
Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 45349271
What's the Difference Between the Right Brain and Left Brain?
(https://www.voicetube.com/videos/123097 ) Recycling
What is up with this idea of people being left-brained and right-brained? Is it a myth?
Actual y, no. The thing is some people are more left-brained and others are more rightbrained.
We found out that what determines which side has dominance happens before we're even
born. In the womb, when our spines develop, the way they wire up to our developing brains
determines which side is dominant. Why do we have a dominant side? Lateralization. This
refers to some brain functions taking place in one hemisphere or one side, rather than the
other. Each hemisphere controls a different body side as well. Your dominant brain side
connects to your dominant body side. The left side of the brain controls the right side of the
body. And the right side, the left. This cross-wiring of the neural pathway means, if you are
left-handed you are relying more on the right side of the brain. And again vice versa. How does
this affect our thinking style? The left side and the right are responsible for very distinct thinking
patterns. Generally, the right brain thinks in pictures instead of words. Using intuition and
focusing on the bigger picture. The left focuses on actual words. Thinking in a very verbal way.
Honing in to details first, and then putting them together to form a whole picture. It's widely
agreed upon that the right side is creative and the left is logical. How is language affected?
The left side is good for vocabulary, grammar, and literal meanings. The right side is great for
intonation and accentuation, basically, how we speak. How is music heard in the brain? We
already know the right side is more creative. Music processing takes place in the entire brain.
With the right side focusing on the melody, while the left side focuses on the motor scale your
hands need to play the instrument. Is it true that math is left-brain business? We assume the
left side, being more logical, does more math. Things such as counting, adding, subtracting,
etc. The right, however, actually helps with estimating the amount of sets of objects. While
your left brain might help you take a test, the right brain can tell you how many boxes are stil
on the delivery pal et at work. Which side handles the memories? The hippocampus is actual y
the part of the brain associated with memory. And it occupies both sides of the brain. The left
side has been deemed more important for storing memories, as its strength is in retrieval. The
right side is good for reciting, like multiplication tables.
What happens in your brain when you exercise? Moving your
body can help you get out of depression
(What happens in your brain when you exercise? Moving your body can help you get out of depression Recycling
Have you ever thought about what happens in your brain when you’re moving around working
up a sweat? Most people know that exercise protects against diseases such as cancer and
diabetes. And if you’ve ever opened a celebrity magazine, you know that exercise helps you
with weight control and building stronger muscles. But what happens inside your body is much
more interesting: moving your body wil actually help you get out of depression! When you lOMoAR cPSD| 45349271
exercise, chemicals that contribute to happiness and pleasure are released in the brain. This
means that someone who has just finished a power walk feels happier immediately! This part
of the brain is called the prefrontal cortex. It has many important responsibilities, and you
activate it when you exercise. The prefrontal cortex acts as an emotional brake that helps you
handle strong emotions,which can be important when you’re going through depression. It’s
also in charge of concentration. Perhaps you have noticed that it’s harder to concentrate?
When you exercise, your prefrontal cortex gets busier, and your ability to concentrate and react
quickly wil improve immediately. A good idea is to do some light jogging an hour before an
exam or an important meeting. Now you know a bit about what happens in your brain
immediately after working up a sweat. But what happens in the long run if you make exercise
a regular thing? Moving your body a few times a week means new brain cells are born inside
your head, both in the prefrontal cortex and in this other neat brain area called the
Hippocampus. These areas of the brain get bigger. The hippocampus is a part of your body
that you real y want to keep as big as possible. Among other things it's responsible for long-
term memory. So, what happens inside your body when you take a sweaty walk is much more
important than what happens on the outside! You wil become better at handling emotions, and
be able to concentrate and remember things. Perhaps most importantly, it wil affect your mood in a positive way.
What is “normal” and what is “different”? - Yana Buhrer Tavanier
(https://www.ted.com/talks/yana_buhrer_tavanier_what_is_normal_and_what_is_different ) Recycling
"If you are always trying to be normal, you wil never know how amazing you can be.", Maya
Angelou. In 1945, two sculptures meant to represent the average man and woman in the
United States went on exhibit at the American Museum of Natural History. Based on
measurements taken from tens of thousands of young men and women, they were called
Norma and Normman. That same year, a contest launched to find a living embodiment of
Norma. Normal is often used as a synonym for "typical", "expected ", or even "correct ". By
that logic, most people should fit the description of normal. And yet, not one of almost 4,000
women who participated in the contest matched Norma, the supposedly "normal" woman. This
puzzle isn't unique to Norma and Normman, either time and time again, so called normal
descriptions of our bodies, minds, and perceptions have turned out to match almost no one.
