

Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 Chapter 20: Job Order Costing
1. Job Order Costing Systems:
● Mục đích: phân chi phí cho mỗi Job cụ thể được hoàn thành (Cost per Job)
● Đặc điểm: áp dụng cho những Job có đặc điểm khác biệt từng sản phẩm (Unique products)
● Example: custom housing construction, marketing and public relations services
2. Job Order Costing Flow: (kèm transactions) Bước 0:
● Mua nguyên vật liệu bằng tiền hoặc ghi nợ mua thiếu: Dr. Raw Materials Inventory
Cr. Accounts Payable / Cr. Cash
● Tính lương phải trả cho công nhân: Dr. Factory Labor Cr. Factory Wages Payable
Cr. Employer Payroll Taxes Payable
● Charge những chi phí sản xuất chung: Dr. Manufacturing Overhead Cr. Accounts Payable
Cr. Accumulated Depreciation- Equipment Cr. Utilities Payable lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 Cr. Prepaid Insurance
Bước 1: Assign Manufacturing Costs ⇒ Work in Process Inventory Dr. Work in Process Inventory Cr. Raw Materials Inventory Cr. Factory Labor Cr. Manufacturing Overhead
**NOTE 1**: Thông thường khi charge từ RM, FL sang WIP Inventory không đơn giản như concept trên mà thường có cả Direct cost
và Indirect cost ở cả RM và FL. Vậy nên sẽ có những transaction dưới đây: Example: Dr. Work in Process Inventory 24,000 Dr. Manufacturing Overhead 6,000 Cr. Raw Materials Inventoty 30,000
(Giải thích: dùng $24,000 direct materials và $6,000 indirect materials ở quá trình đang sản xuất, direct material ⇒
WIP Inventory, indirect material ⇒ Manufacturing Overhead) Example: Dr. Work in Process Inventory 28,000 Dr. Manufacturing Overhead 4,000 Cr. Factory Labor 32,000
(Giải thích: dùng $28,000 direct labor và $4,000 indirect labor ở quá trình đang sản xuất, direct labor ⇒ WIP Inventory, indirect labor
⇒ Manufacturing Overhead) lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
**NOTE 2**: Thông thường công ti sẽ ước tính trước các chi phí sản xuất chung OH sử dụng trong WIP bằng cách sử dụng Rate để
tính (Estimated OH >>> Actual OH) bởi actual cuối kì sau khi sản xuất xong mới biết xài hết nhiêu.
- Công thức tính Predetermined Overhead Rates:
Estimated Annual Overhead Costs : Estimated Direct Labor Costs = Predetermined OH Rate
- Applied OH = Predetermined OH Rate x Direct Labor Costs được sử dụng
Example: Công ti lập ngân sách cho Annual Overhead Cost là $280,000 và Direct Labor Cost là $350,000. Tính applied OH giả định
rằng Direct labor cost là $28,000.
+Compute OH rate: Predetermined OH Rate = Annual OH Cost : Direct Labor Cost = 280,000 : 350,000 = 80%
+Calculate Applied OH = $28,000 x 80% = $22,400 +Record entry:
Dr. Work in Process Inventory 22,400 Cr. Manufacturing Overhead 22,400
Bước 2: Assign Work in Process Inventory ⇒ Finished Goods Inventory (ra thành phẩm cuối) completed goods/jobs Dr. Finished Goods Inventory Cr. Work in Process Inventory
Bước 3: Sau khi thành phẩm đã ra lò, bán hàng và ghi nhận doanh thu sold
Dr. Cash/ Dr. Accounts Receivable Cr. Sales Revenue lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 Dr. Cost of Goods Sold Cr. Finished Goods Inventory
3. Điều chỉnh cuối kì cho Manufacturing Overhead (Adjusting entry):
Đầu kì mình ước tính Applied OH và cuối kì có Actual OH thực tế phát sinh, nếu:
+ Actual OH > Applied OH: Underapplied và Debit to COGS (tăng thêm lượng OH do thực tế xài hao hơn)
+ Actual OH < Applied OH: Overapplied và Credit to COGS (giảm lượng OH do ước tính lố hơn) Example: Dec.31, Dr. Manufacturing Overhead 2,500 Cr. Cost of Goods Sold 2,500
(Giải thích: Applied OH= 22,500 but Actual OH= 20,000. Overapplied OH $2,500 và Credit to COGS 2,500)
4. Ngoài lề: At the end of each month,
Số dư của Work in Process Inventory BẰNG tổng Cost của những Job chưa hoàn thành trong Job Cost Sheet.
