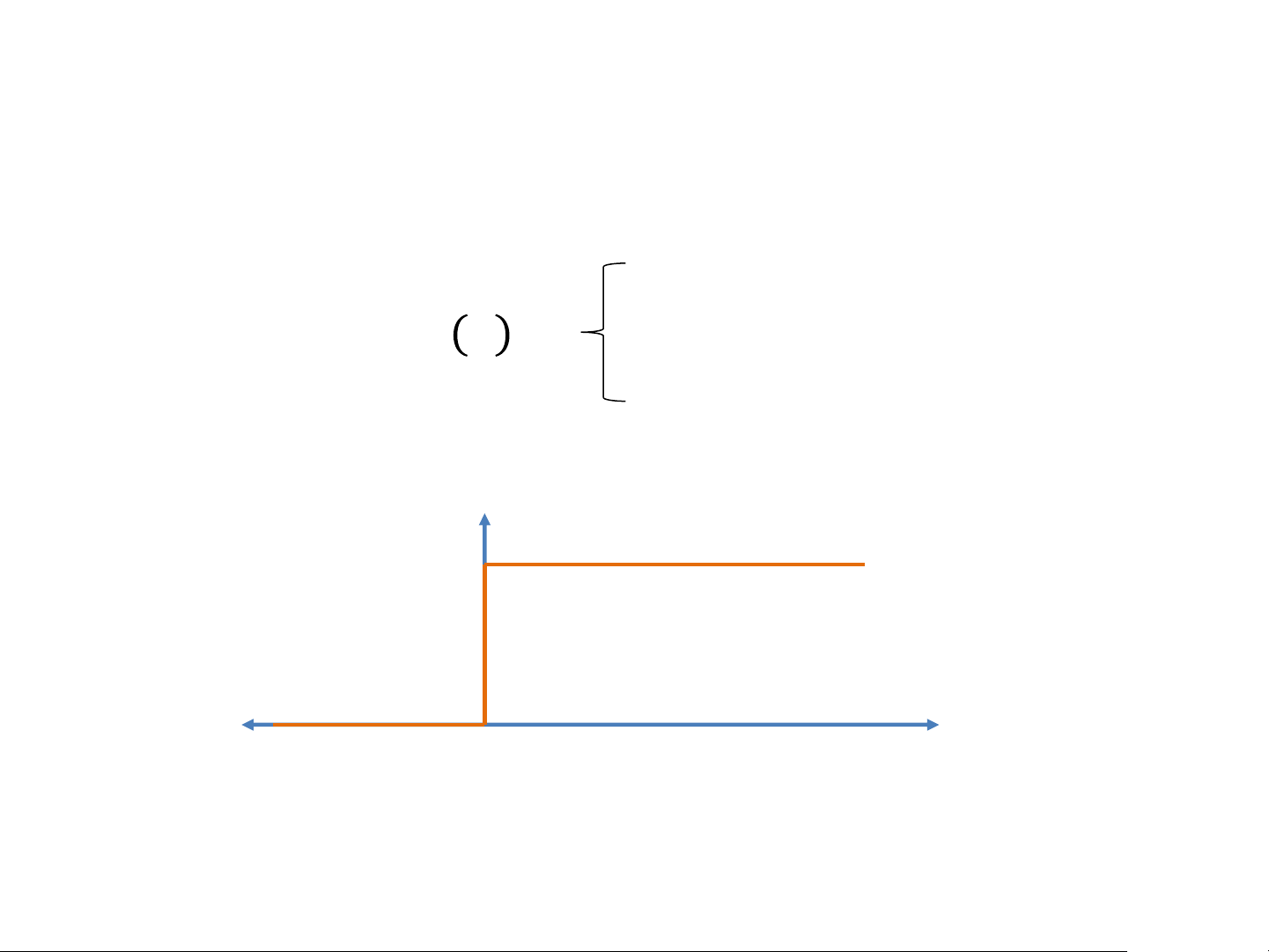
Preview text:
kiến trúc mạng phục vụ cho bài toán phân loại (classification) Lecture 5: The Perceptron (PLA) Sử dụng linear Instructor: Thao. Ng Dac P Major: AI&DS Outlook: ndpthao@tlu.edu.vn Linear Classifiers • Group classifier Group 1 or Group 2 Linear Classifiers • E-mail spam classifier Spam or Non-spam (ham) Linear Classifiers • Image classifier Linear Classifiers
