












Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|46191829
UNIT 5 SV - đáp án sách eco2 unit5
Tiếng Anh chuyên ngành (Trường Đại học Kinh tế Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh) Scan to open on Studocu
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829 UNIT 5 LABOUR MARKETS LEAD-IN
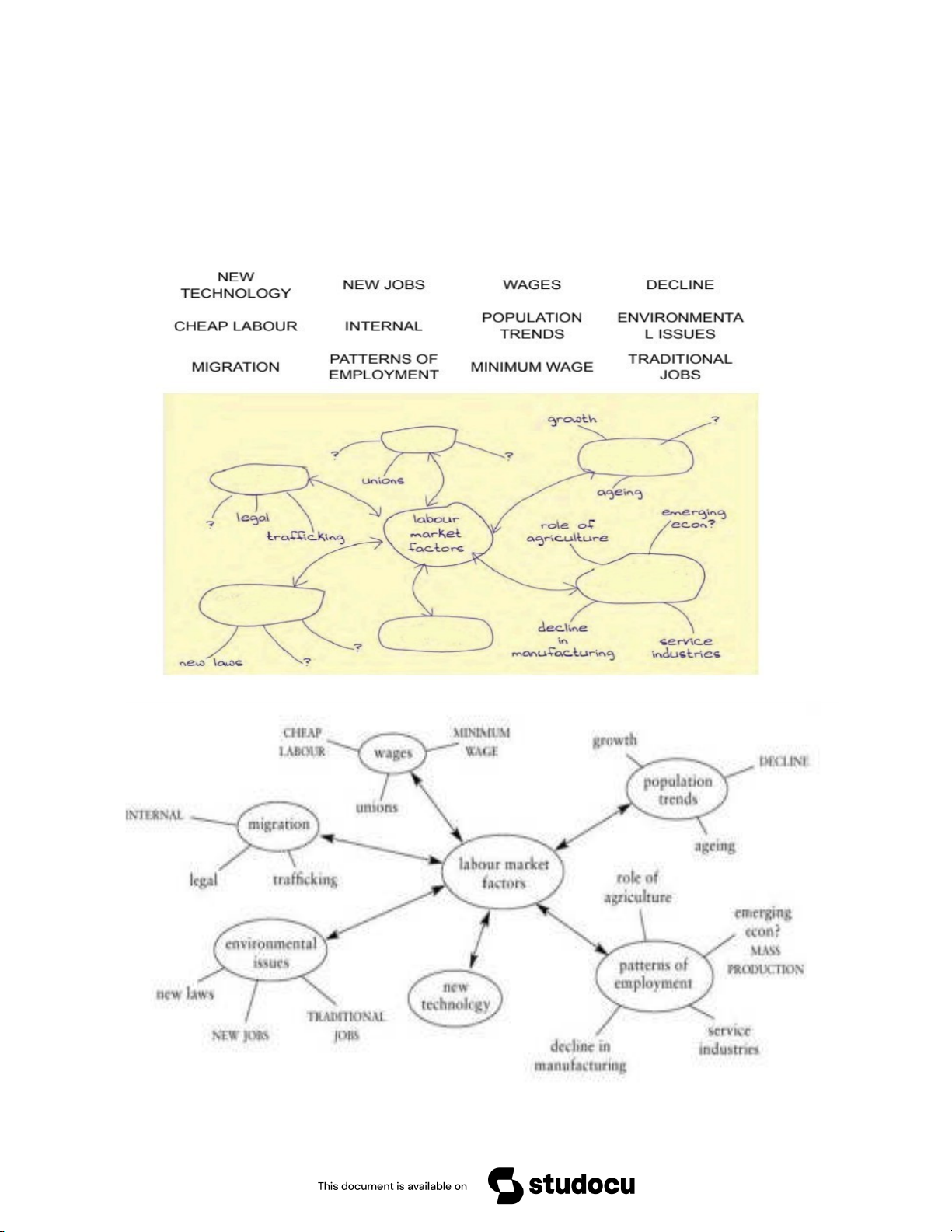
Discuss with your partners and complete the diagram with six labour
markets factors and some examples of each factor. 1
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829 5.1 VOCABULARY
Identifying words in contexts
A. Match each labour market phrase on the left with its corresponding
definition or description on the right. Phrases
Definitions / descriptions 1. Labour supply
A. A. The amount of labour that employers are willing
and able to hire at a given wage rate. 2. Labour demand
B. The process by which wages are set in the labour
market, influenced by supply and demand dynamics. 3. Unemployment rate
C. The percentage of the working-age population
that is either employed or actively seeking employment. 4.
