






Preview text:
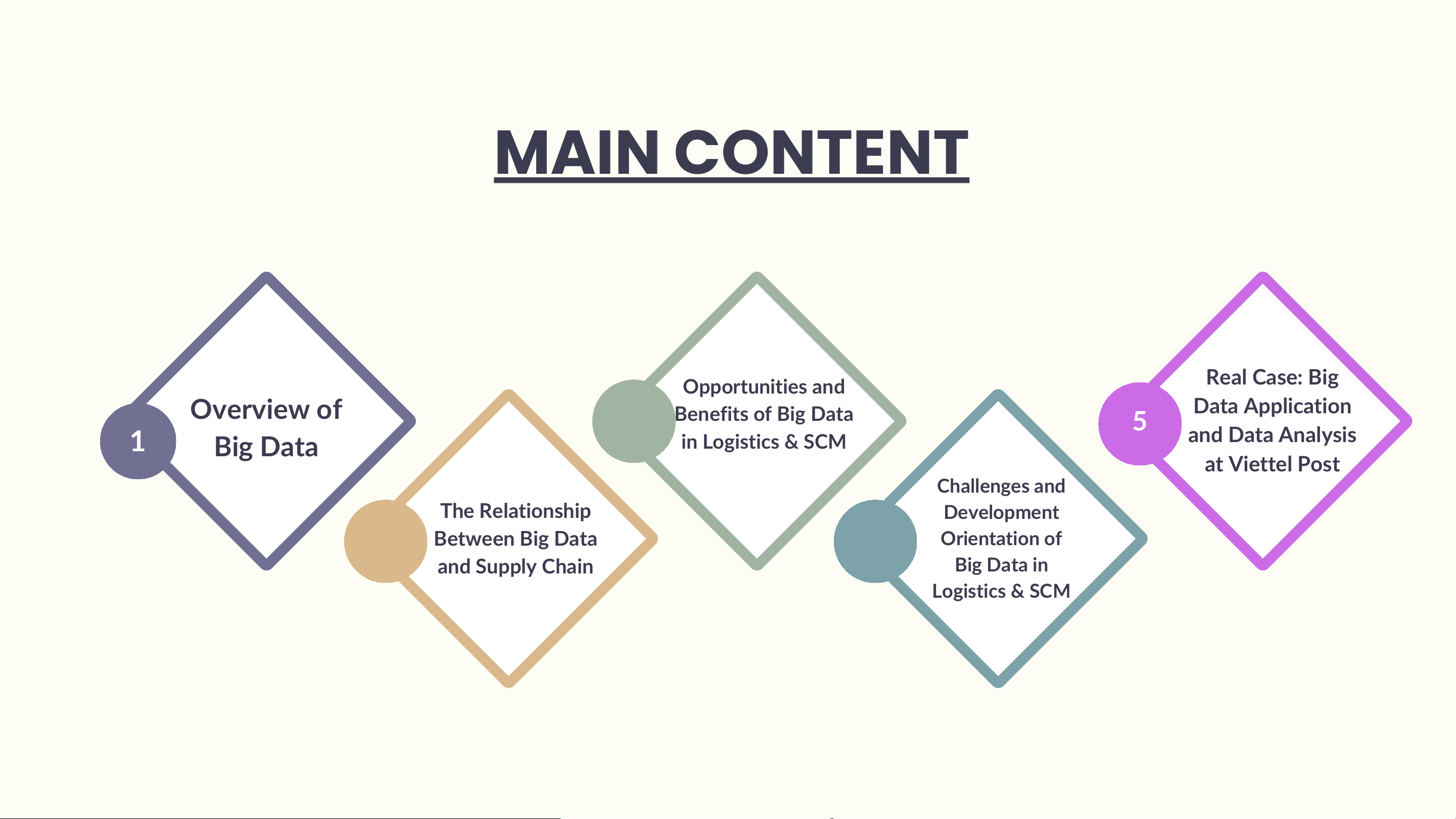
E-logistic BIG DATA Group 5 MAIN CONTENT Opportunities and Real Case: Big Overview of Benefits of Big Data 3 Data Application 5 1 Big Data in Logistics & SCM and Data Analysis at Viettel Post Challenges and The Relationship Development 2 Between Big Data Orientation of 4 and Supply Chain Big Data in Logistics & SCM 1.Overview of Big Data
Big Data is a term used to describe a set of
data that is so large and complex that
traditional data management tools cannot
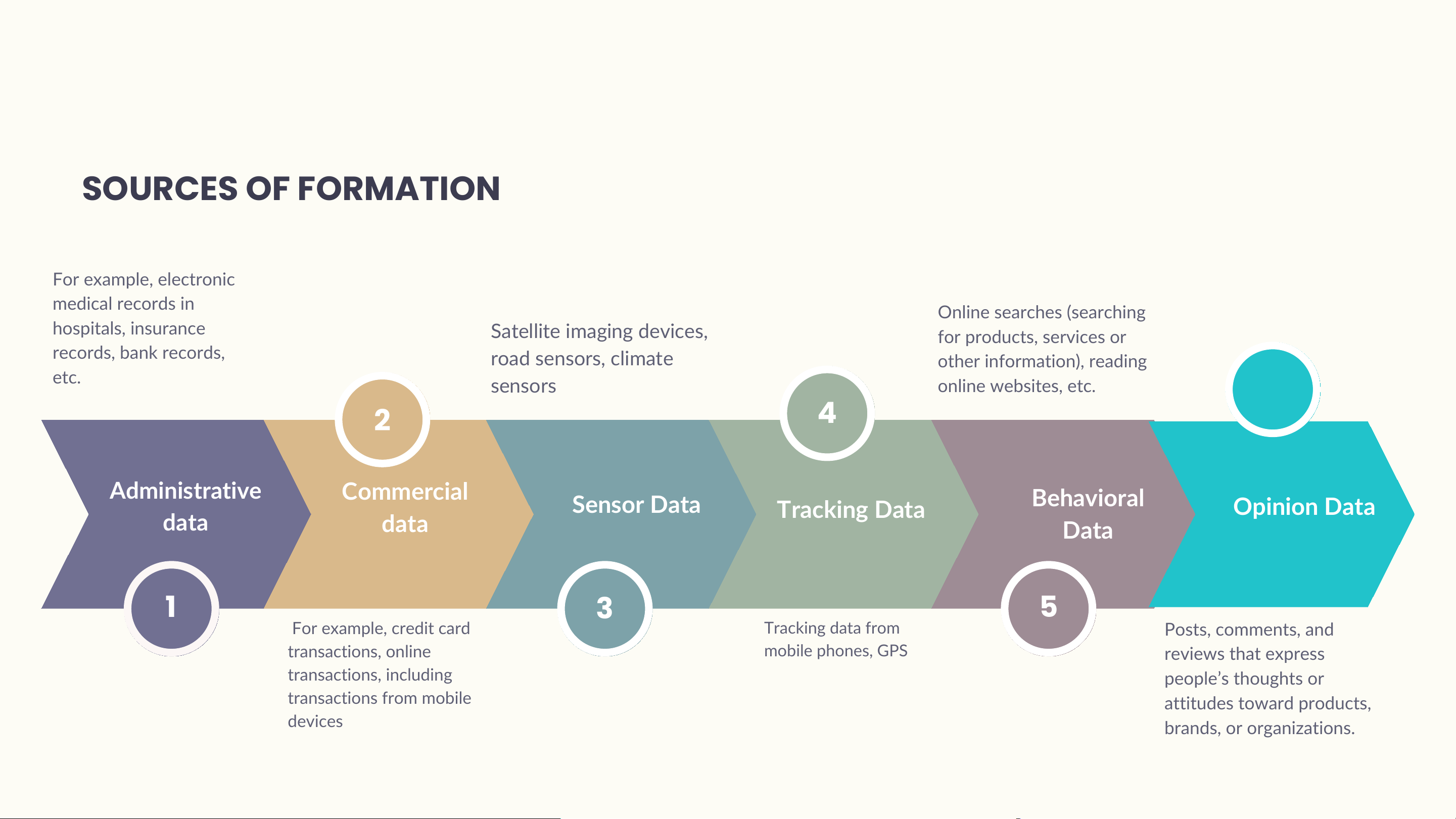
effectively collect, manage, and process it. SOURCES OF FORMATION For example, electronic medical records in Online searches (searching hospitals, insurance