

















Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
CHAPTER 1: THE IMPORTANCE OF BUSINESS ETHICS
Business ethics comprises organization principles, values, and norms that may originate
from individuals, organizational statements, or from the legal system that primarily guide
individual and group behavior in business. EQ: p25
CHAPTER 2: STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS, SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY AND
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
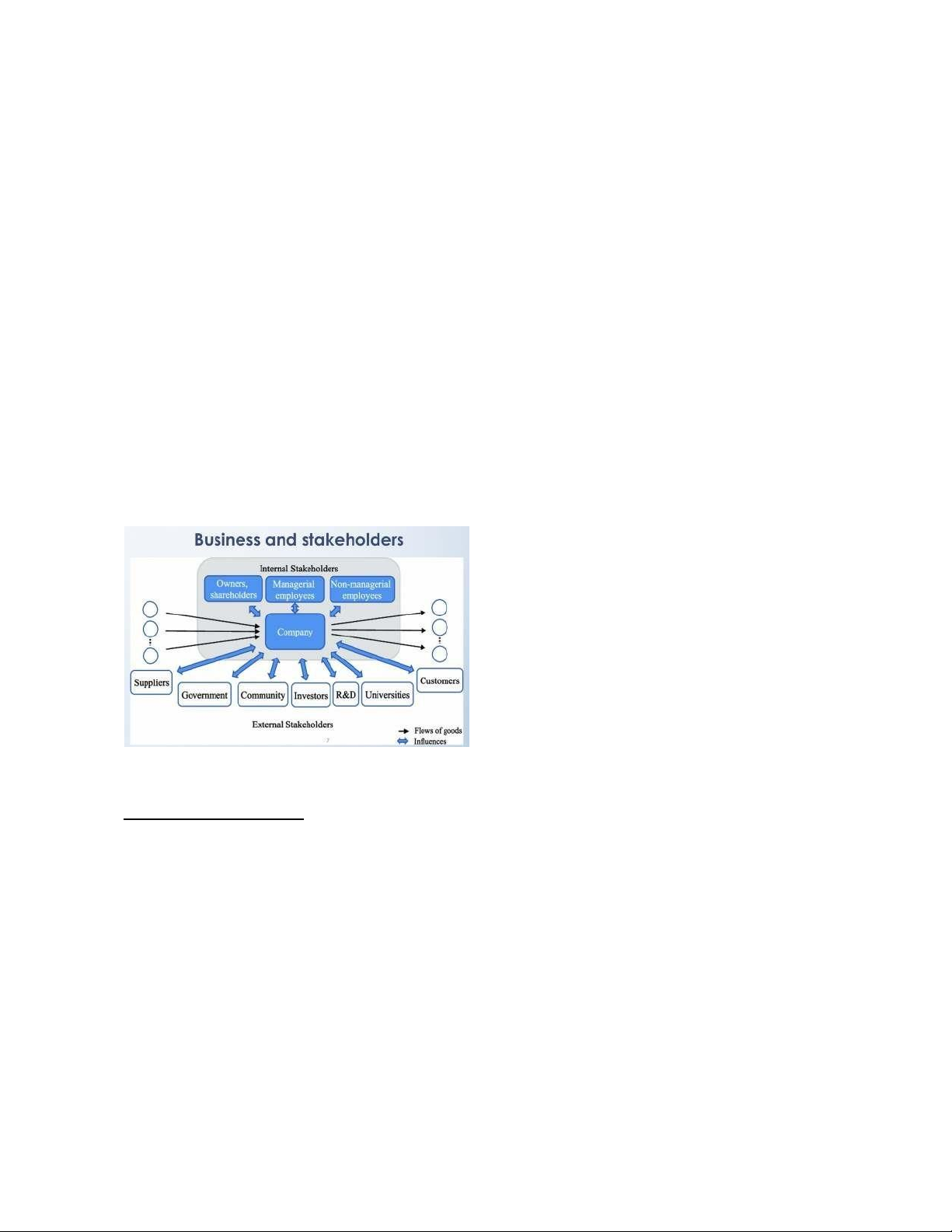
Stakeholder is people who have a “stake” or claim in some aspect of a company’s products,
operations, markets, industry, and outcomes. Identifying stakeholders:
• Primary stakeholders are those whose continued association is absolutely
necessary for a firm’s survival.
