












Preview text:
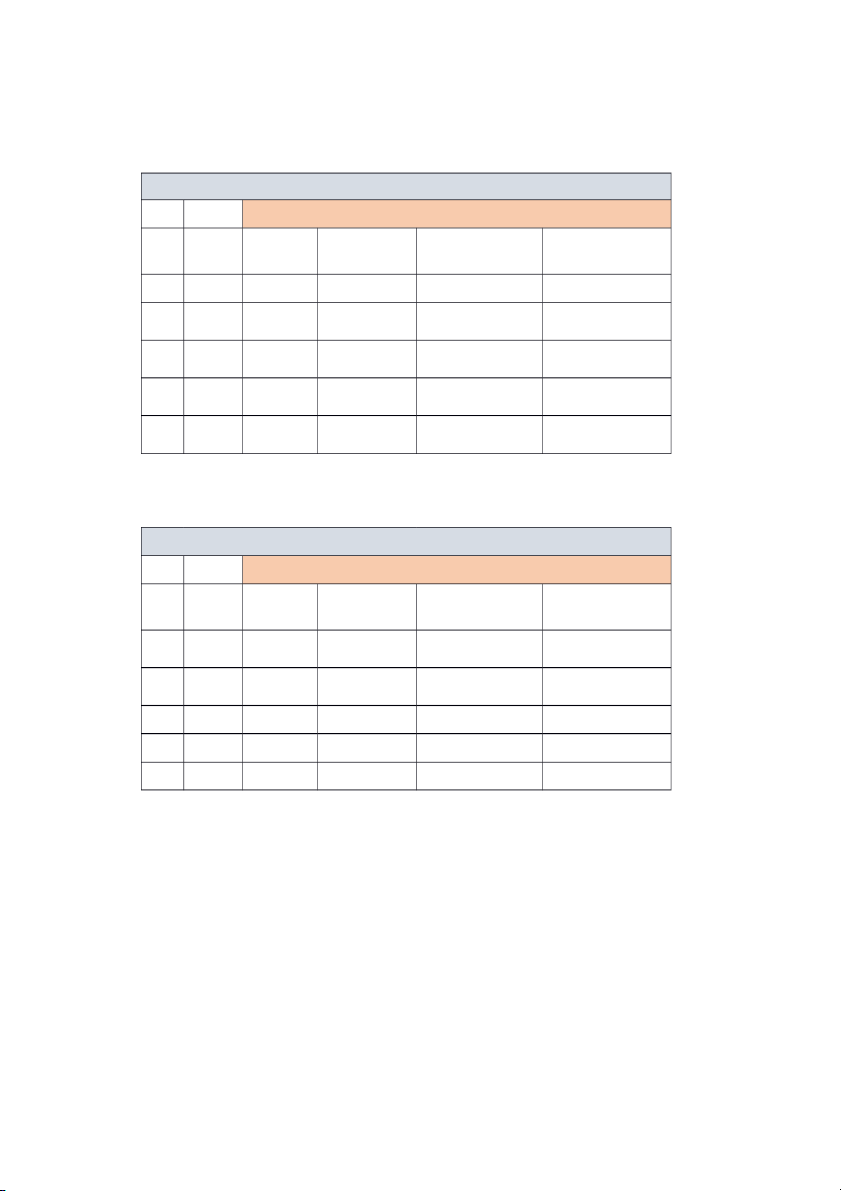
CHAPTER 1 TASK Brief NAME Question Question Exercise Problem A 1 Phát 2, 8 BE1-5 E1-7 P1-3A E1-2 2 Thuận 7, 13 BE1-6 E1-6 P1-1A E1-1 3 Minh 16, 17 BE1-1 E1-5 P1-2A E 1-3 4 Hương 9,10,11 BE 1 -2 E 1-4 E1-8 5 Thảo 3,12 BE1-8 E1-10 CHAPTER 2 TASK Brief NAME Question Question Exercise Problem A E2-5 1 Phát 1,11 BE2-3 E2-6 E2-2 2 Thuận 7,8 BE2-1 E2-3 3 Minh 6, 9 BE2-2 E2-1 P2-1A 4 Hương 9,10 BE 2-4 E 2-4 P2 - 2A 5 Thảo 18,5 BE2-5, BE2-10 E2-7 P2-3A Chapter 1 1. Glossary
1.accounting: Kế toán
2.accounting equation: Phương trình kế toán 3. assets : Tài sản 4. auditing: Kiểm toán
5. balance sheet : Bảng cân đối kế toán
6. CPA: Chứng chỉ dùng để chỉ những kiểm toán viên có trình độ được
chứng nhận trên toàn cầu 7. corporation: Tập đoàn 8. dividends: Cổ tức 9. expenses: Chi phí
10. financial accounting: Kế toán tài chính
11. Financial Accounting Standards Board: Hợp đồng chuẩn mực kế toán tài chính
12. financial statements: Báo cáo tài chính
13. historical cost principle: Một nguyên tắc kế toán quy định rằng các công
ty nên ghi lại tài sản theo giá gốc.
