










Preview text:
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu TAKE OFF & LANDING
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 1
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu Phần 1 Phần 2 Phần 3 Phần 4 Phase of Take off Approach & Wind shear flight Landing
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 2
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 1. Phases of flight
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 3
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 1. Phases of flight
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 4
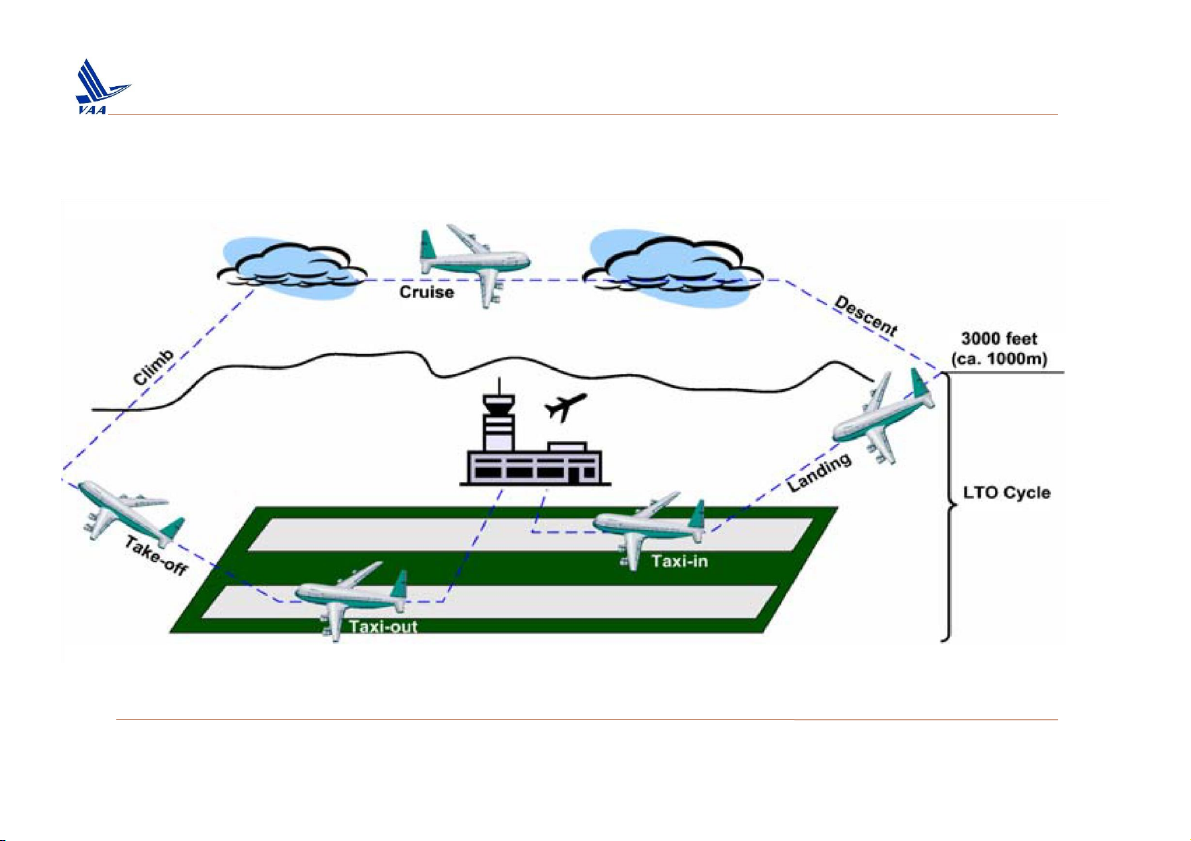
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 1. Phases of flight ❑Flight profile
Step 1- Preflight: Pilot files the flight plan & send to the Tower control er
Tower inform pilot the weather information, runway/ taxiway condition... Flight
checks, push-back from the gate & taxi to the runway.
