
















Preview text:
VIETNAM NATIONAL UNIVERSITY – HO CHI MINH CITY
INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF BUSINESS
BUSINESS RESEARCH METHODS INDIVIDUAL PROPOSAL
TOPIC: ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF FINANCIAL TECHNOLOGY
(FINTECH) ON TRADITIONAL BANKING IN VIETNAM
Student’s name: Pham Tra My
Student’s ID: BAFNIU21495
Class: Business Research Methods
Lecturer: Dinh Thi Le Trinh Ho Chi Minh City, VietNam Table of contents
I. INTRODUCTION ........................................................................................................... 4
1.1 Background Information ......................................................................................... 4 1
1.2 Problem Statement ................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Significance of the Research .................................................................................... 6
1.4 Research Objectives ................................................................................................. 6
1.5 Research Questions .................................................................................................. 6
II. LITERATURE REVIEW .............................................................................................. 7
2.1 Theoretical Background .......................................................................................... 7
2.1.1 Definition of Fintech and Traditional Banking ............................................... 7
2.1.2 Classification and Characteristics of Fintech ................................................. 8
2.1.3 Definition of Financial Innovation ................................................................... 8
2.1.4 Some Other Related Theories ........................................................................... 9
2.2 Literature Review ................................................................................................... 11
2.2.1 Impact of Fintech on Operational Efficiency ................................................ 11
2.2.2 Customer Experience and Fintech ................................................................. 11
2.2.3 Fintech and Financial Performance ............................................................... 12
2.2.4 Strategic Responses of Traditional Banks to Fintech ................................... 12
2.2.5 Regulatory Challenges and Opportunities .................................................... 13
2.3 Theoretical Framework ......................................................................................... 13
2.3.1 Building a theoretical model on the relationship between Fintech and ..... 13
traditional banking ................................................................................................... 13
2.3.2 Identifying Independent, Dependent, and Mediating Variables ................. 13
2.3.3 Explaining the relationship between variables based on theory and ......... 14
previous research ...................................................................................................... 14
2.4 Research Model ..................................................................................................... 15
2.4.1 Developing a specific research model based on a theoretical framework: . 15
2.4.2 Measurement Indicators ................................................................................. 16
2.4.3 Data Collection Methods ................................................................................. 16
2.4.4 Model................................................................................................................. 17
III. METHODOLOGY ..................................................................................................... 18
3.1 Research Design ..................................................................................................... 18
3.2 Research Process .................................................................................................... 19
3.3 Sampling Selection ................................................................................................. 19
3.3.1 Selecting the Bank Sample .............................................................................. 19
3.3.2 Customer Sample Selection ............................................................................ 20
3.3.3 Data Collection Process ................................................................................... 20
3.4 Data Collection Method ......................................................................................... 20
3.4.1 Primary Data: .................................................................................................. 20
3.4.2 Secondary Data: ............................................................................................... 21
3.5 Measurement Scale ................................................................................................ 21
3.5.1 Quantitative Data: ........................................................................................... 21 2
3.5.2 Qualitative Data: .............................................................................................. 22
3.6 Data Analysis Techniques ...................................................................................... 22
3.6.1 Quantitative Analysis: ..................................................................................... 22
3.6.2 Qualitative Analysis: ........................................................................................ 23
IV. REFERENCES ........................................................................................................... 23 3 ABSTRACT
The rapid evolution of Financial Technology (Fintech) has fundamentally transformed the
financial services landscape, posing significant challenges and opportunities for traditional
banking institutions. In Vietnam, a market characterized by its youthful demographic and
accelerating digital adoption, the emergence of Fintech presents a critical inflection point
for the banking sector. This study aims to systematically assess the impact of Fintech on
traditional banking in Vietnam, focusing on key areas such as operational efficiency,
customer engagement, and financial performance.
