




Preview text:
Chapter 1
1. From a batch of 6 red balls, 9 blue balls and 5 yellow balls, 5 balls are drawn. Find the probability of getting a) 2 red balls; b) 2 yellow balls, 3 green balls;
c) at least 1 red ball; d) no more than 1 red ball.
2. A Statistics exam paper contain eight questions, four in Part A and four in Part B.
Candidates are required to attempt five questions. In how many ways can this be done if: a) There are no restrictions,
b) At least two questions from Part A and at least two questions from Part B must be attempted?
3. Let A and B be any two events. Know P(A + B) = 0,7; P(A.B) = 0,22; P(A) = 0,5. Find , .
4. There are three people, each person shoots a bullet at the target with the probability of
hitting is 0.6; 0.7; 0.8, respectively. Find the following probabilities:
a) Only the second person hits b) Exactly one person hits
c) Only the third person missed; d) Exactly two people hit e) All three hit f) No one hits.
5. There are two boxes, each c
ontaining 5 marbles. The first box contains 3 red marbles
and 2 blue marbles. The second box contains 4 red marbles and 1 blue marble. 2 balls are
drawn at random from the first box and 1 ball from the second box. Find the probability
of getting at least 1 green marble.
6. A group of 100 students are asked which of three types of TV programme, drama,
comedy and reality, they watch regularly. They provide the following information: 15
watch all three types; 18 watch drama and comedy; 22 watch comedy and reality TV; 35
watch drama and reality TV; 10 watch of none these programmes. There are three times
as many students who watch drama only than comedy only and two times as many who
watch comedy only than reality TV only.
A random student is chosen out of 100, find the probability that the student watches only one programme.
7. Eight people, A, B, …., H are arranged randomly in a line. What is the probability that
A and B are next to each other.
8. A group of 12 people consisting of 6 married couples is arranged at random in a line
for a photograph. Find the probability that each wife is standing next to her husband.
9. Suppose that P(A|B) = 0.4 and P(A) = 0.3; P(B) = 0.5. Determine P(A.B); ; P(A + B) and P(B|A).
10. In a box there are 6 good products and 4 bad products. The first time took out 2
products, the second time also took out 2 products (without replacement).
a) Find the probability of getting 1 good product each time.
b) Find the probability of getting 2 good products at the second time.
c) Assuming that 2 good products are obtained the second time, find the probability that
at least 1 defective product is obtained the first time.
11. Ali can travel to work either by bus or in his car. The probability that Ali is late for
work when he goes by bus is 0.15, and the probability that he is late when he uses his car
is 0.1. Ali uses his car for 70% of his journeys to work.
a) Find the probability that Ali will be late for work on a randomly chosen day.
b) Find the probability that Ali travels by bus, given that he is late for work.
12. Suppose we are given 3 boxes, Box A contains 6 red balls and 2 blue balls; Box B
contains 4 red balls and 3 blue balls; Box C contains 7 red balls and 2 blue balls. Taking a
box and then choosing a ball at random.
a) What is the probability that the chosen ball is red?
b) Given that the chosen ball is blue, find the probability it is taken from box B.
13. There are 3 packages, each with 10 products. The first package contains 9 products of
type I; the second package contains 8 products of type I; and the third package contains 6 products of type I.
a) From each package, 2 products are randomly selected without replacement for
inspection. If both two checked products are of type I, then buy that package. Find the
probability that at least one package is purchased.
b) Randomly select one package, and then randomly select 2 products from the selected
package. Assume that the 2 products selected are of type I. Find the probability that they
are 2 products of the first package.
14. Before putting product X on the market, a random interview with a number of
customers found that the respondents "will buy", "may buy" and "don't buy" account for a
proportion of 17%, 48% and 35%. Given that the percentage of customers who actually
buy product X corresponding to the above answers is 40%, 20% and 4% respectively.
a) Randomly select a customer. Find the probability that the customer actually buys product X.
b) Randomly select a customer and find that this person has purchased product X. Find
the probability that this customer has answered "no" when interviewed.
15. A factory has 4 machines producing the same products. Assume that the first machine
produces 28% of the total products, the second machine produces 30%, and the third and
fourth machines are equally productive. The rate of qualified products of 4 machines is
95%, 97%, 94% and 96%, respectively.
a) Randomly select a product from the factory. Find the probability of selecting a qualified product.
b) Suppose that when choosing a product in the factory, it is found to be a defective
product. Find the probability that this is produced by the second machine.