Step 2- Take-off: Tower control er gives pilot clearance for take-off, aircraft powers up & take-off.
Step 3- Climb: Aircraft climbs to a define altitude Tower control er pass the
communication with pilot to the Departure Control er. Pilot receives clearance for routing.
Step 4- En-route/ Cruise: Communication with the pilot then pass to the
Area Control Centre. The pilot receives instructions as to what altitude an
heading to maintain, as wel as to which radio frequency to tune during t flight from air control er.
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 5
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 1. Phases of flight ❑Flight profile
Step 5- Descent: Near airport Approach Control er, instructing pilot to descent & change heading.
Step 6- Approach: Pilot receives approach clearance & the then
communication with pilot is passed to the Tower Control er. Step 7- Landing:
Controller at tower gives clearance for landing.
Ground/Tower controller directs the pilot across the taxiways to it
destination gate at the terminal.
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 6
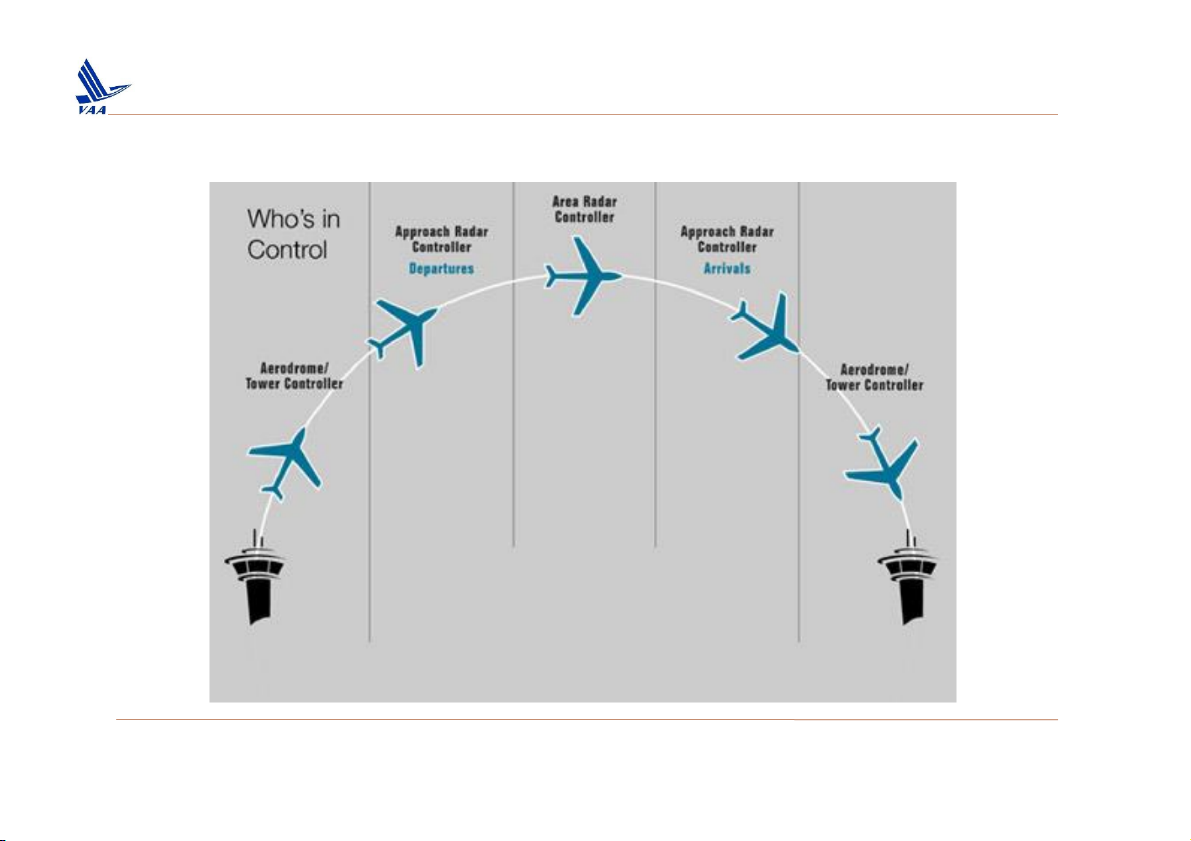
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 1. Phases of flight ❑Tower
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 7
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 1. Phases of flight
❑Approach & Area Control Centre
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 8
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 1. Phases of flight ❑Radar display system
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 9
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 2. Take off
Screen height is an imaginary screen that the aircraft would just clear when taking
(end of the declared take off distance) or landing (commencement of the declared
landing distance) at which the calculated aircraft has climbed to a specified height
35ft (heavy aircraft), 50ft (light aircraft).