• Secondary stakeholders do not typically engage in transactions with a company
and therefore not essential to its survival.
Stakeholders’ different desires/needs
Internal stakeholders: + Owners:
Hold significant shares of the firm Have a significant role in strategy
Often make substantial decisions regarding both internal and external stakeholders. + Managers:
Play a substantial role in determining the strategy of the organization
Have a significant voice in operational decisions.
Accountable for the decisions made, and act as a point of contact between shareholders, the
board of directors, and the organization itself. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 + Employees:
Have significant financial and time investments in the organization
Carry out the strategy, tactics, and operations of the organization
External stakeholders: ● Customers
Consume goods and services → profits for the business ● Suppliers
Supply inputs and create values to the business
Timely payments, shipments, communication, and operational processes are key to maintaining
a strong relationship with this stakeholder group ● Local community
Good: Providing tax money, local access to unique goods and services, jobs, and community development programs.
Bad: Increasing traffic, creating pollution, hurting small businesses, and altering real estate prices. ● Government Tax businesses.
Provide regulatory oversight, ensuring that accounting procedures, ethical practices, and legal
concerns are being handled responsibly by business representatives. ● Broader Society
Traditional Business Ethics Approach ●
Ultimate objective: Maximize Profit/Well-being of shareholders ●
Management of stakeholders Minimize negative influence on Business
Practice management for shareholders benefit, treat others depend on their power
What is Responsible Business?
Responsible Business Approach ●
Ultimate objective: Fulfill Organization objectives ($) while well-being of other stakeholders lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 ● Responsible for stakeholders
Well-being of all stakeholders is the Ultimate objective to run Business Stakeholder
Management Practice – Regardless of stakeholder power
Employee Happy → Customer Happy → Shareholder happy !
Stakeholders’ rights -
Shareholders are the owner of the company with limited liability. They have
various rights, along with obligations. -
Shareholder agreement: How the company will be operated, what is the
objective of the company, how the shareholder’s rights will be protected, how
they can sell their shares, or other things that are related to the shareholder are
mentioned in the shareholder agreement. 1.
Right to Participate in Profit 2. Voting Rights 3.
Right to Inspect Books & Records of Company 4. Right to Transfer Ownership 5. Liability Limited by Shares 6.
Right to Claim During Liquidation 7. Right Issue 8.
Right to Sue for Wrongful Acts How a business responsible for Shareholders? 1.
To ensure safety of investment. 2.
To provide a fair and regular dividend or interest. 3.
Growth of the business should be planned. 4.
There must be effective communication. 5.
It must utilize resources properly. 6.
To offer reasonable opportunity for participation of shareholders in policy decisions.
Employee’s rights – How business responsible for employees?
Well run organizations take into account employee opinions, concerns, and values in shaping
the strategy, vision, and mission of the firm. 1. Right to make complaints 2. Right to be paid correctly lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 3.
Right to be protected from discrimination 4.
Right to be protected from bullying 5.
Right to be protected from unfair dismissal 6.
Right to be protected from sexual harassment 7.
Right to receive the fair work information 8.
Right to request employment records -
To provide them fair wages and full employment. -
They should be provided good working conditions. -
They should be provide d suitable opportunities of advancement. -
There must be security of service and job satisfaction. -
To develop a sense of belonging and dignity of labour.
Customer’s rights: 1.
The right to satisfaction of basic needs 2.
The right to safety – to be protected against products, production processes and
services that are hazardous to health or life. 3.
The right to be informed – to be given the facts needed to make an informed choice,
and to be protected against dishonest or misleading advertising and labelling. 4.
The right to choose – to be able to select from a range of products and services, offered
at competitive prices with an assurance of satisfactory quality. 5.
The right to be heard – to have consumer interests represented in the making and
execution of government policy, and in the development of products and services. 6.
The right to redress – to receive a fair settlement of just claims, including
compensation for misrepresentation, shoddy goods or unsatisfactory services. 7.
The right to consumer education – to acquire knowledge and skills needed to make
informed, confident choices about goods and services, while being aware of basic
consumer rights and responsibilities and how to act on them. 8.
The right to a healthy environment – to live and work in an environment that is
nonthreatening to the well-being of present and future generations.
How a business responsible for Customers? 1.
To ensure regular supply of goods and services. 2.
