Preview text:
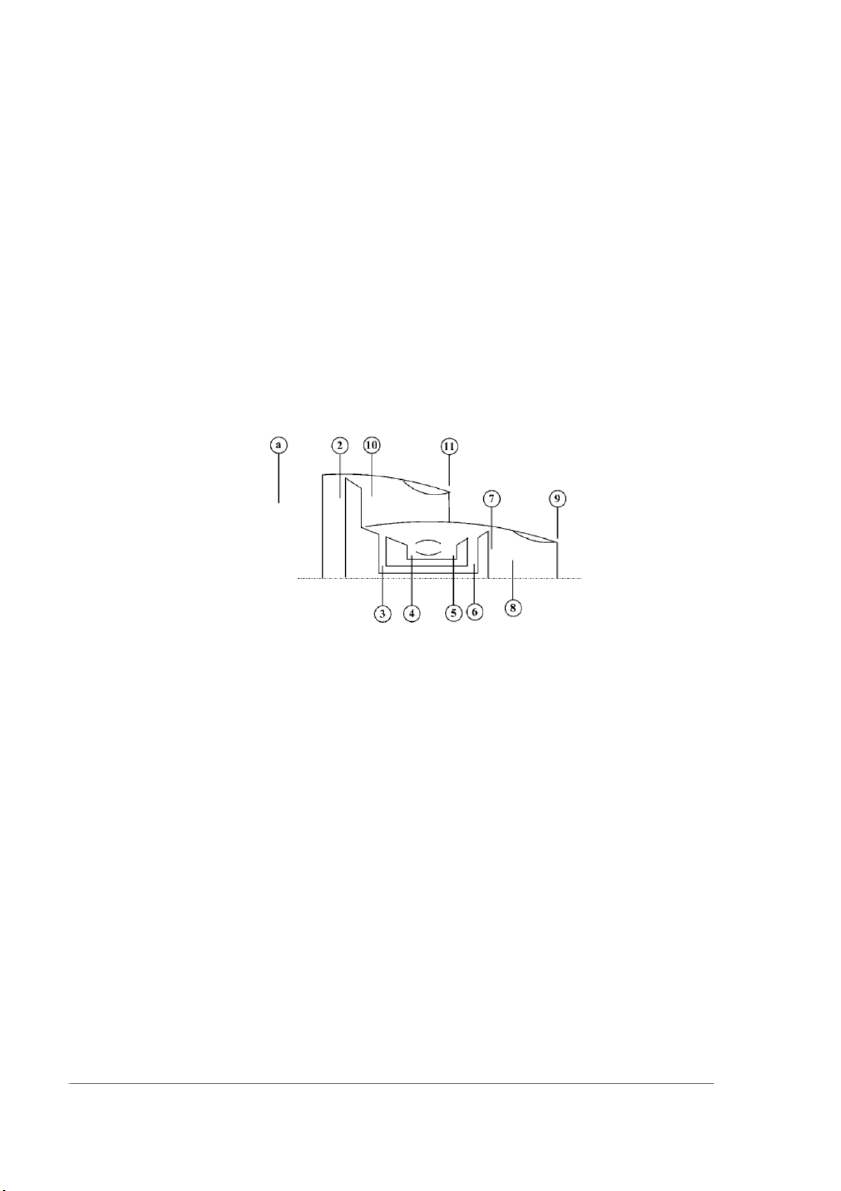
Problem 1. A high-bypass ratio (separate-exhaust) turbofan engine powers a
commercial transport. At the cruise condition, the flight and engine operating conditions are:
- M0 = 0,88; p0 = 15 kPa; T0 = −40◦C; 𝛾c = 1,4; cpc = 1004 J∕kg.K; 𝜋d = 0,995; 𝜋f = 1,6. ef = 0,90; 𝛼 = 8,0.
- Fan nozzle is convergent with 𝜋fn = 0,95; 𝜋c = 40; ec = 0,90; 𝜏𝜆 = 8,0; cpt = 1152
J∕kg.K. 𝛾t = 1,33, QR = 42000 kJ∕kg, 𝜋b = 0,95, 𝜂b = 0,992, 𝜂m = 0,95, et = 0.85.