Số dư của Finished Goods Inventory BẰNG tổng Cost của những Job đã hoàn thành và chưa sold trong Job Cost Sheet.
Những Job sold thì sẽ thành Cost of Goods Sold và ghi nhận Sales Revenue. lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
—------------------------------------BÀI TẬP ÁP DỤNG—---------------------------------------
Problem Set P20-1A page 933 (pdf)
Lott Company uses a job order cost system and applies overhead to production on the basis of direct labor costs. On January
1, 2017, Job 50 was the only job in process. The costs incurred prior to January 1 on this job were as follows: direct materials
$20,000, direct labor $12,000, and manufacturing overhead $16,000. As of January 1, Job 49 had been completed at a cost
of $90,000 and was part of finished goods inventory. There was a $15,000 balance in the Raw Materials Inventory account.
During the month of January, Lott Company began production on Jobs 51 and 52, and completed Jobs 50 and 51. Jobs 49
and 50 were also sold on account during the month for $122,000 and $158,000, respectively. The following additional
events occurred during the month.
1. Purchased additional raw materials of $90,000 on account.
2. Incurred factory labor costs of $70,000. Of this amount $16,000 related to employer payroll taxes.
3. Incurred manufacturing overhead costs as follows: indirect materials $17,000, indirect labor $20,000, depreciation
expense on equipment $12,000, and various other manufacturing overhead costs on account $16,000.
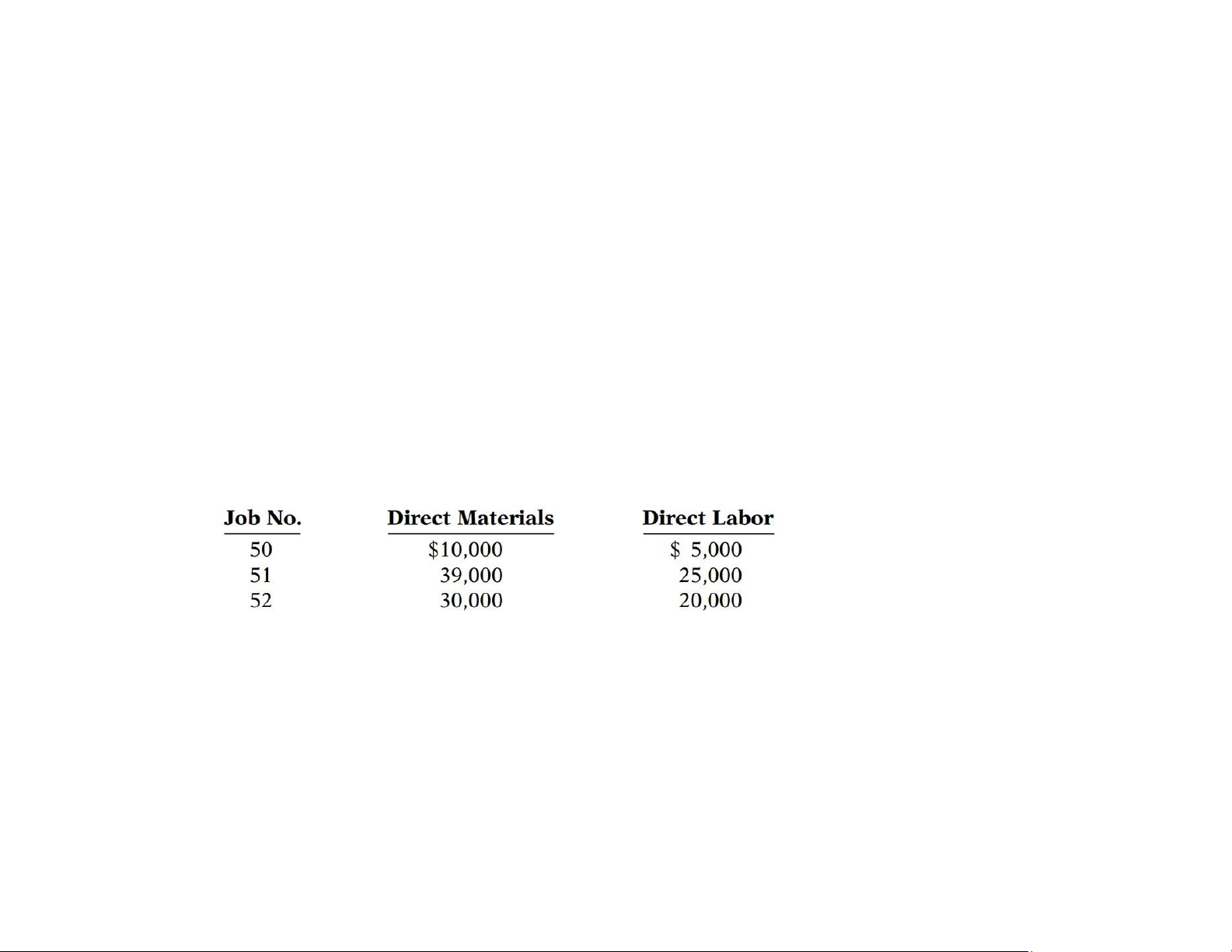
4. Assigned direct materials and direct labor to jobs as follows. Instructions:
(a) Calculate the predetermined overhead rate for 2017, assuming Lott Company estimates total manufacturing overhead costs
of $840,000, direct labor costs of $700,000, and direct labor hours of 20,000 for the year. (b) Open job cost sheets for Jobs 50,
51, and 52. Enter the January 1 balances on the job cost sheet for Job 50. (c) Prepare the journal entries to record the purchase
of raw materials, the factory labor costs incurred, and the manufacturing overhead costs incurred during the month of January.
(d) Prepare the journal entries to record the assignment of direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead costs to
