









Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056
HỌC VIỆN CÔNG NGHỆ BƯU CHÍNH VIỄN THÔNG BÀI GIẢNG MÔN Lập trình Web Giảng viên: Nguyễn Trọng Khánh Điện thoại/E-mail: khanhnt@ptit.edu.vn Bộ môn: HTTT - Khoa CNTT1
Học kỳ/Năm biên soạn: 1/2024 lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Web Programming - Overview
Some materials in this slide were inspired by the course taught by Tubagus Rafi Kusuma, ST, MM.2 lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 ❖ Definition ❖ Web evolution ❖ Architecture ❖ Conclusion lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 ? 4
Downloaded by Bao Ngoc (baongoc32@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 What is World Wide Web
1. Introduced by Tim Burners-Lee in 1989
2. The World Wide Web (WWW) is an information space where documents and
other web resources are identified by URLs, interlinked by hypertext links, and
can be accessed via the Internet.
3. The World Wide Web was central to the development of the Information Age
and is the primary tool billions of people use to interact on the Internet.
4. Web pages are primarily text documents formatted and annotated with
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). In addition to formatted text, web pages
may contain images, video, and software components that are rendered in the
user's web browser as coherent pages of multimedia content.
Embedded hyperlinks permit users to navigate between web pages. 5
Downloaded by Bao Ngoc (baongoc32@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 WWW ≠ Internet World Wide Web ≠ Internet Web based on hypertext The Internet is collection of
Web based on Client/Server Model
interconnected Computer Network 6
Downloaded by Bao Ngoc (baongoc32@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 WebPAGES 8
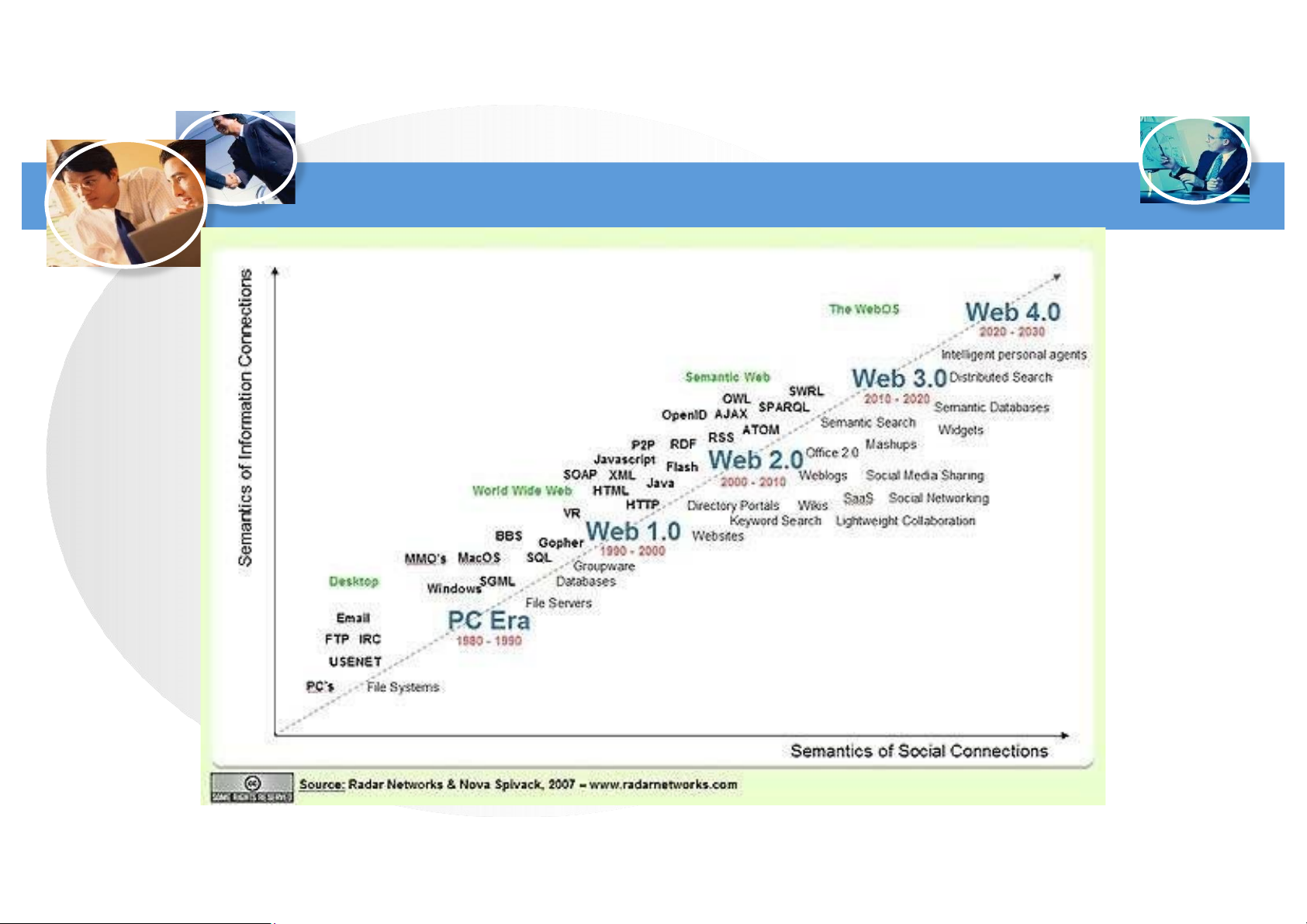
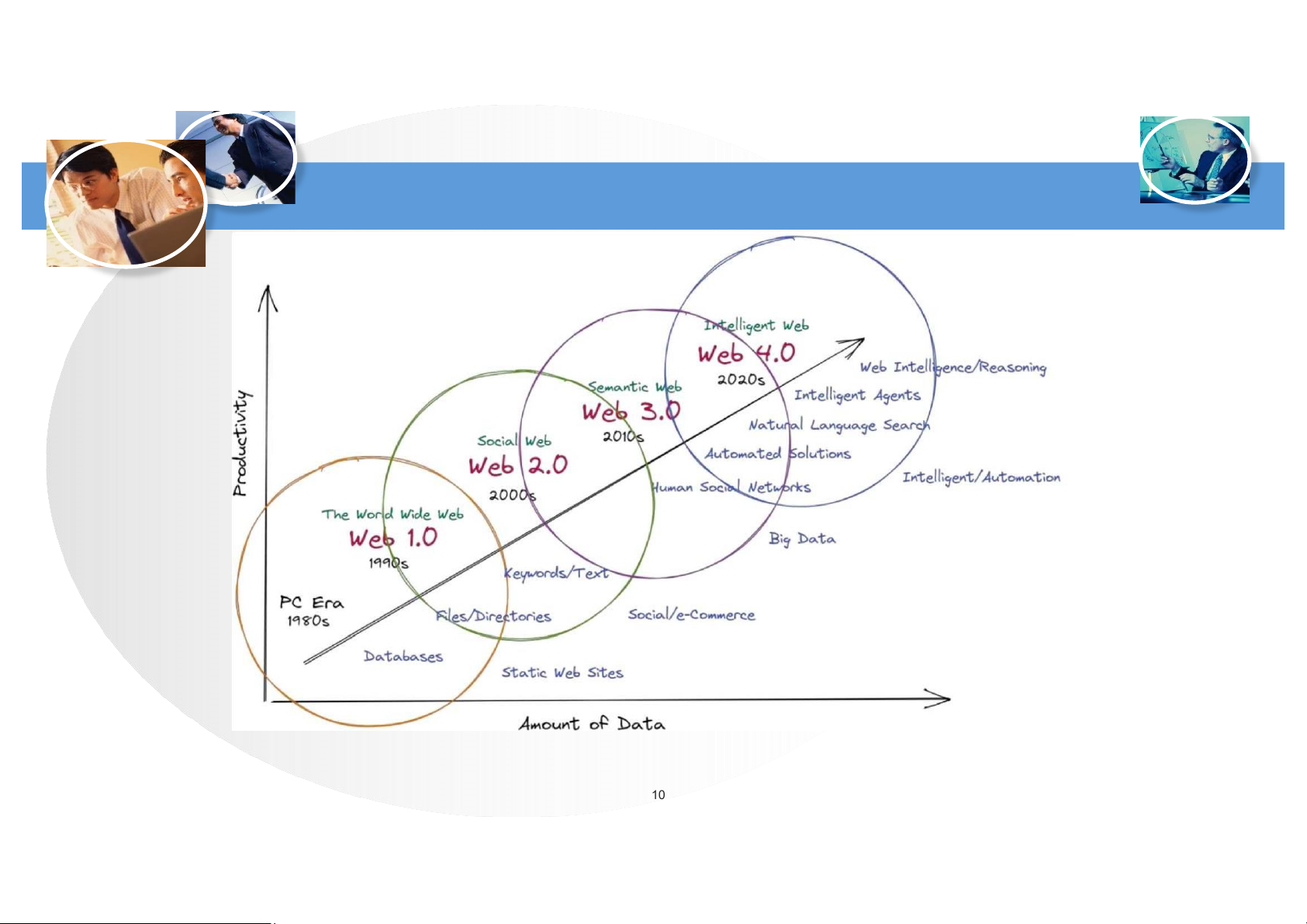
Downloaded by Bao Ngoc (baongoc32@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Web Technology AGE 9
Downloaded by Bao Ngoc (baongoc32@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Web Technology AGE
Kenwright, Benjamin. "Exploring the Power of Creative AI Tools and Game-Based Methodologies for 10
Interactive Web-Based Programming."arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.11649(2023).