To offer good quality products and services at reasonable prices. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 3.
To provide information about the product and company. 4. Fair trade 5.
To settle quickly the grievances of the consumers. 6.
Honest advertising and true pricing
How a business responsible for Suppliers? 1. Right information 2. Transparency 3. Fair treatment 4. Well payment implementation
Supplier’s rights 1.
Suppliers also have the right to transparency, fairness and equality. 2.
Right to get suitable and time bound response to the Q&A logs at either stage of the procurement. 3.
Right to be paid correctly and timely
How a business responsible for Government? 1.
To set up business as per guidelines issued by the government. 2.
To ensure regularity and honesty in the payment of fees, duties and taxes. 3.
To follow pollution control norms set up by the government. 4.
To establish new business units in rural and backward areas for balanced regional development of the country. 5.
To avoid indulging into monopolistic and other trade restrictive practices. 6.
To avoid indulging in unlawful activities like bribing, etc. 1. To obey Laws 2. Payment of taxes 3.
Providing inputs to the government 4.
Active participation in politics 5.
Implementation Socio-economics programs
How a business responsible for Community and Society? lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Business should work for the economic and social well-being of the community. 1.
Maximum utilisation of natural resources. 2.
To provide maximum employment opportunities. 3.
To preserve social and cultural values. 4.
To uplift weaker section of the society. 5.
Work towards the upliftment of democratic institutions and national integration. 6.
To provide assistance to hospitals, educational institutions, etc. 7.
To protect the environment from all types of pollution.
1. 2 cách tiếp cận trong BE
Traditional business ethics approach: maximize profit of shareholders. Companies have a
single-minded focus on their shareholders at the cost of everybody else’s interest. Traditional
companies added up elements that contributed to cost—raw material, labour, other overheads,
financing, etc.—and added their profit margin to arrive at a selling price to achieve the
company’s profit objectives. In doing so, they were only considering the economic cost of
doing business and ignored the social and environmental cost of doing business.
Responsible business ethics approach: fulfill organizations while benefit other
stakeholders. In the process, companies start focusing on maximizing the interests of all
stakeholders—which includes promoters, investors, vendors, customers, employees, the
community, government and the environment— instead of just maximizing profit for shareholders.
Example: Unilever is working towards maximizing benefits for all its stakeholders—investors,
consumers, employees, and the communities where it operates—rather than pursuing the
narrow path of maximizing returns only for its investors. Unilever adopted a Sustainable
Living Plan in 2010 as a way of doing business. The goal is to double sales by 2020 even as it
halves its environmental footprint and helps more than a billion people improve health and well-being.
2. How responsible business make sense?
Responsible business means business that considers society, economy, and environment.
A responsible business can build greater trust and strengthen its relationships to its stakeholders
on every level, including its consumers, employees, investors, and the communities it operates
in, which generates greater value over time. Applying sustainable business practices can also
help reduce costs, and drive innovation, which are both positive contributors to the bottom line. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Social responsibility is an effective tool to increase employee engagement. With large
companies, there is strength in numbers, and collective employee efforts can achieve
substantial results, which increases workplace morale and boosts productivity. According to
Harvard Business School, 92% of employees who work at a socially responsible company say
they would be more likely to recommend their employer to those in their network who are looking for a job.
Social responsibility works as a platform for companies and consumers alike to make a positive
impact on local and global communities. Businesses that implement a social responsibility
initiative that’s in line with their values have the opportunity to increase customer retention and
loyalty. Community- oriented companies often enjoy a leg up on their competition as well,
thanks to superior brand imaging.
For example, Tesla Inc. CEO Elon Musk has successfully attracted environmentally-minded
consumers with his line of cutting-edge electric cars and green automotive products.
Example: In 2010, Coca-Cola started the “5by20” initiative to empower women across the globe.
The company stated: Through 5by20 programs around the world, we equip women
entrepreneurs to overcome social and economic barriers by providing business skills training,
access to financial services, and assets, and connections with peers and mentors. The women
participating in 5by20 work in roles across our value chain include retailers, suppliers,
producers, artisans, and more.
As a brand, Coca-Cola is putting a huge focus on sustainability. The key areas are climate,
packaging and agriculture along with water stewardship and product quality. Their message is
‘a world without waste’, with the aim of collecting and recycling every bottle, making their
packaging 100% recyclable and replacing all water used in creating their drinks back to the
environment to ensure water security. They aim that by 2030, they will have reduced their carbon footprint by 25%. 3. Shareholders
Shareholders are the owner of the company with limited liability. They have various rights, along with obligations.
