
Preview text:
Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols
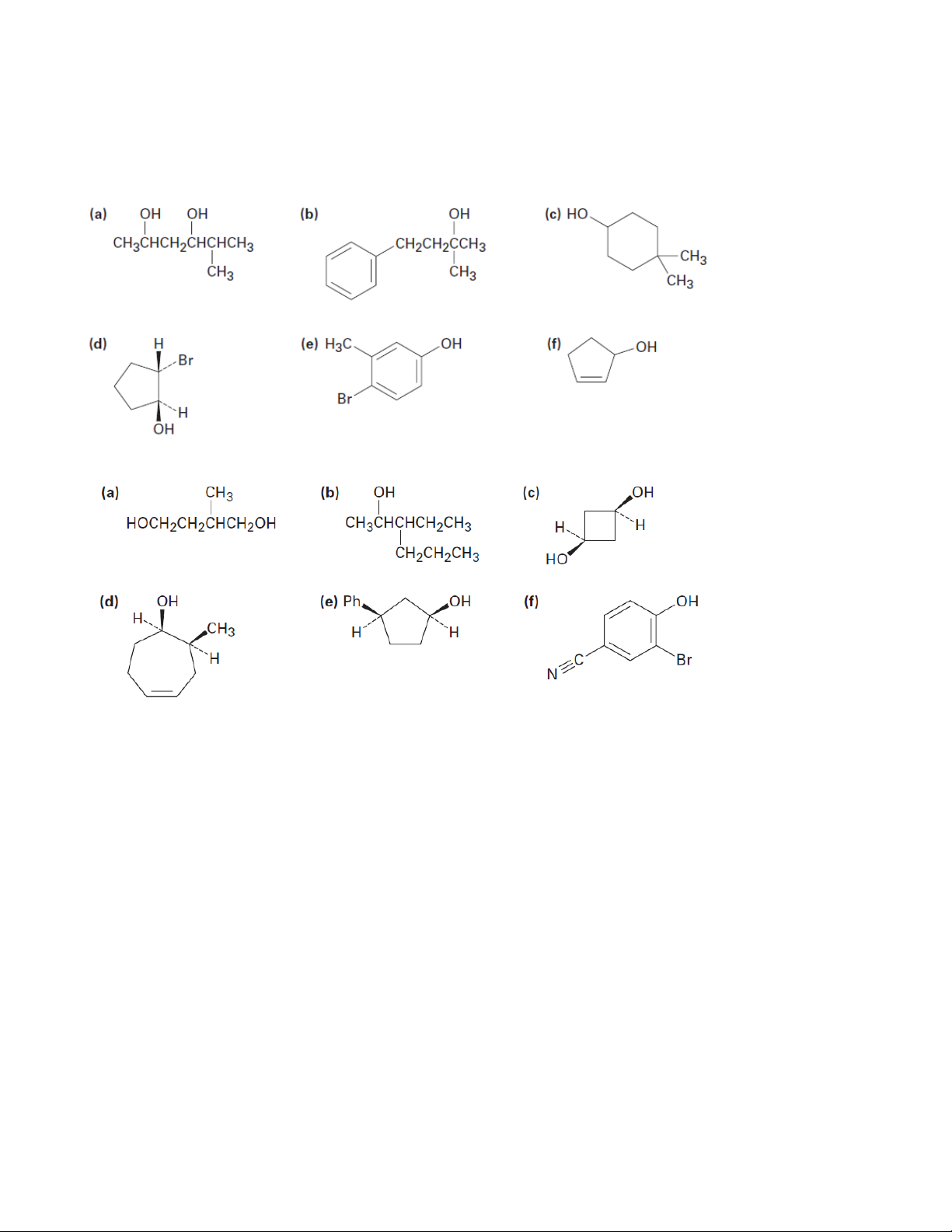
1. Give IUPAC names for the following compounds 1.1. 1.2.
2. Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names:
a) (Z)-2-Ethyl-2-buten-1-ol b) 3-Cyclohexen-1-ol
c) trans-3-Chlorocycloheptanol d) 1,4-Pentandiol e) 2,6-Dimethylphenol
f) o-(2-Hydroxyethyl)phenol
3. Explain the trend in boiling points of the following compounds:
1-Butanol (bp 117.5 °C), 2-butanol (bp 99.5 °C), 2-methyl-2-propanol (bp 82.2 °C)
4. Rank the following substances in order of increasing acidity:
a/ (CH3)2CHOH, HC≡CH, (CF3)2CHOH, CH3OH
b/ Phenol, p-methylphenol, p-trifluoromethylphenol
c/ Benzyl alcohol, phenol, p-hydroxybenzoic acid
d/ p-Nitrobenzyl alcohol, benzyl alcohol, p-methoxybenzyl alcohol
e/ p-CH3O-C6H4-OH, C6H5-OH, p-F-C6H4-OH, p-NC-C6H4-OH 1 Organic Chemistry 2
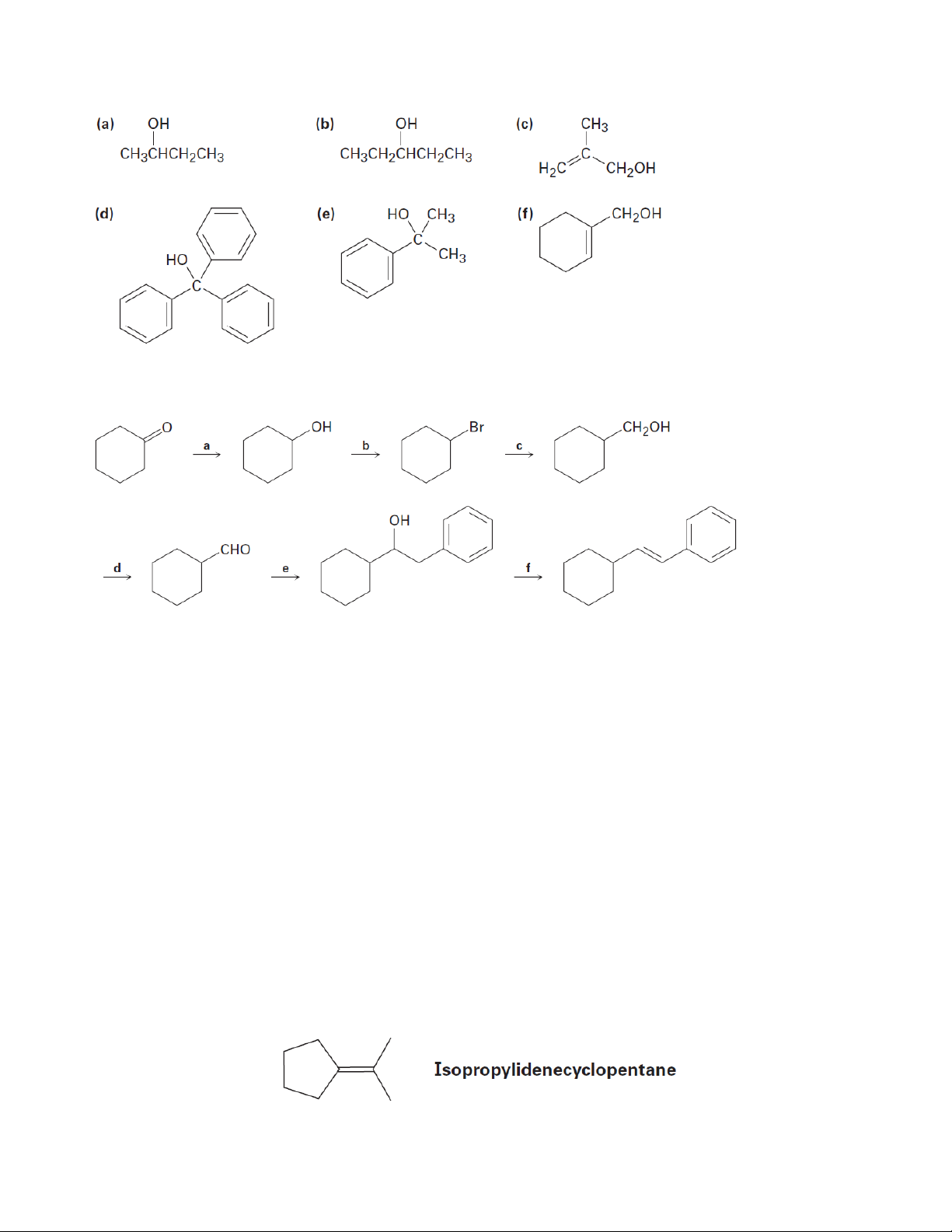
5. Prepare the following alcohols using Grignard reagents
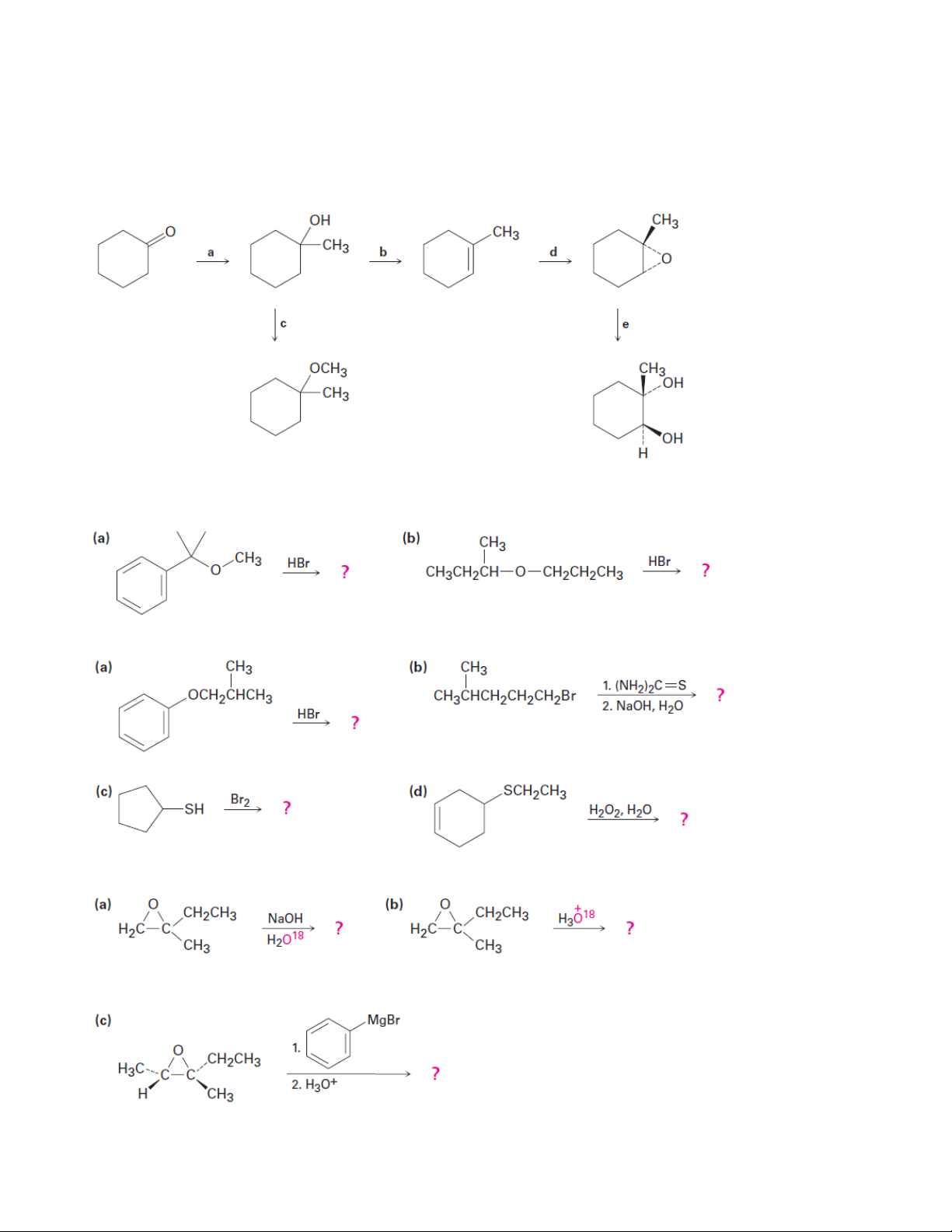
6. Identify the reagents a–f in the following scheme:
7. Prepare the following compounds from 2-phenylethanol (a) Styrene (PhCH=CH2)
(b) Phenylacetaldehyde (PhCH2CHO)
(c) Phenylacetic acid (PhCH2CO2H) (d) Benzoic acid (e) Ethylbenzene (f) Benzaldehyde (g) 1-Phenylethanol (h) 1-Bromo-2-phenylethane (i) PhCOCH3 (j) PhCH2OH (k) 2-Phenyl-2-propanol
8. Prepare the following substances from cyclopentanol (a) Cyclopentanone (b) Cyclopentene (c) 1-Methylcyclopentanol
(d) trans-2-Methylcyclopentanol
9. Acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2,2-dimethylcyclohexanol yields a mixture of 1,2-
dimethylcyclohexene and isopropylidenecyclopentane. Propose a mechanism to account for the
formation of both products. 2 Organic Chemistry 2
Chapter 18: Ethers and Epoxides; Thiols and Sulfides
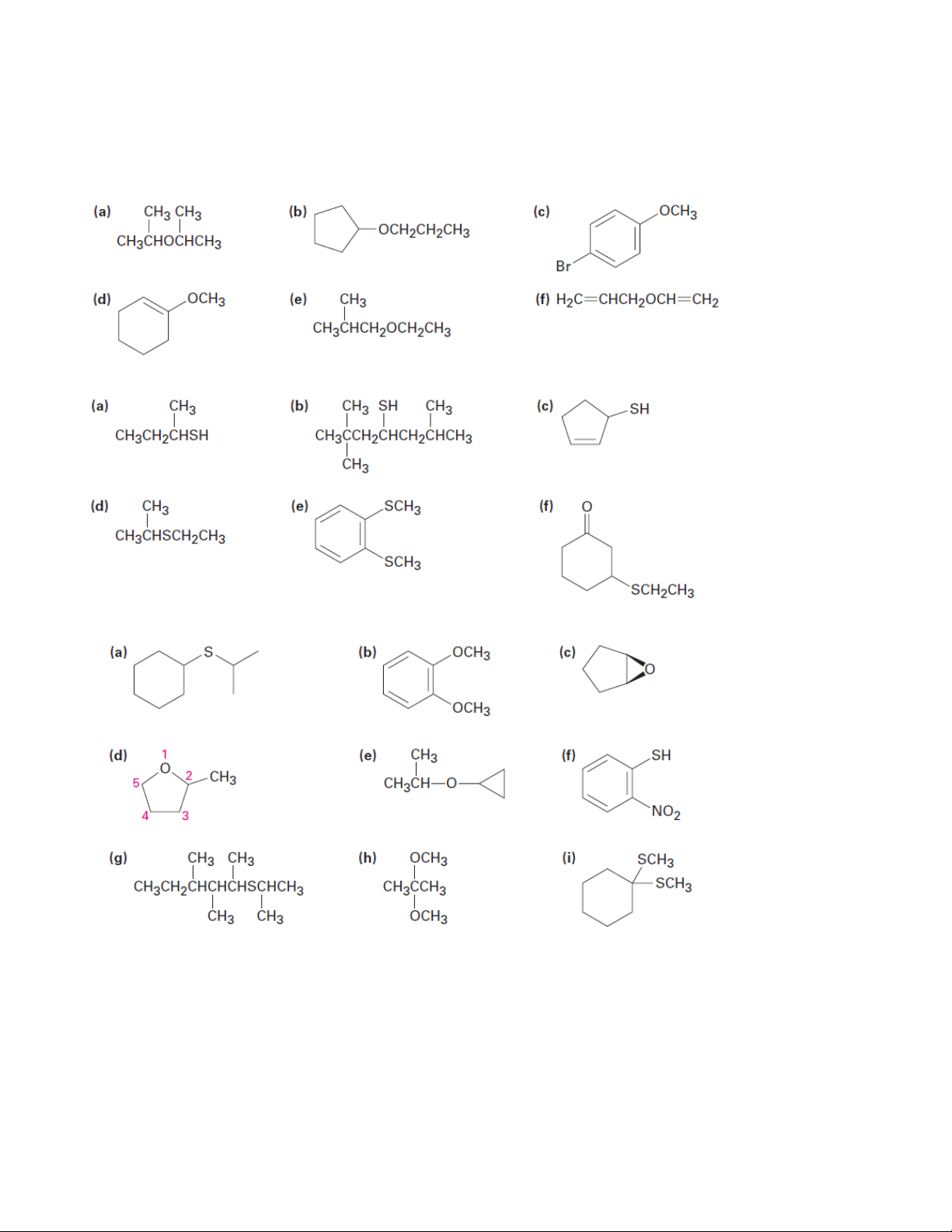
1. Give IUPAC names for the following compounds 1.1. 1.2. 1.3.
2. Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names: (a) Ethyl 1-ethylpropyl ether
(b) Di(p-chlorophenyl) ether (c) 3,4-Dimethoxybenzoic acid (d) Cyclopentyloxycyclohexane