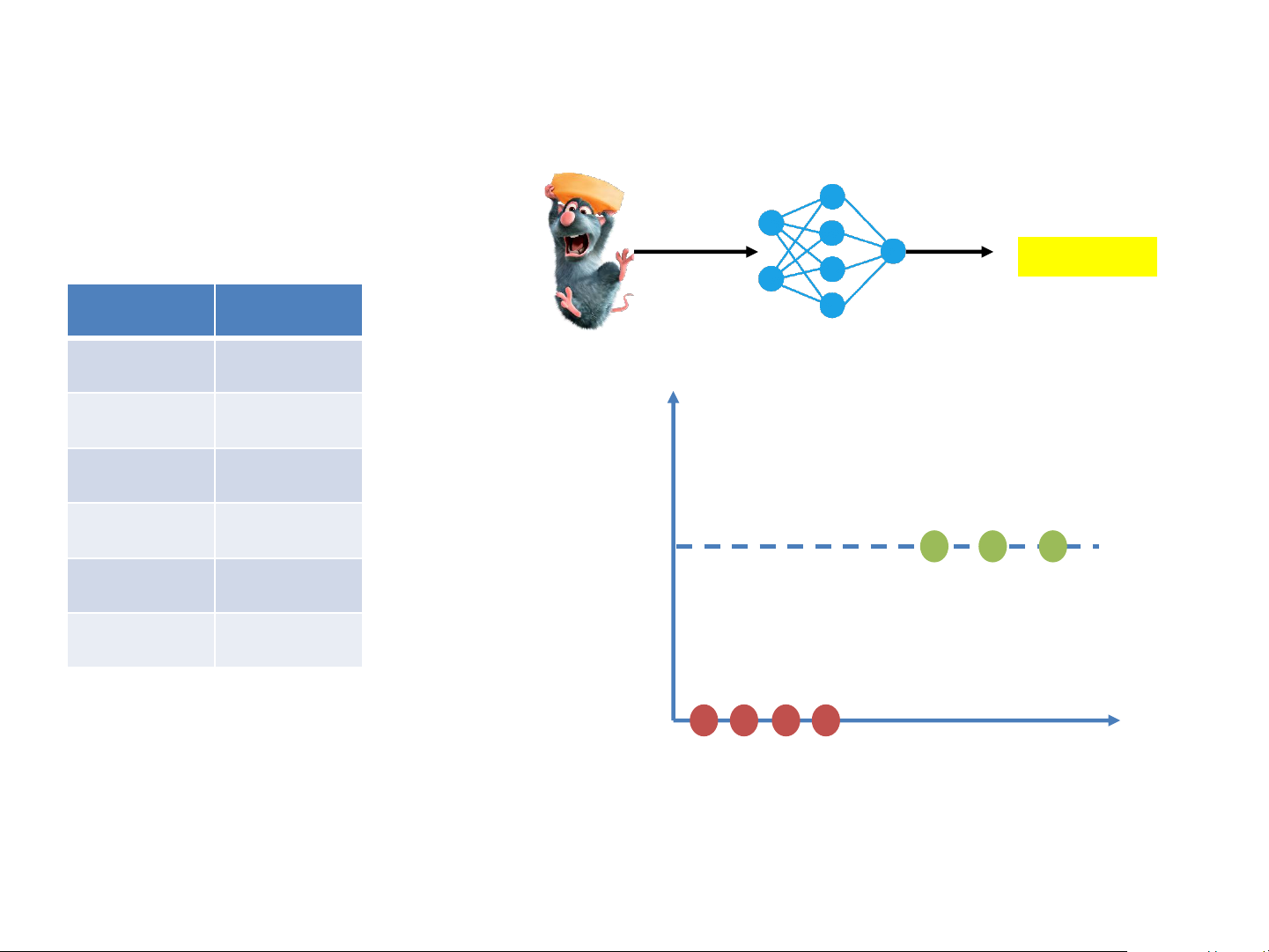
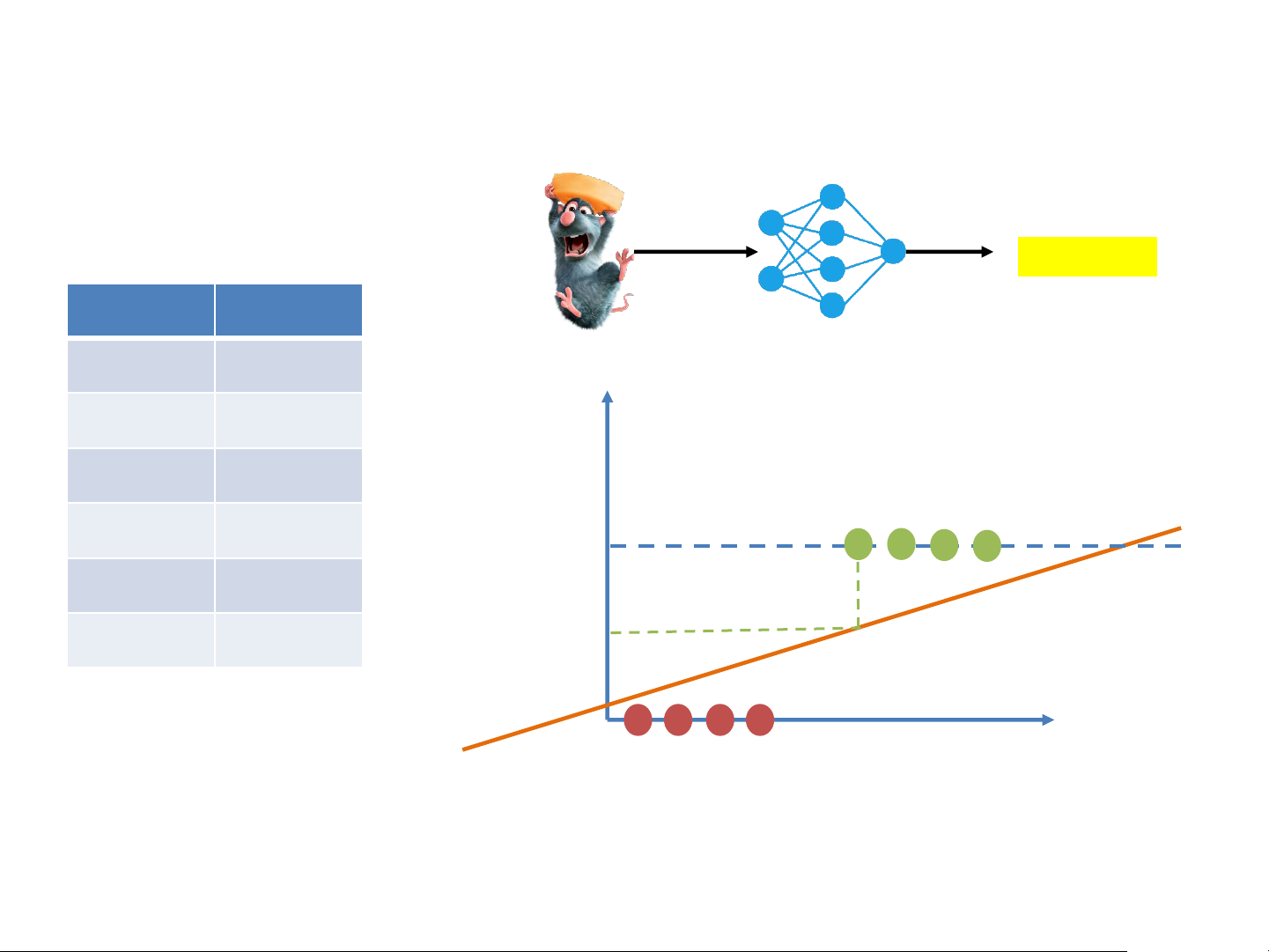
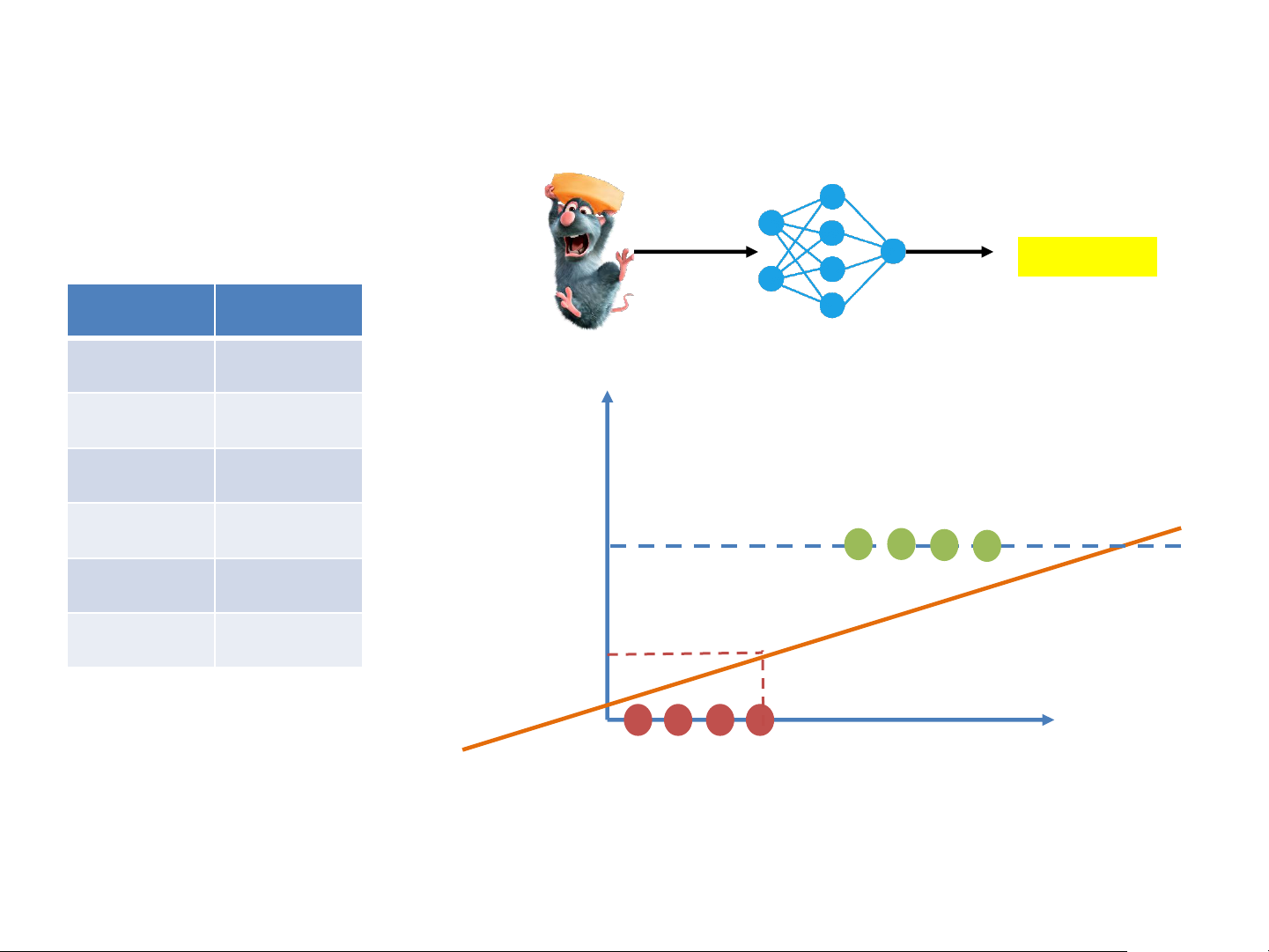
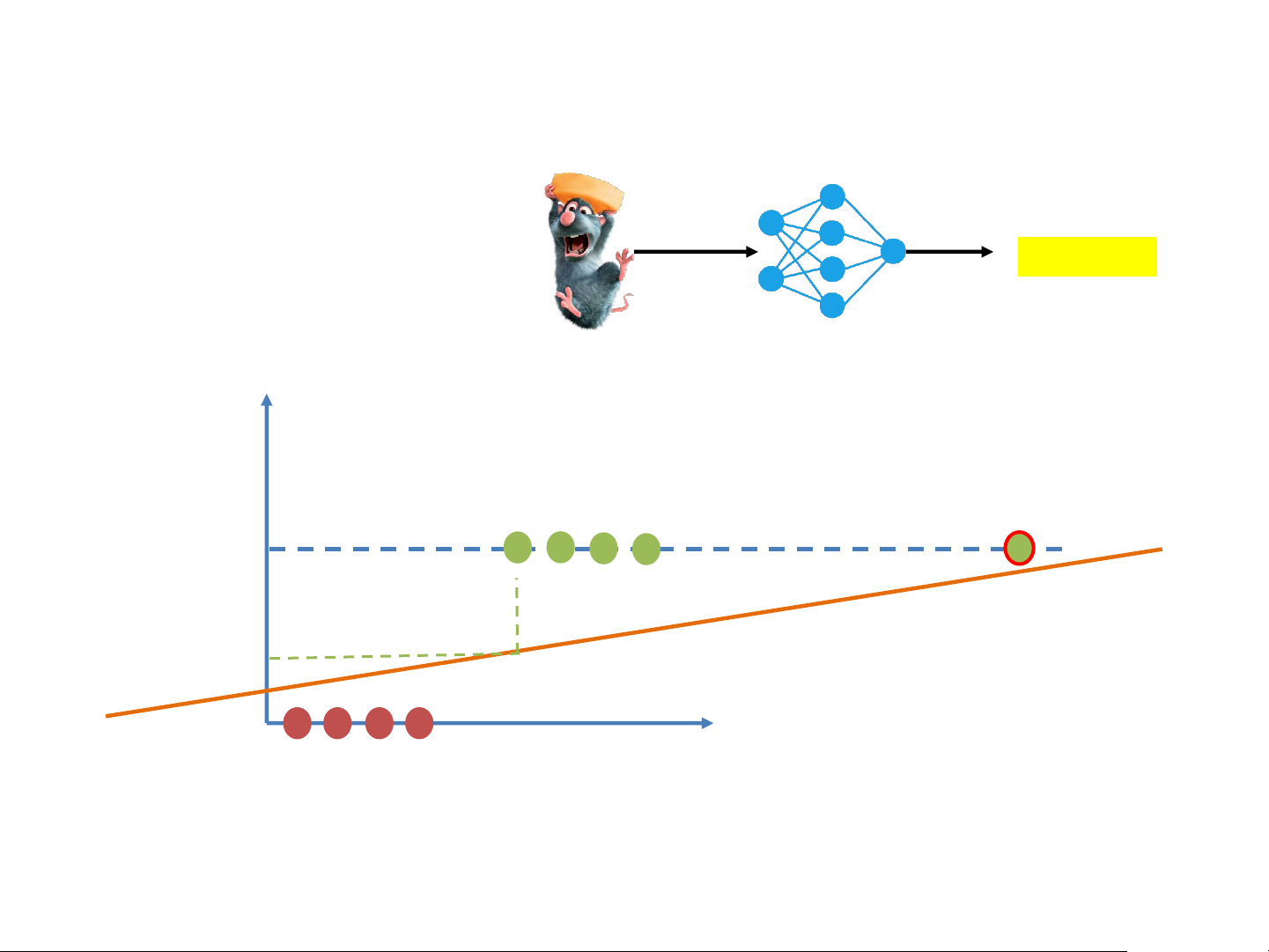
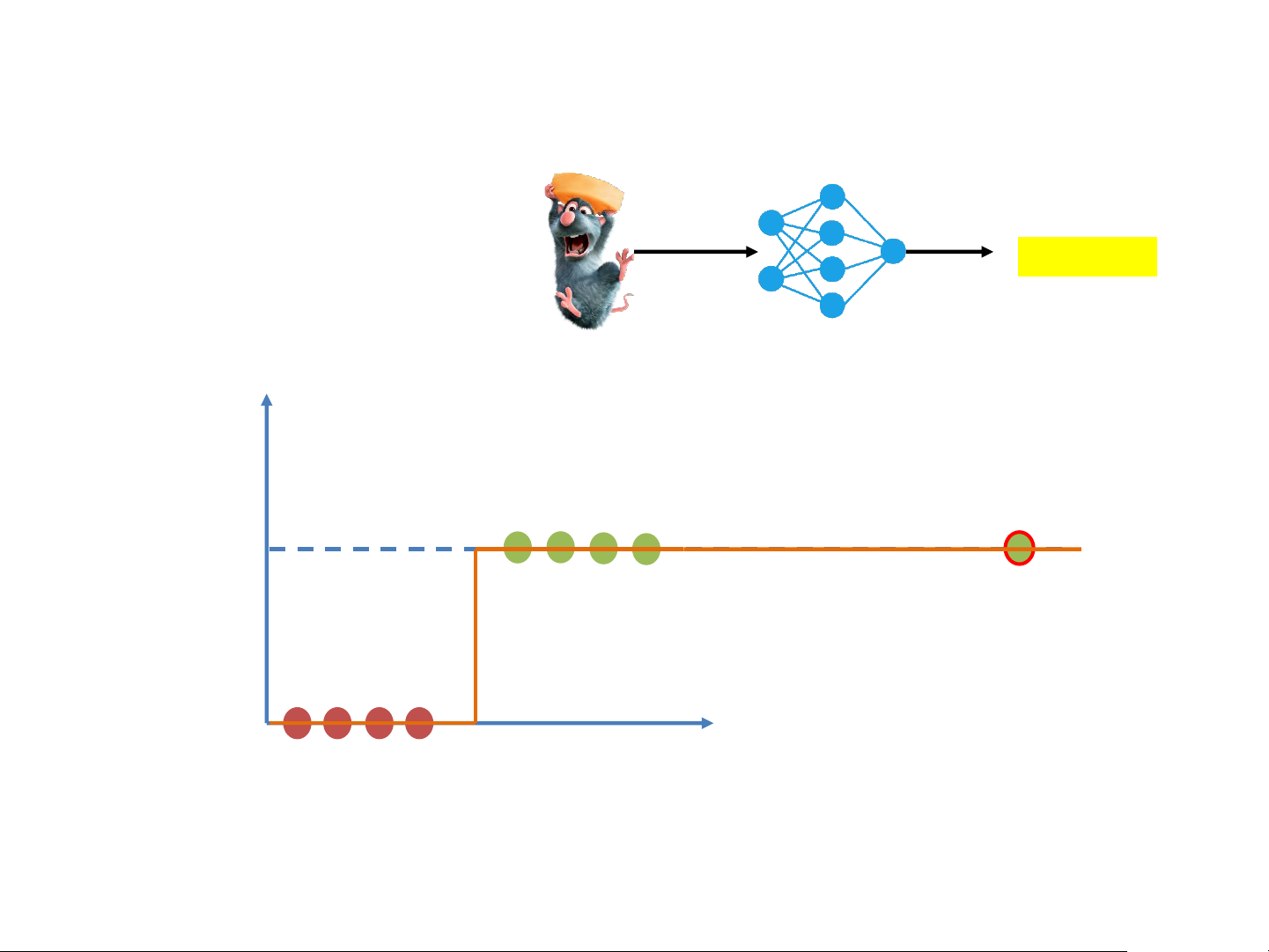
Thiết kế mạng dự đoán sự béo phì của chuột • Obesity classifier Obesity? Weight Obesity