production. In assigning manufacturing overhead costs, use the overhead rate calculated in (a). Post all costs to the job cost sheets as necessary. lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
(e) Total the job cost sheets for any job(s) completed during the month. Prepare the journal entry (or entries) to record the completion
of any job(s) during the month.
(f) Prepare the journal entry (or entries) to record the sale of any job(s) during the month.
(g) What is the balance in the Finished Goods Inventory account at the end of the month? What does this balance consist of?
(h) What is the amount of over- or underapplied overhead?
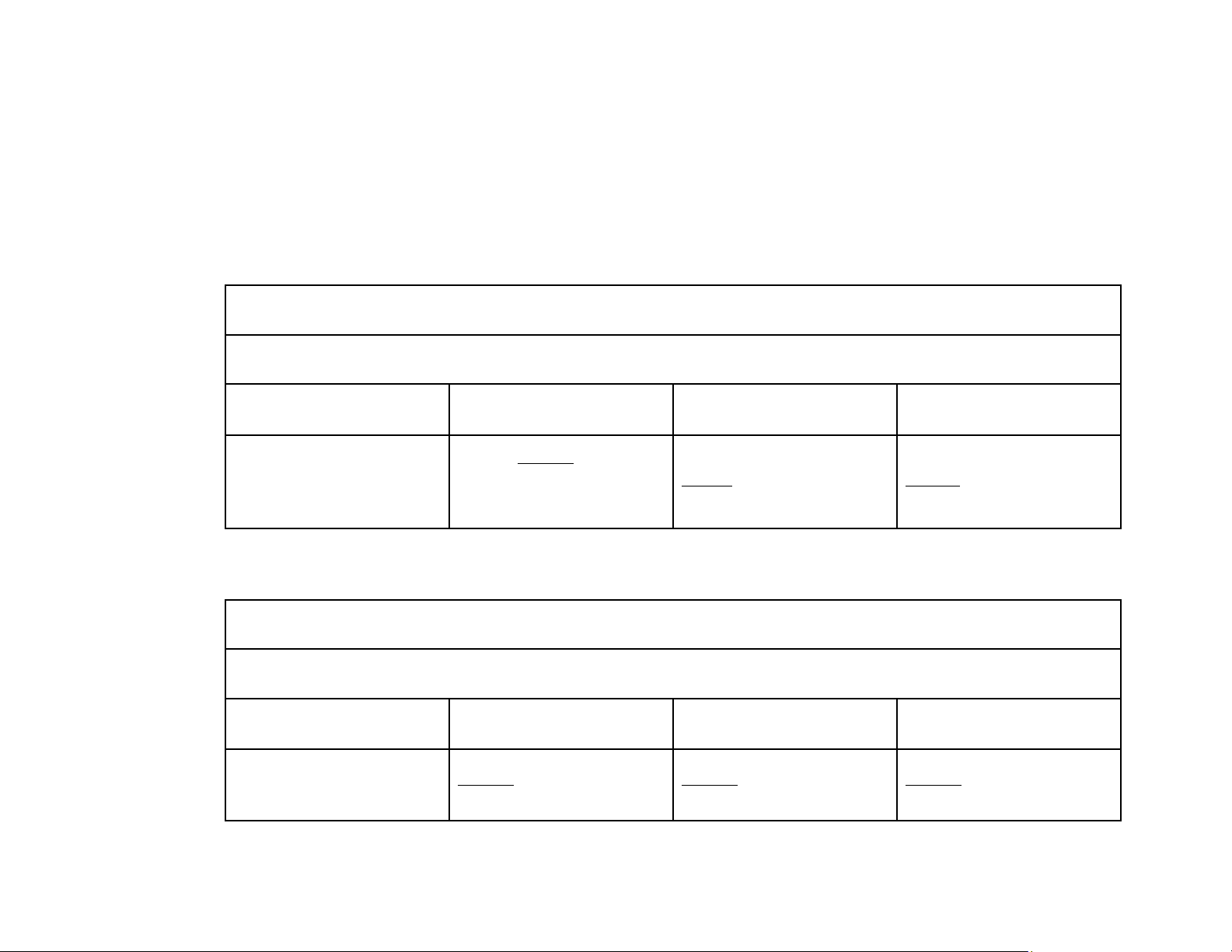
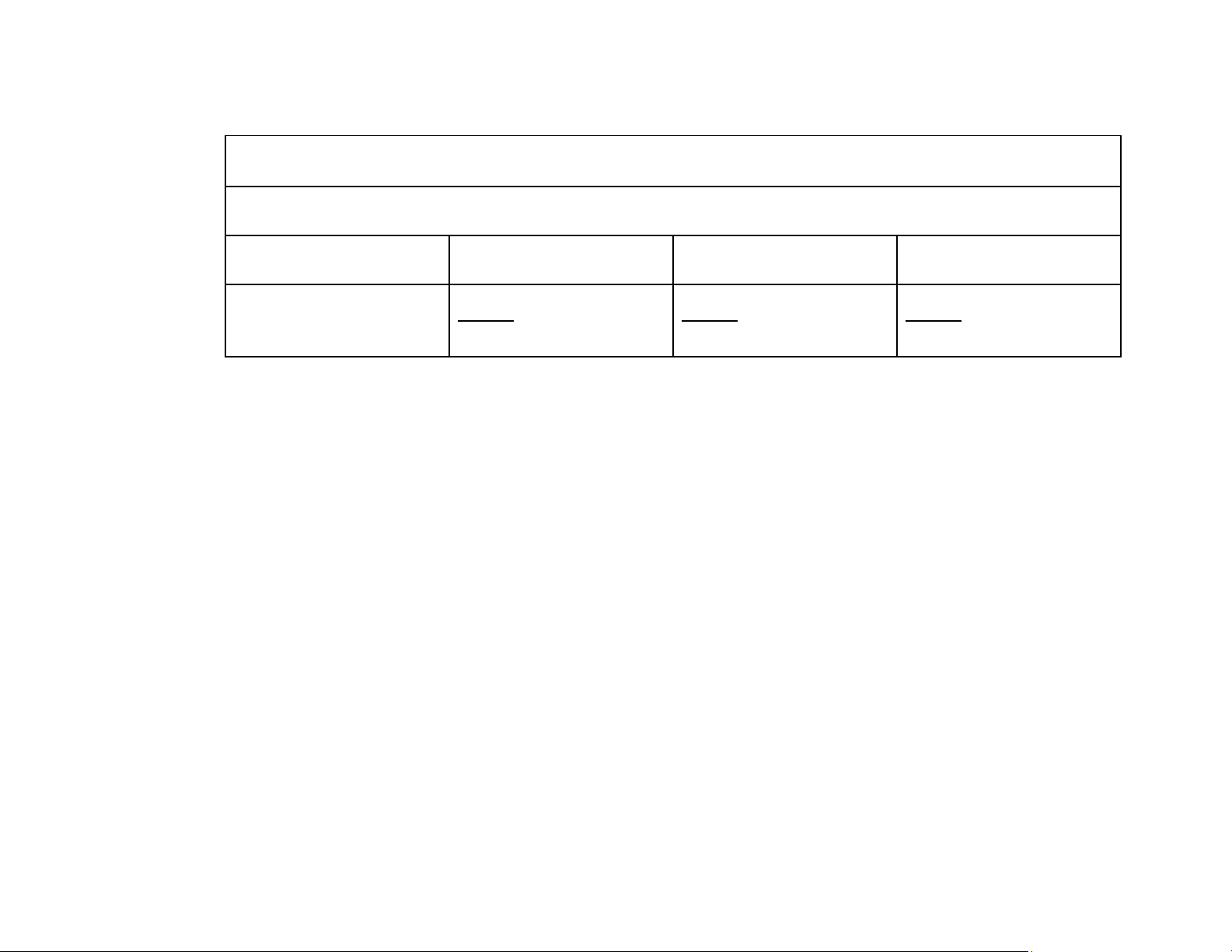
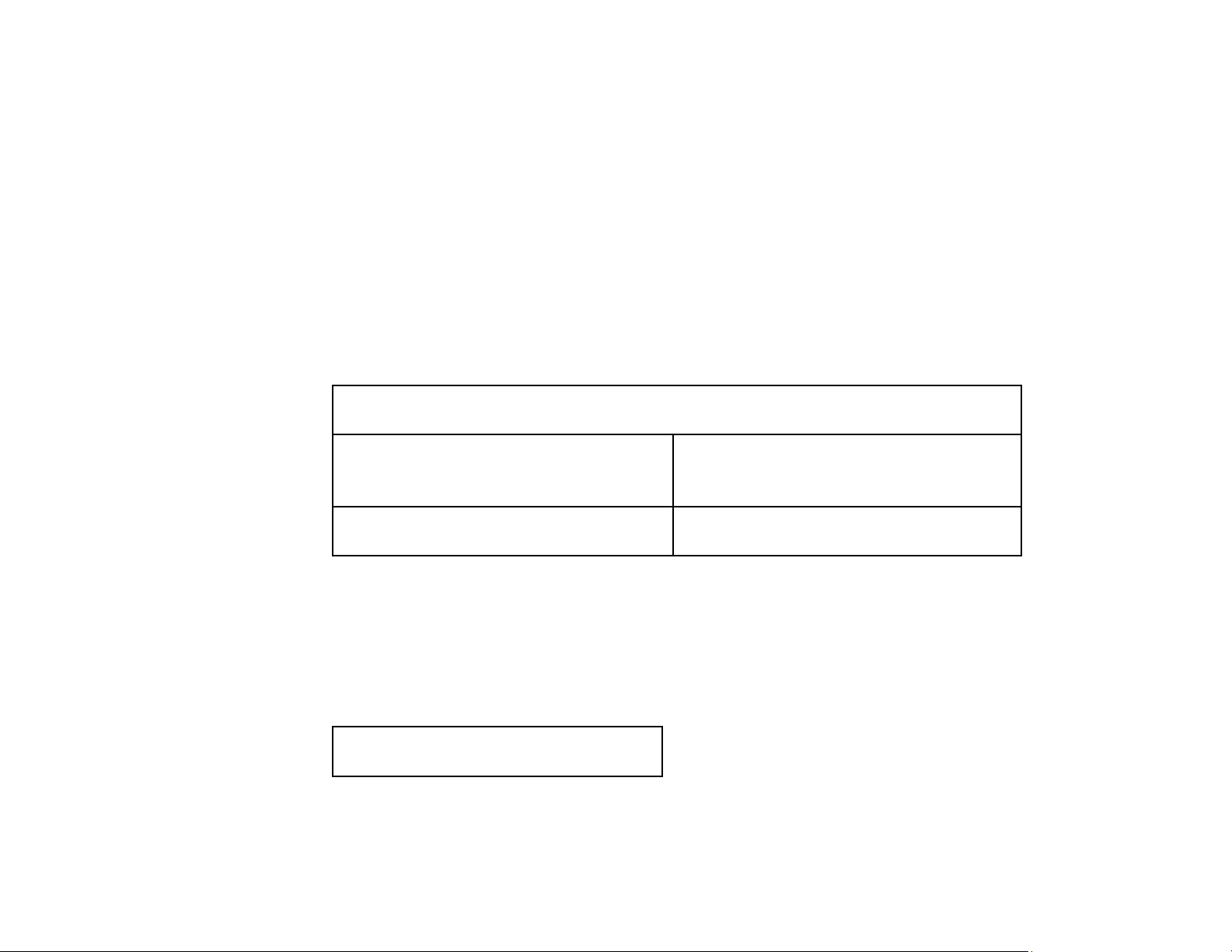
a) Predetermined Overhead Rate = Estimated annual OH cost : estimated DL cost = 840,000 : 700,000 = 120% b) Job Cost Sheet Job No. 50 Date Direct Materials Direct Labor Manufacturing Overhead Beg. Jan. $20,000 10,000 $12,000 $16,000 $30,000 5,000 $17,000 6,000 (5,000 x 120%) $22,000 Job Cost Sheet Job No. 51 Date Direct Materials Direct