16. An insurance company divides insurance coverage into 3 categories: low risk
(accounting for 30%), medium risk (accounting for 45%) and high risk (accounting for
25%). Knowing the rate of customers having an accident within a year corresponding to
the above subjects are 0.04; 0.16 and 0.35.
a) Randomly select one customer. Find the probability that this person has an accident within one year.
b) If the selected customer has an accident, which group of people is most likely to be in? Chapter 4
1. The probability distribution of the random variable X is given in the following table: X 1 2 3 4 5 Pc3c c2 c2 15/32 a) Find the value c.
b) Find P(2X > 3); E(X); E(Y); var(X); var(Y), where Y = 2X + 3.
2. A box contains 10 white chalks and 4 blue chalks. Randomly select 3 chalks. Let X be
the number of blue chalks taken. Make a table of the probability distribution, the
probability distribution function and calculate the expectation, variance, and standard deviation of X.
3. When the health department tested private wells in a country for two impurities
commonly found in drinking water, it found that 40% had impurity A, and 50% had
impurity B, 20% had neither impurity. If a well is randomly chosen from those in the
country, find the probability for X, the number of impurities found in the well.
4. A gunner is given 3 bullets and is allowed to shoot each one in turn until it hits the
target, then stops shooting. The probability of hitting each bullet is 0.8. Make a table of
the probability distribution and calculate the expected, variance, and standard deviation of the number of bullets: a) hit the target; b) used.
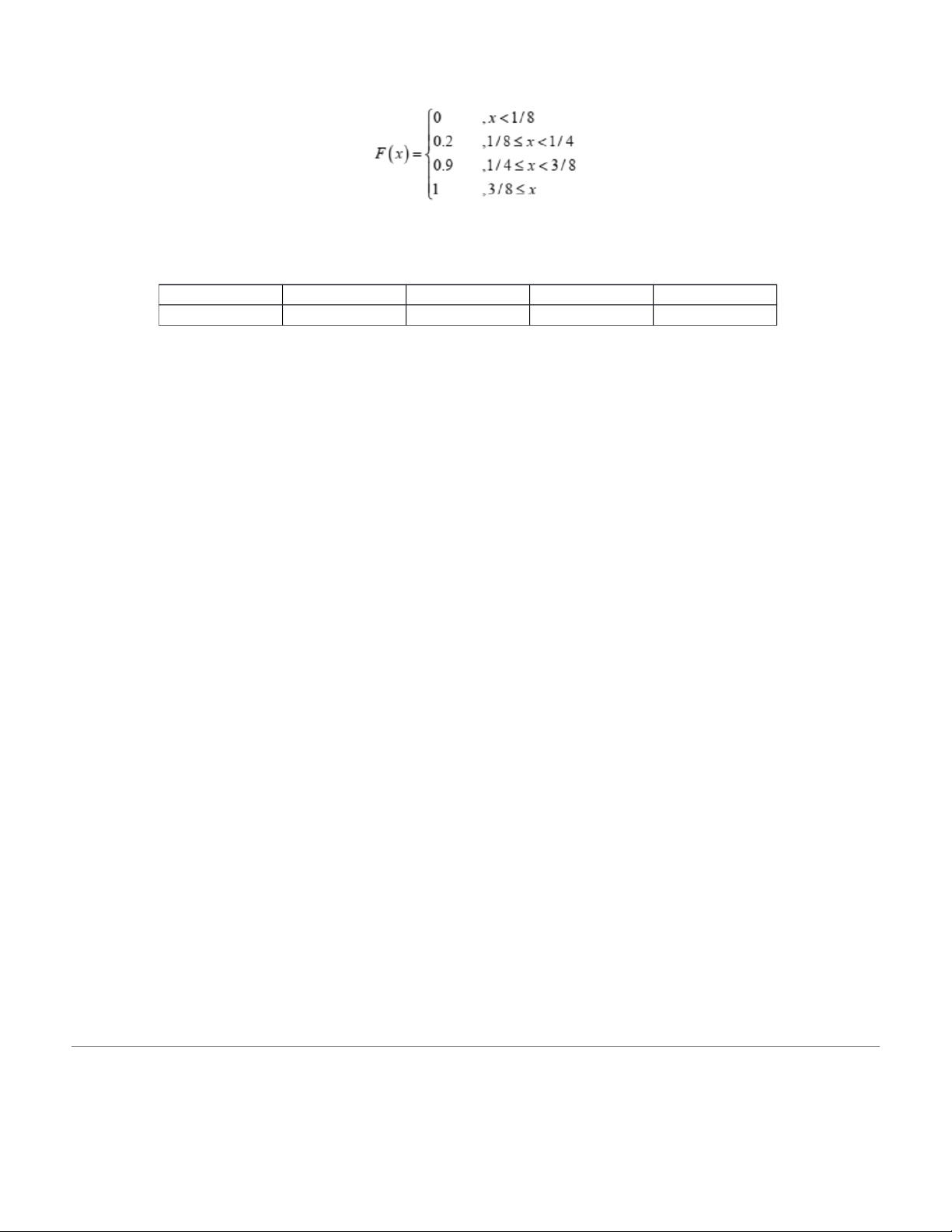
5. A random variable X has the following cumulative distribution function:
Determine the table of probability distribution of X.
