




Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 36443508
Nội dung n tập thi học kỳ m n hệ điều h nh
- H nh thức thi: trắc nghiệm online -
Thời gian dự kiến: 75 phœt - Nội dung:
o C u hỏi l thuyết thuần tœy
o C u hỏi dạng b i tập o CÆc phần nội dung:
Tổng quan về hệ điều h nh quản l tiến tr nh
deadlock, đồng bộ h a tiến tr nh
bộ nhớ, bộ nhớ ảo hệ thống tập tin
Một số c u hỏi mẫu
1. An optimal scheduling algorithm in terms of minimizing the average waiting time of a given set of process is … a. FCFS scheduling
b. Round robin scheduling algorithm
c. Shortest job first scheduling algorithm
d. Priority scheduling algorithm
2. The hardware mechanism that enables a device to notify the CPU is called ……. a. polling b. interrupt c. system call d. none of the above
3. Inter process communication can be done through …. a. mails b. messages c. system calls d. traps
4. Which scheduler controls the degree of multiprogramming? a. Short term scheduler b. Long term scheduler c. Middle term scheduler d. Pre term scheduler
5. For a multiple instances of resource type which algorithm is used …….
a. divide and conquer algorithm b. banker’s algorithm c. partition algorithm d. sorting algorithm
6. The methods for dealing with the deadlock problem is lOMoARcPSD| 36443508
a. Use a protocol to make sure that the system never enters in to the deadlock state.
b. Allow the system to enter a deadlock state and then recover.
c. Ignore the problem, and pretend that deadlocks never occur in the system. The UNIX
operating system uses this solution. d. all of these
7. A system has 3 processes sharing 4 resources. If each process needs a maximum of 2 units, then a. deadlock can never occur b. deadlock may occur c. deadlock has to occur d. none of these
8. Access to moving head disks requires three periods of delay before information is
brought into memory. The response that correctly lists the three time delays for the
physical access of data in the order of the relative speed from the slowest to the fastest is
a. latency time, cache overhead time, seek time
b. transmission time, latency time, seek time
c. seek time, latency time, transmission time
d. cache overhead time, latency time, seek time
9. If a disk has a seek time of 20 ms, rotates 20 revolutions per second, has 100 words per
block, and each track has capacity of 300 words. Then the total time required to access one block is a. 25 b. 30 c. 40 d. 60
10. Consider a computer with 8 Mbytes of main memory and a 128 K cache. The cache block
size is 4 K. It uses a direct mapping scheme for cache management. How many different
main memory blocks can map onto a given physical cache block ? a. 2048 b. 256 c. 64 d. None of these
11. Consider a logical address space of 8 pages of 1024 words mapped into memory of 32
frames. How many bits are there in the physical address? a. 9 bits b. 11 bits c. 13 bits d. 15 bits
12. In five state process model …………………… state is a process that is prepared to execute when given the opportunity. lOMoARcPSD| 36443508 a. Ready b. Paused c. Queued d. Blocked
13. …………………….. transition occurs when it is time to select a new process to run, the
operating system chooses one of the processes in the ready state. e. Null → Ready f. Ready → Running g. New → Ready h. Running → Ready
14. Which of the following is/are the characteristics of suspended process.
i) The process is not immediately available for execution. ii)
The process may or may not be waiting on an event
iii) The process will remove from this state whether the agent explicitly orders the removal or not. i. i and ii only j. ii and iii only k. i and iii only l. All i, ii and iii
15. The process image includes which of the following elements
i) user data ii) user program iii) system stack iv) process control block m. i, ii and iv only n. ii, iii and iv only o. i, iii and iv only p. All i, ii, iii and iv
16. With respect to ………………………. , in virtually all operating systems each process is
assigned a unique numeric identifier, which may simply be an index into the primary process table. q. Process identification
r. Processor sate identification
s. Processor state information
t. Process control information
17. ………………. is a decision to add a new process to the set of processes that are currently
active. It is performed when a new process is created. a. Long term scheduling b. Medium term scheduling c. Short term scheduling d. I/O scheduling
18. …………….. is the actual decision of which ready process to execute next. u. Long term scheduling lOMoARcPSD| 36443508 v. Medium term scheduling w. Short term scheduling x. I/O scheduling
19. Which of the following are the algorithms have been developed for making the
shortterm-scheduling decision.