How a business responsible for shareholders?
The responsibility of a company to its shareholders, who are the owners, is indeed a primary one.
The fact that the shareholders have taken a great risk in making investment in the business
should be adequately recognized.
First of all, the company has to strengthen and consolidate its position to safeguard the capital
of the shareholders. Hence, it should develop and improve its business and build up its
financial independence. This will ensure the safety of investment. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Secondly, the owners should be given the full information regarding the working of the
company. In other words, accurate and comprehensive reports have to be supplied. Financial
information must be disclosed and doubts must be clarified.
Finally, it is the responsibility of the company to utilize resources properly, minimize the
wastage so that maximum profits can be earned. Increasing profit means that the shareholder’s
income might be higher, and this can attract more investment in the company. Besides,
business need to offer reasonable opportunity for participation of shareholders in policy decisions.
4. How business responsible for employees?
No enterprise can succeed without the whole-hearted cooperation of the employees. Well-run
organizations take into account employee opinions, concerns, and values in shaping the
strategy, vision, and mission of the firm. The responsibilities of business towards employees are explained as follow:
The company must pay adequate and attractive salaries along with incentives such as overtime
allowance, bonus, etc. to all employees. Wages payable to employees should be fixed by
considering nature of work. The company should frame suitable wage plans for increments and timely revision of wages.
The business organizations must provide good working conditions to their employees such as
adequate lighting, safe drink water, minimizing sound pollution, etc. They also need to make
sure that working conditions protect their employee’s physical and psychological health.
Business organizations should offer enough opportunities of promotion to their talented and
qualified employees. Also, they should encourage other employees to express themselves. This
will increase awareness and motivate the workers to work hard.
The security of job provides mental peace and employees can work with full dedication and
concentration. Commitment to the work will raise the morale and loyalty towards the organization.
Example: Google encourages creativity by placing no restrictions on where employees must
work. Unlike other organizations that force employees to sit in front of a desk all through
working hours, Google focuses on what works best for employees. The award-winning tech
company does this to encourage employees and help them turn their workspace into a fun
environment to enhance their productivity.
CHAPTER 3: EMERGING BUSINESS ETHICS ISSUES FOUNDATIONAL VALUES
FOR IDENTIFYING ETHICAL ISSUES ●
Integrity relates to product quality, open communication, transparency, and
relationships. Therefore, integrity is a foundational value for managers to build an
internal organizational culture of trust. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 ●
Honesty refers to truthfulness or trustworthiness. To be honest is to tell the truth to the
best of your knowledge without hiding anything. ●
Fairness is the quality of being just, equitable, and impartial. There are three
fundamental elements that motivate people to be fair: equality, reciprocity, and optimization.
- In business, equality is about the distribution of benefits and resources. This distribution could
be applied to stakeholders or the greater society.
- Reciprocity is an interchange of giving and receiving in social relationships. Reciprocity
occurs when an action that has an effect upon another is reciprocated with an action that has
an approximately equal effect. Reciprocity is the return of favors approximately equal in value.
- Optimization is the trade-off between equity (equality) and efficiency (maximum
productivity). Discriminating on the basis of gender, race, or religion is generally considered
unfair because these qualities have little bearing upon a person’s ability to do a job. The
optimal way to hire is to choose the employee who is the most talented, proficient, educated,
and able. Ideas of fairness are sometimes shaped by vested interests. One or both parties in the
relationship may view an action as unfair or unethical because the outcome was less beneficial than expected.
ETHICAL ISSUES AND DILEMMAS IN BUSINESS
- An ethical issue is a problem, situation, or opportunity that requires an individual, group, or
organization to choose among several actions that must be evaluated as right or wrong, ethical or unethical.
- An ethical dilemma is a problem, situation, or opportunity that requires an individual, group,
or organization to choose among several actions that have negative outcomes.
- There is not a right or ethical choice in a dilemma, only less unethical or illegal choices as
perceived by any and all stakeholders.
