









Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|61803383
Nguyen Ly He Dieu Hanh - xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
VKU_Nguyên lý hệ điều hành (Trường Đại học Công nghệ Thông tin và Truyền thông Việt - Hàn) Scan to open on Studeersnel
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383
What is not a main function of an operating system?
(Chức năng nào không phải là chức năng chính của hệ điều hành?)
a. Provide the users with an extended (virtual) machine b. Manage the I/O devices c. Provide user interfaces d. Support virtual memory
Which of the following statements about Random Access Memory (RAM) is correct?
(Phát biểu nào sau đây về bộ nhớ truy cập ngẫu nhiên (RAM) là đúng?)
a. Stores all the files on the computer b. Is volatile
c. Can only be read sequentially
d. Is typically faster than cache memory
The four main structural elements of a computer system are:
(Bốn thành phần cấu trúc chính của hệ thống máy tính là:)
a. Processor, Main Memory, I/O Modules, System Bus b. None of the other choices
c. Processor, Registers, Main Memory, System Bus
d. Processor, Registers, I/O Modules, Main Memory
The language of the CPU is known as it...?
(Ngôn ngữ của CPU được gọi là...?) a. None of the other choices b. Register set
c. Instruction set (tập lệnh) d. Control unit set
A entry of the Process table is called?
(Một mục trong bảng tiến trình được gọi là gì?)
Process Control Block (PCB)
Which of the following cannot be shared among different threads of a process?
(Thành phần nào sau đây không thể được chia sẻ giữa các luồng của cùng một tiến trình?) a. File handles b. Process code c. Process data d. Stack (ngăn xếp)
A ...... is a portion of a process that can run independently
(...... là một phần của tiến trình có thể chạy độc lập.) a. Thread b. Program c. Miniprocess
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383 d. Subprocess
Which of the following process state transitions is correct, when the external event for
which a process was waiting happens?
(Chuyển đổi trạng thái tiến trình nào sau đây là đúng khi sự kiện bên ngoài mà tiến trình
đang chờ đợi xảy ra?) a. Running → Ready b. Blocked (waiting) → Ready
c. Running → Blocked (waiting) d. Ready → Running Hệ điều hành
Hệ điều hành là một chương trình quản lý tài nguyên phần cứng và phần mềm máy tính,
cung cấp nền tảng cho các ứng dụng phần mềm khác chạy. Nó đóng vai trò trung gian giữa
người dùng và phần cứng máy tính, cho phép người dùng tương tác với hệ thống và thực hiện
các tác vụ một cách hiệu quả. Operating System
An operating system is a program that manages computer hardware and software resources,
providing a platform for other software applications to run. It acts as an intermediary between
the user and the computer hardware, allowing users to interact with the system and perform tasks efficiently.
Mục đích của một hệ điều hành
Mục đích chính của hệ điều hành là cung cấp một môi trường trong đó các ứng dụng có thể
chạy trơn tru và sử dụng tài nguyên của máy tính một cách hiệu quả. Nó quản lý bộ nhớ, bộ
xử lý, thiết bị đầu vào/đầu ra và các tài nguyên hệ thống khác để đảm bảo hiệu suất và độ ổn định tối ưu.
Purpose of an Operating System
The main purpose of an operating system is to provide an environment in which applications
can run smoothly and utilize the computer's resources efficiently. It manages memory,
processors, input/output devices, and other system resources to ensure optimal performance and stability.
Có phải tất cả các hệ điều hành đều tương thích với mọi loại phần cứng?
Hệ điều hành được thiết kế để hoạt động với các kiến trúc phần cứng cụ thể. Điều quan trọng
là chọn một hệ điều hành tương thích với phần cứng của bạn.
Are All Operating Systems Compatible with All Types of Hardware?
Operating systems are designed to work with specific hardware architectures. It is important
to choose an operating system that is compatible with your hardware.
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383
Chức năng của hệ điều hành
(1) Quản lý tiến trình: Nó quản lý việc thực hiện các tiến trình, lập kế hoạch thực hiện và
phân bổ tài nguyên hệ thống cho chúng.
(2) Quản lý bộ nhớ: Nó kiểm soát việc phân bổ và phân bổ không gian bộ nhớ cho các tiến
trình, đảm bảo sử dụng bộ nhớ hiệu quả.