14. income statement: Một báo cáo tài chính trình bày doanh thu và chi phí
và kết quả là thu nhập ròng hoặc lỗ ròng của một công ty trong một khoảng thời gian cụ thể.
15. internal auditor: Kiểm toán nội bộ là một chức năng đánh giá độc lập
bên trong tổ chức, để kiểm tra và đánh giá các hoạt động của tổ chức, như
là một hoạt động phục vụ tổ chức
16. International Accounting Standards Board: Cơ quan thiết lập chuẩn
mực kế toán ban hành các chuẩn mực được nhiều quốc gia bên ngoài Hoa Kỳ áp dụng.
17. liabilities: Yêu cầu của chủ nợ so với tổng tài sản.
18. net income: Số tiền mà doanh thu vượt quá chi phí.
19. net loss: Số tiền mà chi phí vượt quá doanh thu.
20. owner investments: Các khoản đầu tư của chủ sở hữu
21. owners' equity: Vốn chủ sở hữu
22. partnership: Một doanh nghiệp thuộc sở hữu của hai hoặc nhiều người
được liên kết với tư cách là đối tác
23. public accounting: Kế toán công chứng là thuật ngữ dùng để chỉ lĩnh
vực chuyên môn trong đó các hoạt động liên quan đến nghề nghiệp kế
toán được cung cấp cho các cá nhân, doanh nghiệp, tổ chức dưới dạng dịch vụ.
24. retained earnings: Thu nhập ròng được giữ (giữ lại) trong doanh nghiệp.
25. revenue: Sự gia tăng tổng vốn chủ sở hữu của các cổ đông do các
hoạt động kinh doanh được thực hiện nhằm mục đích kiếm thu nhập.
26. sole proprietorship: Doanh nghiệp tư nhân là một hình thức kinh doanh
mà một người sở hữu và điều hành toàn bộ doanh nghiệp.
27. statement of retained earnings: là một báo cáo tài chính ghi lại những
thay đổi về lợi nhuận giữ lại của một công ty trong một khoảng thời gian xác định. 2. Questions
2. Identify and describe the steps in the accounting process. Three Activities:
1. Identification: Select economic events (transactions)
2. Recording: record, classify, and summarize
3. Communication: prepare accounting reports
3. (a) Who are internal users of accounting data?
(b) How does accounting provide relevant data to these users?
a. Internal users are people within a business organization who use
financial information. Examples of internal users are owners, managers, and employees.
a. Accounting provides guidelines and standards on how to prepare
and present financial statements or reports. It helps in the
preparation and presentation of the balance sheet, cash flow, and income statements. 7.
The monetary unit assumption requires that companies include in the
accounting records only transaction data that can be expressed in money
terms. This assumption enables accounting to quantify (measure)
economic events. The monetary unit assumption is vital to applying the historical cost principle.
This assumption prevents the inclusion of some relevant information in the
accounting records. For example, the health of a company’s owner, the
quality of service, and the morale of employees are not included. The
reason: Companies cannot quantify this information in money terms.
Though this information is important, companies record only events that can be measured in money.