D. D. Situation where workers are employed in jobs Workforce participation
that are inadequate with respect to their skills, rate education, or economic needs. 5. Human capital
E. The lowest wage that employers are legally
allowed to pay their employees. 6. Wage determination
E. F. The total number of people available for work in a certain area. 7. Labour mobility
G. The ability and willingness of workers to move
between different jobs, occupations, or locations. 8. Underemployment
H. Organizations formed by workers to protect their 2
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
rights and interests in the workplace. 9. Trade unions
I. The knowledge, skills, and experience possessed
by an individual or workforce, seen as an asset in the economy. 10. Minimum wage
J. J. The percentage of the total workforce that is
unemployed and actively seeking employment.
1-F, 2-A, 3-J, 4-C, 5-I, 6-B, 7-G, 8-D, 9-H, 10-E
1. Labour supply = F. The total number of people available for work in a certain area.
2. Labour demand =A. The amount of labour that employers are willing and able to hire at a given wage rate.
3. Unemployment rate = J. The percentage of the total workforce that is unemployed and actively seeking employment.
4. Workforce participation rate =C. The percentage of the working-age population that is either employed
or actively seeking employment.
5. Human capital = I. The knowledge, skills, and experience possessed by an individual or workforce, seen
as an asset in the economy.
6. Wage determination = B. The process by which wages are set in the labour market, influenced by
supply and demand dynamics.
7. Labour mobility = G. The ability and willingness of workers to move between different jobs,
occupations, or locations.
8. Underemployment = D. Situation where workers are employed in jobs that are inadequate with respect
to their skills, education, or economic needs.
9. Trade unions = H. Organizations formed by workers to protect their rights and interests in the workplace.
10. Minimum wage = E. The lowest wage that employers are legally allowed to pay their employees.
B. Choose the correct labour market phrase to complete each sentence.
1. The number of people actively seeking work compared to the total labour force is called the _______. 3
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
(a) Workforce participation rate (b) Underemployment rate (c) Unemployment rate (d) Labour mobility rate
2. The skills, education, and experience that workers bring to the job is referred to as _______. (a) Wage determination (b) Human capital (c) Labour demand (d) Minimum wage
3. The willingness and ability of people to work for a certain wage is known as _______. (a) Labour supply (b) Underemployment
(c) Workforce participation rate (d) Trade unions
4. A government-mandated minimum hourly pay is called the _____. (a) Labour mobility (b) Minimum wage (c) Wage determination (d) Human capital
5. The process of how wages are set in the labour market is known as _______. (a) Labour demand (b) Underemployment (c) Wage determination (d) Trade unions
6. The number of people actively participating in the labour force, either
employed or unemployed, is the _______.
(a) Workforce participation rate (b) Labour mobility (c) Human capital (d) Unemployment rate 4
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
7. The ease with which workers can move between jobs or locations is _______. (a) Trade unions (b) Labour mobility (c) Underemployment (d) Minimum wage
8. Organizations that represent workers' interests in collective bargaining are called _______.
(a) Workforce participation rate (b) Trade unions (c) Human capital (d) Labour demand
9. The number of businesses seeking workers for open positions reflects _______. (a) Underemployment (b) Labour mobility (c) Labour demand (d) Minimum wage
10. A situation where someone is working part-time but would prefer full-time work is an example of _______. (a) Unemployment (b) Underemployment (c) Labour mobility
(d) Workforce participation rate
1. (c) Unemployment rate 2. (b) Human capital 3. (a) Labour supply 4. (b) Minimum wage
5. (c) Wage determination
6. (a) Workforce participation rate 7. (b) Labour mobility 8. (b) Trade unions 9. (c) Labour demand 5