Labor Manufacturing Overhead Jan. $39,000 $25,000 $30,000 (25,000 x 120%) $39,000 $25,000 $30,000 lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 Job Cost Sheet Job No. 52 Date Direct Materials Direct Labor Manufacturing Overhead Jan. $30,000 $20,000 $24,000 (20,000 x 120%) $30,000 $20,000 $24,000 c) (1) Dr. Raw Materials Inventory 90,000 Cr. Accounts Payable 90,000 (2) Dr. Factory Labor 70,000 Cr. Factory Wages Payable 54,000
Cr. Employer Payroll Taxes Payable 16,000 (3) Dr. Manufacturing Overhead 65,000 Cr. Accounts Payable 16,000
Cr. Accumulated Depreciation- Equipment 12,000 Cr. Raw Materials Inventory 17,000 Cr. Factory Labor 20,000
d) Dr. Work in Process Inventory 79,000 Cr. Raw Materials Inventory 79,000
(10,000 + 39,000 + 30,000 của Job 50, Job 51, Job 52) Dr. Work in Process Inventory 50,000 lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 Cr. Factory Labor 50,000
(5,000 + 25,000 + 20,000 của Job 50, Job 51, Job 52) Dr. Work in Process Inventory 60,000 Cr. Manufacturing Overhead 60,000