And yet, a lot of the world is constructed around a foundation of normalcy. So what does
normal actual y mean and should we be relying on it so much? In statistics, a normal
distribution describes a set of values that fall along a bel curve. The average, or mean, of all
the values is at the very center, and most other values fall within the hump of the bell. These
curves can be tall, with most values inside a narrow range, or long and flat, with only a slight
bias towards the average. What makes the distribution normal is that it follows this curved
shape. Normal doesn't describe a single data point, but a pattern of diversity. Many human
traits, like height, follow a normal distribution. Some people are very tall or very short, but most
people fall close to the overall average. Outside of statistics, normal often refers to an average
like the single number pul ed from the fattest part of the bel curve that eliminates all the
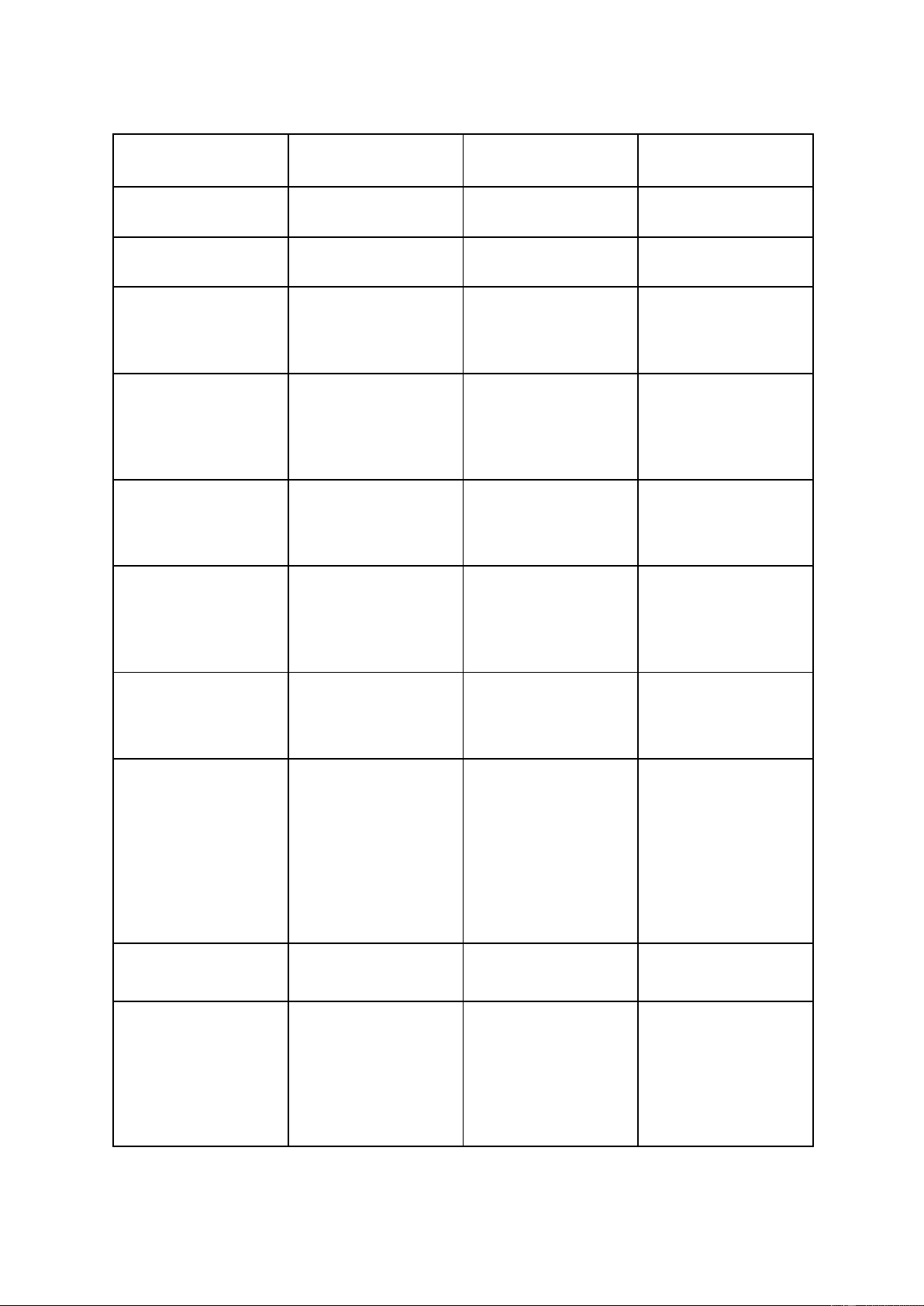