- Primary nozzle is of convergent design and operates at 𝜋n = 0,98 Calculate
1. Plot T-s diagram for the cycle
2. Total pressures and temperatures throughout the engine and the fuel-to-air ratio
3. Nozzle exit static pressure p11 and p9
4. Ratio of fan-to-core thrust
5. Nondimensional specific thrust and TSFC in mg/s/N
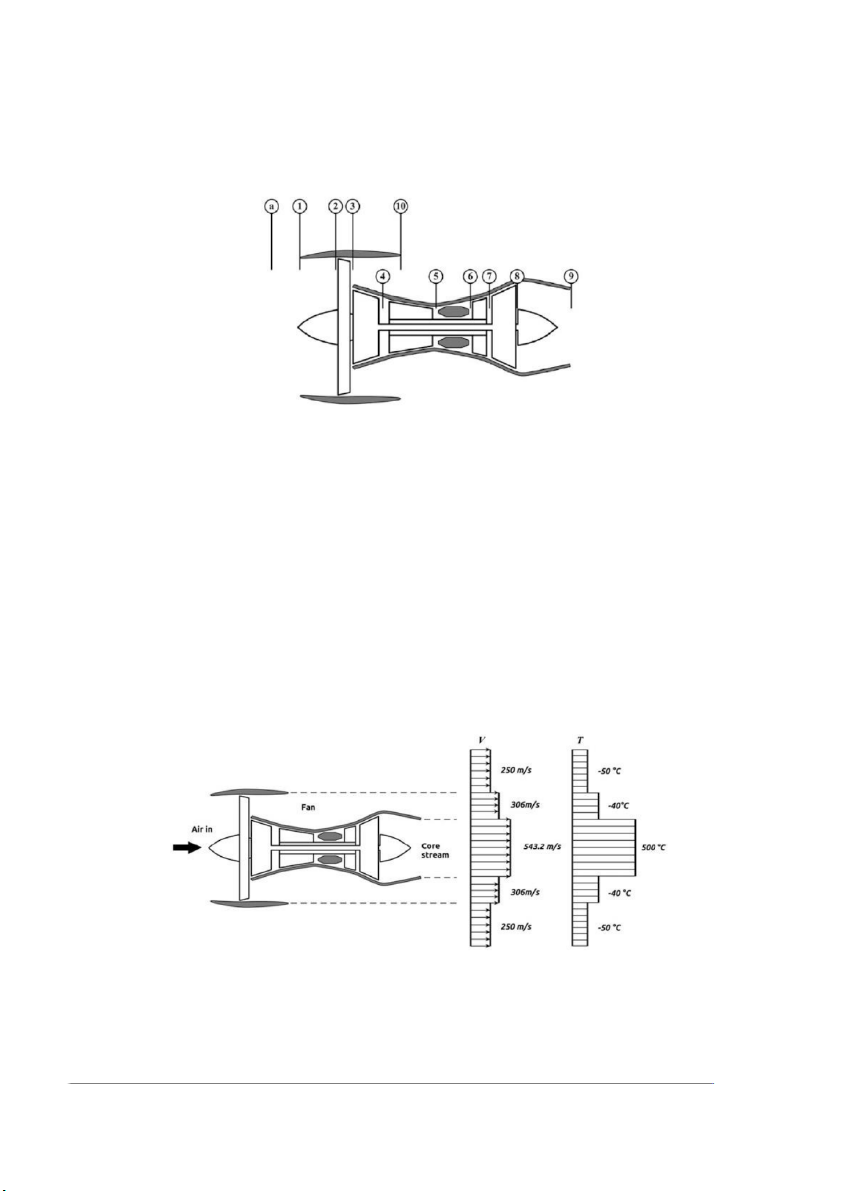
Problem 2 A double-spool turbofan engine; below figure blow, is used to power an
aircraft flying at speed of 250 m/s at an altitude of 11,000 m. As shown in the figure
below, the low-pressure turbine drives the fan and low-pressure compressor, while the
high-pressure turbine drives the high-pressure compressor. The engine has the fol owing data: - Bypass ratio=8.
- Total ingested air flow rate=180 kg/s.
- Overal pressure ratio OPR=35. - Fan pressure ratio=1.6.
- Pressure ratio of high-pressure compressor is four times that of the low-pressure compressor; πHPC=4 πLPC.
- Turbine inlet temperature=1650 K.
- Fuel heating value=43 MJ/kg.
Assuming all processes are ideal and neglecting any pressure drop, it’s required to: 1. Plot - T s diagram for the cycle 2. Find the thrust, 3. TSFC, 4. Efficiencies of the engine
5. Plot the velocity and temperature distribution over the engine cross section (rear end)
Problem 3 A double-spool turbofan engine is used to power an aircraft flying at speed
of 250 m/s at an altitude of 11,000 m. As shown in Figure, the low-pressure turbine
drives the fan and low-pressure compressor, while the high-pressure turbine drives the
high-pressure compressor. Inlet and outlet temperature and velocity of engine are
plotted beside the engine layout. The engine has the fol owing data: - Bypass ratio=8.
- Total ingested air flow rate=180 kg/s.
- Overal pressure ratio OPR=35.
- Pressure ratio of high-pressure compressor is four times that of the low-pressure compressor; πHPC=4 πLPC.
- Fuel heating value=43 MJ/kg.
Assuming all processes are ideal and neglecting any pressure drop, it’s required to find: 1. Plot - T s diagram for the cycle
2. Whether the nozzles are choked or not? 3. Fan pressure ratio 4. TIT 5. The thrust force