Satel ite imaging devices, for products, services or records, bank records, road sensors, climate other information), reading etc. sensors online websites, etc. 6 2 4 Administrative Commercial Sensor Data Opinion Data data data Tracking Data Behavioral Data 1 3 5 For example, credit card Tracking data from Posts, comments, and transactions, online mobile phones, GPS reviews that express transactions, including people’s thoughts or transactions from mobile attitudes toward products, devices brands, or organizations.
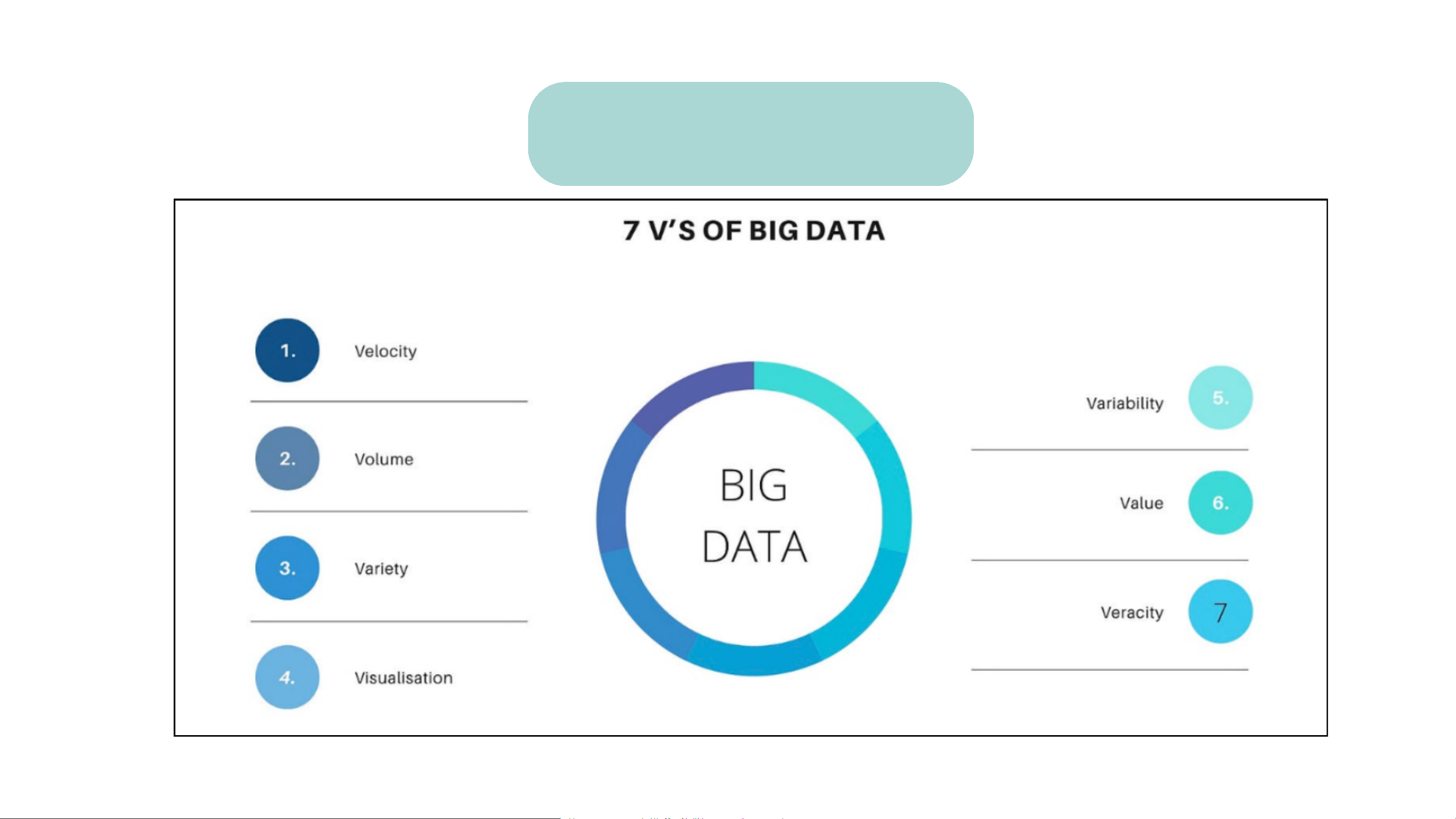
7 important characteristics
and properties of Big Data
2.The Relationship Between Big Data and Supply Chain
Supply Chain includes activities: production, warehousing,