8. What is the economic entity assumption?
Answer: An economic entity can be any organization or unit in society. It
may be a company, a governmental unit, a municipality, a school district, or
a church. The economic entity assumption requires that the activities of the
entity be kept separate and distinct from the activities of its owner and all other economic entities.
9. There are three common types of businesses—sole proprietorship,
partnership, and corporation—and each comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
There are three common types of businesses—sole proprietorship,
partnership, and corporation—and each comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. 10.
One of the advantages Juana would enjoy is that ownership of a
corporation is represented by transferable shares of stock. This would allow
Juana to raise money easily by selling a part of her ownership in the
company. Another advantage is that because holders of the shares
(stockholders) enjoy limited liability, they are not personally liable for the
debts of the corporate entity. Also, because ownership can be transferred
without dissolving the corporation, the corporation enjoys an unlimited life. 11.
The accounting equation is a basic principle of accounting and a
fundamental element of the balance sheet. The equation is as follows:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholder’s Equity 12.
(a) Define the terms assets liabilities and stockholder’s equity
Assets are the total of your cash, the items that you have purchased, and
any money that your customers owe you.
Liabilities are the total amount of money that you owe to creditors.
Stockholders' equity represents the cumulative net contributions by
stockholders plus retained earnings. 13. (g), (i), (b) 16.
a. Paid cash for janitorial services: Assets will be decreased, and decrease in stakeholder equity.
b. Purchased equipment for cash: assets don change
c. Invested cash in the business: assets are increased, and the owner's equity also increases
d. Paid account payable in full: decrease the assets, a decrease in liabilities. 17.
Income statement: (a) Service revenue: (c) Advertising expense: (f) Salaries and wage payable
Balance sheet: (b) Equipment: (d) Account reveivable
Retained Earnings statement: (e) Retained earnings 3. Brief Excercises BE1-1 Assets = Liabilitie + Stockholders' Equity s (a) $78,000 $50,000 $28,000 (b) $115,000 $45,000 $70,000 (c ) $94,000 $34,000 $60,000 BE1-2 Answer of Part a:
Holland Company’s Total Assets = $120,000 + $232,000
Holland Company’s Total Assets = $352,000 Answer of Part b:
Holland Company’s Total Liabilities = $190,000 - $86,000
Holland Company’s Total Liabilities = $104,000 Answer of Part c:
Holland Company’s Stockholders Equity = $600,000 – ($600,000 × ½ ×1/2)
Holland Company’s Stockholders Equity = $600,000 - $300,000
Holland Company’s Stockholders Equity = $300,000 BE1-5
BE1-5 Indicate whether each of the following items is an asset (A), liability (L), or part of stockholder's equity (SE). a. Accounts receivable: A
a. Salaries and wages payable: SE a. Equipment: A a. Supplies: A a. Owner’s investment: SE a. Notes payable: L BE1-6 a)
Asset = liabilities + stockholders’ equity Increase Increase NE b)
Asset = liabilities + stockholders’ equity Increase NE Increase c)
Asset = liabilities + stockholders’ equity Decrease NE Increase BE1-8 a. Advertising expense: E a. Service revenue: R a. Insurance Expense: E a. Salaries and wages : E a. Dividends: D a. Rent revenue: R a. Utilities expense: E 4. Excercises E1-1 1.Analyzing and
Communcating This task can only be performed interpreting
after the information has been information.
