 !
6 !! 70
%' M1.:DDO;0:/2-./-F+36/9.132+:35/14-F/01F9/9.11FF16/2-FGD-B:D;:.J35GR
10 30
0 0
$
!
$
<' P0:/32/032+:22:G1R
10 30.
0 $ 0.
=' .'K:M341DM3DD129GG12/2/0:/35F9/9.1J-.1F--46-9D4B13J+-./1435/--5G
-5G'1/035E2/0121J1:29.126-9D4B1 S'
10 7 30 7 0 7 07
>' 01J:35+-35/-F+:.:G.:+0=32/-4126.3B1SSSSSS'
10 ! !!
30 ! !!0
0 ! !!!.
0 :! !!
225 394
*' 01J:35+-35/-F+:.:G.:+0*32/-4126.3B1SSSSSS'
10 $.
30 ! $.
0 ! : $.
0 ! $.
?' P074-12/01;.3/1.:44/0135F-.J:/3-5352Q9:.1B.:6E1/235+:.:G.:+0*R
10 $ !( .! !
30 $ * !! ! ! (* !
!
0 $ !. (!
0 $ !.. ! =!! .
@' 5+:.:G.:+0@O;0360+-35/32.'1DM3DD1J:E35GR
10 !! F
30 ! %
0 =
0 %
A' -;;-9D47-94126.3B1/01K.'1J:5T2://3/941/-;:.42035:R
10 $ 30 0 ! 0
H' 5+:.:G.:+0<OU51G:/14V326D-212/35J1:535G/-____S'
10 $ 30 0 0
%&' 5+:.:G.:+0@OU41+D1/14V6-9D4B1.1+D:614B7;0360-F/01F-DD-;35GR
10 30 0 0
-9.:52;1.2
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
16/3-5>'1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:544-/01/:2E2/0:/F-DD-;')<&+,
UI.11B31V:.E1/35G
' >!8@A .! > !.0%*;
0F02$ !.! %$ .
0! *! !!7!.
$ 02 *!. . 0
2!! . $%!!.! .! !$=?
.* 7* !( !
$ 01 * $$!$!...!.
7 *! 01!1;
I=@A*! +8$ @A""0+&8$
0
' 6!F02 !$.
!*!.* ! $ . %. C$ %D! !
! 0 24 ! . !
. ! * .!!!! *$*!!(*
.!!!7. !$ $ 0

226 394
'$% .

227 394
! ! * $! (
! $ 0>! *! .!
7 01 ! $
! ! *!.*! !70
' '$%.% !! $
! $! $ 0>! !*!
! ! $> $*!
.! 70!1** 1
+AA .! 70;
1*!.*$.1 .!!!
(0;01. .!.%0B. $%
1 * 1 $ $ (
)AA-8AA 0
K' >! * 7!
! ! $ 0 ! ! . %. ! 7 !
$ 0! ..!!6=
.! ! > ! ! . $ $ $
!$! .7. 0O *
!.*!!! $ 7 ! * !
$ $ $% 01 .
!$.6> = $ $ 0.. *
(*!$ $$(
)AA0AAA O;PA0"A!0
(' $%0,$! > !
$ % C !D !$ .! ! !.
%0 ' $ * ! ! $ ! 4
*$! $% ! $*!*
! .$ ! ! $
.!! . $ $ 0
I' 1!! !$ . $%
%. CD0! .! % ! !
( 0>! *!7
!! $*.!!0 $01 $.!!
!! $! !!**!.
! ! $! $ %! 0
3 ! !!!
$* ! . $!0
BA#% 1B ! %
32/-F1:435G2
> .
>> ; =$
>>> 5 $
>9 9? %$
9 1!%
9> '$%
9>> 3$%
228 394
9>>> 1%
>Q
Q
1
5$!!?(
(N:J+D1!16/3-5!
0;3
"0;
)0;'
0;
&0;
8B;#!&!!&%7'
(')*+,*-'-'. !@
?' , *.!$ 7. !!
$0
@' 6!.! $! !$ 0
!!
'$ % $ . ! )A,
0 ! ! $!
.!! ! ($.0
CD !$0! .!! )H,!! !0>
.!! %
$)%&,0
-9.:52;1.2
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
16/3-5 *! -9 :.1 G-35G /- .1:4 :5 :./36D1 :B-9/ :4M1./3235G 35 +9BD36 +D:612' I-.
Q912/3-52%#%&O60--21F.-J/01+1-+D1)#(,'01+1-+D1J:7B160-215')%&+/2,
KW(('(W(R
93)3:;<333='3')
P0360+1.2-52:72/0:/:4M1./3235GR
0$ !4 %
0! !$ <
"0!! <
&0$. <
)0$%:$<
+0 !$.$ <
-0$ <
80 %$<

229 394
@0 % !%$ !<
A0 .%
' (W(OD-..74.3M1.
!$ !! $ !=!$%.
: 0>4 $! !*: $!
! !0>4! !*!!!
%0#
7 $ !
. !.0!
$ $ ! ' .!
!*$> !%$ !0,!.!*
! 4 ! R .!
>4
!!0
' X((O:B35.1;
6%!! *>%!0!4 $ >
! %$ %( $ .! %.*$
!! :$03 !$
! .! $ * !
! .% . ! 0 6! *
$!*$> $% !
!47!L# $ 0
> . ! >$=0. !<
' K(O:;71.
$! *>% 0>4!
4!$ 0>4 ! *!!>%.!4
0;! $$9 0>
!$ !%* ! .!
034 ! ! $
! $ . $ 0 1
.! .4 $ .
* 9
.! !
0
K' KO5/1.3-.K123G51.
> $ * $%0>
!; .!!.4
! . ! 0 >4 ! ! S 4
=* $ > 7 ! .! ! S4 !
!$ ! !

230 394
$ 0, *!!* 7. !4
!!%! $ 0;$>4 !!0
(' ((O/9415/
>.% ! !.4!*$ $
! 0>%! !0>!%
. !.$.!! *.$7
!06!.%$ <>!% **
% ! 0>.!$ % !
$ *$!4 !..!! ! 0 !
%!$!0
-9.:52;1.2
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
W'P)*&+-35/2,
:./%!I353201:60-F/01F-DD-;35G215/15612352960:;:7/0:/3/J1:52/012:J1:2
/01215/1561B1F-.13/')%&+,
%' >. 4 !!. !$. 0
B0
<' I want you to apologize to him for being rude immediately
E0
=' 6!!. !. .
$0! !0
>' >4.!!H*>!%.!0
'0
*' 1!!$! $.! 0
!!$0
:./<!1;.3/1/0121215/156129235G/01;-.4235'-9J92/5-/60:5G1/01
G3M15;-.42')%&+,
%' / !!
/ 0
<' ! ! %! $
HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤM
231 394
! ! 0
=' ! 0 )K,
50
&0 >4%..!*$>4 !0 I(
> $>4 !0
*' >. $!.!>. ),
>. .!>. 0
:./=! :.:G.:+0;.3/35G)=&+,
!&&:!&#:#?
!, %:C
E !.!)A8A. .0
YZW[
\K]
!"#
$!%&
T!- !U- VA@
WXU Y!Z[U "
'()*&+-35/2,
16/3-5%!)%>+-35/2#<'&+-35/2^6-..16/:52;1.,
-9.61!(6/9:D12/_W-D># https://ieltsmaterial.com/ielts-listening-recent-
actual-tests- volume-4-ebook-audio/
0 0;#% "0 &0$\
)0! +0 $ -0
16/3-5<!)%?+-35/2#<'&+-35/2^6-..16/:52;1.,
-9.61!I(.:6/36112/2(N/.:+:./<_12/=
0! 0 7 "0! &0
)0 +0% -0.%4 ! 80+]
16/3-5=!)%&+-35/2#<'&+-35/2^6-..16/:52;1.,
-9.61!++1.#5/1.J143:/1-D9/3-59J9D:/3M1
12/2
%'I <' =' >' *'I
16/3-5>!)%&+-35/2#<'&+-35/2^6-..16/:52;1.,
-9.61!I(.:6/36112/2D92O12/*_+:./>

232 394
%' <' =' >' *'K
'(#)>&+-35/2,
16/3-5%' 0--21/01;-.4-.+0.:21/0:/B12/C3/21:60BD:5E35/01F-DD-;35G
215/15612')<&+-35/2,
%' <' ='K >'K *'K
?' @' A' H' %&'K
%%'K %<' %=' %>'K %*'
%?'K %@' %A'K %H' <&'
16/3-5<'I3DD1:60G:+;3/0/016-..16/F-.J-F/01;-.4235B.:6E1/2')%&+-35/2,
0 7 0 $ "0 = &0% )0
+0$ -0 80! @0 A0 =$
16/3-5='01+:22:G1B1D-;6-5/:352(J32/:E12'541.D351/01J32/:E12:54
+.-M341/016-..16/3-5235/012+:612B1D-;')%&+-35/2,
3512 32/:E1:546-..16/3-5 351 32/:E1:546-..16/3-5
0 JK +0A JK
0" !JK! -0 JK \
"0& JK 80" JK
&0- JK @0& !JK!
)0@ JK A0) $JK$
'(K)?&+-35/2,
16/3-5%'1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:54416341;0360:52;1.)OOO-.K,B12/C3/2
1:60G:+')%&+-35/2,
-9.61!B`16/3M14M:5614.:6/36112/2#/03.4143/3-5O12/%#+:G1%*
0 03 "01 &01 )0
+0 -01 803 @0 A0
16/3-5<'1:4/01+:22:G1:54C3DD351:60G:+;3/0(293/:BD1;-.4')%&+-35/2,
-9.61!(129D/;-.EB--EO53/>O+:G1<H
0 0 . "0 . &0
)0 !
+0 -0 !\ \ 80 7 @0 . A0 !
16/-5='1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:5460--21/016-..16/:52;1./-1:60-F/01
F-DD-;35GQ912/3-52')%&+-35/2,
-9.61!97a5/b+cd/03D7J+36=&/0e5G>Df5/0g_<&%*O+:G1%%@
%' <'K =' >' *'K
?' @' A' H' %&'
16/3-5>'1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:544-/01/:2E2/0:/F-DD-;')<&+-35/2,
233 394
-9.61!(3J9D:/3-512/2O12/>O+:./%
09>>> 0>>> "09>> &0> )09
+0 $ -0
80!$ @0 A0
$!
16/3-5*'-9:.1G-35G/-.1:4:5:./36D1:B-9/:4M1./3235G35+9BD36+D:612'I-.Q912/3-52
%#%&O60--21F.-J/01+1-+D1)#(,'01+1-+D1J:7B160-215')%&+-35/2,
-9.61!I(12/D92<O12/>O+:./@O+@@
%' <'K =' >' *'
?'( @' A' H'K %&'(
(W!P)*&+-35/2,
:./%!I353201:60-F/01F-DD-;35G215/15612352960:;:7/0:/3/J1:52/012:J1:2
/01215/1561B1F-.13/')%&+,
0 B.=\%.!!. !$.
0 E=!$\ 0
"0 ! ! \ . .!!0
&0 '$.!!*>!%.!0
)0 !!$! $! 0
:./<!1;.3/1/0121215/156129235G/01;-.4235'-9J92/5-/60:5G1/01
G3M15;-.42')%&+,
0 / $0
0 ! . !.!! \ \
! 0
"0 5 . %0
&0 >47! $>4 !0
)0 >. !\!!.!>.
0
:./=!P.3/1:+:.:G.:+0')=&+-35/2,
!&&:!&#:#?
!, %:C
E !.!$)A8A. .0
h/i/3j960kce50G3e 3aJ/l3c:
%' l6m6
o ^Y!_ `[a!a
o 3Za !Xa Ub T*!T !Xa XU ^[_ `[$T
o 3Za c!cWT X_ $T`Z%Z^a
?

234 394
<' 0e//.3a5n
o #!U cUUdT!Wa
o UY!WU *dUa *e`_ `c$_^aU%Z_ dT!
?
=' o4m5G5Gh5/p
o ;W_ a^ WT !T!Xa XU ^a
o ;W_ a^ WT `U V!*!ca
o ;W_ aWT Z!UUc!c
?
>' q3495G
o f_ !Z!a WXT `a
o f_ Y!WU *dUa*^a^a
o f^aT;ZWT %!^ ![!VadU!X(`a!A]
?
*' Gr+0e+O4s96t9O60k50/i
o ;W_ a`U Z^
o !dU!_9Z`U !dU!_
BY !dU!_ ^!c[\ ^a!U b$adU!^a Y WT ]
`c_ $TZ
T ^aY !dU!_Vaa!d_dU!^a Y
o ;W_ a `U !XT *!c*ZU ^`U Wb !U0BYWb !U
^!c[\ ^a!U b$aWT ]`c_$TZ
?
u5G
=&
"
Trường THPT Chuyên Vĩnh
Phúc Đề đề xuất
ĐỀ THI TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG-LỚP 10
Môn: Tiếng anh
Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút
SECTION A: Listening
Part 1: Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS for each answer.

235 394
Which documents could Sam use as proof of her name
Example: passport
1……………..
2……………..
Which could she use as proof of her
address council tax bill
3…………….
phone bill (fixed
line) 4……………
Complete note below
Name of bank? Savings Bank
Open which days?
Monday-
Friday
Opening hours? 5……………….
Where? 6……………….
Free gift? 7……………….
Part 2: Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS for each answer.
Photographing
waterfalls
Hannah took her first waterfall photo when she was (1)..............years old.
She used a camera belong to her (2)…...........to take the photos in the mountains.
She believes that (3)…...........is the best time of the year to photograph waterfalls.
She avoids photographing waterfalls in (4).............weather.
She loves taking photos of water hitting (5)…............below.
In winter, the photographer should avoid treading on any (6)…................that may appear
in a picture.
Hannah likes to take pictures from the (7)................of smaller waterfalls.
Hannah once took a photo of (8)….............in a waterfall.
Part 3: Listen to part of a radio programme about a psychological
condition known as prosopagnosia. Decide whether the statements are
true (T) or false (F). (10 points)
1. The speaker compares face-blindness to the inability to hear.
2. Scientists do not understand how normal people remember faces.
3. The face-blind subjects could not distinguish between the faces or the objects.
4. Some people with this condition are so severely affected that they
cannot recognise members of their own family.

236 394
5. It could help scientists to understand human evolution if they knew more
about face-blindness.
Part 4: Choose the best answer A,B or C
1. Why did Sophie take up translating ?
A. She had studied modern languages as university
B. She sometimes used to translation for friends
C. She enjoyed reading texts in other languages.
2. Which, according Sophie, are the most difficult things to translate?
A. cultural references
B. informal expressions
C. scientific and technical. words
3. Where does Sophie get most of work?
A. directly from official organizations
B. through translation agencies
C. from contacts in private companies
4. What does she say about money?
A. She earns less now than she used to
B. She thinks she pays too much tax
C. She seldom get paid on time
5. Sophie believes that in the future
A. translating will all the done by machines
B. more languages will need to translated
C. translators will have to better trained
SECTION B: Lexico-Grammar
I. Choose the letter A,B,C or D on your answer sheet to indicate the
correct answer to each of the following questions.
1. There has been a lot of surrounding the government’s proposed scheme.
A. controversy B. consent C. conformity D. consequence
2. Our town has a real problem with youth crime, do many other
British towns.
A. so B. nor C. as D. like
3. Warning: anyone caught stealing from these premises will be .
A. advocated B. undermined C. prosecuted D. enforced

237 394
4. The local authorities need to down on illegal parking, in my opinion.
A. hit B. force C. move D. crack
5. If the service isn’t up to standard, I think you have right to complain.
A. all B. each C. much D. every
6. Jim’s tough character and certainly won’t let anyone push him .
A. up B. off C. around D. through
7. The I don’t understand is why Emily lets her boyfriend get away with it.
A. reason B. object C. item D. thing
8. My uncle pulled a few and got me a job in the company where he works.
A. ropes B. strings C. threads D. chords
9. Although she would have preferred to carry on working, my mum her career in order to
have children.
A. devoted B. repealed C. sacrificed D. abolished
10. I find the offer quite , but I think I’d rather study at Oxford.
A. tempting B. desirous C. inclined D. envious
11. I don’t normally like noisy clubs, but I had a sudden to see
what the Blue Parrot was like.
A. force B. motive C. pressure D. impulse
12. Jerry loves snowboarding so much that it’s almost like a drug .
A. passion B. obsession C. addiction D. requirement
13. I don’t want to do the course in applied statistics, but it’s .
A. compulsory B. inevitable C. bound D. indecisive
14. Don’t worry about me – I’m quite to sit here and wait for you to
come back.

238 394
A. ecstatic B. delighted C. joyful D. content
15. When I was pregnant, I often got a sudden for tinned sardines.
A. preference B. craving C. envy D. greed
16. Thank you for thinking of us, but I’m afraid we’re going to have to your kind
invitation.
A. decline B. deny C. condemn D. reject
17. I’ve never seen anyone so to their job as Philip is.
A. eager B. keen C. dedicated D. interested
18. Why do you have such a with model railways?
A. desire B. fascination C. love D. preference
19. I wish you would stop wasting so much time on computer games
and do something a little more .
A. welcome B. enviable C. feasible D. worthwhile
20. Olivia has always to return to the country she was born in.
A. favoured B. yearned C. urged D. inclined
II. Complete these sentences, using the suitable form of the words in brackets.
1. Computers were sold for the first time in the 1950s. (COMMERCE)
2. He was deeply about his late arrival. (APOLOGIZE)
3. Family members discuss problems frankly and find quickly. (SOLVE)
4. There are differences and between Vietnamese and American
cultures. (SIMILARLY)
5. At weekends, early morning phone calls can be so because it is
the time when people sleep late. (STARTLE)

239 394
6. This is only hatred by racial prejudice. (GENERATION)
7. He is not able to read or write; he is a(an) child. (LITERACY)
8. She’s involved in many activities, such as music, sport and
drama. (CURRICULUM)
9. The of this document is wrong! There’s no page 13. (PAGE)
10. The general director was blamed for his of the company’s
business. (HANDLE)
III. The passage below contains 10 mistakes. Find out and correct them.
Even before the turn of the century, movies began to develop in two
major directions: the realistic and the formalistic. Realism and
formalism are merely general, rather than absolute, terms. When using
to suggest a tendency toward either polarity, such labels can be helpful,
but at the end they are still just labels. Few films are exclusive formalist
in style, and fewer yet are completely realist. There is also an important
difference between realism and reality, although this distinct is often
forgotten. Realism is a particular style, where physical reality is the
source of all the raw materials of film, both realistic and formalistic.
Virtually all movie directors go to the photographable world for their
subject matter, but what they do with this material - what they shape
and manipulate it - determines their stylistic emphasis.
Generally speaking, realistic films attempt to reproduce the surface of
concrete reality with a minimum of distortion. In photographing objects
and events, the filmmaker tries to suggest the copiousness of life
himself. Both realist and formalist film directors must select (and hence
emphasize) certain details from the chaotic sprawl of reality. But the
element of selectivity in realistic films is less obvious. Realists, in
short, try to preserve the illusion that their film world is unmanipulated,
an objective mirror of the actual world. Formalists, on the other hand,
make no such pretense. They deliberately stylize and distort their crude
materials so that only the very naive should mistake a manipulated
image of an object or event to the real thing.
SECTION C: Reading comprehension

240 394
I. Choose the correct answer from the four options marked A, B, C,
or D to complete each numbered gap in the following passage.
These days in business, people have to face many challenging
questions when designing and implementing new projects in underdeveloped
areas of the countryside. One issue which has to be faced is whether it is
possible to introduce new technology without destroying the local
environment.
Economic (1) and environment conservation are often seen
as natural enemies. It is unfortunate that in the past this has often been true,
and it has been necessary to choose between (2) the project or protecting
the environment. However, by taking environmental considerations (3) at an early stage in
a project, companies can significantly reduce any impact on local plants and
animals.
For example, in southern Africa, a company called CEL, was asked to
put up 410 km of a power transmission line without disturbing the rare birds
which inhabit that area. The project was carried out with (4) disturbance last
summer. What may surprise many business people is the fact that this
consideration for local wildlife did not in any way (5) down the
project. Indeed, the necessary advance planning (6) with local
knowledge and advanced technology, (7) that the project was actually
completed ahead of schedule. CEL was contracted to finish the job by
October and (8) to do so two months earlier.
CEL is one of those companies which is (9) to the
principle of environmental conservation. Many other companies have yet to
be (10) of the
importance of balancing the needs of people with those of the environment.
However, it may be the only realistic way forward.
1. A. progression B. development C. rise D. increase
2. A. dealing B. leading C. running D. controlling
3. A. severely B. gravely C. seriously D. deeply
4. A. minimal B. bare C. least D. smallest
5. A. slow B. speed C. turn D. hold
6. A. related B. added C. combined D. tied
7. A. led B. meant C. resulted D. caused
8. A. achieved B. managed C. succeeded D. fulfilled
9. A. persuaded B. convicted C. promised D. committed
10. A. urged B. impressed C. argued D. convinced
II. Read the text and fill in each blank with one most suitable word.
It was an unusually dark night. In the middle of 1 enjoyable dream, Jim

241 394
thought he heard his dog 2 loudly. He groaned and glanced at his
clock sleepily. Twelve o'clock the green fluorescent hands of his clock
read. Suddenly,

242 394
Jim heard hushed voices outside his house. He immediately became alert and
jumped
3
of bed. As his parents had gone on a holiday. Jim was alone
at home. He decided to investigate who was outside.
As he walked towards his bedroom door, Jim, however, became afraid. He wondered
4
could be outside his house in the dead of
5
night. His
imagination began to run wild. He pictured in his mind armed robbers who
were waiting to break into the house. He even imagined supernatural forces
such as ghosts and werewolves. In the end, Jim changed his
6
about
going out of the house.
7
, he locked his bedroom door and crawled under his bed. With his
heart in his mouth, he waited for the intruders. Suddenly, there was a clicking
sound and he heard the front door open.
"Jim?" said a familiar
8
. It was his father! Jim felt weak with relief. His
parents must 9 returned home earlier than he had expected. 10 a fright they
had given him!
III. Read the passage and then choose the correct option (A, B, C, or D)
for each question below.
1) Science plays a crucial role in identifying problems related to how natural
systems function and deteriorate, particularly when they are affected by an
external factor. In turn, scientific findings shape the policies introduced to
protect such systems where necessary. Experts are frequently called upon by
politicians to provide evidence which can be used to make scientifically
sound, or at least scientifically justifiable policy decisions.
2) Issues arise as there are frequent disagreements between experts over the
way data is gathered and interpreted. An example of the former is the first
scientific evidence of a hole in the ozone layer by the British Antarctic
Survey. (A) The findings were at first greeted by the scientific community
with scepticism, as the British Antarctic Survey was not yet an established
scientific community. (B) Moreover, it was generally believed that satellites
would have picked up such ozone losses if they were indeed occurring. (C) It
was not until the methodology of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center was
reviewed that it became apparent that data had been overlooked. (D)
3) With regards to the latter, controversy between scientists may arise where
data analysis appears to support one policy over another. In 1991, the World
Resource Institute (WRI) published estimates of net emissions and sinks of
greenhouse gases for a number of countries, including India. The report
provoked criticisms among Indian scientists who argued that the figures had
failed to take some significant factors into account, leading to overestimated
emission values. The WRI was accused of blaming less economically
developed countries for global warming; a stance which, if accepted, could

243 394
impede industrialisation and sustain, even widen, the wealth gap.