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
10. (b) Underemployment
1. The number of people actively seeking work compared to the total labour force is called the _______.
(a) Workforce participation rate (b) Underemployment rate (c) Unemployment rate (d) Labour mobility rate
2. The skills, education, and experience that workers bring to the job is referred to as _______. (a) Wage determination (b) Human capital (c) Labour demand (d) Minimum wage
3. The willingness and ability of people to work for a certain wage is known as _______. (a) Labour supply (b) Underemployment
(c) Workforce participation rate (d) Trade unions
4. A government-mandated minimum hourly pay is called the _______. (a) Labour mobility (b) Minimum wage (c) Wage determination (d) Human capital
5. The process of how wages are set in the labour market is known as _______. (a) Labour demand (b) Underemployment (c) Wage determination (d) Trade unions
6. The number of people actively participating in the labour force, either
employed or unemployed, is the _______. 6
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
(a) Workforce participation rate (b) Labour mobility (c) Human capital (d) Unemployment rate
7. The ease with which workers can move between jobs or locations is _______. (a) Trade unions (b) Labour mobility (c) Underemployment (d) Minimum wage
8. Organizations that represent workers' interests in collective bargaining are called _______.
(a) Workforce participation rate (b) Trade unions (c) Human capital (d) Labour demand
9. The number of businesses seeking workers for open positions reflects _______. (a) Underemployment (b) Labour mobility (c) Labour demand (d) Minimum wage
10. A situation where someone is working part-time but would prefer full-time work is an example of _______. (a) Unemployment (b) Underemployment (c) Labour mobility
(d) Workforce participation rate 5.2 READING
Getting detailed ideas from the text Lead-in 7
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
Brainstorm what you think are the main trends and challenges
in the labour market for this year. Trends Challenges ____________ ____________ _____________ ____________ _____________ _____________ ____________ _____________ Vocabulary building
A. Complete the chart below with the correct word form. NOUNS VERBS ADJECTIVES ADVERBS 1 resignation 2 precarious 3 stabilize 4 coincide 5 competitively 6 beneficial 7 volatility 8 voluntarily 9 flexibility resilient 8
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
B. Combine the word or phrases from box A with words from box B to make
partnership and then match them to their correct definitions below: NOUNS VERBS ADJECTIVES ADVERBS 1.resignation resign resigned resignedly precariousness ------------ precarious precariously stability stabilize stable stably coincidence coincide coincident coincidently competition compete competitive competitively benefit benefit beneficial beneficially volatility ----------- volatile ---------- volunteer volunteer voluntary voluntarily flexibility -------------- flexible flexibly 10 resilience resile resilient resiliently A B 1. skills shortages
a. the percentage of employees retained by a company over a
given period, indicating workforce stability. 2. budget tightening
b. a work arrangement where employees perform their job
tasks outside the traditional office setting, often facilitated by technology. 9
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829 3. wage growth
c. a flexible work model that combines both remote and in
office work, providing employees with a balance between
flexibility and in-person collaboration. 4. retention rates
d. the reduction of expenses and spending by businesses in
response to economic challenges.
e. a significant trend where a large number of employees 5. job openings
voluntarily leave their jobs, leading to a labor market shift. 6. remote working
f. the ability of a business to effectively position itself and its
products or services against competitors in the market. 7. hybrid work
g. situations where there is a lack of qualified individuals with
the necessary skills, creating challenges for employers. 8. great resignation
h. available positions within a company that are yet to be filled by suitable candidates. 9. marketplace
i. a mindset characterized by a hopeful outlook on the future, competitiveness
tempered by a realistic awareness of potential challenges and uncertainties. 10. cautious
j. the increase in average wages over a specific period, optimism
reflecting changes in income levels. 1. g 2. d 3.j 4.a 5. h 6. b 7. c 8. e 9.f 10. i
1. Skills Shortages: Situations where there is a lack of qualified individuals with the necessary
skills, creating challenges for employers.
2. Budget Tightening: The reduction of expenses and spending by businesses in response to 10
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829 economic challenges.
3. Wage Growth: The increase in average wages over a specific period, reflecting changes in income levels.
4. Retention Rates: The percentage of employees retained by a company over a given period,
indicating workforce stability.