chuột đc đưa vào 1 cái mạng --> định nghĩa ngưỡng béo 500g No phì của chuột Y 250g No 1kg Yes Obesity 2kg Yes 1 3kg Yes 150g No 0 X Strong Linear Classifiers • Obesity classifier Obesity? Weight Obesity 500g No Y 250g No 1kg Yes Obesity y=𝜔x 2kg Yes 1 3kg Yes 150g No > 0.5 0 X Strong Linear Classifiers • Obesity classifier Obesity? Weight Obesity 500g No Y 250g No 1kg Yes Obesity y=𝜔x 2kg Yes 1 3kg Yes 150g No < 0.5 0 X Strong Linear Classifiers • Obesity classifier Obesity? Y Obesity 1 < 0.5? 0 X Strong Linear Classifiers • Obesity classifier Obesity? Y Obesity 1 0 X Strong The Perceptron
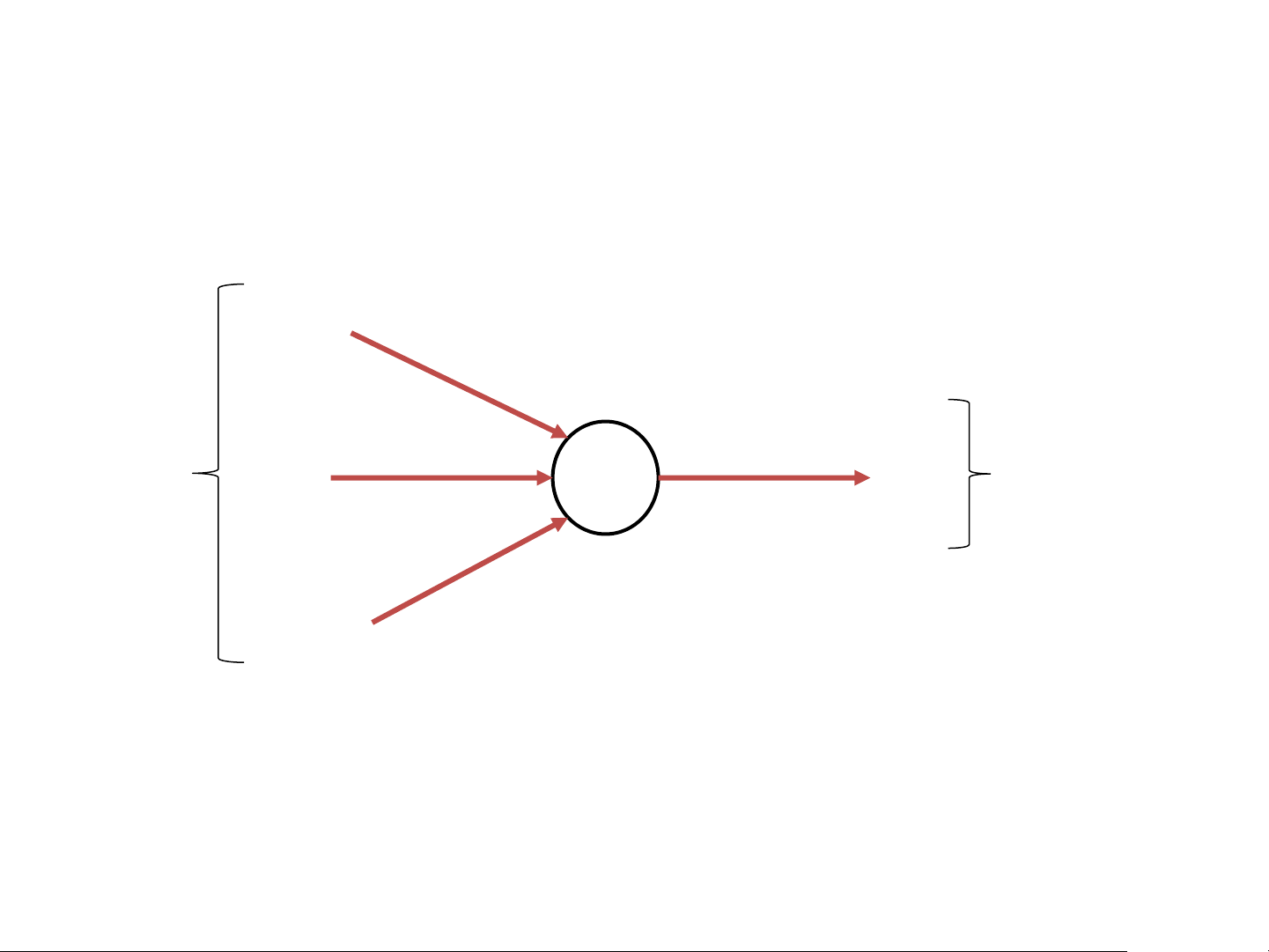
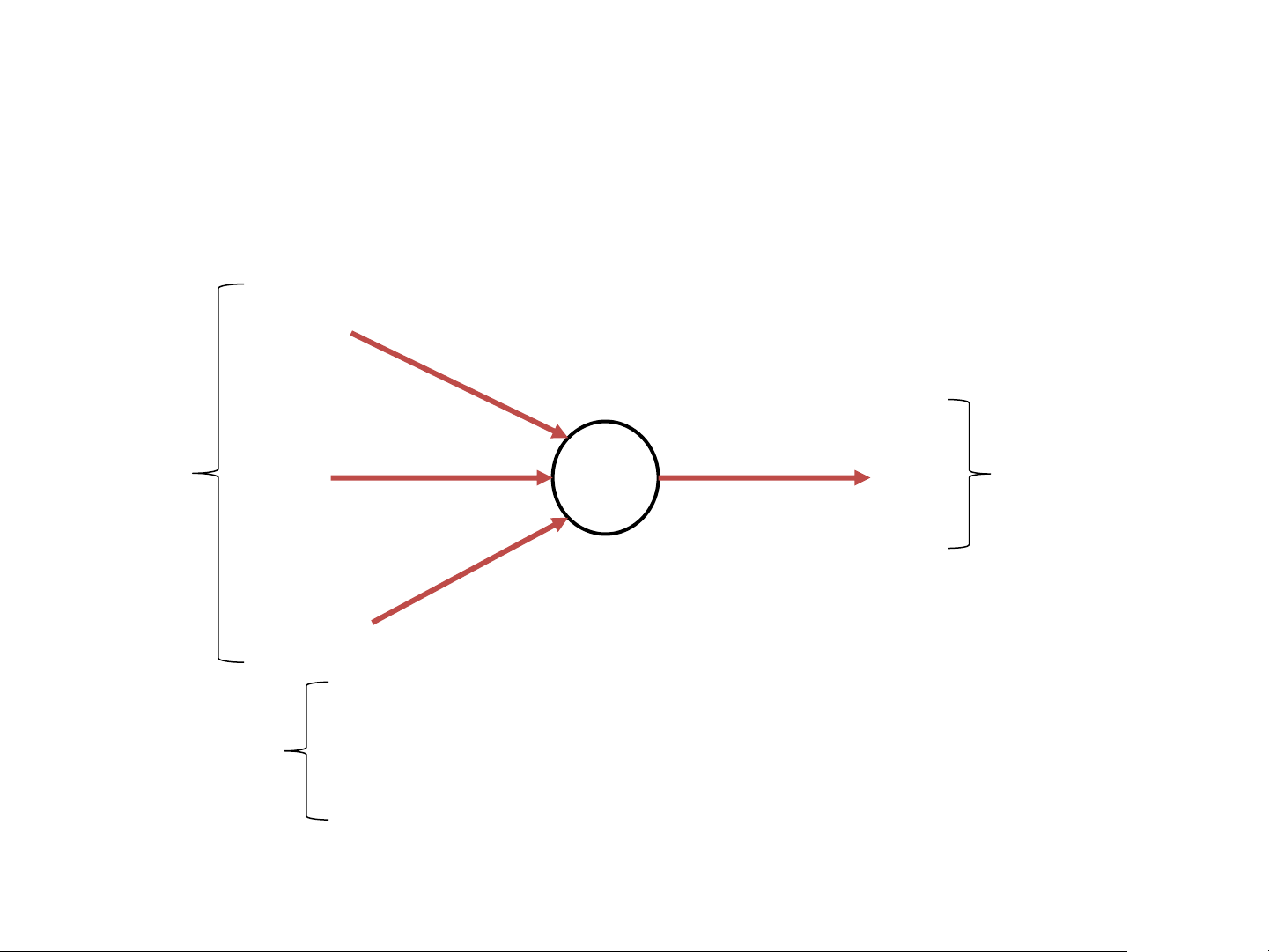
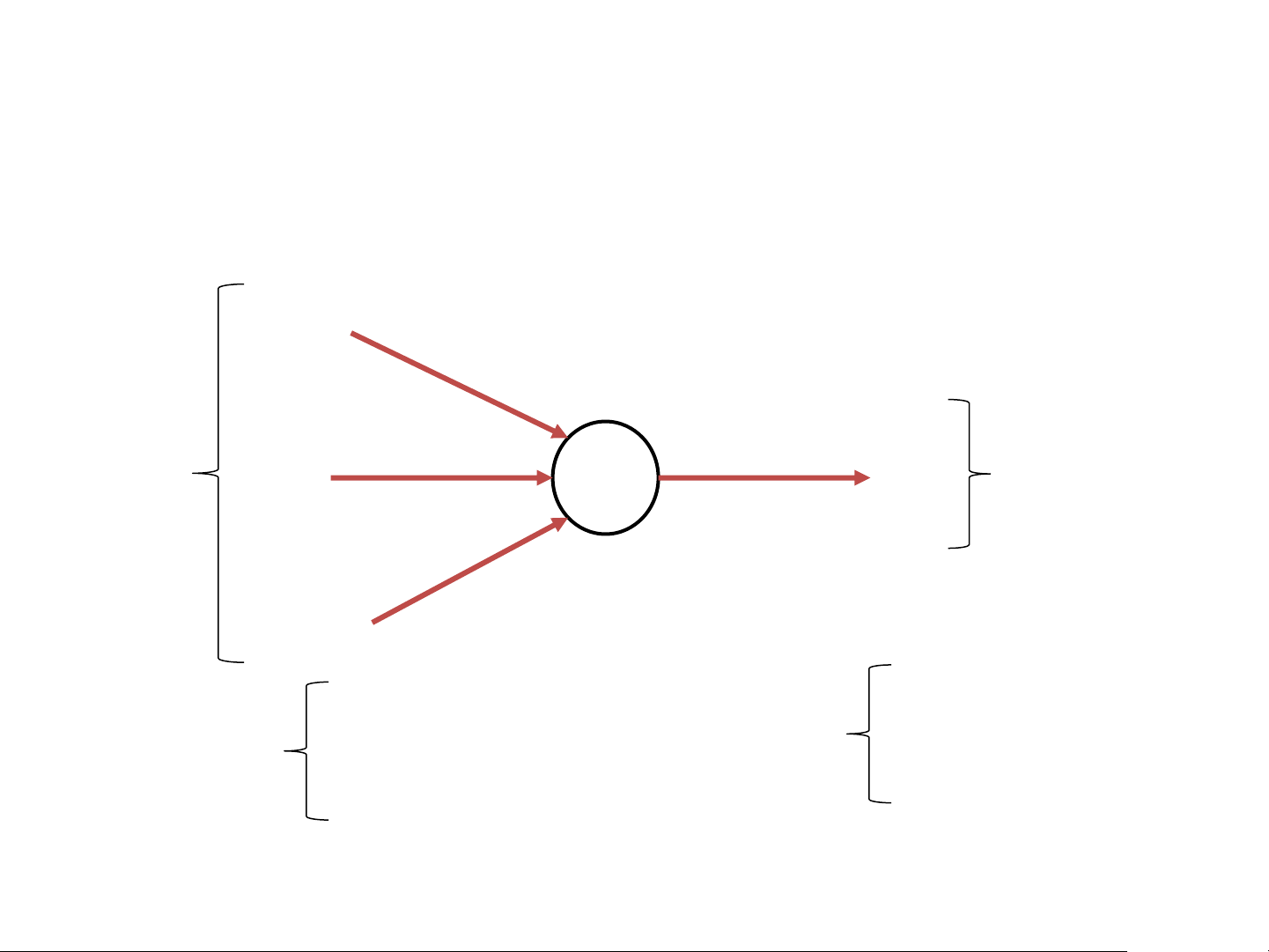
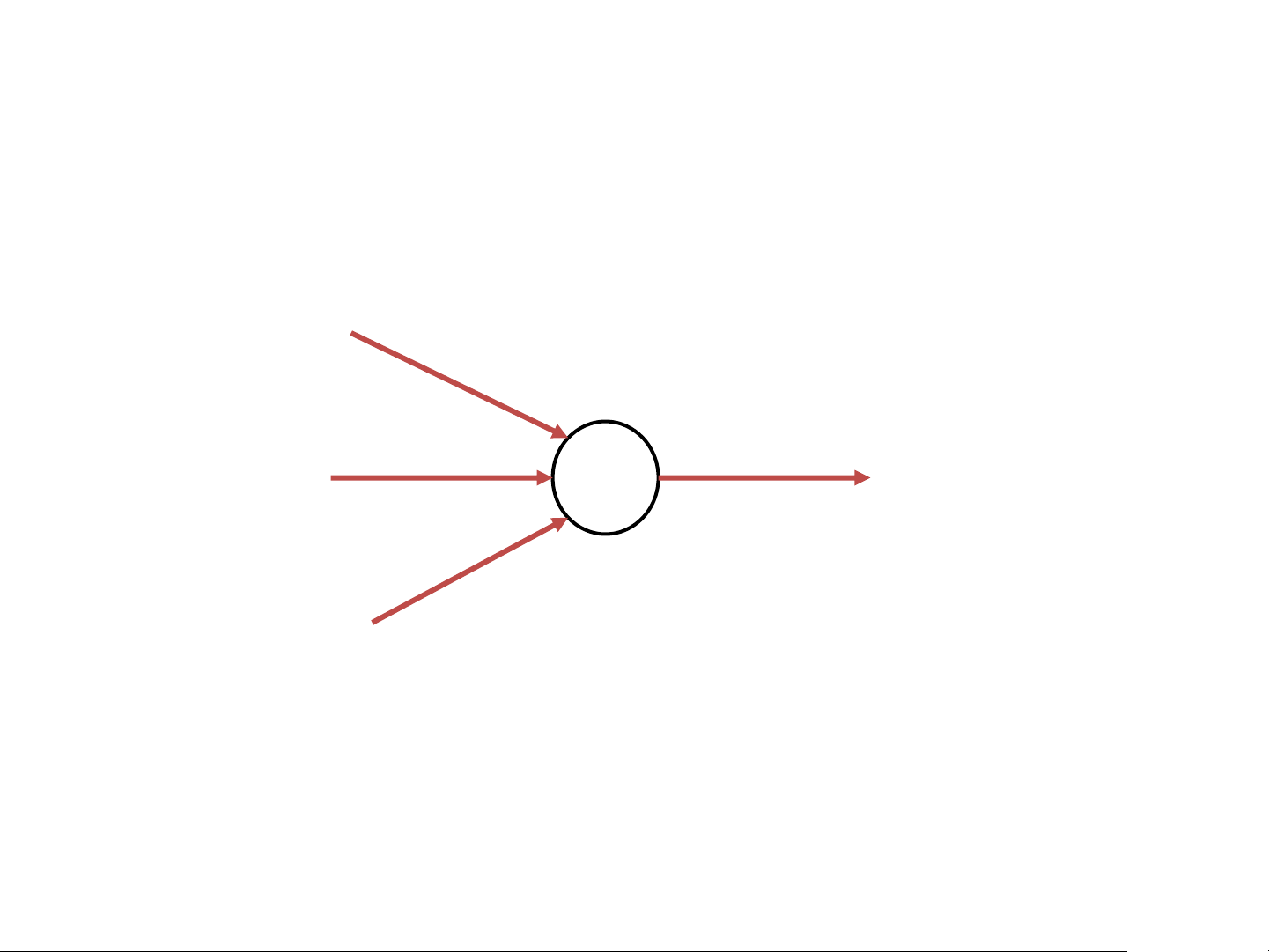
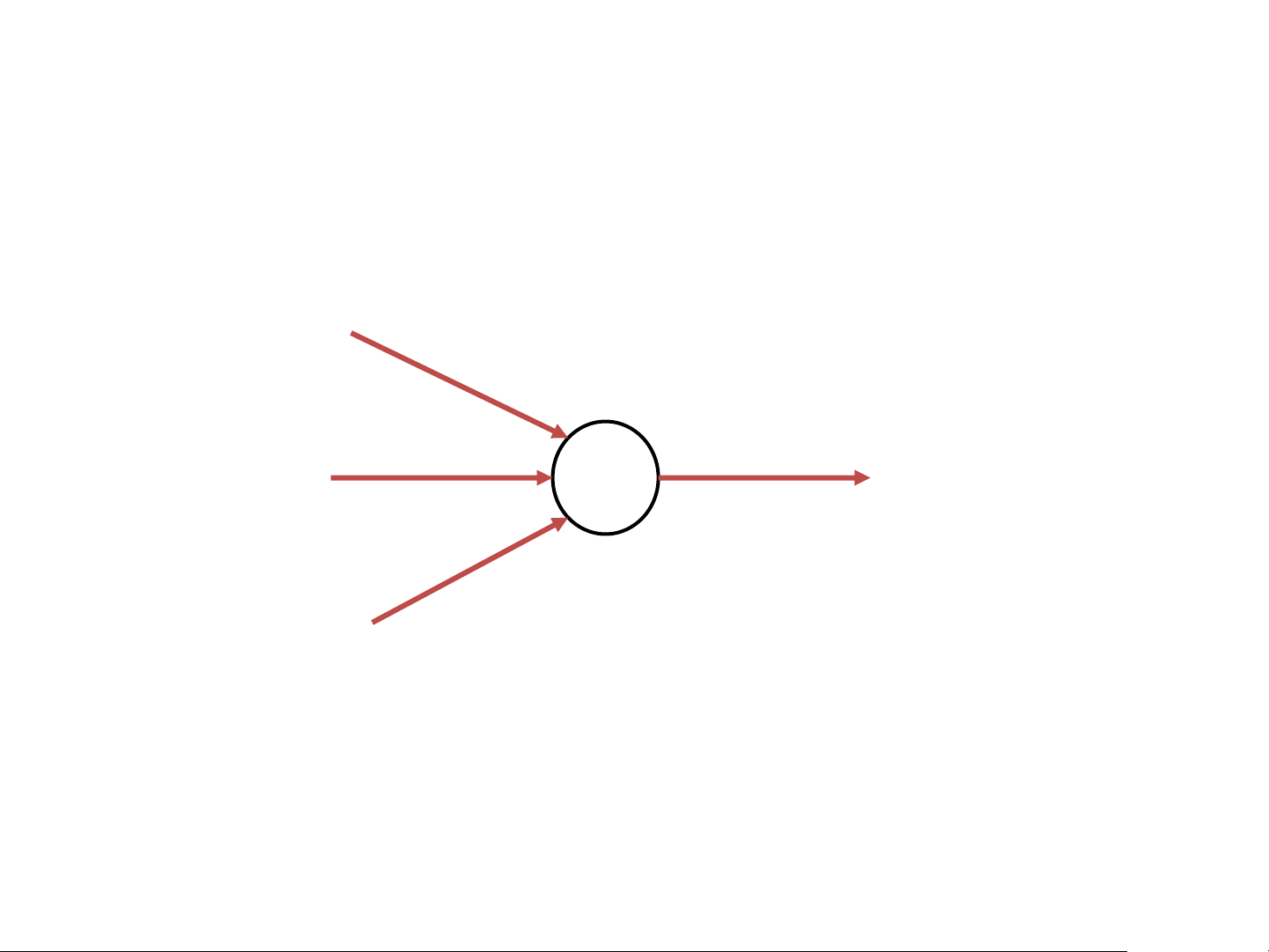