Downloaded by Bao Ngoc (baongoc32@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Web 1.0
1. Web 1.0 is an old internet that only allows people to read from the internet.
2. First stage of theWorld Wide linking web pages and hyperlink
3. Most read-only Web. It focused on companies home pages
4. Dividing the world wide web into usable directories
5. It means Web is use as “Information Portal” 12
Downloaded by Bao Ngoc (baongoc32@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Web 1.0 Characteristic
1. Static pages instead of dynamic HTML.
2. Content served from the server's filesystem instead of a relational database management system (RDBMS).
3. Pages built using Server Side Includes or CGI (Common Gateway Interface)
instead of a web application written in a dynamic programming language
such as Perl, PHP, Python or Ruby.
4. The use of HTML 3.2-era elements such as frames and tables to position
and align elements on a page. These were often used in combination with
spacer GIFs.[citation needed]
5. Proprietary HTML extensions, such as the and tags,
introduced during the first browser war. 6. Online guestbooks. 7. HTML forms sent via email. lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Web 1.0 Example lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Web 2.0 ❖ What is Web 2.0?
▪ Describes evolving trends in Web technology and design post-Web 1.0. ❖ Key Objectives
▪ Enhance creativity, secure and information sharing. ▪ Increase collaboration.
▪ Improve Web functionality. ❖ Impact and Evolution
▪ Development of Web-based communities and services.
▪ Emergence of social networks (e.g., Facebook, MySpace), video
sharing (e.g., YouTube), wikis, blogs. lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Web 2.0 Features
Web 2.0 Websites typically include some of the following features/techniques:
1. Search: the ease of finding information through keyword searching.
2. Links: guides to important pieces of information. The best pages are the most frequently linked to.
3. Authoring: the ability to create constantly updating content that is co-created by users. In
wikis, the content is iterative in the sense that the people undo and redo each other’s work. In
blogs, it is cumulative in that posts and comments of individuals are accumulated over time.
4. Tags: categorization of content by creating tags that are simple, one-word descriptions to
facilitate searching and avoid having to fit into rigid, pre-made categories.
5. Extensions: automation of pattern matching for customization by using algorithms (i.e. Amazon.com recommendations).
6. Signals: the use of RSS (Real Simple Syndication) technology to create a subscription model
which notifies users of any content changes. 19 lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Web 2.0 Tools ❖Blogs ❖Podcasts ❖Social Networks ❖Wikis ❖ePortfolios ❖Micro-Blogs ❖Social Bookmarking 20 lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Blogging ❖What is a Weblog (Blog)?
▪ A personal journal on the Web.
❖Diversity of topics and opinions
▪ Covers a wide range of topics, reflecting varied opinions. ❖Readership and influence
▪ From highly influential blogs with vast readership to
personal blogs for family and friends. 22 lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Weblog 23 lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056
Why are blogs important?
❖Empowerment through Weblogs: Allows millions to easily publish and
share ideas. Enables millions more to engage through comments.
❖Nature of blogs: Fluid and dynamic, resembling a conversation. A shift from
the traditional 'library-like' Web.
❖Changing Web usage: Growing numbers reading, writing, and commenting
on blogs. Fundamental shift in how we interact with the Web.
❖From Passive to Active: Internet users evolving from passive consumers to active participants.
❖Voice for everyone: Weblogs provide a platform for all to express their voice. 25 lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Weblog
❖ What is a blogger? A blogger is someone who writes a blog. ❖ What is the
blogosphere? Blogosphere is a word used to describe the online community of bloggers and their writings.
❖ How is a Weblog different from a Website? A Weblog is a Website that is
updated frequently, most often displaying its material in journal-like chronological
dated entries or posts. Most blogs allow readers to post comments to your post,
and link from their blog to your posts using the permanlink URL or address. In a
blog, the content can be published and syndicated separate from the formatting
using an RSS feed. Readers can then subscribe to the feed to automatically receive updates.
❖ What is a Weblog post or entry? An entry, a post, or a posting, are the terms
often used to refer to a specific article or commentary written by the blogger on his or her Weblog.
❖ What is a comment? Many Weblogs allow readers to write a reaction to what
was written in the blog entry. Comments can often be found directly following the blog entry. 28 lOMoAR cPSD| 58737056 Podcast
❖What is a Podcast?: A podcast is essentially an audio (or video) file.
❖Distinct Features of a Podcast: What sets a podcast apart from
other types of audio on the Internet is the ability of a “podcaster” to
solicit subscriptions from listeners. When new podcasts are
released, they are automatically delivered, or fed, to a subscriber's computer or mobile device.
❖Format and Frequency: Typically, a podcast features an audio show
with new episodes that are fed to your computer either sporadically
or at planned intervals, such as daily or weekly.
❖Encouraging Subscriptions: This format encourages listeners to
“subscribe” to the podcast. 34