

Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Business Strategic Management CHAPTER 1: Key term in ● External O and T: strategic + PESTLE (society) management + 5 FORCE (trong ngành)
- Threat of New Entrants (Nguy cơ từ các đối thủ mới)
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers (Sức mạnh đàm phán từ phía nhà cung cấp)
- Bargaining Power of Buyers (Sức mạnh đàm phán từ phía người mua)
- Threat of Substitutes (Nguy cơ từ các sản phẩm thay thế)
- Competitive Rivalry (Sự cạnh tranh giữa các đối thủ) ● Internal S and W
- Porter’s Value Chains - SWOT
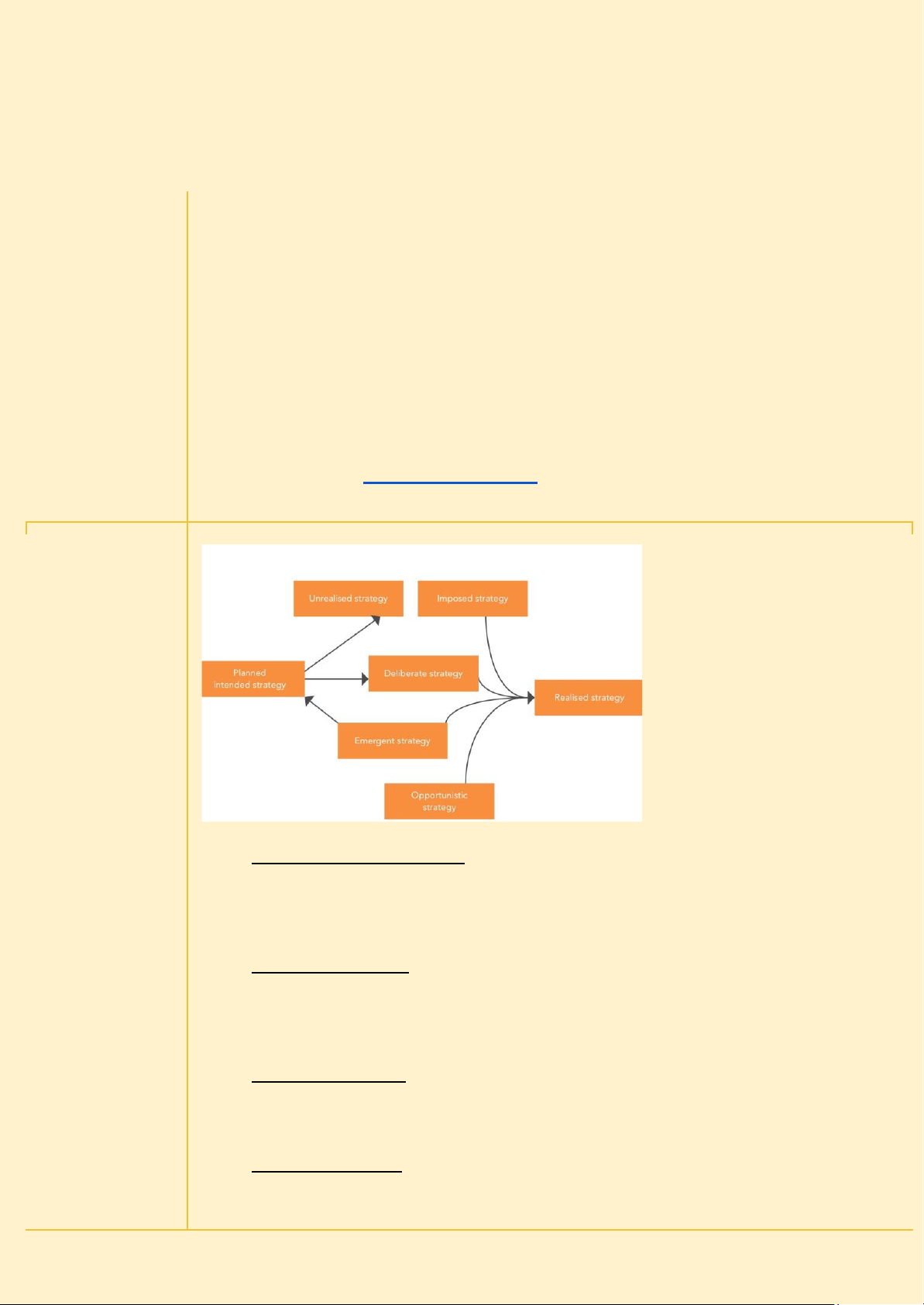
7 loại chiến lược
1. Planned Intended Strategy
○ This is the strategy that a company initially plans based on its goals, vision, and market analysis.
○ However, not all intended strategies become realized due to unforeseen challenges.
2. Unrealised Strategy
○ Part of the intended strategy that fails to materialize due to changes in the
environment, poor execution, or internal constraints.
○ This represents the gap between what was planned and what actually happened.
3. Deliberate Strategy
○ The portion of the intended strategy that is successfully implemented as planned.
○ It moves forward as expected and contributes to the realized strategy. 4. Emergent Strategy
○ Unexpected strategies that arise due to external opportunities or internal learning. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
○ These are not planned but develop organically in response to changing conditions.
○ Emergent strategies often help businesses adapt and stay competitive.
5. Opportunistic Strategy
○ A subset of emergent strategy that occurs when a company actively takes
advantage of unforeseen opportunities in the market.
○ This is more flexible and can be seen in businesses that pivot their approach. 6. Imposed Strategy
○ Strategies that are forced upon a company due to external factors (e.g.,
government regulations, economic crises, or market disruptions).
○ These may not align with the original strategic intent but must be adopted to survive. 7. Realised Strategy
○ The final actual strategy that a company ends up implementing.
○ It is a mix of deliberate, emergent, opportunistic, and imposed strategies.
○ Rarely does a company’s realized strategy match 100% with its planned intended strategy. Key Takeaways:
● Strategy is not always linear – what a company plans may not always happen as expected.
● Adaptability is crucial – successful companies balance deliberate planning with emergent flexibility.
● Realized strategy is a mix of intentions, reactions, and imposed changes in the business environment. PHÂN LOẠI
1. Phân cấp quản lý doanh nghiệp: CHIẾN LƯỢC
● SBU (Strategic Business Unit) Strategy - Chiến lược đơn vị kinh doanh KINH DOANH
- A distinct business division within a larger company CỦA DNTM
- Operates independently: mission, goals, and competitive strategy.
- Focuses on how each unit can compete effectively in its market while aligning
with the overall corporate strategy. 16/1/2024 lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 - Product life cycle:
- 3 Basic Goals of a Business + Maximizing Profit + Expanding Influence + Ensuring Security
- 7 Criteria for Objectives + Specificity + Flexibility + Measurability + Feasibility + Consistency + Advancement + Rationality