transportation, distribution, marketing and customer service.
Each stage generates a huge amount of data. Big Data plays the role of:
Connect information between entities in the chain.
Optimize the flow of materials - information - finance.
Increase the ability to forecast and coordinate between departments.
2.The Relationship Between Big Data and Supply Chain
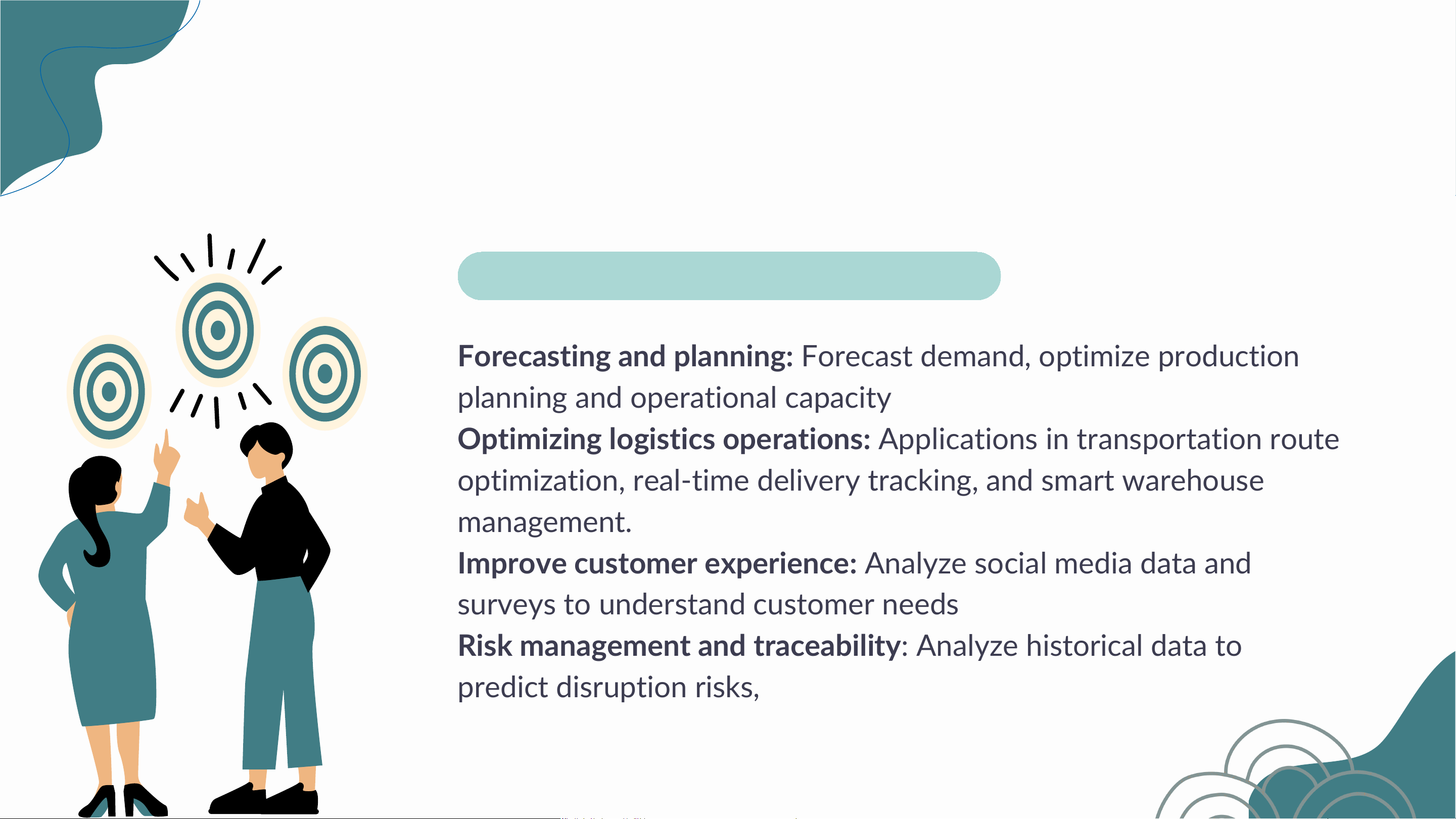
Applications of Big Data in Logistics & SCM
Forecasting and planning: Forecast demand, optimize production
planning and operational capacity
Optimizing logistics operations: Applications in transportation route
optimization, real-time delivery tracking, and smart warehouse management.
