










Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
NATIONAL ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY
SCHOOL OF ADVANCED EDUCATION PROGRAMS
Course: International Marketing
Class: Marketing Management 63E GROUP 7 NAME STUDENT ID
LƯƠNG NGUYỄN MAI KHANH 11219710
NGUYỄN THỊ DIỆU LINH 11219609 NGUYỄN QUỲNH CHI 11211113 NGUYỄN THÀNH LONG 11213546 TRẦN HẢI ĐĂNG 11211240
NGUYỄN LÊ KHÁNH LINH 11213278 Ha Noi, November 2023 TABLE OF CONTENT
I. Introduction ............................................................................................................... 4 lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
II. Home country (Vietnam) situation ........................................................................ 4
1. Political Stability................................................................................................... 4
2. Promotional Activities .......................................................................................... 5
3. Export Experience of Alluvia Chocolate Company ............................................. 6
4. Alluvia Chocolate’s SWOT Analysis .................................................................... 6
III. International Market Selection (IMS) ................................................................. 9
1. Criterias and Developing Segments ...................................................................... 9
2. Preliminary Screening......................................................................................... 10
3. Fined - grained Screening ................................................................................... 11
IV. Host country (India) Situation ............................................................................ 12
1. Political Environment ......................................................................................... 12
1.1. Political System .......................................................................................... 12
1.2. Import situation of food in India ................................................................ 12
2. Economic Environment ...................................................................................... 14
2.1. Exchange rate of Indian rupee (INR) and Vietnam dong (VND) .............. 14
2.2. AIFTA ......................................................................................................... 14
3. Social Environment............................................................................................. 15
3.1. Cultural Features ........................................................................................ 15
3.2. Cultural Elements ....................................................................................... 16
3.2.1. Language ............................................................................................ 16
3.2.2. Manners and Custom ......................................................................... 17
3.2.3. Education ........................................................................................... 17
3.2.4. Attitudes and Value ............................................................................ 17
3.2.5. Aesthetics ........................................................................................... 18
3.3. Hofstede’s Model Analysis ........................................................................ 19
3.4. Cultural Dimensions affects Ethical Decision-making .............................. 20
4. Competitors Analysis .......................................................................................... 21
4.1. Indirect Competitors ................................................................................... 21
4.2. Direct Competitors ..................................................................................... 23
5. Targeted Customer .............................................................................................. 24
5.1. Population demographics ........................................................................... 24
5.2. Income ........................................................................................................ 24
5.3. Consumer trends ......................................................................................... 25
V. Brand Position ........................................................................................................ 26
VI. Marketing Objectives .......................................................................................... 26 lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
1. Quantitative Objectives....................................................................................... 26
2. Qualitative Objectives......................................................................................... 26
VII. Entry Mode ......................................................................................................... 27
1. Firm size ............................................................................................................. 27
2. International experience ...................................................................................... 27
3. Product characteristic .......................................................................................... 27
4. Product differentiation advantage ....................................................................... 27
5. Transaction specific factors ................................................................................ 28
6. Cultural distance ................................................................................................. 28
7. Country risk ........................................................................................................ 29
8. Conclusion .......................................................................................................... 30
VIII. Programme Strategy ......................................................................................... 30
1. Product ................................................................................................................ 31
1.1. Product Decision ........................................................................................ 31
1.1.1. Product Portfolio ................................................................................ 31
1.1.2. Standardization .................................................................................. 32
1.2. Brand Decision ........................................................................................... 33
2. Price .................................................................................................................... 33
2.1. Penetration Pricing Strategy ....................................................................... 33
2.2. Bundle Pricing Strategy ............................................................................. 34
3. Place .................................................................................................................... 34
3.1. Direct - selling to big retailer ..................................................................... 34
3.2. Open Representative Office ....................................................................... 35
3.3. E - commerce activities .............................................................................. 35
4. Promotion ............................................................................................................ 35
4.1. One - way Communication ........................................................................ 35
4.1.1. Online Newspaper ............................................................................. 35
4.1.2. Sales promotions ................................................................................ 36
4.2. Two - way Communication ........................................................................ 36
4.2.1. Internet Marketing ............................................................................. 36
4.2.2. Personal Selling ................................................................................. 37
IX. Control Marketing Programme .......................................................................... 37
1. Budget ................................................................................................................. 37
1.1. Budget assumptions ....................................................................................... 37
1.2. Budget Allocation ......................................................................................... 38 lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
2. Control Activities ................................................................................................ 41
CONCLUSION ........................................................................................................... 42
EVALUATE MEMBER’S CONTRIBUTION ......................................................... 44
REFERENCES ........................................................................................................... 45 I. Introduction
ALLUVIA is a Vietnamese chocolate brand produced by a closed process from Tien
Giang cocoa beans, Ben Tre, one of the most delicious nut regions in Vietnam and the
world. Xuan Ron Cho Gao Cocoa Co., Ltd. (Alluvia Chocolate) is the parent company
of the ALLUVIA brand, established in 2014, headquartered at No. 5, Hoang Dieu Street,
Ward 13, District 4, Ho Chi Minh City.
The company has also carried out many brand promotion activities overseas, such as
participating in the chocolate exhibition in Paris, exporting chocolate to Japan, and
being a chocolate supplier for Jetstar airline. Vision
Alluvia’s vision is to promote Mekong Delta chocolate and cocoa, with local natural
origins, designed with respect for the environment and fair trade. Mission
Alluvia's mission is to introduce Vietnamese and gourmets around the world to artisanal
chocolates on the banks of the Mekong River. Cocoa trees are grown & maintained by
local farmers according to international processes and certified by UTZ. Product
Alluvia's products include bean chocolates, bars, pellets and ice cream, in a variety of
flavors such as 70% cocoa, 80% cocoa, cashews, almonds, coconut, coffee, chili peppers and more.