identified and recorded and has to
do with producing clear, useful reports 2. Classifying Recording After transactions has been economic events. identified, they need to be
classified in order to be recorded 3. Explaining uses,
Communicating Users must be made aware of this meaning, and limitations of data. 4. Keeping a Identifying The diary would be used to systematic identify transactions chronological diary of events. 5. Measuring events
This is essential in the recording in dollars and cents. phase Recording
Communicating Reports are prepared after all recording has been done 6. Preparing accounting reports. 7. Reporting
Communicating Accounting reports are the information in a formats used to communicate standard format. data consistently 8. Accounting
Communicating After completing the accounting reports can include
operations, it is necessary to economic
make predictions and reports to summaries the company 9. Summarizing
Communicating Accounting reports can include economic events economic summaries E1-2 a) Customers: E
Securities and Exchange Commission: I Store manager: I Internal Revenue Service: E Labor unions: E Suppliers: I Marketing manager: I Production supervisor: I Vice president of finance: I
b) Can we afford to give our employees a pay raise?: I
Did the company earn a satisfactory income?: I
Do we need to borrow in the near future?: I
How does the company's profitability compare to other companies?: E
What does it cost us to manufacture each unit produced?: E
Which product should we emphasize?: I
Will the company be able to pay its short-term debts?: E E1-3
If Sharon would agree to the idea of the president, she would be violating
the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). According to GAAP,
land cannot be classified in the financial statements on its fair value. Cost
principle should be followed when reporting land on the financial
statements. This would be a collusion (fraud) among them if she agrees to
the idea of the president of the company. E1-4
1. Incorrect, cost principle 2. correct, Monetary 3. Economic entity assumption E1-5
Asset: Cash: Equiment; Supplies; Accounts reveiable
Liabilitises: Account payable; notes payable; Salaries and wages payable
Stockholder’s equity: common stock E1-6
1. Increase in assets and increase in stockholders’ equity
2. Decrease in assets and decrease in stockholders’ equity
3. Increase in assets and increase in liabilities
4. Increase in assets and increase in stockholders’ equity
5. Decrease in assets and Decrease in stockholders’ equity
6. No effect on assets and stockholders’ equity
7. Decrease in assets and increase in liabilities
8. No effect on assets and stockholders’ equity
9. Increase in assets and increase in stockholders’ equity E1-7
Keystone Computer Timeshare Company entered into the following transactions during May 2015.
QUESTION 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ANSWER C D A B D B E F E1-8 (a)