(e) 4-Allyl-2-methoxyphenol (eugenol; from oil of cloves) 3 Organic Chemistry 2
3. How would you prepare the following ethers using a Williamson synthesis? (a) Methyl propyl ether
(b) Anisole (methyl phenyl ether) (c) Benzyl isopropyl ether
(d) Ethyl 2,2-dimethylpropyl ether
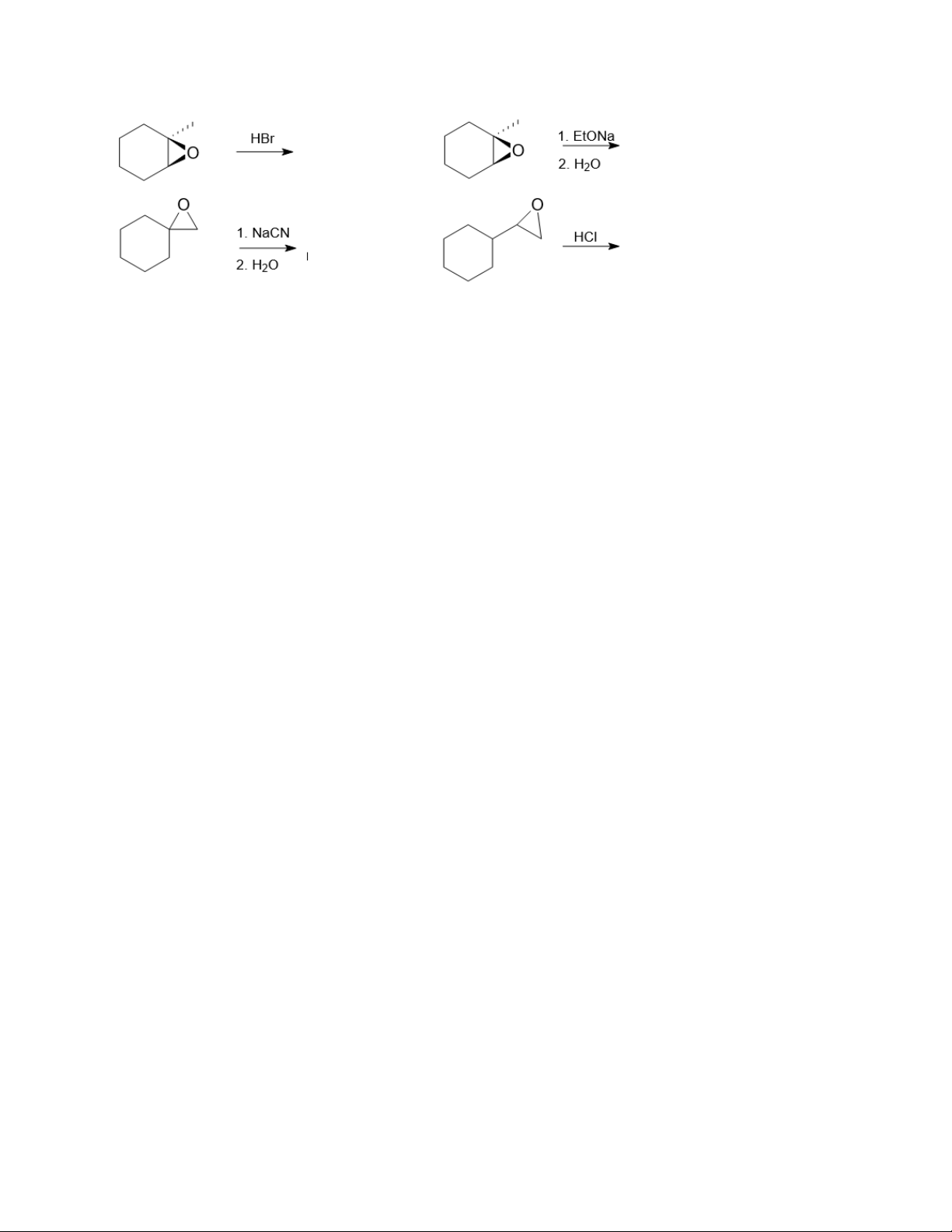
4. Identify the reagents a–e in the following scheme:
5. Predict the products of the following reactions: 5.1. 5.2. 5.3. 4 Organic Chemistry 2 5.4.
6. Prepare the following compounds from 1-phenylethanol:
(a) Methyl 1-phenylethyl ether (b) Phenylepoxyethane
(c) tert-Butyl 1-phenylethyl ether (d) 1-Phenylethanethiol 5 Organic Chemistry 2
Chapter 19: Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
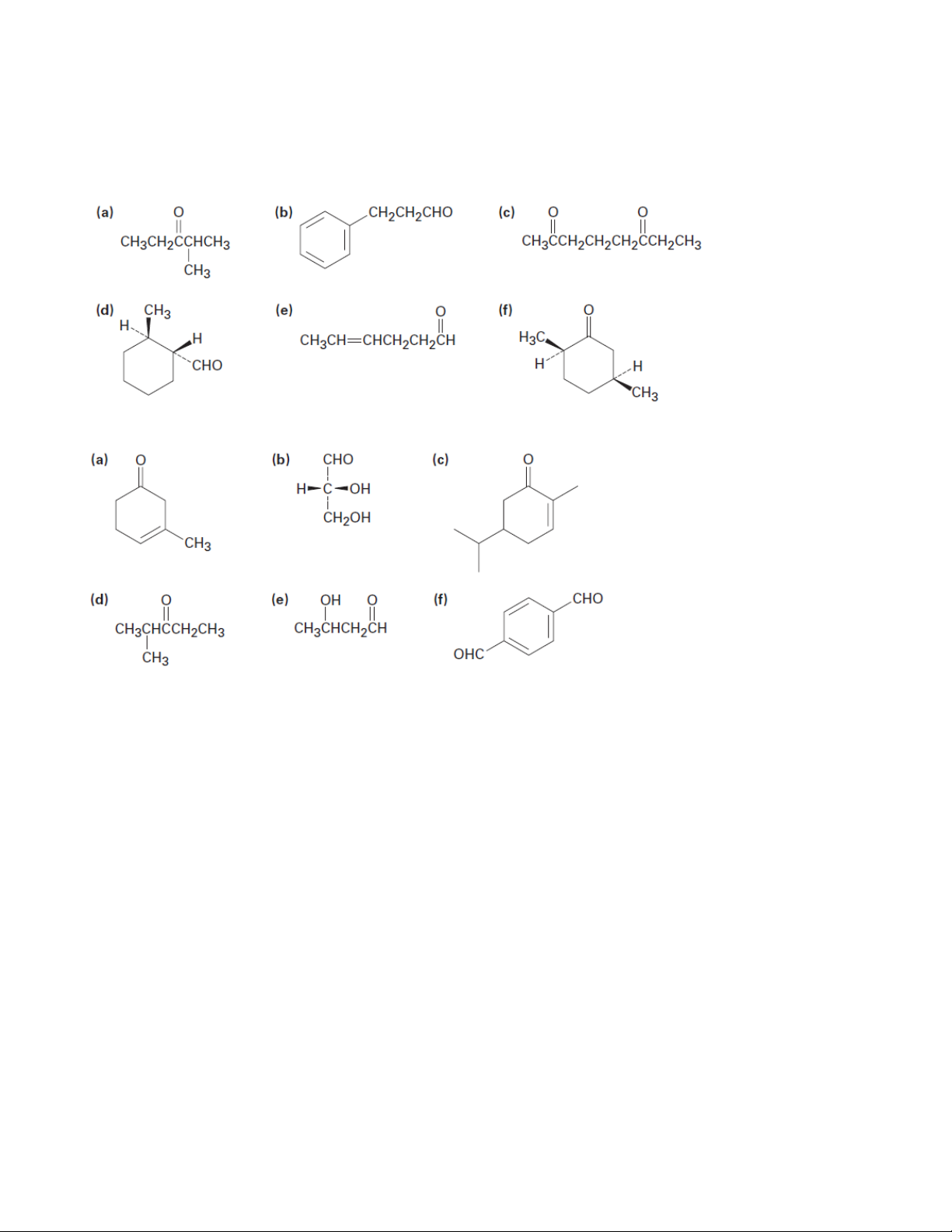
1. Give IUPAC names for the following compounds 1.1. 1.2.
2. Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names: (a) 4-Chloro-2-pentanone (b) Phenylacetaldehyde
(c) cis-3-tert-Butylcyclohexanecarbaldehyde (d) 3-Methyl-3-butenal
(e) 2-(1-Chloroethyl)-5-methylheptanal
(f) (S)-2-Hydroxypropanal
(g) (2S,3R)-2,3,4-Trihydroxybutanal (h) Butanedial
(i) 6,6-Dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone (j) p-Nitroacetophenone
Propanone: Phân cực có thể trải qua tương tác lưỡng cực-lưỡng
cực. Các lực này mạnh hơn lực van der Waals
3. Explain the trend in boiling points of the following compounds:
Propan-2-ol (bp 87 °C), Propanone (bp 57 °C), 2-methylpropene (bp -7 °C) Không phân c
Lực liên kết hydrogen mạnh ực, lực van der Waals yếu
4. Use a Grignard reaction on an aldehyde or ketone to synthesize the following compounds (a) 2-Pentanol (b) 1-Butanol (c) 1-Phenylcyclohexanol (d) Diphenylmethanol
5. Use lithium diorganocopper reagents (Gilman reagents) to synthesize the following compounds 6 Organic Chemistry 2
6. What carbonyl compound and what phosphorus ylide might you use to prepare each of the following compounds?
7. Each of the following reaction schemes contains one or more flaws. What is wrong in each case?
How would you correct each scheme?
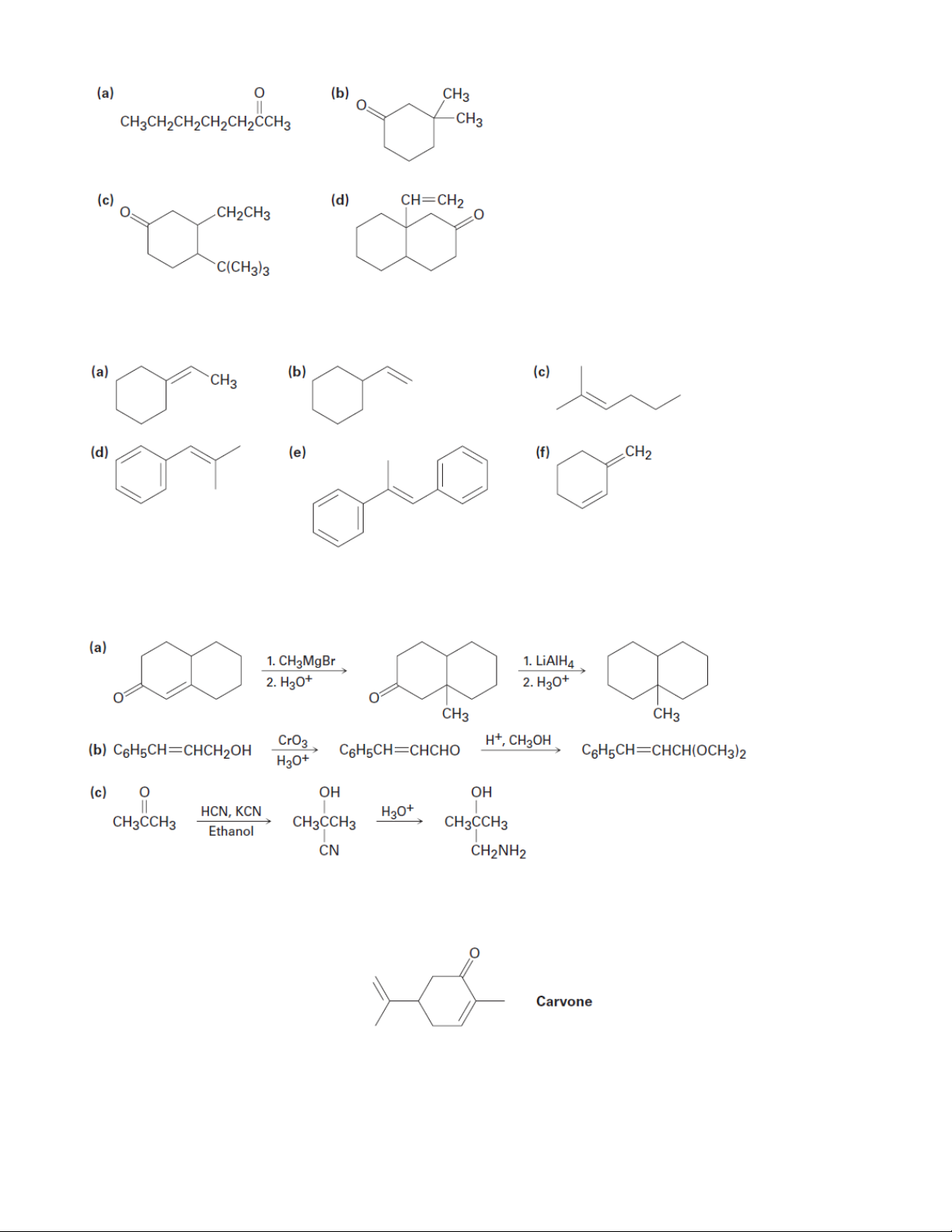
8. Carvone is the major constituent of spearmint oil. What products would you expect from
reaction of carvone with the following reagents? (a) (CH3)2CuLi, then H3O+ (b) LiAlH4, then H3O+ (c) CH3NH2 (d) C6H5MgBr, then H3O+ (e) H2/Pd (f) CrO3, H3O+ 7 Organic Chemistry 2 (g) (C6H5)3P=CHCH3 (h) HOCH2CH2OH, HCl