II. Home country (Vietnam) situation 1. Political Stability
The political landscape of Vietnam presents an intriguing context for Small and
Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) seeking to engage in international export activities.
Characterized by a stable political regime, Vietnam's government exerts substantial
control, providing a predictable environment for businesses, including SMEs, to
formulate long-term strategies and invest in market expansion. lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
Furthermore, Vietnam's active participation in various international trade agreements,
such as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership
(CPTPP) and the ASEAN - India Free Trade Agreement (AIFTA), has bestowed
significant opportunities upon SMEs for exporting goods and services to global markets.
Nonetheless, concerns regarding human rights, including freedom of speech and
religion, have been expressed by international organizations, potentially affecting the
nation's reputation and raising concerns for some enterprises. This necessitates a
meticulous consideration by companies before entering the international arena. In
addition, potential alterations to regulations and policies by the Vietnamese government
underscore the importance of continuous monitoring of pertinent information and close
engagement with governmental bodies to ensure compliance and capitalize on emerging prospects.
In summary, Vietnam's political situation appears conducive for SMEs venturing into
foreign exports, contingent upon a thorough appraisal of the specific business
environment and an understanding of the prevailing political and legal challenges and
opportunities. It is imperative to approach the Vietnamese market with informed
deliberation and a proactive stance toward evolving dynamics. 2. Promotional Activities
In recent years, the Vietnamese government has carried out a series of activities and
events to promote the export of agricultural processing products in general, creating
opportunities to promote the export sector in general to quickly recover and develop after the COVID pandemic.
● To support export businesses in finding outlets in the context of export difficulties,
helping Vietnamese businesses participate more deeply in the international supply
chain of goods, on August 11, 2023, the Ministry of Industry and Trade organized a
Seminar, interview between export businesses in the textile, agricultural and
processed food industries, domestic and international experts with international
distribution and procurement channels.
● The Ministry of Industry and Trade of Vietnam provides market information, trade
policies, and export incentives to Vietnamese enterprises that want to enter the Indian market. lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
● The Vietnam Trade Promotion Agency (VIETRADE) facilitates trade promotion
activities such as trade missions, trade shows, and online platforms for Vietnamese
exporters and Indian importers
3. Export Experience of Alluvia Chocolate Company
Alluvia Chocolate, as an experienced SME, has successfully ventured into the Japanese
market and actively participated in food exhibitions in France. This demonstrates their
capability to navigate international markets. Therefore, it is prudent for Alluvia to
strategically expand its export efforts to additional countries beyond Japan and France.
Their established track record and expertise can be leveraged to tap into new markets,
fostering growth and global recognition for their premium chocolate products.
4. Alluvia Chocolate’s SWOT Analysis STRENGTHS WEAKNESSES lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
Standard and Safe Ingredients for
Varied Chocolate Flavors May Not Health: Suit Everyone's Taste:
Alluvia is known as a chocolate brand
While Alluvia is praised for its delicious
using 100% pure cocoa from the fertile
chocolate flavors, some of its products,
Mekong Delta region, cultivated
such as chili or ginger-flavored
according to international standards and chocolates, may be off-putting to certain
UTZ certified. Additionally, Alluvia
consumers due to their unconventional
openly shares its ingredient processing
ingredients. Therefore, these product
procedures on its official website and
lines could pose a challenge for
emphasizes meticulous handmade
consumers who prefer traditional
processing at each stage. This ensures chocolate flavors.
the product's quality and safety.
Unique and Diverse Product Lines
Relatively Young Brand:
In addition to products like Single-
Alluvia is considered a latecomer in the Origin Chocolate, filled
Vietnamese chocolate market, having
chocolates, and fruit-covered chocolates, been introduced in 2014. It faces intense
Alluvia also produces a variety of
competition and the possibility of being
products such as cocoa powder, cocoa
overshadowed by more established
beans, chocolate gift boxes, and unique
brands with a longer history, such as
chocolates like ginger or chili-flavored Legendary Chocolatier.
chocolates. Customers can easily find
chocolates that suit their preferences due
to the wide range of options, from mildly
sweet to intensely bitter, and various sizes. Limited Recognition: Affordable Pricing
Despite opportunities for collaboration
Another strength of Alluvia is its
with major partners, the Alluvia brand
affordable pricing. Despite offering
has not yet gained significant
high-quality and delicious products
recognition in the chocolate market,
made from pure ingredients, the brand is both domestically and internationally.
known for its relatively reasonable
This poses a challenge for a brand with
prices, ranging from 80,000 to 100,000
aspirations for international expansion. VND per product. OPPORTUNITIES THREATS lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
International Expansion: Entering Competitive Landscape:
new markets offers the potential for
Established competitors in the target
significant growth, especially in
markets may pose a challenge in terms
regions with a growing appetite for
of market share and customer loyalty. chocolate products.
Global Trend Towards Premium Regulatory Hurdles: Chocolate:
Complying with different international
The worldwide shift towards premium
regulations, including import/export
and artisanal chocolates presents an
requirements and food safety standards,
opportunity for the company to can be cumbersome.
showcase its quality products. E-commerce: Currency Fluctuations:
The growth of online shopping provides Exchange rate fluctuations can impact
a platform for reaching international pricing and profitability.
customers without the need for physical stores in every market.