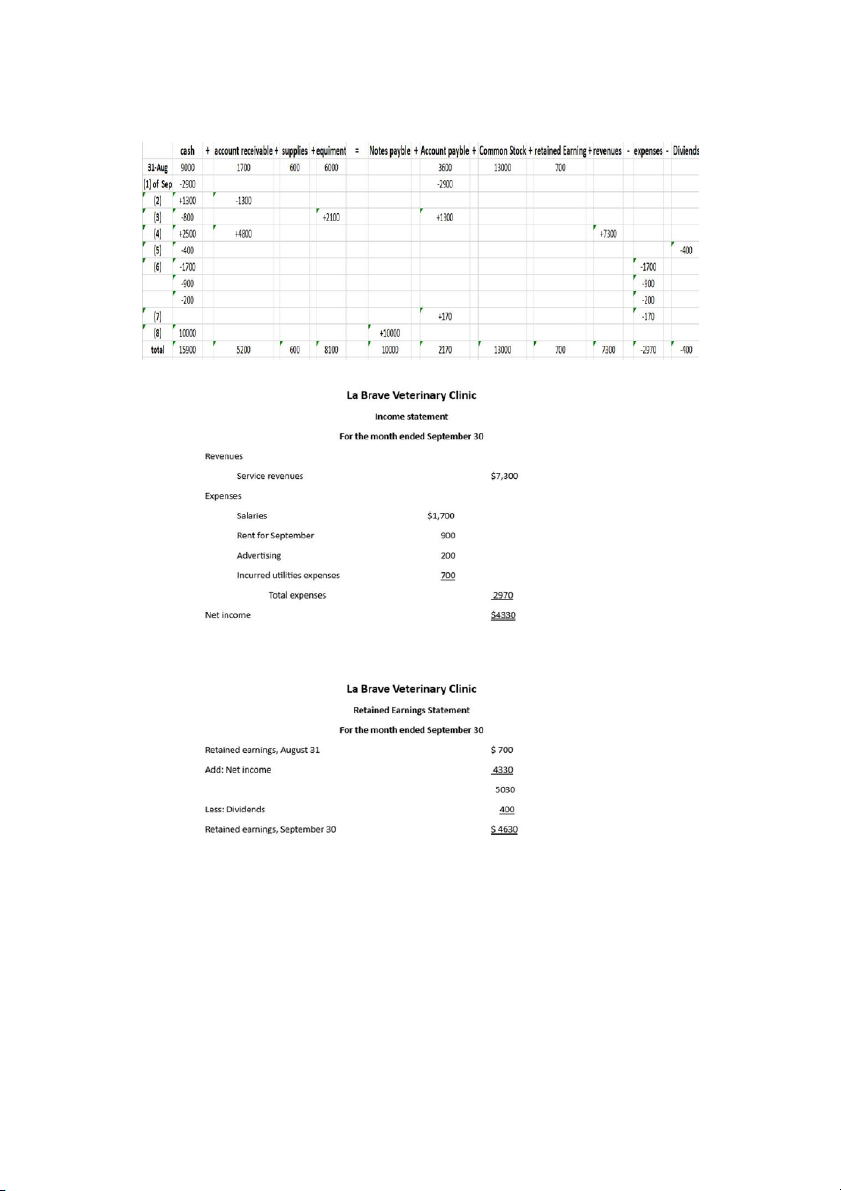
1. Shareholders invested $15,000 cash in the business.
2. Purchased equipment for $5,000, paying $2,000 in cash and the balance of $3,000 on account.
3. Paid $750 cash for supplies.
4. Earned $9,100 in revenue, receiving $4,600 cash and $4,500 on account.
5. Paid $1,500 cash on accounts payable.
6. Paid $2,000 cash dividends to shareholders. 7. Paid $650 cash for rent.
8. Collected $450 cash from clients on account.
9. Paid salaries and wages of $3,900.
10. Incurred $500 of utilities expense on account.
(b) Investment.....................................................................15,000
Service revenue............................................................................. 9,100
Dividends..................................................................................... (2,000)
Rent expense................................................................................ (650)
Salaries and wages expense...................................................... (3,900)
Utilities expense.......................................................................... (500 )
Increase in equity..................................................................... 17,050
(c) Service revenue...................................................................... 9,100
Rent expense............................................................................ (650 )
Salaries and wages expense................................................... (3,900)
Utilities expense....................................................................... (500 )
Net income................................................................................ 4,050 E1-10
Total equity is the difference between total assets and total liabilities. The
amount of equity each year is shown below:
Dec 31, 2014 Dec 31, 2015 Dec 31, 2016 Total Assets $400,000 $480,000 $590,000 Less: Total Liabilities 260,000 300,000 400,000 Total Equity $140,000 $180,000 $190,000
Total equity at the end of the year is calculated as follows
Equity, end = Equity, beg + Additional investment + Net income - Dividends declared
Therefore, net income can is calculated:
Net income = Equity, end + Dividends declared - Equity, beg
a. For 2014, beginning equity balance is equal to the initial investment, which is $100,000.
Net income, 2014 = Equity, end + Dividends declared - Additional investment - Equity, beg
Net income, 2014 = $140,000 + $15,000 - $0 - $100,000
Net income, 2014 = $55,000
The company earned a net income of $55,000 in 2014.
b. For 2015, the beginning equity balance is equal to the ending balance of
equity in 2014, which is $140,000
Net income, 2015 = Equity, end + Dividends declared - Additional investment - Equity, beg
Net income, 2015 = $180,000 + $0 - $50,000 - $140,000
Net income, 2015 = ($10,000)
The company incurred a net loss of $10,000 in 2015.
c. For 2016, the beginning equity balance is equal to the ending balance of
equity in 2015, which is $180,000
Net income, 2016 = Equity, end + Dividends declared - Additional investment - Equity, beg
Net income = $190,000 + $30,000 - $15,000 - $180,000
Net income = $25,000
The company earned a net income of $25,000 in 2016 5. Problem P1-1A Cash Account supplie equiment Account owner’ Rev owner’s Exp receivable s payable s Drawing capital +10000 +10000 -5000 +5000 -400 -400 -300 -250 +300 -250 +4700 +4700 -700 -700 -1000 -1000 -140 -140 +1000 - 1000 +1000 +1000 +120 +120 7030 1120 300 5000 1000 9300 5700 2790 Revenues Service revenue 5700 Expenses Rent expense 400 Salaries and wages expense 1000 Utiltites expense 140 Advertising expense 250 Total expense 3910 Net income 1790 P1-2A a/ b/ P1-3A
P1-3A On May 1, Nimbus Flying School, a company that provides fl ying lessons, was
started with an investment of $45,000 cash in the business. Following are the assets and
liabilities of the company on May 31, 2015, and the revenues and expenses for the month of May.