9. Prepare the following substances from 2-cyclohexenone. More than one step may be needed.
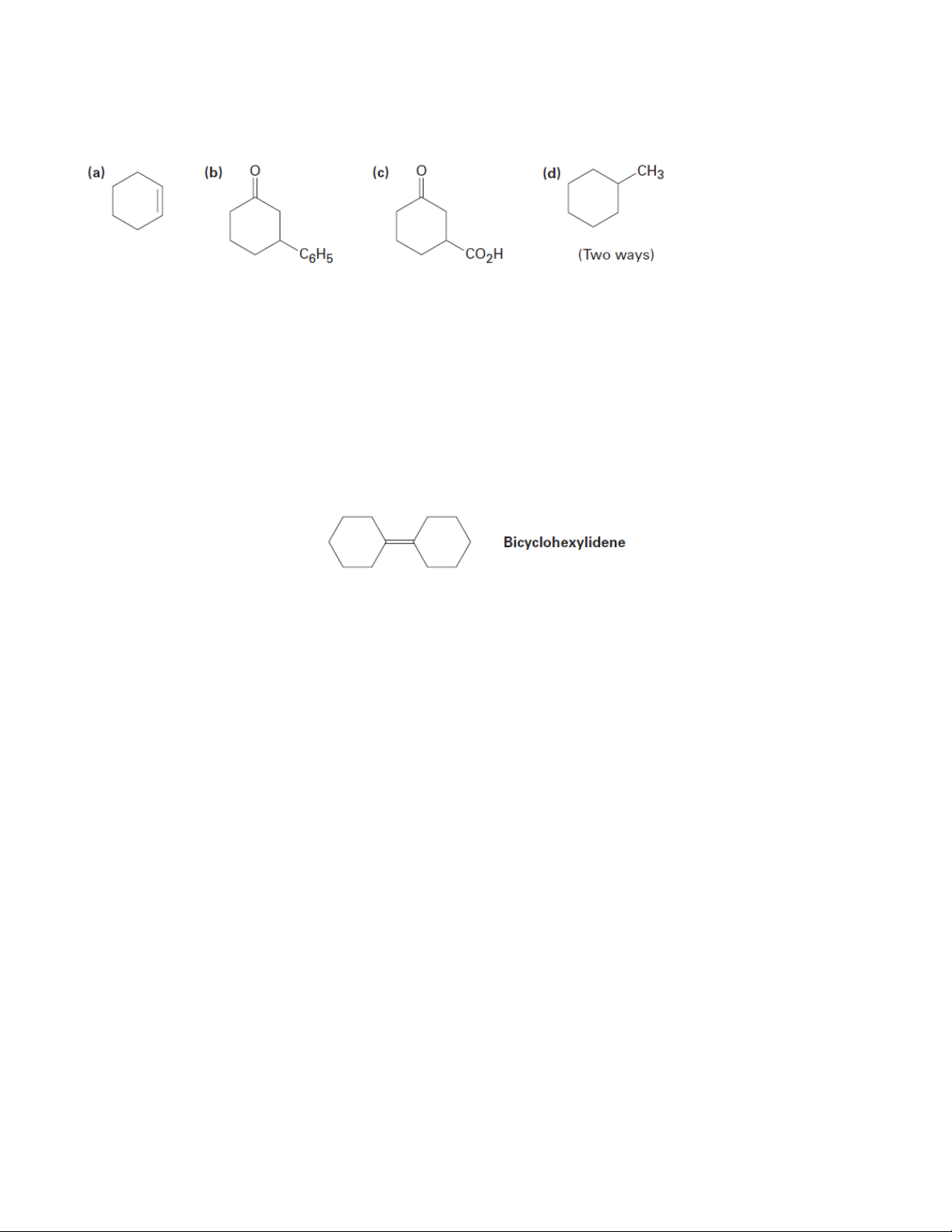
10. How would you synthesize the following compounds from cyclohexanone? (a) 1-Methylcyclohexene (b) 2-Phenylcyclohexanone
(c) cis-1,2-Cyclohexanediol (d) 1-Cyclohexylcyclohexanol
11. Propose a synthesis of PhCH2CHO from benzaldehyde.
12. Propose a synthesis of bicyclohexylidene, starting from cyclohexanone as the only source of carbon 8 Organic Chemistry 2