Based on the SWOT analysis, the company needs to undertake several strategic actions
to leverage its strengths, address its weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and
mitigate threats when exporting its chocolate products to other countries:
Quality Assurance and Compliance: Ensure stringent quality control and compliance
with international regulations and food safety standards. This includes maintaining
certifications and adapting product labeling and packaging as required by each market.
Cultural Adaptation: Customize marketing and branding strategies to resonate with the
local culture and values. This may involve adapting advertising campaigns and product messaging.
Economic Monitoring: Keep a close eye on economic conditions in target markets and
be prepared to adjust pricing and marketing strategies accordingly during economic downturns or upturns.
Marketing and Promotion: Create a strong international marketing strategy that focuses
on the company's brand, quality, and uniqueness in the premium chocolate market.
Utilize digital marketing and social media to reach a global audience. lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
Trade Shows and Exhibitions: Continue participation in international exhibitions and
trade shows to showcase products, build brand awareness, and connect with potential partners and distributors.
E-commerce Expansion: Embrace e-commerce as a platform for international sales,
ensuring a user-friendly online shopping experience, secure payment options, and efficient logistics.
Overall, the company should adopt a flexible and market-specific approach, recognizing
that each target market may require unique strategies. Successful international
expansion will depend on a combination of adaptation, quality assurance, and strategic
partnerships while effectively navigating potential challenges. III.
International Market Selection (IMS)
Based on the criteria outlined in Svend Hollensen's Global Marketing textbook, the key
factors used to segment international markets are divided into the following groups:
market potential and market competition.
1. Criterias and Developing Segments
In the process of market research, our research team conducted an investigation into
information from market research companies regarding countries in the Asia-Pacific
region with the highest growth potential for the chocolate market. According to Mordor
Intelligence, a reputable market research company based in India, there are six markets
in the Asia-Pacific region that show the most promising growth potential for the
chocolate product category. These markets include Australia, Japan, Indonesia, India, China, and South Korea. Knock - out criteria
With the aim of entering a new market, Alluvia, as a small business, will focus on
finding a niche and limiting intense competition and confrontation. Therefore, countries
that are already involved in cocoa cultivation and chocolate exports will be excluded
from consideration. In this case, Japan will be removed from the list due to prior