i) Round robin ii) Shortest Process Next (SPN) iii) Shortest Remaining Time (SRT) iv) Feedback a. i, ii and iii only b. ii, iii and iv only c. i, iii and iv only d. All i, ii, iii and iv
20. …………….. algorithm use time slicing to limit any running process to a short burst of
processor time, and rotate among all ready processes. a. Round robin
b. Shortest Process Next (SPN)
c. Shortest Remaining Time (SRT) d. Feedback
21. …………… policy reduces the bias in favor of long processes inherent in first come first served (FCFS). a. Round robin
b. Shortest Process Next (SPN)
c. First Come First Served (SCFS) d. Feedback
22. A ……………… is one that can be safely used by only one process at a time and is not depleted by that use. a. Reusable Resource b. Single Process Resource c. Consumable Resource d. Produced Resource
23. ……………….. is needed to ensure consistency of results and integrity of a database. a. Mutual Exclusion b. Hold and Wait c. Preemption d. Circular Wait
24. …………………… cannot be done arbitrary and especially when data resources are involved,
must be supported by a rollback recovery mechanism. a. Mutual Exclusion b. Hold and Wait c. Preemption d. Circular Wait lOMoARcPSD| 36443508
25. Invoking periodically to test for deadlock is one of the way for deadlock ……………….. a. Prevention b. Avoidance c. Detection d. Deletion
26. The indirect method of …………………. is to prevent the occurrence of one of the three
necessary conditions: Mutual exclusion, Hold and Wait and No preemption. a. deadlock prevention b. deadlock avoidance c. deadlock detection d. deadlock deletion
27. …………….. is based on the use of one or both of two basic techniques: segmentation and paging. a. memory partitioning b. virtual memory c. real memory d. memory organization
28. In …………… there is no internal fragmentation and is more efficient use of main memory. a. Fixed partitioning b. Dynamic partitioning c. Virtual memory paging d. Simple segmentation
29. Which of the following is/are the strengths of virtual memory segmentation techniques used in memory management.
i) No internal fragmentation ii) Higher
degree of multi programming iii) More
efficient to use of main memory iv) Large virtual address space