5. Job Openings: Available positions within a company that are yet to be filled by suitable candidates.
6. Remote Working: A work arrangement where employees perform their job tasks outside
the traditional office setting, often facilitated by technology.
7. Hybrid Work: A flexible work model that combines both remote and in-office work,
providing employees with a balance between flexibility and in-person collaboration.
8. Great Resignation: A significant trend where a large number of employees voluntarily
leave their jobs, leading to a labor market shift.
9. Marketplace Competitiveness: The ability of a business to effectively position itself and its
products or services against competitors in the market.
10. Cautious Optimism: A mindset characterized by a hopeful outlook on the future, tempered
by a realistic awareness of potential challenges and uncertainties. Guiding questions
What is the text about? (Tick as many as possible)
□ Businesses are urged to embrace declining wage growth as an opportunity to
innovate, invest in technology, and strategically expand operations, thereby
enhancing financial resilience in the face of potential economic challenges.
□ Companies are encouraged to integrate eco-friendly practices into their operations,
promoting sustainability and reducing their environmental impact.
□ In response to the evolving workforce landscape, companies should consider
adopting flexible remote and hybrid work options to align with employee
preferences while maintaining productivity and collaboration levels.
□ Anticipating potential economic shifts, organizations should proactively navigate
uncertainties by prioritizing reskilling initiatives and implementing accessible hiring 11
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
policies to address the challenges presented by a forecasted shallow recession in
2023. □ Fostering a positive workplace culture that prioritizes mental health and
well-being can contribute to employee satisfaction and overall organizational success. Reading
LABOR MARKET TRENDS IN 2023 (Greaves, 2023)
Source: https://laboriq.co/news/labor-market-trends-in-2023
The last few years have been pretty turbulent for the labor market. From the great
resignation resulting in significant skills shortages, to record low unemployment
rates, to our first glimpses of post-pandemic life, so much has happened that we're
waiting with bated breath for what 2023 has in store. New words
pretty adverb / pr ˈ ɪ ·
t̬ i/ : (used to give emphasis) to a large degree; to some degree: khá
i’ve got a pretty clear idea of what’s going on.
turbulent adjective / t ˈ ɜ b
ː jələnt/: experiencing many problems, disagreements, or changes: biến động
The publishing world is going through a turbulent time at the moment.
with bated breath: in an anxious (= worried and nervous) or excited way:hồi hộp
I waited for the results with bated breath.
in store idiom: going to happen soon: sắp xảy ra
in store for You never know what's in store for you.
Challenges Facing The 2023 Labor Market 12
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
Various indicators suggest that at the beginning of 2023, we'll enter a shallow
recession. For example, inflation in the U.S. and Europe hit highs of 8% in 2022,
which (among other factors) prompted the increased cost of living. On top of that,
experts predict a 2.7% fall in economic growth.
In response to this slightly precarious economic climate, many businesses will likely
tighten their budgets. For example, tech giants like Apple and IBM reportedly laid
off 58,000 workers in January 2023. Sadly, this sits among other tumultuous labor
reductions in the private and public tech sector last year, which saw companies
cutting 140,000 jobs in an attempt to tackle the adverse impacts of rising inflation and stock market dips. New words
a precarious situation is likely to get worse:
many borrowers now find themselves caught in a precarious financial position. tumult noun / t ˈ u·m l
ʌ t/: noise and excitement, or a state of confusion, change, or uncertainty: ồn ào
tumultuous adjective /tʊ m ˈ l ʌ ·t u· ʃ əs/
the honoree received tumultuous applause.
dip verb: to go down to a lower level, often by a small amount or for a short time:
House prices are likely to dip in the first three months of the year.
But, fortunately, it’s not all doom and gloom. Forecasts suggest we’re already over
the peak of these trending layoffs. In fact, by mid-2023, we should see job cuts taper off to pre-pandemic levels.
Similarly, as this year continues to unfold, experts predict we’ll also see inflation
decrease, averaging out at 4%, with some economists suggesting that the worst is likely behind us. 13
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
With this in mind, some positive momentum may come to the labor market. For
instance, WEF suggests that we might see employers reskilling their workforces and
creating more accessible hiring policies to overcome market uncertainties. New words
doom and gloom collocation: bad news and unhappiness:
There is widespread gloom and doom about the company's future.
taper off phrasal verb / t ˈ e .