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
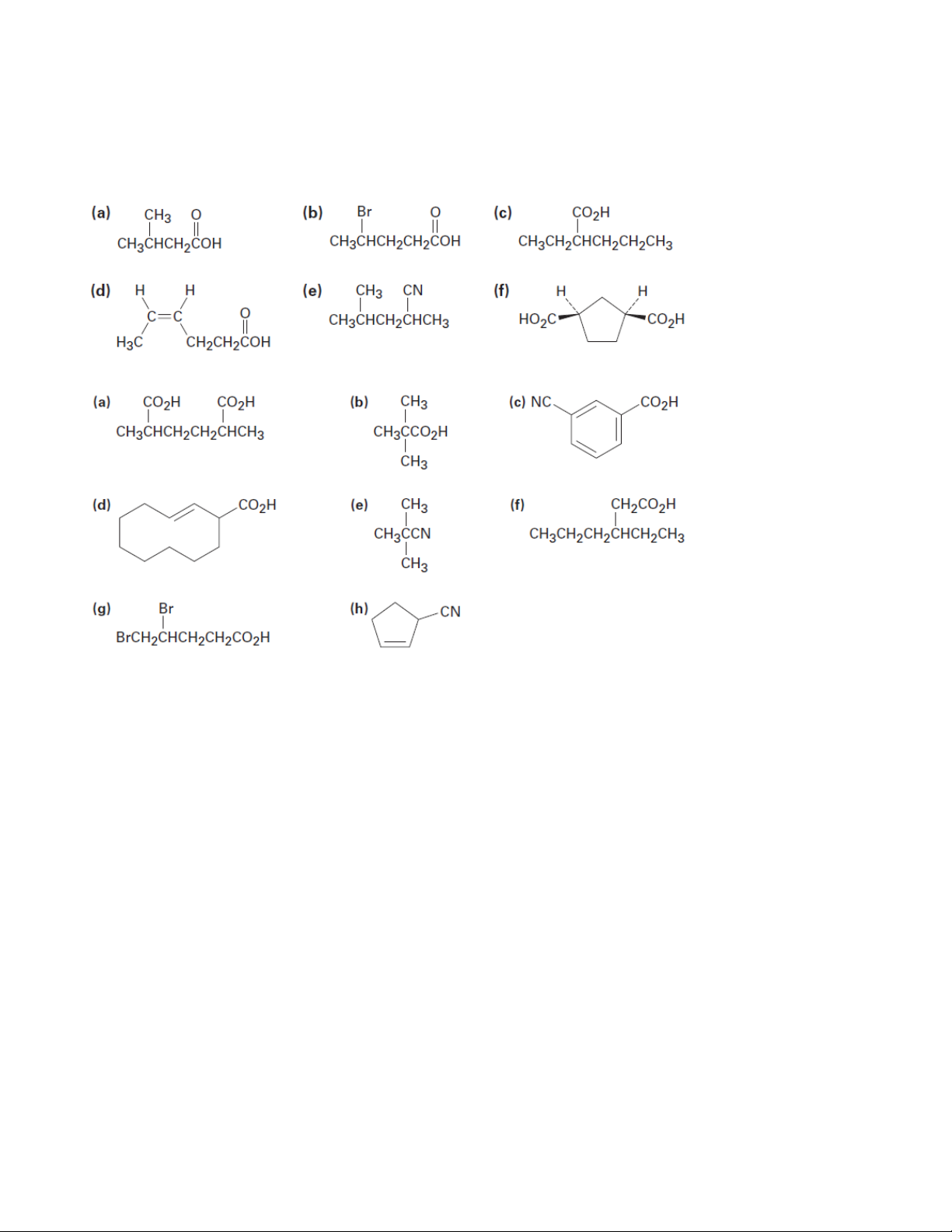
1. Give IUPAC names for the following compounds 1.1. 1.2.
2. Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names: (a) 2,3-Dimethylhexanoic acid
(b) trans-1,2-Cyclobutanedicarboxylic acid
(c) o-Hydroxybenzoic acid
(d) (9Z,12Z)-9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (e) 2-Pentenenitrile (f) 2-Hexen-4-ynoic acid
(g) (2R,3S)-3-carboxy-2-hydroxypentandioic acid (h) 2-Cyclobutenecarbonitrile
(i) m-Benzoylbenzonitrile (j) 3-Chlorophthalic acid
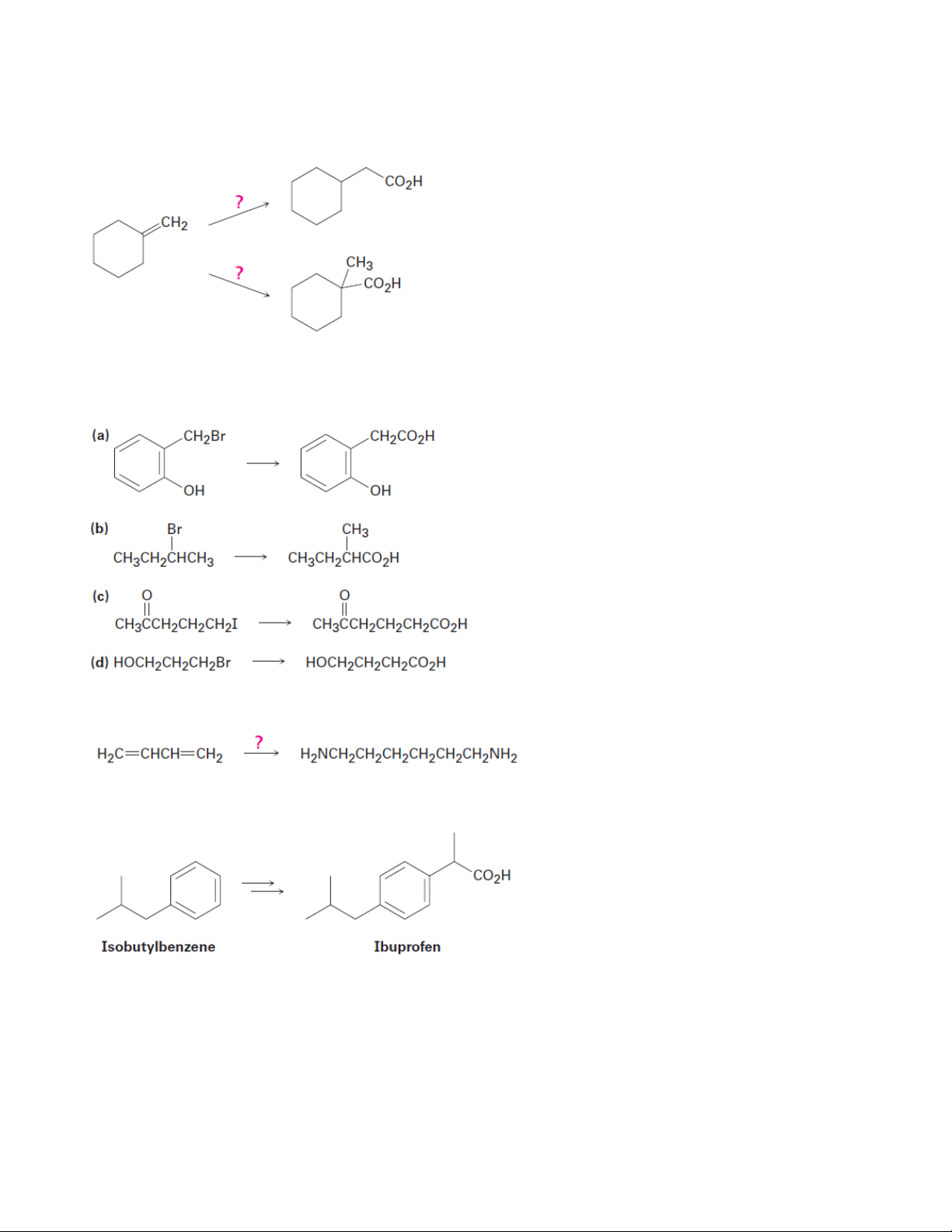
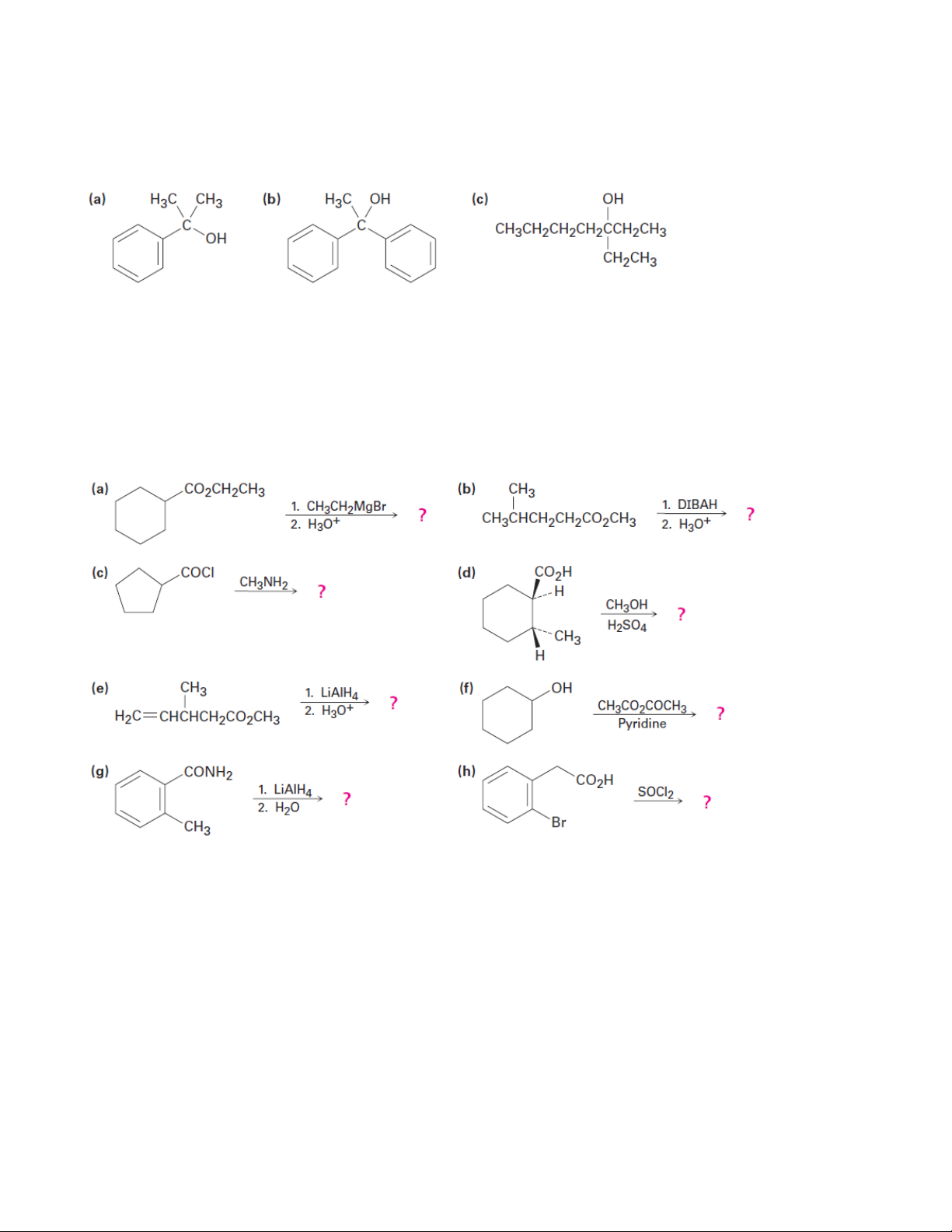
3. How could you convert butanoic acid into the following compounds? (a) 1-Butanol (b) 1-Bromobutane (c) Pentanoic acid (d) 1-Butene (e) Octane
4. How could you convert each of the following compounds into butanoic acid? (a) 1-Butanol (b) 1-Bromobutane (c) 1-Butene (d) 1-Bromopropane (e) 4-Octene