The research employs a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative analysis of
financial data from traditional banks with qualitative insights from industry experts,
banking professionals, and customer experience through surveys. By examining the
influence of Fintech innovations—including mobile payments, peer-to-peer lending,
digital wallets, and blockchain technology—on the traditional banking sector, this study
seeks to delineate the extent to which these technologies disrupt conventional banking practices.
Findings from this research are expected to reveal that while Fintech offers enhanced
convenience and lower transaction costs, it also pressures traditional banks to rethink their
business models and operational strategies. The study anticipates identifying a significant
shift in consumer behavior toward Fintech services, necessitating a strategic response from
traditional banks to remain competitive. Moreover, the research will explore the potential
for collaboration between traditional banks and Fintech companies as a means to harness
innovation while mitigating the risks of disintermediation. I. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background Information
Vietnam has experienced an increase, in the adoption of technology (Fintech) in recent
times. This shift to platforms is reshaping the sector bringing both opportunities and
challenges for traditional banks. The growing Fintech industry in Vietnam driven by a tech- 4
savvy population along with increasing internet usage has led to the introduction of
financial services. Mobile payments, digital lending, and wealth management stand out as
segments within the Fintech realm. The supportive regulatory environment in the country
has also played a role in fostering the growth of Fintech. Traditional banks are facing
heightened competition from Fintech companies that offer convenient and cost-effective
services. Appealing especially to younger customers. Nevertheless, banks are recognizing
the benefits of partnering with Fintech firms strategically. Collaborations between banks
and Fintech entities are emerging to capitalize on their strengths and expand their market presence.
This study seeks to examine the interplay between Fintech and traditional banking in
Vietnam. It will delve into how Fintech impacts facets of banking such, as customer
outreach, service provision, risk management, and profitability. By grasping the dynamics
of this evolving landscape, policymakers, banks, and Fintech organizations can devise
strategies to navigate changes effectively and seize opportunities. 1.2 Problem Statement
The rapid adoption of Fintech has created significant challenges for traditional banks in
Vietnam, which risk being left behind if they do not adapt as Fintech firms leverage
technology to provide faster, cheaper, and more user-friendly financial services. This
problem is particularly acute in Vietnam, where the banking industry still relies heavily on
traditional business models that may not be as agile or innovative as Fintech startups.
Although some banks have begun to embrace digital transformation, the extent to which
Fintech has impacted the operational and financial performance of traditional banks in
Vietnam is unclear. Without a clear understanding of these impacts, it may be difficult for
traditional banks to develop effective strategies to compete with Fintech firms. This study
attempts to fill this gap by systematically examining how Fintech has impacted Vietnam's
traditional banking industry and identifying the associated challenges., Fintech firms can
develop strategies to navigate the changing landscape and maximize opportunities. 5
1.3 Significance of the Research
This research is significant for several reasons. First, it will provide insights into the
dynamics between Fintech and traditional banking in Vietnam and contribute to a broader
understanding of how new technologies are reshaping financial services in developing
markets. Second, the findings of this study will be critical for bank managers and
policymakers to address the challenges and opportunities presented by Fintech.
For traditional banks, the study will focus on areas where they may need to innovate or
transform their operations to remain competitive. For policymakers and regulators, the
study will provide valuable information on how to create a regulatory framework that
supports innovation while ensuring stability and consumer protection. Finally, the study
will provide practical recommendations to help Vietnamese banks better integrate Fintech
into their operations, ultimately improving their services and increasing customer satisfaction.
1.4 Research Objectives
The primary objective of this research is to assess the impact of Fintech on traditional
banking in Vietnam. The specific objectives of the study are:
• To identify the key components of Fintech that are influencing the traditional banking sector in Vietnam.
• To evaluate the impact of these Fintech components on the operational efficiency,
customer interactions, and financial performance of traditional banks in Vietnam.
• To explore the strategic responses of traditional banks to the rise of Fintech,
including digital transformation initiatives, partnerships, and innovation strategies.
• To provide recommendations for traditional banks in Vietnam on how to effectively
adapt to and leverage Fintech innovations to enhance their competitive position. 1.5 Research Questions
The study seeks to answer the following research questions: 6
• What are the main components of Fintech that are impacting traditional banking in Vietnam?