(3) Quản lý hệ thống file: Nó cung cấp cấu trúc phân cấp để tổ chức và truy cập các file (tệp) trên thiết bị lưu trữ.
(4) Quản lý thiết bị: Nó tương tác với các thiết bị phần cứng, chẳng hạn như máy in, máy
quét và ổ đĩa, tạo điều kiện thuận lợi cho việc truyền dữ liệu.
(5) Giao diện người dùng: Nó cung cấp phương tiện để người dùng tương tác với hệ thống,
chẳng hạn như thông qua giao diện dòng lệnh hoặc giao diện người dùng đồ họa.
1. Process Management: It manages the execution of processes, schedules their execution,
and allocates system resources to them.
2. Memory Management: It controls the allocation and deallocation of memory space for
processes, ensuring efficient memory usage.
3. File System Management: It provides a hierarchical structure for organizing and
accessing files on storage devices.
4. Device Management: It interacts with hardware devices such as printers, scanners, and
drives, facilitating data transfer.
5. User Interface: It provides a means for users to interact with the system, such as through a
command-line interface or a graphical user interface.
1. What is the role of an operating system in a computer?
(Hệ điều hành đóng vai trò gì trong máy tính?) a) Only runs office programs
b) Manages hardware and software resources
(Quản lý tài nguyên phần cứng và phần mềm)
c) Only manages the computer’s memory
d) Only supports software installation
2. How does an operating system work?
(Hệ điều hành hoạt động như thế nào?)
a) Acts as an intermediary between the user and hardware
(Là trung gian giữa người dùng và phần cứng)
b) Operates independently without hardware
c) Only interacts with software without managing hardware
d) Does not affect the computer’s performance
3. What is the main purpose of an operating system?
(Mục đích chính của hệ điều hành là gì?)
a) Speed up the Internet connection
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383
b) Ensure that the computer never crashes
c) Provide an environment for applications to run and manage resources efficiently
(Cung cấp môi trường để các ứng dụng chạy và quản lý tài nguyên hiệu quả)
d) Only used to display graphical interfaces
4. Which system resources does the operating system manage?
(Hệ điều hành quản lý tài nguyên nào của hệ thống?)
a) Memory, processor, input/output devices
(Bộ nhớ, bộ xử lý, thiết bị đầu vào/đầu ra) b) Only application software c) Only user data d) Only files and folders
5. Can every operating system run on any type of hardware?
(Mọi hệ điều hành đều có thể chạy trên mọi loại phần cứng đúng không?) a) True b) False
6. Why is it necessary to choose a compatible operating system for your hardware?
(Tại sao cần chọn hệ điều hành tương thích với phần cứng?)
a) Because each OS is designed for a specific hardware architecture
(Vì mỗi hệ điều hành được thiết kế cho một kiến trúc phần cứng cụ thể)
b) Because hardware can run any OS without modifications
c) Because the OS determines the speed of the hardware
d) Because the OS only works with certain types of memory
7. Which of the following is a function of the operating system?
(Chức năng nào sau đây thuộc về hệ điều hành?) a) Process management b) Memory management c) Device management d) All of the above
8. What does the process management function of an OS involve?
(Chức năng quản lý tiến trình của hệ điều hành liên quan đến việc gì?)
a) Creating, executing, and managing processes running on the system
(Tạo, thực thi, quản lý các tiến trình chạy trên hệ thống)
b) Only storing data on the hard drive c) Only monitoring CPU speed
d) Helping users create text files
9. What is the role of memory management in an operating system?
(Quản lý bộ nhớ của hệ điều hành có nhiệm vụ gì?)
a) Allocating and deallocating memory for processes
(Cấp phát và thu hồi bộ nhớ cho các tiến trình)
b) Managing the battery capacity of the computer c) Controlling Internet speed
d) Installing antivirus software
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383
10. What means does the OS provide for users to interact with the system?
(Hệ điều hành cung cấp phương tiện nào để người dùng tương tác với hệ thống?)
a) Command Line Interface (CLI) Giao diện dòng lệnh (CLI)
b) Graphical User Interface (GUI) Giao diện đồ họa (GUI) c) Both a and b d) None
Tiến trình là khái niệm cơ bản và quan trọng bậc nhất trong hệ điều hành.
