




Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Chapter 1: WHAT IS BUSINESS ETHICS? Business Ethics Defined
=> understanding and implementing principles, values, and norms that guide
behavior in a business context. (originate from individuals, organizational
statements, or from the legal system) - Ethics’s determination:
Morals: Personal beliefs about right and wrong. These are individual and subjective.
E.g: If you believe lying is wrong, that’s your moral belief.
Principles: Specific boundaries for behavior, often becoming the basis for
rules (e.g., human rights, freedom of speech).
E.g: The principle of honesty means always telling the truth.
Values: enduring beliefs and ideals that are socially enforced. Several
desirable or ethical values for business today are teamwork, trust, and integrity.
E.g: If a company values teamwork, it encourages employees to work
together and support each other.
- an individual’s personal moral values are only one factor in the ethical decision-making process
Investors, employees, customers, interest groups, the legal system, and the
community => often determine whether a specific action or standard is
ethical or unethical => (their judgements) influence the determination of
what is ethical or unethical for business and society’s acceptance or
rejection of business practices => can be at odds with one another ( btw wrong and right )
Reasons for studying business ethics
This course aims at introducing students to various ethical concepts in
business related to the practice of your professions
A Crisis in Business Ethics => is a major concern totday
Surveys like the National Business Ethics Survey (NBES) reveal that a significant
number of employees observe misconduct in their workplaces. For example,
45% of employees reported seeing misconduct, and 65% of these cases were
reported to management, indicating an increase in awareness and reporting. (tr 6)
To handle the financial cricis => come under greater scrutiny by many
different constituents (consumers, employees, investors, government regulators,
and special interest gorup) Effects of Misconduct: lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 Decreased Trust
Reduced trust results in Lower customer satisfaction and loyalty,
=> negatively impacting the firm or industry
Specific Ethical Issues => becoming worse Evidence of declining ethical standards:
Misuse of company resources: Misappropriation or wastage of resources for personal benefit. abusive behavior harassment accounting fraud
conflicts of interest: Personal interests conflicting with professional duties, as
seen with Chesapeake Energy’s CEO, Aubrey McClendon.
defective products: Selling products known to be unsafe
bribery: the crime of giving someone money or something else of value, often
illegally, to persuade that person to do something you want
employee theft: stealing from the company by employees
In every realm, for example, business, politics, science, spot, etc. most
decisions are judged either right or wrong, ethical or unethical. Regardless
of what an individual believes about a particular action, if society judges it
to be unethical or wrong, new legislation usually follows. Whether correct
or not, that judgment directly affects a company’s ability to achieve its
business goals. Furthermore, the public is more tolerant of questionable
consumer practices than of similar business practices. The more successful
a company, the more the public is critical when misconduct occurs.
Although large companies like Whole Foods have significant power,
pressures from the community still limit what they can do.For this reason
alone, it is important to understand business ethics, identify ethical issues,
and recognise the approaches available for resolving them.
Furthermore, Individuals’ personal moral philosophies and decision-
making experience may not be sufficient to guide them in the business
world. Just being a good person and having sound personal values may not
be sufficient to handle the ethical issues that arise in a business
organization. ( Real-World Examples: Zale Corp.'s
claim that its Celebration Fire diamonds were the "most brilliant diamonds in the world" led to a
lawsuit from Sterling Jeweler’s Inc. for false advertising. The judge ruled it was puffery, an
exaggerated claim, rather than a serious attempt to mislead. tr ) lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Understanding business ethics is crucial for several reasons: •
Maintaining Trust: Ethical practices help build and maintain trust with the public and stakeholders. •
Ensuring Sustainability: Ethical behavior promotes long-term success and sustainability. •
Navigating Regulations: Awareness of ethical issues helps businesses
navigate and comply with evolving regulations, reduce risk of the company under strict laws in place •
Enhancing Reputation: Upholding ethical standards enhances a company’s
reputation and can lead to better customer and employee loyalty. The Nature Of Ethics
Normative ethics: Provide a general theory that tells us what is right or wrong
Deontology => Concentrate on the act being performed. According
to deontological theories, certain types of act are intrinsically
good or bad, e.g: good or bad in themselves. These acts ought or
ought not to be performed, irrespective of the consequences.