• How do these Fintech components affect the operational efficiency and financial
performance of traditional banks in Vietnam?
• What are the key challenges faced by traditional banks in Vietnam due to the rise of Fintech?
• How are traditional banks in Vietnam responding to the competitive pressures created by Fintech?
• What strategies can traditional banks in Vietnam adopt to successfully integrate
Fintech and enhance their competitive advantage? II. LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Theoretical Background
2.1.1 Definition of Fintech and Traditional Banking
Fintech, also known as Financial Technology, is the use of innovative, high-tech digital
solutions by financial technology companies to enhance financial transactions and services.
It covers different areas such as digital banking, financial management, remittances, and
peer-to-peer transactions. The main purpose of Fintech is to improve the efficiency of
banking and investment, by using advanced technology to optimize and deliver cost-
effective solutions quickly for individuals and businesses.
Traditional banking is the banking of manual, mechanical processes, mostly connected to
users directly through specific bank branches. With the growing technological age, it is
precisely because of this that the use of banking services has to reach the branch during
office hours that many people find it difficult and difficult to access.
However, fintech and traditional banking are not mutually exclusive; they often
complement each other in today's financial landscape. 7
2.1.2 Classification and Characteristics of Fintech 2.1.2.1 Classification
Fintech is divided into two groups that are categorized according to the purpose of use:
Group One: Products that serve consumers, providing digital and other technology tools
for individuals to borrow, fund capital, or manage personal and business money.
Group two: "Back-office" technology products to support its operations and financial institutions.
2.1.2.2 Characteristics
Fintech will optimize financial resources in the future when just one employee can already
support a lot of different customers on the same service.
Fintech is the constant technological innovation, the development of artificial intelligence
that encompasses all service operations including the identification, statistics, and
establishment of the needs of each customer through algorithms.
Fintech provides the convenience that users do not need to go to the headquarters to make
transactions or services but can operate directly through online activities.
In the modern era of technology, Fintech has come into existence and brought about many
positive effects. It saves time, optimizes services in a simple way, and uses utilities quickly.
Helping clients secure their rights. In addition, Fintech knows how to identify each
customer, and each service that makes the security and safety of customers more important.
2.1.3 Definition of Financial Innovation
Financial innovation is a term that collectively refers to specific service categories based
on updated tables in various areas of the financial system. It will create products and
services or processes that are changed and updated including risk management, risk transfer,
credit generation, updated technology as well as other innovations. Recent financial
innovations include crowdfunding, mobile banking technology, and remittance technology.
Financial innovations are aimed at reforming and promoting the development and efficient 8
functioning of financial systems. This can lead to positive changes, towards a positive
business environment and efficiencies in the financial system.
2.1.4 Some Other Related theories
a) Theories related to competition and innovation
• Theory of perfect competition
An economic model of market structure is called the perfect competition model. This model
is used by economists to analyze behavior and outcomes in highly competitive markets
where there are no monopolistic sellers or buyers. All market participants interact on a level
playing field when there is perfect competition. This implies that no individual or business
can influence market prices; instead, prices are set only by supply and demand.
Furthermore, under conditions of perfect competition, businesses cannot be prevented from
joining or leaving, allowing for unrestricted competition and efficient allocation of resources.
• Theory of monopolistic competition
A monopolistically competitive market is a market structure in which there are a large
number of firms producing similar products that are not perfect substitutes. It combines
elements of a monopoly market and a perfectly competitive market. Companies in the
market will generate economic profit in the short term. However, one of its downsides is
that it keeps competitors constantly entering the market to prevent companies from
generating high profits. The main characteristics of a monopolistically competitive market
are many sellers and buyers, product differentiation, low barriers to entry and exit, and
finally short-term hyper-margin profit.