Cash $ 4,650 Notes Payable $28,000
Accounts Receivable 7,400 Rent Expense 900
Equipment 64,000 Maintenance and
Service Revenue 6,800 Repairs Expense 350
Advertising Expense 500 Gasoline Expense 2,500
Accounts Payable 1,400 Utilities Expense 400
No additional investments were made in May, but the company paid dividends of $500 during the month. Instructions
(a) Prepare an income statement and a retained earnings statement for the month of May and a balance sheet at May 31.
(b) Prepare an income statement and a retained earnings statement for May assuming
the following data are not included above: (1) $900 worth of services were performed
and billed but not collected at May 31, and (2) $1,500 of gasoline expense was incurred but not paid. Answer: (a)
Nimbus Flying School Income Statement For the month of May, 2015 Particulars Amount ( In $ ) Service Revenue 6,800
Less : Advertising Expense ( 500 ) Less : Rent Expense ( 900 )
Less : Maintenance Expense ( 350 )
Less : Gasoline Expense ( 2,500 )
Less : Utilities Expense ( 400 ) Net Income 2,150
Nimbus Flying School Statement of Retained Earnings For the month of May, 2015 Particulars Amount ( In $ )
Net Income from Income Statement 2,150 Less : Dividends Paid ( 500 )
Closing Balance of Retained Earnings 1,650
Nimbus Flying School Balance Sheet As on 31 May, 2015 Assets Amount ( In $ ) Cash 4,650 Equipment 64,000 Accounts Receivable 7,400 Total 76,050 Liabilities Amount ( In $ ) Accounts Payable 1,400 Notes Payable 28,000 Retained Earnings 1,650 Share Capital 45,000 Total 76,050 Point of Explanation
In Liabilities side of Balance Sheet Share Capital of $ 45,000 is shown because it is the
same amount with which the business was started on May 1, 2015 with investment in Cash for amount of $ 45,000 (b)
Nimbus Flying School Income Statement For the month of May, 2015 Particulars Amount ( In $ )
Service Revenue [ 6,800 + 900 ] 7,700
Less : Advertising Expense ( 500 ) Less : Rent Expense ( 900 )
Less : Maintenance and Repairs Expense ( 350 )
Less : Gasoline Expense [ 2,500 + 1,500 ] ( 4,000 )
Less : Utilities Expense ( 400 ) Net Income 1,550
Nimbus Flying School Statement of Retained Earnings For the month of May, 2015 Particulars Amount ( In $ )
Net Income from Income Statement 1,550 Less : Dividends Paid ( 500 )
Closing Balance of Retained Earnings 1,050 Chapter 2 1. Glossary 1. Account: tài khoản
2. Accounting cycle: Chu kỳ kế toán
3. Accrual basis of accounting: Cơ sở dồn tích của kế toán
4. Recognizes expenses as incurred, whether or not cash has been paid out.
5. Business transactions Measurable events that affect the financial condition of a business.
6. Chart of accounts: sơ đồ tài khoản
7. Compound journal entry: mục ghi sổ tổng hợp 8. Credit: tín dụng
9. Credit balance: số dư tín dụng 10.
Cross-indexing: lập chỉ mục chéo 11. Debit: ghi nợ 12. Debit balance: dư nợ 13.
Double-entry procedure - Một hệ thống ghi lại trong các tài
khoản thích hợp tác động kép của mỗi giao dịch. 14.
Horizontal analysis - Một kỹ thuật phân tích tài chính được sử
dụng để đánh giá hiệu suất của công ty theo thời gian. 15.
Journal - Một hồ sơ kế toán trong đó các giao dịch ban đầu
được ghi lại theo thứ tự thời gian. 16.
Journal entry - một thuật ngữ kế toán ghi nhận giao dịch vào sổ
kế toán. Một bút toán có thể gồm nhiều hạng mục mà mỗi hạng mục
có thể là một định khoản nợ hoặc định khoản có. 17.
