





Preview text:
Unit 1: The Natural World
Bài 1: Thế giới tự nhiên
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF LOGGING
TÁC ĐỘNG MÔI TRƯỜNG CỦA LOGING Words
Look for the following words as you read the passage. Match
each word with its correct definition.
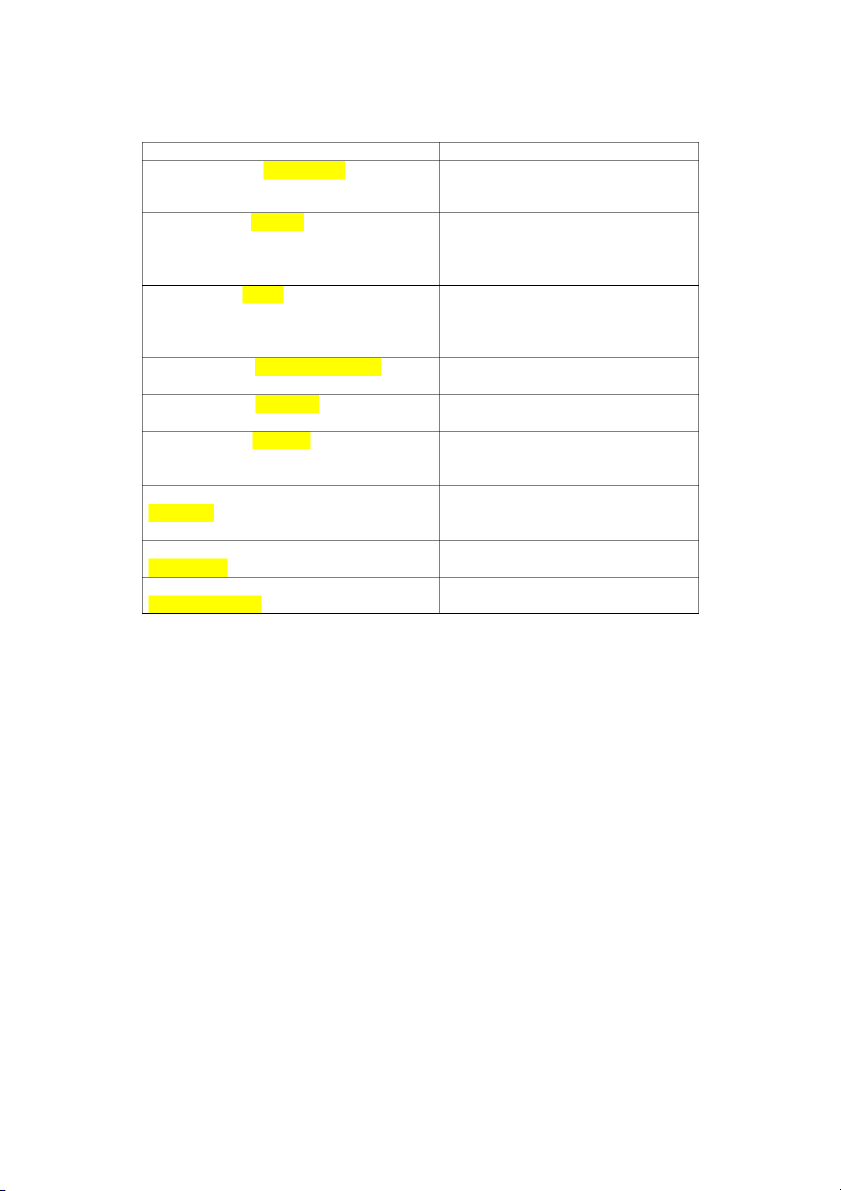
Tìm những từ sau khi bạn đọc đoạn văn. Nối mỗi từ với định nghĩa Words Definitions 1. aquatic A. n., the natural world thủy sinh 2. array
B. v., to reach past, get bigger mảng Vượt qua, lớn hơn 3. defense' C. n., a large number, a Phòng thủ collection Số lớn 1 bộ sưu tập 4. deforestation
D. n., loss of soil from action of nạn phá rừng water or wind
Mất đất từ tác động của nước và gió 5. environment E. adj., living in the water môi trường 6. erosion F. adj., living on the land xói mòn Sống trên đất liền 7. extend G. v., to cut down mở rộng Cắt giảm 8. fell
H. n., the natural area where a ngã plant or animal lives
khu vực tự nhiên nơi thực vật và động vật sống 9. habitat I. n., a strong effect môi trường sống tác động mạnh 10. Impact J. n.. protection Tác động
Bảo vệnga8n chặn , làm chậm lại 11. Inhibit: ức chế K. v., to prevent, slow down
Ngăn chặn , làm chậm lại 12. Intercept : đánh chặn L. n.. plants Thực vật 13. logging : đốn gỗ
M. n., the removal of all trees from a large area
Việc chặt bỏ tất cả cây cối khỏi 1 khu vực rộng lớn 14. myriad: vô số
N. n., the cutting down of trees for commercial purposes
Việc chặt phá cây vì mục đích thương mại
15. nutrient : chất dinh dưỡng O. v., to disappear Biến mất 16. pollution: ô nhiễm P. adj.. many, numerous Nhiều, vô số 17. stabilize: ổn định Q. n., damage to air, water, etc.