Theory of technological innovation
The diffusion theory of innovation is a theory that outlines how new technologies and other
advances are spread throughout societies and cultures, especially in popular adoption. It
describes the pattern and rate at which new ideas, activities, or products spread throughout 9
the population. Innovation is understood as reform, change that helps to renew problems,
but they also have certain risks. However, in today's modern society, innovation and reform
is very important and necessary, it helps people to move up and develop more outstandingly.
b) The technology acceptance model (TAM)
The technology adoption model (TAM) is a theory of information systems that models how
users adopt and use technology. The model represents an overview of a new technology,
the factors that will influence decisions, and how users can use it. TAM is constantly being
researched, improved, and expanded. The model is expressed in two parts: -
Cognitive usefulness (PU): Bnagwf how to use the system to describe the degree
towhich a person believes performance at work can be improved. -
Perceived ease of use (PEU): Indicates the degree to which a person has to make
mentalor physical effort to use technology.
Despite being subjected to various criticisms from users such as its complexity and lack of
features, TAM has been constantly improving. More than that, it also demonstrates a high
degree of predictability as well as the ability to look at external influences in society so that
it can easily take action and create concrete, successful directions.
c) Disruptive Innovation Theory
Breakthrough innovation describes the process by which products and services originate
from simple applications in the lowest segment of the market (by lowering costs to make
them more accessible) and then continuously moving up to the higher segments, replacing
competitors that already have a foothold. The theory was put forth by Harvard Business
School professor Clayton Christensen in the early 1990s. Clayton Christensen popularized
the idea of disruptive innovation in his book The Innovator's Solution, which is the sequel
to The Innovator's Dilemma published in 1997.
The advantages of disruptive innovation are aimed at improving products and services for
existing customers. However, disruptive innovation will require enabling technology, 10
innovative business models, and unified value networks to innovate effectively and drive growth in the process.
d) Financial Inclusion Theories
Financial inclusion is the ease of access and availability of basic financial services to all
members of a population. It is also understood that all individuals and businesses have
access to useful and affordable financial products and services. Financial inclusion plays a
very important role in reducing poverty and promoting economic growth by enabling
individuals with different services such as savings, investment and risk management.
Whether it's individuals or small businesses, having access to financial services, raising
housing prices and the overall market economy, is not just about providing access to
traditional banking services but also promoting financial education and understanding.
Educating individuals and giving them the tools to make informed financial decisions is
key to achieving true financial inclusion. 2.2 Literature Review
2.2.1 Impact of Fintech on Operational Efficiency
Numerous studies have documented how Fintech has improved operational efficiency
within the financial services sector. For example, Zhu, Ongena, and Tan (2019) found that
Fintech innovations reduce transaction costs and streamline operations by automating
processes that were traditionally manual and labor-intensive. In Vietnam, where banking
infrastructure has historically been less developed, Fintech offers a pathway for banks to
modernize their operations and reduce inefficiencies. This section reviews empirical
studies that quantify the impact of Fintech on operational performance metrics such as cost-
to-income ratios and processing times in the banking industry.
2.2.2 Customer Experience and Fintech
The rise of Fintech has fundamentally reshaped customer expectations in the financial
services industry. Studies such as those by Gomber, Koch, and Siering (2017) have 11
highlighted how Fintech firms leverage user-friendly interfaces, personalized services, and
24/7 accessibility to enhance customer experience. Traditional banks in Vietnam must
respond to these heightened expectations by investing in digital platforms that offer similar
levels of convenience and personalization. This section examines the literature on the
shifting landscape of customer experience in banking, focusing on how traditional banks
can adapt to meet the demands of tech-savvy consumers.
2.2.3 Fintech and Financial Performance
The financial performance of traditional banks is increasingly influenced by the
competition from Fintech firms. Research by Philippon (2016) indicates that the entry of
Fintech has led to increased competition, which can compress margins and challenge the
profitability of traditional banks. In Vietnam, where Fintech is rapidly gaining traction,
traditional banks must navigate these competitive pressures while maintaining financial
stability. This section reviews studies that analyze the impact of Fintech on key financial
performance indicators such as return on assets (ROA), return on equity (ROE), and net
interest margins (NIM) within the banking sector.