Improve customer experience: Analyze social media data and
surveys to understand customer needs
Risk management and traceability: Analyze historical data to predict disruption risks,
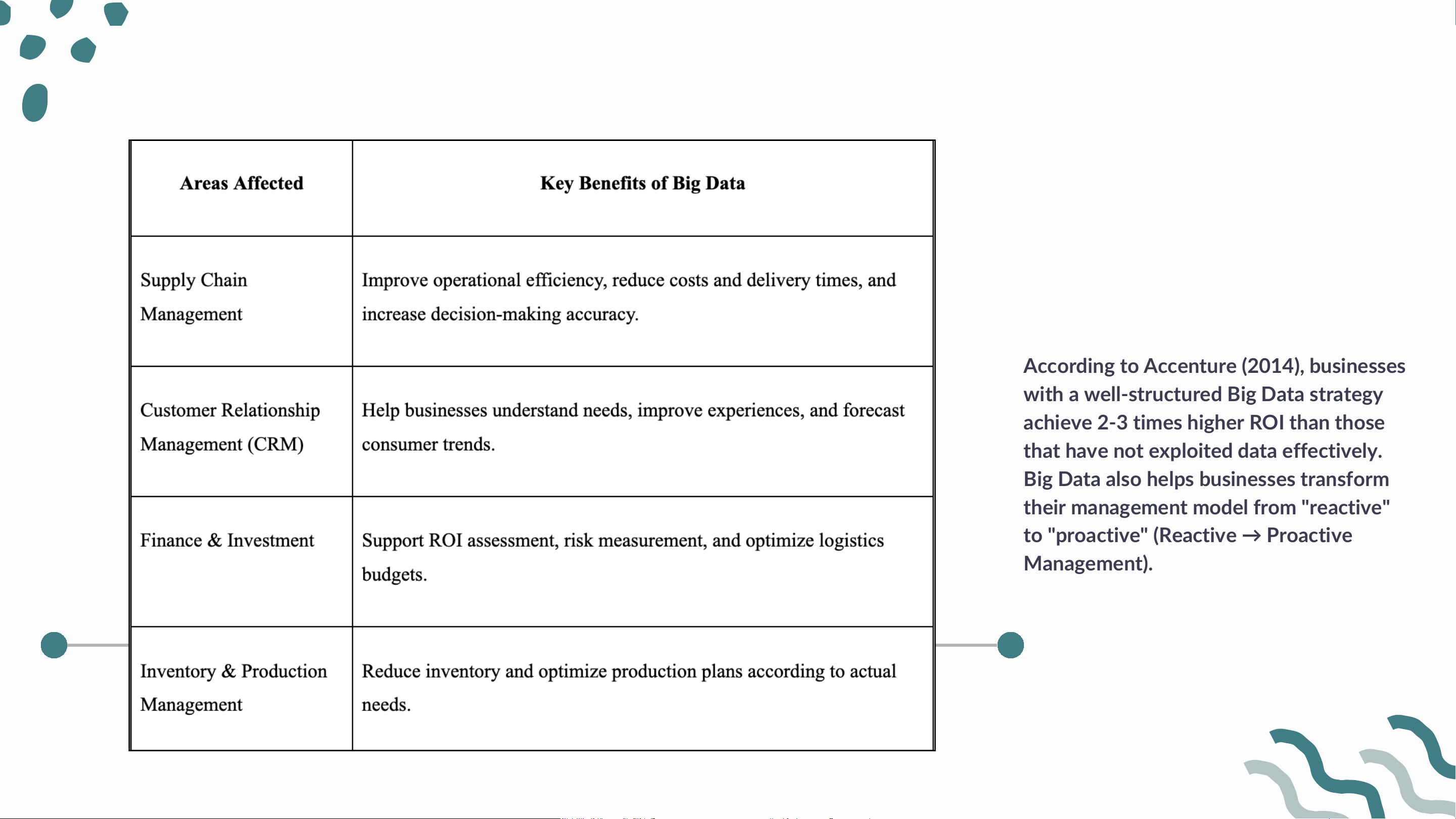
3. Opportunities and Benefits of Big Data in Logistics & SCM
According to Accenture (2014), businesses
with a well-structured Big Data strategy
achieve 2-3 times higher ROI than those
that have not exploited data effectively.
Big Data also helps businesses transform
their management model from "reactive"
to "proactive" (Reactive → Proactive Management).
3. Opportunities and Benefits of Big Data in Logistics & SCM
Development opportunities Global Perspective
In developed regions such as the US, EU, and China, Big Data is already deeply integrated into
logistics and supply chain systems.
Companies like Amazon, Alibaba, and DHL use Big Data to analyze mil ions of transactions in
real time, improving delivery speed and customer experience.