Một tiến trình là một chương trình đang được thực thi, có không gian địa chỉ riêng, bộ đếm
chương trình, thanh ghi, ngăn xếp, và các tài nguyên khác.
Hệ điều hành hỗ trợ thực thi đồng thời nhiều tiến trình qua mô hình đa chương trình (Multiprogramming).
Mỗi tiến trình có thể tạo ra tiến trình con, tạo thành cây tiến trình. UNIX hỗ trợ nhóm tiến
trình, còn Windows thì không.
A process is one of the most fundamental and important concepts in operating systems.
A process is a program in execution, which has its own address space, program counter,
registers, stack, and other resources.
The operating system supports the concurrent execution of multiple processes through the multiprogramming model.
Each process can create child processes, forming a process tree. UNIX supports process
groups, while Windows does not. Tạo tiến trình
Theo nhiều cách khác nhau, chẳng hạn như khởi tạo từ hệ thống, lời gọi hệ thống, yêu cầu từ
người dùng hoặc thực thi job hàng loạt.
Việc tạo tiến trình bao gồm:
+ Khởi tạo PID (Process Identification)
+ Phân bổ các tài nguyên cần thiết.
+ Thiết lập môi trường thực thi.
+ Khởi tạo khối điều khiển tiến trình PCB (Process Control Block) + v.v..
In many different ways, such as system initialization, system calls, user requests, or batch job execution. Process creation includes:
Initializing PID (Process Identification)
Allocating the necessary resources
Setting up the execution environment
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383
Initializing the Process Control Block (PCB) Etc.
After being created, the process will transition to the New state and wait for execution.
Sau khi được tạo, tiến trình sẽ chuyển sang trạng thái Mới và chờ thực thi.
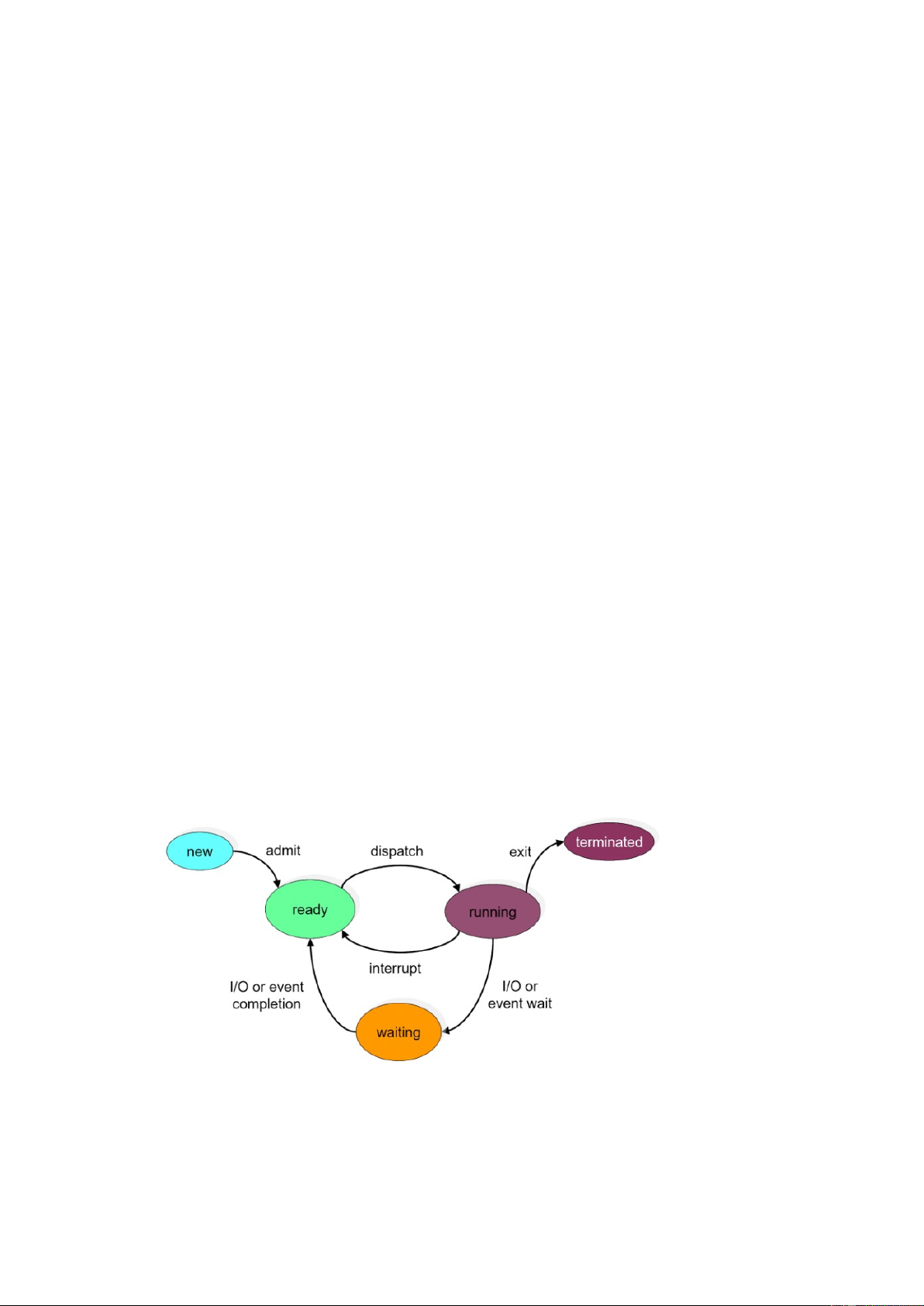
Các trạng thái của tiến trình:
Một tiến trình có thể tồn tại ở nhiều trạng thái khác nhau trong suốt vòng đời của nó:
Mới (New): Đây là trạng thái ban đầu khi một tiến trình được khởi tạo.
Sẵn sàng (Ready): Quá trình được tải vào bộ nhớ chính và chờ xử lý.
Đang chạy (Running): Quá trình đang được thực thi bởi bộ xử lý.