Misuse of Company Time and Resources ●
Time theft can be difficult to measure but is estimated to cost companies hundreds of
billions of dollars annually. It is widely believed the average employee “steals” 4.25
hours per week with late arrivals, leaving early, long lunch breaks, inappropriate sick
days, excessive socializing, and engaging in personal activities such as online
shopping and watching sports while on the job. ●
Using company computer software and Internet services for personal business is one
of the most common ways employees misuse company resources. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 ●
While it may not be acceptable for employees to sit in the lobby chatting with relatives
or their stock brokers, these same employees go online and do the same thing, possibly unnoticed by others. ●
Typical examples of using a computer to abuse company time include sending
personal emails, shopping, downloading music, doing personal banking, surfing the
Internet for information about sports or romance, or visiting social networking sites such as Facebook.
Example: Boeing, implemented policies delineating the acceptable use of such resources.
Boeing’s policy states resource use is acceptable when it does not result in “significant
added costs, disruption of business processes, or any other disadvantage to the company.”
The policy further states use of company resources for non-company purposes is only
acceptable when an employee receives explicit permission to do so.
Abusive or Intimidating Behavior
These terms refer to many things— physical threats, false accusations, being annoying,
profanity, insults, yelling, harshness, ignoring someone, and unreasonableness—and their
meaning differs from person to person.
Example: Bullying also occurs between companies that are in intense competition. Even
respected companies such as Apple have been accused of monopolistic bullying. Former Palm
CEO Edward Colligan accused the late Steve Jobs, former CEO of Apple, of anti- competitive
behavior toward his firm. Jobs allegedly contacted Colligan to propose an agreement not to
hire workers from each other’s companies.
According to the allegations, Jobs went on to state if Palm continued to poach Apple
employees, it could expect a law- suit from Apple accusing Palm of patent infringement. Five
tech workers filed lawsuits against Apple, Google, and other tech firms regarding the existence
of “no hire” agreements. If these agreements were made, they would most likely be considered
anticompetitive because they place both employees and rival companies at a disadvantage. Lying ●
Commission lying is creating a perception or belief by words that intentionally deceive
the receiver of the message; for example, lying about being at work, expense reports,
or carrying out work assignments. ●
Commission lying also entails intentionally creating “noise” within the communication
that knowingly confuses or deceives the receiver. ●
Omission lying is intentionally not informing others of any differences, problems,
safety warnings, or negative issues relating to the product or company that
significantly affect awareness, intention, or behavior.
Example of commission lying: A company owned by Pepsi Co, Naked Juice claimed their
juiced were ‘All Natural’, which was challenged in court and found to be untrue. Even though lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Pepsi Co. defended the claims, they ended up settling for $9 million and removing the ‘All
Natural’ tag from their juices.
Example of omission lying: the behavior of FreeCreditReport.com, a company that promotes
itself as a way for consumers to check their credit scores. Many customers do not realize that
FreeCreditReport.com is a credit-monitoring service that costs $14.95 per month and they will
be charged if they do not cancel the service within 30 days.
Conflicts of Interest ●
A conflict of interest exists when an individual must choose whether to advance his or
her own interests, those of the organization, or those of some other group. ●
To avoid conflicts of interest, employees must be able to separate their private interests
from their business dealings. Organizations must also avoid potential conflicts of
interest when providing products.
Ex: The three major bond rating agencies - Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch Ratings—
analyze financial deals and assign letters (such as AAA, B, CC) to represent the quality of
bonds and other Investments. Prior to the financial meltdown, these rating agencies had
signficant con flicts of interest. The agencies earned as much as three times more for grading
complex products than for corporate bonds. They also competed with each other for rating
jobs, which contributed to lower rating standards. Bribery ●
Bribery is the practice of offering something (often money) in order to gain an illicit
advantage from someone in authority. ●
Gifts, entertainment, and travel can also be used as bribes. ●
The key issue regarding whether or not something is considered bribery is whether it is
used to gain an advantage in a relationship. ●
Bribery can be defined as an unlawful act, but it can also be a business ethics issue in
that a culture includes such fees as standard practice. ●
active corruption or active bribery, meaning the person who promises or gives the bribe commits the offense. ●
Passive bribery is an offense committed by the official who receives the bribe. It is not
an offense, however, if the advantage was permitted or required by the written law or
regulation of the foreign public
Example: The producers of one of the most famous brands in the automobile industry,
Mercedez- Benz, paid $185 million to the United States against charges of bribery and
corruption in 2010. Foreign officials were provided with money and gifts between the time
period of 1998 and 2008 to get government contracts, and more than $56 million were paid on
around 200 occasions in at least 22 countries.official’s country, including case law. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Corporate Intelligence ●
Corporate intelligence is the collection and analysis of information on markets,
technologies, customers, and competitors, as well as on socioeconomic and external political trends. ●
There are three distinct types of intelligence models: -
a passive monitoring system for early warning, - tactical field support, -
and support dedicated to top management strategy. ●
Corporate intelligence (CI) involves an in-depth discovery of information from
corporate records, court documents, regulatory filings, and press releases, as well as any
other background information about a company or its executives. Corporate intelligence
can be a legitimate inquiry into meaningful information used in staying competitive. ●
For instance, it is legal for a software company to monitor its competitor’s online
activities such as blogs and Facebook posts. If the company learns from monitoring its
competitor’s public postings it is likely planning to launch a new product, the company
could use this intelligence to release the product first and beat the competition. Such an activity is acceptable. ●
Hacking is considered one of the top three methods for obtaining trade secrets.