v) Protection and sharing support a. i, ii, iii and iv only b. i, ii, iii and v only c. i, ii, iv and v only d. ii, iii, iv and v only
30. A ……………… is a reference to a memory location independent of the current assignment
of data to memory in which a translation must be made to a physical address before the
memory access can be achieved. a. virtual address b. relative address c. physical address d. logical address lOMoARcPSD| 36443508
Một số b i tập mẫu
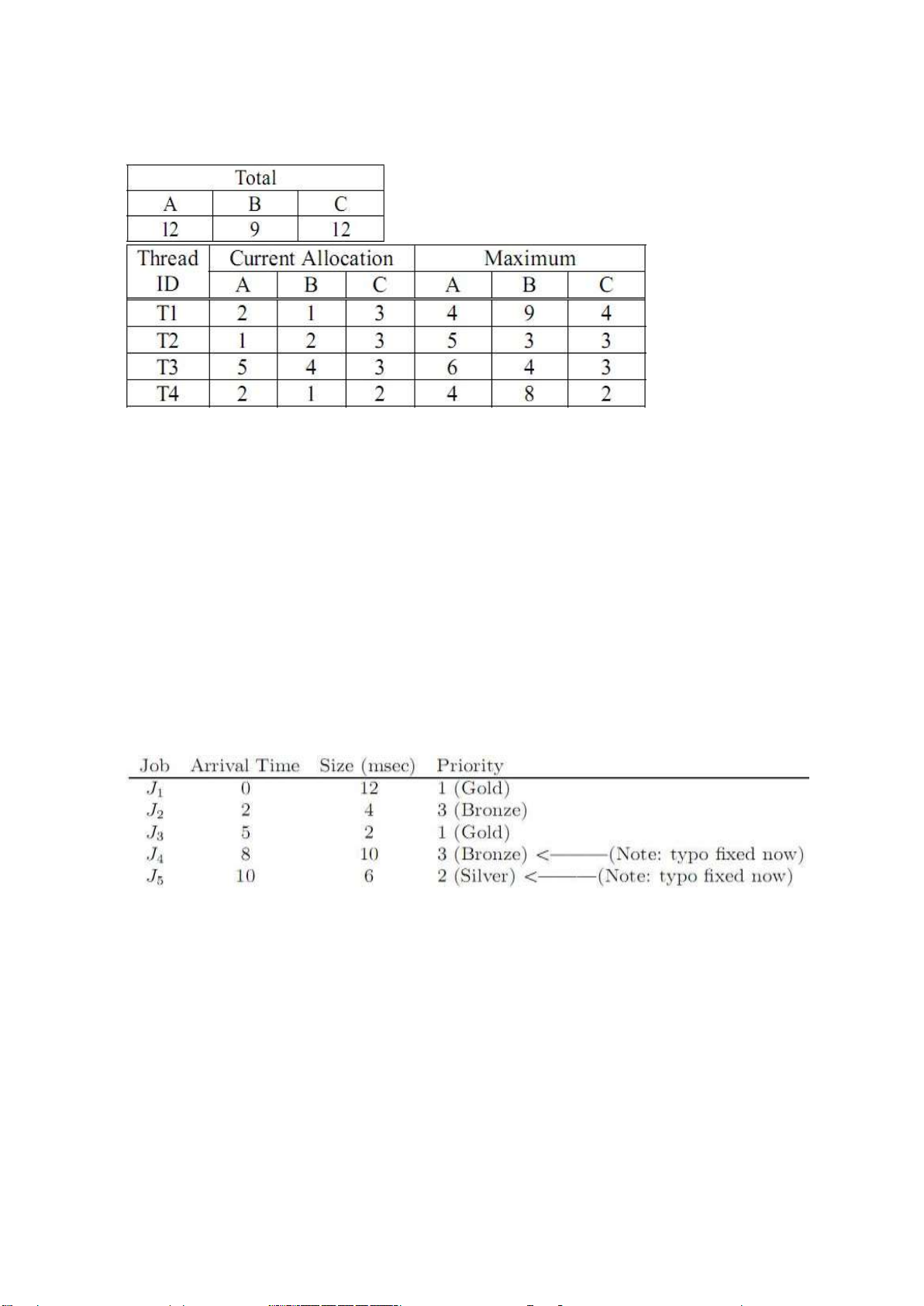
1. Giả sử chœng ta c cÆc t i nguyŒn A,B,C v cÆc thread T1, T2, T3, T4, tổng số t i nguyŒn,
yŒu cầu tối đa và trạng thÆi cấp phÆt hiện tại l :
a. Hệ thống c ở trạng thÆi an to n kh ng ? nếu c tr nh b y thứ tự thực thi cÆc thread,
ngược lại chứng minh hệ thống kh ng an to n
b. Giả sử trạng thÆi của hệ thống như trong câu a, giả sử T1 yŒu cầu thŒm 2 bản sao t i
nguyŒn A ? hệ thống c thể gÆn cho n kh ng ? giải th ch
c. Giả sử trạng thÆi hệ thống như ở trong c u a. t nh số t i nguyŒn tối đa A, B, C mà T1 có
thể được gÆn trong 1 yŒu cầu m kh ng g y rủi ro deadlock. Giải th ch
2. XØt 1 hệ thống tập tin với cÆc khối 4096Bytes v cÆc con trỏ khối đĩa và tập tin 32 bit, mỗi
tập tin c 13 con trỏ trực tiếp, 4 con trỏ giÆn tiếp cấp 1, 1 con trỏ giÆn tiếp cấp 2, 1 con
trỏ giÆn tiếp cấp 3. T nh :
a. Kích thước đĩa tối đa có thể được hỗ trợ
b. Kích thước tập tin tối đa
3. Giả sử cÆc Job sau tới như được chỉ ra trong hình để điều phối v thực thi trŒn 1 CPU
Vẽ biểu đồ Gantt tr nh b y cho thuật toán điều phối sau v t nh thời gian chờ trung b nh cho cÆc Job a. FCFS b. SJF kh ng trưng dụng c. SJF chưng dụng d. RR với quantum =4 e. Ưu tiên (trưng dụng)
4. Consider the following paging memory system: There are 4 page table entries (with
values of 0xC, 0x2, 0x8, 0x5 for entries 0…3, respectively). The physical memory is 128
bytes, with frames of 8 bytes each.
a. How large (the number of bits) is the physical address?
b. How large is the virtual address? lOMoARcPSD| 36443508
c. What is the physical address (in hex) that corresponds to virtual address 0x1D
d. What is the physical address (in hex) that corresponds to virtual address 0x03?