2.2.4 Strategic Responses of Traditional Banks to Fintech
Traditional banks worldwide have responded to the rise of Fintech in various ways, ranging
from outright competition to strategic partnerships. Studies by Hornuf and Schwienbacher
(2017) suggest that collaboration between banks and Fintech firms can create synergistic
benefits, allowing traditional banks to leverage technological innovations while Fintech
firms gain access to established customer bases. In Vietnam, such collaborations are
increasingly common as banks seek to integrate digital capabilities without disrupting their
core operations. This section reviews the literature on the strategic responses of banks to
Fintech, including digital transformation initiatives, strategic alliances, and mergers and acquisitions. 12
2.2.5 Regulatory Challenges and Opportunities
The regulatory environment plays a crucial role in shaping the development of both Fintech
and traditional banking sectors. In Vietnam, regulatory frameworks are evolving to
accommodate the rapid growth of Fintech while ensuring financial stability and consumer
protection. Studies by Zalan and Toufaily (2017) discuss the challenges regulators face in
balancing innovation with risk management. This section reviews the literature on the
regulatory landscape in Vietnam, focusing on the opportunities and challenges it presents
for both Fintech firms and traditional banks.
2.3 Theoretical Framework
2.3.1 Building a theoretical model on the relationship between Fintech and traditional banking
In the context of Vietnam, the rapid development of financial technology (Fintech) has
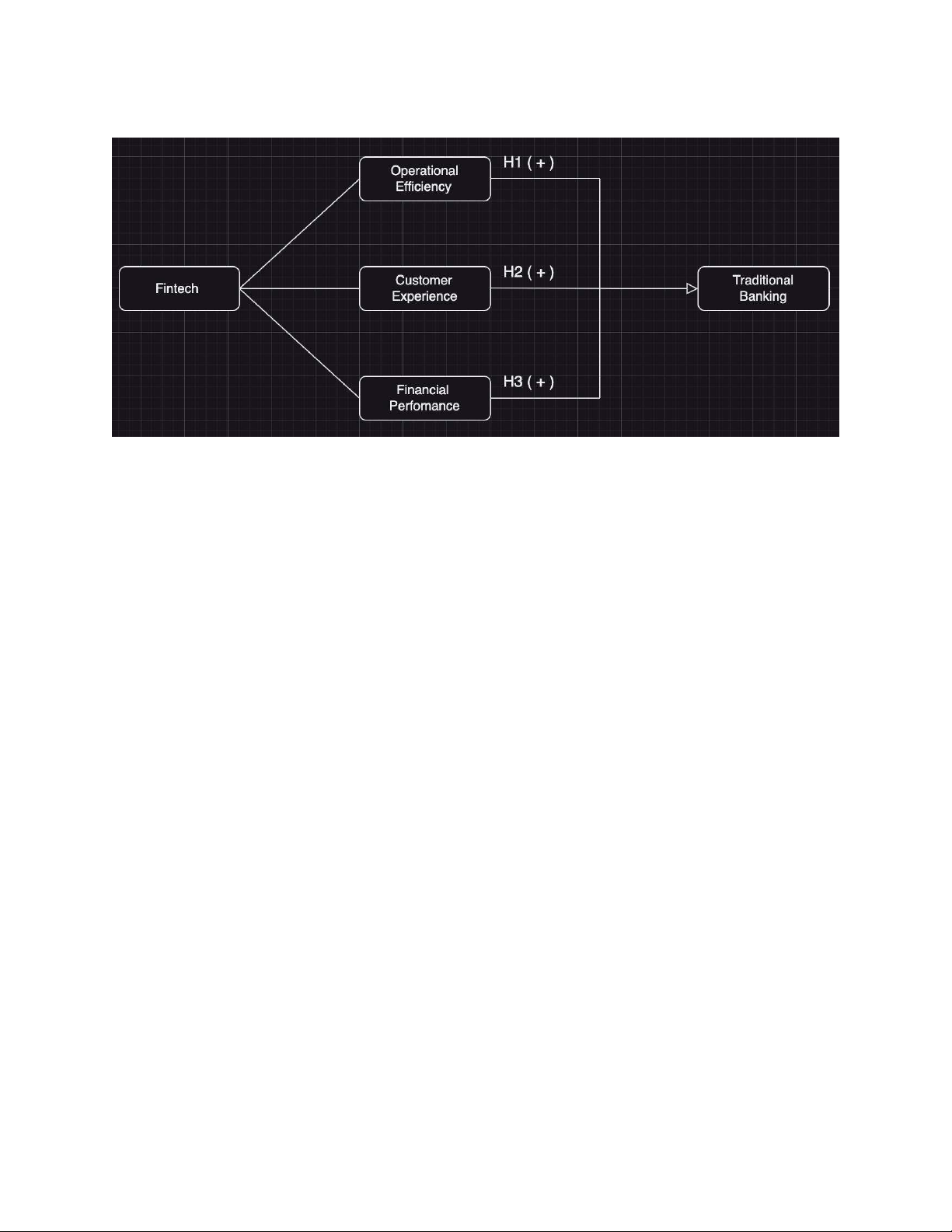
been creating significant changes in the traditional banking sector. The theoretical model
is built to identify and analyze the main relationships between Fintech factors and different
aspects of traditional banking. This model will focus on three main factors: (1) Operational
efficiency, (2) Customer experience, and (3) Financial performance of banks. These factors
will be considered in the context of banks' strategic response to the rise of Fintech.
2.3.2 Identifying Independent, Dependent, and Mediating Variables
In the theoretical model, the variables are identified as follows:
Independent variables:
Dependent variables: 13
Fintech technology: Includes specific Bank performance: Measured through
applications such as mobile payments, indicators such as cost/income ratio, peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, digital banking, and blockchain.
transaction processing time, and level of process automation.
Customer experience: Includes the level
of satisfaction, convenience in using
services, and the level of customer