(50,000 x 120% tổng OH của Job 50, Job 51, Job 52 hoặc 6,000+30,000+24,000) e) Cost of completed Job 50 Direct materials $30,000 Direct labor 17,000 Manufacturing overhead 22,000 Total cost $69,000 Cost of completed Job 51 Direct materials $39,000 Direct labor 25,000 Manufacturing overhead 30,000 Total cost $94,000 Dr. Finished Goods Inventory 163,000
Cr. Work in Process Inventory (69,000 + 163,000 94,000 của Job 50, Job 51) Dr. Finished Goods Inventory 90,000 Cr. Work in Process Inventory 90,000 lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 (90,000 của Job 49) f) Dr. Accounts Receivable 280,000 Cr. Sales Revenue 280,000
(122,000 + 158,000 từ Job 49 và Job 50 sold) Dr. Cost of Goods Sold 159,000 Cr. Finished Goods Inventory 159,000
(90,000 + 69,000 của Job 49 và Job 50) g) Finished Goods Inventory
Beg. Balance (Job 49) 90,000 (Cost
159,000 (Cost of Job 49, 50 are sold)
of completed job 50, 51) 163,000 End. Balance 94,000
The balance of this account approximately includes the cost of completed Job No.51 which has been sold. (Giải thích: Các
Job 50, 51 hoàn thành sẽ chuyển stage từ WIP Inventory sang Finished Goods Inventory, Job 49, 50 sold nên sẽ từ Finished
Goods Inventory thành COGS và ghi nhận Revenue.