presence in the market, and Indonesia will also be eliminated for its involvement in
cocoa cultivation and chocolate exports. Screening Criteria lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
In general, the factors within the market potential group will be primarily used for
market segmentation. These factors include economic factors, political factors, and
language. Specific criteria will be developed based on Svend Hollensen's Global Marketing textbook. 2. Preliminary Screening
In this section, the group uses political, economic, and linguistic factors to evaluate four
countries: India, China, Australia, and South Korea. A rating scale from 1 to 5 is used
for the assessment. The total weight is 1, and the maximum score is 5.
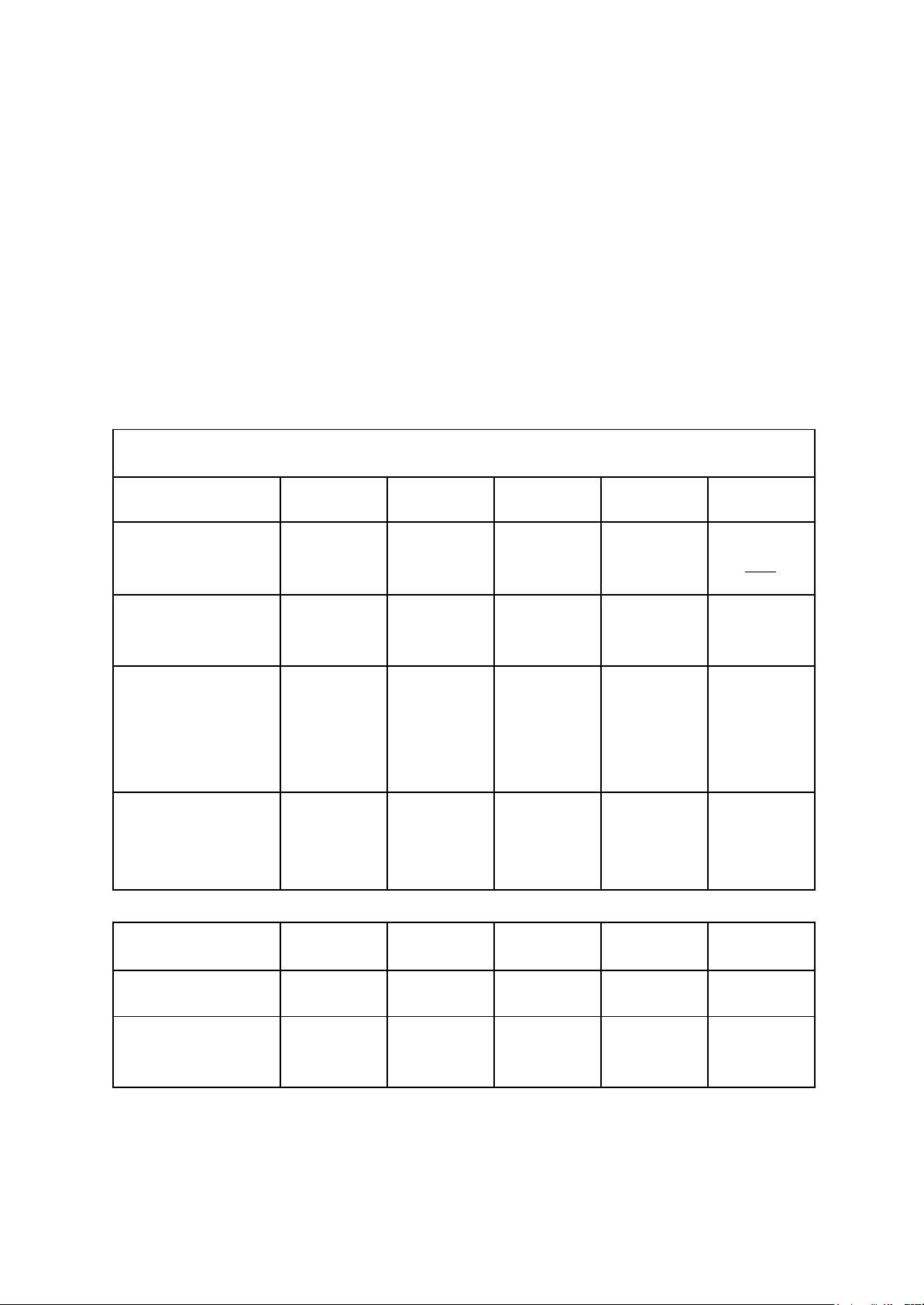
The table below illustrates how the scoring is calculated for each factor. Preliminary Screening Score Weight 1 3 5 Source - 2.5 - Political stability 0.3 <= -0.5 - 0.5 - 0.5 0.5 =< link GDP (trillions GDP + USD) 0.2 1 - =< 7 7 - 12 12 =< Country Average percentage of growth of GDP in 0.25 <= 3 3 - 5 5 =< Calculation 2018 - 2022 (%) Level of Key word prevalence in 0.25 Very Low Moderate Very High + country English
After collecting the data, our group has obtained the following assessment results: Weight India China Korea Australia Political stability 0.3 0.3 0.6 0.6 0.6 GDP (trillions USD) 0.25 0.2 1 0.2 0.2 lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467 Average percentage of growth of GDP in 0.25 0.75 0.75 0.25 0.25 2018 - 2022 (%) Level of prevalence in 0.25 1.25 0.25 0.75 1.25 English Total Score 2.5 2.6 1.8 2.3
Based on the calculated results, the countries selected to continue the evaluation are
those with scores greater than 2. South Korea has been excluded from the assessment
list due to its score falling below this threshold.
3. Fined - grained Screening
In this section, the group uses factors related to market potential and trade barriers to
evaluate four countries: India, China, and Australia. A rating scale from 1 to 5 is used
for the assessment. The total weight is 1, and the maximum score is 5.
The table below illustrates how the scoring is calculated for each factor.
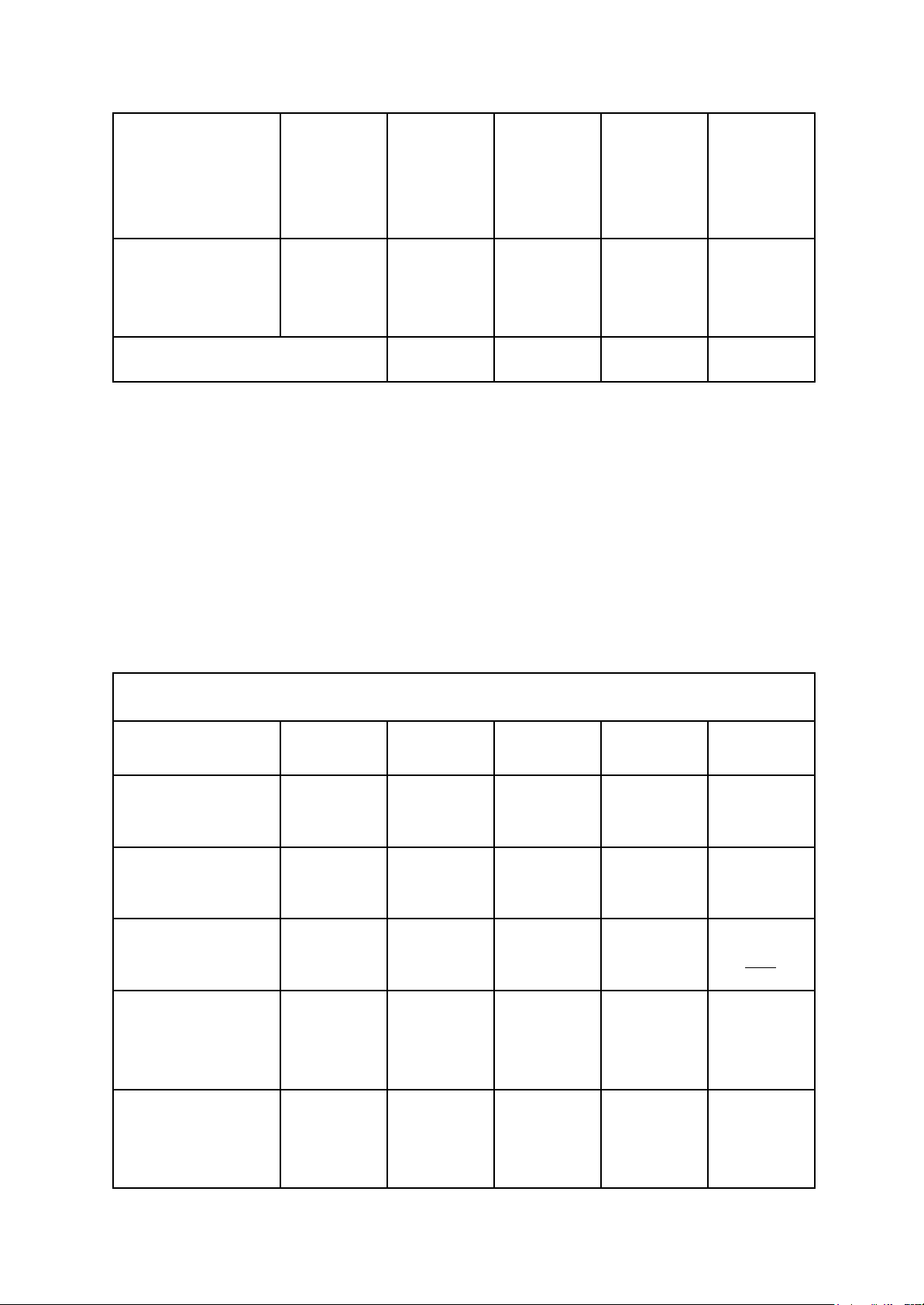
Fined - grained Screening Weight 1 3 5 Source Market size Key word + 0.15 <=1 1 - 3 3 =< (billions USD) Country Market Growth in Key word + 0.25 <= 3 3 - 6 6 =< 2023 - 2028 (%) Country Trade Barrier Index 0.2 5.5 =< 4.5 - 5.5 4.5 >= link Consumption of chocolate per Key word + 0.15 <=1 1 - 3 3=< capita (kg) Country Competitive intensity (HHI Key word + 0.25
2500 =< 1500 - 2500 1500 >= Country Index) lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
After collecting the data, the group has obtained the following assessment results: Weigh India China Australia Market size 0.15 0.45 0.75 0.15 (billions USD) Market Growth in 0.25 1.25 0.75 1.25 2023 - 2028 (%) Trade Barrier Index 0.2 0.2 0.6 0.6 Consumption of 0.15 0.45 0.15 0.75 chocolate per capita (kg) Competitive intensity (HHI 0.25 1.25 0.75 0.25 Index) Total Score 3.6 3 3