interaction with banking services. Financial performance: Evaluated
through indicators such as return on assets
(ROA), return on equity (ROE), and net profit margin (NIM).
2.3.3 Explaining the relationship between variables based on theory and previous research
The relationship between Fintech and traditional banks can be explained through some classic theories:
Disruptive Innovation Theory: argues that Fintech is a disruptive factor for traditional
banks, forcing them to improve operational efficiency and provide better customer
experiences to stay competitive. Fintech technologies such as mobile payments or P2P
lending can directly affect the operational efficiency of banks by reducing transaction costs and improving efficiency.
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM): is used to explain customer behavior in
accepting Fintech services. Customers who perceive the convenience and benefits of
Fintech can easily switch from using traditional banking services to using new technology
solutions, which directly affects the customer experience and indirectly affects the financial performance of the bank. 14
Michael Porter's Competitive Strategy Theory: explains that banks need to develop
competitive strategies to cope with the emergence of Fintech. Banks can focus on creating
differentiation or partnering with Fintech to improve services and strengthen their market
position. This strategic response can act as an intermediary variable, affecting the
operational efficiency and financial performance of the bank.
Financial Inclusion Theories indicate: that Fintech can expand financial access to
underserved customer groups, thereby helping traditional banks expand their market and
improve financial performance.
Overall, this theoretical model proposes that Fintech technology impacts the operational
efficiency, customer experience, and financial performance of traditional banks, through
response strategies driven by competition and the need for innovation. Previous studies
provide evidence that successful integration and adoption of Fintech can help traditional
banks not only maintain but also improve their competitive position in the market. 2.4 Research Model
2.4.1 Developing a specific research model based on a theoretical framework:
This research model is built on the theory of the impact of Financial Technology (Fintech)
on traditional banking, specifically focusing on technology transfer and innovation within
the financial sector. Key elements of the theoretical framework include: a.
Impact of Fintech on Banking Performance: This can be measured through
financialindicators such as profitability ratios, operating costs, and revenue growth. b.