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 10
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 2. Take off
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 11
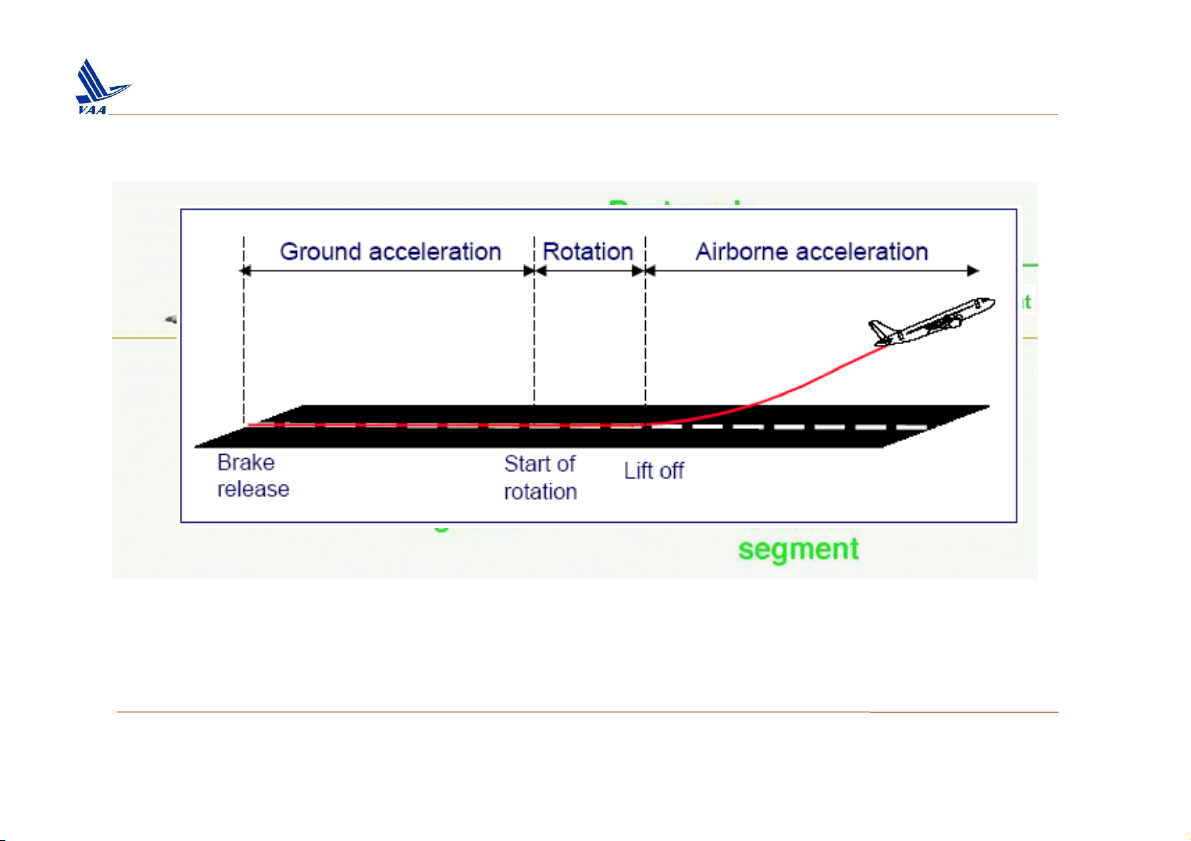
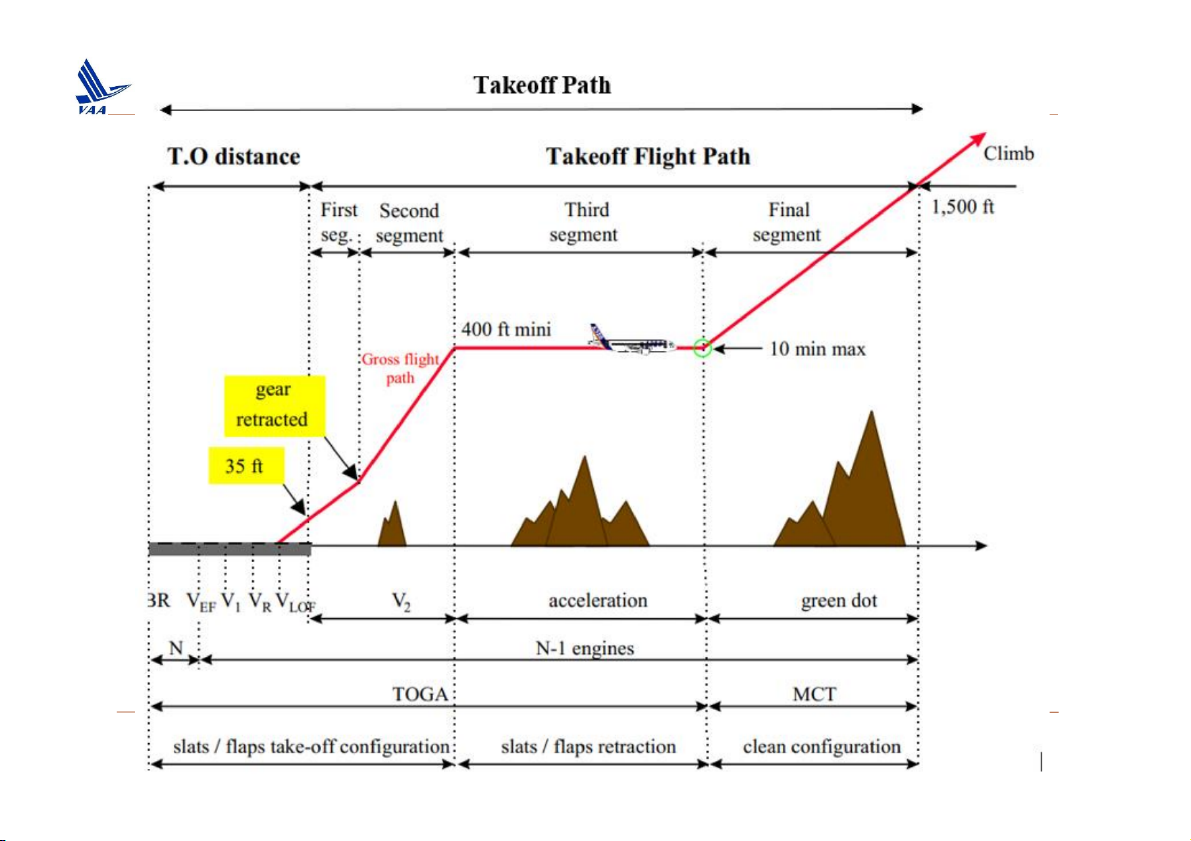
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 1. Take off
The Take-off path extends from a standing start to a point in th
take-off at which the aeroplane is 457 m (1500 ft) above the take-
surface, or at which the transition from the take-off to the en-rout
configuration is completed and VFTO is reached, whichever point is higher. (…)”.