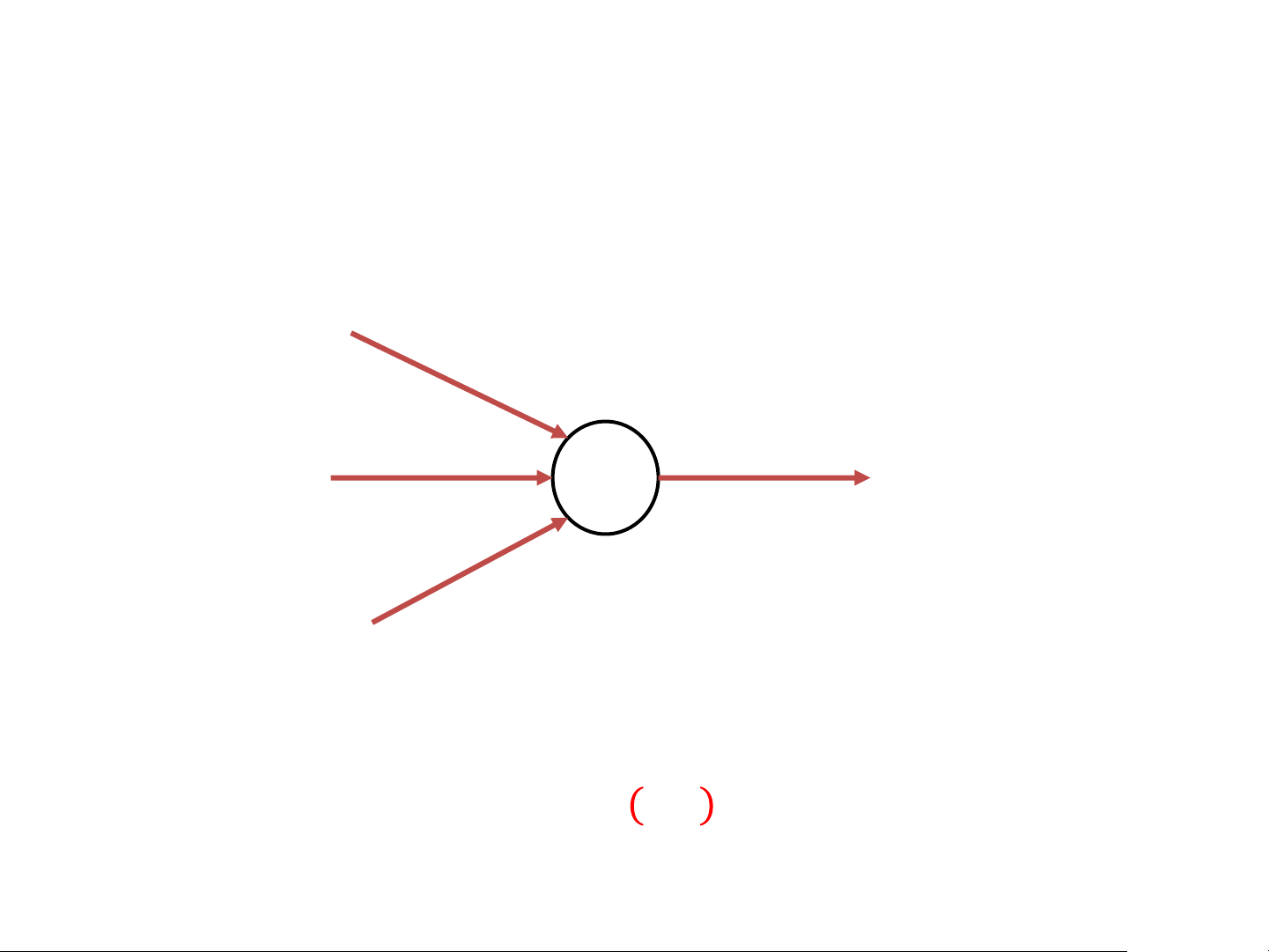
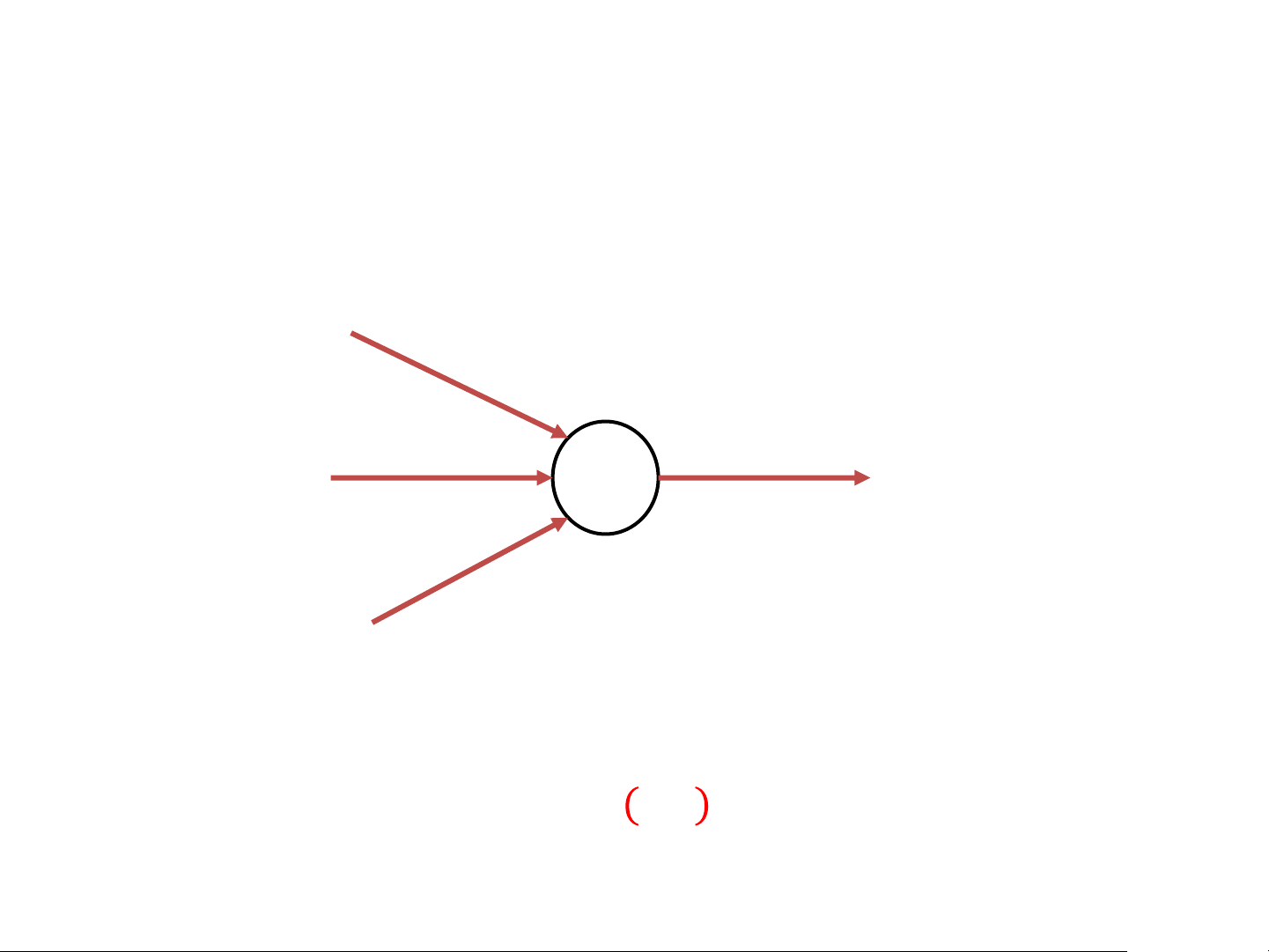
Takes several inputs and gives a single binary output (Decision) 𝑥1 𝜔1 𝜔2 Input 𝑥2 b 𝑓 Output 𝜔3 𝑥3
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OFbnpY_k7js The Perceptron
Takes several inputs and gives a single binary output (Decision) 𝑥1 𝜔1 𝜔2 Input 𝑥2 b 𝑓 Output 𝜔3 𝑥3