- System hacking assumes the attacker already has access to a low-level, privileged-user account.
- Remote hacking involves attempting to remotely penetrate a system across the Internet. A
remote hacker usually begins with no special privileges and tries to obtain higher level or administrative access.
- Physical hacking requires the CI agent enter a facility personally. Once inside, he or she can
find a vacant or unsecured workstation with an employee’s login name and password. Discrimination ●
Discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, marital status, sexual
orientation, public assistance status, disability, age, national origin, or veteran status is illegal in many countries. ●
Discrimination on the basis of political opinions or affiliation with a union is defined as harassment. ●
Discrimination remains a significant ethical issue in business despite decades of
legislation attempting to outlaw it . lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 ●
Discrimination can also be an ethical issue in business when companies use race or
other personal factors to discriminate against specific groups of customers. Many companies
have been accused of using race, disabilities, gender, or age to deny service or to charge higher
prices to certain ethnic groups.
Sexual Harassment
Sexual harassment can be defined as any repeated, unwanted behavior of a sexual nature
perpetrated upon one individual by another. It may be verbal, visual, written, or physical and
can occur between people of different genders or those of the same gender.
● The key ethical issues associated with sexual harassment are dual relationships and
unethically intimate relationships.
- A dual relationship is defined as a personal, loving, and/or sexual relationship with someone
with whom you share professional responsibilities.
- Unethical dual relationships are those where the relationship could potentially cause a direct
or indirect conflict of interest or a risk of impairment to professional judgment. Fraud ●
Fraud is any purposeful communication that deceives, manipulates, or conceals facts in order to harm others. ●
Fraud can be a crime and convictions may result in fines, imprisonment, or both.
- Accounting fraud usually involves a corporation’s financial reports, in which companies
provide important information on which investors and others base decisions involving millions of dollars.
- Marketing fraud—the process of dishonestly creating, distributing, promoting, and pricing products .
- Consumer fraud occurs when consumers attempt to deceive businesses for their own gain.
Consumers engage in many other forms of fraud against businesses, including price tag
switching, item switching, lying to obtain age-related and other discounts, and taking
advantage of generous return policies by returning used items, especially clothing that has been
worn (with the price tags still attached).
Financial Misconduct (Sai phạm tài chính) ●
The failure to understand and manage ethical risks played a significant role in the financial crisis. ●
The difference between bad business decisions and business misconduct can be hard to
determine, and there is a thin line between the ethics of using only financial incentives to gauge
performance and the use of holistic measures that include ethics, transparency, and
responsibility to stakeholders lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 ●
Risk management in the financial industry is a key concern, including paying bonuses
to executives who failed in their duties Insider Trading ●
An insider is any officer, director, or owner of 10 percent or more of a class of a company’s securities. ●
Illegal insider trading is the buying or selling of stocks by insiders who possess
information that is not yet public. This act, that puts insiders in breach of their fiduciary duty,
can be committed by anyone who has access to nonpublic material, such as brokers, family,
friends, and employees. In addition, someone caught “tipping” an outsider with nonpublic
information can also be found liable. To determine if an insider gave a tip illegally the SEC
uses the Dirks test, that states if a tipster breaches his or her trust with the company and
understands that this was a breach, he or she is liable for insider trading. ●
Legal insider trading involves legally buying and selling stock in an insider’s own
company, but not all the time. Insiders are required to report their insider transactions within
two business days of the date the transaction occurred.
