













Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 Week 7: Corporate Governance
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Educat i
on. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior writt
en consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 Learning Outcomes
• Explain the term corporate governance.
• Understand the responsibilities of the board of directors and
the major governance committees.
• Explain the significance of the “King One” and “King Two” reports.
• Explain the differences between the following two governance
methodologies: “comply or explain” and “comply or else.”
• Identify an appropriate corporate governance model for an organization. Corporate Governance
System by which business corporations are directed and controlled.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
• Good corporate governance: Plays a vital role in underpinning the integrity
and efficiency of financial markets.
• Poor corporate governance: Weakens a company’s potential and can lead to
financial difficulties and fraud.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
What Does Corporate Governance Look Like?
Owners: Supply equity or risk capital to the company by
purchasing shares in the corporation.
Board of directors: Group of individuals who oversee governance of an organization.
• Elected by vote of the shareholders at the annual general meeting (AGM).
Audit and Compensation Committees
Operating committees staffed by members of the board of
directors plus independent or outside directors.
• Audit committees are responsible for monitoring the financial policies and
procedures of the organization.
• Compensation committees are responsible for setting the compensation
for the chief executive officer (CEO) and other senior executives.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
Corporate Governance Committee
• Monitors the ethical performance of the corporation.
• Oversees compliance with the company’s internal code of
ethics as well as any federal and state regulations on corporate conduct.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
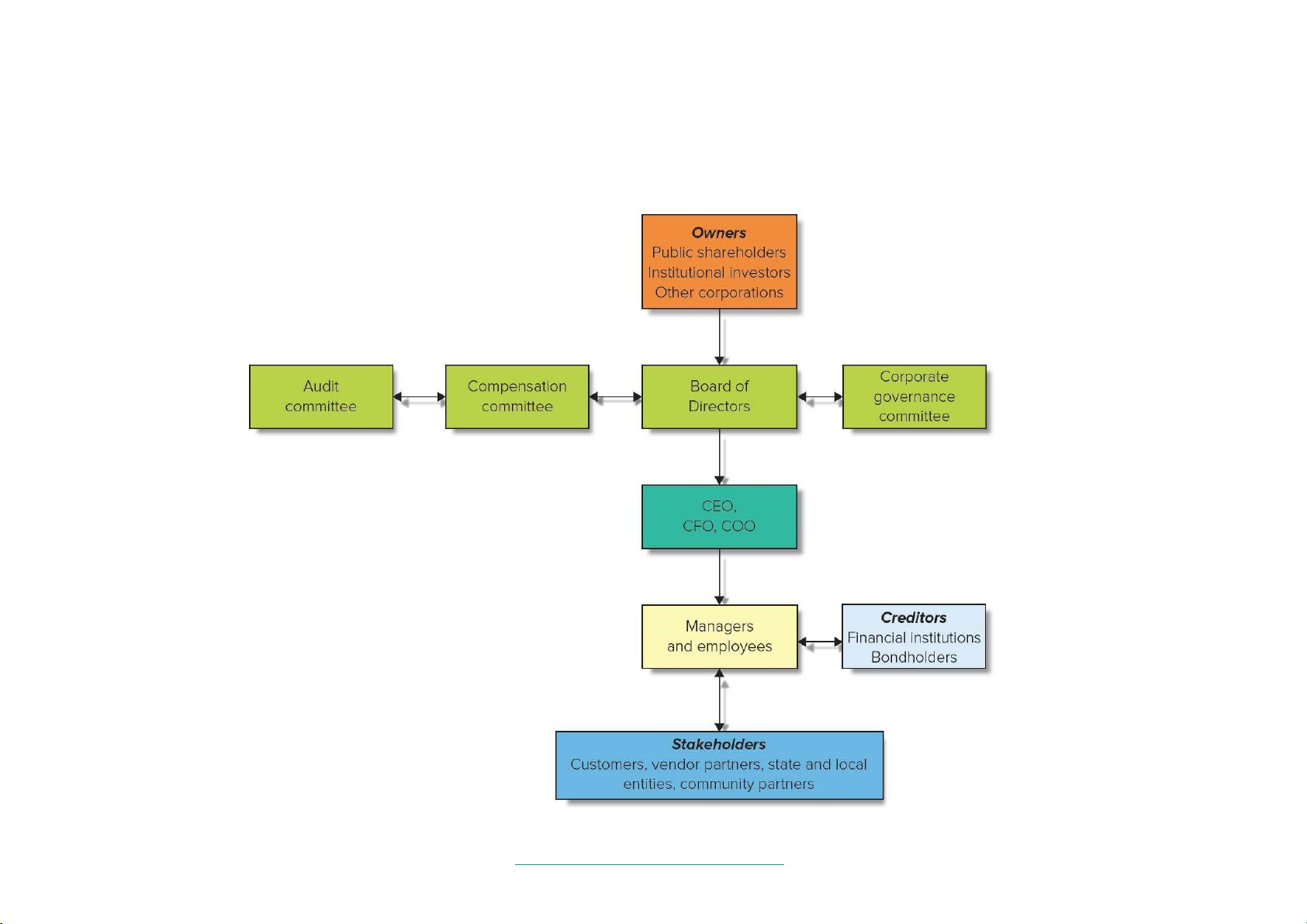
Figure 5.1: Governance of the Modern Corporation
Source: Adapted from Fred R. Kaen, A Blueprint for Corporate Governance (New York: AMACOM, 2003).