244 394
4) Problems regarding the scientific method are well documented and it is
widely accepted by the scientific community that, however consistent
scientists are in their procedures, the results born under different
circumstances can vary markedly. A number of factors influence research,
among them the organisation of a laboratory, the influence of prevailing
theories, financial constraints and the peer review process. Consequently,
scientists tend to believe they are not in a position to bear universal truths but
to reveal tendencies.
5) However, this is countered by two factors. Firstly, certain scientific
institutions wish to maintain a degree of status as ‘bearers of truth’. Further,
policy makers uphold this understanding by requesting scientific certainties
in order to legitimise their policy decisions. According to a number of authors
who have documented this process, decision makers do not necessarily try to
obtain all the information which is or could be made available regarding an
issue. Rather, they select that information which is necessary to fulfil their
goals, information termed as ‘half-knowledge’. Attempts to underplay
transboundary issues such as water provision and pollution are cases in point.
Politicians clearly cannot pretend that certain data do not exist if they are
well-known in scientific communities or national borders, but some
discretion is evident, especially where there is controversy and uncertainty.
6) It is important to note that policies regarding scientific issues are
influenced in no small part by societal factors. These include the relative
importance of certain environmental issues, the degree of trust in the
institutions conducting the research, and not least the social standing of those
affected by the issue. In other words, environmental problems are in many
ways socially constructed according to the prevailing cultural, economic and
political conditions within a society. It has been suggested, for example, that
contemporary 'post-materialist' Western societies pay greater attention to
'quality' - including environmental quality – than 'quantity'. This theory does
not necessarily assume that people of low-income countries have no interest
in environmental protection, as the example of the Chipko movement in India
clearly demonstrates, but demonstrates that the way a resource is valued
varies widely among different communities.
7) Finally, it cannot be denied that the ‘issue of the day’ changes constantly.
One issue becomes more or less urgent than another, based on current events.
Concurrently, new issues enter the political agenda. It has been noted that it
often takes a 'policy entrepreneur', someone who dedicates time, energy and
financial resources to a certain issue, to raise its profile. Furthermore,
whether an issue is taken up by political, environmental or media groups,
depends very much on the degree to which it suits their particular agenda, not

245 394
to mention budget.
1. With reference to paragraph 1, which of the following pieces of research
would be NOT be relevant to this article?
A. the effect of climate change on weather patterns in Africa

246 394
B. whether or not low level radiation increases the risk of cancer
C. how acid rain impacts species within a lake ecosystem
D. a comparison of the species present in two areas of woodland
2. What is the purpose of the example of ozone data given in paragraph 2?
A. to show that NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center used unreliable
methods of gathering scientific data
B. to show how data gathering methods and the status of scientists may
affect the way data is regarded
C. to prove that it is wrong to dismiss evidence which comes from
a non- established source
D. to show how NASA and the British Antarctic Survey disagreed over the
correct way to gather ozone data.
3. Where in paragraph 2 does this sentence best fit?
This was because of the way their computers had been programmed to
discard any readings which appeared anomalous.
A. (A) B. (B) C. (C) D. (D)
4. Paragraph 3 gives an example of a dispute over…
A. which country was most responsible for producing greenhouse gases
B. the pollution caused by multinational companies in India.
C. how statistics were interpreted and presented.
D. erroneous data which resulted from a poorly-funded experiment.
5. In paragraph 5, ‘this’ refers to…
A. the scientific method and its inherent problems.
B. the belief that scientists cannot reveal universal truths.
C. the variation in scientific results under different circumstances.
D. the list of factors which influence scientific research.
6. What is meant by this sentence?
‘Further, policy makers uphold this understanding by requesting scientific
certainties in order to legitimise their policy decisions.’
A. Politicians when seeking evidence for policy-making, do not understand
the fact that scientists are unable to act as ‘bearers of truth’.
B. Politicians consider the scientific research that supports their policies as
more legitimate than other research.
C. Scientific institutions encourage politicians to use them for policy-
making in order to improve their status.
D. Politicians, when seeking evidence for policy-making, encourage the
belief that scientists can produce incontestable facts.
7. Which sentence best sums up the ideas in paragraph 4?
A. Scientists are aware that their work cannot present incontrovertible facts.
B. If scientists were more consistent, they could create more reliable evidence.

247 394
C. Variations in how research is conducted often affect its validity.
D. Scientists spend more time documenting problems than conducting research.
8. Why are ‘transboundary issues such as water provision and pollution’
referred to in paragraph 5?
A. to illustrate situations in which politicians pretend that certain data
does not exist
B. to illustrate situations in which incorrect information is given by
scientific institutions keen to maintain their status.
C. to illustrate situations in which politicians are selectiive with regards
to what data they gather
D. to illustrate situations in which policy makers request scientists to
present them with scientific certainties, even though none exist.
9. What can be inferred about the Chipko movement?
A. It was an example of how people in low-income countries have little
interest in environmental protection.
B. It was an example of how different people within a community
valued a resource differently.
C. It was an example of how people in a low-income community showed
interest in protecting the environment.
D. It was an example of how people in a low-income community valued
quantity over quality.
10. Which of the following arguments is NOT presented in paragraph 7?
A. An issue only get political or media attention if someone with a high
profile is supporting it.
B. Politicians are only interested in environmental issues if it benefits them.
C. Issues don’t get public attention unless a particular person advocates it strongly.
D. Issues may be overlooked if there are other significant events happening
at the time.
IV. Read the passage and do the tasks that follow.
RISING SEA
Paragraph 1 - INCREASED
TEMPERATURES
The average air temperature at the surface of the earth has risen this century,
as has the temperature of ocean surface waters. Because water expands as it
heats, a warmer ocean means higher sea levels. We cannot say definitely that
the temperature rises are due to the greenhouse effect; the heating may be
part of a ‘natural’ variability over a long time - scale that we have not yet
recognized in our short 100 years of recording. However, assuming the build
up of greenhouse gases is responsible, and that the warming will continue,

248 394
scientists – and inhabitants of low-lying coastal areas – would like to know
the extent of future sea level rises.

249 394
Paragraph 2
Calculating this is not easy. Models used for the purpose have treated the
ocean as passive, stationary and one -dimensional. Scientists have assumed
that heat simply diffused into the sea from the atmosphere. Using basic
physical laws, they then predict how much a known volume of water would
expand for a given increase in temperature. But the oceans are not one -dime
nsional, and recent work by oceanographers, using a new model which takes
into account a number of subtle facets of the sea –including vast and complex
ocean currents –suggests that the rise in sea level may be less than some
earlier estimates had predicted.
Paragraph 3
An international forum on climate change, in 1986, produced figures for
likely sea- level rises of 20 cms and 1.4 m, corresponding to atmospheric
temperature increases of 1.5 and 4.5C respectively. Some scientists estimate
that the ocean warming resulting from those temperature increases by the
year 2050 would raise the sea level by between 10 cms and 40 cms. This
model only takes into account the temperature effect on the oceans; it does
not consider changes in sea level brought about by the melting of ice sheets
and glaciers, and changes in groundwater storage. When we add on estimates
of these, we arrive at figures for total sea-level rises of 15 cm and 70 cm
respectively.
Paragraph 4
It’s not easy trying to model accurately the enormous complexities of the
ever- changing oceans, with their great volume, massive currents and
sensitively to the influence of land masses and the atmosphere. For example,
consider how heat enters the ocean. Does it just ‘diffuse’ from the warmer air
vertically into the water, and heat only the surface layer of the sea? (Warm
water is less dense than cold, so it would not spread downwards).
Conventional models of sea-level rise have considered that this the only
method, but measurements have shown that the rate of heat transfer into the
ocean by vertical diffusion is far lower in practice than the figures that many
modelers have adopted.
Paragraph 5
Much of the early work, for simplicity, ignored the fact that water in the
oceans moves in three dimensions. By movement, of course, scientists don’t
mean waves, which are too small individually to consider, but rather
movement of vast volumes of water in huge currents. To understand the
importance of this, we now need to consider another process – advection.
Imagine smoke rising from a chimney. On a still day it will slowly spread out
in all directions by means of diffusion. With a strong directional wind,

250 394
however, it will all shift downwind, this process is advection
– the transport of properties (notably heat and salinity in the ocean) by the
movement of bodies of air or water, rather than by conduction or diffusion.
Paragraph 6

251 394
Massive ocean currents called gyres do the moving. These currents have far
more capacity to store heat than does the atmosphere. Indeed, just the top 3m
of the ocean contains more heat than the whole of the atmosphere. The origin
of gyres lies in the fact that more heat from the Sun reaches the Equator than
the Poles, and naturally heat tends to move from the former to the latter.
Warm air rises at the Equator, and draws more air beneath it in the form of
winds (the “Trade Winds”) that, together with other air movements, provide
the main force driving the ocean currents.
Paragraph 7
Water itself is heated at the Equator and moves poleward, twisted by the
Earth’s rotation and affected by the positions of the continents. The resultant
broadly circular movements between about 10 and 40 North and South are
clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. They flow towards the east at mid
latitudes in the equatorial region. They then flow towards the Poles, along the
eastern sides of continents, as warm currents. When two different masses of
water meet, one will move beneath the other, depending on their relative
densities in the subduction process.The densities are determined by
temperature and salinity. the convergence of water of different densities from
the Equator and the Poles deep in the oceans causes continuous subduction.
This means that water moves vertically as well as horizontally. Cold water
from the Poles travels as depth – it is denser than warm water –until it
emerges at the surface in another part of the world in the form of a cold
current.
Paragraph 8
HOW THE GREEN HOUSE EFFECT WILL CHANGE OCEAN
TEMPERATURES
Ocean currents, in three dimensions, form a giant ‘conveyor belt’,
distributing heat from the thin surface layer into the interior of the oceans and
around the globe. Water may take decades to circulate in these 3-D gyres in
the lop kilometer of the ocean, and centuries in the deep water. With the
increased atmospheric temperatures due to the greenhouse effect, the oceans
conveyor belt will carry more heat into the interior. This subduction moves
heat around far more effectively than simple diffusion. Because warm water
expands more than cold when it is heated, scientists had presumed that the
sea level would rise unevenly around the globe. It is now believed that these
inequalities cannot persist, as winds will act to continuously spread out the
water expansion. Of course, of global warming changes the strength and
distribution of the winds, then this ‘evening-out’ process may not occur, and
the sea level could rise more in some areas than others.
Questions 1 - 6

252 394
There are 8 paragraphs numbered 1 – 8 in the Reading Passage. The first
paragraph and the last paragraph have been given headings.
From the list below numbered A – I, choose a suitable heading for the
remaining 6 paragraphs.

253 394
Write your answers A – I, in the spaces numbered 1 –6 on the answer sheet.
There are more headings than paragraphs, so you will not use all the
headings. List of headings
A THE GYRE PRINCIPLE
B THE GREENHOUSE
EFFECT C
HOW
OCEAN WATERS MOVE D
STATISTICAL EVIDENCE
E THE ADVECTION PRINCIPLE
F DIFFUSION VERSUS ADVECTION
G FIGURING THE SEA LEVEL
CHANGES H ESTIMATED
FIGURES
I THE DIFFUSION MODEL
1. Paragraph 2
2. Paragraph 3
3. Paragraph 4
4. Paragraph 5
5. Paragraph 6
6. Paragraph 7
Questions 7–10 Do the following statements agree with the information
given in the reading passage? In boxes 7-10 in your answer sheet write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts with the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
7. The surface layer of the oceans is warmed by the atmosphere.
8. Advection of water changes heat and salt levels.
9. A gyre holds less heat than there is in the atmosphere.
10. The process of subduction depends on the water density.
V. Read some book reviews about earth exploration. For questions 1-10,
choose from the reviews (A-F). The reviews may be chosen more than
one.
In which review is the following mentioned?
1. Someone who left almost no stone unturned around the world.
2. The surprising anonymity of someone.
3. Disappointment that flora and other fauna are not mentioned.

254 394
4. A book that is physically difficult to carry around with you.

255 394
5. Some details are inaccurate in this book.
6. Information written like an old-fashioned diary.
7. Text that adds something to the images.
8. A collaboration that produced great results.
9. A book that covers all of nature’s seasons.
10. A wide variety of subject matter.
A. A Complete Guide to Life in a Cold Climate by Richard Sale
This book is packed with information and deserves to be the ultimate
Arctic wildlife for a long time to come. It begins well, with an introduction
to Arctic geology, climate and habitats, an overview of all the people living
and working in the region. The bulk of the book is an extensive field guide
to Arctic birds and mammals, with distribution maps and information on
confusing species. Its scope is broad and generous, but I have a few niggles.
It should really include Arctic plants, fish and invertebrates. This would
have doubled the size of the book and made it unwieldy and impractical, but
it’s fair to say that the title is misleading.
But I’m being picky here, and these minor shortcomings don’t detract from
the overall value of the book.
B. Burton Holmes Travelogues
Burton Holmes was the greatest traveler not just of his own time but
perhaps of all time. A pretty big claim, but there’s evidence to back it up.
Over a 60-year period, Holmes visited nearly every country on the planet,
photographed all he saw, and invented the term ‘travelogue’. His pictures are
stunning, both as social history and as art. Holmes photographed everything;
the dead on battle-fields; the running of bulls in Spain; a mule train in Dead
Valley. A sequence of Vesuvius erupting in 1906 includes a short of a
woman under ash-strewn sky that is positively apocalyptic, but Holmes’
work wasn’t restricted to the large canvas – he was as capable of capturing
an intimate portrait of a chicken vendor in a Bangkok market as he was
revealing the vastness and intricacy of the construction of the Panama Canal.

256 394
C. No More Beyond by Simon Nasht
In Simon Nasht’s brilliant biography of Sir Hubert Wilkins, he says
that his subject isn’t like other great explorers, primarily because most of us
have never heard of him. He had no lust for fame, instead being driven by a
thirst that led him to remote environments and places that cried out for
exploration, rather than towards the popular challenges so desired by
newspaper editors of the day. Nasht couldn’t believe “a man could achieve
so much and yet be so little remembered”. In 1917 Wilkin was under the
command of veteran polar explorer and photographer Frank Hurley in the
Australian Flying Corps. Their mutual interests were vital to development of
aerial photography as an integral part of modern geography.
D. Farmland Wildlife by James McCallum
As a refuge for wildlife, British farmland has had a bad press in recent years.
Fortunately, the artist’s beautiful visual journey through the seasons
presented in this book reveals that there is still an abundance of wildlife if
you know where to look for it and what to look for. McCallum shuns detailed
portraiture in favour of sketches capturing the spirit of his subjects – and
hooray for that. If I need precise anatomical detail, I can look at a
photograph. But if I want to grasp how to stoat roll an egg, how a male
whitethroat makes his fluttering display-flights or how long-tailed tits work
together to build their nests, then I need something more – and McCallum is
stunningly good at translating these complex movements and behaviours onto
the page. His simple explanatory captions – taken from his field notebook –
are a bonus.
E. Troubled Waters by Sarah Lazarus
Sometimes it seems as though the size of book on whales is led by the
size of the subject matter. This, however, is a small, readable book. There
are no detailed species accounts and the text is almost entirely devoted to the
threats that whales and dolphins face, such as chemical and noise pollution,
ship strikes and entanglement in fishing nets. A careful read reveals factual
errors but, on the whole, these do not affect the thoughtful and concise
discussion. It is notoriously difficult to get to the bottom of the whaling
issue, and here Lazarus struggles a bit. The International Whaling
Commission comes in for a lot of criticism, which

257 394
would perhaps have been better directed at the three of its members who have
chosen not to abide by the spirit of its conservation decisions.
F. The High Lowland by Derek Ratcliffe
For some, the south of Scotland is the plainer and less charismatic
sibling of the breathtaking Highlands and the rugged West Coast. But it’s
every bit as wild as those famed areas, but with a gentler appeal. This book
describes an unexpected Eden, a place whose heart pulses to a different beat.
This is an epic piece of writing, its subject matter converted in a manner
more akin to the journals of a Victorian chronicler than a modern natural
history book. Derek Ratcliffe’s recordings of the natural goings-on in this
lonely land spanned 50 years. His intimacy is apparent on every page.
Everything is catalogued and described in meticulous detail, and few
questions are left unanswered. It’s a great pity that Derek did not live to see
his life’s work in print. This is a book for everyone, but it’s a huge volume
that you couldn’t take with you on holiday unless you’ve got a pretty hefty
rucksack and a strong back.
SECTION D: WRITING
1. For questions 1-5, complete the second sentence so that it has a similar
meaning to the first sentence, using the word given. Do not change the
word given. You must use between three and six words, including the word
given.
1. If there is a fire, you must not use the lift to leave the building. (EVENT)
, you must not use the lift to leave the building.
2. Jack has such a vivid imagination, it is possible that he invented the whole
story. (MADE)
Jack has such a vivid imagination that he might the whole story.
3. She hated publicity so much that she never gave any interviews to the
media. (HER)
Such of publicity that she never
gave any interviews to the media
4. I just didn’t know what to say.
(LOST) I was
.
5. Tim looks nothing like his father.
(TAKE) Tim his
father.

258 394
2. For questions 6-10, complete the second sentence so that it has a
similar meaning to the first sentence, using the words given.
6. You can use it as long as you like, and it will not wear
out. No matter
7. John didn’t celebrate a party until he received the offer of promotion in
writing. It was
8. Please check for damage before signing the delivery note.
Do not
9. I write to Alice almost every day.
Hardly
10. All books have something to teach you.
Every
3. In about 140 words, write a paragraph about the changes that
information technology bring to your study.

259 394
HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤM
SECTION A: Listening 50 points
Part 1:
1. driving license
2. benefit book
3. insurance certificate
4. electric
ity bill 5.
9.30-
3.30
6. ground floor
7. no/
nothing
Part 2
1. nearly 13/12
2. teacher
3. the spring
4. sunny
5. the rocks
6. snow
7. side
8. a
huge
fish Part
3:
1. F
2. T
3. F
4. T
5. T
Part 4:
1.
C
2.
A
3.
B
4.
A
5.
B

260 394
SECTION B: Lexico-Grammar 40 points
I. Choose the letter A,B,C or D on your answer sheet to indicate the
correct answer to each of the following questions.20 points

261 394
1. A 3. C 5. D 7. D 9. C 11. D 13. A 15. B 17. C 19. D
2. C 4. D 6. C 8. B 10. A 12. C 14. D 16. A 18. B 20. B
II. Complete these sentences, using the suitable form of the words in
brackets. 10 points
0" )4 + 1 34
4 4 / 2% 0
III. The passage below contains 10 mistakes. Find out and correct
them. 10 points
1. using -> used 6. what -> how
2. at -> in 7. himself -> itself
3. exclusive -> exclusively 8. crude -> raw
4. distinct -> distinction 9. should -> would
5. where -> whereas/while 10. to -> for
SECTION C: Reading comprehension 60 points
I. Choose the correct answer from the four options marked A, B, C,
or D to complete each numbered gap in the following passage. 10
points
0& ) ( +( / 1& 2& 35 05
II. Read the text and fill in each blank with one most suitable
word. 10 points
0
/
!6!
17
)
2$
3$
+
08
III. Read the passage and then choose the correct option (A, B, C, or D)
for each question below. 10 points
05 & )5 +& /5 1( 2 3 0(

262 394
IV. Read the passage and do the tasks that follow. 20 points
09 : )7 ; +( / 1<( 2- 3= 0-
V. Read some book reviews about earth exploration. For questions 1-10,
choose from the reviews (A-F). The reviews may be chosen more than
one.10 points
1. B 2. C 3. A 4. F 5. E 6. F 7. D 8. C 9. D 10. B
SECTION D: WRITING 50 points
1. For questions 1-5, complete the second sentence so that it has a similar
meaning to the first sentence, using the word given. Do not change the
word given. You must use between three and six words, including the word
given.
10 points
1. In the event of a fire, you must not use the lift to leave the building.
2. Jack has such a vivid imagination that he might have made up the whole story.
3. Such was her hatred/dislike of publicity that she never gave any
interviews to the media.
4. I was lost for words.
5. Tim doesn’t take after his father.
2. For questions 6-10, complete the second sentence so that it has a similar
meaning to the first sentence, using the words given. 10 points
6. No matter how long you use it, it will not wear out.
7. It was not until John received the offer of promotion in writing
that he celebrated a party.
8. Do not sign the delivery note without checking for damage.
9. Hardly does a day pass without my writing to him.
10. Every book has something to teach you.

263 394
3. In about 140 words, write a paragraph about the changes that
information technology bring to your study. 30 points
1. Convincing ideas: 6 points
2. Good organization: 6 points
3. Logical cohesion: 6 points
4. Accurate grammar and spelling: 6 points
5. Wide range of vocabulary and clear expression: 6
points TRANSCRIPT
Part 1:

264 394

265 394

266 394
.

267 394

268 394
)
Presenter: (>%4""$$
!:(%,%
Professor: :8?""!4
-,>?!"4'>@7?A
?$"!B-
4"?!-
4?
$"!?!?C!
=!@.!??!
4!D"!-D
!!$"DB7
!?!"
7$4?!"
B$-!""!!
$%E

269 394
Part 4:

270 394

271 394
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG LẦN THỨ XII ĐỀ THI MÔN
TIẾNG ANH
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN TỈNH HÀ GIANG LỚP 10
ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT (Đề này có 15 trang, gồm
15 câu)
PART I- LISTENING (50 POINTS)
272 394
Question 1. Listen and fill the missing words in the blanks. Write NO
MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER for each answer.
(14 points)
THE URBAN LANDSCAPE
Two areas of focus:
1. the effect of vegetation in the urban climate
2. ways of planning our (1) better
Large-scale impact of trees:
11.they can make cities more or less (2)
12.in summer they can make cities cooler.
13.they can make inland cities more (3)
Local impact of tress:
1. they can make local areas
- more (4)
- cooler
- more humid
- less windy
- less dangerous
Comparing tress and buildings
Temperature regulation:
2. trees (5) water through their leaves
3. building surfaces may reach high temperatures
Wind force:
1. tall buildings cause more wind at ground level
2. trees (6) the wind force
Noise:
1. trees have a small effect on traffic noise
2. (7) noise passes through trees
Important points to consider:
1. trees require a lot of sunlight, water and space to grow.
Your answers
273 394
1
.
………………
.
2
.
………………
.
3
.
………………
.
4
.
………………
.
5
.
………………
.
6
.
………………
.
7
.
………………
.
Question 2. You will hear an interview with a man called Daren
Howarth, who works as a carbon coach. Listen and complete the
sentences. (16 points)
The Carbon Coach
Daren says that a carbon coach works full-time as a (1) with
various clients.
Before becoming a carbon coach, Daren trained to be an (2) .
When assessing a family's carbon footprint, Daren looks first at their (3)
.
Daren uses what's called a (4) to see how much electricity things use.
Daren points out that the government will help pay for roof insulation.
Daren feels that using (5) of the old type is the worst waste of
energy he sees.
Daren helped to reduce a band's carbon footprint at their concerts as well as on
its CDs.
Daren mentions a new type of green home called an (6) .
The new green home uses both the sun and (7) to produce electricity.
Daren suggests buying a (8) which gives more information about the
new green home..
Your answers
1
.
………………
.
2
.
………………
.
3
.
………………
.
4
.
………………
.
5
.
………………
.
6
.
………………
.
7
.
………………
.
8
.
………………
.
Question 3. You will hear a woman asking a tutor for more information
about a Media Studies course at a university. Listen and decide whether
the following statements are true (T) or false (F). (10 points)
1. Louise worked at a radio station for about 4 years.
2. Louise wants to do a Masters because employers like post-
graduate qualifications.
3. It will take 4 years to do the Masters part-time rather than the modular route.
4. To join the course, Louis must have research experience and a completed thesis

274 394

275 394
5. Students can find the details on funding on the university website.
Your answers
1.
……………
2.
……………
3.
……………
4.
……………
5.
……………
Question 4. You will hear an interview with the television actress Donna
Denton. Choose the best answer (A, B, or C) for each of the following
questions. (10 points)
1. As a child, Donna started going to dancing classes because .
A. her mother persuaded her to
B. they were relatively expensive
C. she wanted to be with friends
2. What did Donna do to get a place at Knightswell Stage School?
A. She took part in a musical show.
B. She got her parents to pay in advance.
C. She gave a demonstration of her skills.
3. Donna believes that she won the school singing competition because .
A. she had learnt to be less nervous when performing.
B. she had chosen to perform her favourite song.
C. she had been practicing one particular song for years.
4. What does Donna say about her first parts on television?
A. A private teacher helped her find them.
B. They were useful in developing her career.
C. It was easy enough for students to get them.
5. When talking about near future, Donna says that .
A. she has agreed to record a music CD soon.
B. she has accepted an unexpected invitation.
C. she has had to make a difficult choice.
Your answers
1.
……………
2.
……………
3.
……………
4.
……………
5.
……………
PART II – LEXICO AND GRAMMAR (40 POINTS)
Question 1. Choose the option (A, B, C or D) that best completes each of
the following sentences. (20 points)
1. One problem for teacher is that each student has his/ her own needs.
A. separate B. divided C. individual D. distinctive
2. They talked for three days before finally to a decision.

276 394
A. reaching B. coming C. bringing D. arriving
3. The workers decided to until their demands were met.
A. stand up B. lie behind C. sit in D. sleep out
4. I must take this watch to be repaired; it over twenty
minutes a day.
A. increases B. progresses C. accelerates D. gains
5. John has painting since he retired.
A. taken up B. taken off C. taken over D. take in
6. stay the night if it’s too difficult to get home.
A. At all costs B. By all means C. In all D. On the whole
7. Robert and his wife to my house for tea yesterday evening.
A. came round B. came about C. came down D. came away
8. Each of the guests a bunch of flowers.
A. are given B. is given C. were given D. give
9. To everyone’s surprise, Mr. Brown at the Trade Union meeting.
A. turned in B. turned over C. turned up D. turned round
10. The company directors asked the government to
in the dispute and prevent a strike.
A. intervene B. interact C. intercept D. interpose
11. Don’t worry. We the report by 11 o’clock.
A. will be finishing B. will have finished
C. are going to finish D. finish
12. the ball, we would have won the game.
A. Should Thomson catch B. Were Thomson to catch
C. If Thomson catches D. Had Thomson caught
13. Fred was pleased to the college.
A. admitting B. to admit C. being admitted D. to be admitted
14. My decision to leave university after a year is one I now regret.
A. harshly B. painfully C. keenly D. heavily
15. I enjoy going to school by bike. But on rainy days, I to going by bus.
A. prefer B. would rather C. would like D. resort
16. He spoke to me as if he my father.
A. is B. would be C. were D. had been
17. She pleaded him not to take her child .
A. to – off B. with – away C. at – off D. about – out
18. My mother goes to church every Sunday morning.