Thiệt hại về không khí, nước 18. terrestrial R. v., to keep from changing, Trên cạn maintain
Tránh sự thay đổi, duy trì 19. vanish S. v., to catch Phòng thủ Bắt 20. vegetation T. n., food Thảm thực vật Reading
Environmental Impacts of Logging
A. From shipping crates to paper bags, the logging industry supplies
the raw materials for an array of products. However, this is not
without untold harm to the environment. The damage includes
habitat loss, pollution, and climate change, with the effects
spanning the globe from the rain forests of Central Africa,
Southeast Asia, and South America to the northern forests of
Canada and Scandinavia. The effects of logging extend beyond
just the felling of a swath of trees. Nutrients, water, and shelter
for plants, animals, and microorganisms throughout the
ecosystem are also lost; many life forms--both terrestrial and
aquatic—are becoming endangered as forests vanish.
Một. Từ thùng vận chuyển đến túi giấy, ngành khai thác gỗ
cung cấp nguyên liệu thô cho một loạt các sản phẩm. Tuy
nhiên, điều này không phải là không có tác hại không kể xiết
đối với môi trường. Thiệt hại bao gồm mất môi trường sống,
ô nhiễm và biến đổi khí hậu, với những ảnh hưởng trải dài
trên toàn cầu từ các khu rừng mưa ở Trung Phi, Đông Nam Á
và Nam Mỹ đến các khu rừng phía bắc Canada và
Scandinavia. Tác động của việc khai thác gỗ vượt ra ngoài
việc chặt hạ một dải cây. Chất dinh dưỡng, nước và nơi trú ẩn
cho thực vật, động vật và vi sinh vật trong toàn bộ hệ sinh
thái cũng bị mất; Nhiều dạng sống - cả trên cạn và dưới nước
- đang trở nên nguy cấp khi rừng biến mất.
B. Trees protect the soll beneath them; thus, tree loss can affect soli
Integrity. For example, the rain forest floor, home to myriad plant
life as well as insects, worms, reptiles and amphiblans, and small
mammals, reiles on a dense canopy of branches and leaves to
keep it healthy and intact. The canopy prevents surface runofi by
intercepting heavy rainfall so that water can drip down slowly
onto the porous earth. Tree roots also stabilize the soll and help
prevent erosion. In return, a healthy soil encourages root
development and microblal activity, which contribute to tree
growth and well-belng. A major factor in logging-related soil dam-
age comes from road bullding, with trucks and other heavy
equipment compressing the spongy soil, creating furrows where
water collects, and disrupting the underground water flow.
Eventually, the topsoll wears away, leaving behind an infertile layer of rocks and hard clay.
B. Cây cối bảo vệ cây cối bên dưới chúng; do đó, mất cây có
thể ảnh hưởng đến tính toàn vẹn của soli. Ví dụ, sàn rừng
mưa, nơi sinh sống của vô số loài thực vật cũng như côn
trùng, giun, bò sát và lưỡng cư, và động vật có vú nhỏ, di
chuyển trên một tán cây và lá rậm rạp để giữ cho nó khỏe
mạnh và nguyên vẹn. Tán cây ngăn chặn chảy nước bề mặt
bằng cách chặn lượng mưa lớn để nước có thể nhỏ giọt từ từ
xuống đất xốp. Rễ cây cũng ổn định soll và giúp chống xói
mòn. Đổi lại, một loại đất khỏe mạnh khuyến khích sự phát
triển của rễ và hoạt động của vi sinh vật, góp phần vào sự
phát triển của cây và tốt. Một yếu tố chính trong tuổi đập
đất liên quan đến khai thác gỗ đến từ việc bò tót trên đường,
với xe tải và các thiết bị hạng nặng khác nén đất xốp, tạo ra
các rãnh nơi nước tích tụ và làm gián đoạn dòng nước ngầm.