nuance of the normal distribution. lOMoAR cPSD| 45349271 Word Pronunciation Meaning Example Left-brained /l ft-bre nd/ɛ ɪ Não trái Right-brained /ra t-bre nd/ɪ ɪ Não phải Myth /m θ/ɪ Thần thoại -Most societies have their own creation myths. Dominance / d m nəns/ˈ ɒ ɪ
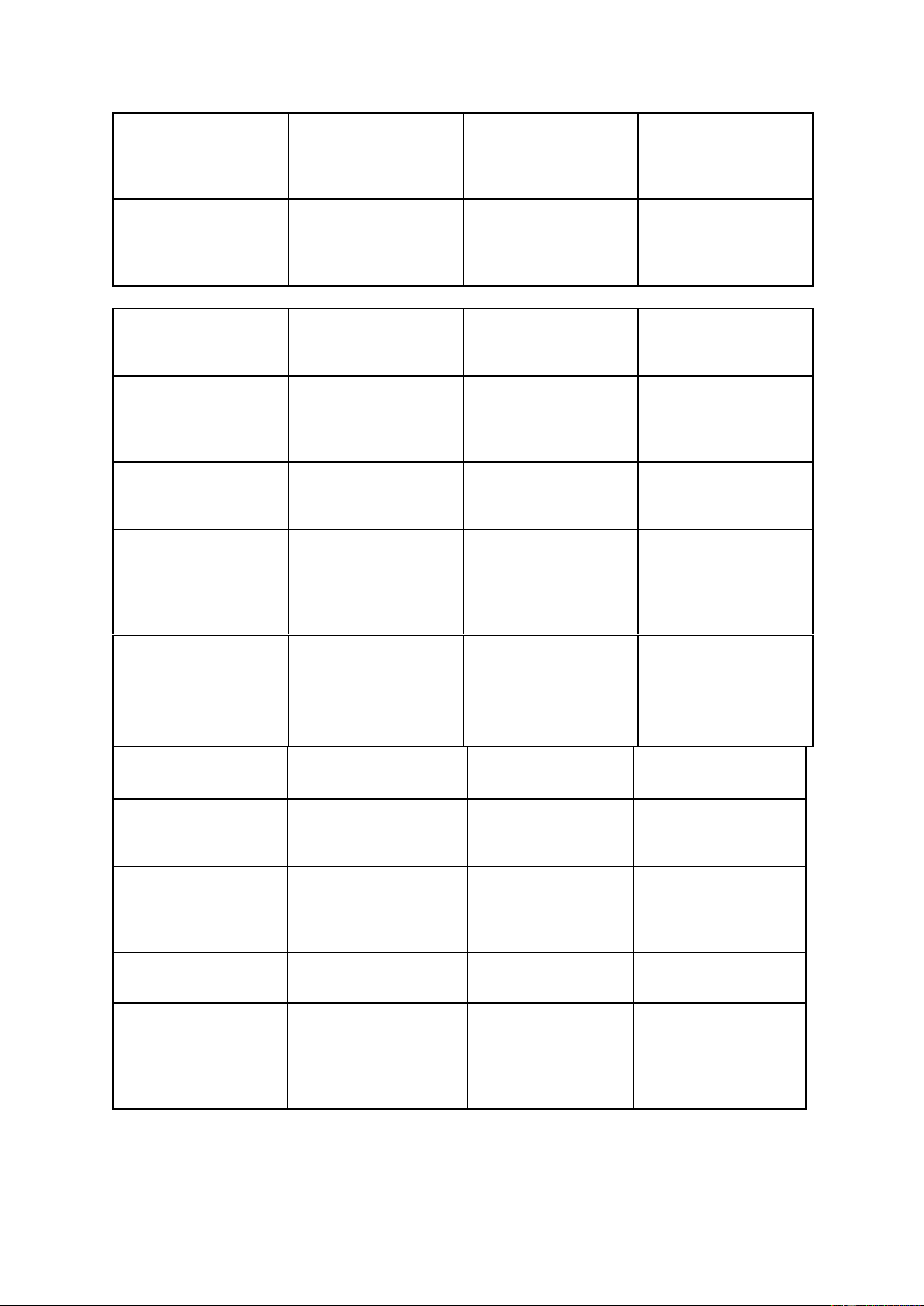
Sự ưu thế, Thống trị -The company's growing dominance of the sports shoe industry. Dominant / d m nənt/ˈ ɒ ɪ Trội, Có ảnh hưởng -Unemployment wil lớn be a dominant issue at the next election. Wire up / wa ər p/ˈ ɪ Kết nối -She WIRED her ʌ new stereo system UP as soon as she got home. Spines /spa nz/ɪ Xương sống -She injured her spine in a riding accident. Hemisphere / h m sf ə/ˈ ɛ ɪ Bán cầu( não) -They argue that if ɪ both hemispheres can be accessed during a task, the brain's ability to deal with the problem wil be enhanced. /kr s- wa ər ŋ/ɒ Cross-wiring Sự liên kết chéo ˈ ɪ ɪ Intuition / n uˌɪ ʧ ːˈɪʃᵊn/ Trực giác -Often there's no clear evidence one way or the other and you just have to base your judgment on intuition. lOMoAR cPSD| 45349271 Honing (hone) / hə n ŋ/ˈ ʊ ɪ To improve or -The bone had been perfect (abilities or honed to a point. skil