277 394
A. Þ – Þ B. the – every C. the – the D. a – Þ
19. It took us quite a long time to get here. It was journey.
A. 3 hour B. a 3-hours C. a 3-hour D. 3-hours
20. Mary bought hat yesterday.
A. a red big plastic hat B. a big red plastic hat
C. a plastic big red hat D. a bit plastic red hat
Your answers:
1. …………….. 2. ……………. 3. ……………. 4. …………….
5. ……………. 6. ……………. 7. ……………. 8. …………….
9. …………….. 10. ……………. 11. ……………. 12. …………….
13. ……………. 14. ……………. 15. ……………. 16. …………….
17. ……………. 18. ……………. 19. ……………. 20. …………….
Question 2. Use the word given in capitals at the end of each sentence to
form a word that fits in the space in the sentence. There is an example.
(10 points) E
Your answers:
1. …………. 2. …………. 3. …………. 4. …………. 5. ………….
6. …………. 7. …………. 8. …………. 9. …………. 10. ………….
Question 3. Each line of the following passage contains ONE mistake.
Identify and correct them. Write your answer in the space given. (10
points)
Sport in society
xample:
0.
admirable
0. Mr. Brown has a great many qualities.
1. Deaths caused by reckless driving are .
2. The coat was in shades of blue and green.
3. Most tinned fruits contain amounts of sugar.
4. He fell off the bike, but his were not serious.
5. In electronics, we learn to repair appliances.
6. Trung's sense of humor him from other students.
7. People use first-aid to ease the victim's pain and .
8. The scenery was really beautiful.
9. You don't respond well to positive , which is
only made to help you.
10. as it may seem, mammoths were alive only five
thousand years ago.
ADMIRE
AVOID
PATTERN
EXCESS
INJURE
HOUSE
DISTINCT
ANXIOUS
BREATHE
CRITIC
CREDIBLE

278 394
The position of sport in today’s society has changed out of all
recognization. People no longer seem to think about sport as ‘just a game’ –
to be watched or played for the sake of enjoyment. Instead, it has become
large business worldwide. It has become accepted practice for heading
companies to provide sponsorship. TV companies pay large sums of money
to screen important matches. The result has been huge financial awards for
athletes, some of them are now very wealthy, particularly top football
players, golfers and tennis players. In addition, it is not usual for some
athletes to receive large fees on top of their salary, for advertising products
or making individual appearances. A trend towards shorter working hours
mean that people generally tend to have more free time, both to watch and
to take part in sport activity.
Your answers:
Mistake Correction Mistake Correction
1.
………………… …………………
6.
………………… …………………
2.
………………… …………………
7.
………………… …………………
3.
………………… …………………
8.
………………… …………………
4.
………………… …………………
9.
………………… …………………
5.
………………… …………………
10.
………………… …………………
PART III – READING (60 POINTS)
Question 1. Choose the best option (A, B, C or D) that best fits the blank
space in the following passage. (10 points)
Proof that silence is golden for studying
The combination of music and study has long been a source of
disagreement between adults and children. Parents and teachers alike
maintain that silence is important when learning, (1) youngsters insist that
their favourite sounds help them concentrate.
Now a study shows the grown-ups have been right all along.
Psychologists in Florida tested how fast students wrote essays with and
without music in the (2)
. They found that the sounds (3) progress down by about
sixty words per hour. 'This demonstrates clearly that it is difficult to (4) with listening and
writing at the same time,' said Dr Sarah Randall. She also (5) to
conclusion that it is a myth that instrumental music is less distracting that
vocals. 'All types of music had the same (6) ,' she said in her report. 'One's
ability

279 394
to pay attention and write fluently is likely to be (7) by both
vocal and instrumental music,' she added.
Dr Randall claimed the research demonstrated that the idea that music
could improve performance was wrong. 'Writing an essay is a complex (8) . You are (9)
information and putting it in order. An additional stimulus
in the form of music is bound to distract. But music is not the only distractor.
What is (10)
worrying is that more and more teenagers are studying in front of
the television.
1. A. whereas B. unlike C. besides D. despite
2.
A. setting B. background C. surrounding D. circumstances
3.
A. slowed B. reduced C. lowered D. decreased
4.
A. manage B. support C. cope D. stand
5.
A. reached B. drew C. arrived D. came
6.
A. affect B. effect C. consequence D. result
7.
A. disturbed B. interfered C. bothered D. shocked
8.
A. project B. concern C. scheme D. task
9.
A. recalling B. memorizing C. remembering D. organizing
10.
A. partly B. largely C. particularly D. mainly
Your answers:
1. …………. 2. …………. 3. …………. 4. …………. 5. ………….
6. …………. 7. …………. 8. …………. 9. …………. 10. ………….
Question 2. Read the text below and think of the word which best fits
each space. Use only ONE word in each space. (10 points)
SHARKS
For anyone who wants either to film or study great white sharks, Australian
expert, Rodney Fox, is the first contact. Fox knows exactly (1) the sharks
will be at different times of the year; and can even predict (2) they will
behave around blood, divers and other sharks. He understands them as well as
anyone else alive. In fact, he’s lucky to be alive; a ‘great white’ once (3)
to bite him
in half.
Three decades (4) this near-fatal attack, Fox still carries the
physical scars, but feels no hate for his attacker. Instead he organizes
three or four trips (5)
year to bring scientists and photographers to the kingdom of the great

280 394
white shark. The main aim of these trips is to improve people’s
understanding of an animal (6) evil reputation has become an excuse for
killing it.
Great white sharks are not as amusing as dolphins and seals, (7)
their role in the ocean is critical. They kill off sick
animals, helping to prevent the spread of disease and to maintain the balance
in the ocean’s food chains. Fox feels a responsibility to act (8) a
guardian of great white sharks. (9) the
scientists, film makers and photographers can communicate their sense of
wonder (10) other people, he is confident that understanding will
replace hatred.
Your answers:
1. …………. 2. …………. 3. …………. 4. …………. 5. ………….
6. …………. 7. …………. 8. …………. 9. …………. 10. ………….
Question 3. Read the passage and choose the option (A, B,C or D)
that best answer each of the following questions. (10 points)
Printmaking is the generic term for a number of processes, of which
woodcut and engraving are two prime examples. Prints are made by pressing
a sheet of paper (or other material) against an image-bearing surface to which
ink has been applied. When the paper is removed, the image adheres to it, but
in reverse.
The woodcut had been used in China from the fifth century A.D. for
applying patterns to textiles. The process was not introduced into Europe
until the fourteenth century, first for textile decoration and then for printing
on paper. Woodcuts are created by a relief process; first, the artist takes a
block of wood, which has been sawed parallel to the grain, covers it with a
white ground, and then draws the image in ink. The background is carved
away, leaving the design area slightly raised. The woodblock is inked, and
the ink adheres to the raised image. It is then transferred to damp paper either
by hand or with a printing press.
Engraving, which grew out of the goldsmith's art, originated in Germany
and northern Italy in the middle of the fifteenth century. It is an intaglio
process (from Italian intagliare, "to carve"). The image is incised into a
highly polished metal plate, usually copper, with a cutting instrument, or
burin. The artist inks the plate and wipes it clean so that some ink remains in
the incised grooves. An impression is made on damp paper in a printing
press, with sufficient pressure being applied so that the paper picks up the
ink.
Both woodcut and engraving have distinctive characteristics. Engraving
lends itself to subtle modeling and shading through the use of fine lines.

281 394
Hatching and cross-hatching determine the degree of light and shade in a
print. Woodcuts tend to

282 394
be more linear, with sharper contrasts between light and dark. Printmaking is
well suited to the production of multiple images. A set of multiples is called
an edition. Both methods can yield several hundred good-quality prints
before the original block or plate begins to show signs of wear. Mass
production of prints in the sixteenth century made images available, at a
lower cost, to a much broader public than before.
1. What does the passage mainly discuss?
A. The origins of textile decoration
B. The characteristics of good-quality prints
C. Two types of printmaking
D. Types of paper used in printmaking
2. The word "prime" in the first paragraph is closest in meaning to .
A. principal B. complex C. general D. recent
3. The author's purposes in paragraph 2 is to describe .
A. the woodcuts found in China in the fifth century
B. the use of woodcuts in the textile industry
C. the process involved in creating a woodcut
D. the introduction of woodcuts to Europe
4. The word "incised" in paragraph 3 is closest in meaning to .
A. burned B. cut C. framed D. baked
5. Which of the following terms is defined in the passage?
A. "patterns" (paragraph 2) B. "grain" (paragraph 2)
C. "burin" (paragraph 3) D. "grooves" (paragraph 3)
6. According to the passage, all of the following are true about engraving
EXCEPT that it .
A. developed from the art of the goldsmiths
B. requires that the paper be cut with a burin
C. originated in the fifteenth century
D. involves carving into a metal plate
7. The word "yield" in paragraph 4 is closest in meaning to .
A. imitate B. produce C. revise D. contrast
8. According to the passage, what do woodcut and engraving have in common?
A. Their designs are slightly raised.
B. They achieve contrast through hatching and cross-hatching.
C. They were first used in Europe.
D. They allow multiple copies to be produced from one original.

List of Headings
i. The connection between health-care and other human rights
ii. The development of market-based health systems.
iii. The role of the state in health-care
iv. A problem shared by every economically developed country
v. The impact of recent change
vi. The views of the medical establishment
vii. The end of an illusion
viii. Sustainable economic development
283 394
9. According to the author, what made it possible for members of the
general public to own prints in the sixteenth century?
A. Prints could be made at low cost.
B. The quality of paper and ink had improved.
C. Many people became involved in the printmaking industry.
D. Decreased demand for prints kept prices affordable.
10. According to the passage, all of the following are true about prints
EXCEPT that they .
A. can be reproduced on materials other than paper
B. are created from a reversed image
C. show variations between light and dark shades
D. require a printing press
Your answers:
1. …………. 2. …………. 3. …………. 4. …………. 5. ………….
6. …………. 7. …………. 8. …………. 9. …………. 10. ………….
Question 4. Read the passage and do the tasks that follow.
Task 1. Choose the correct heading for section A-E from the list of
headings below. Write the correct number i-viii in the space provided.
(10 points)
1. Section A ………………….
2. Section B ………………….
3. Section C ………………….
4. Section D ………………….
5. Section E ………………….

284 394
The Problem of Scarce Resources
Section A
The problem of how health-care resources should be allocated or
apportioned, so that they are distributed in both the most just and most
efficient way, is not a new one. Every health system in an economically
developed society is faced with the need to decide (either formally or
informally) what proportion of the community’s total resources should be
spent on health-care; how resources are to be apportioned; what diseases and
disabilities and which forms of treatment are to be given priority; which
members of the community are to be given special consideration in respect of
their health needs; and which forms of treatment are the most cost-effective.
Section B
What is new is that, from the 1950s onwards, there have been certain general
changes in outlook about the finitude of resources as a whole and of health-
care resources in particular, as well as more specific changes regarding the
clientele of health-care resources and the cost to the community of those
resources. Thus, in the 1950s and 1960s, there emerged an awareness in
Western societies that resources for the provision of fossil fuel energy were
finite and exhaustible and that the capacity of nature or the environment to
sustain economic development and population was also finite. In other words,
we became aware of the obvious fact that there were ‘limits to growth’. The
new consciousness that there were also severe limits to health-care resources
was part of this general revelation of the obvious. Looking back, it now
seems quite incredible that in the national health systems that emerged in
many countries in the years immediately after the 1939-45 World War, it was
assumed without question that all the basic health needs of any community
could be satisfied, at least in principle; the ‘invisible hand’ of economic
progress would provide.
Section C
However, at exactly the same time as this new realization of the finite
character of health-care resources was sinking in, an awareness of a contrary
kind was developing in Western societies: that people have a basic right to
health-care as a necessary condition of a proper human life. Like

285 394
education, political and legal

286 394
processes and institutions, public order, communication, transport and money
supply, health-care came to be seen as one of the fundamental social facilities
necessary for people to exercise their other rights as autonomous human
beings. People are not in a position to exercise personal liberty and to be self-
determining if they are poverty-stricken, or deprived of basic education, or do
not live within a context of law and order. In the same way, basic health-care
is a condition of the exercise of autonomy.
Section D
Although the language of ‘rights’ sometimes leads to confusion, by the late
1970s it was recognized in most societies that people have a right to health-
care (though there has been considerable resistance in the United Sates to the
idea that there is a formal right to health-care). It is also accepted that this
right generates an obligation or duty for the state to ensure that adequate
health-care resources are provided out of the public purse. The state has no
obligation to provide a health-care system itself, but to ensure that such a
system is provided. Put another way, basic health-care is now recognized as a
‘public good’, rather than a ‘private good’ that one is expected to buy for
oneself. As the 1976 declaration of the World Health Organisation put it:
‘The enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of health is one of the
fundamental rights of every human being without distinction of race, religion,
political belief, economic or social condition’. As has just been remarked, in
a liberal society basic health is seen as one of the indispensable conditions for
the exercise of personal autonomy.
Section E
Just at the time when it became obvious that health-care resources could not
possibly meet the demands being made upon them, people were demanding
that their fundamental right to health-care be satisfied by the state. The
second set of more specific changes that have led to the present concern
about the distribution of health- care resources stems from the dramatic rise
in health costs in most OECD countries, accompanied by large-scale
demographic and social changes which have meant, to take one example, that
elderly people are now major (and relatively very expensive) consumers of
health-care resources. Thus in OECD countries as a whole, health costs
increased from 3.8% of GDP in 1960 to 7% of GDP in 1980, and it has been
predicted that the proportion of health costs to GDP will continue to increase.
(In the US the current figure is about 12% of GDP, and in Australia about
7.8% of GDP.)

287 394
As a consequence, during the 1980s a kind of doomsday scenario (analogous
to similar doomsday extrapolations about energy needs and fossil fuels or
about population increases) was projected by health administrators,
economists and politicians. In this scenario, ever-rising health costs were
matched against static or declining resources.
Task 2. Decide if the following statements are True (T), False (F) or Not
given (NG) according to the information in the passage. (10 points)
6. Personal liberty and independence have never been regarded as directly
linked to health-care.
7. Health-care came to be seen as a right at about the same time that the
limits of health-care resources became evident.
8. In OECD countries population changes have had an impact on health-care
costs in recent years.
9. OECD governments have consistently underestimated the level of
health-care provision needed.
10. In most economically developed countries the elderly will have to make
special provision for their health-care in the future.
Your answers:
6. …………. 7. …………. 8. …………. 9. …………. 10. ………….
Question 5. You are going to read an article in which four people
comment on a book they have read recently. Choose from the people A-
D to answer the questions that follow. The people may be chosen more
than once. (10 points)
A. Kerry: Sundance by Teresa Wilson
I really don't know why this book is so popular. I mean, I suppose it is going
to appeal to young girls who want danger and romance, but I found this book
really tedious. For a start, the characters were really unconvincing. The
author went out of her way to add lots of details about the characters, but I
found these details really pointless. I thought that some of the facts she
presented about the main characters would become significant in some way
later in the novel, but they didn't. They were just worthless bits of
information. I also was disappointed that, although this book is meant to be
about kids at high school, the writer seems to have no recollection at all about
what it's like to be 17. The main character thought and acted like a 32-year

288 394
old. It just wasn't believable. I'm not saying Teresa Wilson is a bad writer.
She can obviously string words together and come up with a story that is
appealing to a large number of people, but she lacks anything original. There
is no flair. It just uses the same sort of language as you can see in many other
mediocre novels.
B. Liz: Wild Ways by Margery Emerson
I have to say that I won't forget this book for a long time. I was hooked from
the very first chapter. The devastating story affected me so much that I don't
know if I'll ever feel the same again. I was close to tears on several occasions.
I've got images in my brain now that I don't think will ever leave me. It's
incredibly well-researched and, although it is fiction, is based on shocking
real-life events. I learned an awful lot about things that went on that I never
knew before. Margaret Emerson has a brilliant way with words and I really
felt real empathy towards the characters, although I was sometimes irritated
by the choices they made. However, the parallel story, the part that is set in
the present, is not quite so good. I found myself just flicking through that part
so that I could get back to 1940s Paris.
C. Imogen: Orchid by Henry Rathbone
This is a delightful novel full of wonderful imagery, a paints a remarkable
picture of life in a distant time and a far-away place. If you're looking to learn
about Eastern culture in great detail, then this is probably not the book for
you, as the writer skims over most of the more complicated aspects of the
country's etiquette. The historical aspects are also not covered in much depth.
However, I wonder whether this was the writer's intention. By doing this, he
symbolizes the superficiality of the girl's life. She, like the book, is beautiful
and eager to please, but remains too distant from us, the readers, to teach us
much. Although I loved the book and read it in one sitting, the ending was a
bit of a disappointment. A story which involves so much turmoil, in a place
where the future is uncertain, should not have a happy-ever-after fairy-tale
ending.
D. Hannah: High Hills by Mary Holland
I read this book for a literature class. I know it's a classic, and I did try to like
it, but I just didn't get into it. I kept persevering, hoping that I'd start to enjoy

289 394
it, but no such

290 394
luck. The famous scene out on the moors was definitely the best bit of the
book, but even that I found ridiculous when it is clearly supposed to be
passionate. As I approached the end of the book, I figured there must be some
kind of moral to the story, something that I would learn from the experience
of trudging through seven hundred long pages, but there was nothing
worthwhile. I don't know why the literary world sees this book as such a
masterpiece. The characters are portrayed as being intelligent, but they do
such stupid things! And as for it being a love story - marrying someone you
don't love and then being abused by them - that doesn't spell love to me.
Which person reads a book which…
1. was set in an Oriental country?
2. finished in an unrealistic way?
3. had characters that the reader could sympathize with?
4. is well-known and was written a long time ago?
5. contained two stories?
6. was not set in the past?
7. made the reader cry?
8. had unbelievable characters?
9. contains nothing new in the way of writing?
10. has an attractive but shallow heroine?
Your answers:
1. …………. 2. …………. 3. …………. 4. …………. 5. ………….
6. …………. 7. …………. 8. …………. 9. …………. 10. ………….
PART IV – WRITING (50 POINTS)
Question 1. Complete the second sentence so that it has a similar
meaning to the first sentence, using the words given. (10 points)
1. Martin may not be very well but she still manages to enjoy life.
Martin’s
poor……………………………………………………………………………
…
2. The Pacific Ocean is on average deeper than the
Atlantic. The average
………………………………………………………………………………
3. The fire led to the setting up of a public
enquiry. As a
……………………………………………………………………………………

291 394
4. Vitamin intake and intelligence are not connected.
There is ……………………………………………………………………………
5. The only reason the party was a success was that a famous film star
attended. Had it
…………………………………………………………………………………
… Question 2. For each of the sentences below, write a new sentence as
similar as possible in meaning to the original one, using the word
given. DO NOT CHANGE the word given. (10 points)
1. A rise in temperature in the next century seems likely. (CHANCE)
………………………………………………………………………………………
……
2. You must accept the fact that she has left you. (RESIGN)
………………………………………………………………………………………
……
3. They arrived at the station with only a minute to spare. (NICK)
………………………………………………………………………………………
……
4. They sent him to prison for three years. (SENTENCED)
………………………………………………………………………………………
……
5. I don’t intend to tell you my plans. (INTENTION)
………………………………………………………………………………………
……
Question 3. Write a paragraph (120-150 words) on the following topic.
(30 points)
‘Books are the best source of knowledge’
To what extent do you agree or disagree with this statement? Give
example and explanation to justify your viewpoint.
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG LẦN THỨ XII HƯỚNG
DẪN CHẤM
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN TỈNH HÀ GIANG MÔN: TIẾNG
ANH, LỚP 10
ĐỀ THI ĐÈ XUẤT
TOTAL MARK: 200 POINTS
PART I- LISTENING (50 POINTS)

292 394
Question 1. You will hear part of a talk about dolls. Fill the missing
information into the blanks. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS
for each blank. (14 points)
* 2.0 points for each correct answer.
1. environment/cities 2. Windy 3. Humid 4. Shady 5. Evaporate
6. filter/reduce/decrease
7. Low frequency
Question 2. On a travel programme, you will hear a man, Jeremy Clark,
reporting from Mapé, a tropical island where people go on holiday.
Listen and complete the sentences. (16 points)
* 2.0 points for each correct answer.
1. consultant 2. Ecologist 3. Bills 4. Carbon meter
5. light bulbs 6. Earthship 7. (the) wind (power) 8. handbook
Question 3. You will hear a woman asking a tutor for more information
about a Media Studies course at a university. Listen and decide whether
the following statements are true (T) or false (F). (10 points)
* 2.0 points for each correct answer.
1. F 2. T 3. F 4. F 5. T
Question 4. You will hear an interview with the television actress Donna
Denton. Choose the best answer (A, B, or C) for each of the following
questions. (10 points)
* 2.0 points for each correct answer.
1. B 2. C 3. A 4. B 5. C
PART II – LEXICO AND GRAMMAR (40 POINTS)
Question 1. Choose the option (A, B, C or D) that best complete the
following sentences. (20 points)
* 1.0 point for each correct answer.
1. C 2. B 3. C 4. C
5. A 6. B 7. A 8. B
9. C 10. A 11. B 12. D
13. D 14. A 15. D 16. C
17. B 18. A 19. C 20. B
Question 2. Use the word given in capitals at the end of each sentence to
form a word that fits in the space in the sentence. (10 points)
* 1.0 points for each correct answer.
1. unavoidable 2. patterned 3. excessive 4. injuries
5. household 6. distinguishes 7. anxiety 8. breathtakingly
9. criticism 10. incredible
293 394
Question 3. Each line of the following passage contains ONE mistake.
Identify and correct them. Write your answer in the space given. (10
points)
* 1.0 point for each correct answer.
Mistake Correction Mistake Correction
1. recognization recognition 6. them whom
2. about of 7. usual unusual
3. large big 8. individual personal
4. heading leading 9. mean means
5. awards rewards 10. sport sporting
PART III – READING (60 POINTS)
Question 1. Choose the best option (A, B, C or D) that best fits the blank
space in the following passage. (10 points)
*1.0 point for each correct answer.
1. A 2. B 3. A 4. C 5. D
6. B 7. A 8. D 9. A 10. C
Question 2. Read the text below and think of the word which best fits
each space. Use only ONE word in each space. (10 points)
*1.0 point for each correct answer.
1. where 2. how 3. seemed 4. after 5. a/per/one
6. whose 7. but 8. as 9. If 10. like
Question 3. Read the passage and choose the option (A, B,C or D) that
best answer each of the following questions. (10 points)
*1.0 point for each correct answer.
1. C 2. A 3. C 4. B 5. C
6. D 7. B 8. D 9. A 10. A
Question 4. Read the passage and do the tasks that follow. (20 points)
Task 1. Choose the correct heading for section A-E from the list of
headings below.
* 2.0 points for each correct answer.
1. iv 2. viii 3. i 4. iii 5. v
Task 2. Decide if the following statements are True (T), False (F) or Not
given (NG) according to the information in the passage.

294 394
* 2.0 points for each correct answer.
6. F 7. T 8. T 9. NG 10. NG
Question 5. You are going to read an article in which four people
comment on a book they have read recently. Choose from the people A-
D to answer the questions that follow. The people may be chosen more
than once. (10 points)
* 1.0 points for each correct answer.
1. C 2. C 3. B 4. D 5. B
6. A 7. B 8. A 9. A 10. C
PART IV – WRITING (50 POINTS)
* Lưu ý: Các cách giải khác hướng dẫn chấm, giám khảo cân nhắc, nếu
đúng cho điểm tối đa theo thang điểm đã định.
Question 1. Complete the second sentence so that it has a similar
meaning to the first sentence, using the words given. (10 points)
* 2.0 points for each correct answer.
1. health doesn’t prevent her from enjoying life.
2. depth of the Pacific Ocean is much greater than that of the Atlantic.
3. result of the fire, a public enquiry was set up.
4. no connection between vitamin intake and intelligence.
5. not been for the attendance of a famous film star, the part would not
have been successful/would not have succeeded.
Question 2. For each of the sentences below, write a new sentence as
similar as possible in meaning to the original one, using the word given.
DO NOT CHANGE the word given. (10 points)
* 2.0 points for each correct answer.
1. There is a chance that the temperature in the next century may rise.
2. You must resign yourself to the fact that she has left you.
3. They arrived at the station in the nick of time.
4. He was sentenced three-year imprisonment.
5. I have no intention of telling you my plans.
Question 3. Write a paragraph (120-150 words) on the following topic.
(30 points)
No. Criteria for judgment Mark
1 Task completion 4.0

295 394
- Consist of three parts: topic sentence, supporting
sentences and concluding sentence.
- Length: only 5 % less or more than the required
number of words is acceptable.
2 Organization 6.0
- Topic sentence is clearly stated.
- Present the right form of a paragraph.
- The ideas are well-organized and developed with
unity, cohesion and coherence.
3 Language use 8.0
- Use wide range of vocabulary and structures.
- Convey precise meanings with appropriate use of
vocabulary and grammatical structures.
- Use appropriate linking words or connectors.
4 Content 8.0
- Provide relevant and convincing ideas, supported
by specific examples and/or reasonable
justification.
5 Punctuation and spelling 4.0
TOTAL 30 POINTS
TAPESCRIPT
Question 1.
Good day, ladies and gentlemen. I have been asked today to talk to you about
the urban landscape. There are two major areas that I will focus on in my
talk: how vegetation can
have a significant effect on urban climate, and how we can better plan our
cities using trees to provide a more comfortable environment for us to live in.
Trees can have a significant impact on our cities. They can make a city, as a
whole, a bit less windy or a bit more windy, if that's what you want. They can
make it a bit cooler if it's a hot summer day in an Australian city, or they can
make it a bit more humid if it's a dry inland city. On the local scale - that is,
in particular areas within the city - trees can make the local area more shady,
cooler, more humid and much

296 394
less windy. In fact trees and planting of various kinds can be used to make
city streets actually less dangerous in particular areas. How do trees do all
that, you ask?
Well, the main difference between a tree and a building is a tree has got an
internal mechanism to keep the temperature regulated. It evaporates water
through its leaves and that means that the temperature of the leaves is never
very far from our own body temperature. The temperature of a building
surface on a hot sunny day can easily be twenty degrees more than our
temperature. Trees, on the other hand, remain cooler than buildings because
they sweat. This means that they can humidify the air and cool it - a property
which can be exploited to improve the local climate.
Trees can also help break the force of winds. The reason that high buildings
make it windier at ground level is that, as the wind goes higher and higher, it
goes faster and faster. When the wind hits the building, it has to go
somewhere. Some of it goes over the top and some goes around the sides of
the building, forcing those high level winds down to ground level.
That doesn't happen when you have trees. Trees filter the wind and
considerably reduce it, preventing those very large strong gusts that you so
often find around tall buildings.
Another problem in built-up areas is that traffic noise is intensified by tall
buildings. By planting a belt of trees at the side of the road, you can make
things a little quieter, but much of the vehicle noise still goes through the
trees. Trees can also help reduce the amount of noise in the surroundings,
although the effect is not as large as people like to think. Low-frequency
noise, in particular, just goes through the trees as though they aren't there.
Although trees can significantly improve the local climate, they do however
take up a lot of space. There are root systems to consider and branches
blocking windows and so on. It may therefore be difficult to fit trees into the
local landscape. There is not a great deal you can do if you have what we call
a street canyon - a whole set of high-rises enclosed in a narrow street. Trees
need water to grow. They also need some sunlight to grow and you need
room to put them. If you have the chance of knocking buildings down and
replacing them, then suddenly you can start looking at different ways to
design the streets and to introduce ...