5. How would you prepare the following compounds from benzene? 9 Organic Chemistry 2
(a) m-Chlorobenzoic acid
(b) p-Bromobenzoic acid
(c) Phenylacetic acid, C6H5CH2CO2H
6. How would you carry out the following transformations?
7. Which method—Grignard carboxylation or nitrile hydrolysis—would you use for each of the following reactions?
8. Prepare 1,6-Hexanediamine from 1,3-butadiene
9. Show how you might prepare the anti-inflammatory agent ibuprofen from isobutylbenzene.
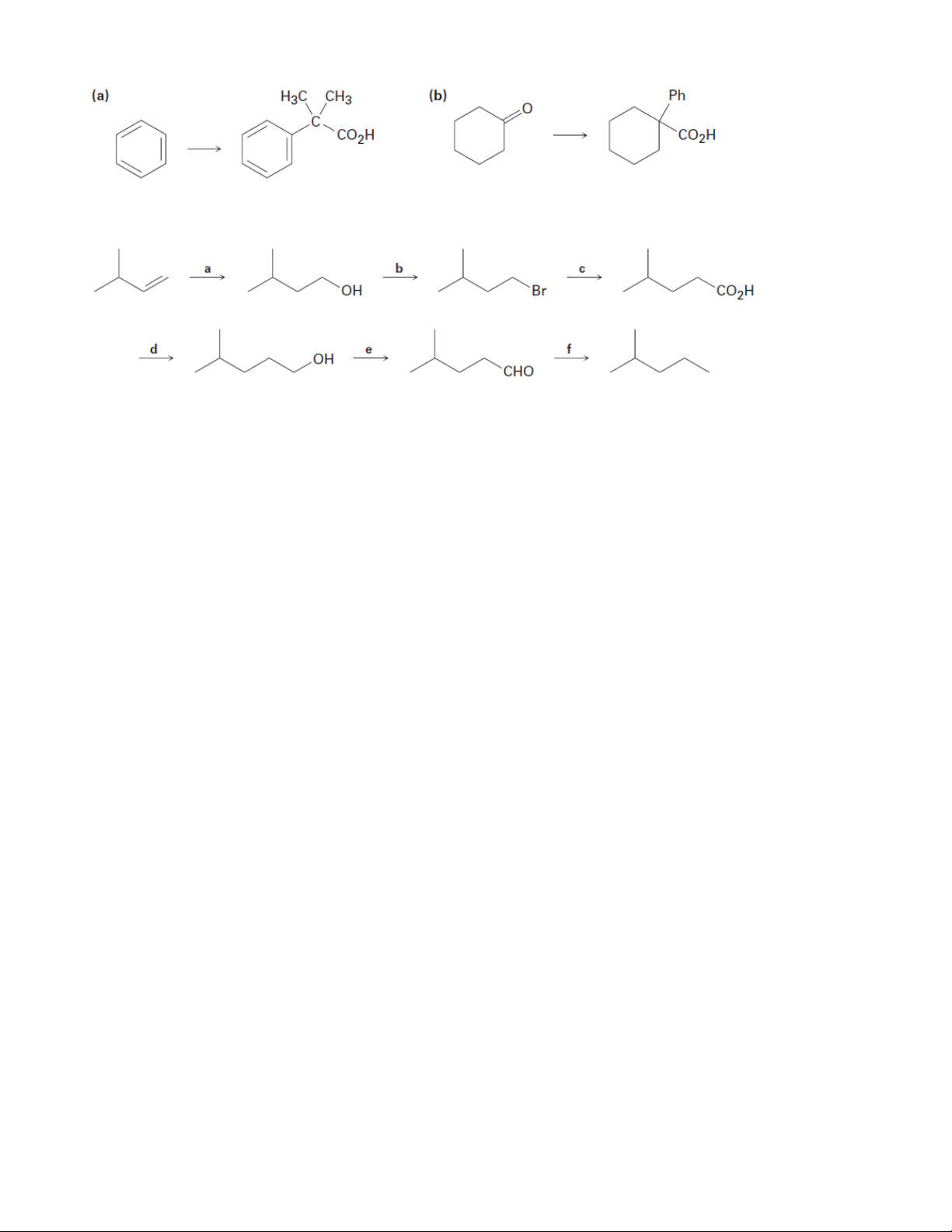
10. How would you carry out the following transformations? More than one step is needed. 10 Organic Chemistry 2
11. Identify the missing reagents a–f in the following scheme: 11 Organic Chemistry 2
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
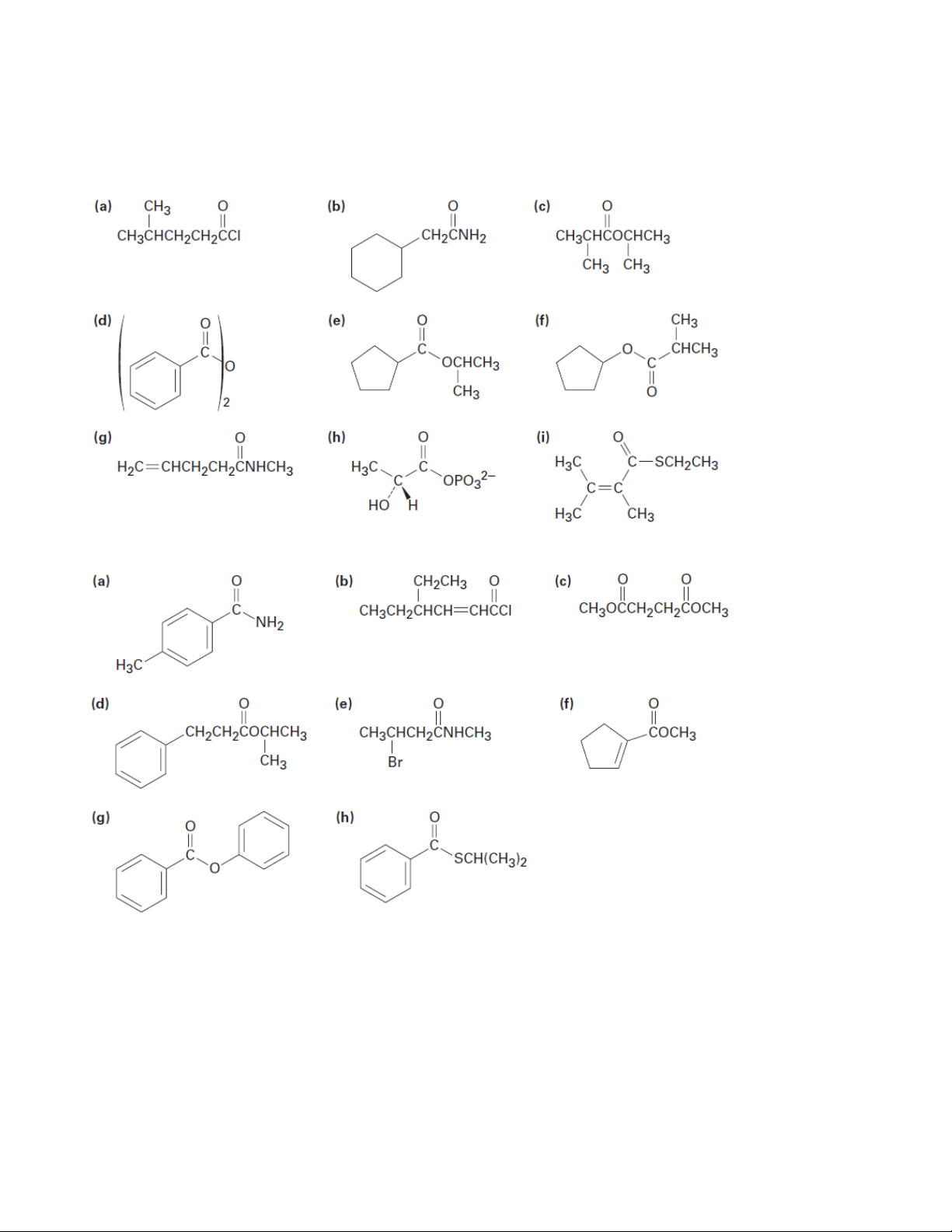
1. Give IUPAC names for the following compounds 1.1. 1.2.
2. Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names: (a) Phenyl benzoate
(b) N-Ethyl-N-methylbutanamide
(c) 2,4-Dimethylpentanoyl chloride
(d) Methyl 1-methylcyclohexanecarboxylate (e) Ethyl 3-oxopentanoate
(f) Methyl p-bromobenzenethioate
(g) Formic propanoic anhydride
(h) cis-2-Methylcyclopentanecarbonyl bromide
(i) p-Bromophenylacetamide (j) m-Benzoylbenzamide 12 Organic Chemistry 2 (k) 2,2-Dimethylhexanamide
(l) Cyclohexyl cyclohexanecarboxylate
(m) Ethyl 2-cyclobutenecarboxylate (n) Succinic anhydride
3. What ester and Grignard reagent might you start with to prepare the following alcohols?