Bị chặn (Blocked): Quá trình không thể thực thi thêm cho đến khi một sự kiện nhất định xảy
ra, chẳng hạn như chờ người dùng nhập hoặc hoàn thành các thao tác I/O.
Chấm dứt (Terminated): Quá trình đã hoàn thành việc thực thi hoặc Đã bị chấm dứt một cách cưỡng ép.
A process can exist in many different states throughout its lifecycle:
New: This is the initial state when a process is created.
Ready: The process is loaded into main memory and waiting for execution.
Running: The process is being executed by the processor.
Blocked: The process cannot execute further until a specific event occurs, such as
waiting for user input or completing I/O operations.
Terminated: The process has completed execution or has been forcibly terminated. Kết thúc tiến trình
Sau khi chấm dứt, hệ điều hành sẽ giải phóng các tài nguyên được phân bổ, cập nhật trạng
thái của tiến trình thành “Terminated” và loại bỏ PCB của nó khỏi hệ thống. Process Termination
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383
After termination, the operating system will release the allocated resources, update the
process state to "Terminated", and remove its Process Control Block (PCB) from the system.
Khối điều khiển tiến trình PCB (Process Control Block)
Vì hệ điều hành hỗ trợ đa chương trình nên nó cần theo dõi tất cả các tiến trình thông qua hệ
thống Khối điều khiển tiến trình (PCB). Tất cả thông tin trong một PCB là bắt buộc và phải
được lưu trữ và cập nhật khi tiến trình được chuyển từ trạng thái này sang trạng thái khác.
PCB là một cấu trúc dữ liệu nằm trong Kernel của hệ điều hành có tất cả thông tin cần thiết
để phục vụ lên lịch (quản lý lịch trình) cho một tiến trình cụ thể. Các dữ liệu trong PCB thường gồm:
Since the operating system supports multiprogramming, it needs to track all processes
through the Process Control Block (PCB) system. All information in a PCB is mandatory
and must be stored and updated when a process transitions from one state to another.
PCB is a data structure located in the Kernel of the operating system, containing all
necessary information for scheduling a specific process.