297 394
Question 2.
Interviewer: Tonight my guest is Daren Howarth who works as a carbon
coach. What exactly does that mean Daren?
Daren Howarth: Well, most people know about global warming and would
like to do something to reduce the amount of carbon they send out into the
atmosphere, but they don't always know the best way of doing this. What I do
as a carbon coach is give them advice about how to achieve environmentally
friendly living. I'm now a full-time consultant, and my clients include both
companies and private individuals.
Interviewer: What made you decide to become a carbon coach?
Daren Howarth: Well it all started about fifteen years ago. I'd always been
interested in energy-saving and the environment and I trained as an ecologist.
At that time, people were talking about very technical things like greenhouse
gas emissions, then someone came up with the term 'carbon footprint', which
is much easier for people to understand.
Interviewer: And you can tell ordinary families what their carbon footprint
is, can't you?
Daren Howarth: That's right. I work out how much carbon dioxide the
family's generated over a year; firstly by studying their bills, then finding out
how much waste they produce, how much they use the car, and so on. Adding
together all these figures, I calculate their total carbon footprint in tonnes of
carbon dioxide. Then I take a look around their home and suggest ways of
reducing their carbon footprint.
Interviewer: How do you work out how much carbon each machine around
the house emits?
Daren Howarth: By switching off all the things that use electricity, then
turning each one on one at a time, you can see the amount of energy each one
uses. I use something known as a 'carbon meter' which measures the amount
of electricity being used in the house at any one time. It also shows how
much carbon dioxide this represents.
Interviewer: What's the least energy efficient thing you've seen in homes?
Daren Howarth: I go into so many places where I look in the roof and
there's no insulation, so there's nothing stopping all the heat just going
straight out into the

298 394
outside air. Insulation massively reduces your carbon footprint; it's cheap and
the government will help with the cost of it.
Interviewer: So is that the worst thing?
Daren Howarth: Well, central heating systems can be very inefficient and
people use things like electric knives and mixers which are unnecessary, but
the thing I really can't stand is when people are still using old-fashioned light
bulbs. People can't resist them because they're so cheap, but up to ninety
percent of the energy they produce is lost as heat. If you have one, put it in a
box and smash it up, so no one else can use it.
Interviewer: What other type of clients do you have?
Daren Howarth: We work with both individuals and businesses - and even
some celebrities, such as the band Supergrass. For one of their albums about
three years ago, the band decided to minimise their carbon footprint at their
concerts and then also cut the amount of carbon produced when making a
CD. The carbon footprint for a disc is just a few grams, but a big band like
Supergrass will produce thousands of copies, which means several tonnes of
carbon.
Interviewer: And what are your plans for the future?
Daren Howarth: I'm working hard on introducing a really green type of
home in this country known as an Earthship. It's a building that creates its
own energy, heats and cools itself, collects its own water and deals with its
own waste. It's also built from recycled materials. It doesn't need electricity
or gas for heating, as it captures and stores energy by using wind power,
and solar panels on the roof charge up batteries which provide power.
Interviewer: Any disadvantages?
Daren Howarth: You have to change your lifestyle and keep an eye on
changes in the weather. There are thousands of examples around the world
and there's a handbook on sale that explains everything about it - you'll find
the details on my website - and it's something you can do for yourself - you
don't have to employ someone to do the work for you.
Question 3.
Loius: I’m looking for some advice about doing a Master’s Degree in Media
Studies. Am I at the right place?
Mark: Yes, my name’s Mark, I’m head of the Media Studies course. Nice to
meet you, and you are…
Louis: I’m Louise, nice to meet you too.

299 394
Mark: So how can I help you?
Louis: Well I’ve seen the prospectus for the course but I’m still a bit
confused about a few things and about some of the options for studying.
Mark: What’s your situation at the moment? Are you working?
Louis: Yes, I’ve been working as a journalist for a local newspaper for the
last 3 months. Prior to that I had two jobs in the media – at a small local radio
station for about 2 years and at a TV station for about 4 years. So I’ve worked
in media for about six years in total.
Mark: Ok well that’s useful if you want to do the course. What is your
motivation to do further study?
Louis: I enjoy my job a lot at the moment but I feel the opportunities for
promotion are quite limited. It’s not that I think a masters will help with this
though. I’ll probably leave my job, maybe to go into TV or something, but
basically I think wherever I end up going in the future, employers prefer to
see someone with post-graduate qualifications these days.
Mark: And are you intending to study full-time?
Louis: Well I’d really like to keep working as I need an income. What are the
options for me if I want to work whilst studying?
Mark: You could do certain modules over a number of years you like. It’s up
to you how many you do. Basically you get credits for the ones you
complete. People usually do the Masters in anything from 18 months up until
4 years. It depends on your time. If you wanted a fixed schedule and
attendance and did it part time then that would be a total of 3 years.
Louis: So what is the admission criteria to join the course?
Mark: Well there are a few things that are useful but not essential, but there
are some requirements. Usually to join a Masters people must have a
bachelor’s degree, but we are prepared to overlook this if someone has
enough work experience. But you must have one or the other. It’s useful if
you have research experience as you have to complete a thesis but we can
train you on this if not. It’s essential that you have motivation if you want to
join the course as it is very demanding.
Louis: What about the costs for the course?
Mark: The fees for a year if you are studying part-time are £2250. No sorry,
they have gone up this year – £2400. Of course you are paying for all other
living costs. Louis: Is there any kind of bursary or scholarship available to
help with the fees?

300 394
Mark: Yes there are things available but you have to meet the criteria to get
funding. Often though the university will actually contact you about funding.
Universities have a certain budget available to provide funds so they will
look for the best students and offer them something if they think they will be
suitable. You would have to have a firm offer in place to join the course
though before you’d be considered for any funding.
Louis: Where can I go to find out more about it?
Mark: The best place to look for information about funding is on our
university website. All the details about whether you’re eligible, what help
is on offer, and how to apply will be there. If you can’t find the information
you’re looking for, you can always come and speak to us again and there
will be a number you can ring.
Louis: Ok thanks for that. And is it easy to get hold of you if I need to
speak to you further?
Mark: Yes, I’m here most days, but you can always phone the office first
to check. It’s best to book an appointment in case I’m not around.
Question 4:
301 394
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN THÁI NGUYÊN
ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT
ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
MÔN: TIẾNG ANH - KHỐI 10
Ngày thi: …. tháng …. năm 2019
Thời gian: 180 phút
Đề thi gồm: 13 trang
302 394
I. Part 1- LISTENING (50 points) :
HƯỚNG DẪN PHẦN THI NGHE HIỂU
- Bài nghe gồm 4 phần, mỗi phần được nghe 2 lần, mỗi lần cách nhau 15 giây, mở đầu và kết
thúc mỗi phần nghe có tín hiệu.
- Mở đầu và kết thúc bài nghe có tín hiệu nhạc. Thí sinh có 3 phút để hoàn chỉnh bài trước tín
hiệu nhạc kết thúc bài nghe.
- Mọi hướng dẫn cho thí sinh (bằng tiếng Anh) đã có trong bài nghe.
1. Complete the following notes using NO MORE THAN THREE words/
number for each answer. (14 points)
Borchester University
Example: Where to get …food…on campus
PLACE CAPACITY REGULAR MENU COST
Main Refectory Hall
Open: (2)
Arts Building Café
Open: 9 - 6
(6) Bar
Open: 10 - 4
$ (4)
people
Vegetarian, fish, (1)
.
tea, coffee, hot chocolate,
sandwiches
tea, coffee, (7)
sandwiches
(3) £3
(5) £1.30
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7.
2. You will hear part of a radio talk about how to choose houseplants. For
questions 8-1, complete the sentences that summarize what the speaker says
with NO MORE THAN THREE words. You will hear the recording twice.
Write your answer in the box provided. (16 points)
Before you get the plant, choose the (8) . You must make sure there is enough (9)
. Check that plants have
been well looked after at the garden centre.
Plants in poor condition mean the garden centre might
not be (10) .
Choose plants with healthy green (11) .
It could take months or years for a plant to reach the size you want.
It may be better to buy a large plant even if it is (12) .

303 394
Do not buy plants that have just been put (13) . It is not a good idea
to buy plants in (14) .
You should look under the leaves for unwanted (15) .
Your answers:
8. 9. 10. 11.
12. 13. 14. 15.
3. Listen to a nutritionist called Penny Flack talking about the effects of
health and diet in some countries around the world. Are these statements
True (T) or False (F)? (10 points)
EATING FOR HEALTH
1 A quarter of Europeans and Americans are now said to be obese.
2 American politicians have been discussing how to tackle the
causes and consequences of obesity.
3 High-fat cheese and meat is causing the French to become obese.
4 Heart disease is becoming more common in Japan and Greenland.
5 Scientists have discovered that a number of spices used in Indian
cooking can improve brain health.
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
4. You are going to listen to a journalist called Max Wilson talking about
a book about luck in sport by Matthew Syed. Listen to the whole interview
and choose the best answer A, B, or C. (10 points)
1. Max says that top sportspeople usually believe their success is due to
A. good fortune
B. hard work
C. natural skill
2. According to Max, the examples of recent sporting achievements prove
A. that people in general have become stronger and fitter
B. that standards are getting higher
C. that technology is responsible for improved performance
3. In the book Matthew Syed says he had a greater chance of success because of
A. his parents’ love of table tennis.
B. his competitive brother.
C. his own ambition.
4. That advantage is mentioned of the Omega Club when Matthew joined?
A. It was open all the time.

304 394
B. It had a lot of good players.
C. It had great facilities.
5. Max says that a ten-year investigation has shown that lucky people
A. believe they will succeed.
B. look for good opportunities.
C. depend less on talent.
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Part II: LEXICO-GRAMMAR: 40/200
1. Choose the best opon A, B, C, or D to complete the following sentences and
write your !!%
1. I always take my lucky with me into an exam.
A. sign B. item C. charm D. spell
2. I didn’t know my guess was going to be right – It was just
A. pot luck B. odds C. draw D. gamble
3. Why are all your clothes in a on the floor?
A. bulk B. heap C. batch D. sum
4. Sending out e-mails that people haven’t asked for to addresses is
often known.
A. sufficient B. countless C. widespread D. multiple
5. We all have to follow the rules, and none of us is the law.
A. beyond B. over C. above D. onto
6. We are pleased to inform you that we have decided to your
request for British citizenship.
A. give B. grant C. permit D. donate
7. We can only as to the causes of the disaster.
A. think B. consider C. speculate D. ponder
8. The professor’s theory is that singing preceded speech.
A. preferable B. pet C. fond D. fancied
9. I’m not sure if I’m doing it right, but I’ll try to ahead
with it anyway.
A. drive B. bang C. touch D. press
10. Could you lend me some money to me over to the end
of the month?
A. hand B. tide C. get D. make
11. I’m not a serious investor, but I like to in the stock market.
A. splash B. splatter C. paddle D. dabble
12. Who else is of the that we should break the camp?
A. conclusion B. opinion C. remark D. theory
305 394
13. The local press has been pouring on the mayor for
dissolving the council.
A. blame B. hatred C. disapproval D. scorn
14. I’m too keen on visiting the Parkers again so soon.
A. that B. none C. such D. very
15. If I make a fool of myself in front of my friends, I’ll never it down.
A. let B. give C. settle D. live
16. Because of his poor health, it took him along time to his bad cold.
A. throw off B. throw away C. throw down D. throw over
17. In spite of his poor education, he was the most speaker.
A. articulate B. ambiguous C. attentive D. authoritarian
18. “Another cup of coffee?” — “No, but thanks .
A. not at all B. for all C. all the same D. you for all
19. He said he would contribute money, but later he backed of it.
A. down B. away C. off D. out
20. Can you recite the alphabet ?
A. reverse B. around C. backwards D. returned
Your answers:
0 ) +
/ 1 2 3 0
00 0 0) 0 0+
0/ 01 02 03
2. Give the correct form of the word in the brackets. (10 pts)
1. Deforestation and excessive farming have the soil. (POOR)
2. In his , Mike smashed all the breakable items in the kitchen.
(FURIOUS)
3. The building looks a bit from the outside but it’s
quite traditional inside. (FUTURE)
4. I sat completely as the spider crawled along my arm. (MOTION)
5. The heavy snow meant that the mountain roads were for
over a week. (PASS)
6. She was charged with being disorderly and
7. The damage caused by the terrible storm two days ago
was
. (INTOXICANT)
b
y
the government. The real figures go up every minute. (ESTIMATE)
8. They exchanged for a few minutes before saying goodbye.
(PLEASANT)

306 394
9. There is a decline in the of cigarette smoking among
young men. (PREVAIL)
10. They are planning for an advertising campaign to the new film.
(PUBLIC)
Your answers:
0 ) +
/ 1 2 3 0
3. There are 10 mistakes in the passage. Find out and correct them. (10 points)
Line
5
10
15
After inventing dynamite, Swedish-born Alfred Nobel became very
rich man. Therefore, he foresaw its universally destructive powers too
late. Nobel preferred not to remember as the inventor of dynamite, so
in 1895, just two weeks before his death, he created a fund to be used
for rewarding prizes to people who had made worthwhile contributions
to mankind. Originally there were five awards: literature, physics,
chemistry, medicine, and peace. Economy was added in 1968, just
sixty- seven years after the first award ceremony. Nobel’s original
legacy of nine millions dollars was invested, and the interest in this
sum is used for the awards which vary from 30,000 to 125,000.
Every year on December 10, the anniversary of Nobel’s death, the
awards (gold medal, illuminated diploma, and money) is presented to
the winners. Sometimes politics plays an important role in the judges
decisions. Americans have won numerous science awards, but
relatively few literature prizes. No awards were presented from 1940 to
1942 at the beginning of World War II. Some people have won two
prizes, but this
is scarce; others have shared their prizes.
Your answers:
Line Mistakes Corrections
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.

307 394
8.
9.
10.
Part III.
READING (60 pts)
1. Fill the blanks with one of four options to complete the passage (10 points)
Romania’s name itself suggests what makes it different from its
neighbours. The connection is with the Imperial Rome and coming from that
is the language which sounds like Italian. The country is about the (1) of
Great Britain and has a population of 23 million, of whom ninety percent are
Romanians.
The scenery is (2) : mountainous areas with summer and winter
resorts, a marvellous stretch of the Danube as it descends towards the
Iron Gates, not to mention castles, palaces and monasteries with impressive
frescoes. There are also historic towns from the 13
th
of century, Black Sea
beach resorts and the astonishing bird-life of the (3) Danube delta.
And if this is not enough, there are no
(4) than 160 spas offering cures for nearly every illness (5) to man.
Romania is perhaps most famous abroad for being the home of Dracula the
famous creation of the Irish writer, Bram Stoker. However, while the story is
(6) , the character is based on a Romanian prince called
Vlad Dracula (son of Dracul) or Tepes (the Impaler) because of such cruelty
(7) his enemies. On one occasion he is supposed to have
sat down to a meal to enjoy the spectacle of some prisoners (8) their arms and legs cut
He asked for their blood to be collected and brought to him as a dip for his
bread.
So, when you visit Romania you may like to visit Bran Castle which was
built in 1377 and is the castle most (9) identified with Dracula. But, if
you do, don’t forget how much (10) there is to see in Romania.
1. A. size B. area C. proportion D. extent
2. A. different B. various C. varied D. diverse
3. A. tremendous B. vast C. huge D. gigantic
4. A. better B. less C. more D. fewer
5. A. belonging B. familiar C. known D. accustomed
6. A. false B. fiction C. fake D. unauthentic
7. A. regarding B. with C. for D. towards
8. A. when B. while C. having D. with
9. A. tightly B. closely C. nearly D. strictly

308 394
10. A. else
Your answers:
B. more C. remaining D. left
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
2. Fill each of the blanks with ONE suitable word. (10 pts)
THE CUCKOO ROLLER OF MADAGASCAR
This bird is about the same size as the European roller, and has many
features in common (1) its near relatives. (2) the European family,
however, the cuckoo roller can reverse its outer toes, (3) it to
perch by gripping a branch with two toes forward and two back. Its eating
habits are also quite different. (4) nearly
all other rollers take food on the wing or pluck reptiles or large insects from
the ground, the cuckoo roller stays high up in the forest canopy, (5)
on caterpillars, stick insects and, most important of
all, chameleons.
Subtly blending its colours to the forest backcloth, and (6) leaving
the safety of the branches except to cross from one tree to another, the
chameleon is an elusive prey. Even on open ground, (7) myriad dangers it
normally avoids, the chameleon’s slow, swaying walk makes it difficult to
see against the leaves. (8) good is it camouflage that
the cuckoo roller has to put up with long periods of watching and waiting, (9)
a tell-tale movement
betrays its victim’s presence. At least, experts assume this is what happens,
because despite the fact that this bird is widespread throughout Madagascar,
(10)
observer has yet seen it in the process of catching its prey.
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
3. Read the passage and choose one of four options to answer the
questions (10 pts)
It is estimated that over 99 percent of all species that ever existed have
become extinct. What causes extinction? When a species is no longer
adapted to a change environment, it may perish. The exact causes of a

309 394
species’ death vary from situation to situation. Rapid ecological change may
render an environment hostile to a species. For example, temperatures may
change and a species may not be adapt. Food resources may be affected by
environmental changes, which will then cause problems for a species
requiring these resources. Other species may become better adapted to an
environment, resulting in competition and, ultimately, in the death of a
species.
The fossil record reveals that extinction has occurred throughout the history of

D. dramaticallyC. eventually
B. unfortunatelyA. exceptionally
A. helpB. death.C. recoveryD. change
310 394
Earth. Recent analyses have also revealed that on some occasions many
species became extinct at the same time - a mass extinction. One of the best -
known examples of mass extinction occurred 65 million years ago with the
demise of dinosaurs and many other forms of life. Perhaps the largest mass
extinction was the one that occurred 225 million years ago, when
approximately 95 percent of all species died. Mass extinctions can be caused
by a relatively rapid change in the environment and can be worsened by the
close interrelationship of many species.
If, for example, something were to happen to destroy much of the plankton in
the oceans, then the oxygen content of Earth would drop, affection even
organisms not living in the oceans. Such a change would probably lead to a
mass extinction.
One interesting, and controversial, finding is that extinctions during the past
250 million years have tended to be more intense every 26 million years.
The periodic extinction might be due to intersection of the earth’s orbit with
a cloud of comets, but this theory is purely speculative. Some researchers
have also speculated that extinction may often be random. That is, certain
species may be eliminated and others may survive for no particular reason.
A species’ survival may have nothing to do with its ability or inability to
adapt. If so, some of revolutionary history may reflect a sequence of
essentially random events.
1: The underlined word “ ultimately “ is closest in meaning to
2: What does the author say in paragraph 1 regarding most species in Earth’s
history?
A. They have been able to adapt to ecological changes.
B. They have caused rapid change in the environment .
C. They have remained basically unchanged from their original forms
D. They are no longer in existence.
3: Which of the following is NOT mentioned in paragraph 1 as resulting
from rapid ecological change?
A. Availability of food resources B. Introduction of new
species C. Temperature changes D. Competition among
species 4: The word “demise” is closest in meaning to
5: Why is “ plankton” mentioned in the second paragraph?
A. To emphasize the importance of food resources in preventing mass
extinction B. To illustrate a comparison between organisms that live on the
311 394
land and those that live in the ocean
C. To point out that certain species could never become extinct
D. To demonstrate the interdependence of different species

312 394
6: According to paragraph 2, evidence from fossils suggests that
A. There has been only one mass extinction in Earth’s history.
B. Extinction of species has occurred from time to time throughout Earth’s history.
C. Extinctions on Earth have generally been massive.
D. Dinosaurs became extinct much earlier than scientists originally believed.
7: The underlined word “ finding” is closest in meaning to
A. published information
B. research method
C. scientific discovery.
D. ongoing experiment
8: Which of the following can be inferred from the theory of periodic
extinction mentioned in paragraph 3?
A. The theory is no longer seriously considered.
B. Most scientists believe the theory to be accurate.
C. Many scientists could be expected to disagree with it.
D. Evidence to support the theory has recently been found.
9: In paragraph 3, the author makes which of the following statements about
a species’ survival?
A. It is associated with astronomical condition
B. It may depend on chance events.
C. It does not vary greatly from species to species
D. It reflects the interrelationship of may species.
10: According to the passage, it is believed that the largest extinction of the
species occurred
C. 225 million years ago D. 26 million years ago
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
4. Read the following passage then do the tasks that follow. (10 pts)
HOW DOES THE BIOLOGICAL CLOCK TICK?
A Our life span is restricted. Everyone accepts this as 'biologically' obvious.
‘Nothing lives for ever!’ However, in this statement we think of artificially
produced, technical objects, products which are subjected to natural wear and
tear during use. This leads to the result that at some time or other the object
stops working and is unusable ('death' in the biological sense). But are the
wear and tear and loss of function of technical objects and the death of living
organisms really similar or comparable?
A. 65 million years ago B. 250 million years ago

313 394
B Our ‘dead’ products are ‘static’, closed systems. It is always the basic
material which constitutes the object and which, in the natural course of
things, is worn down and becomes 'older’. Ageing in this case must occur
according to the laws of physical chemistry and of thermodynamics.
Although the same law holds for a living organism, the result of this law is
not inexorable in the same way. At least as long as a biological system has
the ability to renew itself it could actually become older without ageing; an
organism is an open, dynamic system through which new material
continuously flows. Destruction of old material and formation of new
material are thus in permanent dynamic equilibrium. The material of which
the organism is formed changes continuously. Thus our bodies continuously
exchange old substance for new, just like a spring which more or less
maintains its form and movement, but in which the water molecules are
always different.
C Thus ageing and death should not be seen as inevitable, particularly as the
organism possesses many mechanisms for repair. It is not, in principle,
necessary for a biological system to age and die. Nevertheless, a restricted
life span, ageing, and then death are basic characteristics of life. The reason
for this is easy to recognise: in nature, the existent organisms either adapt or
are regularly replaced by new types. Because of changes in the genetic
material (mutations) these have new characteristics and in the course of their
individual lives they are tested for optimal or better adaptation to the
environmental conditions. Immortality would disturb this system - it needs
room for new and better life. This is the basic problem of evolution D Every
organism has a life span which is highly characteristic. There are striking
differences in life span between different species, but within one species the
parameter is relatively constant. For example, the average duration of human
life has hardly changed in thousands of years. Although more and more
people attain an advanced age as a result of developments in medical care and
better nutrition, the characteristic upper limit for most remains 80 years. A
further argument against the simple wear and tear theory is the observation
that the time within which organisms age lies between a few days (even a few
hours for unicellular organisms) and several thousand years, as with
mammoth trees.
E If a lifespan is a genetically determined biological characteristic, it is
logically necessary to propose the existence of an internal clock, which in
some way measures and controls the aging process and which finally
determines death as the last step in a fixed programme. Like the fife span, the
metabolic rate has for different organisms a fixed mathematical relationship
to the body mass. In comparison to the life span this relationship is ‘inverted’:

314 394
the larger the organism the lower its metabolic rate. Again this relationship is
valid not only for birds, but also, similarly on average within the systematic
unit, for all other organisms (plants, animals, unicellular organisms).