Journalizing - Việc nhập dữ liệu giao dịch vào tạp chí. 18.
Ledger - Toàn bộ nhóm tài khoản được duy trì bởi một công ty. 19.
Nominal accounts - một tài khoản trong đó các giao dịch kế
toán được lưu trữ trong một năm tài chính. 20. Note - ghi chú 21.
Permanent accounts - những tài khoản tiếp tục ghi lại số dư tích lũy theo thời gian. 22.
Posting Recording - Các mục được đăng có nguồn gốc từ việc
thêm thu nhập và trừ các khoản nợ phải trả trong Tạp chí Kế toán. 23.
Simple journal entry - Một mục nhật ký chỉ liên quan đến hai Tài khoản. 24.
T-account - Hình thức cơ bản của một tài khoản. 25.
Trial balance - Danh sách các tài khoản và số dư của chúng tại một cho thời gian. 26.
Vertical analysis - Một phương pháp phân tích báo cáo tài
chính liệt kê từng mục hàng theo tỷ lệ phần trăm của một con số cơ sở trong báo cáo. 2. Questions
1. Describe the parts of a T-account.
Answer: In its simplest form, an account consists of three parts:
a title, a left or debit side, and a right or credit side. Because the
format of an account resembles the letter T, we refer to it as a T- account.
5. State the rules of debit and credit as applied to (a) as
set accounts, (b) liability accounts, and (c) the stock
holders’ equity accounts (revenue, expenses, dividends,
common stock, and retained earnings)
a. Assets are debited for every increase in the amount and credited for every decrease.
a. Liability account have a normal credit balance and are credited for
every increase and debited for every decrease in the amount.
a. Stock holders’s equity credited for every increase in the amount and
debited for every decrease (revenue, expenses, dividends, common stock, and retained earnings) 6. Normal balance Debit: (a); (b)
Normal balance Credit: (c); (d); (e); (f); (g) 7.
- Accounts Receivable is an asset and has normal debit balance
- Accounts Payable is a liability and has normal credit balance
- Equipment is an asset and has normal debit balance
- Dividends is a stockholders’ equity and has normal debit balance
- Supplies is an asset and has normal debit balance 8. a) debit b) credit c) credit
9.. (a) Cash—both debit and credit entries.
(b) Accounts Receivable—both debit and credit entries.
(c) Dividends—debit entries only.
(d) Accounts Payable—both debit and credit entries.
(e) Salaries and Wages Expense—debit entries only.
(f) Service Revenue—credit entries only 10.
The basic steps in the recording process are:
(a) Analyze each transaction in terms of its effect on the accounts
(b) Enter the transaction information in a journal
(c) Transfer the journal information to the appropriate accounts in the ledger.
11. What are the advantages of using a journal in the recording process?
Answer: The journal makes several significant contributions to the recording process:
1. It discloses in one place the complete effects of a transaction.
2. It provides a chronological record of transactions.
3. It helps to prevent or locate errors because the debit and credit amounts for
each entry can be easily compared.
18. What is a trial balance and what are its purposes?
A trial balance is used in bookkeeping to list all the balances in your
business’s general ledger accounts. It consists of two columns: one for
debit balances, and one for credit balances. To keep the books balanced,
the total of each column should be equal.
The purpose of a trial balance is only to show the ending balance in each
account, while a general ledger also shows detailed transactions that
comprise the ending balance. A trial balance is done to check that the debit
and credit column totals of the general ledger accounts match each other,
which helps spot any accounting errors. If the totals don't match, a missing
debit or credit entry, or an error in copying over from the general ledger account may be the cause.
19. The following steps to flow the accounting information
(a) Debits and credits posted to the ledger to their respective accounts
(b) Business transaction occurs.
(c) Information entered in the journal. It includes the narration part
(d) Financial statements are prepared so that it could analyze the financial
performance, position of the business organization
(e) A trial balance is prepared. It aims to match the total debit and total credit columns
All these above steps are to be followed systematically so that the financial
statement could be present in an accurate and ethical way. It must be free
from any bias, it always be presented independently 3. Brief Excercises BE 2-1 1. Accounts Payable Debit: decrease Credit: increase