The data in a PCB typically includes:
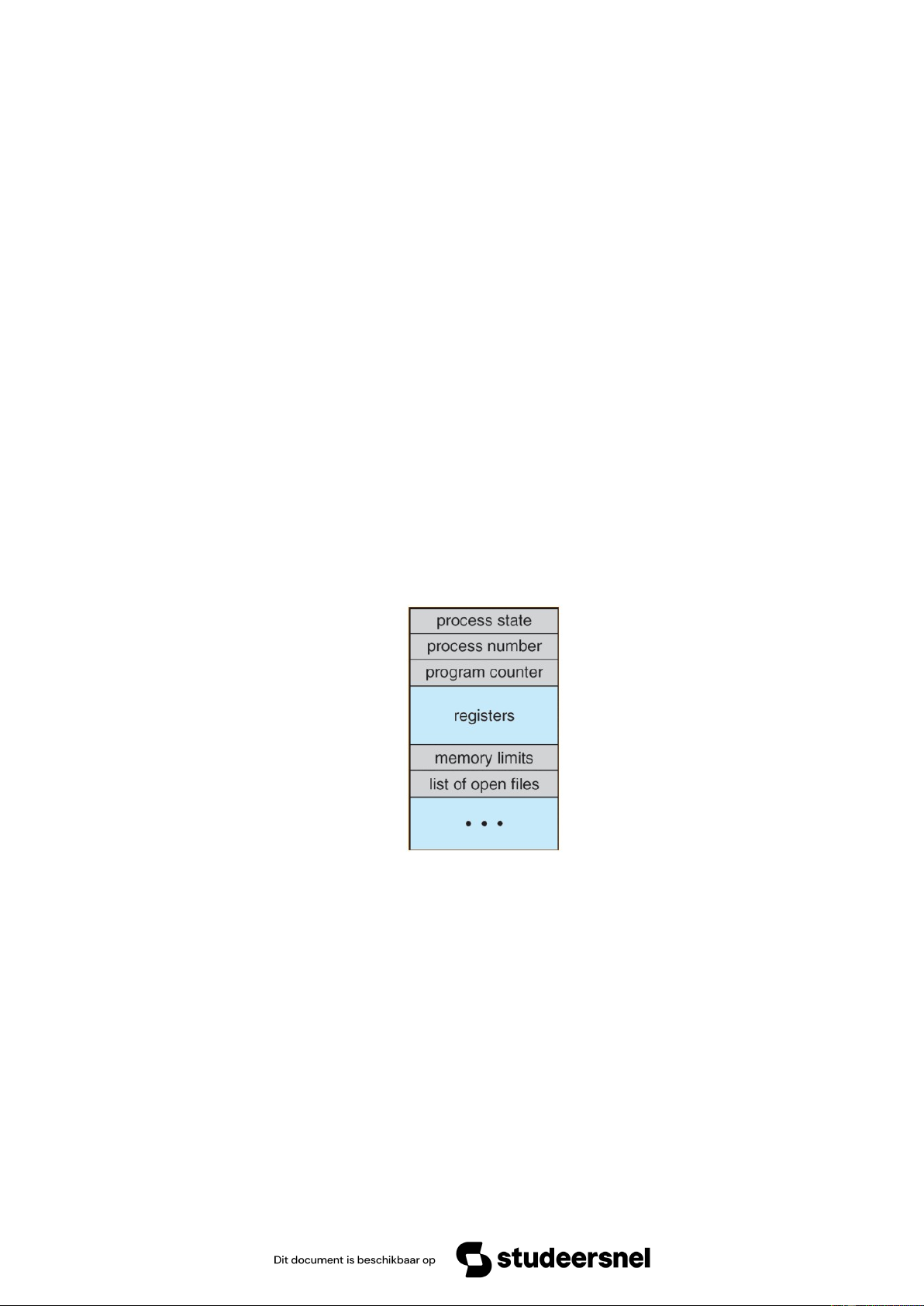
+ Trạng thái tiến trình (Process state): lưu trữ trạng thái hiện tại của tiến trình.
+ PID (Process number): mã định danh tiến trình, là số nguyên duy nhất cho mỗi tiến trình
trong bất kỳ giai đoạn thực thi nào.
+ Bộ đếm chương trình (Program counter): Nó lưu trữ bộ đếm (chứa địa chỉ của lệnh tiếp
theo sẽ được thực thi cho tiến trình).
+ Thanh ghi (Register): Đây là các thanh ghi CPU bao gồm thanh ghi tích lũy, cơ sở, thanh
ghi và thanh ghi đa năng v.v..