0 𝑖𝑓 𝜔𝑗𝑥𝑗 ≤ −𝑏 𝑓 = 𝑗
1 𝑖𝑓 𝜔𝑗𝑥𝑗 > −𝑏 𝑗
𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒: 𝜔𝑗 = weights b = bias(threshold) The Perceptron
Takes several inputs and gives a single binary output (Decision) 𝑥1 𝜔1 𝜔2 Input 𝑥2 b 𝑓 Output 𝜔3 𝑥3 0 𝑖𝑓 𝜔 0 𝑖𝑓 𝜔 𝑗𝑥𝑗 + 𝑏 ≤ 0 𝑗𝑥𝑗 ≤ −𝑏 𝑗 𝑓 = 𝑗 𝑓 = 1 𝑖𝑓 𝜔 1 𝑖𝑓 𝜔 𝑗𝑥𝑗 + 𝑏 > 0 𝑗𝑥𝑗 > −𝑏 𝑗 𝑗
𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒: 𝜔𝑗 = weights b = bias(threshold)
Activation function of the Perceptron Let: z = 𝜔𝑇𝑥 + 𝑏 0 𝑖𝑓 𝑧 ≤ 0 Activation: 𝑎 = 𝑓 𝑥 = 1 𝑖𝑓 𝑧 > 0 Activation, a 1 z = 𝜔𝑇𝑥 + 𝑏 0
Activation Function for a Perceptron is a Step Function Perceptron: Example Will you go to the movies? Weather 𝑥1 𝜔1 𝜔2 Companion 𝑥2 b 𝑎 Activation 𝜔3 Proximity 𝑥3 𝑥1: Is the weather good?