Intellectual Property Rights ●
Intellectual property rights involve the legal protection of intellectual property such as music, books, and movies Privacy Issues ●
Consumer advocates continue to warn consumers about new threats to their privacy,
especially within the health care and Internet industries. As the number of people using the
Internet increases, the areas of concern related to its use increase as well. ●
Some privacy issues that must be addressed by businesses include the monitoring of
employees’ use of available technology and consumer privacy. Current research suggests that
even when businesses use price discounts or personalized services, consumers remain suspicious. ●
However, certain consumers are still willing to provide personal information despite the potential risks.
Ex: In 2018, news outlets revealed that the UK political consulting firm acquired and used
personal data from Facebook users that was initially collected from a third party for academic
research. In total, Cambridge Analytica misused the data of nearly 87 million Facebook
users— many of whom had not given any explicit permission for the company to use or even
access their information. Within two months of the scandal, Cambridge Analytica was bankrupt
and defunct, while Facebook was left with a $5 billion fine by the Federal Trade Commission. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
CHAPTER 5: ETHICAL DECISION MAKING Ethical awareness
Ethical awareness is the ability to perceive whether a situation or decision has an ethical dimension.
Ethical awareness ●
Ethical issue intensity can be defined as the relevance or importance of an event or
decision in the eyes of the individual, work group, and/or organization. ●
Moral intensity relates to individuals’ perceptions of social pressure and the harm they
believe their decisions will have on others. ●
Individual Factors: gender, Education, Nationality, age, Locus of control ●
Organizational Factors: Corporate culture, ethical culture ●
Opportunity: describes the conditions in an organization that limit or permit ethical or unethical behavior.
Implementing Principles and Core Values in Ethical Decision Making
Chapter 6: INDIVIDUAL FACTORS: MORAL PHILOSOPHIES AND VALUES lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Moral philosophy ●
Moral philosophy refers to the specific principles or values people use to decide what is right and wrong. ●
Moral philosophies are person-specific, while business ethics is based on decisions
made by groups or when carrying out tasks to meet business objectives. ●
A moral philosophy is a person’s principles and values.
Table 6-1 A Comparison of the Philosophies Used in Business Decisions
Moral Relativism ●
is the idea that there is no universal or absolute set of moral principles. ●
“When in Rome, do as the Romans do.” What is Moral Relativism? ● The basis idea: ●
Different cultures have different moral codes ●
Ethics are relative to individuals, groups, cultures, and societies ● Relativism resists universal moral norms.
The Cultural Differences Argument -
Different cultures have different moral codes.
- Therefore, there is no objective ‘truth’ in morality.
- Right and wrong are only matters of opinion, and opinions vary from culture to culture.
What Follows If Cultural Relativism Is True? ●
We could no longer justifiably criticize the customs of other societies. ●
We could no longer justifiably criticize the code of our own society. ●
The idea of moral progress is called into doubt lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 UTILITARIANISM
What is Utilitarianism? ●
Utilitarianism is a normative ethical theory that places the locus of right and wrong
solely on the outcomes (consequences) of choosing one action/policy over other actions/policies. ●
As such, it moves beyond the scope of one's own interests and takes into account the interests of others. ●
Utilitarianism is the belief that if an action is good if it benefits someone and an action is bad if it harms someone.
Negative Responsibility ●
Negative Responsibility holds that people are just as culpable for what they fail to
prevent as they are for what they actively do. ●
Example: A is just as guilty for failing to prevent B from pushing C off a cliff as if A had pushed C off a cliff. ●
If absolute negative responsibility is unreasonable, and if Utilitarianism requires
absolute negative responsibility, then Utilitarianism is unreasonable. Integrity ●
Both the George and Jim cases require their subjects to give up on their personal moral
projects whenever circumstances demand it. This is the opposite of Integrity. Integrity
requires that people hold to their considered moral judgments. ●
If integrity is a genuinely important part of moral life, and if utilitarianism is
incompatible with integrity, then utilitarianism is incompatible with moral life. EGOISM
What is Egoism? ●
Ethical egoism is the normative ethical position that moral agents ought to do what is in their self-interest. ●
In Egoism, right vs. wrong is defined based on the consequences to self. ●
This theory requires us to choose solely on the basis of self-interest. DEONTOLOGY
What is deontological ethics? ● Deon is Greek for duty ●
Morality is a matter of duties lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 ●
Determining what it is right to do and wrong to do does not always require knowing
what are good and bad ends to pursue or what one’s real interests are. ●
Whether something is right or wrong doesn’t depend on its consequences. Actions are right or wrong in themselves. ●
General duties toward anyone. Special duties resulting from personal relationships. ●
We each have duties regarding our own actions.