This global success creates a benchmark and motivation for developing countries, including
Vietnam, to accelerate digital transformation in logistics. In Vietnam
A the rapid growth of e-commerce logistics and multi-channel retail platforms such as MWG, Tiki, and Shopee.
The Vietnamese government also promotes digital transformation programs in logistics,
encourages data-driven management.
Forecast delivery demand, manage inventory more effectively, and improve service reliability.
Vietnam needs better data infrastructure, more skil ed data scientists, and stronger public–
private partnerships to build a national logistics data network.
3. Opportunities and Benefits of Big Data in Logistics & SCM
Development opportunities Future Trends
The future of logistics lies in integration and intel igence.
Combining Big Data with AI, Machine Learning,
Blockchain, and IoT wil help create a “smart, automated,
and flexible” supply chain that can adapt quickly to market fluctuations.
Improves efficiency, supports sustainable logistics,
reducing carbon emissions through data-optimized transportation.
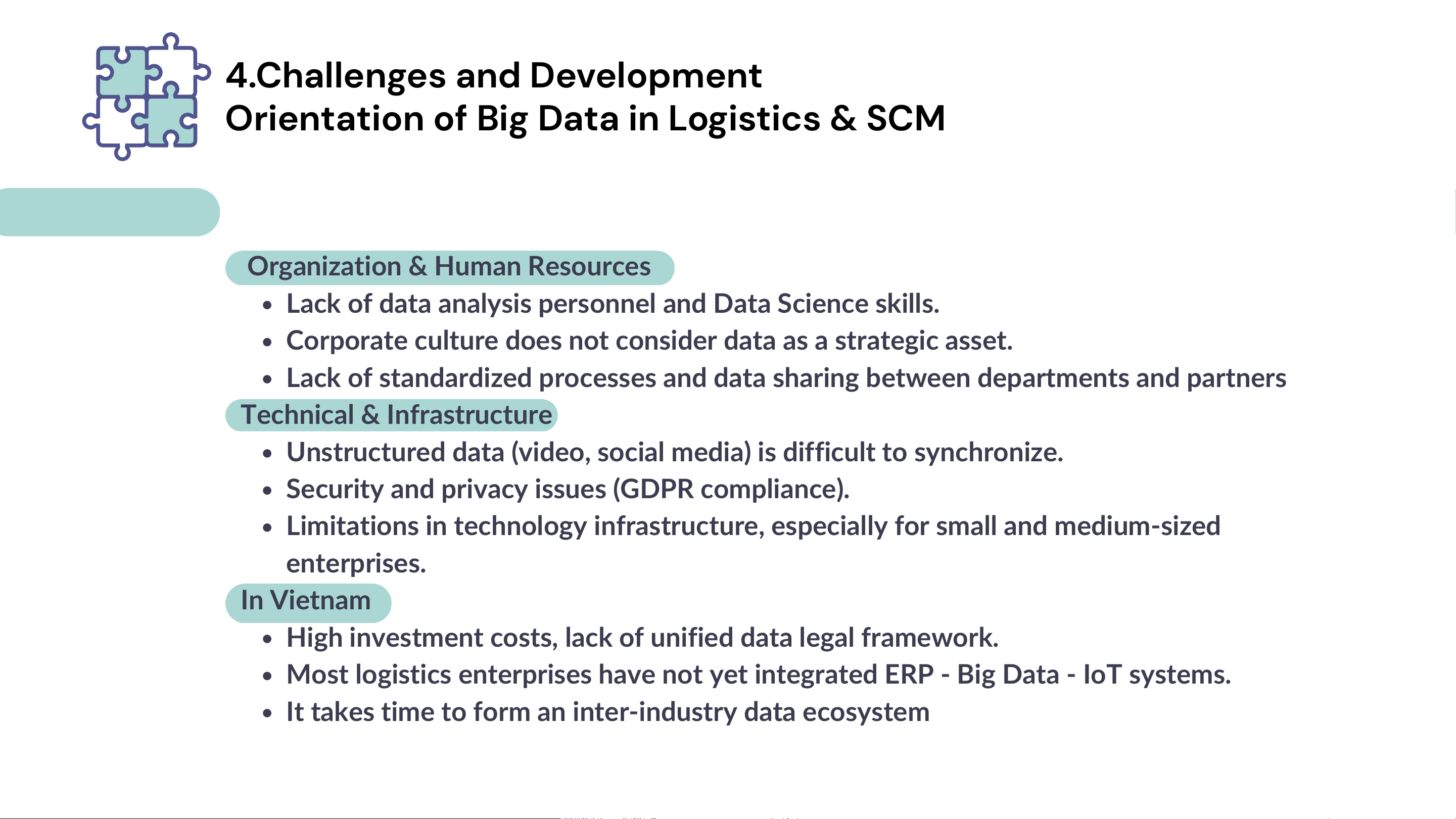
4.Chal enges and Development
Orientation of Big Data in Logistics & SCM Main Challenges
Organization & Human Resources
Lack of data analysis personnel and Data Science skills.
Corporate culture does not consider data as a strategic asset.
Lack of standardized processes and data sharing between departments and partners
Technical & Infrastructure
Unstructured data (video, social media) is difficult to synchronize.
Security and privacy issues (GDPR compliance).
Limitations in technology infrastructure, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises. In Vietnam
High investment costs, lack of unified data legal framework.
Most logistics enterprises have not yet integrated ERP - Big Data - IoT systems.