4. How might you prepare the following compounds from butanoic acid? (a) 1-Butanol (b) Butanal (c) 1-Bromobutane (d) Pentanenitrile (e) 1-Butene (f) N-Methylpentanamide (g) 2-Hexanone (h) Butylbenzene (i) Butanenitrile
5. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions:
6. Predict the product, if any, of reaction between propanoyl chloride and the following reagents: (a) Li(Ph)2Cu in ether (b) LiAlH4, then H3O+ (c) CH3MgBr, then H3O+ (d) H3O+ (e) Cyclohexanol (f) Aniline (g) CH3CO2Na
7. Answer Problem 6 for reaction of the listed reagents with methyl propanoate.
8. Answer Problem 6 for reaction of the listed reagents with propanamide. 13 Organic Chemistry 2
9. Prepare acetophenone (phenyl methyl ketone) starting from the following: (a) Benzene (b) Bromobenzene (c) Methyl benzoate (d) Benzonitrile (e) Styrene
10. N,N-Diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET) is the active ingredient in many insect-repellent
preparations. How might you synthesize this substance from m-bromotoluene? 14 Organic Chemistry 2
Chapter 22: Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
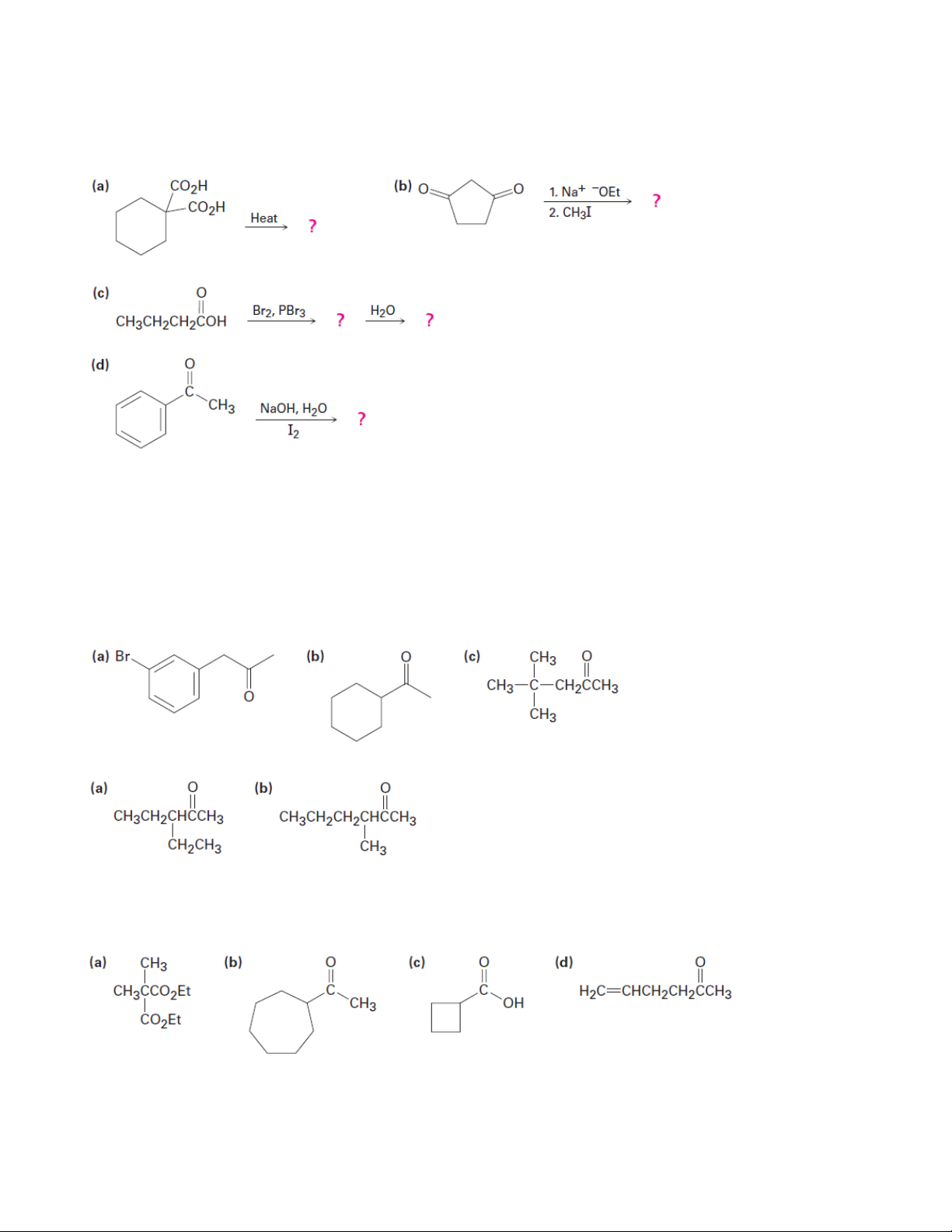
1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions:
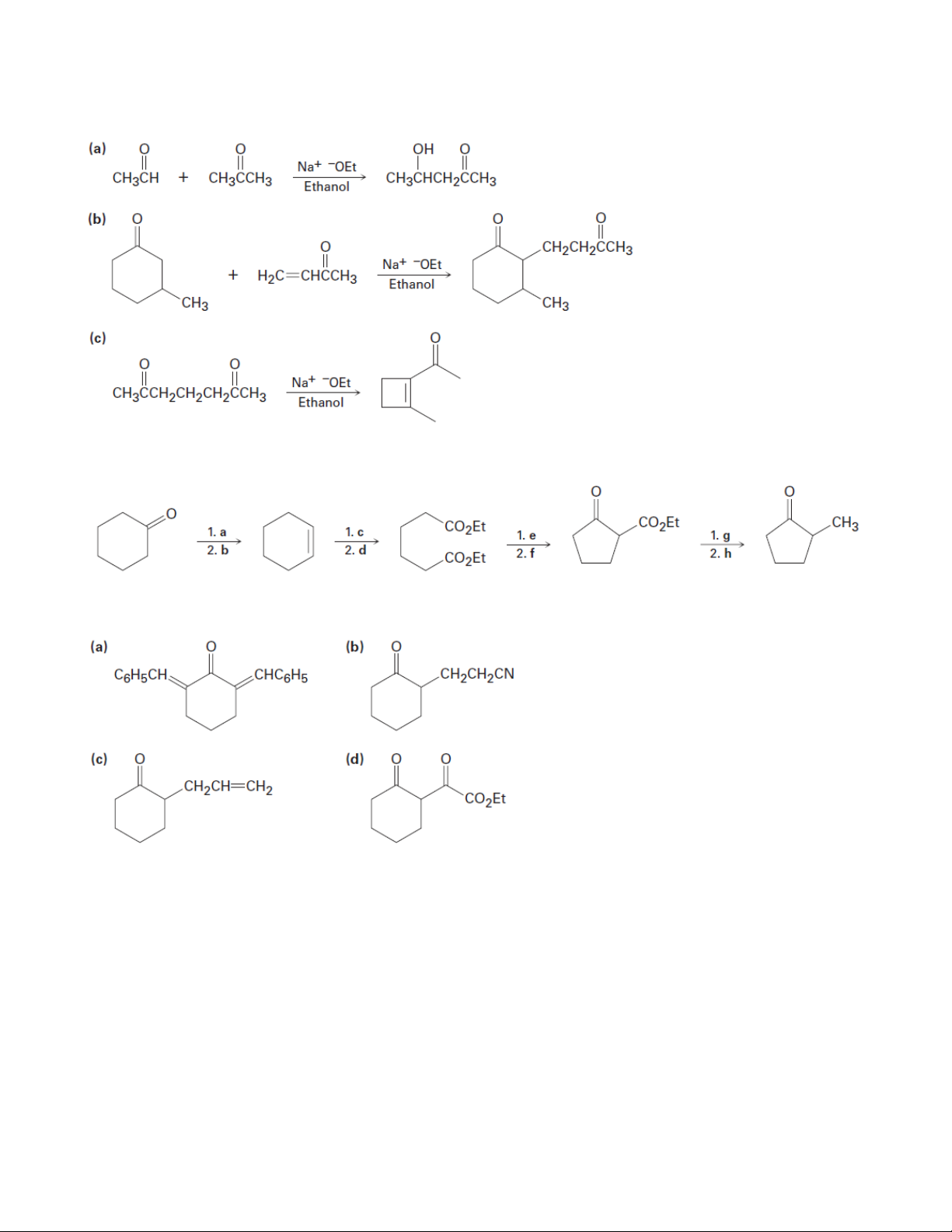
2. Prepare the following compounds using a malonic ester synthesis (a) Ethyl pentanoate (b) Ethyl 3-methylbutanoate (c) Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate
(d) Ethyl 2,2-dimethylpropanoate
3. Prepare the following ketones using an acetoacetic ester synthesis 3.1. 3.2.
4. prepare the following compounds using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or a malonic ester synthesis
5. Fill in the reagents a–c that are missing from the following scheme: 15 Organic Chemistry 2
6. Synthesize the following compounds from cyclohexanone
7. The following synthetic routes are incorrect. What is wrong with each?
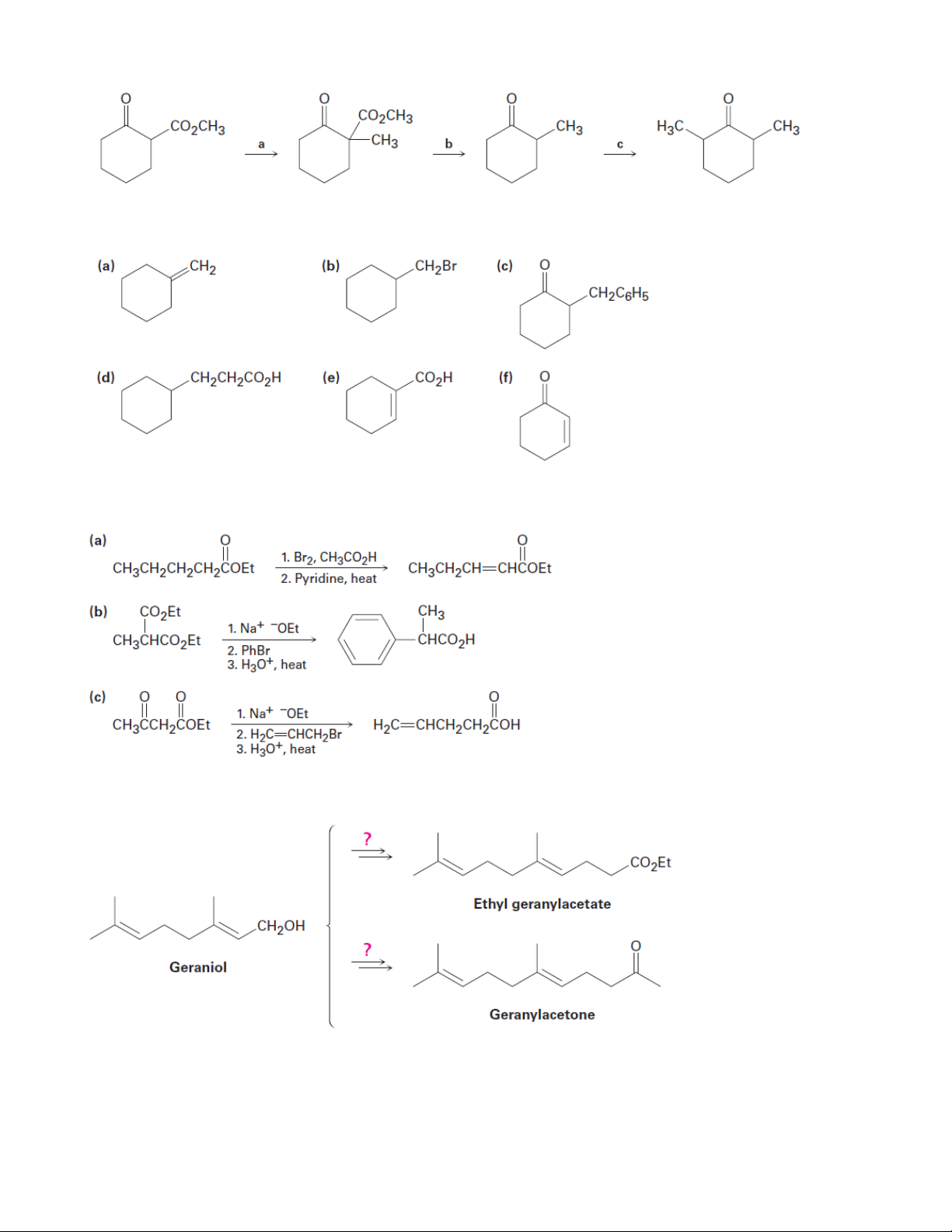
8. How might you convert geraniol into either ethyl geranylacetate or geranylacetone? 16 Organic Chemistry 2
Chapter 23: Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
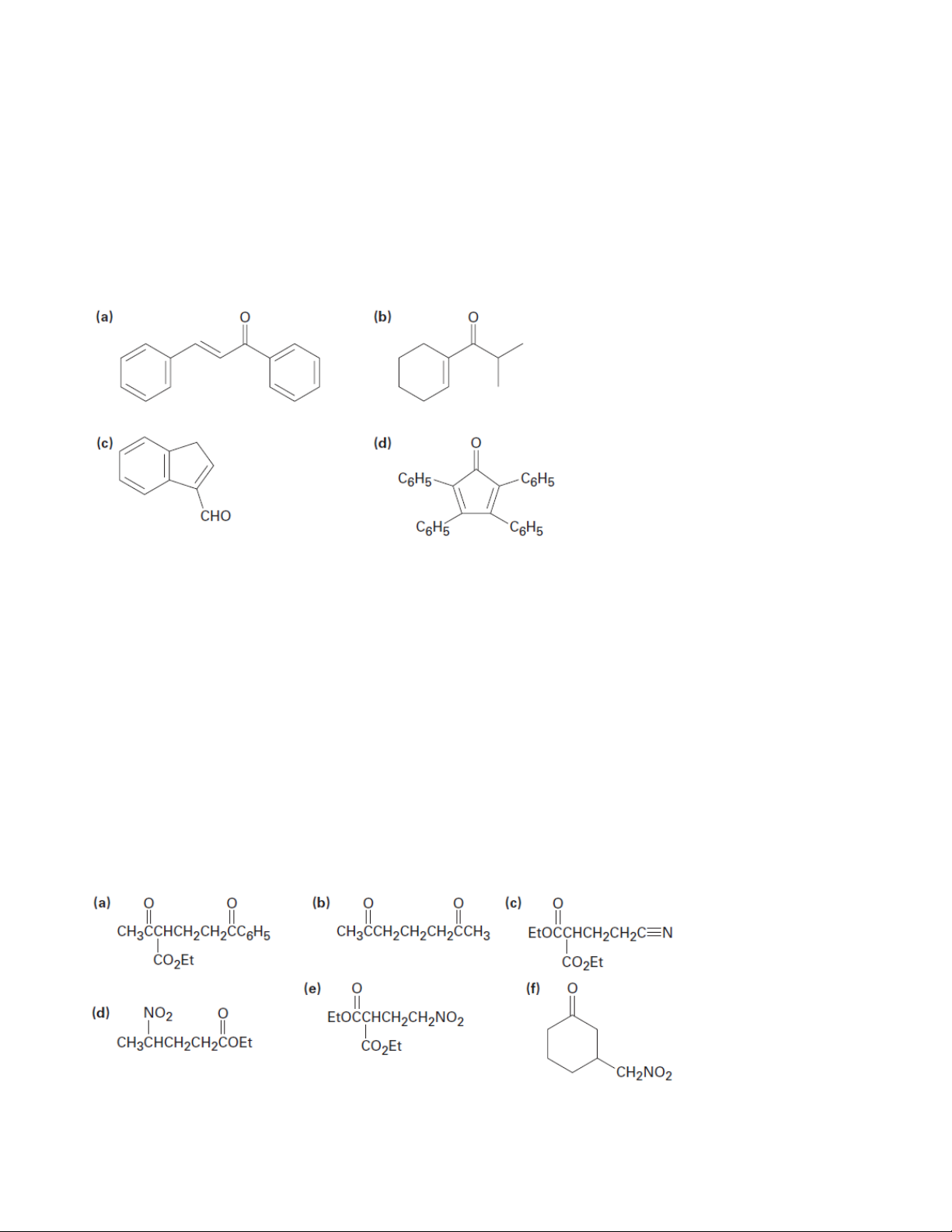
1. Which of the following compounds can undergo aldol self-condensation? Show the product. (a) Trimethylacetaldehyde (b) Cyclobutanone
(c) Benzophenone (diphenyl ketone) (d) 3-Pentanone (e) Decanal (f) 3-Phenyl-2-propenal
2. How might you synthesize each of the following compounds using an aldol reaction?
3. Intramolecular aldol cyclization of 2,5-heptanedione with aqueous NaOH yields a mixture of
two enone products in the approximate ratio 9:1.
a. Write their structures, and show how each is formed.
b. The major product has two singlet absorptions in the 1H NMR spectrum, at 1.65 ppm and 1.90
ppm, and has no absorptions in the range 3 to 10 ppm. What is its structure?