The Take-off flight path must be considered to begin 11 m (35 ft
above the Take-off surface at the end of the take-off distance.(…)”
The Take-off path and Take-off flight path regulatory definitions assume that
the aircraft is accelerated on the ground to VEF, at which point the criti
engine is made inoperative and remains inoperative for the rest of the tak
off. Moreover, the V2 speed must be reached before the aircraft is 35 fee
above the Take-off surface, and the aircraft must continue at a speed no
less than V2, until it is 400 feet above the Take-off surface.
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 12
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 1. Take off
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 13
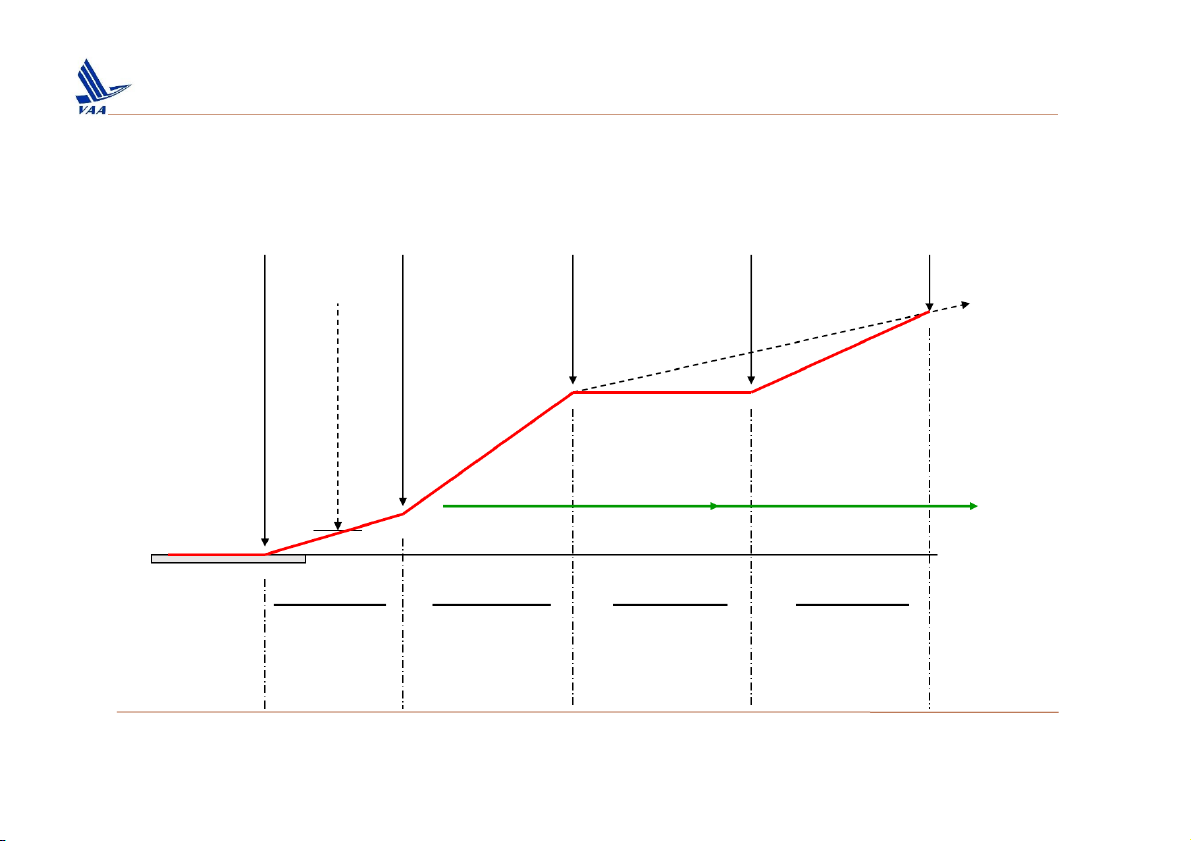
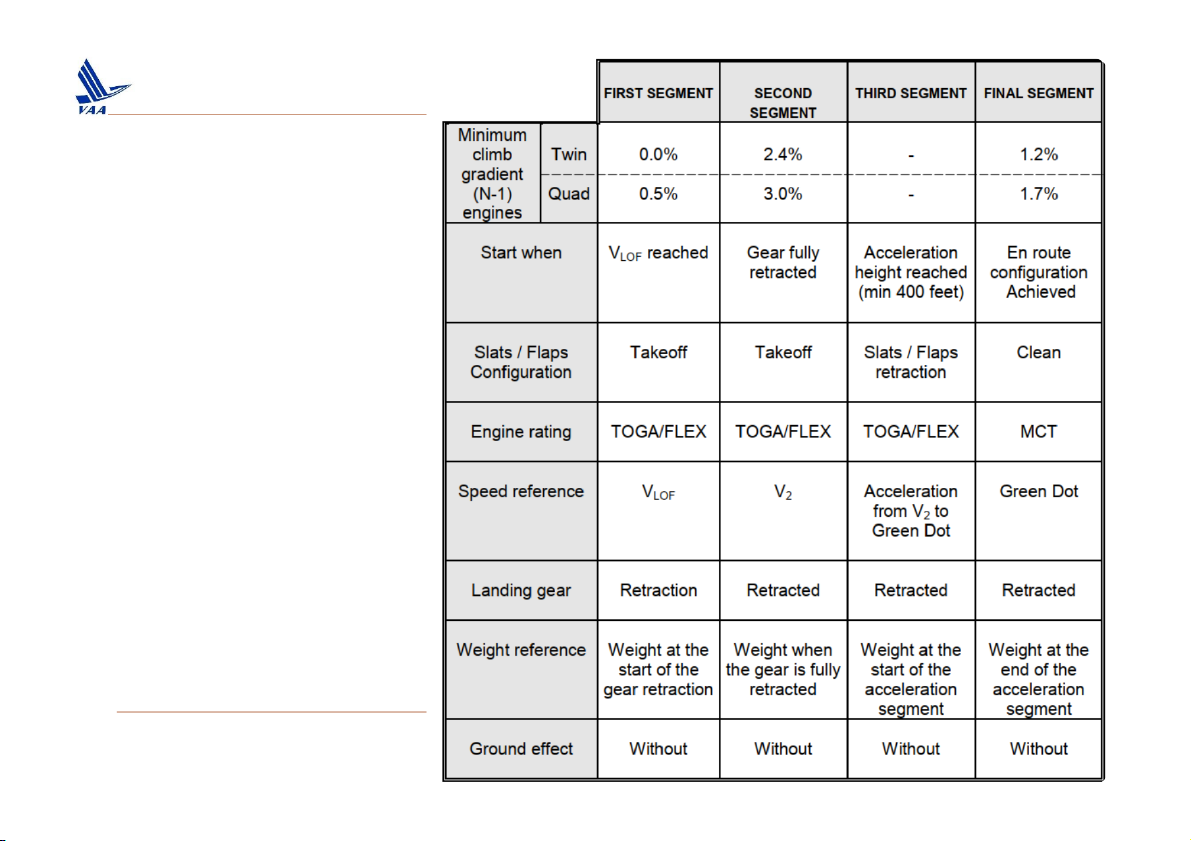
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 2. Take off 1500 Ft Flap retraction or Lift-Off Gear Retracted 400 Ft Min Clean Clear of Obstacles V2 V2 Acceleration Clean TO Thrust MCT 35 ft Max 5 min 1st Segment 2nd Segment 3rd Segment 4th Segment TWIN >0 2.4% acceleration 1.2% (min) or 1.2% avail.