Changes in Customer Behavior: The adoption and use of Fintech products alter
theway customers interact with traditional banking services. c.
Impact on the Strategic Business Model of Traditional Banks: Fintech may drive
banksto alter their strategies to remain competitive. 15
2.4.2 Measurement Indicators a.
Banking Performance: Return on Assets (ROA), Return on Equity (ROE), Cost-to-
Income Ratio (CIR), Annual Revenue Growth. b.
Customer Behavior: Rate of Fintech service usage Customer satisfaction with
bothbanking and Fintech services Frequency of transactions via Fintech platforms. c.
Business Strategy: Changes in the banking services offered Investment in
newtechnologies and Research & Development (R&D) Changes in fee structures and service pricing.
2.4.3 Data Collection Methods a. Interviews:
Conduct in-depth interviews with bank executives, Fintech experts, and customers to
gather information about the impacts and strategic changes due to Fintech.
Interviews may focus on topics such as strategic adjustments, customer feedback on
Fintech services, and how banks are modifying their operations. b. Surveys:
Administer online or telephone surveys with bank customers and Fintech users to measure
usage levels and satisfaction.
Surveys can include questions about frequency of use, acceptance of new technologies, and
the impact of Fintech on personal financial decisions.
Secondary Data: Collect and analyze data from bank financial reports, market research,
and previous studies to assess trends and the impact of Fintech.
Sources of secondary data may include reports from financial regulatory bodies, banking
associations, and research organizations. 16 2.4.4 Model
H1: Fintech factors have a positive impact on the Operational Efficiency of traditional banks in Vietnam.
H2: Fintech factors have a positive impact on the Customer Experience of traditional banks in Vietnam.
H3: Fintech factors have a positive impact on the Financial Performance of traditional banks in Vietnam. 17 III. METHODOLOGY 3.1 Research Design
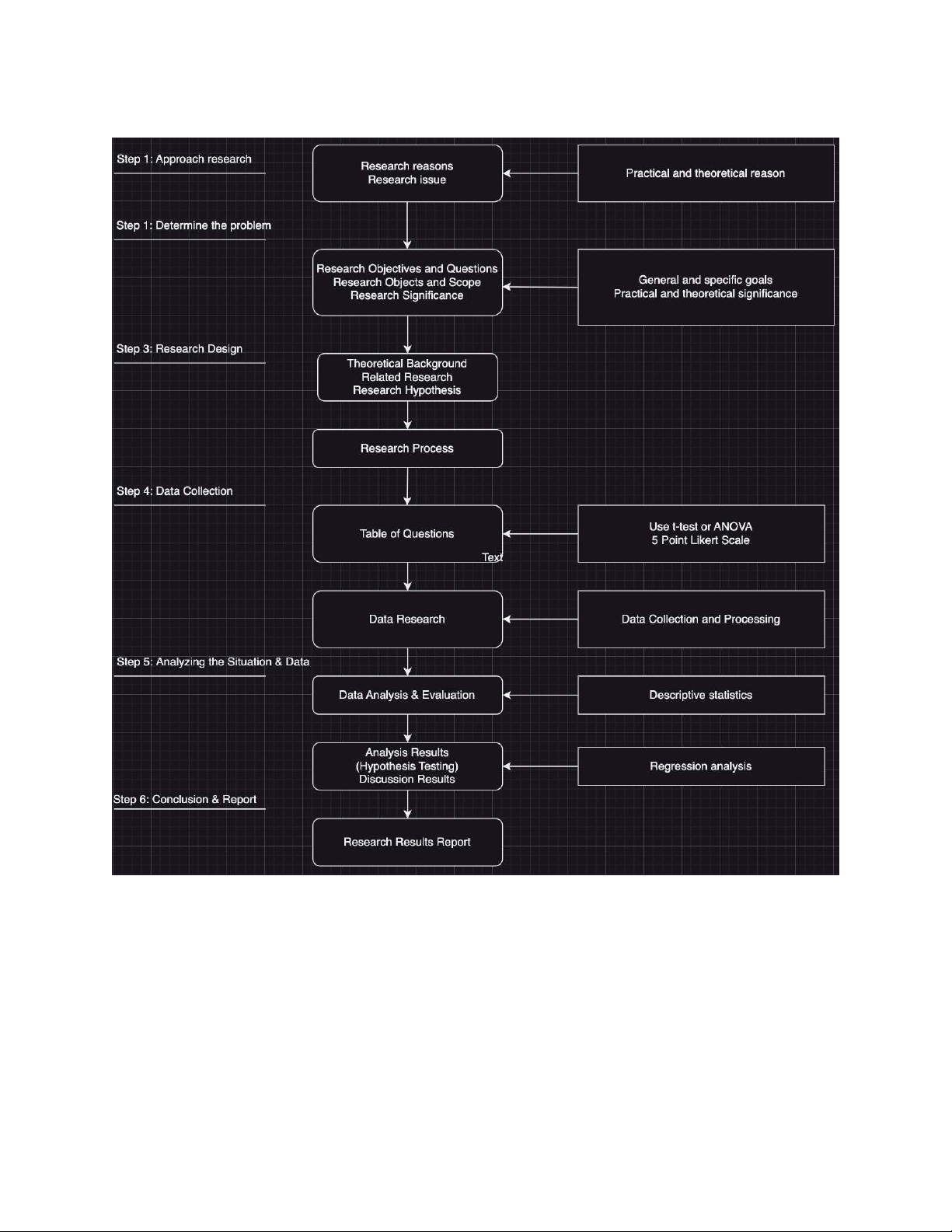
This study adopts a mixed-methods research design to evaluate the impact of Financial
Technology (Fintech) on traditional banking in Vietnam. The research design integrates
both quantitative and qualitative approaches to provide a comprehensive analysis.
Quantitative Approach: Employs statistical methods to measure the impact of Fintech
adoption on various performance indicators of traditional banks. This involves analyzing
financial data and survey responses to determine correlations and causal relationships.