s) Intonation / ntəˌɪʊˈneɪʃᵊn/ Âm điệu -The end of a sentence that is not a question is usually marked by falling intonation. Accentuation /æk s ntjˌ ɛʊˈ ɪʃᵊe -Sự nhấn mạnh -Accentuation when n/ -The act of reading poetry is emphasizing very important. Subtracting /səb trækt ŋ/ˈ ɪ Phép trừ -Four subtracted from ten equals six.
Associated with St /ə səˈʊʃɪ ɪ ɪe t d w Kết hợp với -I don't want my ð/ɪ children associating with drug addicts and alcoholics. Retrieval /r tri vəl/ˈ ː Truy xuất -The data management system facilitates easy retrieval of evidence. Word Pronunciation Meaning Example Sweat /sw t/ɛ Vận động; Mồ hôi -The athletes were drenched in sweat. Muscles / m slz/ˈ ʌ Cơ bắp -These exercises build muscle and increase stamina. Get out of /ɡɛt a t v/ʊ ɒ Thoát khỏi
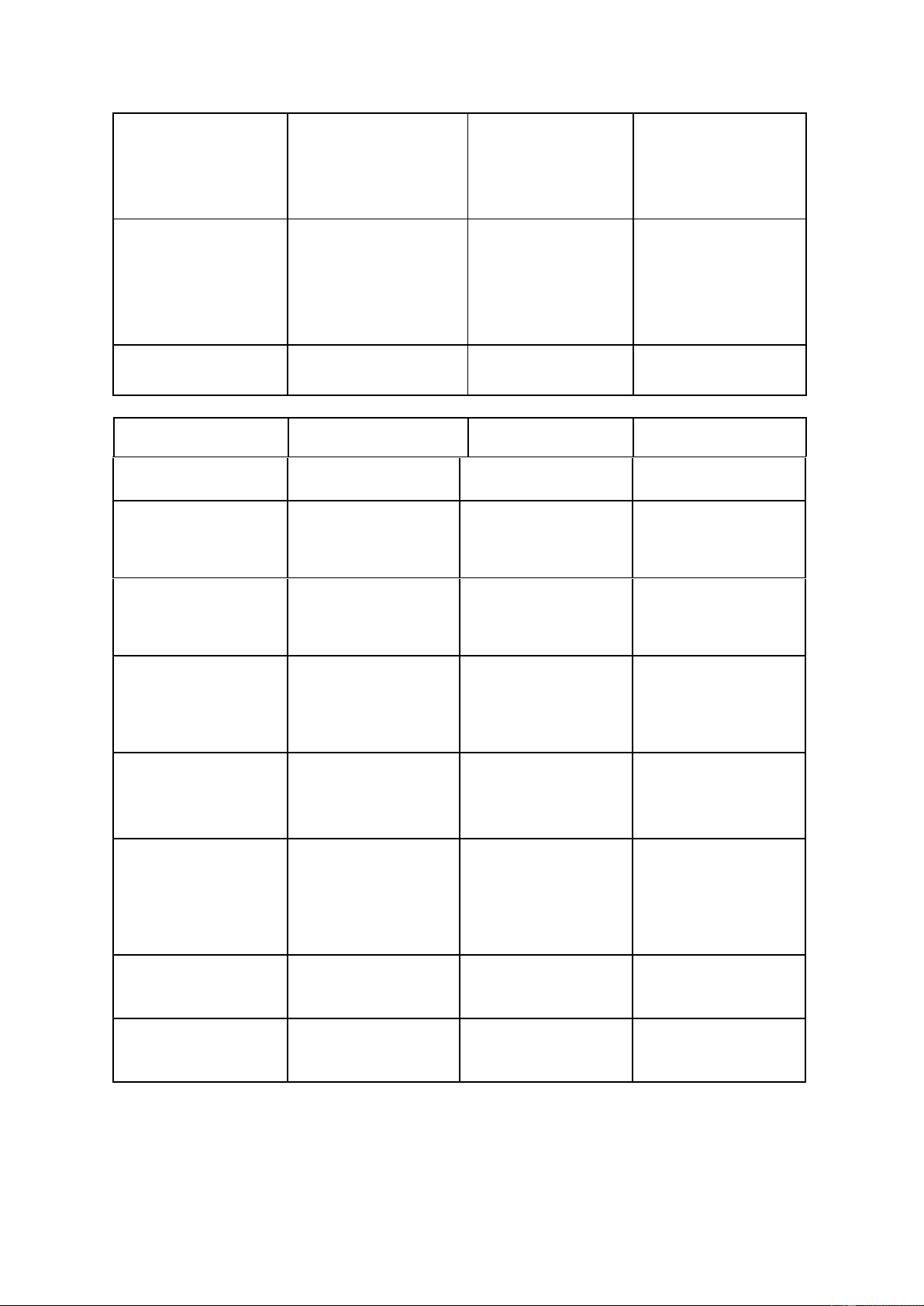
The prefrontal / pri .fr n.təl k .teks/ˌ Vỏ não trước trán -Exercise counters cortex ː ʌ age-related ˈ ɔː shrinking of the prefrontal cortex. lOMoAR cPSD| 45349271 in charge(of st/sb) / n ɪʧɑːʤ ɒ v/ Responsible for -The teacher put me idiom something