ɪ pər/: to become gradually smaller or weaker, or happen less often:
Sales have gradually tapered off. unfold verb / n ʌ f ˈ o l
ʊ d/: (of a situation or story) to develop or become clear:
Events unfolded in a way that no one could have predicted.
momentum /məʊ me ˈ
ntəm/: the force that keeps an object moving or keeps an event
developing after it has started: động lực
There is worrying evidence that the economy is losing momentum.
Labor Market-Related Opportunities in 2023
The so-called “return to normal” is essentially already underway. This could mean
wages stabilize as inflation drops, fewer employees voluntarily quit their jobs and
the labor market opens up a bit more.
One component of this will be a decline in wage growth. During the last few years,
average wages in the U.S. climbed to exceptionally high levels. For instance, in
2021, U.S. wages were the highest on record in more than a decade. In contrast, EU
salaries (according to average year-on-year euro-area wage growth) peaked at the
start of 2020. This, coinciding with the pandemic, meant employers were under
considerable strain to keep up with market demand.
In contrast, the general prognosis for wage growth in 2023 is as follows: Europe, on
average, will see a peak wage growth of 2.6% in Q1 of 2023. However, by the end
of 2023 (Q4 2023/Q1 2024), growth rates will decline to 1.9%. 14
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
The U.S. will see slightly higher wage growth, particularly within Q1 and Q2 of
2023 (5.5% and 3.8%, respectively). However, this is also predicted to decline to 2.5% by the end of the year.
A decline in wage growth presents an opportunity for employers because it enables
them to save on labor costs. This can be especially beneficial for companies feeling
the pinch as it could help them to maintain profitability and avoid layoffs. In
addition, with labor costs stabilizing, employers might be better positioned to invest
in new technologies and expand their operations to increase their competitiveness in the marketplace. New words
feel the pinch idiom: to have problems with money because you are earning less than before:
When my father lost his job and we had to live on my mother's earnings, we
really started to feel the pinch.
prognosis noun /pr nə ɒɡˈ ʊ.s s
ɪ / (also prognostication):
1. a doctor's judgment of the likely or expected development of a disease or of
the chances of getting better:
The prognosis after the operation was for a full recovery.
2. (nghĩa trong bài đọc) a statement of what is judged likely to happen in the
future, especially in connection with a particular situation:
I was reading a gloomy economic prognosis in the paper this morning. Q= quarter : 3 months
It’s also worth noting that voluntary job leavers were at an all-time high in Q2 of
2022. Quit rates hit a 10-year high of 2.9%. While the numbers still haven’t dropped
to pre-pandemic levels, on average, we see those voluntarily leaving the workforce
decreasing. This, combined with a decline in wage growth, likely means there’s less 15
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
potential for salary climbing vis-à-vis jumping into new roles. Hence, employees are
more likely to stay in their current position, thus increasing retention rates.
Similarly, job openings gradually declined over 2022. From highs of 11.8 million in
March 2022, this fell to 11 million by December. While statistics from the World
Forum show that the labor market is still tight compared to pre-pandemic levels, the
severity is decreasing. In light of this, we’ll likely see the labor market’s favor shift
ever so slightly from job seekers to employers. New words
vis-à-vis preposition / vi ˌ ·zə vi ˈ , -z -
ɑ /: in relation to, or in comparison with:
Later I asked him more directly about government’s role vis-a-vis the environment.
The bottom line: As inflation declines, the evidence suggests that wage growth will
stabilize, the labor market won’t be quite as tight for employers and people won’t be
as quick to quit their jobs - all of which is good news for employers!
the bottom line : the most important fact in a situation:
The bottom line is that we need another ten thousand dollars to complete the project.
Will Remote Working Remain Popular?
Working from home remains contentious. However, there’s certainly a push from
employees to keep working from home on the table. For instance, McKinsey reports
87% would take the opportunity to work flexibly when offered, with 32% saying
they already work remotely up to five days a week.