+ Giới hạn bộ nhớ (Memory limits): Trường này chứa thông tin về hệ thống quản lý bộ nhớ
được hệ điều hành sử dụng. Điều này có thể bao gồm các bảng trang, bảng phân đoạn, v.v.
+ Danh sách tệp mở (Open files list): Thông tin này bao gồm danh sách các tệp được mở cho tiến trình.
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383
+ Ngoài ra còn khá nhiều thông tin khác như: Thông tin lập lịch trình, Trạng thái I/O, Đặc
quyền của tiến trình, Con trỏ (Pointer: con trỏ ngăn xếp cần được lưu khi tiến trình được
chuyển từ trạng thái này sang trạng thái khác).
* PCB cho phép hệ điều hành quản lý và chuyển đổi hiệu quả giữa các tiến trình, đảm bảo
phân bổ tài nguyên hợp lý.
Chuyển đổi ngữ cảnh (Context Switch) xảy ra khi hệ điều hành thay đổi tiến trình đang thực thi.
+ Process state: Stores the current state of the process.
+ PID (Process number): A unique integer identifier for each process at any stage of execution.
+ Program counter: Stores the counter (containing the address of the next instruction to be executed for the process).
+ Registers: These are CPU registers, including the accumulator, base register, general- purpose registers, etc.
+ Memory limits: This field contains information about the memory management system
used by the operating system. This may include page tables, segment tables, etc.
+ Open files list: This information includes a list of files that are currently open for the process.
+ Additionally, there are several other pieces of information such as: Scheduling information I/O status Process privileges
Pointer (Stack pointer that needs to be saved when a process transitions from one state to another).
*The PCB allows the operating system to efficiently manage and switch between
processes, ensuring proper resource allocation.
Context Switching occurs when the operating system changes the currently executing process.
1. What does the Process Control Block (PCB) store? A. Only the process ID B. Only the process state
C. Information necessary for process management D. Only the program counter
2. Which field in the PCB contains the address of the next instruction to be executed? A. Process ID B. Registers C. Program counter D. Open files list
3. What is the role of the PID in the PCB?
A. It stores the process execution time
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383
B. It uniquely identifies each process
C. It determines the memory allocation
D. It tracks the number of active processes
4. Which of the following is NOT stored in the PCB? A. Process state B. CPU temperature C. Open files list D. Memory limits
5. What is the function of the "Registers" field in the PCB?
A. To store the list of open files
B. To hold CPU register values for the process C. To manage I/O devices
D. To determine process scheduling
6. Which part of the PCB contains information about memory management? A. Process ID B. Memory limits C. Scheduling information D. Program counter
7. What happens during a Context Switch?
A. The operating system switches from one process to another
B. The program counter is deleted
C. The process executes its final instruction D. The system shuts down
8. Which of the following best describes Context Switching?
A. A process terminating itself
B. Storing and restoring process state during a switch
C. Deleting a process from memory D. Creating a new process
9. Why does the OS need to store the stack pointer in the PCB? A. To allocate memory
B. To keep track of the process’s execution state C. To store process privileges D. To manage open files
10. Which component of the PCB ensures that a process gets the correct amount of CPU time? A. Memory limits B. Open files list C. Scheduling information D. Registers LẬP LỊCH TIẾN TRÌNH
Trọng tâm của lập lịch trình:
+ Giữ CPU bận rộn nhất có thể nếu có các tiến trình đang chờ thực thi.
+ Giảm thời gian hoàn thành các tiến trình quan trọng.
+ Thông minh trong việc ưu tiên thực thi các tiến trình ưu tiên.
+ Giữ thời gian phản hồi của các tiến trình ở mức tối thiểu.
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383 PROCESS SCHEDULING Core Objectives of Scheduling:
+ Keep the CPU as busy as possible if there are processes waiting for execution.
+ Minimize the completion time of important processes.
+ Prioritize the execution of high-priority processes efficiently.
+ Maintain process response time at a minimal level.
Các loại bộ lập lịch
- Bộ lập lịch dài hạn (Long-term Scheduler): Trình lập lịch công việc (Job Scheduler)
- Bộ lập lịch trung hạn (Medium-term Scheduler): Tập trung hoán đổi lưu trữ tại bộ nhớ chính/phụ.
- Bộ lập lịch ngắn hạn (Short-term Scheduler): Bộ lập lịch CPU (CPU Scheduler) Types of Schedulers:
Long-term Scheduler (Job Scheduler): Controls job admission into the system.