6. A random variable X, has the probability distribution shown below. X1234 P 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
Two observations are made of X and the random variable Y is equal to the larger minus
the smaller; if the two observations are equal, Y takes the value 0. Find the probability
distribution of Y. Which value of Y is most likely?
7. Suppose the probability of giving birth to baby boy is 0.53. A family with 4
children. Find the probability that the family has: a) exactly one boy;
b) the same number of boys and girls; c) at most one boy d) at least one boy.
8. The multiple-choice test has 20 questions, each with 4 answer options, of which only 1
is correct. A student did not study, so when he took the exam, he randomly chose one
option for each question. Let X be the number of questions that the student answered
correctly. Find the probability distribution of X and calculate the expectation, variance, and standard deviation of X.
9. There are 20 independent machines in one factory. The probability that each machine
fails in a day is 0.16. Find the probability in a day that at least 2 machines fail. Calculate
the expectation and variance of the number of machine failures in a day.
10. The seller packs the products into boxes, each box contains 10 products, including 7
products of class A. The buyer checks by randomly taking 1 product from the box, if it is
found that the product is class A. then he buys the box, otherwise he doest not buy.
a) Suppose that the buyer has checked 10 boxes. Find the probability that the he bought at least 3 boxes.
b) At least how many boxes must be checked so that the probability that at least 1 box is
purchased is not less than 0.95?
11. A Machine produces items of which 1% at random are defective. How many items
can be packed in a box while keeping the chance of one or more defectives in the box to
be no more than 0.5? What are the expected value and standard deviation of the number
of defectives in a box of that size?
12. A bag contains two biased coins: coin A shows Heads with probability 0.6, and coin
B shows Head with probability 0.25. A coin is chosen at random from the bag, and tossed three times.
a) Find the probability that the three tosses of the coin show two Heads and one Tail in any order.
b) Find the probability that the coin chosen was coin A, given that the three tosses result in two Heads and one Tail. 13. Given that and Find the values of n and p.
14. The number of eggs, X, laid by the female tawny owl has the probability distribution given in the following table: X 2 3 4 P 0.1 0.2 0.7
For any egg, the probability that it is hatched is 0.8, independently of all other eggs. Let
Y denote the number of hatched eggs in a randomly chosen net.
a) Obtain the probability distribution of Y. b) Find E(Y) and Var(Y).
15. At a traffic control station, 42 cars passed in 10 minutes. Find the probability that:
a) 5 cars pass in 1 minute b) At least 1 car passes in 1 minute.
16. At an airline ticketing point, on average, 2 people come to buy tickets every 5
minutes. Find the probability that 5 people come to buy tickets in 10 minutes.
17. Randomly select 2 marbles from a box containing 3 red, 2 yellow, and 4 green
marbles. Let X and Y be the number of red marbles and the number of yellow marbles,
respectively, from the 2 marbles.
a) Write down a table showing the joint probability mass function for X and Y . b) Find
c) Find the marginal probability mass function for X and Y.
d) Find the conditional probability mass function of e) Are X and Y independent? f) Find Cov(X, Y) and .