315 394
F Animals which behave ‘frugally’ with energy become particularly old for
example, crocodiles and tortoises. Parrots and birds of prey are often held
chained up. Thus they are not able to ‘experience life’ and so they attain a
high life span in captivity. Animals which save energy by hibernation or
lethargy (e.g. bats or hedgehogs) live much longer than those which are
always active, The metabolic rate of mice can be reduced by a very low
consumption of food (hunger diet) They then may live twice as long as their
well fed comrades. Women become distinctly (about 10 per cent) older than
men. If you examine the metabolic rates of the two sexes you establish that
the higher male metabolic rate roughly accounts for the lower male life span.
That means that they live life ‘energetically’ - more intensively, but not for as
long.
G It follows from the above that sparing use of energy reserves should tend
to extend life. Extreme high performance sports may lead to optimal
cardiovascular performance, but they quite certainly do not prolong life.
Relaxation lowers metabolic rate, as does adequate sleep and in general an
equable and balanced personality. Each of us can develop his or her own
‘energy saving programme’ with a little self observation, critical self-control
and, above all, logical consistency. Experience will show that to live in this
way not only increases the life span but is also very healthy. This final aspect
should not be forgotten.
The Reading Passage has seven paragraphs, A-G,
For question 1-6, choose the correct heading for paragraphs A-G from
the list of headings below.
Write the correct number, i-x, in the corresponding numbered boxes.
LIST OF HEADINGS
i
ii
iii
iv
v
vi
vii
viii
ix
x
The biological clock
Why dying is beneficial
The ageing process of men and women
Prolonging your life
Limitations of life span
Modes of development of different species
A stable life span despite improvements
Energy consumption
Fundamental differences in ageing of objects and
organisms
Repair of genetic material
Example answer: Paragraph A: v

316 394
Your answers

317 394
1. Paragraph B
….............
2. Paragraph C
….............
3. Paragraph D
….............
4. Paragraph E
….............
5. Paragraph F
….............
6. Paragraph G
….............
Questions 7-10, complete the notes below
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each
answer. Write your answers in boxes 7-10
Objects age in accordance with principles of (7) and of (8)
Through mutations, organisms can (9) better to the environment
(10) would pose a serious problem for the theory of evolution
Your answers
7. 8. 9. 10.
5. You are going to read an article in which four people comment on a
book they have read recently. For questions 1-10, choose from the people
A-D. The people may be chosen more than once (10pts)
A - Sundance by Teresa Wilson
Kerry:
I really don't know why this book is so popular. I mean, I suppose it is going
to appeal to young girls who want danger and romance, but I found this book
really tedious. For a start, the characters were really unconvincing. The
author went out of her way to add lots of details about the characters, but I
found these details really pointless. I thought that some of the facts she
presented about the main characters would become significant in some way
later in the novel, but they didn't. They were just worthless bits of
information. I also was disappointed that, although this book is meant to be
about kids at high school, the writer seems to have no recollection at all
about what it's like to be 17. The main character thought and acted like a 32-
year old. It just wasn't believable. I'm not saying Teresa Wilson is a bad
writer. She can obviously string words together and come up with a story that
is appealing to a large number of people, but she lacks anything original.
There is no flair. It just uses the same sort of language as you can see in
many other mediocre novels.
B - Wild Ways by Margery Emerson

318 394

319 394
Liz:
I have to say that I won't forget this book for a long time. I was hooked from
the very first chapter. The devastating story affected me so much that I don't
know if I'll ever feel the same again. I was close to tears on several
occasions. I've got images in my brain now that I don't think will ever leave
me. It's incredibly well- researched and, although it is fiction, is based on
shocking real-life events. I learned an awful lot about things that went on
that I never knew before. Margaret Emerson has a brilliant way with words
and I really felt real empathy towards the characters, although I was
sometimes irritated by the choices they made. However, the parallel story,
the part that is set in the present, is not quite so good. I found myself just
flicking through that part so that I could get back to 1940s Paris.
C - Orchid by Henry Rathbone
Imogen:
This is a delightful novel full of wonderful imagery, a paints a remarkable
picture of life in a distant time and a far-away place. If you're looking to learn
about Eastern culture in great detail, then this is probably not the book for
you, as the writer skims over most of the more complicated aspects of the
country's etiquette. The historical aspects are also not covered in much depth.
However, I wonder whether this was the writer's intention. By doing this, he
symbolise the superficiality of the girl's life. She, like the book, is beautiful
and eager to please, but remains too distant from us, the readers, to teach us
much. Although I loved the book and read it in one sitting, the ending was a
bit of a disappointment. A story which involves so much turmoil, in a place
where the future is uncertain, should not have a happy-ever-after fairy-tale
ending.
D - High Hills by Mary Holland
Hannah:
I read this book for a literature class. I know it's a classic, and I did try to like
it, but I just didn't get into it. I kept persevering, hoping that I'd start to enjoy
it, but no such luck. The famous scene out on the moors was definitely the
best bit of the book, but even that I found ridiculous when it is clearly

320 394
supposed to be passionate. As I approached the end of the book, I figured
there must be some kind of moral to the story, something that I would learn
from the experience of trudging through

321 394
seven hundred long pages, but there was nothing worthwhile. I don't know
why the literary world sees this book as such a masterpiece. The characters
are portrayed as being intelligent, but they do such stupid things! And as for
it being a love story - marrying someone you don't love and then being
abused by them - that doesn't spell love to me.
Which person read a book which….
1. was set in an Oriental country
2. finished in an unrealistic way
3. had characters that the reader could sympathise with
4. is well-known and was written a long time ago
5. contained two stories
6. was not set in the past
7. was historically accurate
8. made the reader cry
9. contained insignificant details
10. has a well-known scene
Your answers:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Part
IV
WRITING: 50/200
1. Rewriting sentences (Beginning with the given
words)
5 10
2. Rewriting sentences (Key words given)
5 10
3. Writing a paragraph
1 30
PART IV: WRITING ( 50 pts)
1/ Complete the second sentence so that it has a similar meaning to the
first one, using the word given. Don’t change the word given. You must
use between three and eight words including the word given. (10pts)
1. Carol has trouble communicating her ideas to other.
(ACROSS) Carol
……………………………………………..............
2. Tom’s presence at parties adds to everyone’s enjoyment.
(SOUL). Tom
parties.

322 394
3. His colleague will do anything to avoid confrontation. (LENGTHS)

323 394
His colleague.........................................................................to avoid confrontation.
4. Margaret is said to be a very good cook. (REPUTATION)
-> Margaret..............................................................................very good cook.
5. I think this word comes from ancient Greece. (DERIVED)
-> ……………………………………………………………………………………
b/ Complete the second sentence so that it has similar meaning to the
first sentence.(10 pts)
1. Whatever the methods used to obtain the result, drugs were definitely
not
involved.
-> There was no question
......................................................................................................................................
2. She chooses the kinds of the hotels she stays in very carefully.
-> She is very fussy…………………………………………………………………
3. Although the papers claim that they are going to get divorced, they are not.
-> Contrary ………………………………………………………………………..
4. I have been told that you have been late for work every day this week.
-> It has been brought …………………………………………………….
5. The fund-raisers haven’t officially decided where to send the proceeds of the concert.
-> No …………………………………………………………………………
3. Write a paragraph of about 150 -180 words to express your opinion on
the following topic (30 points
“Modern technology has increased our material wealth but not our happiness”
ĐÁP ÁN
1. Complete the following notes using NO MORE THAN THREE words/ number for
each answer. (14 points)
Your answers:
1.
pasta and salad
2.
11.30-2.30
3.
£1.50
4.
50
5.
£1.15
6.
Theatre
7.
toasted
2. You will hear part of a radio talk about how to choose houseplants. For questions
8-1, complete the sentences that summarize what the speaker says with NO MORE
THAN THREE words. You will hear the recording twice.
Your answers:
8. location 9. sunlight 10. very trustworthy 11. leaves and stems
12. more expensive 13. in pots 14. plastic bags 15.insects or diseases
324 394
3. Listen to a nutritionist called Penny Flack talking about the effects of health and
diet in some countries around the world. Are these statements True (T) or False
(F)? (10 pts)
Your answers:
1. T 2. F 3. F 4. F 5. T
4. You are going to listen a journalist called Max Wilson talking about a book about
luck in sport by Matthew Syed. Listen to the whole interview and choose the best
answer A, B, or C.(10 pts)
Your answers:
1. B 2. B 3. B 4. A 5. B
Part II: LEXICO-GRAMMAR: 40/200
Your answers:
1. C 2. A 3. B 4. D 5. C
6.B 7.C 8.B 9.D 10.B
11.D 12.B 13.D 14.B 15.D
16.A 17.A 18.C 19.D 20.C
2. Give the correct form of the word in the brackets.
Your answers:
1. impoverished 2. fury 3. futuristic 4. motionless 5. impassable
6. intoxicated 7. underestimated 8. pleasantries 9. prevalence 10. publicize
3. There are 10 mistakes in the passage. Find out and correct them. (10 3. There are 10
mistakes in the passage. Find out and correct them. (10 points)
Line Mistakes Corrections
1. 1 very -> a very
2. 2 Therefore -> However
3. 3 remember -> be remembered
4. 5 rewarding -> awarding
5. 7 Economy -> Economics
6. 9 millions -> million
7. 9 in -> on
8. 12 is -> are
9. 13 judges -> judges’
10. 17 scarce -> rare
C. READING
1. Fill the blanks with one of four options to complete the passage (10 points)
1. A 2.C 3.B 4.D 5.C
6.B 7.D 8.C 9.B 10.A
2. Fill each of the blanks with ONE suitable word.
325 394
1. with 2. Unlike 3. enabling/
allowing
4. While/ Whereas/
Although
5. feeding
6. seldom/rarely/
never
7. whose 8. so 9. until/ before 10. no
3. Read the passage and choose one of four options to answer the questions (10 pts)
1. C 2. D 3. B 4. B 5. D
6. B 7.C 8. C 9. B 10. C
4. Read the following passage then do the tasks that follow. (10 pts)
0 %
) $
+ $
/ $
1 ""
2 "
3
0 "
12!
5. You are going to read an article in which four people comment on a book they
have read recently. For questions 1-10, choose from the people A-D. The people may
be chosen more than once
Which person read a book which...
1. was set in an Oriental country _
Imogen _
2. finished in an unrealistic way
Imogen
3. had characters that the reader could sympathise with Liz
4. is well-known and was written a long time ago Hannah:
5. contained two stories Liz
6. was not set in the past Kerry _
7. was historically accurate Liz
8. made the reader cry Liz
9. contained insignificant details Kerry
10. has a well-known scene Hannah:
PART IV: WRITING ( 60 pts)
1/ Complete the second sentence so that it has a similar meaning to the first one, using
the word given. Don’t change the word given. You must use between three and eight
words including the word given.
1. Carol has trouble getting her ideas across
2. Tom is (always) the life and soul of parties
3. His colleague will go to any lengths to avoid
confrontation 4.Margaret has a reputation for being a
very good cook
5. I think this word is derived from ancient Greek.
2/ Complete the second sentence so that it has similar meaning to the first sentence.

326 394

327 394
1.There was no question of drugs being involved, whatever the methods used to obtain the result
2. she is very fussy about the kind of the hotels she stays in.
3. Contrary to what the papers claim, they are not going to get divorced.
4. It has been brought to my attention that you have been late for work every day this week.
5. No official decision(s) on where to send the proceeds of the concert has (/have) been
made by the fund-raisers.
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN
NGUYỄN TẤT THÀNH –YÊN BÁI
(Đề thi gồm 01 trang)
FG-:7FGHIJ-
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
LẦN THỨ XV, NĂM HỌC 2018 – 2019
ĐỀ THI MÔN: TIẾNG ANH LỚP 10
Thời gian: 180 phút (Không kể thời gian giao đề)
LISTENING (50/200)
Part 1. Listen and complete the form below
Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND / OR A NUMBER for each answer
Product Incident Report
Example: Answer
Product: Rice cooker
Model Number: 1:……………………………………
Price of the product: 2: …………………………………..
Name of the branch: City Centre
Problem: 3: …………………………………..
Customer’s Information Details
Name: 4: …………………………………..
Address: 84 Park Road
Postcode: 5: …………………………………..
Card’s expire Date: 6: …………………………………..
Method of Compensation: Refund
Shopping Frequency: 7: …………………………………..
Part 2. Listen and complete the following passage. NO MORE THAN THREE
WORDS in each blank.
Hi, there, everyone. I hope Ron (1)..............................................at the meeting before lunch. Any
question? …. Just in case you’re not sure, I’ll give you the details about the trip today and
about what you will be doing tomorrow. (2)..................................., this journey should
take about
7 hours, so we (3)...............................................we’ll be in Newcastle at 8’oclock this evening.
There’ll be dinner as soon as we get there. The camp manager normally makes us (4)
…………………………… Bolognese, there is always plenty of (5).............................................,
so you should sleep pretty well. There are two people to a tent, and make sure you get
the right one! Erm, the camp manager’s got a list of which tent you will be in, so don’t
worry. They are clearly marked. Tomorrow, we have to be (6)...................at 7:30 for
breakfast.
We start work at 9:00 am. We’ll need at least a few hours to get things ready. The
festival opens at 1:00 in the afternoon, and you’ll get a chance to go and see some of the

328 394
bands playing. Please let your supervisor know when you want your 2 hours off.
Anyway, I hope we have a good trip,

329 394
and I am sure the festival’s going to (7)...............................................If you have any question,
please (8)..............................................to ask.
Part 3.True / False statements
Listen to a report on football and decide whether the following statements are True / False
1. Fans should sit down when watching a game at top football clubs.
2. Football stadiums are used only during football season because the grass pitch needs
time to recover.
3. Spectators are allowed to touch football players on the pitch if they are close enough
4. A season ticket does not mean you can watch all the matches played by your club
in one season.
5. Most fans must buy a meat pie and a drink at half- time.
Part 4. MCQ questions
You will hear some airport announcements. Circle ONE letter that represents the correct
answer to each.
1. To board the flight to Bangkok, passengers must go to………………..
A. section BD-221 B. the arrivals area
C. the Roberts building D. gate 42
2. The number of the flight to Kiev is……………….
A. CL-525 B. SL – 225S C. SL-525S D. CSL-525
3. The departure of the flight to Chengdu has been delayed by……………
A. 15-30 minutes B. 15 minutes C. 30 minutes D. 50 minutes
4. How long will the flight VD-624 to St Petersburg?
A. 30 minutes B. 30 minutes longer than originally expected
C. 4 hours D. 5 hours 10 minutes
5. Airport tax
A. must be paid at a machine near immigration
B. is more expensive for international passengers
C. can be paid at the immigration desk
D. is not payable by domestic passengers
LEXICO –GRAMMAR (40/200)
Part 1. Choose the best answer to complete the following sentences (20 questions)
1. The increased pay offer was accepted although it short of what the
employees wanted
A. fell B. arrived C. came D. ended
2. His poor handling of the business on negligence.
A. bordered B. edged C. approached D. neared
3. Price increase are now running at a(n) level ò thirty percent.
A. highest B. record C. uppermost D. top
4. This monument is to the memory of the distinguished former students.
A. erected B. dedicated C. commissioned D. associated
5. To begin study chemistry at this level, you must already have proved your ability in a related
A. line B. discipline C. region D. rule
6. The stage designed was out of this but unfortunately the acting was
not so impressive.
A. moon B. planet C. world D. earth

330 394
7. I on the grapevine that George is in the line for promotion.
A. heard B. collected C. picked D. caught
8. the US superiority at that time, it was probable that any threatened US
response would have deterred the Soviet Union.
A. If B. Given C. Although D. Since
9. They have made a plan to build a suspension bridge over the river
A. bald B. bound C. bold D. bare
10. In the 1850’s Harriet Beecher’s “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” became the best
seller of the generation, a host of imitators.
A. inspiring B. inspired C. inspired by D. to inspire
11. After so many years, it is great to see him his ambition.
A. get B. realize C. possess D. deserve
12. The review committee three practicing lawyer s and a retired businessman.
A. consists B. comprises C. is made up D. encloses
13. I doubt whether he will actually carry out his threats.
A. highly B. deeply C. absolutely D. seriously
14. When the funds finally , they had to abandon the scheme.
A. faded away B. clamped down C. petered out D. fobbed off
15. The team won the championship four years
A. running B. passing C. following D. rotating
16. I couldn’t get a wink of sleep last night, so I’m not really on the today.
A. mark B. fringe C. ball D. weakness
17. We know people are generally more aware of the importance of a
healthy and active lifestyle than they were.
A. leading B. taking C. doing D. making
18. My cousin was nervous about being interviewed on television, but he to the occasion wonderfully.
A. raised B. rose C. fell D. faced
19. Mr Pike is certainly a writer, he has written quite a few books this year.
A. prolific B. fruitful C. fertile D. successful
20. as a masterpiece, a work of art must transcend the ideals of the period in
which it was created.
A. Ranks B. The ranking C. To be ranked D. For being ranked
Part 2. Write the correct form of each word in the numbered space provided
1. The victims of the mistaken bombing are just the latest of the
increasingly bloody war. (casual)
2. A gesture of , the commission tested our products, too (partial)
3. The project went over budget because of at the planning stage (calculate)
4. We have obligations to control prices. (contract)
5. He insisted that his project be by the Council thought it was
costly and impractical. (prior)
6. The destruction caused by Alzheimer’s disease has been likened to the _ of the hard drive, beginning
with the most recent files and working backward. (erase)
7. A popular type of vaccine contains living that have been caused
harmless. (organic)
8. Foreign language learning is an issue that has attracted a lot of attention (Argue)

331 394
9. If you look on the other side of the cup you will find a small with the
name of the original manufacturer. (grave)
10. The fact that numerous factories dumping waste into the area’s rivers has led to high level of
(toxic)
Part 3. Identify 10 errors in the following passage and correct them
The BBC World Service on radios claims a regular worldwide audience of some 25
million for its English language programmes. It is funded directly by the British Foreign
Office, despite any Government attempt to control the content of programmes are
vigorously fought off. It is broadcast around the world and nobody who has access to a
radio with short wave need be without it. The archetype listener today is under 30, male,
likely to be the second or even third language. Few women tune in, which is why there is
no women’s programme including in its 24- hour services. The biggest and the most
important of the news programme is Newshour, a 60- minute survey of world news which
goes out at night at 10 p.m.British time. This slot cannot please everyone but be the
optimum time to catch any listeners having breakfast in Hongkong or settling down
during the night in West African. It can recommend to anyone who wants to understand
the world, not just Britain. At any rate, which is its aim and certainly by comparison, most
British domestic news programmes seem trivial and parochial.
READING (60/200)
Part 1. Read the following passage and choose the best answer to complete the passage
The return of the airship
The first balloon flew in the 18
th
century. BY 1900 the Germans were producing rigid
airships capable of carrying (1) _ loads over long distances. These airships
consisted of a cigar shaped, covered frame (2) hydrogen gas. The first craft
reached speeds (3)
32 km/h. By the mid – 1930s, the zeppelins had (4) in size.
The largest airship ever built, the Hindenburg, was 245 metres long and could reach a
maximum speed of 135 km / h. In 1936, this airship carried a (5) of 1,002
passengers on 10 scheduled round (6)
between Germany and the United States. On 6 May 1937, while (7)
at Lakehurst, New Jersey, the Hindenburg was completely (8)
when it crashed and burst into (9) _ , with a loss of 36 lives.
Now, over 60 years since the last giant commercial airship was built, a new (10) of
high tech giant airships is being planned.
1. A. strong B. considerable C. notable D. important
2. A. containing B. consisting C. comprising D. composing
3. A. arriving B. almost C. nearly D. approaching
4. A. twofold B. multiplied C. doubled D. duplicated
5. A. total B. sum C. figure D. number
6. A. travels B. trips C. voyages D. journeys
7. A. grounding B. getting down C. landing D. returning
8. A. demolished B. ruined C. damaged D. destroyed
9. A. flames B. fires C. blazes D. burns
10. A. brand B. breed C. race D. family
Part 2: Read the text below and use only ONE word to fill in each space.
Invisible Highways
Virtually (0)….every……sacred site in the prehistoric world was linked with others, both

332 394
major and minor, by a radiating network of straight lines. Few were as elaborate or as
easily detected in their heyday as the Anasazis’ strange highways in America. Most, (1)
...................................................................................................................................the Ley
lines of

333 394
Europe, were invisible – which (2) …………….. them, in a way, all the (3) …………….
mysterious. In a rare case, like the vast drawing-board that covered the desert floor at
Nazca, Peru, entire sites were devoted to creating miles of straight lines and, (4)........more
bewildering, very precise pictures that (5).....................be appreciated only from the air.
In cultures that had (6)......................a magical sense of the continuous life rolling through
the whole of creation – which today we sterilise and alienate by calling it the
“environment”- the lines, visible or invisible, (7) …………… to have meaning. The role
they played has been the greatest enigma of all in the study of ancient sacred places. It was
also, (8)................................................................................................................................a
handful
of researchers have now (9) ……………to realize, by far the biggest clue (10).......................the
meaning and use these sites, and it was staring them in the face all the time.
Part
3:
Read the passage then choose the best answer (A, B, C, D) to each question that follows.
MUSICAL TALENT
Among all the abilities with which an individual may be endowed, musical talent
appears earliest in life. Very young children can exhibit musical precocity for different
reasons. Some develop exceptional skill as a result of a well- designed instructional
regime, such as the Suzuki method for the violin. Some have the good fortune to be born
into a musical family in a household filled with music. In a number of interesting cases,
musical talent is part of an otherwise disabling condition such as autism or mental
retardation. A musically gifted child has an inborn talent; however, the extent to which the
talent is expressed publicly will depend upon the environment in which the child lives.
Musically gifted children master at an early age the principal elements of music,
including pitch and rhythm. Pitch – or melody –is more central in certain cultures, for
example, in Eastern societies that make use of tiny quarter – tone intervals. Rhythm,
sounds produced at certain auditory frequencies and grouped according to a prescribed
system, is emphasized in sub – Saharan Africa, where the rhythmic ratios can be very
complex.
All children have some aptitude for making music. During infancy, normal
children sing as well as babble, and they can produce individual sounds and sound
patterns. Infants as young as two months can match their mother’s songs in pitch,
loudness, and melodic shape, and infants at four months can match rythmic structure as
well. Infants are especially predisposed to acquire these core aspects of music, and they
can also engage in sound play that clearly exhibits creativity. Individual differences begin
to emerge in young children as they learn to sing. Some children can match large
segments of a song by the age of two or three. Many others can only approximate pitch
at this age and may still have difficulty in producing accurate melodies by the age of five
or six. However, by the time they reach school age, most children in any culture have a
schema of what a song should be like and can produce a reasonably accurate imitation
of the
songs commonly heard in their environment.
The early appearance of superior musical ability in some children provides
evidence that musical talent may be a separate and unique form of intelligence. There are
numerous tales of young artists who have a remarkable “ear” or extraordinary memory for
music and natural understanding of musical structure. In many of these cases, the child is
average in every other way but displays an exceptional ability in music. Even the most
gifted child, however, takes about ten years to achieve the levels of performance or

334 394
composition that would constitute mastery of the musical sphere.
Every generation in music history has had its famous prodigies – individuals with
exceptional musical powers that emerge at a young age. In the eighteenth century,
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart began composing and performing at the age of six. As a child,
Mozart could play

335 394
the piano like an adult. He had perfect pitch, and at age nine he was also a master of the art
of modulation – transitions from one key to another – which became one of the hallmarks
of his style. By the age of eleven, he had composed three symphonies and 30 other major
works. Mozart’s well- developed talent was preserved into adulthood.
Unusual musical ability is a regular characteristic of certain anomalies such as
autism. In one case, an autistic girl was able to play “Happy birthday” in the style of
various composers, including Mozart, Beethoven, Verdi, and Schubert. When the girl was
three, her mother called her by playing incomplete melodies, which the child would
complete with the appropriate tone in the proper octave. For the autistic child, music may
be the primary mode of communication, and the child may cling to music because it
represents a haven in a world that is largely confusing and frightening.
1. The word “precocity” in paragraph 1 is closest in meaning to .
A. strong interest B. good luck C. advanced skill D. personal style
2. The author makes the point that musical elements such as pitch and rhythm .
A. distinguish music from other art forms B. vary in emphasis in different cultures
C. make music difficult to learn D. express different human emotions
3. The word “predisposed” in paragraph 3 is closest in meaning to .
A. inclined B. gifted C. pushed D. amused
4. According to the passage, when does musical talent usually begin to appear?
A. when infants start to babble and produce sound patterns
B. between the ages of two and four months
C. when children learn to sing at two or three years old
D. between ten years old and adolescence
5. According to the passage, which of the following suggests that musical talent is a
separate form of intelligent?
A. exceptional musical ability in an otherwise average child
B. recognition of the emotional power of music
C. the ability of all babies to acquire core elements of music
D. differences between learning music and learning language
6. Why does the author discuss Mozart in paragraph 6?
A. To compare past and present views of musical talent
B. To give an example of a well-known musical prodigy
C. To list musical accomplishments of the eighteenth century
D. To describe the development of individual musical skill
7. In music, the change from one key to another is known as .
A. rhythm B. prodigy C. perfect pitch D. modulation
8. All of the following are given as examples of exceptional musical talent EXCEPT .
A. a remarkable “ear” or perfect memory for music
B. ability to compose major works at a young age
C. appreciation for a wide variety of musical styles
D. playing a single song in the style of various composers
9. The word “haven” in paragraph 7 is closest in meaning to .
A. beautiful art B. safe place C. personal goal D. single problem
10. Which of the following can be inferred from the passage about exceptional musical ability?
A. It occurs more frequently in some cultures than in others.
B. It is evidence of a superior level of intelligence in other areas.