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 14
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 2. Take off
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 15
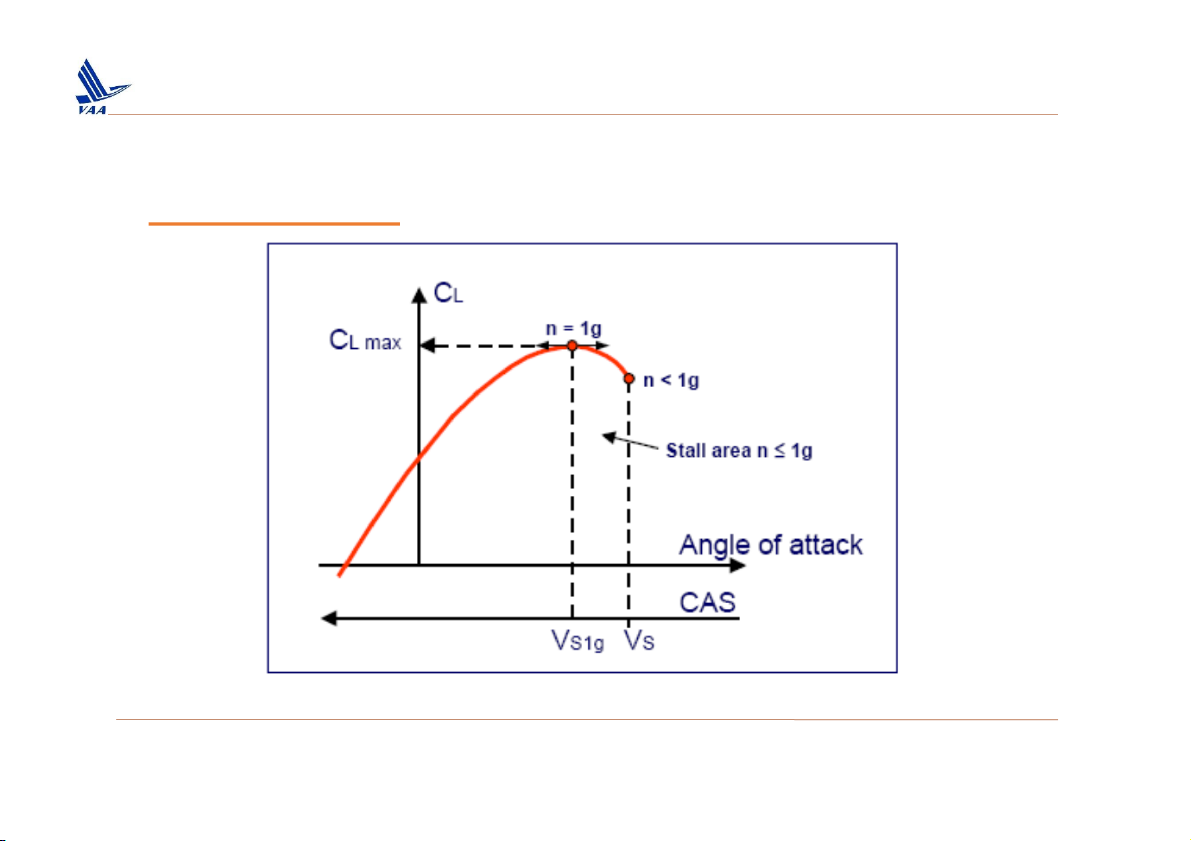
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 2. Take off ❑Take – off speed One g - Stall speed (V ) : s1g
which corresponds to the maximum lift
coefficient (i.e. just before the lift starts decreasing); at that moment,
the load factor is still equal to one.
Stal speed (Vs) : which corresponds to the conventional stal (i.e.
when the lift suddenly collapses); at that moment, the load factor is always less than one.