Qualitative Approach: Uses in-depth interviews and Thematic Analysis with Content
Analysis to gain deeper insights into the strategic and operational adjustments made by
banks in response to Fintech. This approach aims to uncover the nuanced effects of Fintech
on customer behavior and banking practices. 18 3.2 Research Process 3.3 Sampling Selection
3.3.1 Selecting the Bank Sample
To ensure the representativeness of different segments of the traditional banking industry
in Vietnam, this study applies the stratified sampling method. Banks will be classified into
two main strata based on size and scale of operation: large banks and small banks. 19
This stratification is intended to reflect the diversity and distinctive characteristics between banks in different segments.
In each stratum, banks will be randomly selected from the available list of banks.
Specifically, the study plans to select 5 to 10 representative banks, including large banks
such as Vietcombank and VietinBank, as well as some small and medium-sized banks.
This method ensures that the research results will accurately reflect the factors affecting
FinTech on traditional banking in different segments.
3.3.2 Customer Sample Selection
For the customer group, the study will use the Simple Random Sampling method combined
with Systematic Sampling. It is expected that 300 to 500 customers will be selected from
the databases of the participating banks.
Customers will be randomly selected from the bank's customer list according to the system,
for example, every nth customer in the list will be selected. This method is to ensure the
randomness and representativeness of the sample and to collect information from a diverse
group of customers in terms of age, gender, and account type. This will provide a
comprehensive view of customers' experiences and responses to the impact of FinTech.
3.3.3 Data Collection Process
Data will be collected through two main methods: surveys and interviews. A survey
questionnaire will be distributed to banks and their customers, including questions
designed to measure operational efficiency, customer experience, and financial
performance. To collect detailed and qualitative information, in-depth interviews will be
conducted with bank managers and FinTech experts. This method is intended to
complement and enrich the quantitative data collected from the survey.
3.4 Data Collection Method 3.4.1 Primary Data: a. Surveys:
Target Audience: Bank customers and Fintech users.
Format: Structured online surveys administered via email or web platforms. 20