18. A game consists in rolling one red die and one blue die. Define the random
variables X and Y as follows:
X = The number showing on the red die; Y = The number of dice that show the number six
So that, for example, if the red and blue dice show the numbers 6 and 5, then X Y X Y
= 6 and = 1, while if they both show the number 6, then = 6 and = 2.
a) Write down a table showing the joint probability mass function for X and Y .
b) Find the marginal probability mass function for X and Y.
19. The statistics of stock interest calculated for 100 USD when investing in two banks A
and B for 1 year are X (%) and Y (%), respectively, giving the results in the table: X Y -2 5 10 -1 0.1 0.15 0.1 4 0.05 0.2 0.1 8 0.1 0.15 0.05
a) Find the marginal probability mass function for X and Y. b) Find c) Are X and Y independent? d) Find Cov(X, Y) and .
e) Write a table of probability distribution of T = X + Y. Find E(T) and Var(T). 20. Chapter 5
1. Let X be a randomly continuous variable with the probability density function: Find k, E(X) and Var(X).
2. Let X be a randomly continuous variable with the probability density function: a) Find E(X); Var(X) ≤X≤ π b) Find P(0 ). 4
3. The time taken by a garage to replace worn-out brake pads follows a normal
distribution with mean 90 minutes and standard deviation 5.8 minutes.
a) Find the probability that the garage takes longer than 105 minutes.
b) Find the probability that the garage takes less than 85 minutes.
c) The garage claims to complete the replacements in “a to b minutes”. If this claim is to
be correct for 90% of the repairs, find a and b, based on a symmetrical interval centred on the mean.
4. The lengths of sweetpea flower stems are normally distributed with mean 18.2cm and standard deviation 2.3 cm.
a) Find the probability that the length of a flower stem is between 16 cm and 20 cm.
b) 12% of the flower stems are longer than h cm. 20% of the flower stems are shorter than k cm. Find h and k.
c) Stem lengths less than 14 cm are unacceptable at the florist’s shop. In a batch of 500
sweetpeas estimate how many would be unacceptable.
6. One factory reported that the time it took workers to assemble car parts was normally
distributed with a mean of 80 seconds and a standard deviation of 10 seconds. Assuming
an assembly time of 60 to 70 seconds is considered to be quick.
a) Find the percentage of factory workers who can do quick assembly.
b) Randomly select a group of 10 workers, find the probability that there are 2 to 3 quick
assembly workers in this group.
5. In a statistics examination, 15% of the candidate scored more than 63 marks and 10%
of the candidates scored less than 32 marks. Assuming that the marks were distributed
normally. Find the mean mark and the standard deviation.
7. A random variable X has a binomial distribution with parameters n = 80 and p = 0.4.
Use a suitable approximation to calculate the following probabilities.
a) P(X ≤34 ) b) P(X ≥26 ) c) P(X = 33) d) P(30 40 <X≤ )
8. A manufacturer of spice jars know that 8% of the jars produced are defective. He
supplies jars in cartons containing 12 jars. He supplies cartons of jars in crates of 60
cartons. In each case making clear the distribution that you are using, calculate the probability that:
a) A carton contains exactly two defective jars.
b) A carton contains at least one defective jar.
c) A crate contains between 39 and 44 (inclusive) cartons with at least one defective jar.
9. Sales (unit: VND million/day) of a grocery store is a normally distributed random
variable with mean sales of VND 15 million/day and standard deviation of VND 5
million. / day. A day is considered a “good sale” if the sales reach over 18 million dong.
a) Calculate the percentage of “good sale” days.
b) Calculate the probability that in a year (360 days) the store has at least 90 days of “good sale”.
10. A sociologist claims that only 3% of all suitably qualified students from inner city
schools go on to university. Use an approximation to estimate the probability that in a
randomly chosen group of 200 such students:
a) Exactly five go to university.
b) More than five go to university.
c) If the probability that more than n of the 200 students go to university is less than 0.2,
find the lowest possible value of n.
11. In one part of the country, one person in 80 has blood of Type A. A random sample of
150 blood donors is chosen from that part of the country. Find the probability that in that
sample at least two have blood of Type A.
12. The distributions of the independent random variable X, Y, Z are N(35, 9), N(30, 8)
and N(35, 9). Write down the distributions of a) X + Y + Z b) 5X + 4Y c) X + 2Y + 3Z d) 4X – Y – 5Z.