It takes time to form an inter-industry data ecosystem
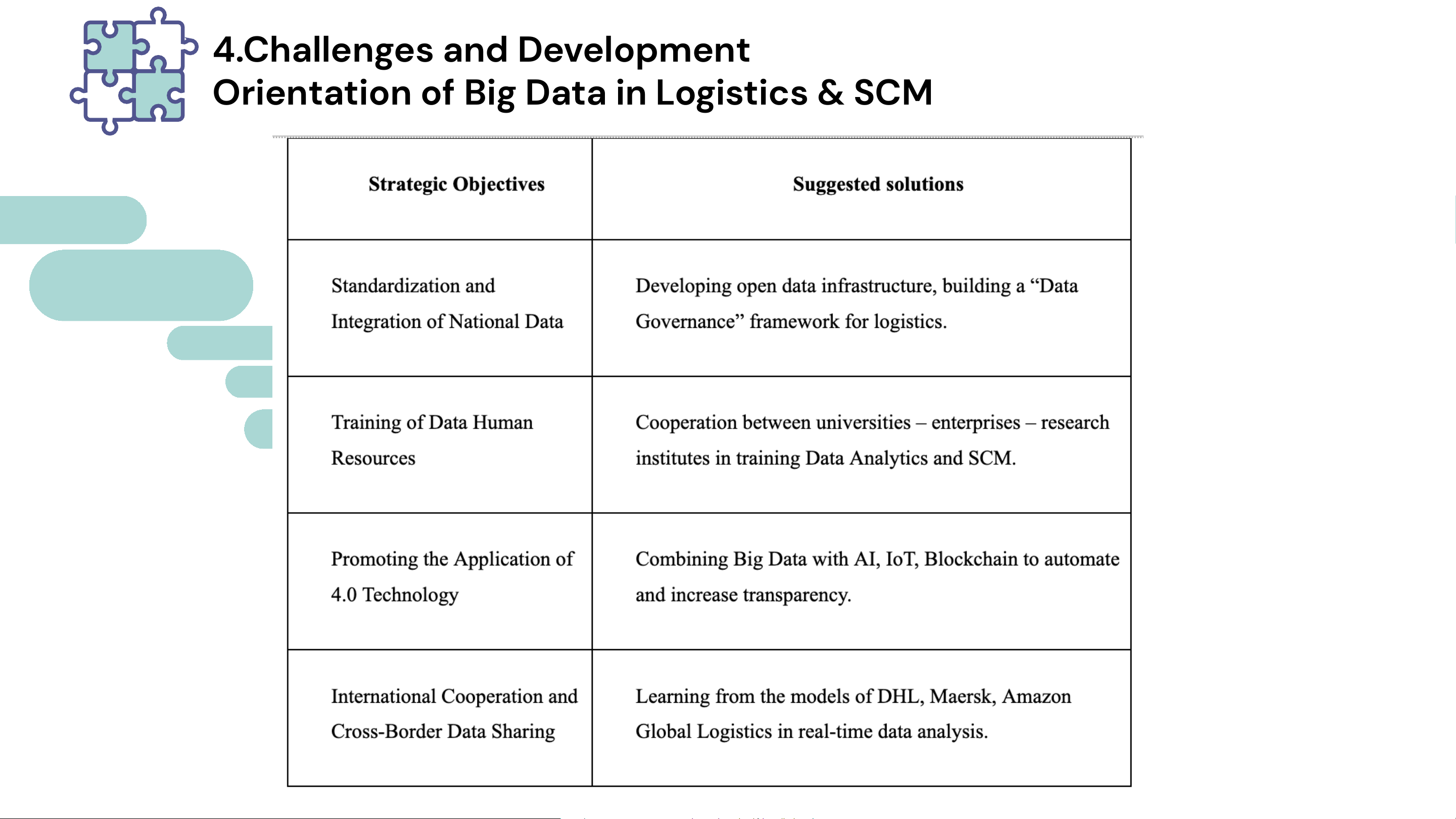
4.Chal enges and Development
Orientation of Big Data in Logistics & SCM Development orientation
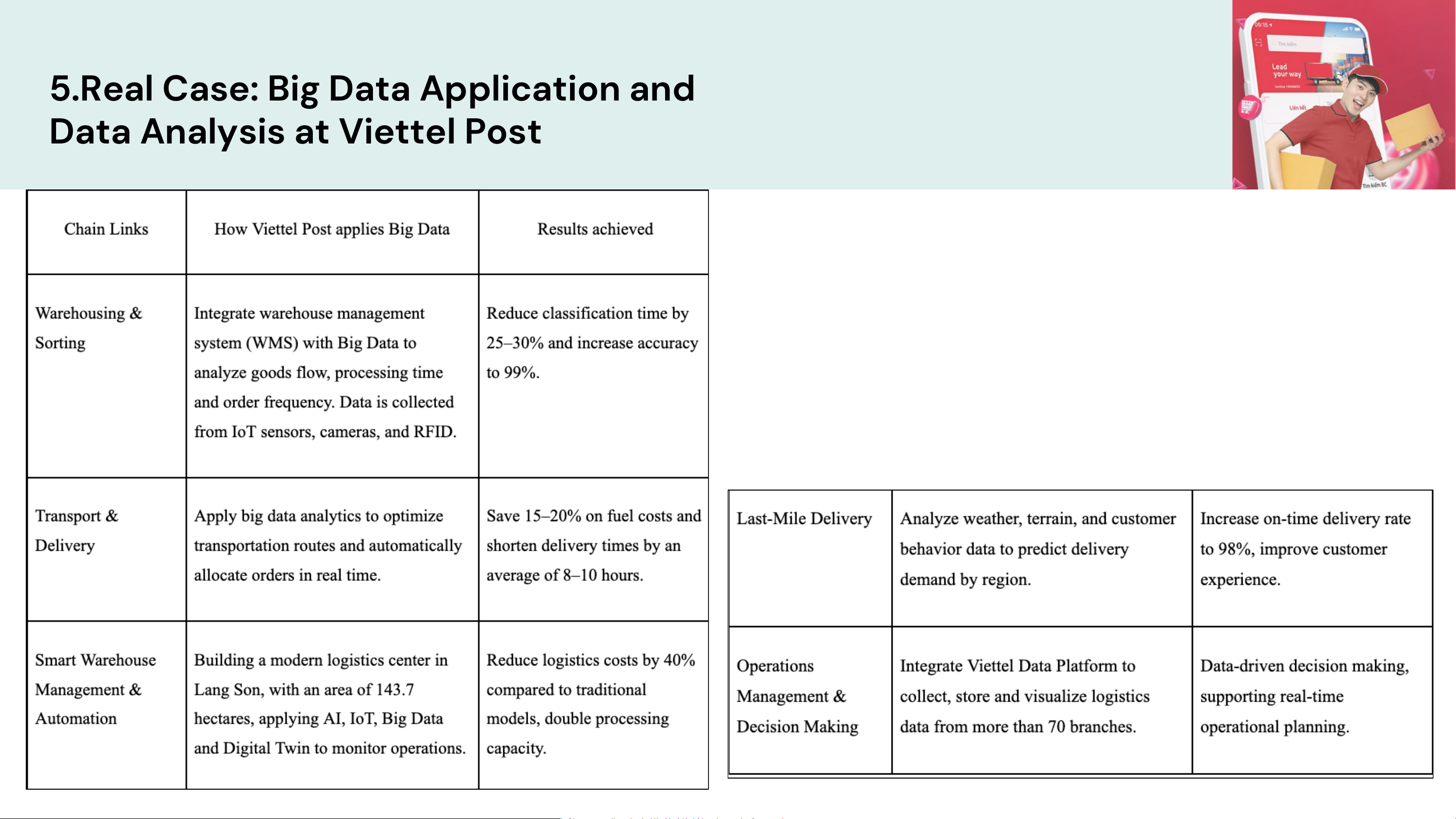
5.Real Case: Big Data Application and
Data Analysis at Viettel Post
5.Real Case: Big Data Application and
Data Analysis at Viettel Post Opportunities
Increasing national logistics efficiency: Viettel Post's investment of