336 394
C. It has been documented and studied but is little understood.
D. It is the result of natural talent and a supportive environment.
Part 4. Read the passage and do the tasks that follow.
Communicating Styles and Conflict
Knowing your communication style and having a mix of styles on your team can
provide a positive force for resolving conflict.
A
As far back as Hippocrates’ time (460-370B.C.), people have tried to understand other
people by characterizing them according to personality type or temperament. Hippocrates
believed there were four different body fluids that influenced four basic types of
temperament. His work was further developed 500 years later by Galen. These days there
are a number of self-assessment tools that relate to the basic descriptions developed by
Galen, although we no longer believe the source to be the types of body fluid that
dominate our systems.
B
The value in self-assessments that help determine personality style, learning styles,
communication styles, conflict-handling styles, or other aspects of individuals is that they
help depersonalize conflict in interpersonal relationships. The depersonalization occurs
when you realize that others aren’t trying to be difficult, but they need different or more
information than you do. They’re not intending to be rude: they are so focused on the task
they forget about greeting people. They would like to work faster but not at the risk of
damaging the relationships needed to get the job done. They understand there is a job to
do, but it can only be done right with the appropriate information, which takes time to
collect. When used appropriately, understanding communication styles can help resolve
conflict on teams. Very rarely are conflicts of true personality issues. Usually, they are
issues of style, information needs, or focus.
C
Hippocrates and later Galen determined there were four basic temperaments: sanguine,
phlegmatic, melancholic and choleric. These descriptions were developed centuries ago
and they are still somewhat apt, although you could update the wording. In today’s world,
they translate into the four fairly common communication styles described below:
D
The sanguine person would be the expressive or spirited style of communication. These
people speak in pictures. They invest a lot of emotion and energy in their communication
and often speak quickly, putting their whole body into it. They are easily sidetracked onto
a story that may or may not illustrate the point they are trying to make. Because of their
enthusiasm, they are great team motivators. They are concerned about people and
relationships. Their high levels of energy can come on strong at times and their focus is
usually on the bigger picture, which means they sometimes miss the details or the proper
order of things. These people find conflict or differences of opinion invigorating and love
to engage in a spirited discussion. They love change and are constantly looking for new
and exciting adventures.
E
The phlegmatic person - cool and persevering - translates into the technical or systematic
communication style. This style of communication is focused on facts and technical
details. Phlegmatic people have an orderly methodical way of approaching tasks, and their

337 394
focus is very much on the task, not on the people, emotions, or concerns that the task may
evoke. The focus is also more on the details necessary to accomplish a task. Sometimes
the details overwhelm the big

338 394
picture and focus needs to be brought back to the context of the task. People with this style
think the facts should speak for themselves, and they are not as comfortable with conflict.
They need time to adapt to change and need to understand both the logic of it and the steps
involved.
F
The melancholic person who is soft hearted and oriented toward doing things for others,
translates into the considerate or sympathetic communication style. A person with this
communication style is focused on people and relationships. They are good listeners and
do things for other people- sometimes to the detriment of getting things done for
themselves. They want to solicit everyone’s opinion and make sure everyone is
comfortable with whatever is required to get the job done. At times this focus on others
can distract from the task at hand. Because they are so concerned with the needs of others
and smoothing over issues, they do not like conflict. They believe that change threatens
the status quo and tends to make people feel uneasy, so people with this communication
style, like phlegmatic people, need time to consider the changes in order to adapt to them.
G
The choleric temperament translates into the bold or direct style of communication. People
with this style are brief in their communication - the fewer words the better. They are big
picture thinkers and love to be involved in many things at once. They are focused on tasks
and outcomes and often forget that the people involved in carrying out the tasks have
needs. They don’t do detail work easily and as a result, can often underestimate how much
time it takes to achieve the task. Because they are so direct, they often seem forceful and
can be very intimidating to others. They usually would welcome someone challenging
them, but most other styles are afraid to do so. They also thrive on change, the more the
better.
H
A well-functioning team should have all of these communication styles for true
effectiveness. All teams need to focus on the task, and they need to take care of
relationships in order to achieve those tasks. They need the big picture perspective or the
context of their work, and they need the details to be identified and taken care of for
success. We all have aspects of each style within us. Some of us can easily move from one
style to another and adapt our style to the needs of the situation at hand-whether the focus
is on tasks or relationships. For others, a dominant style is very evident, and it is more
challenging to see the situation from the perspective of another style. The work
environment can influence communication styles either by the type of work that is
required or by the predominance of one style reflected in that environment. Some people
use one style at work and another at home.
The good news about communication styles is that we have the ability to develop
flexibility in our styles. The greater the flexibility we have, the more skilled we usually are
at handling possible and actual conflicts. Usually, it has to be relevant to us to do so, either
because we think it is important or because there are incentives in our environment to
encourage it. The key is that we have to want to become flexible with our communication
style. As Henry Ford said, “Whether you think you can or you can’t, you’re right!”

339 394
Questions 1-6
The reading passage has eight sections A-H. Choose the correct heading for each
section from the list of headings below. Write the correct number i-x in boxes 1-8.

340 394
List of Headings
i Summarising
personality types ii
Combined styles for workplace
iii Physical explanation
iv A lively person who encourages
v Demanding and unsympathetic
personality vi Lazy and careless
personality
vii The benefits of understanding
communication styles viii Cautious and caring
ix Factual and analytical personality
x Self-assessment determines one’s temperament
Section A ..…iii……
1. Section B ………….
2. Section C ………….
3. Section D ………….
4. Section E ………….
5. Section F ………….
6. Section G ………….
Section H ……ii .….
Questions 7-10
Do the following statements agree with the information given in the reading passage. Write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the
information FALSE if the statement contradicts
the information NOT GIVEN if there is no
information on this
7. It is believed that sanguine people dislike variety.
8. Melancholic and phlegmatic people have similar characteristics.
9. Managers often select their best employees according to personality types.
10. It is possible to change one’s personality type.
Part 5: For questions 1-10, answer by choosing from the sections of the article (A-E).
Some of choices may be required more than once.
A. Today’s proliferating travel journalists and guidebook writers seem to be
portraying the world in an increasingly uniform manner. Superficial responses and
preconceived images alternate with easily digestible bites of cultural and historical
information and with ever- larger doses of ephemeral and often misleading
practical information. It is thus with enormous relief that one comes across
guidebooks written not only with passion and profound knowledge, but also from
an unusual and at times commercially foolhardy perspective.
B. The crisply designed City Secrets, Rome, is one guidebook with a difference.
Unashamedly proclaiming itself to be a ‘highly subjective’ work, it brings together

341 394
the personal choices of what to see and experience in Rome of numerous artists
who are regular associates of the city’s American Academy. Under its influence,
you might well be encouraged, say, to

342 394
undertake such an unusual activity as a “Tosca stroll”. The main problems are that
the entries are often too short to be enlightening, and are sometimes backed up,
unnecessarily, by lists of largely unfamiliar names endorsing the
recommendations.
C. With glorious disregard for current fashions in guidebook production, the recently
founded Signal Books Ltd of Oxford has begun bringing out a series of discursive,
virtually unillustrated, and highly literate city guides. This extremely promising
series, entitled Cities of the Imagination, concentrates as much on the image of a
city as formed by artists and writers as it does on surviving monuments. The series
was launched by Jason Wilson’s masterly Buenos Aires, which, with its
exceptional wealth of literary references, does full justice to a city whose fictional
identity is far more potent than the stereotypical tourist vision. Wilson’s book
inspires the reader to escape into the little-explored world of Argentinian literature.
Later volumes in the series, if the previews are anything to go by, will be equally
rich in their treatment of a place’s artistic associations, which, in guidebooks in
general, have tended to fare far less well than literary ones.
D. Among the very few existing guides devoted solely to retracing an artist’s
footsteps is Ellen Williams’ slight but very readable Picasso’s Paris. She outlines
here four walks which have been intelligently devised so as to give the reader a
sense of the artist’s personal and artistic development, beginning with his
impoverished days in Montmartre and ending with his later years when he spent
time in the area of St-Germain-des-Pres. Another good publisher offering titles
with an artistic slant is Ellipsis, which has deservedly gained widespread respect
for its architectural guides. These guides, almost small enough to be hidden in the
palm of one’s hand, and yet filled with stunning photographs, have dealt until now
mainly with recent architecture. However, they are rapidly branching out into other
areas, and are soon to include a guide to Italian gardens, and an ‘opinioned’ survey
of New York’s museums and art galleries.
E. Appropriately, at a time when publishers are looking ever more favourably on
quirky books, three guides have recently appeared celebrating British quirkiness.
One of these books is the enjoyable Eccentric Britain, which directs travellers to
follies, strange local customs, places associated with famous eccentrics, and
obscure museums. The monumental work Follies, Grottes and Garden Buildings
by Headley and Meulenkamp is a model to which all guidebooks should aspire.
Scholarly yet consistently entertaining, it is also clearly laid out and abundantly
illustrated, making it the ideal companion for any cultural tour of Britain. But or
sheer eccentricity, there is nothing to beat the Dutch author Pieter Boogaart the
essence of Britain, and is transformed by his pen into a route as exotic as the
Golden Road to Samarkand. It is a book replete with witticisms, personal asides,
and cultural and historical gems.
Which section mentions a book or books?
concentrating on some unusual aspects of life in one country? 1
which will cover a particular aspect that has often been neglected? 2
being worthy of their reputation? 3
343 394
which would benefit from more detail in some parts and less detail in others? 4
giving equal importance to both culture and places in a particular city? 5
by writers who are showing less and less variety in their style? 6
combining an academic approach with attractive design? 7
containing factual details which may be unreliable? 8
proudly acknowledging its biased approach? 9
which will depart from the publisher’s normal theme? 10
WRITING ( 50/200)
Part 1. Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means the same as
the original sentence.
1. There is a very good chance that the company ran up those debts intentionally.
The company could ………………………………………………………………………………
2. The gun going off was the signal for everyone to panic.
As soon as…………………………………………………………………………………………
3. As far as I know, this has never happened.
To…………………………………………………………………………………………
……….
4. In a nutshell, Joseph’s not up to the job.
The long and ………………………………………………………………………………………
5. What alienated the workforce was that management never consulted them.
It was the …………………………………………………………………………………………
Part 2. Use the word(s) given in bracket and make any necessary additions to write a
new sentences in such a way that it is as similar as possible in meaning to the original
sentence. DO NOT change the form of the given word(s).
1. His exam results will determine what choice he has for further education. (dependent)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2. If by chance you are arrested, you don’t have to say anything. (under)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3. The new minister seems to be excellent at fielding awkward questions. (flair)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
4. They have narrowed the many applicants down to three. (short)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
5. He made unsuccessful attempt to buy the company. (without)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Part 3.Paragraph writing
Competitiveness is a positive quality in modern life. Do you agree with this
opinion? Write a paragraph of about 150-200 words to express your idea
TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN
NGUYỄN TẤT THÀNH –YÊN BÁI
(Đề thi gồm 01 trang)
HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤM
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG
LẦN THỨ XV, NĂM HỌC 2018 – 2019
ĐỀ THI MÔN: TIẾNG ANH LỚP 10
Thời gian: 180 phút (Không kể thời gian giao đề)

344 394
LISTENING (50/200)
Part 1. Listen and complete the form below (Actual Listening - Test 3 )

345 394
1. R242
2. 89.99
3. escaping steam
4. Herbert
Hewitt 5.
B0241DJ
6. April 2008
7. once a month
Part 2. Listen and complete the following passage. NO MORE THAN THREE
WORDS in each blank.
Hi, there, everyone. I hope Ron (1) covered everything at the meeting before lunch. Any
question? …. Just in case you’re not sure, I’ll give you the details about the trip today and
about what you will be doing tomorrow. (2) Depending on traffic, this journey should
take about 7 hours, so we (3) reckon we’ll be in Newcastle at 8’oclock this evening.
There’ll be dinner as soon as we get there. The camp manager normally makes us (4) an
excellent spaghetti Bolognese, there is always plenty of (5) red wine, so you should sleep
pretty well. There are two people to a tent, and make sure you get the right one! Erm, the
camp manager’s got a list of which tent you will be in, so don’t worry. They are clearly
marked. Tomorrow, we have to be (6) up and out at 7:30 for breakfast. We start work at
9:00 am. We’ll need at least a few hours to get things ready. The festival opens at 1:00 in
the afternoon, and you’ll get a chance to go and see some of the bands playing. Please let
your supervisor know when you want your 2 hours off.
Anyway, I hope we have a good trip, and I am sure the festival’s going to (7) be fantastic.
If you have any question, please (8) feel free to ask.
3. True / False statements (Intensive Listening 6.04)
1T 2F 3F 4T 5F
4. MCQ (Intensive Listening 6.03)
1D 2C 3D 4B 5B
LEXICO – GRAMMAR
Part 1. Choose the best answer to complete the following sentences
1A 2A 3B 4B 5B 6C 7A 8B 9C 10A
11B 12B 13D 14C 15A 16C 17A 18B 19A 20C
346 394
Part 2. Write the correct form of each word in the numbered space provided
1. Casualties 2. Impartiality 3. Miscalculation 4. Contractual
5. prioritized
9. Engraving
6. Erasure
10. Toxicity
7. Organisms 8. Unarguable
Part 3. Mistakes correction
Line Mistake CorrecJon
-
) 7
+ " ("
+
/ 7
1 $ ,$
0 ! 7
0 =
0 !
0)
READING
Part 1. Read the following passage and choose the best answer to complete the passage
1B 2A 3D 4C 5A 6B 7C 8D 9A 10B
Part 2.
1. Like
2. Made
3. More
4. Even
5. Could / can
6. Such
7. Had
8. As
9. Come
10. To
Part
3.
Read the passage then choose the best answer (A, B, C, D) to each question that follows.
0 & )( +( /& 15 2 3& 05
347 394
Part 4.
0 $ ) $ % + $
/ $ 1 =(#,; 2 -'I; 3 <*-97;< 0 -'I;
Part 5
1. E 2. C 3. D 4. B 5. C
6. A 7. E 8. A 9. B 10. D
WRITING ( 50/200)
Part 1. Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means the same as
the original sentence.
1. The company could well have run up those debts intentionally.
2. As soon as the gun went off, everyone started to panic.
3. To the best of my knowledge, this has never happened.
4. The long and the short of it is that Joseph’s not up to the job.
5. It was the fact that management never consulted them that alienated the workforce.
Part 2. Use the word(s) given in bracket and make any necessary additions to write a
new sentences in such a way that it is as similar as possible in meaning to the original
sentence. DO NOT change the form of the given word(s).
1. His choice (what choice he has) for further education is dependent on/ upon his exam results
2. If by chance you are placed (or you find yourself) under arrest, you don’t have
to say anything.
3. The new minister seems to have a flair for fielding award questions.
4. They have short- listed three applicants.
5. He attempted to buy the company without success.
()'*+,-.%/(%0*,

vw
348 394
YZW[
xwW#y<&%A
!"#$!%&
!"#!$%&'
'()*&+,
& @ !"#
$%&'(')*+,*-'-'.,./',0(1)23&4
3.J35G0:J(N03B3/3-5
# 0
,/
/"
!!$. !. .0
; $$ $"0
! !$%! *$%
!0
#%&0 >
5%)03,75
! !!$.$!+00
' * ...0 0
3 .-0
-9.:52;1.2
%' <' =' >'
*' ?' @'
5%!& %'
(')*+,,./'!28&4
K
> %..!!5. 7$!0.!
!C251D8@"0
>. !0. ! !0
! ! "0 C2 5 ED* ! .
C!D . $C!0D
#.!.! ! &00
! . .!C3!D. )0 @"!!@"&0
.!! !+00
3! !-0 ( !0
349 394
5!$ ! 80 ! 9 !. 0
-9.:52;1.2
%' <' =' >'
*' ?' @' A'
9!%:%BA#
!2*4 242;&4
0 !!!$%!! 0
0 !4 ! 0
"0 ! !%! $0
&0 50I$ ! $ 0
)0 50I$ $ 7 !0
%' <' =' >' *'
3 :7 %
!%72D#E#7.4$%
2;&4
0 B:$!! $ 0
10 !! .!
30 $
0 !.% !
0 .!7!!$
0 6! B$!! !$ <
10 !! 30!
0! 0 !(!
"0 1*B $ !!0
10 $ $ !
30 .$.!
0 .!.
0 $$
&0 B!% 0
10 ! 30
0.! !. 0.! !.
)0 !!!$! .!!B.%.0
10 .!$!
30 .!.$!
0 !!!$$
0 $! !$$
%' <' =' >' *'

350 394
'(#)*&+,
16/3-5%' 0--21/01;-.4-.+0.:21/0:/B12/C3/21:60BD:5E35/01F-DD-;35G
215/15612')<&+,
%' #. ! .!!!!/. !0
' 0! 0 K0
<' ;>4 $ !! $! 0
' .% 0 0 K0$%
=' >! . $! * !!!0
' 0 0 K0
>' > *!!!(
0
' ! 0 . 0.%%
K0.
*' > * .*!!.$0
' 0. 0 K0:
?' ,! ! !>4 !0
' 0 0 K0
@' !!! *.!!. 0
' !$ 0 0 K0:
A' !. . H !!! ! !!
! 0
' 0 ! 04 K04
H' 1 .!!! *>!! !$!!0
' 0!! 0 K0
%&' ;!!!.! .! ! 0
0! .% 0! $.%
0. .% K0!$.%
%%' . .! !! !!4.!$ 0
' 0$ 0 K0!
%<' /!! !! .4!! L
5$>!%4 ( 0
' >4 0> .!4
0E4. K0>4 !.
%=' >. !4! 0>4! $ 0
' ! 0 0!! K0!
%>' ! !7 ! 0
' 7 0$ 0 K0
%*' ; .*.! (0
0: 0 0 K0
%?' * !! ! .$0
0>$$. 0'$.
351 394
0!$. K03!.
%@' !. !!$ 0
0 ! 0 0! K0 !
%A' I!3. ! . 0
' 0 0 K0
%H' >.%!%* *!.! 0
0 0$! 0$ K0
<&' !. $! !0
0 $ 0 0 K0 7
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
%%' %<' %=' %>' %*'
%?' %@' %A' %H' <&'
16/3-5<'I3DD1:60G:+;3/0/016-..16/F-.J-F/01;-.4235B.:6E1/2')%&+,
0 !66'.% : *.!!
! ! 0 ((
0 1 %!! !.!
! 0W(
"0 >4$ * > =.!!!..
0(I(
&0 /%$$% ! 0(
)0 ! >$! !4$ 9 !!4
!0(
+0 1 !.!
$0 (((,
-0 !.=!!.
7! !0 (W(,
)0!4 !! $! 0 )(,
80 '! ! . ! 0;*!4 $.!
!$ !. ! 0
,
@0 . !$ .0 )K((,
A0 !!!0 (K,
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
352 394
16/3-5='01+:22:G1B1D-;6-5/:352(J32/:E12'541.D351/01J32/:E12:54
+.-M341/016-..16/3-5235/012+:612B1D-;')%&+,
!.03 .% !!0
3!!!! !!.*!
0#! $*!! $ 0
. !!!1'11'1 !
! 0>!. * !7*$
7 *. $ !.%.0!.
!.4 *! ! !0
> >) = ?* $ ! -@* ! # ! C
$ ! * * !
.!!0D! .?!? $
0
!!O;*5! 1'1
@@&*!! ! !$!1
0; !*!$!5*
! ! 7 ! . ! $
0
B
B
B"
B&
B)
B+
B-
B8
B@
BA
B
B
B"
B&
B)
(N:J+D1!
A0 B JK
%' ?'
<' @'
=' A'
>' H'
*' %&'
16/3-5>' -J+D1/11:60215/1561;3/0:293/:BD1+.1+-23/3-5-.+:./36D1'P.3/1
7-9.:52;1.235/0159JB1.142+:612+.-M3414' )%&+,
0 /
0
0 !
%
!!.! ! *!.
!0
"0 ! % !$ %0
&0 #.G!.! %! .7 0;!G !!!$0
)0 !!>G%$ :$ !.!.%A! !0
+0 6! !. !!!! * !$%.
-0 / ( .!! .%
! !
80 ! :$! .

353 394
@0 E !!
A0 ;. L27!$0
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
'(K)*&+,
16/3-5%'1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:54416341;0360:52;1.)OOO-.K,B12/C3/2
1:60G:+'P.3/17-9.:52;1.356-..12+-5435G59JB1.14B-N12')&,0:2B1154-51:2
:51N:J+D1')%&+,
!(! ! %
0>%
! !0>"
*.
!.% $!.!.!*: 0
&
>. 7 *. )
! !!. $
*!>4!+
.!0
'!7 .! * . $ !!
-
$ $ .% $ 0 ! .4 !
! .%% 0. .4$ %!8
$..4 0> ! @
.! !.*.!
$! ! 0;> A
$
! $%!*!!.$!0
&010 30 0 0
)010$ 30 ! 0 . 0
+010 30 0 0
-0101!! 30. 03 0!
8010 30% 0 0
@010 30 0 0
A010 30 0 0
0107 ! 30 % 0$ 0
010( 30 0 0
"010 30 0 0
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
16/3-5<'1:4/01+:22:G1:54C3DD351:60G:+;3/0(293/:BD1;-.4')%&+,
! ! ! 0
!
! ! !$! !
! !$! 0>*
*! ! $$
!

354 394
!$! ! * !$ .! !*"
*
. * !0 > &
! *
*!$ .0! !
$0
!!! .!!%)
!H!.$
!0'! *! \ ! !% * *
! \ ! ! +
! $ 0 !
-
!
7*!$!$ 8
$
01.!! ! !.
@
!.* ! !% !!!%
A
.! ! $.!0 > *!
*!.! %% ! !$$$ 0
-9.:52;1.2!
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
16/-5='1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:5460--21/016-..16/:52;1./-1:60-F/01
F-DD-;35GQ912/3-52'P.3/17-9.:52;1.235/01B-N+.-M3414')%&+,
1!$ .!.!!$.*
0 9 ! !$ +.16-63/7
0; % . *
! !;=%!!0;!$$
! ! 7 .! 0>$ *
!. $ ! 0 J9236:DD7
G3F/14 603D4 0:2 :5 35B-.5 /:D15/z 0-;1M1.O /01 1N/15/ /- ;0360 /01 /:D15/ 32 1N+.12214
+9BD36D7 ;3DD 41+154 9+-5 /01 15M3.-5J15/ 35 ;0360 /01 603D4 D3M12'
5 ! ! *
!!!0#!??? **
!% (?eI!!*
( $ * ! =
$?;!1*.!!!! $0
1!! % 0*!
. $$$*! 0>
.! !!!4 !* *
!* ! ! !! .0 >
+.1432+-214(! *!
!!$ 0
> $! ! 0;
!! $!.!05!
!! !7 $
! 7 0.*$!!! !* !
! !.!
355 394
!$% $!
!!0
! $ ! !
$ (0!
.!!%$CD
0>! *!!
!.$ $ 0 ! !*
!.* % $ ! ! !
. ! !0
! ! ? .!
. !0>!!!*6
1 5=$ ! 01 !*5=
!%0!!*!*!.
!? %!?.!!$!
!% ! 03!*!! ! ! "A!
:.% 05=g .?. !0
O $ ! !
0> * . $C$!D!
*5=*3!*9*;!$06!!. !*!
!!$ *.!!!!..!!
!0'! !* $!
*!! $ 0:M15
.! !0
%' !.C+.16-63/7D!
0
' 0% 0 % K0
<' 6!! $. $ ! ! !!!
!<
' !$$.! $*$!.
!.! $ 0
' ! * ! $!$ !
=! 0
' !.! .%!$ .
! !! ?%0
K' ; ! $ *
.!! ! 0
=' !!% !! ! !!!0
' ! ! 0!
0% 7 K0 !
>' !.C+.1432+-214D!" 0
' 0 0 ! K0
*' 1! *.! $<
' 6! $$$ 0
' 3.! .! 0
' 6!! .! 0
356 394
K' 3. 0
?' 1! *.!!!. ! !
<
' $!. !0
' I!. 0
' !$$$ ( 0
K' $. 0
@' 6! !! 5=!+<
' . 0
' .?%. 0
' ! !!!0
K' $! %0
A' > *!!%! %. 0
' !! 0 0! K0
H' !.C0:M15D!- 0
' $ 0 0 K0 $
%&' 6!!!.$! $ $<
' > ( !! 0
' > ! 0
' >! $ $ 0
K' > ! 0
-9.:52;1.2
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'
16/3-5>'1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:544-/01/:2E2/0:/F-DD-;'
)<&+,
/! 7$ !
! 6 0 B G
!@+A ! $ ! ! / " ! $
*$ ! . G.G
* .!* * ! . ! 0 !
2 # $ !.
* !. ! !! ! !<
B. ! /! ! *! !
"!!)09 ! !
"! 0;! * .$%
! 0 %
. 0B )A . . $ A
$%*.!! ! !