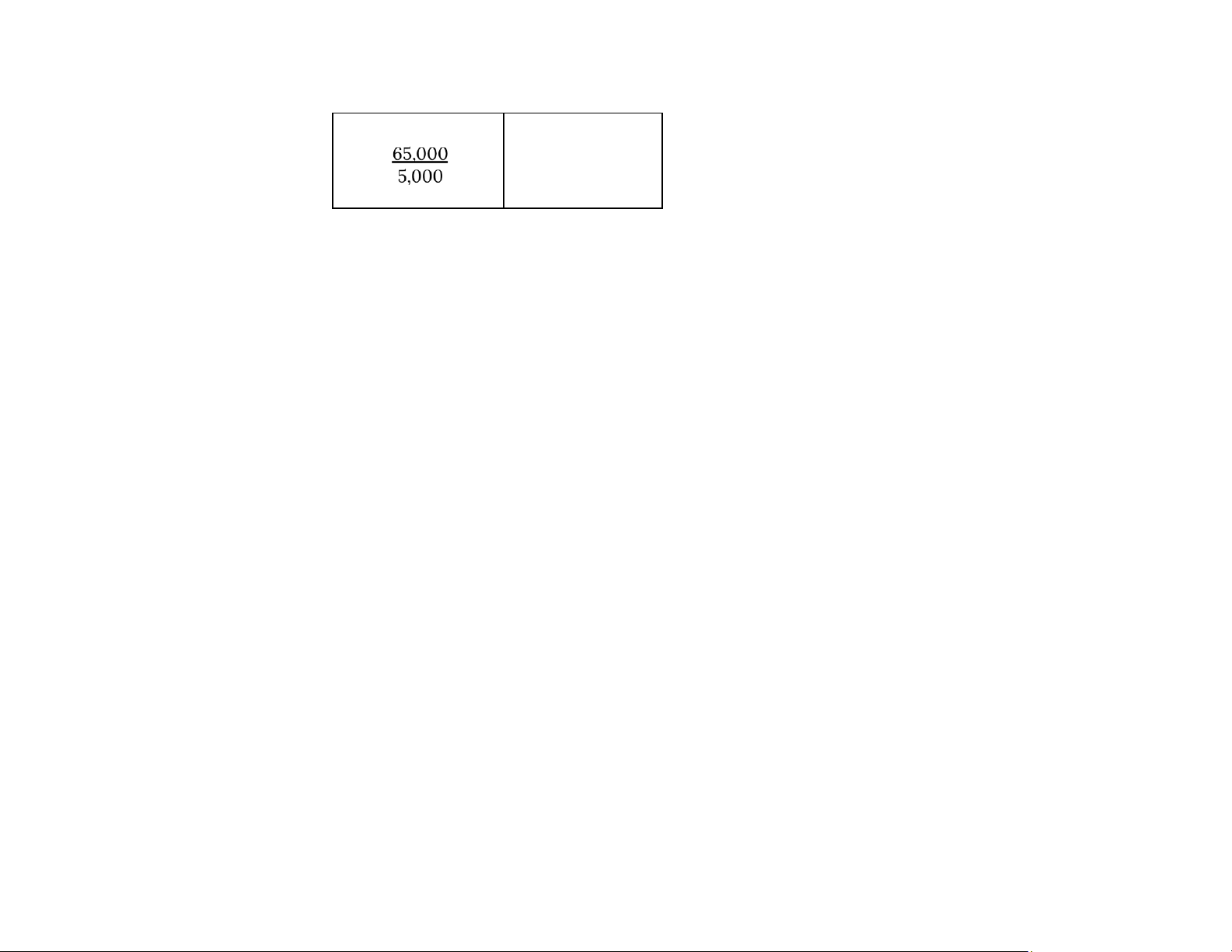
Đề cho Job 49 đã hoàn thành vào ngày 1/1 sẽ là Beginning balance của Finished Goods Inventory) h) Underapplied $5,000 Manufacturing Overhead lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 Actual Applied 60,000