Consequentialism => hold that we ought always to act in the way
that brings about the best consequences. It doesn’t matter what
those acts are; the end justifies the means. All that matters for
ethics is making the world a better place.
Virtue Ethics: Concentrates on the moral character of the agent =>
ought to possess certain character traits–courage, generosity, compassion,
etc.–and these ought to be manifest in our actions. => may act in ways that
exhibit the virtues, even if that means doing what might generally be seen
as bad or bringing about undesirable consequences. Meta ethics
(analytic ethics): Look at the works of ethics and try to make sense of everything that is going on.
is the branch of ethics => focused on understanding the nature and
meaning of ethical properties ( ặc trưng,VD:
right or wrong), statements, attitudes, and judgments.
ethical properties: When we say "honesty is good," what do we mean by "good"?
Ask some fundamental questions to determine ethics pratices such as lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
What does it mean for an action to be right? (what these terms really mean?)
E.g: Does "right" mean that the action leads to happiness, or does it mean something entirely different?
Is good the same thing as desirable?
E.g: If everyone desires something, does that make it good? Or are there good
things that people might not desire?
How can a moral principle be justified?
E.g: If we say "lying is wrong," meta-ethics will find what reasons or evidence
support this principle? Are these reasons objective or subjective?
Is there such a thing as moral truth?
E.g: "kindness is good." Meta-ethics asks if this is an objective truth that applies
universally or if it’s true only within certain contexts
Are statements like "murder is wrong" objectively true regardless of
personal beliefs, or are they true only within certain cultures or perspectives?
Meta-ethics provides a deeper understanding of ethical concepts by
exploring their meanings and the reasons behind moral beliefs.
Applied ethics: The actual application of ethical theory for the purpose of
choosing an ethical action in a given issue.
Apply moral norms to specific moral issues or cases (particularly those
in a profession such as medicine or law).
Applied ethics in these fields goes under names such as medical ethics,
journalistic ethics, and business ethics.
In applied ethics we study the results derived from applying a moral
principle or theory to specific circumstances.
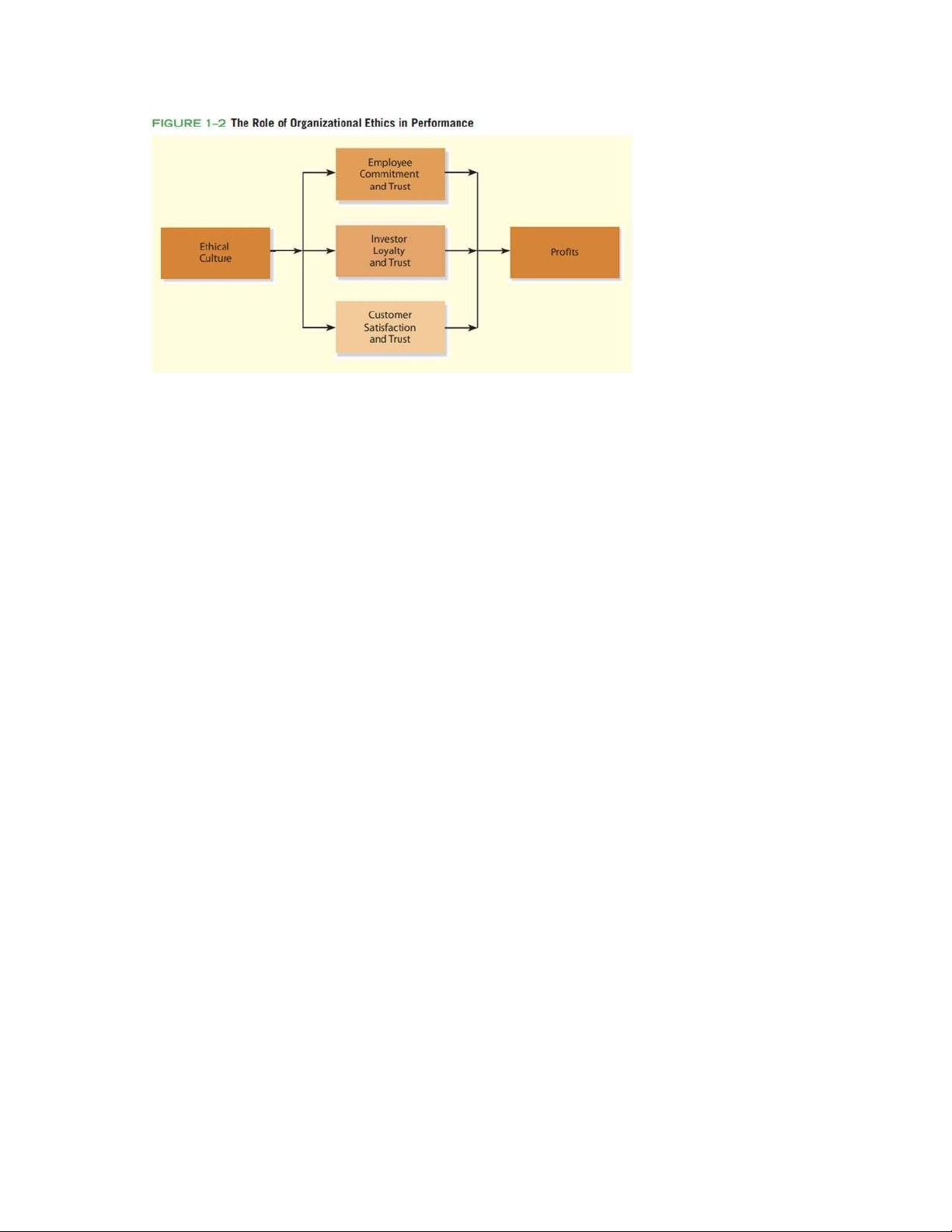
THE BENEFITS OF BUSINESS ETHICS
the rewards for being more ethical and socially responsible in business are:
increased efficiency in daily operations greater employee commitment
increased investor willingness to entrust funds
improved customer trust and satisfaction better financial performance
The reputation of a company has a major effect on its relationships with