357 394
0! $.! $.*!
.! !0
$ &A 0 # !
!! ! ! $
0# ! ! ! . !$!* .!! !
% $ !0 > %*$ ! ! *
! !G$G !0
. !!$ ! !%$(
%!. ! ! 0
! !.!$% $!!*5$ !*
! !)0! $% *
! .!* * $ * $ .
0,!. % !
$% !! .%! $ $!
03 $% *5$ ! !!!
!. $0
K
B .! 01!$*! !
!.% ! $* ! ! ! * $ 0
# %!.!.%! / !
$ .!.!! %* !! $
0 % !0
1!!.%! $ *!! !! *
..!$0 !$H
( !$%.%!!7 .!! *!!
( !$%0, .% !
$! 0! !!!$%
!! * $ .! !
!! * .% ! 01! *!!.
% !! ..0
(
> %$ ! * $ $ % ! !
!! ! ! + )0 ! ! !
! ! !* .% 0>
$ * .$ $!!( %!
! !$0 % %!!!
.* ! ! !0
! (!$ . %0.*!
/ . ! G.%!!*
!G0# % !!G .
!!!%.! * !G/%G
! ! .%!0>
.%* @)! !
358 394
0
I
;.!!:$ ! ! !<*
0 / H!
$:!! !H!! !.%
.! 0
,! ! . .
*!%.! *! !
G . 01!.$
! $!*.!! (/ *$
: 70! .$ 0!.
.. 0
BA#% 1B ! %
32/-F1:435G2
> !75$ !
>>
>>> !
>9 I !7 ! 5!
9 !5!
9> 5!
9>> 3% /
9>> !%/ 5!
>Q !!.%
(N:J+D1!16/3-5!W
0;3
"0;
)0;'
0;
&0;
8B;#&%!@
( ! .!! !.
! ! !.
W( $ .!!.!% $!
+0 ! .! ! 5! !
!/ 0
-0 ! 2 # 7 !
! 0
80 # ! / ! . ! 0
@0 ! %!.%/ ! 0
A0 5! $% / ! . ! ! 0
-9.:52;1.2
%' <' =' >' *'
?' @' A' H' %&'

359 394
W'P)*&+-35/2,
16/3-5%!I353201:60-F/01F-DD-;35G215/15612352960:;:7/0:/3/J1:52/012:J1
:2/01215/1561B1F-.13/')%&+,
%'E!%!. :*$.0
0
<' 1$ . ! ! 0
6!0
='$ $! !
0I 0
>' 5$%>!.0
>0
*';! $(% !$
! 0O0
16/3-5<!1;.3/1/0121215/156129235G/01;-.4235'-9J92/5-/60:5G1
/01G3M15;-.42')%&+,
%' > !. 0
>!!0
<' 6. !! 0 (K5!
0
=' !% . 0
I((L(!%0
>' $!0
( 0
*' 1! $ 0 )K(,
; '16/3-5=! :.:G.:+0;.3/35G)=&+,
-!!& C
E !.!)A8A. .0
'()*&+-35/2,
16/3-5%)%>+-35/2#<'&+-35/2^6-..16/:52;1.,
)((,

360 394
YZW[
xw#y<&%A
\K]
!"#
$!%&
T!@!U-VA8
WXU Y!Z[ U"
HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤM
0! % 0 "0 &0A
)0.! +0;# -0(
(<'32/15/-/01.16-.435GO:546-J+D1/11:60-F/01F-DD-;35G215/15612;3/0
(/;-;-.42K^:59JB1.)%?+-35/2,
)((,
0% 0! "0! &0
)0 !. +0A"A -0!\" 807%
(='.91-.I:D21)%&+-35/2,
)(W,
0' 0' "0' &0 )0'
:./>!0--21/01:52;1.){O|O-.K,;0360C3/2B12/:66-.435G/-;0:/7-901:.')%&
+-35/2,)(,
03 0 "01 &0 )03
'(#)*&+-35/2,
16/3-5%' 0--21/01;-.4-.+0.:21/0:/B12/C3/21:60BD:5E35/01F-DD-;35G
215/15612')<&+-35/2,
)(OOWW(,
03 0 "01 &0 )01
+0 -0 801 @0 A0
03 03 "01 &03 )0
+03 -0 801 @03 A0
16/3-5<'I3DD1:60G:+;3/0/016-..16/F-.J-F/01;-.4235B.:6E1/2')%&+-35/2,
)(O(O(8,
0 0 "0 &0 )0 $
+0 -0 80 @0 $ A0

361 394
16/3-5='01+:22:G1B1D-;6-5/:352(J32/:E12'541.D351/01J32/:E12:54
+.-M341/016-..16/3-5235/012+:612B1D-;')%&+-35/2,
)(W,
0B3JK +0B8$ !JK$ !
0B" JK -0B@! JK
"0B)7JK7 80BJK
&0B+!JK! @0B"JK
)0B- JK A0B)$JK$
16/3-5>' -J+D1/11:60215/1561;3/0:293/:BD1+.1+-23/3-5-.+:./36D1' )%&+-35/2,
)((O,
0\$ 0 "0 &0 )0
+0. -0 80!! @0 A0\
'(K)*&+-35/2,
16/3-5%'1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:54416341;0360:52;1.)OOO-.K,B12/C3/2
1:60G:+')%&+-35/2,
)((,
0 01 "0 &01 )0
+0 -03 803 @01 A03
16/3-5<'1:4/01+:22:G1:54C3DD351:60G:+;3/0(293/:BD1;-.4')%&+-35/2,
)((8,
0;! 0! "0 &0 )0
+0\ -0 80 @0 A0
16/-5='1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:5460--21/016-..16/:52;1./-1:60-F/01
F-DD-;35GQ912/3-52')%&+-35/2,
)(,
0 01 "03 &01 )0
+01 -03 80 @03 A0
16/3-5>'1:4/01F-DD-;35G+:22:G1:544-/01/:2E2/0:/F-DD-;')<&
+-35/2,)(,
09>> 0> "09 &0>> )09>>>
+0E; -0, 80,2>9 @0, A0E;
(W!P)*&+-35/2,
:./%!I353201:60-F/01F-DD-;35G215/15612352960:;:7/0:/3/J1:52/012:J1:2
/01215/1561B1F-.13/')%&+-35/2,
)(,
0 !!\$\\.!!%*. :0
362 394
0 6!$ *! .! \$ \
$ \.!0
"0 I $! !! \$ 0
&0 > .!$%0
)0 O $% !$! 0
:./<!1;.3/1/0121215/156129235G/01;-.4235'-9J92/5-/60:5G1/01
G3M15;-.42')%&+-35/2,
)(K((,
0 >!!! !. % 0
0 5! \=\ !*! .
\! 0
"0 !% =!. 0
&0 $!$!\%!!0
)0 ; $! 0
:./=!P.3/1:+:.:G.:+0')=&
+-35/2,)(,
-!!& C
E !.!$)A8A. .0
h/i/3j960kce50G3e 3aJ/l3c:
%' l6m6
o ^Y!_ `[a!a
o 3Za !Xa Ub T*!T !Xa XU ^[_ `[$T
o 3Za c!cWT X_ $T`Z%Z^a
?
<' 0e//.3a5n
o #!U cUUdT!Wa
o UY!WU *dUa *e`_ `c$_^aU%Z_ dT!
?
=' o4m5G5Gh5/p
o ;W_ a^ WT !T!Xa XU ^a
o ;W_ a^ WT `U V!*!ca
o ;W_ aWT Z!UUc!c
?
>' q3495G
o f_ !Z!a WXT `a
o f_ Y!WU *dUa*^a^a
o f^aT;ZWT %!^ ![!VadU!X(`a!A]
?

363 394
*' Gr+0e+O4s96t9O60k50/i
o ;W_ a`U Z^
o !dU!_9Z`U !dU!_
BY !dU!_ ^!c[\ ^a!U b$adU!^a Y WT ]
`c_ $TZ
T ^aY !dU!_Vaa!d_dU!^a Y
o ;W_ a `U !XT *!c*ZU ^`U Wb !U0BYWb !U
^!c[\ ^a!U b$aWT ]`c_$TZ
?
u5G
=&
S(%&
16/3-5%

364 394

312 338

313 394
16/3-5<
3!! 8@"*.!5*%!
B *F%*! 06!! !
!!*. 7$!h% h * 03.!!
# !. *!.%.
0!251
2
*2
0
2*
!*2
0
251. * * . $ $!
!! !03.!. $ !8@"*$%
% *$ ! !
! *!!!!.*!.h!h.
$h!h0;! !25E0
>! *! !O; $ ! 0! .
253! !!
! *.!#*.!!!..!
!%! !. 0
>@&*251*.!3!E
*. $ !03!*. .$
%!0!3!. ! *@"!
!3. !.36*!$h h6
O@""* >3G !.1 ! !@"&0
!! */ *$!#5 !!!!
. * 7*.$0B@"& !. $
$ !!! ! *. 7$ !
@") 3!0;!*.! 1G ! !
3!!A"A0

314 394
'! $ * 0>!
$!2 3%I !! !
!*.!'G /2'.1B;0
3!!$.!! $.!
! !* ! 0I $!
7% * ! !.*
H $ * $ *.! *$! h h$!
0
!! !. !0B3 G @&& ,!.
3!!$ 0; *! !.
. !$! G . * . .!!!
! 0
1 I G !$*$.
. * !3!01
$G $!3 ;!,! @&+*9=
! *!$7!!.*!$$
! 0
I >; %! 0!
! $ 3!*@))! !
! * . % 0. 7. 0
>.!!!*! $ !
!!.!! .!!*.!!
0>AA!B
3!%5;*.!(! !
.! ! 0
1!!3!! ! ! *
. *! $! 0> !.
$ * !.!
%..!! $*$ : $ 0
16/3-5>
>.>4 !*!$*.! B0B*4
!*$!.!0
BE *> $ 0
>.1.4$ .0>4 ! *.4!
! = *.! $!0
B>*>. ! ! $!$ !!0>
4%!! *$>!!.!! !$! M)N0
E ! .! . $.!0
>.>4!!! %! .!>. !06!
! <
B>4. ! $ 0#! * *.!>.
0!>$%$! !$ *.!! 06!!
!. =.*. ! $!
$ 0!. =

315 394
0!. !%% *.!!! H! %
! H% 2%0;.( *.!! *
! M+N034 H!!$
0>.E.! !0%..
.%! <
BE *7:. $ 0>%
:$ *!4.!! $ 0E!%*
S!! $ !.% %!!. 0
6! !!<46*!4 *.! !4
!! .<> !%$* $
(%M-N0>.%$ * 0
>.6! <
B>4%.0>!%>4!05 .%
! 0!!$ .!!%!01!%
$4%!0>. =*$%$%.%*
.!>!!!0>. $. *
. $ !%0!.! *
. *.! M8N01!!
%!.!! *!7!
!.0>. !.!>!03>!4 0
>.6!!!4 <
B> !>4 !* 4 !%
!03>.0!. ; 41 =
> % % ?%.*! $ .! ..
! 05. **.! 0
> *>. .!!.%M@N*!.
0
>.!$ * !. .! <
B'!*!4 .!>4: $0'!!0
!4 $!$! !!$$ $ $! *$
!. . .!$ !4!MAN0;
!!%$$$!$ 0>! $
*.!$ .%!! 0.!4 !
!! *!% !$ 0>4
$$0
>.1! <
B*! 0>4*>4 !! 0
>.,%0;!..!!<!%*B0
Tổng điểm bài thi Giám khảo
Số phách
Bằng số Bằng chữ
Giám khảo 1
(kí, ghi rõ họ tên)
Giám khảo 2
(kí, ghi rõ họ tên)
(Do chủ tịch HĐ
chấm thi ghi)

316 394
CHÚ Ý : THÍ SINH VIẾT CÂU TRẢ LỜI VÀO BẢNG CHO SẴN TRONG ĐỀ
-
- SECTION I: LISTENING (50 points)
HƯỚNG DẪN PHẦN THI NGHE HIỂU
Bài nghe gồm 4 phần; mỗi phần được nghe 2 lần, mỗi lần cách nhau 05 giây; mở
đầu và kết thúc mỗi phần nghe có tín hiệu. Thí sinh có 15 giây để đọc mỗi phần
câu hỏi.
Mở đầu và kết thúc bài nghe có tín hiệu nhạc.
Mọi hướng dẫn cho thí sinh (bằng tiếng Anh) đã có trong bài nghe.
Part 1: Listen and complete the notes below with ONE WORD AND/OR A
NUMBER for each answer in the numbered boxes provided. (14 points)
FAMILY EXCURSIONS
Can take photos of the (1.) that surround the lake
Farm visit
Children can help feed the sheep
Visit can include a 40-minute ride on a horse
Visitors can walk in the farm’s (2.) by the lake
Lunch is available at extra cost
Cycling trips
Cyclists explore the Back Road
A map is provided
Only suitable for cyclists who have some (3.)
- Bikes can be hired from (4.) (near the Cruise Ship Terminal)
Cyclists need:
- a repair kit
- food and drink
- a (5.) (can be hired)
There are no (6.) or accommodation in the area
Cost
Total cost for whole family of cruise and farm visit (7.) $
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7.
Part 2: You will hear part of an interview with a woman called Sophie Doyle, who

317 394
organizes adventure holidays in Australia for teenagers. Write NO MORE THAN
THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER for each blank. Write your answers in the
answer box below. (16 points)
Australian
Adventure
Holidays
The Australian Adventure Holiday is usually in the month of (1.) . In each
group, there are (2.) teenagers plus four leaders. The price
covers everything except (3.) . When they visit the islands, they will
sleep in a (4.) . They will first meet the other young people at the (5.) .
They will visit the largest sand island in the world.
They will sleep next to a (6.) when they are in the outback. At the
Great Barrier Reef, diving lessons will be available for those who need them.
From the boat on the river, you will see (7.) on the banks.
Teenagers normally stay in touch with people at home by (8.) . Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7. 8.
Part 3: You will hear an interview with Pamela Green, a young fashion designer.
Decide whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F), and write your
answers in the answer box. (10 points)
1. Doing research into the fashion industry helped Pamela to decide to become a fashion designer.
2. When starting your own fashion label, it’s not important to have a business plan.
3. Pamela usually finds inspiration for her fashion designs in the clothes she wears.
4. According to Pamela, successful designers need to be able to recognize all past styles.
5. People who want a career in fashion should be aware of the options available.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Part 4: You will hear a radio interview about a mountain climbing, write the letter A,
B, C or D on your answer box below to indicate the correct answer to each of the
following questions.
1. How did Douglas feel when booked the weekend?
A. sure that he would enjoy training for it.
B. uncertain if it was a good idea for him.
C. surprised that such activities were organized.
318 394
D. bored with exercises.
2. Douglas expected that the experience would help him to .
A. meet people with similar interest
B. be more active and creative
C. improve his physical fitness
D. discover his psychological limits
3. What did one of his friends say to him?
A. He was making a mistake.
B. Climbing was fashionable.
C. She didn’t want him to continue.
D. She was envious of him.
4. In what way did Douglas change as a result of the trip?
A. He developed more interest in people.
B. He took part in many social activities.
C. He became more ambitious.
D. He began to notice more things around him.
5. Douglas’s boots are still muddy because he wants them to .
A. remind him of what he has achieved
B. warn him not to do it again
C. show other people what he has done
D. motivate him to climb again
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
SECTION II: LEXICO-GRAMMAR (50 POINTS)
Part 1: Choose the best answer (A, B, C or D) to complete each sentence below. Write
your answers in the answer box. (20 points)
1. Now that my summer vacation has just begun, I feel free as .
A. a bird B. a cucumber C. a pie D. a pig
2. The whole building collapsed, but fortunately there were no .
A. wounded B. hurts C. casualties D. victims
3. I have got a headache. I need to take a rest and some aspirin.
A. spitting B. raving C. splitting D. burning
4. Martha has been hard to it to organize a fancy dress party for the younger children.
A. forced B. ordered C. put D. made
5. It was a daring robbery, which took place in daylight.
A. broad B. total C. wide D. absolute
6. Their choir stood in four rows according to their heights.
A. respected B. respective C. respectable D. respectful
7. Stop fighting you two; shake hands and your peace with each other.
319 394
A. set B. do C. make D. bring
8. Legal matters are not my . You will have to consult a lawyer.
A. prospect B. excess C. domain D. aspect
9.
Our
host
s
had prepared a meal
wit
h
se
ven course
s
to celebrate our
arrival.
A. generous B. lavish C. spendthrift D. profuse
10. Many children who get into trouble in their early teens go on to become offenders.
A. persistent B. insistent C. inverted D. innate
11. Don’t read in such dim light; it will your eyes.
A. dwindle B. contract C. impair D. decrease
12. Making private calls on the office is severely on in our department.
A. frowned B. criticized C. regarded D. objected
13. I must go to bed early tonight; I sat up till the hours to finish that report.
A. late B. deep C. last D. early
14. An education system that benefits bright children of those who are
slower to learn.
A. at the expense B. at the limit C. at the cost D. at the loss
15. He kept his marriage for years, but eventually the truth .
A. came out B. went out C. came through D. fell out
16. Helen was disappointed when she learned that she hadn’t won the beauty contest.
A. seriously B. bitterly C. strongly D. heavily
17. Doctors are often to accidents in rural areas.
A. called up B. driven out C. called out D. rung up
18. To his own great , professor Howard has discovered a new method of
bulimia treatment.
A. reputation B. name C. fame D. credit
19. We had to the design of the car to take account of the rough terrain.
A. modify B. amend C. transfer D. convert
20. The escaped prisoner fought before he was finally overpowered.
A. foot and mouth B. heart and soul C. head over heels D. tooth and nail
Your answer
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
Part 2: Give the correct form of the word in CAPITAL to fill in the blank of each
sentence. Write your answers in the answer box below. (10 points)
1. She stood there completely , so I had no idea at all what she was thinking. EXPRESS
2. The university has the use of dictionaries during language examinations. AUTHOR
3. A number of religious groups, notably the Shakers, practiced living.
COMMUNITY
4. Her is unbearable, indeed. She wouldn’t even say boo to a goose. COWARD
320 394
5. He wanted Jill to give up her life of alcohol and . DESTROY
6. He was not a particularly good teacher, but his students loved him because
he had such a lively . PERSON
7. For some people the use of Internet has become addictive to the extent RESIST
that is threatening their mental and physical health.
8. Due to a huge pile-up, the motorway will remain until tomorrow. PASS
9. Various by police officers were brought to light by the inquiry. PRACTICE
10. The cost of must be paid by the buyer.
CARRY Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Part 3: The passage below contains 10 mistakes. Identify and correct the mistakes.
Write your answers in the answer box below. Line (0) has been done for you as an
example. (10 points)
Line STRESS
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Stress is often called the 21st century illness but it has always been with us if
perhaps with different names. Those days we regard stress is a necessary evil of
modern living. Yet stress is not negative and without it we will not enjoy some of
the highpoints in life just as the anticipation before a date or the tension leading up
to an important match. All these situations produce stress but unless you can
control it and not the other way around you will feel stimulated, not worn out.
Unlike these situations, what are generally positive and easier to deal with, sitting
in a train that is late, being stuck in a traffic jam, working to a tight deadline are
more harder to manage and control. Stress is now recognized as a medical problem
and as a significant factor in causing coronary heart disease, high blooded pressure
and a high cholesterol count. Patients are often unwilling to admit to stress
problems although they feel they are a form of social failure and it is important that
symptoms should be identified in order to avoid unnecessary suffering. So why
should we be looking out for as danger signals? Common signs of stress are
increased tiredness, irritability
and the inability to solve with certain situations.
Your answers
e.g. Line 0: the a
Line Mistake Correction Line Mistake Correction
321 394
Part 4: Fill in the gaps the most suitable particle or preposition to complete the
sentences. Write your answers in the answer box below. (10 points)
1. You need to key your details and then press “enter”.
2. The problem stems the government’s lack of action.
3. The police arrived immediately after the call and caught the burglar the spot.
4. The party was already full swing by the time they got there.
5. Jane is out in the garden mulling a problem to do with work.
6. I feel very uneasy leaving the baby with Miriam for the evening.
7. She is not very good at putting her view .
8. I am afraid you will have to buy a new hairdryer; this one is repair.
9. There was tremendous excitement in the streets and the shouting didn’t die
till after midnight.
10. The image on the screen faded and I knew it was a computer virus.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
SECTION III: READING COMPREHENSION (50 POINTS)
Part 1: Choose the letter A, B, C, or D that best fits each blank in the passage.
Write your answers in the answer box below. (10 points)
Theodor Seuss Geisel, better known as ‘Dr. Seuss’, began writing for children (1.)
by chance. During a long sea voyage in 1936, Seuss amused himself by (2.)
together a
nonsense poem to the rhythm of the ship’s engine. Later he illustrated the rhyme and
published it as And to think that I saw it on Mulberry Street. Many critics (3.)
it as
Seuss’ best work.
A later book, McElligot’s Pool, (4.)
the first appearance of Seuss’ famous fantasy
characters, and Horton Hatches the Egg introduces an (5.)
of morality. Seuss’
reputation as a major children’s writer was sealed with the publication of The Cat in the
Hat. This book uses easy-to-read words to tell the story of two children alone at home on a
rainy day. A cat wearing a tall hat arrives to entertain them, wrecking their house in the
(6.)
. The enthusiastic (7.)
of this book delighted Seuss and led him to found Beginner Books, a publishing
company specializing in easy-to-read books for children. Some of his books have been
made into cartoons and one of them, How the Grinch stole Christmas, was also made into
an ingenious and (8.)
successful feature film starring Jim Carrey.
At one point in his career, Seuss (9.)
gave up writing for children and (10.)
his
talents to making documentary films. One of these attracted a great deal of attention and won
an Academy Award.
1. A. fully B. quite C. extremely D. fairly
2. A. placing B. laying C. putting D. setting
3. A. look beyond B. look upon C. look through D. look towards
4. A. indicates B. shows C. means D. marks
5. A. amount B. ingredient C. element D. item
322 394
6. A. practice B. method C. process D. action
7. A. reception B. welcome C. greeting D. admission
8. A. highly B. intensively C. strongly D. widely
9. A. shortly B. momentarily C. temporarily D. presently
10. A. assigned B. allocated C. donated D. devoted
Part 2: Read the text below and think of the word which best fits each space. Use
only ONE word in each space. Write your answers in the answer box below. (10
points)
PROBLEMS OF LONGEVITY
It is our nature to try to prolong life, but we should also face (1) to the distinct
diffculties that we would also encounter if we succeed. If a successful longevity treatment
(2)
to
emerge
suddenly out of all the new developments of medical science, tacking on extra decades or
even centuries to our lives, the results could be disastrous.
This could be true even for the individual lucky enough to receive the treament.
Presumably any treatment that conferred long life would keep people generally healthy,
but the extra years would be a (3.) of medical balancing
act, akin to the jugglers who dash about keeping plates spinning on top of poles. It would
be nerve-racking (4.) best.
(5.) if the treatments did little or nothing to help one’s memory? This is a
crucial point that is (6.)
overlooked in discussions of longevity. The brain is by (7.) the most
complex organ known to us, and the workings of memory are (8.) really understood.
Keeping the body alive might be possible before we could do anything to strengthen or
restore lost memories. Even the ordinary lifetime often seems too (9.) for
human memory to hold or recall, and if decades were tacked on, the long middle of a life
might be substantially forgotten, leaving (10.) dim memories of childhood and recent
events.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Part 3: Read the passage and choose the best answer (A, B, C, or D) for each
of the questions. Write your answers in the answer box below. (10 points)
It stands to reason that galaxies, large star systems that contain millions or even
billions of stars, should collide with one another fairly often, given that the average
separation between galaxies is only approximately 20 times the diameter of the average
galaxy. In contrast, stars almost never collide because the average distance between stars
is astronomical, perhaps 10,000,000 times their diameter.
Using a telescope, it is possible to find hundreds of galaxies that appear to be colliding.
However, when two galaxies appear to come into contact, there is in reality no direct
contact between the stars of one galaxy and the stars of the other. Instead, the two galaxies
pass through each other, and the gravitational forces in the two galaxies alter the shapes of
the galaxies, often producing tails and bridges. One well-known pair of colliding
galaxies, for example, is called the Mice because each of the two interacting galaxies
resembles a mouse with a long tail, and the

323 394
Whirlpool galaxy appears to be connected to a smaller galaxy by means of a bridge
extending from one of its long spirals. It is impossible for astronomers to monitor the
changing shapes of colliding galaxies because the interactions between galaxies last
hundreds of millions of years, but it is possible to study galaxies in various stages of
collision and draw conclusions about what happens when galaxies collide.
In certain situations, when two galaxies collide, they do not always pass through each
other and emerge as two separate galaxies. In one situation, if two galaxies are moving
slowly enough, they may collide and then may not have enough velocity to escape each
other’s gravitational pull after the collision. In this case, the two galaxies will collide, and
then move past each other, and then be pulled back to collide again, and continue this way
until they eventually merge into a single galaxy. In another situation, if a much larger
galaxy comes into contact with a smaller galaxy, the larger galaxy may absorb the smaller
one in a process called galactic cannibalism. In this process, a larger galaxy first pulls
away the outer stars of the smaller galaxy and then begins to pull at the denser core. While
the process of galactic cannibalism is taking place and the two galaxies are merging into
one, the cores of both the larger galaxy and the smaller galaxy can be clearly visible.
Some giant elliptical galaxies, with what appear to be multiple nuclei, have been found
in the skies, and astronomers once thought that these giant galaxies were giant galactic
cannibals that had consumed many smaller galaxies recently enough that the cores of the
cannibalized galaxies were still intact. One such galaxy, with what appeared to be eight
separate nuclei, was found and was used to put forth the hypothesis that galaxies could be
voracious monsters capable of swallowing up uncountable other galaxies simultaneously.
However, further studies have shown that the numerous nuclei that seemed to be part of a
single large galaxy were in reality the nuclei of smaller galaxies that were in front of or
behind the larger galaxy. Thus, astronomers are now confident that galactic cannibalism
exists among a limited number of interacting galaxies; however, astronomers are not
convinced of the existence of cannibalistic galactic monsters that swallow up large
numbers of smaller galaxies simultaneously.
Signs of galactic cannibalism exist even in our own galaxy, the Milky Way.
Astronomers have found younger stars south of the galaxy’s disk, where only older stars
should be found, suggesting that
the younger stars formed when our galaxy cannibalized a
smaller galaxy. Furthermore, it can be clearly
seen now that our galaxy is beginning to digest
the Magellanic Clouds, which are small irregular galaxies that are companions to the
Milky Way and are visible in the southern skies over Earth.
1. Which of the following is NOT true according to paragraph 1?
A. Galaxies may contain billions of stars.
B. On the average, the distance between galaxies is around 20 times the diameter of a galaxy.
C. It is unusual for stars to collide.
D. The average distance between stars is 70 times their diameter.
2. The author mentions tails and bridges in paragraph 2 in order to .
A. provide a visual image of the parts of galaxies that have been affected by
gravitational forces
324 394
B. provide examples of the types of galaxies that tend to collide
C. describe the recognizable characteristics of the colliding galaxies called the Mice
D. create a visual roadmap of the routes that galaxies take through the skies
3. The word last in paragraph 2 could best be replaced by .
A. end in B. endure for C. finish with D. lose out to
4. The word merge in paragraph 3 is closest in meaning to .
A. divide B. swallow C. join D. appear
5. What occurs during galactic cannibalism, according to paragraph 3?
A. A larger galaxy is absorbed by a smaller one.
B. The first step involves pulling at the core of the smaller galaxy.
C. The outer stars of the smaller galaxy are absorbed by its core.
D. The core of the smaller galaxy generally manages to remain visible
6. Which of the sentences below expresses the essential information in the highlighted
sentence in paragraph 4?
A. Astronomers have recently found some giant galaxies that have cannibalized a
number of galaxies.
B. Astronomers used to think that certain giant galaxies that appeared to have a
number of nuclei were galactic cannibals.
C. When astronomers find galaxies with multiple nuclei, they know that they
have found galactic cannibals.
D. Even though a galaxy has multiple nuclei, it is not certain whether or not the
galaxy is a galactic cannibal.
7. The phrase put forth in paragraph 4 is closest in meaning to .
A. encounter B. understand C. deny D. promote
8. Why does the author mention voracious monsters in paragraph 4?
A. To emphasize how violently the galaxies strike each other.
B. To emphasize how much energy the giant galaxies consume.
C. To emphasize how many smaller galaxies the giant galaxies seem to consume.
D. To emphasize how really big the giant galaxies are.
9. It is stated in paragraph 4 that scientists today are quite certain that .
A. galactic cannibalism does not really exist
B. there is a limited amount of galactic cannibalism
C. galactic cannibalism is commonplace
D. galactic cannibals are capable of taking over numerous small galaxies at the same time
10. Based on the information in paragraph 5, what will be most likely to
happen to the Magellanic Clouds in the distant future?
A. They will become galactic cannibals. B. They will develop separate nuclei.
C. They will become regular galaxies. D. They will become part of the Milky Way
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.