Access the text alternative for slide images.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
In Pursuit of Corporate Governance
King One report was recognized as advocating the highest
standards for corporate governance.
• Took a more integrated approach to the topic of corporate governance.
• By recognizing the involvement of all the corporation’s stakeholders in the
efficient and appropriate operation of the organization.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 King Two Report 1
Formally recognized the need to:
• Move the stakeholder model forward.
• Consider a triple bottom line as opposed to the traditional single bottom line of profitability.
• Triple bottom line recognizes the economic, environmental, and social aspects of a company’s activities.
Successful governance in the world in the 21st century requires
companies to adopt an inclusive and not exclusive approach.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 King Two Report 2
• Company must be open to institutional activism and should
emphasize the sustainable or nonfinancial aspects of its performance.
• Boards must apply the tests of fairness, accountability,
responsibility, and transparency to all acts and be accountable
to the company and its stakeholders.
• Correct balance between conformance with governance
principles and performance in an entrepreneurial market economy must be found. Two Governance Methodologies Comply or explain.
• Guidelines that require companies to abide by a set of operating standards
or explain why they choose not to.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 Comply or else.
• Guidelines that require companies to abide by a set of operating standards
or face stiff financial penalties. The Chairman and the CEO 1
Disregarding the corporate governance model involves merging
the roles of CEO and chairman of the board into one individual.
• Oversight provided by the board of directors is lost.
• Operational focus changes from long term to short term.
• Merging the two roles may lead to higher efficiency.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 The Chairman and the CEO 2 Advantages of merging.
• Potential for conflict is minimized.
• Board is given the benefit of leadership from someone who is in touch with
the inner workings of the organization rather than an outsider. Disadvantages of merging.
• Governance of the corporation is with one person, which eliminates the
checks and balances process that the board was created for in the first place.
• Independence of the board is compromised, and the power of the stockholders is minimized.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
Effective Corporate Governance 1
INSEAD, the European business school, emphasizes corporate
governance as an organizational culture issue through CRAFTED principles.
• Consistency, responsibility, accountability, fairness, transparency, and
effectiveness that is deployed throughout the organization.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
Effective Corporate Governance 2
To serve the purpose in setting the operational tone for the
organization, the board should be:
• Comprised of members who represent professional conduct.
• Granted proper authority to fulfill their responsibilities of oversight, guidance, and approval.
• Willing to work with the executive leadership to provide feedback and
guidance in a detailed and timely manner.
Electing to take strategic projects under advisement for extended
periods of time may serve to reinforce the power of the board of directors.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
Dangers of a Corporate Governance Checklist
Effective corporate governance is more than just maintaining a
checklist of items to be monitored on a regular basis.
• Having mechanisms in place will not guarantee good governance.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32 A Fiduciary Responsibility
Corporate governance is about managers fulfilling a fiduciary
responsibility to the owners of their companies.
Based on trust, which is a difficult trait to test when hiring a
manager or enforcing it later.
• Enforcement only becomes an option when that trust has been broken.
Key Safeguards for Corporate Governance
• Properly constituted boards.
• Separation of the functions of chairperson and CEO. • Audit committees. • Vigilant shareholders.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. lOMoARcPSD|364 906 32
• Financial reporting and auditing systems that provide full and timely disclosure.
Copyright © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
Document Outline
- Learning Outcomes
- Corporate Governance
- Audit and Compensation Committees
- Corporation
- In Pursuit of Corporate Governance
- King Two Report 1
- King Two Report 2
- Two Governance Methodologies
- The Chairman and the CEO 1
- Effective Corporate Governance 1
- Effective Corporate Governance 2
- Dangers of a Corporate Governance Checklist
- A Fiduciary Responsibility