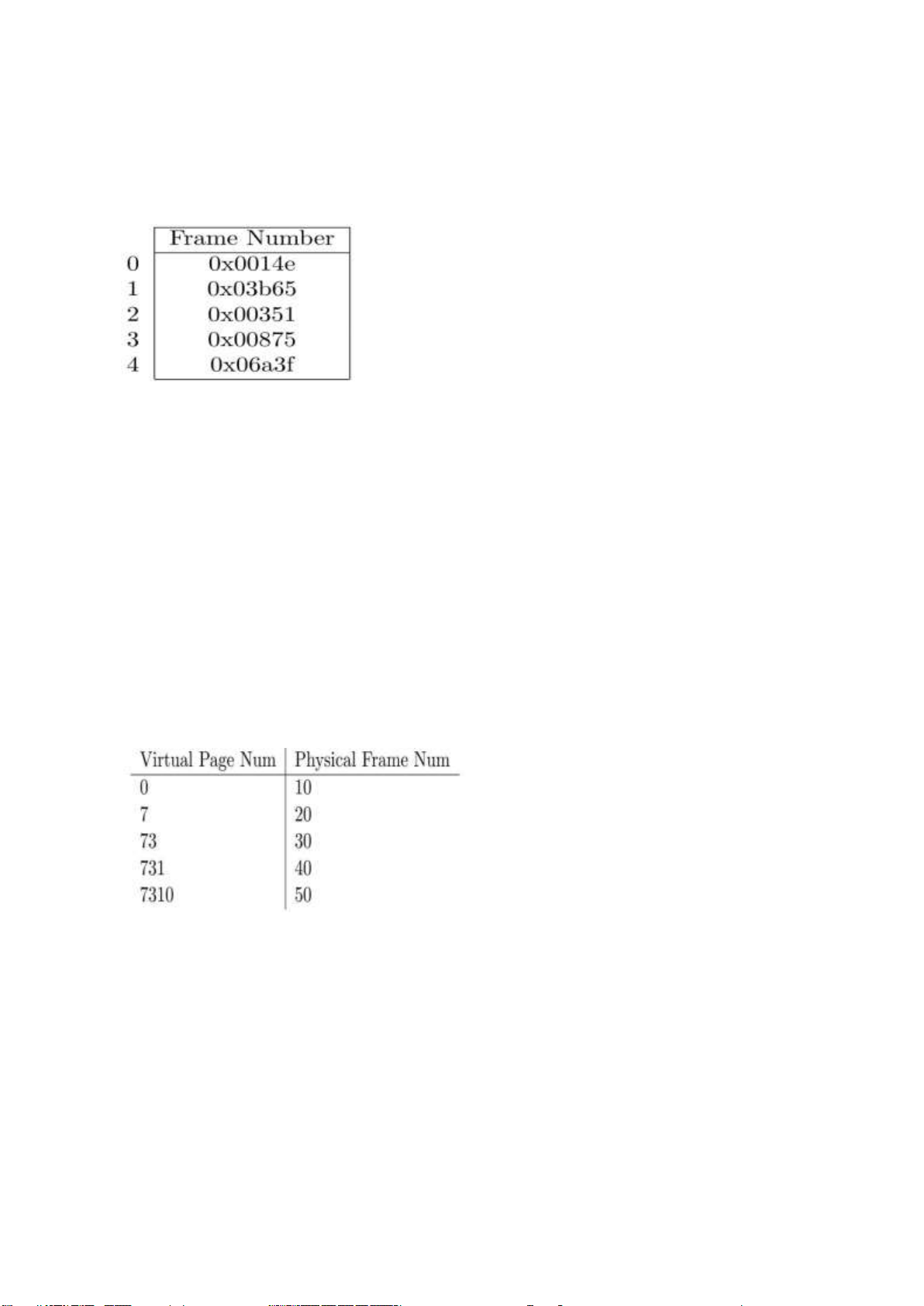
5. Consider a virtual memory system that uses paging. Virtual and physical addresses are
both 32 bits long, and the page size is 4KB = 212 bytes. A process P1 has the following
page table. Frame numbers are given in hexadecimal notation (recall that each
hexadecimal digit represents 4 bits)
a. For each of the following virtual addresses, indicate the physical address to which it
maps. If the virtual address is not part of the address space of P1, write NO
TRANSLATION instead. Use hexadecimal notation for the physical addresses. 0x00003b65 0x00006a3f 0x00000fe6
b. For each of the following physical addresses, indicate the virtual address that maps to it.
If the physical address is not part of the physical memory assigned to P1, write NO
TRANSLATION instead. Use hexadecimal notation for the virtual addresses 0x00351fff 0x03b65000 0x000e3000
6. Consider a machine with 24-bit virtual addresses and a page size of 512 bytes. During a
program execution the TLB contains the following valid entries (all in octal)
Translate the following virtual address (in octal) into a 24-bit physical address (in octal).