Cuối cùng, topsoll bị bào mòn, để lại một lớp đá vô sinh và đất sét cứng.
C. Logging can also damage aquatic habitats. Vegetation along
rivers and stream banks helps maintain a steady water flow by
blocking the entry of soil and other residue, and tree shade
inhibits the growth of algae. Removing trees obliterates these
benefits. When eroding soil flows into waterways, the organic
matter within it consumes more oxygen, which can lead to
oxygen depletion in the water, killing fish and other aquatic wildlife.
C. Khai thác gỗ cũng có thể làm hỏng môi trường sống dưới
nước. Thảm thực vật dọc theo sông và bờ suối giúp duy trì
dòng nước ổn định bằng cách ngăn chặn sự xâm nhập của đất
và các dư lượng khác, và bóng cây ức chế sự phát triển của tảo.
Loại bỏ cây sẽ xóa sạch những lợi ích này. Khi đất xói mòn chảy
vào đường thủy, chất hữu cơ bên trong nó tiêu thụ nhiều oxy
hơn, có thể dẫn đến cạn kiệt oxy trong nước, giết chết cá và
các động vật hoang dã dưới nước khác.
D. Trees provide a natural defense against air pollution. They
remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere while they emit
oxygen, and their leaves filter pollutants from the air. Cutting
down trees keeps pollutants airborne, where they can mix with
water vapor! and form acid rain. Water quality in nearby streams
and rivers also deteriorates as tree loss contributes to increased sedimentation.
D. Cây xanh cung cấp một sự bảo vệ tự nhiên chống lại ô
nhiễm không khí. Chúng loại bỏ carbon dioxide khỏi khí
quyển trong khi chúng thải ra oxy và lá của chúng lọc các
chất ô nhiễm từ không khí. Chặt cây giữ cho các chất ô
nhiễm trong không khí, nơi chúng có thể trộn với hơi nước!
và tạo thành mưa axit. Chất lượng nước ở các dòng suối và
sông gần đó cũng xấu đi vì mất cây góp phần làm tăng trầm tích.
E. In a healthy forest ecosystem, trees draw moisture from the soil
and release It into the atmosphere while they provide shade to
lessen evaporation. Thus, deforestation impacts rainfall patterns,
leading to flooding as well as drought and forest fires.
Deforestation is responsible for about one-fifth of carbon dioxide
emissions worldwide, making it a major contributor to climate
change in particular, global warming. In the Amazon basin alone,
deforestation is responsible for millions of tons of carbon dioxide
being released into the atmosphere annually. Some logging
companies burn large tracts of forest just to facilitate access to
one area—a practice? that discharges even more carbon dioxide.
E. Trong một hệ sinh thái rừng khỏe mạnh, cây hút độ ẩm từ
đất và giải phóng nó vào khí quyển trong khi chúng cung cấp
bóng mát để giảm bớt sự bốc hơi. Do đó, nạn phá rừng ảnh
hưởng đến lượng mưa, dẫn đến lũ lụt cũng như hạn hán và
cháy rừng. Phá rừng chịu trách nhiệm cho khoảng một phần
năm lượng khí thải carbon dioxide trên toàn thế giới, khiến
nó trở thành một đóng góp chính cho biến đổi khí hậu nói
riêng, sự nóng lên toàn cầu. Chỉ riêng trong lưu vực sông
Amazon, nạn phá rừng chịu trách nhiệm cho hàng triệu tấn
carbon dioxide được thải vào khí quyển hàng năm. Một số
công ty khai thác gỗ đốt những vùng rừng rộng lớn chỉ để
tạo điều kiện tiếp cận một khu vực - một thực tế? Điều đó
thải ra nhiều carbon dioxide hơn.
F. Forests, especially the tropical rain forests, are a vital natural
resource with extensive biodiversity and irreplaceable wildlife
habitats. More responsible logging practices would help ensure
that they are protected for future generations.