That said, there are still holdouts. For example, in 2022, 85% of business leaders
said they weren’t confident their employees could be productive when working from
home. But, despite this, it seems many are forced to acknowledge that if they
withdraw remote working altogether, they’ll risk losing staff and miss out on
potentially skilled workers. For instance, Employment Hero reported that 50% of 16
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
hybrid and remote workers said they would quit if their employer forced them to return to the office. New words
holdout noun / hə ˈ
ʊldaʊt/: a person, organization, or country that continues to
refuse to accept something that others have already accepted, despite other people
trying to persuade them to:
Smaller producers, who would receive less than 20% of the $1.2 billion under
the settlement formula, remain holdouts. hybrid noun / ha ˈ br ɪ d
ɪ /: something that is a combination of two different things, so it
has qualities relating to both of them:
a hybrid car/vehicle/engine
Under the hybrid plan, the employee contributes payments to his retirement
fund along with the government.
on the table idiom: being discussed or considered:
There are several important issues on the table.
Overall Forecast: Cautious Optimism
Overall, the forecast for 2023’s labor market is one of cautious optimism. Based on
our findings, we think there will likely be some disruptions to the labor market and
broader economy, but it seems like the labor market is stronger and more resilient
than many expected! As the months go by, inflation rates should gradually decrease,
voluntary quit rates should slow and the labor market won’t be quite as tight. This
does not mean a return to normal; there will still be a lot of competition for talent.
But things should stabilize from the volatility and record growth of the past couple (vài) of years. New words
taper off phrasal verb / t ˈ e .
ɪ pər/ : to become gradually smaller or weaker, or happen less often: 17
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
Sales have gradually tapered off.
contentious adjective /kən t ˈ en. ə
ʃ s/: causing , involving, or likely to cause
disagreement and argument:
she has some very contentious views on education.
resilient adjective /rɪ z ˈ l
ɪ iənt/: able to return quickly to a previous good condition after problems:
The US economy remains amazingly resilient.
A. Read the passage and choose the best summary.
Summary 1: The 2023 labor market foresees challenges, including a potential
recession, job cuts, and budget constraints. Positive mid-year forecasts emerge, and
discussions about remote work persist.
Summary 2: Challenges and improvements are expected in the 2023 labor market,
including a potential recession, job cuts, and budget constraints. Forecasts indicate
positive changes by mid-year, while the debate on remote work continues.
Summary 3: In 2023, the labor market grapples with a potential recession, initial job
cuts, and tight budgets. Mid-year forecasts bring hope with stabilized wage growth
a nd increased employer favor a mid ongoing remote work discussions.
A. Read the passage and choose the best summary.
Summary 1: The 2023 labor market foresees challenges, including a potential recession, job
cuts, and budget constraints. Positive mid-year forecasts emerge, and discussions about remote work persist.
Summary 2: Challenges and improvements are expected in the 2023 labor market, including a
potential recession, job cuts, and budget constraints. Forecasts indicate positive changes by
mid-year, while the debate on remote work continues.
Summary 3 (the best): In 2023, the labor market grapples with a potential recession, initial
job cuts, and tight budgets. Mid-year forecasts bring hope with stabilized wage growth and
increased employer favor amid ongoing remote work discussions. 18
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn) lOMoARcPSD|46191829
B. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
1.What economic indicators suggest challenges for the labor market at the beginning of 2023?
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
2. How did tech giants like Apple and IBM respond to the slightly precarious economic climate in 2023?
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
3. What are some potential benefits for employers with the projected decline in wage growth in 2023?
………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
4. In light of economic challenges, what initiatives do experts suggest businesses
might undertake to navigate uncertainties in the labor market?
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
5. What is the overall forecast for the labor market in 2023, and what is the
underlying sentiment regarding its resilience and strength?
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
1.What economic indicators suggest challenges for the labor market at the beginning of 2023?
Inflation rates in the U.S. and Europe reaching 8% in 2022 and a predicted 2.7% fall in
economic growth are key indicators of challenges. (L8-10)
2. How did tech giants like Apple and IBM respond to the slightly precarious economic climate in 2023?
Tech giants like Apple and IBM reportedly laid off 58,000 workers in January 2023 as a
response to rising inflation and stock market dips. (L12-13)
3. What are some potential benefits for employers with the projected decline in wage growth 19
Downloaded by NHI VÕ LÂM PH??NG (nhivo.31241020370@st.ueh.edu.vn)