Show and explain how you derived your answer. Express the final physical address using
all 24-bits. Virtual address = 07310525
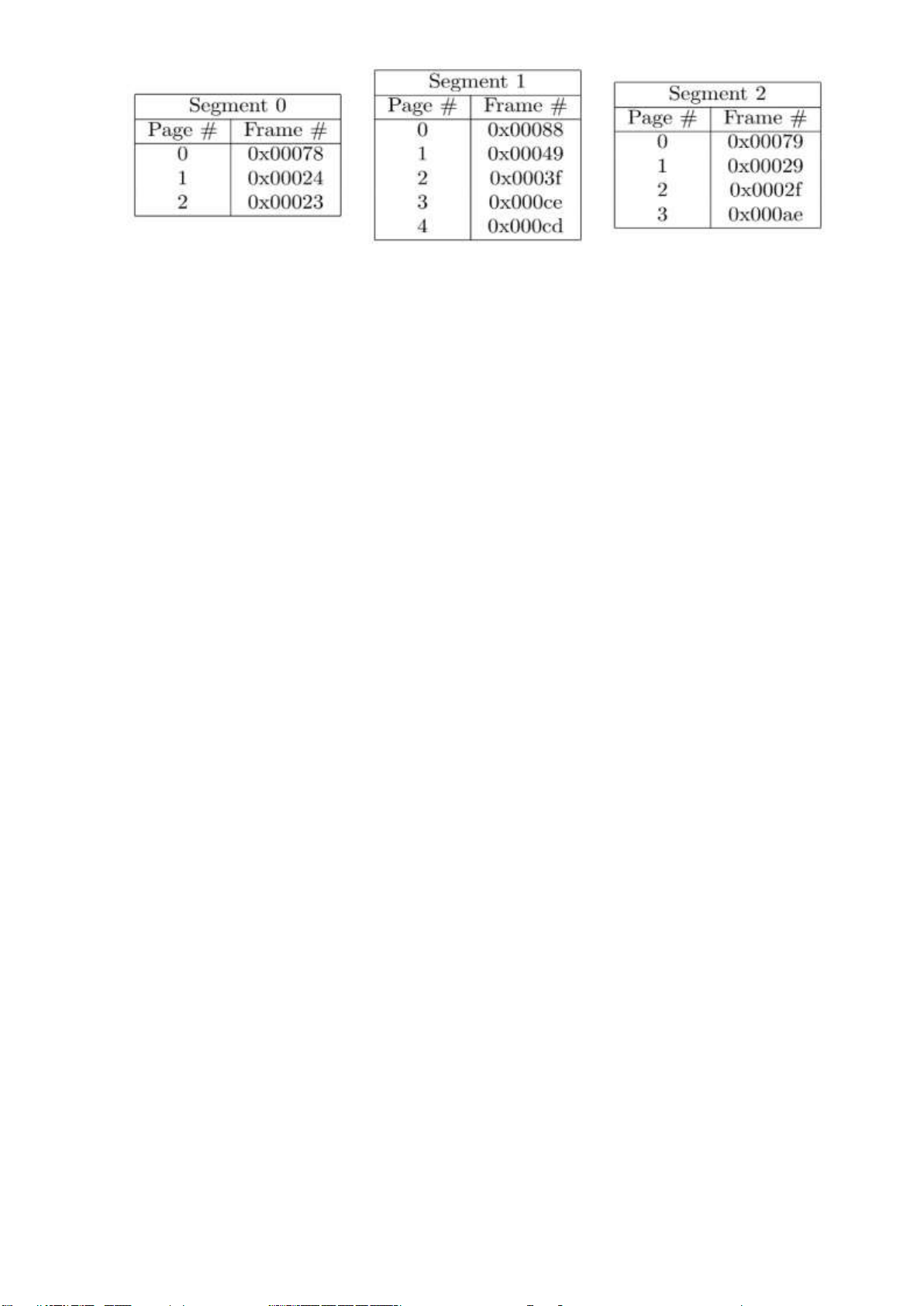
7. Consider a virtual memory system that uses segmentation combined with paging. Virtual
addresses in this case are of the form (seg #, page #, offset). In this system, virtual and
physical addresses are both 32 bits long, a process may have 16 segments, and the page
size is 4KB (212 bytes). A process P has three segments, and the following page tables are
associated with its 3 segments. Frame numbers are given in hexadecimal: lOMoARcPSD| 36443508
a. For each of the following virtual addresses (given in hexadecimal), indicate the
physical address to which it maps. If the virtual address is not part of the address space
of P, write NO TRANSLATION instead. Use hexadecimal notation for the physical addresses. 0x20001a60 0x000052ef 0x10004ab3 0xa00003c9
b. Explain how the virtual memory system would enable another process Q to share Segment 2 with process P.
c. Give one reason that would make it useful to share segments between processes as in part (b) of this question