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 16
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 2. Take off ❑Take – off speed
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 17
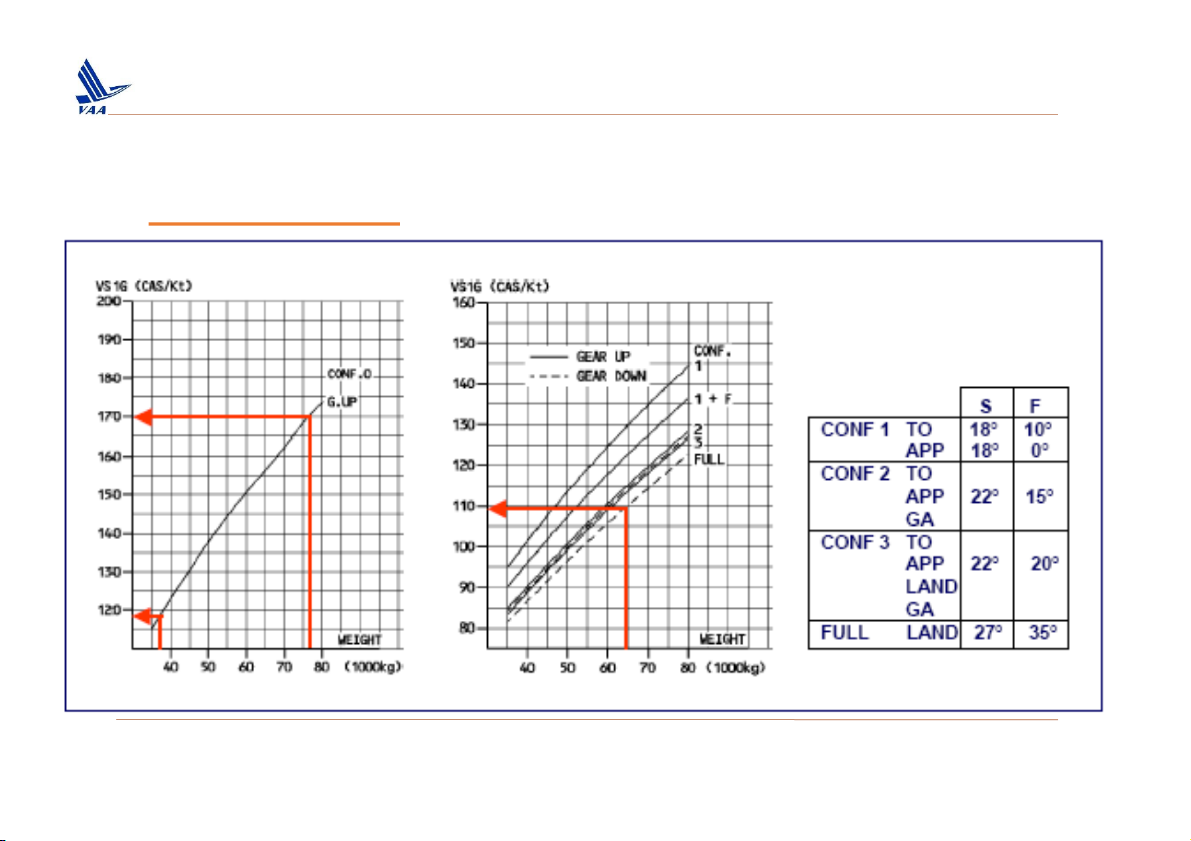
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 2. Take off ❑Take – off speed
The reference stal speed (VSR): is a calibrated airspeed defined by the applicant. V
less than a One-g stall speed. V SR may not be SR i expressed as: VC mLax VSR nw Where: 𝑉𝐶
= speed of maximum lift coefficient, V ; 𝐿max S1g n
= load factor normal to the flight path at 𝑉 w 𝐶 …” 𝐿max
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 18
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 2. Take off ❑Take – off speed
In JAR 25 (October 2010): introduced this notion of reference sta
speed VSR, which is the same as V . S1g VS = 0.94 x Vs1g
IMPORTANT: In Airbus operational documentation, as well as in
this brochure, VSR is referred to as V . S1g
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 19
Học viện Hàng Không Việt Nam – Khoa Không lưu 2. Take off ❑Take – off speed
GVHD: Nguyễn Ngọc Hoàng Quân 20