Based on the assessment, India appears to be a potential market for Alluvia Chocolate.
IV. Host country (India) Situation 1. Political Environment 1.1. Political System
India's multi-party system is dominated by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), which has
recently secured victories in local elections, strengthening its position for the 2024
general elections. India operates as a federal union with both national and state-level
political parties. The country has 28 states and 7 union territories, governed by a
parliamentary democratic system with two houses in the federal parliament. While
states have legislative powers, national laws take precedence. There are two recognized
types of political parties: national parties recognized at the federal (national) level and
state parties recognized at the state level.
1.2. Import situation of food in India
On March 31, 2023, the Directorate General of Foreign Trade of India, under the
Ministry of Commerce and Industry, announced the Foreign Trade Policy 2023,
replacing the previous foreign trade policy that had been in place since 2015. In detail, lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
India has adopted a changed approach in formulating the Foreign Trade Policy 2023,
shifting from direct support to tariff reduction. India's Foreign Trade Policy 2023 is also
closely tied to India's efforts to streamline business operations through online
management, licensing, and approval of documents, reducing administrative
procedures, and cutting the costs associated with administrative procedures for businesses.
The changes in India's Foreign Trade Policy 2023, with a focus on simplifying business
operations, reducing administrative burdens, and promoting trade, present a favorable
opportunity for businesses looking to export their products to India. These reforms aim
to make it easier for foreign companies to enter the Indian market and engage in
international trade with the country. However, businesses should still conduct thorough
market research, understand regulatory requirements, and adapt their strategies to
leverage this opportunity effectively.
Tariff of chocolate products
Specifically, for Vietnam - a partner of India in AIFTA, most of the goods exported from
Vietnam to India as of the current year 2023 only incur customs duties ranging from 0
- 5% - this includes chocolate products. Compared to the standard non-preferential tariff
rate of 35%, this represents a significant advantage for Vietnamese goods to compete in the Indian market.
However, in India, the overall tariff for an imported item is calculated based on the
following formula: IGST + basic customs duty + other protective duties (if
applicable), which IGST means “Integrated Goods and Services Tax”, that is applied
to goods and services moving between states, as well as those being exported or imported into India.
For chocolate products imported from Vietnam, the IGST rate is specified as 18%.