325 394
Part 4: Reading passage 4 has seven paragraphs A-G.
For questions 1-5, choose the correct heading for paragraphs B, C, D, E, and F from
the list of the headings below. Write your answers in answer box below. (20 points)
List of Headings
i The reaction of the Inuit community to climate change
ii
Understanding of climate change remains limited
iii
Alternative sources of essential supplies
iv
Respect for Inuit opinion grows
v
A healthier choice of food
vi
A difficult landscape
vii
Negative effects on well-being
viii
Alarm caused by unprecedented events in the Arctic
ix
The benefits of an easier existence
Example Paragraph A Answer viii
1. Paragraph B
2. Paragraph C
3. Paragraph D
4. Paragraph E
5. Paragraph F
Climate change and the Inuit
A
Unusual incidents are being reported across the Arctic. Inuit families going off on
snowmobiles to prepare their summer hunting camps have found themselves cut off from
home by a sea of mud, following early thaws. There are reports of igloos losing their
insulating properties as the snow drips and refreezes, of lakes draining into the sea as
permafrost melts, and sea ice breaking up earlier than usual, carrying seals beyond the
reach of hunters. Climate change may still be a rather abstract idea to most of us, but in the
Arctic it is already having dramatic effects - if summertime ice continues to shrink at its
present rate, the Arctic Ocean could soon become virtually ice-free in summer. The knock-
on effects are likely to include more warming, cloudier skies, increased precipitation and
higher sea levels. Scientists are increasingly keen to find out what’s going on because they
consider the Arctic the ‘canary in the mine’ for global warming - a warning of what’s in
store for the rest of the world.
B
For the Inuit the problem is urgent. They live in precarious balance with one of the toughest

326 394
environments on earth. Climate change, whatever its causes, is a direct threat to their way
of life. Nobody knows the Arctic as well as the locals, which is why they are not content
simply to stand back and let outside experts tell them what’s happening. In Canada, where
the Inuit people are jealously guarding their hard-won autonomy in the country’s newest
territory, Nunavut, they believe their best hope of survival in this changing environment
lies in combining their ancestral knowledge with the best of modern science. This is a
challenge in itself.
C
The Canadian Arctic is a vast, treeless polar desert that’s covered with snow for most of
the year. Venture into this terrain and you get some idea of the hardships facing anyone
who calls this home. Farming is out of the question and nature offers meagre pickings.
Humans first settled in the Arctic a mere 4,500 years ago, surviving by exploiting sea
mammals and fish. The environment tested them to the limits: sometimes the colonists
were successful, sometimes they failed and vanished. But around a thousand years ago,
one group emerged that was uniquely well adapted to cope with the Arctic environment.
These Thule people moved in from Alaska, bringing kayaks, sleds, dogs, pottery and iron
tools. They are the ancestors of today’s Inuit people.
D
Life for the descendants of the Thule people is still harsh. Nunavut is 1.9 million square
kilometers of rock and ice, and a handful of islands around the North Pole. It’s currently
home to 2,500 people, all but a handful of them indigenous Inuit. Over the past 40 years,
most have abandoned their nomadic ways and settled in the territory’s 28 isolated
communities, but they still rely heavily on nature to provide food and clothing. Provisions
available in local shops have to be flown into Nunavut on one of the most costly air
networks in the world, or brought by supply ship during the few ice-free weeks of
summer. It would cost a family around £7,000 a year to replace meat they obtained
themselves through hunting with imported meat. Economic opportunities are scarce, and
for many people state benefits are their only income.
E
While the Inuit may not actually starve if hunting and trapping are curtailed by climate
change, there has certainly been an impact on people’s health. Obesity, heart disease and
diabetes are beginning to appear in a people for whom these have never before been
problems. There has been a crisis of identity as the traditional skills of hunting, trapping
and preparing skins have begun to disappear. In Nunavut’s ‘igloo and email’ society,
where adults who were born in igloos have children who may never have been out on the
land, there’s a high incidence of depression.
F
With so much at stake, the Inuit are determined to play a key role in teasing out the
mysteries of climate change in the Arctic. Having survived there for centuries, they
believe their wealth of traditional knowledge is vital to the task. And Western scientists
are starting to draw on this wisdom, increasingly referred to as ‘Inuit Qaujimajatugangit’,
or IQ. ‘In the early days scientists ignored us when they came up here to study anything.
They just figured these people don’t know very much so we won't ask them,’ says John
Amagoalik, an Inuit leader and politician. ‘But in recent years IQ has had much more
credibility and weight.’ In fact it is now a requirement for

327 394
anyone hoping to get permission to do research that they consult the communities, who are
helping to set the research agenda to reflect their most important concerns. They can turn
down applications from scientists they believe will work against their interests, or research
projects that will impinge too much on their daily lives and traditional activities.
G
Some scientists doubt the value of traditional knowledge because the occupation of the
Arctic doesn’t go back far enough. Others, however, point out that the first weather
stations in the far north date back just 50 years. There are still huge gaps in our
environmental knowledge, and despite the scientific onslaught, many predictions are no
more than best guesses. IQ could help to bridge the gap and resolve the tremendous
uncertainty about how much of what we’re seeing is natural capriciousness and how much
is the consequence of human activity.
For questions 6 - 10, Choose NO MORE THAN ONE WORD from paragraphs C, D
and E to complete the summary of paragraphs C, D, E below.
If you visit the Canadian Arctic, you immediately appreciate the problems faced by people
for whom this is home. It would clearly be impossible for the people to engage in 6.
as a means of supporting themselves. For thousands of years they have
had to rely on catching sea mammals and fish as a means of sustenance. The harsh
surroundings saw many who tried to settle there pushed to their limits, although some were
successful. The 7. people were an example of the latter and for them the
environment did not prove unmanageable. For the present inhabitants, life continues to be a
struggle. The territory of Nunavut consists of little more than ice, rock and a few 8.. In recent years,
many of them have been obliged to give up their 9. lifestyle, but they continue to
depend mainly on nature for their food and clothes. Imported produce is particularly
expensive. Besides, with the spread of common diseases and the loss of conventional
techniques, the 10. problem and a crisis of identity are becoming a matter of
concern of almost everyone.
Your answers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
SECTION
IV:
WRITING
Part 1: Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means the same as
the sentence before it. (10 points)
1. It was not until five years had elapsed that the whole truth about the murder
came out. Not for another
2. At the moment, people think the accident is Nick’s fault.
Nick is currently
3. Even though it was raining heavily, the explorers decided to continue their
journey. The heavy rain could _
4. This scheme is too risky for my liking.

328 394
The risks
5. The fund-raisers haven’t officially decided where to send the proceeds of the
concert. No
Part 2: Rewrite these sentences using the words in CAPITAL. You must not change
the given words. (10 points)
1. The two theories appear to be completely different. COMMON
The two theories appear
2. Someone rang the police with information about an impending robbery. TIPPED
The police about an impending robbery.
3. I really admire you for your improvement. HAT
I improvement.
4. Williams tried to remain impartial in the quarrel between his two cousins. SIDES
Williams between his two cousins.
5. They will consider age and experience when they decide the salary. ACCOUNT
They will when they decide the salary.
Part 3: Write a paragraph. (30 points)
“Classmates are a more important influence than parents on a child’s success at school.”
Do you agree or disagree with the statement? You should write a paragraph of about 150 words to
TRẠI HÈ HÙNG VƯƠNG LẦN THỨ XIII
TUYÊN QUANG 2017
ĐÁP ÁN VÀ HƯỚNG DẪN CHẤM
ĐỀ THI OLYMPIC MÔN TIẾNG ANH
LỚP 10
Ngày thi: 29 tháng 7 năm 2017
express your viewpoint.
-
-
SECTION I: LISTENING COMPREHENSION (50 POINTS)
Part 1. ( 14 points) Each correct answer scores 2.0 points
1.
mountains
2. garden(s) 3. experience 4. Ratchesons 5. helmet
6. shops 7. 267

329 394
Part 2. ( 16 points) Each correct answer scores 2.0 points
1. August 2. 18 3. (the) air fares / airfares
4. Boat 5. Beach 6. Campfire / camp fire
7. (huge) crocodiles 8. E-mail (s) / email(s)
Part 3. (10pts) Each correct answer scores 2.0 points
1. T 2. F 3. F 4. T 5. T
Part 4. (10 points) Each correct answer scores 2.0 points
1. B 2. D 3. B 4. D 5. A
SECTION II. LEXICO-GRAMMAR (50 POINTS)
Part 1. (20 points) Each correct answer scores 1.0 point
1. A 2. C 3. C 4. C 5. A 6. B 7. C 8. C 9. B 10. A
11. C 12. A 13. D 14. A 15. A 16. B 17. C 18. D 19. A 20. D
Part 2. (10 points) Each correct answer scores 1.0 point
1. expressionless 2. authorized 3. communal 4. cowardliness 5. self-destruction
6. personality 7. irresistibly 8. impassable 9. malpractices 10. carriage
Part 3. (10 points) Each correct answer scores 1.0 point
Line Mistake Correction Line Mistake Correction
1 is x 8 more much
2 will would 9 blooded blood
3 just such 11 although because
4 unless if 12 why what
6 what which 14 solve cope/deal
Part 4. (10 points) Each correct answer scores 1.0 point

330 394
1. in 2. from 3. on 4. in 5. over
6. about 7. across 8. beyond 9. down 10. away
SECTION III: READING COMREHENSION (50 POINTS).
Part 2. (10 points) Each correct answer scores 1.0 point
1. B 3. B 5. C 7. A 9. C
2. C 4. D 6. C 8. A 10. D
Part 2. (10 points) Each correct answer scores 1.0 point
1. up 2. were 3. kind/sort 4. at 5. What
6. often/sometimes 7. far 8. not 9. much 10. only/just
Part 3. (10 points) Each correct answer scores 1.0 point
1. D 2. A 3. B 4. C 5. D
6. B 7. D 8. C 9. B 10. D
Part 4. (20 points) Each correct answer scores 2.0 points
1. Paragraph B: i
2. Paragraph C: vi
3. Paragraph D: iii
4. Paragraph E: vii
5. Paragraph F: iv
6. farming 7. Thule 8. islands 9. nomadic 10. health
SECTION IV: WRITING (50 POINTS)
Part 1. (10 points) Each correct answer scores 2.0 points
1. Not for another five years did the whole truth about the murder come out.
2. Nick is currently being blamed for the accident.

331 394
3. The heavy rain could not stop/prevent the explorers from continuing their journey.
4. The risks of this scheme (or involved in this scheme) are too great for my liking.
5. No official decision(s) on where to send the proceeds of the concert has (/have) been
made by the fund-raisers.
Part 2. (10 points) Each correct answer scores 2.0 points
1. The two theories appear to have (got) nothing in common.
2. The police were tipped off information about an impending robbery.
3. I take my hat off to you for your improvement.
4. Williams tried not to take sides in the quarrel between his two cousins.
5. They will take age and experience into account when they decide the salary.
Part 3. Write a paragraph. (30 points)
Mô tả tiêu chí đánh giá Điểm tối đa
1. Bố cục
o Câu dẫn chủ đề mạch lạc
o Bố cục hợp lý rõ ràng, phù hợp với yêu cầu của đề bài
o Bố cục uyển chuyển từ mở bài đến kết luận
6
2. Phát triển ý
o Phát triển ý có trình tự logic
o Có dẫn chứng, ví dụ,… đủ để bảo vệ ý kiến của mình
6
3. Sử dụng ngôn từ
o Sử dụng ngôn từ phù hợp với nội dung
o Sử dụng ngôn từ đúng văn phong, thể loại
o Sử dụng từ nối cho các ý uyển chuyển
6
4. Nội dung
o Đủ thuyết phục người đọc
o Đủ dẫn chứng, ví dụ, lập luận
o Độ dài: Số từ không nhiều hoặc ít hơn quy định 10%
6

332 394
5. Ngữ pháp, dấu câu, chính tả
o Sử dụng đúng dấu câu
o Chính tả: Viết đúng chính tả
Lỗi chính tả gây hiểu lầm/ sai lệch ý sẽ bị tính một lỗi (trừ
1% điểm của bài viết)
Cùng một lỗi chính tả lặp lại chỉ tính một lỗi
o Sử dụng đúng thời, thể, cấu trúc câu đúng ngữ pháp. (Lỗi ngữ pháp
gây hiểu lầm/ sai lệch ý sẽ bị trừ 1% điểm của bài viết)
6
Tổng 30
Part 1
Hi. Can I help
you?
-----HẾT-----
TAPESCRIPTS
I’d like to find out if you have any excursions suitable for families.
Sure. How about taking your family for a cruise? We have a steamship that takes
passengers out several times a dav - it’s over 100 years old.
That sounds interesting. How long is the trip?
About an hour and a half. And don’t forget to take pictures of the mountains. They’re
all around you when you’re on the boat and they look fantastic.
OK. And I assume there’s a cafe or something on
board? Sure. How old are your children?
Er, my daughter’s fifteen and my son’s seven.
Right. Well there are various things you can do once you’ve crossed the lake, to
make a day of it. One thing that’s very popular is a visit to the Country Farm You’re
met off the boat by the farmer and he’ll take you to the holding pens, where the sheep
are kept. Children love feeding them!
My son would love that. He really likes animals.
Well, there’s also a 40-minute trek round the farm on a horse, if he
wants. Do you think he’d manage it? He hasn't done that before.
Ah, good.
And again, visitors are welcome to explore the farm on their own, as long as they take
care to close gates and so on. There are some very beautiful gardens along the side of
the lake which also belong to the farm - they’ll be just at their best now. You could
easily spend an hour or two there.
OK. Well that all sounds good. And can we get lunch there?
You can, and it’s very good, though it’s not included in the basic cost. You pay when
you get there.
Right.
So is there anything else to do over on that side of the lake?
Well, what you can do is take a bike over on the ship and then go on a cycling trip.

333 394
There’s a trail there called the Back Road - you could easily spend three or four hours
exploring it, and the

334 394
scenery’s wonderful. They’ll give you a map when you get your ticket for the cruise -
there’s no extra charge.
What’s the trail like in terms of difficulty?
Quite challenging in places. It wouldn’t be suitable for your seven-year-
old. It needs someone who’s got a bit more experience.
Hmm. Well, my daughter loves cycling and so do I, so maybe the two of us could go,
and my wife and son could stay on the farm. That might work out quite well. But we
don’t have bikes here... is there somewhere we could rent them?
Yes, there’s a place here in the city. It’s called
Ratchesons. I’ll just make a note of that - er, how do
you spell it?
R-A-T-C-H-E-S-O-N-S. It’s just by the cruise ship
terminal. OK.
You’d also need to pick up a repair kit for the bike from there to take along with you, and
you’d need to take along a snack and some water - it’d be best to get those in the city.
Fine. That shouldn’t be a problem. And I assume I can rent a helmet from the bike
place? Sure, you should definitely get that. It’s a great ride, but you want to be well
prepared because it’s very remote - you won’t see any shops round there, or anywhere
to stay, so you need to get back in time for the last boat.
Yeah. So what sort of prices are we looking at here?
Let’s see, that’d be one adult and one child for the cruise with farm tour, that’s $117, and
an adult and a child for the cruise only so that’s $214 dollars altogether. Oh, wait a
minute, how old did you say your daughter was?
Fifteen.
Part 2
You will hear part of an interview with a woman called Sophie Doyle, who
organizes adventure holidays in Australia for teenagers. For questions 9 to 18,
complete the sentences.
Interviewer: Today I have with me in the studio Sophie Doyle from the travel organization
Adventure Holidays International, and she’s going to be telling us about some exciting
ideas for teenagers for the summer. Sophie, what kind of holidays do you organize?
Sophie: They’re three-week trips to a variety of destinations in the country chosen,
normally from late June to mid-July in the USA and the first three weeks of (9) August in
the case of Australia. Trips in New Zealand are available from early September, when the
weather is a little warmer, bearing in mind that our summer is their winter. The
Australian holidays are currently the most popular though, probably because they’re
mainly in the north of the country where it never gets really cold.
Interviewer: And who goes on the Australian ones? Who looks after the people on them?
Sophie: There are always four experienced leaders with (10) every group, which consists
of 18 young people aged 15 or 16 at the time of the trip. This means there’s one leader for
every 4 or 5 teenagers, all of whom are close to each other in age.

335 394
Interviewer: Is it very expensive? What’s included in the price?
Sophie: For next year, it’ll be 4,990 euro. For that you get accommodation, three meals a day,
(11) all transport apart from air fares, entry fees and any equipment needed for activities.
Interviewer: And what kind of accommodation is there? Tents?
Sophie: No, it’s not like a summer camp. In fact there’s a whole range of places, from huts
in the rainforest to motels on the desert roads, (12) boats when we’re visiting tropical
islands and comfortable apartments in surfing resorts.
Interviewer: So where do you actually go?
Sophie: Well, for the teen it all begins when we meet you at Brisbane Airport Arrivals.
We take you to a hostel on the coast and help you settle in. After a good night’s sleep,
which you’ll probably need after all that travelling, (13) we’ll introduce you to your
travelling companions, and what better place to do that could there be than the beach?
You’ll spend all day there, swimming and surfing if you like. Then, the next morning, it’s
off to Fraser Island, on the Pacific coast of Queensland.
Interviewer: What are the attractions there?
Sophie: Well, it has the most wonderful beaches, including one that’s 75 miles - 120
kilometres - long. It seems to go on forever! In fact, the island as a whole is in the record
books as (14) the biggest one on Earth made entirely of sand. It’s a long way from being a
desert island, though. It has beautiful lakes, huge forests and some fascinating wildlife.
Interviewer: And where do you go next?
Sophie: Inland. The next stop is in the outback; it really is a huge area where almost
nobody lives. There you have the chance to see some remarkable animals including
kangaroos of course, swim in a lake and then (15) spend the night Australian-style: by the
campfire in a sleeping bag.
After several days in the outback, it’s back to the coast, but further north, and out to the
islands of the Great Barrier Reef, for over a week.
Interviewer: That sounds wonderful, but don’t you need to be an experienced diver?
Sophie: No, because (16) we’ll arrange diving lessons if you don’t already have a
certificate. That’s all included. As are wetsuits and other diving equipment for everyone,
of course.
Interviewer: And after that?
Sophie: It’s north again, towards the north-eastern tip of Australia and into the tropical
rainforest. You start with a cruise along the fast-moving river there, which cuts right
through the forest.
Interviewer: What do you usually see there?
Sophie: Well, there are some very big fish in the water and colorful tropical birds in the
trees, as well as some (17) huge crocodiles in the mud on either side. You might also have

336 394
the odd giant butterfly fluttering around the boat - there are some wonderful species
unique to the area.

337 394
Interviewer: Do you spend quite some time in the
rainforest? Sophie: Yes, most of the rest of the trip, in fact.
Interviewer: And in all these remote places, how do you stay in touch with your family
and friends?
Sophie: Well, you can bring your mobile phone but normally we ask people to keep them
switched off. Otherwise there are constant incoming calls, which interrupt everything. But
(18) every few days we make sure we’re somewhere you can email people. Of course, if
there’s an emergency, we’ll arrange it so you can speak to your family, but that rarely
seems to happen.
Part 3:
Part 4
Interviewer: My guest today is Douglas Turner, who recently spent a weekend climbing a
mountain in Africa. Douglas, how did this come about?
Douglas: Well, I suppose it started with seeing adverts for activity holidays in the
national press week after week; it somehow got into my subconscious. Then there was
one which said, “Are you ready for the greatest physical challenge of your life? Five
thousand metres. One weekend.” And somewhat against my better judgement, I found
myself picking up the phone straight away. You see, I simply hadn’t trained for it; the
nearest I’d got was a bit of hill-walking five years ago.
Interviewer: What did you think you would get out of the weekend?
Douglas: Generally when I go to things, I enjoy meeting people, but in this case I was
afraid the rest of the group would be a bunch of healthy types and I wouldn’t have much in
common with them. And as for the weekend at all. It was more a kind of wanting to see
what I was mentally capable of doing. Would I get cold feet and not go at all? Or go, but
give up halfway up? That sort of thing.
Interviewer: But you made it to the top.
Douglas: Yes, I did. Much to my surprise, I can tell you.
Interviewer: And were you right about the other people?
Douglas: No, actually. There were a few serious walkers and climbers, but most of the
participants were professional people who wanted to do something quite different once in
a while, more or less like me, in fact. So not intimidating after all. Though I have to admit
that nearly all of them were fitter than me. Actually, I hadn’t realized so many people did
this sort of

338 394
thing. It was funny-When I told a friend that I was going, she said, “Oh, not another one.
Every one I know’s going climbing this year. There’s a big thing about pushing yourself to
your limit at the moment, isn’t there? You’re welcome to it,” she said. “You won’t catch
me up there”.
Interviewer: How did you all get on together?
Douglas: I suppose we were a bit suspicious of each other at first, but that soon went, and
we somehow developed a really close group feeling, and nobody complained about
having to wait for the slow ones, which usually included me. Or at least, if they did
complain, they did it out of earshot. In fact, on the fight home we were busy exchanging
cards and decided to book another weekend trip as a party-but without a mountain in
sight this time.
Interviewer: So how did the weekend compare with your expectations?
Douglas: It was much better than I’d expected. It made me change in subtle ways. As I’d
hope, I gained in self-knowledge, and I learned to get in with people I couldn’t escape
from, but I also became much more observant, of the tiny little wild flowers, for instance,
and that was quite a bonus.
Interviewer: I suppose you’re going to be a regular mountain climber now.
Douglas: The pair of boots I wore I’m keeping with the mud still on them on my desk at
work. They’re a kind of trophy, to prove to myself that I’ve done it. But I somehow don’t
think I’ll be using them again. I’m going to have to put them somewhere less visible,
though, because it’s sometimes a bit embarrassing when other people are impressed.
Interviewer: Douglas Turner, thank you very much.
Douglas: Thank you./.

339 394

340 394
Bấm Tải xuống để xem toàn bộ.