Deontological ethics ●
Deontological ethics says that being good consists in following the right rules/meeting all your obligations. ●
Unlike consequentialism, it is highly un-situational.
e.g. if killing is wrong, it is always wrong even if killing someone will save 1 million lives. Kantian ethics
Kantian ethics rests on two major claims: 1.
The sole source of moral goodness is the Will 2.
A Good Will is one which acts from universalizable reasons
Deontological ethics 1. Universal X
– If you can universalize an act and still it is right, then it is ethical. 2. Self X
– Are you ready to accept the same act on yourself. 3. Means X
– Any person should not be used as the means to an end. 4. Long-term societal impact X
– Will the society become better in the long term if this act is practiced?
All the 4 conditions of deontology are not satisfied for this act, hence this act is UNETHICAL.
What is Virtue Ethics? ●
Virtue ethics is currently one of three major approaches in normative ethics. ●
Virtue theory is concerned with identifying and cultivating character traits that enable
individuals to flourish as members of a community. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 ●
Father of virtue ethics theory: - Plato - Aristotle ●
Virtue theories rely on an analogy between health (the good of the body), and
eudaimonia (the good of the mind).
What is virtue? ● Virtue means “excellence” ● To do something well Virtue ●
A virtue (arete, excellence) is a character trait ●
Acquired by practice, that disposes a person to adopt the right course of action in morally charged situations. ●
Virtues are life-skills that enable a person to realize their potential for living the good
life as a rational, social, animal (naturally).
What is the good? ●
A Relative good useful for something else ● Non - Relative good in itself
Becoming Excellent ●
As a skill or craft, virtue is acquired by practice. ●
Patterns of behavior produce states of character. ●
Good character produces good behavior. ●
If you imitate good people, you’ll become one. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 ●
Moral virtues control natural feelings (passions, appetites) and actions, making them
arise in the right amounts at the right times for the right reasons (such a rule or
principle as would arise in the mind of the practically wise person).
Table 6-2 p165 Virtues That Support Business Transactions
Chapter 7: ORGANIZATIONAL FACTORS: THE ROLE OF ETHICAL CULTURE
AND RELATIONSHIPS CORPORATE CULTURE ●
Culture is a word people generally use in relation to country of origin, language and
the way people speak, the types of food they eat, and other customs. Many define
culture as nationality or citizenship. ●
All organizations, not just corporations, have some sort of culture, and therefore we
use the terms organizational culture and corporate culture interchangeably. Table 7.1
Ethical Frameworks and Evaluations of Corporate Culture ●
An apathetic culture shows minimal concern for either people or performance. ●
Caring culture exhibits high concern for people but minimal concern for performance issues. ●
Exacting culture shows little concern for people but a high concern for performance; it
focuses on the interests of the organization. ●
An integrative culture combines a high concern for people and performance. An
organization becomes integrative when superiors recognize employees are more than
interchangeable parts—employees have an ineffable quality that helps the firm meet its performance criteria.
Integrative Culture: This culture is the best culture an organization can have. In such an
organizational culture, the importance of people and performance is equal and quite high. This
culture means that the organization focuses not only on performance but also on its
employees. The best example of such an organization is Google. Google has an extremely
high reputation for its employees. At the same time, the company is in high demand. The
organization is known for its products, services, and high-level f innovation. The organization
also provides a variety of facilities for employees to take care of and entertain, eat, and
relaxing. Therefore, Google's focus on performance as well as its employees put them in the
category of Integrative culture. Such a culture tends to show the best of all stakeholders.
Another best example of integrative culture is Starbucks. Starbucks strives to improve the
performance of the organization, as well as to improve the employees greatly
Exacting culture: One of the organizations describing the exacting culture is Amazon Inc.
The organization expects high performance from its employees but pays little attention to the
employees. From the outside, it may seem that employees are valued, but this is not true for Amazon