Therefore, the total tariff on this item in India will be 23%. lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467 2. Economic Environment
2.1. Exchange rate of Indian rupee (INR) and Vietnam dong (VND)
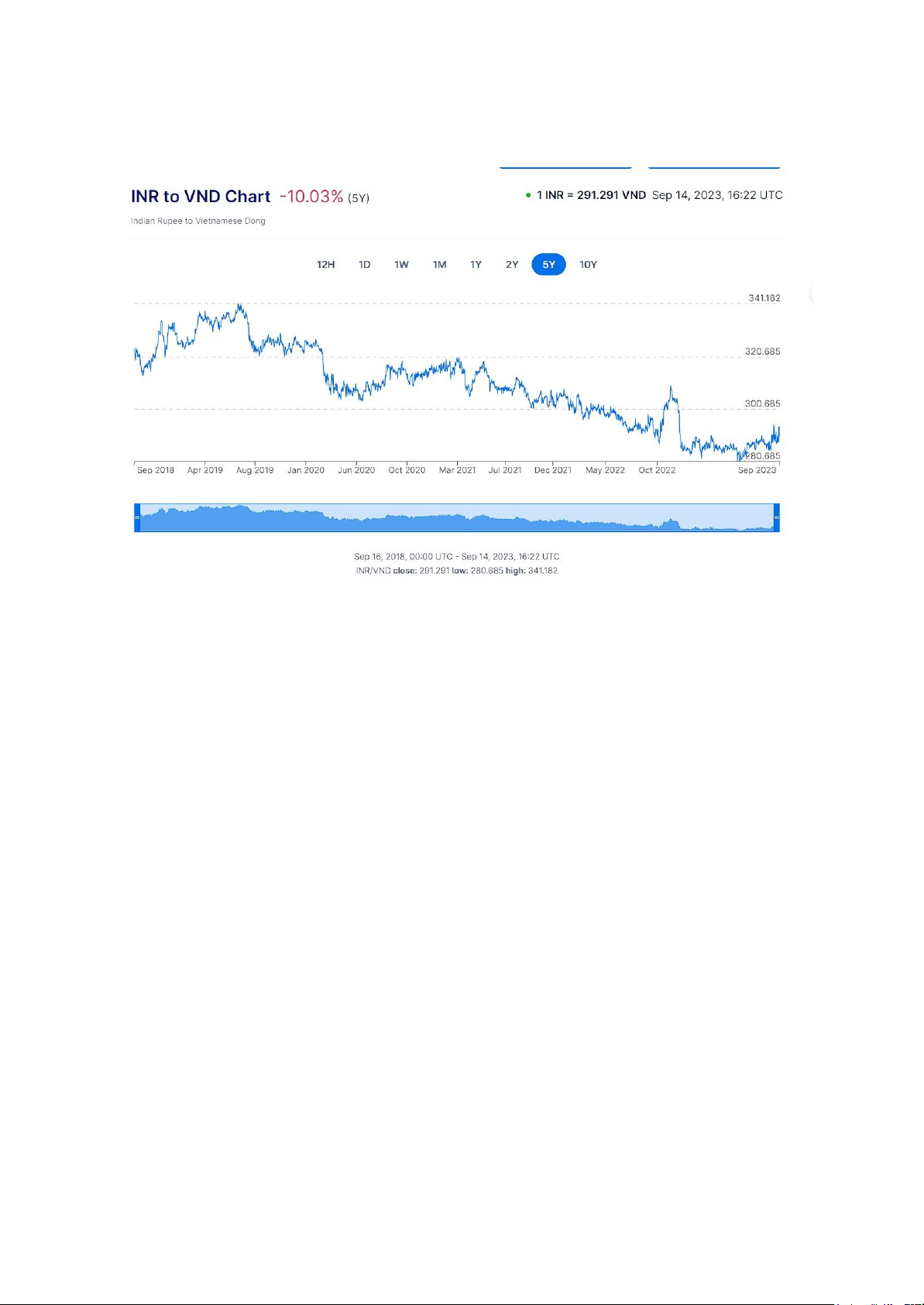
According to the exchange rate chart of the Indian Rupee to the Vietnamese Dong, we
can see that this rate has fluctuated significantly over the past 5 years. In general, the
exchange rate between two countries has experienced a downward trend that indicates
a decrease in INR power. The main reasons might be the US-China trade war, political
tensions between India and Pakistan, the Covid-19 pandemic, and economic support
measures from central banks affected this rate, and the oil price crisis is also a reason
for the strong depreciation of the rupee. This is the advantage for Vietnamese companies
to export goods to India, due to the low exchange rate. And this level of exchange rate,
in the recent macroeconomic context, is predicted to maintain a low level in the medium-term. 2.2. AIFTA
The ASEAN-India Free Trade Area (AIFTA) is a free trade agreement between India
and the 10 member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). It
was signed in 2009 and came into effect in 2010.
The AIFTA aims to eliminate tariffs on most goods traded between India and ASEAN,
and to reduce non-tariff barriers. It also includes provisions on investment, intellectual property, and services. lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467 Agreement
As in this agreement, there is a commitment from the first parties, the Indian side
commits to eliminate 80% of tariff lines by 2016, increasing to 100% in 2023. The
accession to AIFTA facilitates trade between Vietnam and India. Thanks to trade
commitments, trade and exchanges between the two countries have been enhanced. The
elimination of tariff barriers helps businesses from AIFTA members have the
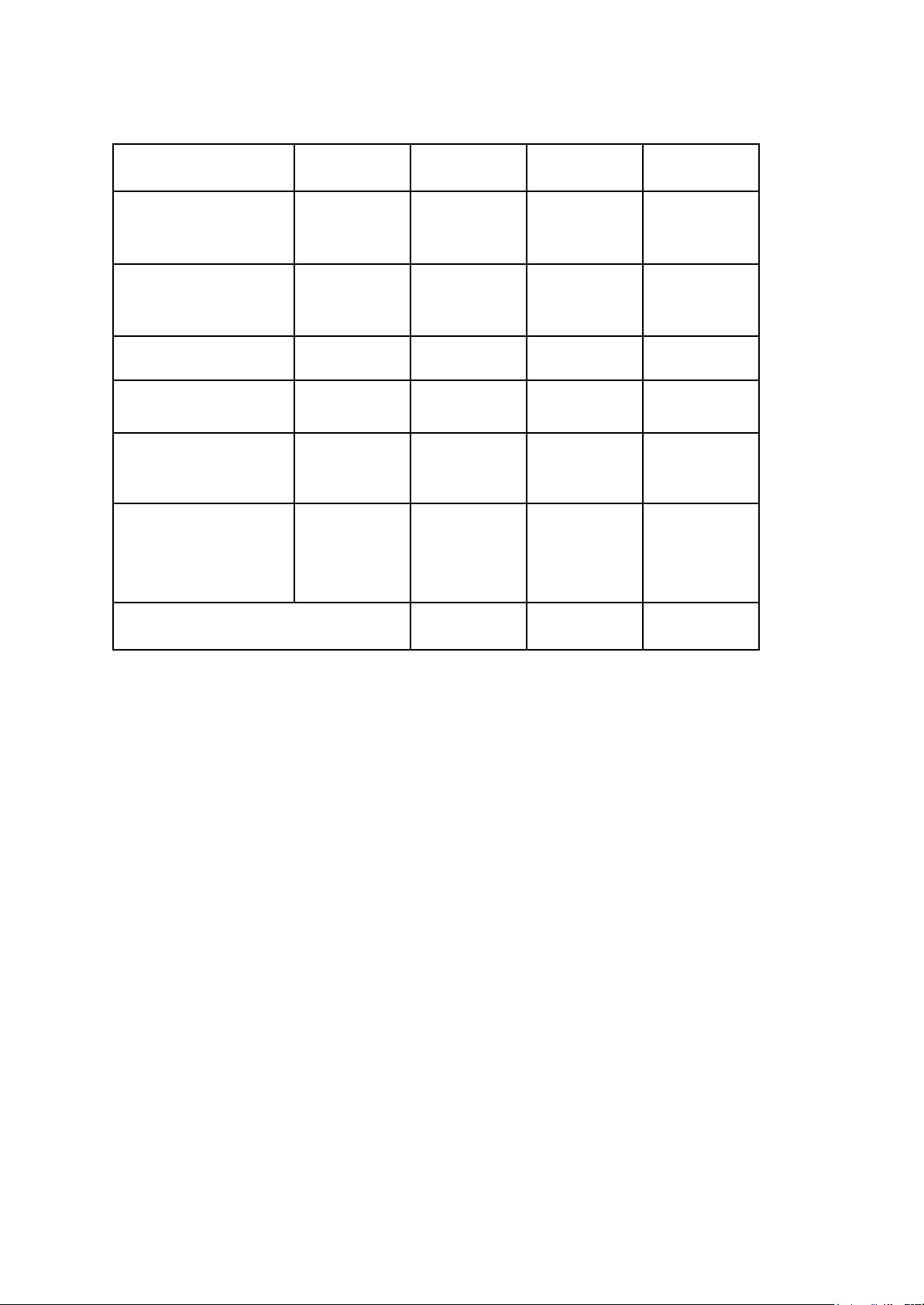
opportunity to expand the market, have a competitive advantage in price in the market of AIFTA member countries. 3. Social Environment 3.1. Cultural Features Characteristic India Communication & Language indirect, implicit
minimize body contact, respect other’s Sense of self and space personal space
quite simple and typically untailored, Dress and appearance religious rule Food and eating habits eating is a social event Time-consciousness time = relationship extended family, Family and friends
loyalty and responsibility, respect for old age
group conformity, harmony, hospitality, Values and norms religion and spirituality
individuals accept fate, believe in Beliefs and attitudes astrology, gender roles Mental process and learning creativity, problem-solving lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
relationship-oriented, rewards based on Business/work habits
seniority, work is a necessity 3.2. Cultural Elements 3.2.1. Language
India is a multilingual nation with 22 recognized languages; however, not all 22
languages are widely used throughout the country. Instead, different regions will utilize different regional languages.
After India gained independence, the states within India used regional languages to
establish their boundaries. Northern India is often described as the "Hindi belt,"
meaning that Hindi is predominantly used in states within this region. In contrast,