4. Give the structures of the possible Claisen condensation products from the following reactions.
Tell which, if any, you would expect to be the major product. (a) CH3CO2Et + CH3CH2CO2Et (b) C6H5CO2Et + C6H5CH2CO2Et (c) EtOCO2Et + cyclohexanone (d) C6H5CHO + CH3CO2Et
5. How might the following compounds be prepared using Michael reactions? Show the reactions. 17 Organic Chemistry 2
6. The following reactions are unlikely to provide the indicated product in high yield. What is wrong with each?
7. Fill in the missing reagents a–h in the following scheme:
8. How would you prepare the following compounds from cyclohexanone? 18 Organic Chemistry 2
Chapter 24: Amines and Heterocycles
1. Give IUPAC names for the following compounds 1.1. 1.2. 1.3.
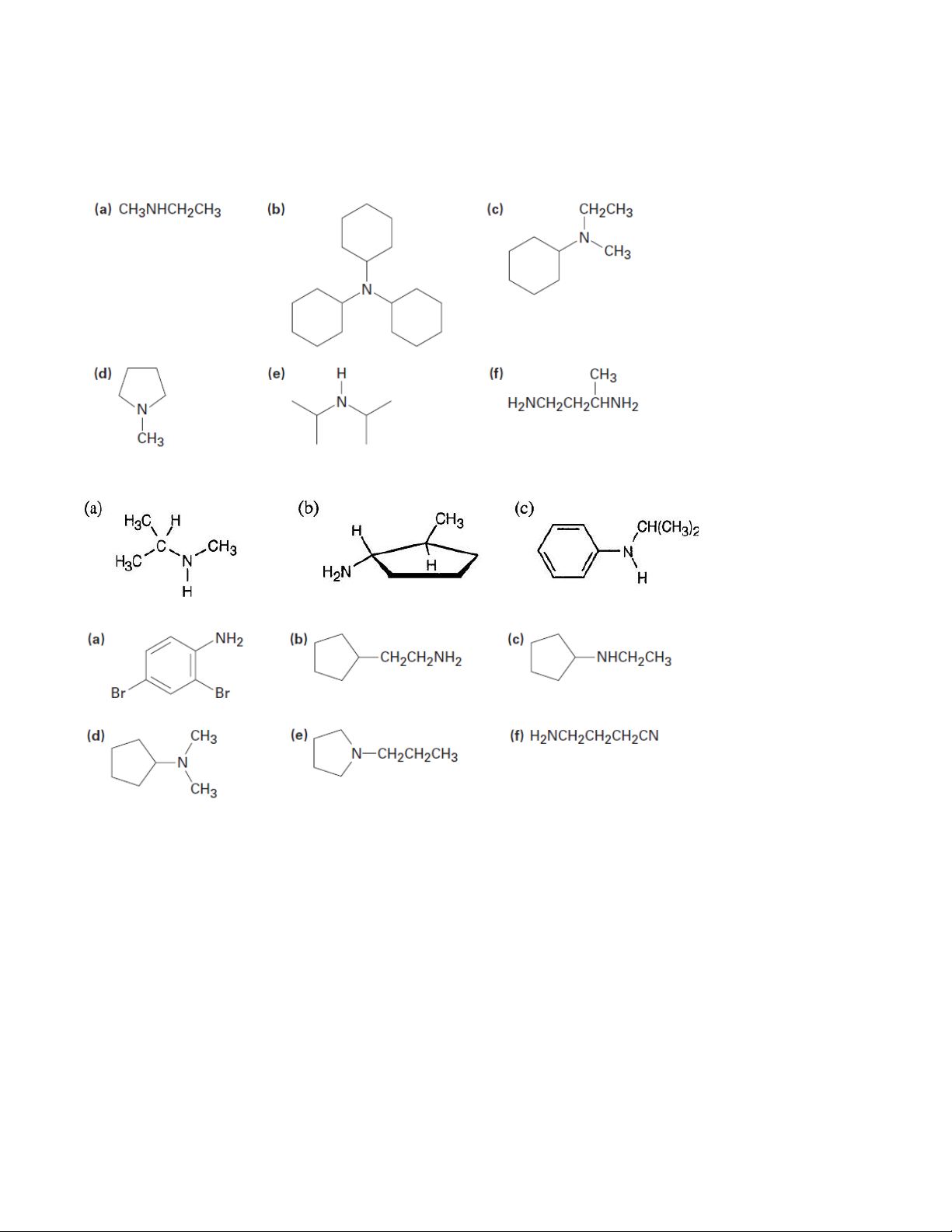
2. Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names: (a) Triisopropylamine (b) Triallylamine (c) N-Methylaniline
(d) N-Ethyl-N-methylcyclopentylamine
(e) N-Isopropylcyclohexylamine (f) N-Ethylpyrrole (g) 1,3-Dimethylpyrrole
(h) 4-(N,N-Dimethylamino)pyridine
(i) N,N-Dimethylaniline (j) (Cyclohexylmethyl)amine
(k) N-Methylcyclohexylamine (l) (2-Methylcyclohexyl)amine
(m) 3-(N,N-Dimethylamino)propanoic acid
3. Rank the following compounds in order of increasing basicity
(a) p-Nitroaniline, p-aminobenzaldehyde, p-bromoaniline 19 Organic Chemistry 2
(b) p-Chloroaniline, p-aminoacetophenone, p-methylaniline
(c) p-(Trifluoromethyl)aniline, p-methylaniline, p-(fluoromethyl)aniline
4. How would you prepare the following compounds from benzene?
(a) N,N-Dimethylaniline (b) p-Chloroaniline (c) m-Chloroaniline (d) 2,4-Dimethylaniline
(e) p-Bromobenzoic acid
(f) m-Bromobenzoic acid
(g) m-Bromochlorobenzene
(h) p-Methylbenzoic acid (i) 1,2,4-Tribromobenzene
(j) p-(Dimethylamino)azobenzene (k) Benzylamine
5. How would you prepare the following substances from 1-butanol? (a) Butylamine (b) Dibutylamine (c) Propylamine (d) Pentylamine
(e) N,N-Dimethylbutylamine (f) Propene
6. How would you prepare the following substances from pentanoic acid? (a) Pentanamide (b) Butylamine (c) Pentylamine (d) 2-Bromopentanoic acid (e) Hexanenitrile (f) Hexylamine
7. How would you prepare aniline from the following starting materials? (a) Benzene (b) Benzamide (c) Toluene
8. How might you prepare pentylamine from the following starting materials? (a) Pentanamide (b) Pentanenitrile (c) 1-Butene (d) Hexanamide (e) 1-Butanol (f) 5-Decene (g) Pentanoic acid
9. How would you convert aniline into each of the following products? (a) Benzene (b) Benzamide (c) Toluene
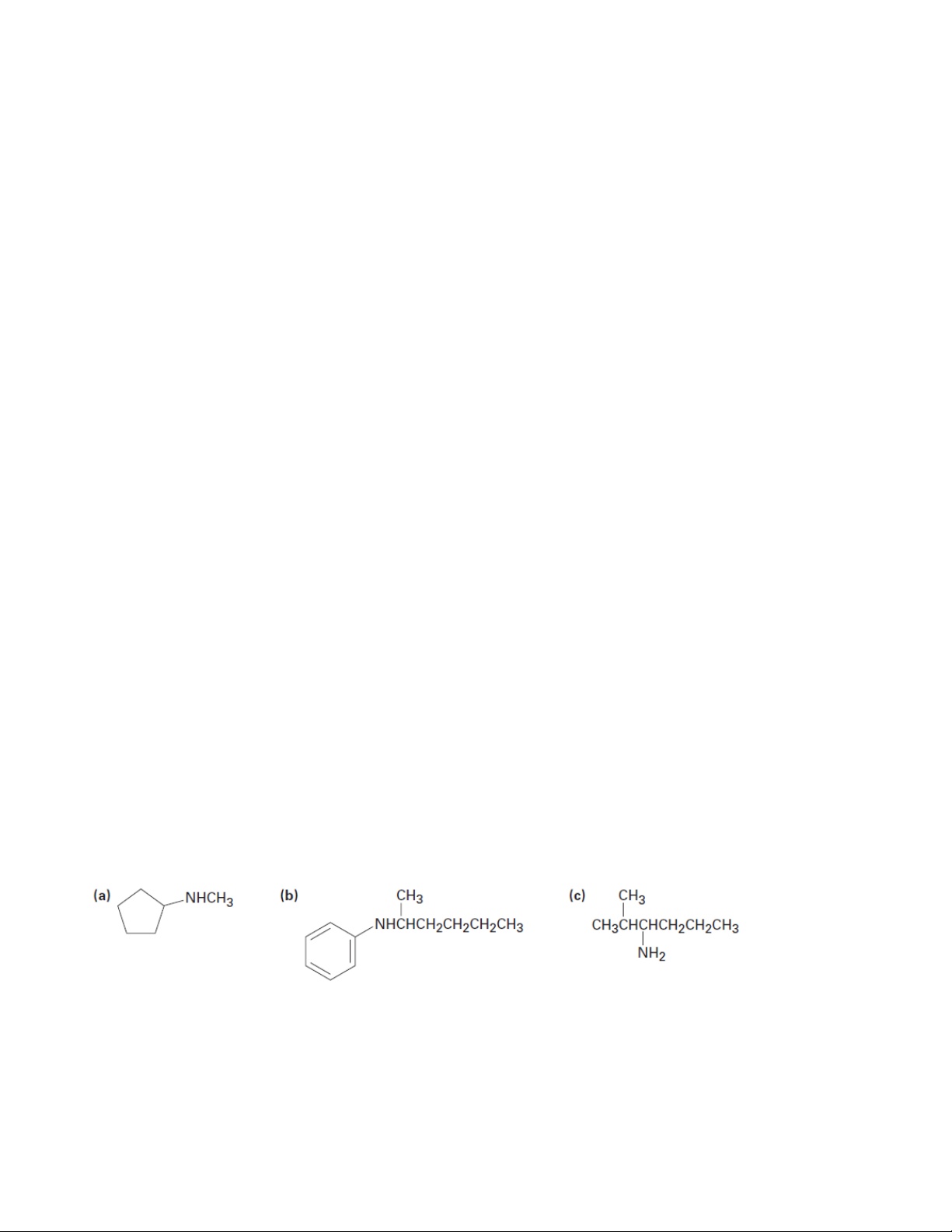
10. What are the major products from Hofmann elimination of the following amines?
11. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions. If more than one product is formed, tell which is major. 20 Organic Chemistry 2