employees, investors, customers, and many other parties. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
a, Ethics Contributes to Employee Commitment
- Employee commitment arises when workers believe their future is tied to the
organization and are willing to make personal sacrifices for it. Companies
perceived as highly ethical by their employees are more likely to retain them and foster a loyal workforce.
- An ethics and compliance program can support values and appropriate conduct.
- Employees’ perceptions that their firm has an ethical culture lead to
performance enhancing outcomes within the organization.
- A strong ethical culture within a company leads to enhanced performance,
creativity, job satisfaction, and lower turnover.
- Trust among employees and management improves decision-making
efficiency and overall organizational performance.
One survey found that when employees see values such as honesty, respect, and trust applied
frequently in the workplace, they feel less pressure to compromise ethical standards, observe
less misconduct, are more satisfied with their organizations overall, and feel more valued as employees.
b, Ethics Contributes to Investor Loyalty
- Ethical conduct builds shareholder loyalty and supports broader social causes.
- Investors today are increasingly concerned with the ethics and social
responsibility of companies they invest in. They recognize that an ethical
culture provide foundations for efficiency, productivity, and profit.
Negative publicity, lawsuits, and fines can lower stock prices and diminish
customer loyalty => threaten a company’s long-term viability.
- One survey shows that investors prefer companies with strong ethical
standards over those with higher returns but questionable ethics. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Therefore, gaining investors’ trust and confidence is vital to sustaining the
financial stability of the firm
c, Ethics Contributes to Customer Satisfaction
- Customer satisfaction is one of the most important factors in a successful
business strategy. High levels of corporate misconduct decrease consumer
trust. On the other hand, increasing trust and sastification.
- Focus on customer satisfaction => deepens the customer’s dependence on
the company => as the confidence grow => gain a better understanding of how to serve the company.
A happy customer will come back
- Trust is essential to a good long-term relattionship between a business and customer
c, Ethics Contributes to Profits
- Ethical conduct is linked to better financial performance
- A company cannot nurture and develop an ethical culture unless it has
achieved adequate financial performance in terms of profits.
- Companies perceived by their employees as having a high degree of honesty
and intergrity have a higher average total return to shareholders.
Ethics, rather than being just a function of compliance, becoming an
integral part of management’s effort to achieve competitive advantage