Southern India has a greater linguistic diversity, with languages like Telugu, Marathi,
Odia, etc. Notably, when Hindi, recognized as the national language, was rejected as
the primary language across all regions, English was capable of filling that role. English,
recognized as the language that plays the role of communication bridge in this
multilingual nation, is not only widely used nationwide but also plays a predominant
role in the fields of business and education in India.
English is recognized as the country's second language and plays a vital role in
connecting the diverse regions of this multicultural nation. English makes India a hub
for international companies and corporations, as most office environments use English
for communication – an advantage for foreign managers who may not have had the
opportunity to learn an Indian language to interact with their Indian staff. Company
owners can hire labor from across the country because English is a common language
among people with different mother tongues. It cannot be emphasized enough that as
access and proliferation of English varies substantially along socioeconomic class lines,
access to English in business, education, and media is linked to international capital and
has a great capacity to increase one's economic and social position.
On the other hand, one cannot deny the role of regional languages in India. Each
regional language contributes to shaping the policies, and laws of each Indian state, as
well as the behavior, lifestyle, and daily activities of each region's population.
Therefore, enhancing and practicing multilingualism in India is not only about
preserving the unique regional identity but also has a significant impact on how Indians
interact with their fellow Indians and the larger world. lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467 3.2.2. Manners and Custom Guest is God
In India, the saying "Atithi Devo Bhavah" is always put first by Indians. This sentence
means "The guest is God". This is a Sanskrit verse taken from Hindu scriptures and later
became part of the code of conduct of Hindu society. Accordingly, guests always play
the most important role for Indians. 3.2.3. Education
In India, it is common for people to pursue higher education even if they do not come
from wealthy families. India is very strong in technology education. To be able to get a
good job with a high salary, Indians must have a university degree. 3.2.4. Attitudes and Value To Community
As a country of Eastern culture, Indians are often not sympathetic to acts of affection in
crowds or public places. These actions will receive curious, confusing, and even
discriminatory looks from Indians. Indians often value community and are willing to
help others in the community. They often participate in social and charitable activities to support those in need.
Religion often deeply influences the daily lives of Indians and plays an important role
in festivals, rituals, and even personal life decisions. Believe, respect beliefs and pass
them on to future generations to create a big and strong religion. To Family
In India, both patriarchal families as well as mother-centric families are found. Respect
to the elder members of the family, especially taking care of the parents in their old age
is considered as the utmost duty of every son and daughter.