F. Rừng, đặc biệt là rừng mưa nhiệt đới, là một nguồn tài
nguyên thiên nhiên quan trọng với đa dạng sinh học rộng lớn
và môi trường sống hoang dã không thể thay thế. Thực hành
khai thác gỗ có trách nhiệm hơn sẽ giúp đảm bảo rằng chúng
được bảo vệ cho các thế hệ tương lai.
Answer the questions about Environmental Impacts of Logging. Questions 1-4
The reading passage contains six paragraphs, A-F.
Which paragraphs discuss the following information? Write the correct letter, A-F.
1. ……………….The impact of logging on the weather
2…………………... How trees inhibit soil erosion
3.,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,. How deforestation contributes to air pollution
4……………………… The impact of erosion on fish Questions 5-8
Complete the summary using words from the list below.
The logging industry 5....... trees to get the wood that is used to make
many products. This practice has 6......... effects on the environment.
The natural 7......... of many terrestrial and aquatic animals are
damaged. Trees protect the environment in many ways. They are an
effective 8……………….against both air pollution and soil erosion.
Ngành khai thác gỗ 5....... cây để lấy gỗ dùng làm nhiều sản
phẩm. Thực hành này có 6........... ảnh hưởng đến môi trường.
Thiên nhiên của nhiều loài động vật trên cạn và dưới nước bị hư
hại. Cây xanh bảo vệ môi trường bằng nhiều cách. Chúng là
biện pháp hiệu quả chống lại cả ô nhiễm không khí và xói mòn đất. aquatic defense habitats myriad arrays fells intercepts vegetation My Words
Write the words that are new to you. Look them up in the dictionary and write their definitions. Words Definitions WORD FAMILIES Noun Defense The shade from trees provides a defense against the drying effects of the sun. Noun Defender Defenders of the environment work to protect plants and animals from damage caused by logging. verb Defend Fish cannot defend themselves from the effects of water pollution. Noun Environment The environment needs to be protected from the effects of logging. Adjective Environmental Logging causes a great deal of environmental damage. Adverb Environmentally It is important to develop more environmentally friendly logging practices Noun Erosion Soil erosion leads to the pollution of streams and rivers. verb Erode When soll erodes, there are no nutrients left to help plants grow. N Extent The extent of environmental damage caused by logging is frightening V Extend The Amazon rain forest extends from Brazil into neighboring countries. Adj Extensive The Amazon rain forest is the most extensive rain forest in the world. adv extensively Rain forests around the world have been extensively logged. N Pollution Deforestation contributes to the ellects of both air and water pollu- tion. N Pollutant Factories add pollutants to the air and water. verb pollute Eroding soll pollutes water. N stability The stability of the natural environment depends on the interaction of many factors. V stabilize We need to stabilize the damage caused by logging before it gets worse. adj stable If the banks of the river continue to erode, they will no longer be stable. Word Family Practice
Choose the correct word family member from the list below to complete each blank.
Modern Industry has caused damage to our natural 1.......... In many
ways. The air and water are Alled with 2.......... One result of this is acid
rain, which has caused 3......... damage to vegetation in many areas.
When large amounts of vegetation die off. the environment loses 4...........
If there are no plants to hold the soil, it starts to 5........... This leads to
myriad problems, Including water pollution and habitat loss. 6.......... of
wildlife work hard to prevent further damage to natural areas. Environment Environmental Environmentally Pollution Pollutants Pollutes Extent Extend Extensive Stability Stabilizes Stable Erosion Erode Eroded Defenses Defenders Defends Word Skill Prefix de-
The prefix de- can mean remove.*
Read the sentences. Write a definition for each underlined word.
1. When we deforest an area, many animals lose their habitat. deforest:
2. Some people prefer to deseed fruit before eating it. deseed:
3. I had to deice the windshield before I could drive. deice: Listening
Listen to the lecture. Choose the correct letter, A, B, or C.
1. Trees provide a habitat for A. birds only. B. B a myriad of animals. C. C aquatic animals.
2………………….are a source of nutrients for birds. A Insects B Roots C Leaves
3. Trees provide aquatic animals with a defense from A coolness. B rain. C heat.
4. ……………………._ inhibit soil erosion. A Branches B Roots C Trunks Writing