VND3,300 billion in a smart logistics zone in Lang Son has created a
turning point in the Vietnam-China cross-border supply chain, helping to
increase customs clearance and handle 1,500 vehicles/day - double the current capacity.
Leading the digital logistics trend in Vietnam: With a strong data
infrastructure and technology ecosystem (AI, IoT, 5G, Cloud)
Opportunities for a rapidly growing e-commerce market: The delivery and
express delivery market in Vietnam is growing 25-30%/year (2024),
expanding opportunities to exploit Big Data in route optimization, demand
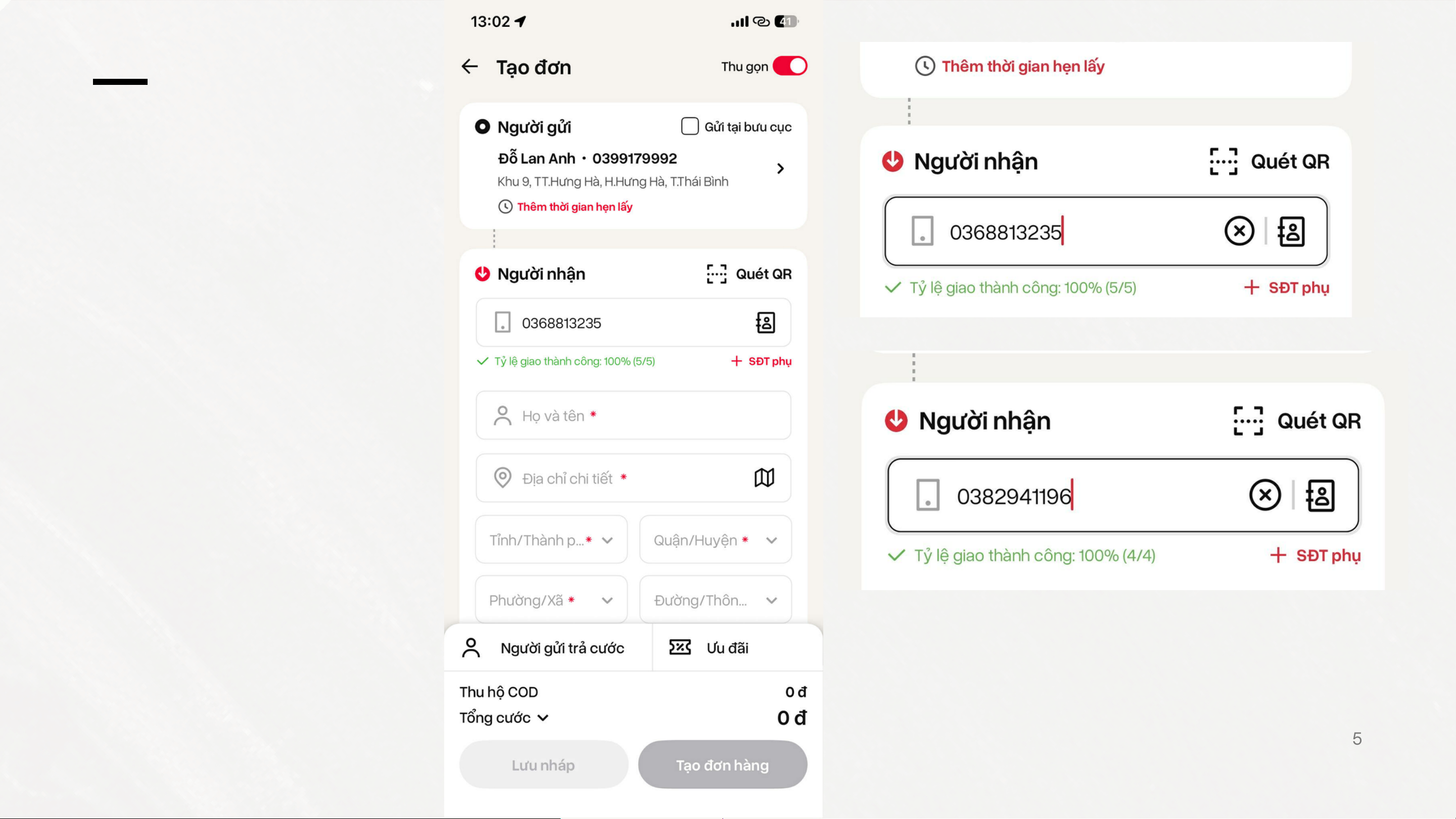
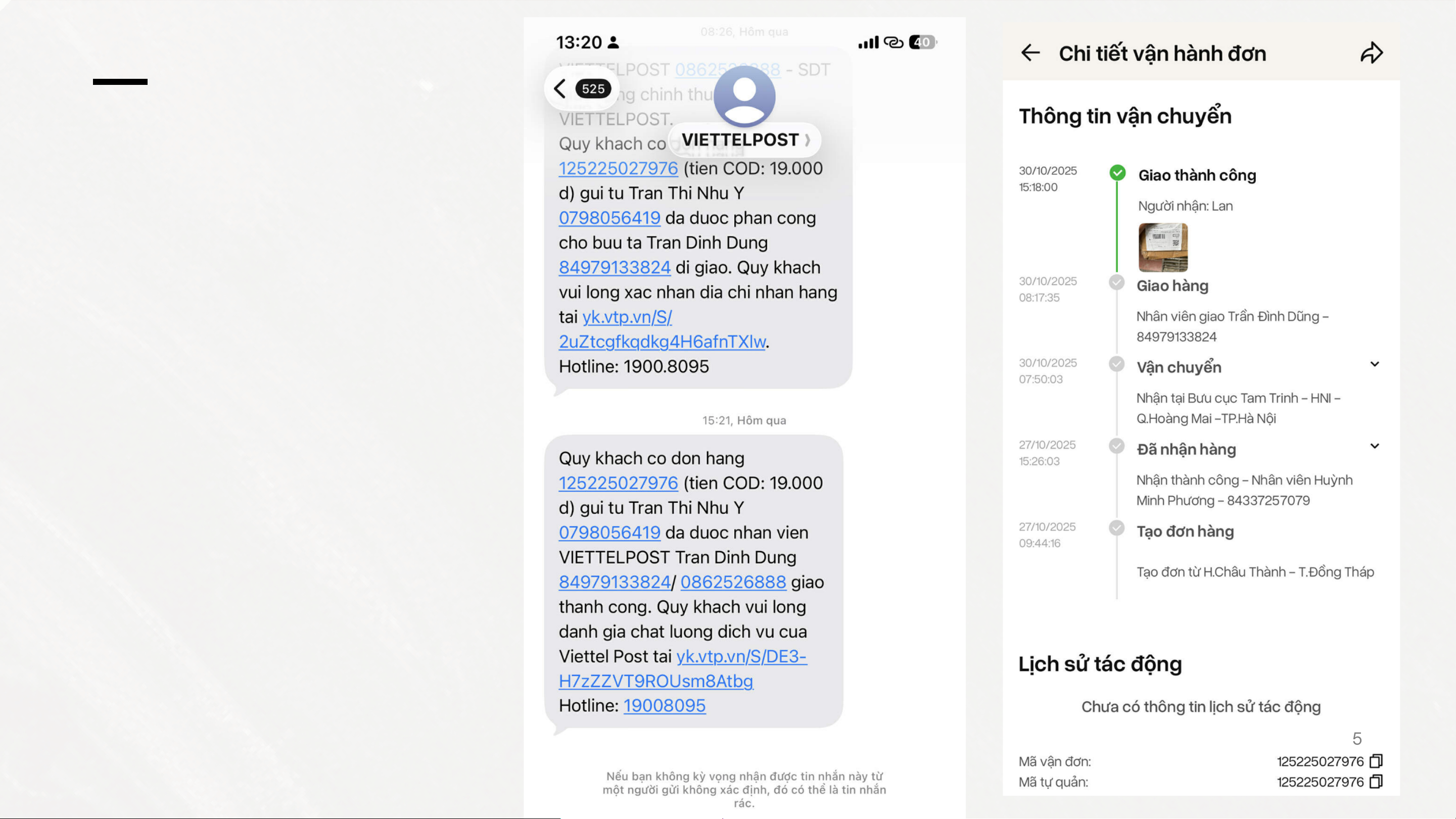
forecasting and shopping behavior analysis. Big data of Viettel Post 5 Big data of Viettel Post 5 Big data of Viettel Post 5 The End THANK YOU FOR LISTENING