Medium-term Scheduler: Focuses on swapping processes in and out of main/secondary memory.
Short-term Scheduler (CPU Scheduler): Decides which process will be executed by the CPU next.
Các thuật toán lập lịch CPU
+ FCFS (First Come First Served)
+ SJF non-preemptive (Shortest Job First non-preemptive)
+ SRTF - Shortest Remaining Time First (SJF preemptive) + RR (Round-Robin) + Priority non-preemptive + Priority preemptive Ngoài ra:
+ HRRN - Highest Response Ratio Next + MLQ - Multilevel Queue
+ MLFQ - Multilevel Feedback Queue
+ Lập lịch thời gian thực
1. What is the main goal of process scheduling?
(Mục tiêu chính của lập lịch tiến trình là gì?)
A. To execute all processes at the same time
B. To ensure the CPU remains busy if there are waiting processes
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383
(Đảm bảo CPU luôn bận rộn nếu có tiến trình đang chờ thực thi)
C. To terminate processes as quickly as possible D. To increase memory usage
2. Which type of scheduler controls job admission into the system?
(Bộ lập lịch nào kiểm soát việc đưa tiến trình vào hệ thống?) A. Short-term Scheduler B. Medium-term Scheduler
C. Long-term Scheduler (Bộ lập lịch dài hạn) D. Real-time Scheduler
3. Which scheduler is responsible for swapping processes between main and secondary memory?
(Bộ lập lịch nào chịu trách nhiệm hoán đổi tiến trình giữa bộ nhớ chính và bộ nhớ phụ?) A. Long-term Scheduler B. Short-term Scheduler
C. Medium-term Scheduler (Bộ lập lịch trung hạn) D. Real-time Scheduler
4. Which of the following scheduling algorithms executes processes in the order they arrive?
(Thuật toán lập lịch nào thực thi tiến trình theo thứ tự chúng đến trước?) A. SJF B. FCFS C. Round-Robin D. Priority Scheduling
5. Which CPU scheduling algorithm selects the process with the shortest remaining time?
(Thuật toán lập lịch CPU nào chọn tiến trình có thời gian còn lại ngắn nhất?) A. FCFS B. RR C. SRTF D. Priority Scheduling
6. In Round-Robin (RR) scheduling, what determines when a process is switched out?
(Trong thuật toán Round-Robin (RR), điều gì quyết định khi nào một tiến trình bị chuyển ra?) A. Process priority B. Process arrival time
C. A fixed time quantum (Một khoảng thời gian cố định) D. The process execution time
7. Which of the following is a preemptive scheduling algorithm?
(Thuật toán lập lịch nào có tính chất ưu tiên cưỡng bức (preemptive)?) A. FCFS B. SJF Non-preemptive C. Priority Preemptive D. HRRN
8. What is the main purpose of the Multilevel Feedback Queue (MLFQ) scheduling?
(Mục đích chính của thuật toán Multilevel Feedback Queue (MLFQ) là gì?)
A. To execute processes in the order they arrive
B. To assign processes to different priority levels and allow movement between them
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn) lOMoARcPSD|61803383
(Phân tiến trình vào các mức ưu tiên khác nhau và cho phép chúng di chuyển giữa các mức)
C. To execute the shortest job first
D. To ensure fairness in CPU time allocation
9. Which scheduling algorithm is typically used in real-time systems?
(Thuật toán lập lịch nào thường được sử dụng trong các hệ thống thời gian thực?) A. FCFS B. RR C. SRTF D. Real-time Scheduling
10. that is the main difference between Priority Preemptive and Priority Non- preemptive scheduling?
(Sự khác biệt chính giữa Priority Preemptive và Priority Non-preemptive là gì?)
A. In Preemptive, a higher-priority process can interrupt a running process, whereas in Non-preemptive, it cannot
(Trong Preemptive, tiến trình có độ ưu tiên cao hơn có thể ngắt tiến trình đang chạy,
còn Non-preemptive thì không)
B. In Non-preemptive, processes execute randomly
C. Preemptive scheduling always runs the longest process first
D. Non-preemptive scheduling is faster than preemptive scheduling
Downloaded by TR?N ??C D?NG (dungtd.24ite@vku.udn.vn)