India's culture has a strong belief in the law of karma. ‘As you sow, so shall you reap.’
Hence it is ingrained from a very young age that if we do not take care of our parents
when they are old we would be left in the cold during our twilight years. Also, it is a
great way to express our gratitude to our parents for all that they have done when we were young. lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467 To Self-owned
Indians generally place a high value on harmony and unity with others, keeping a strong
nexus with their community and relatives. A unified and interdependent community or
family provides a support system that an individual can rely on daily.
A typical Indians can be described as:
● Respect family: Family plays an important role in Indian life. Often, they will put
family first, and taking care of their parents and elderly family members is
considered a respectful and sacred duty.
● Religion and beliefs: Many Indians adhere to their religion and beliefs firmly. They
may perform religious ceremonies and rituals, regularly attend temples, churches,
or sacred places, and consider religion an important part of daily life.
● Career guidance: In India, it is not uncommon for people to pursue higher education
even if they do not come from wealthy families. This is because education is seen
as a way to improve one’s station in life. Indians often aim high in their studies and
career development. Fields such as information technology, engineering, medicine,
and business are often popular career choices.
● Respect for traditions: Indians generally respect their traditions and festivals.
Traditional festivals and ceremonies may incorporate religion, culture, and history,
and people often respect and follow these rules and traditions.
● Sociable and hospitable: Indians are known for their hospitality. They believe in
treating guests with respect and offering them the best of what they have. This value
is evident in the way that Indians welcome tourists from all over the world.Many
Indians have a sociable and hospitable attitude. They often open their doors to
friends and others enthusiastically and kindly. 3.2.5. Aesthetics
Indian aesthetics can exhibit a wide range of diversity among individuals in India, just
like other cultures. However, these are some key features about the Indian aesthetics. Vibrant colors
Indian aesthetics are known for their vibrant color tones, which are usually lively and
eye-catching such as orange, red, yellow…since color has great impacts on Indian art,
clothing, and celebrations. It symbolizes various emotions, deities, and cultural
significance. For instance, according to Indian notions, the color red often symbolizes love, passion and even power. lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467 Intricate patterns
Indian art and design often depict intricate and detailed patterns, not only on jewelries
but also on textiles and architecture. These patterns are often symmetrical and are
famous for their complexity. Indian’s intricate patterns can also be easily seen on
clothes, architecture and even paintings. Symbolism
Another key point in the Indian aesthetics is that they are filled with symbols and
iconography as these symbols represent deep cultural, religious as well as spiritual
meanings. Indian symbols are also used extensively in art and rituals. Spirituality and religion
Being known as one of the earliest cradles of human civilization, India is famous for its
spiritual and religious culture, which can be reflected in the architecture of temples,
meditation as well as the practices of yoga. It can be easily seen that religion as well as
spirituality are the main cores of Indian culture and Indian aesthetics.
3.3. Hofstede’s Model Analysis Power distance
India has a high power distance score, which means that people accept that power is
unequally distributed in society. This is reflected in the hierarchical nature of Indian
society, with clear expectations about who should be obeyed and who should be in
charge. The high power distance in India means that people are expected to show respect
for their elders and superiors. This is reflected in the way that people address each other,
with younger people using more honorific language than older people. In the workplace,
employees are expected to show respect for their managers and supervisors. Moreover,
people are more likely to accept decisions made by their superiors, even if they disagree with them. Uncertainty avoidance
India has a medium low preference for avoiding uncertainty. In India, there is
acceptance of imperfection; nothing has to be perfect nor has to go exactly as planned.
India is traditionally a patient country where tolerance for the unexpected is high ; even
welcomed as a break from monotony. People generally do not feel driven and compelled
to take action-initiatives and comfortably settle into established rolls and routines
without questioning. Rules are often in place just to be circumvented and one relies on
innovative methods to “bypass the system”. A word used often is “adjust” and means a lOMoAR cPSD| 59691467
wide range of things, from turning a blind eye to rules being flouted to finding a unique
and inventive solution to a seemingly insurmountable problem.
The high uncertainty avoidance in India means that people are often reluctant to take
risks or try new things. This is reflected in the Indian education system, which is very
traditional and focused on rote learning. There is a strong emphasis on tradition and on
doing things the way they have always been done. Individualism-collectivism
India is a collectivist society, which means that people identify strongly with their in-
groups, such as their family, caste, or religion. This leads to a strong sense of community
and cooperation, but also to a focus on group harmony rather than individual achievement.
The collectivist nature of Indian society means that people are more likely to put the
needs of their group ahead of their own needs. This is reflected in the way that Indian
families often live together for many generations. There is a strong sense of community and belonging in India Masculinity-femininity
India is a masculine society, which means that there is a strong emphasis on
achievement, success, and competition. This is reflected in the Indian workplace, where
there is a clear focus on results and performance. The masculine nature of Indian society
means that men are often seen as being more important than women. This is reflected
in the fact that women are underrepresented in positions of power in India. There is also
a strong emphasis on achievement, success, and competition.
3.4. Cultural Dimensions affects Ethical Decision-making
In a high power distance society, people are more likely to obey the orders of their
superiors, even if those orders are unethical. For example, a manager may ask an
employee to falsify financial records, and the employee may feel obligated to comply
because the manager is in a position of power.
In a high uncertainty avoidance society, people are more likely to make decisions that
avoid risk, even if those decisions are not ethical. For example, a company may decide
to bribe a government official in order to get a permit, even though bribery is illegal.
In a collectivist society, people are more likely to make decisions that benefit their in-
group, even if those decisions are not ethical. For example, a company may decide to