𝑥2: Do you have a companion with you 𝑥3: Is the theater nearby? Perceptron: Example Will you go to the movies? Weather 𝑥1 4 2 Companion 𝑥2 -5 𝑎 Activation 2 Proximity 𝑥3
Assume that weather is the most important factor:
𝜔1 = 4, 𝜔2 = 2, 𝜔3 = 2
Go to the movies only if the weather is good and if one of the
other factor is favor: 𝑏 = −5 Perceptron: Example
Will you go to the movies? No Weather 0 4 2 Companion 1 -5 0 Activation 2 Proximity 1
0 ∙ 4 + 1 ∙ 2 + 1 ∙ 2 + −5 = −1 < 0 Perceptron: Example
Will you go to the movies? Yes Weather 1 4 2 Companion 1 -5 0 Activation 2 Proximity 0
1 ∙ 4 + 1 ∙ 2 + 0 ∙ 2 + −5 = 1 > 0
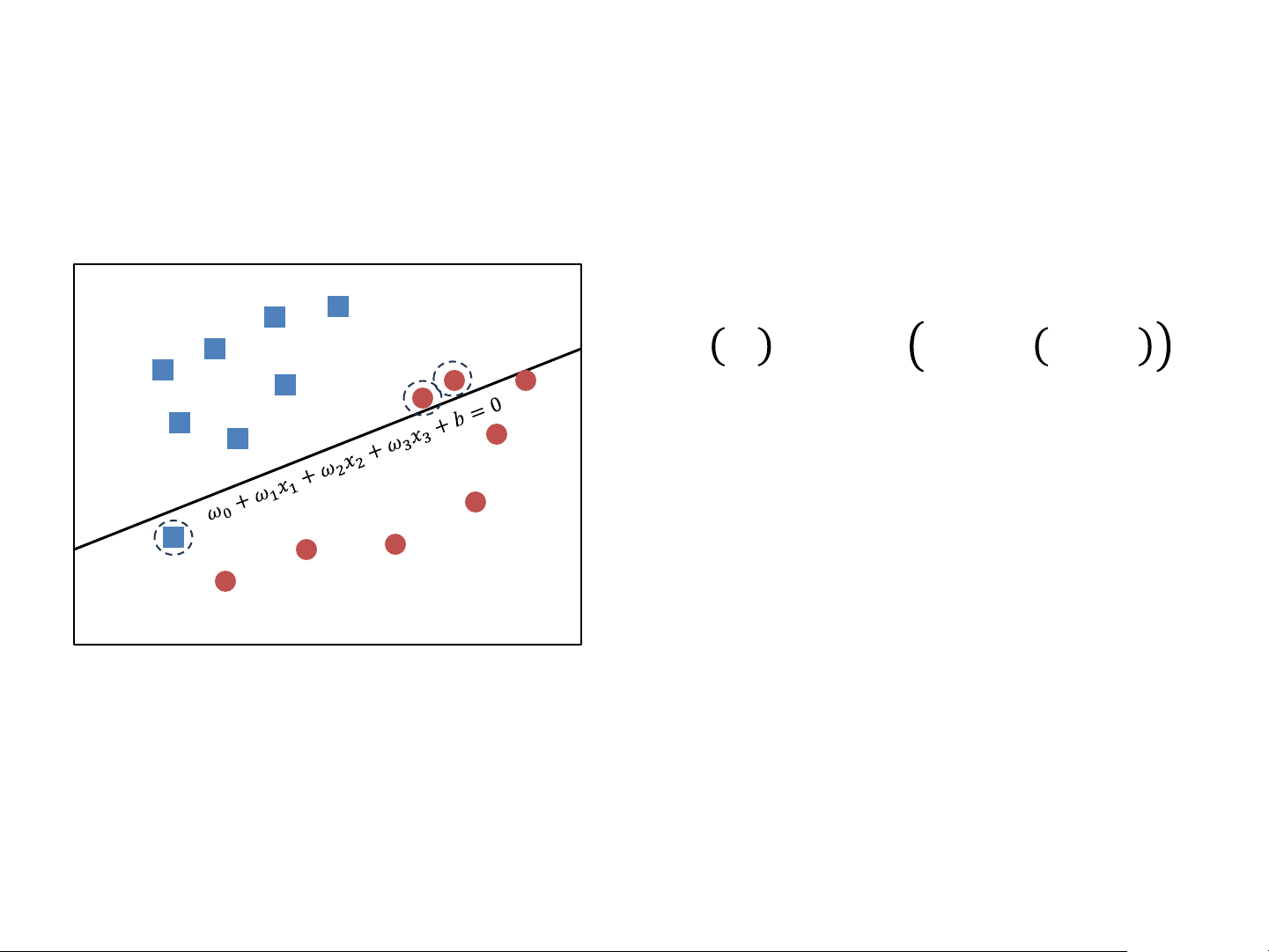
Perceptron as a Linear Classifier Will you go to the movies?
Weather (𝑥1) Companion (𝑥2) Proximity (𝑥1) Label y 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 … … … … Perceptron loss
Perceptron loss is based on the margin:
For a point 𝑥𝑖 , the loss becomes:
𝐿𝑖 𝜔 = max 0, −𝑦𝑖 𝜔𝑇𝑥𝑖 + - Perceptron loss
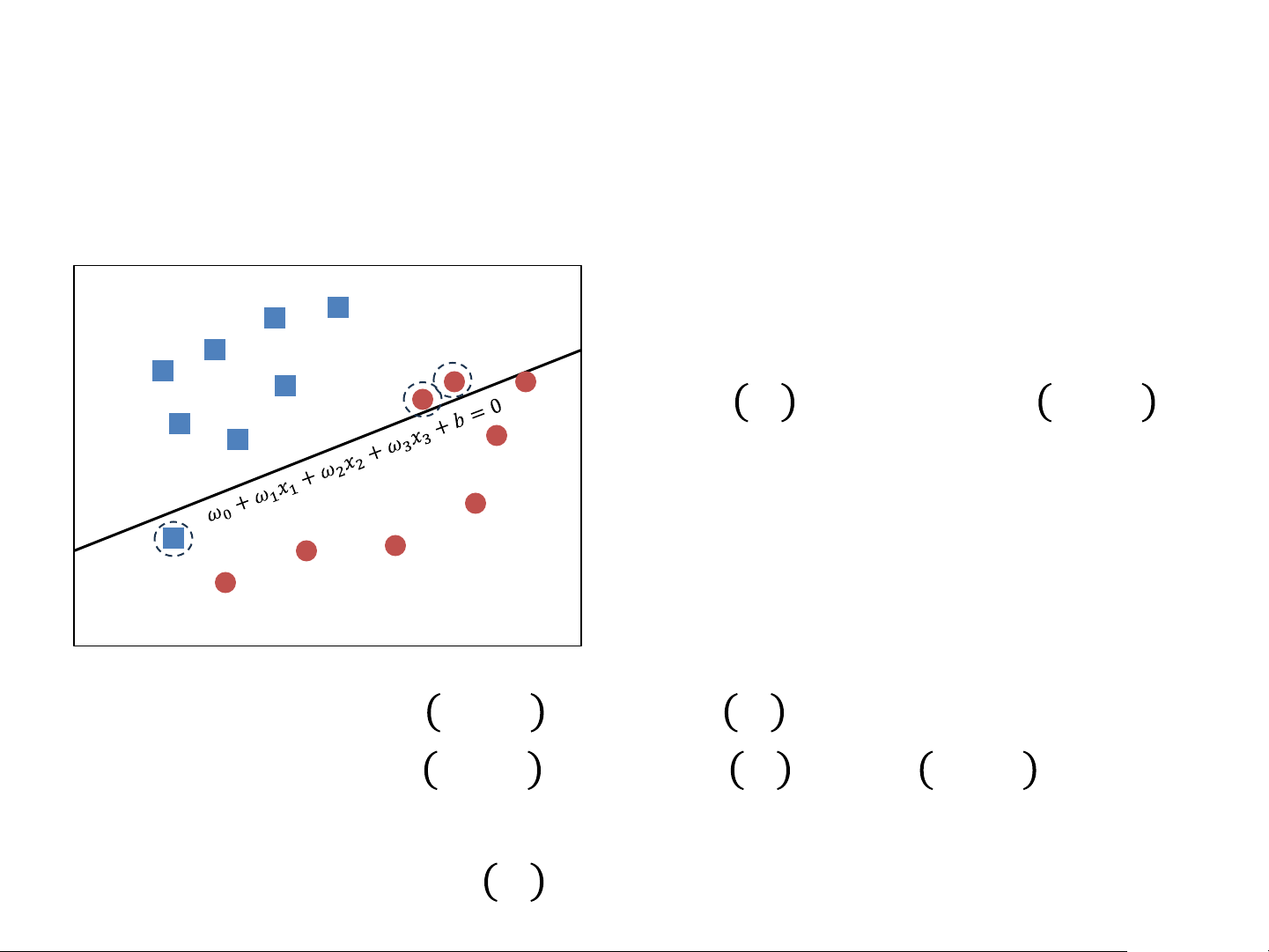
Perceptron loss is based on the margin:
For a misclassified point 𝑥𝑖 , the loss becomes:
𝐿𝑖 𝜔 = −𝑦𝑖 ∙ 𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛 𝜔𝑇𝑥𝑖 + - 𝑦
If ൝ 𝑖 ∙ 𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛 𝜔𝑇𝑥𝑖 > 0 → 𝐿𝑖 𝜔 = 0
𝑦𝑖 ∙ 𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛 𝜔𝑇𝑥𝑖 ≤ 0 → 𝐿𝑖 𝜔 = −𝑦𝑖 𝜔𝑇𝑥𝑖 > 0
Gradient: ∇𝜔𝐿𝑖 𝜔 = −𝑦𝑖 𝑥𝑖