or in charge of someone organizing the project. Brain cells /bre n s lz/ɪ ɛ Tế bào não -Moving your body a few times a week means new brain cells are born inside your head. As big as possible /æz bɪɡ æz Lớn nhất có thể ˈ ɒp səb l/ᵊ Word Pronunciation Meaning Example Sculptures / sk lp əz/ˈ ʌ Nhà điêu khắc -This 25-foot-high ʧ sculpture is her latest creation. Exhibit /ɪɡˈ ɪ ɪz b t/ To show something -He frequently publicly exhibits at the art gal ery. Measurements / mˈɛʒəmənts/ Sự đo lường; phép -The machine đo makes thousands of measurements every day. / m b d mənt/ -He was the Embodiment (the ɪ ˈ ɒ ɪ Hiện thân Sự biểu hiện embodiment of the embodiment of English gentleman. something) Perceptions
/pə s p nzˈ ɛ ʃᵊ / Sự nhận thức -We have to change the public's perception that money is being wasted. Foundation
of /fa n deʊ ˈɪʃᵊn v ɒ Nền tảng của sự normalcy ˈ ɔːn məlsi/ bình thường The hump of the /ðə h mp v ðə b l/ʌ bell ɒ ɛ lOMoAR cPSD| 45349271 Nuance / njuˈːɑːns/ Sắc thái -The painter has managed to capture every nuance of the woman's expression.




