

Preview text:
Final Exam Study Guide Question 1-8: Overview
1. Know what a population parameter is -
A population parameter is a number that describes something about an entire group or population.
2. Definition of interquartile range, variance, standard deviation, and range
-Range = Largest value – smallest value = MAX(A2:A11) – MIN(A2:A11
-IQR focuses only on the middle 50% of the data. = QUARTILE.EXC(A2:A11, 3) - QUARTILE.EXC(A2:A11, 1)
-Variance is a measure of how far a set of data are dispersed out from their mean or
average value. It is denoted as ‘σ ’. 2
-Standard Deviation: The spread of statistical data is measured by the standard deviation.
The degree of dispersion is computed by the method of estimating the deviation of data
points. It is denoted by the symbol, ‘σ’. Population: “=STDEV.P(A1;A20)”; Sample: “=STDEV.S(A1:A20)”
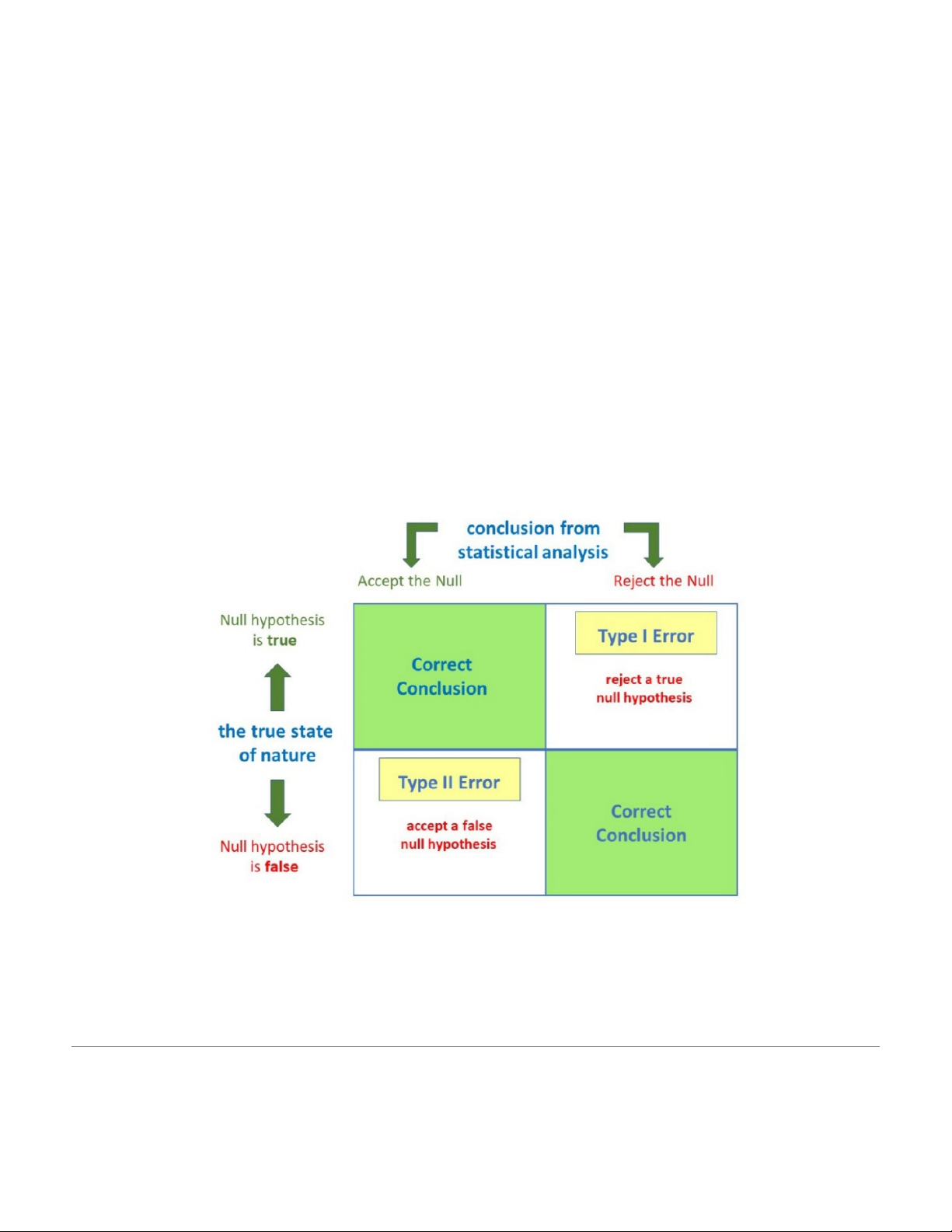
3. Type I error and type II error
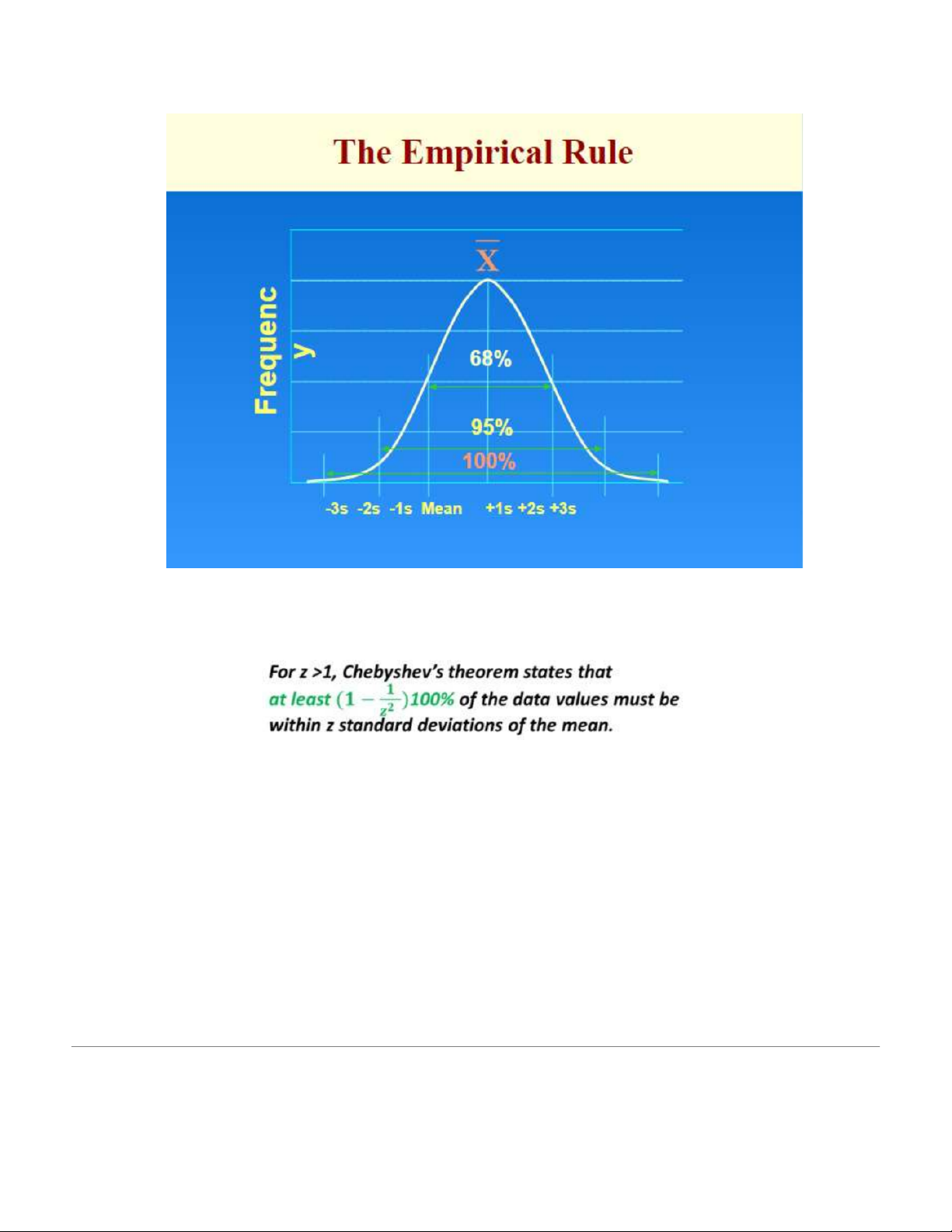
4. Definition of empirical rule 5. Definition of Chebyshev
When the data does not resemble NORMAL, we use what is known as Chebyshev’s Theorem
in place of the Empirical rule.
6. Identify statistic, sample, parameter, population
We have a single population – target of interest.
From this population, we identify a parameter.
This parameter is a fixed numerical value
7. Definition of inferential statistic
Inferential statistic refers to drawing conclusions about a large set of data, called a population,
based on a smaller set of sampled data.
8. What are we studying in this class?
Questions 9-11 two sample hypothesis testing
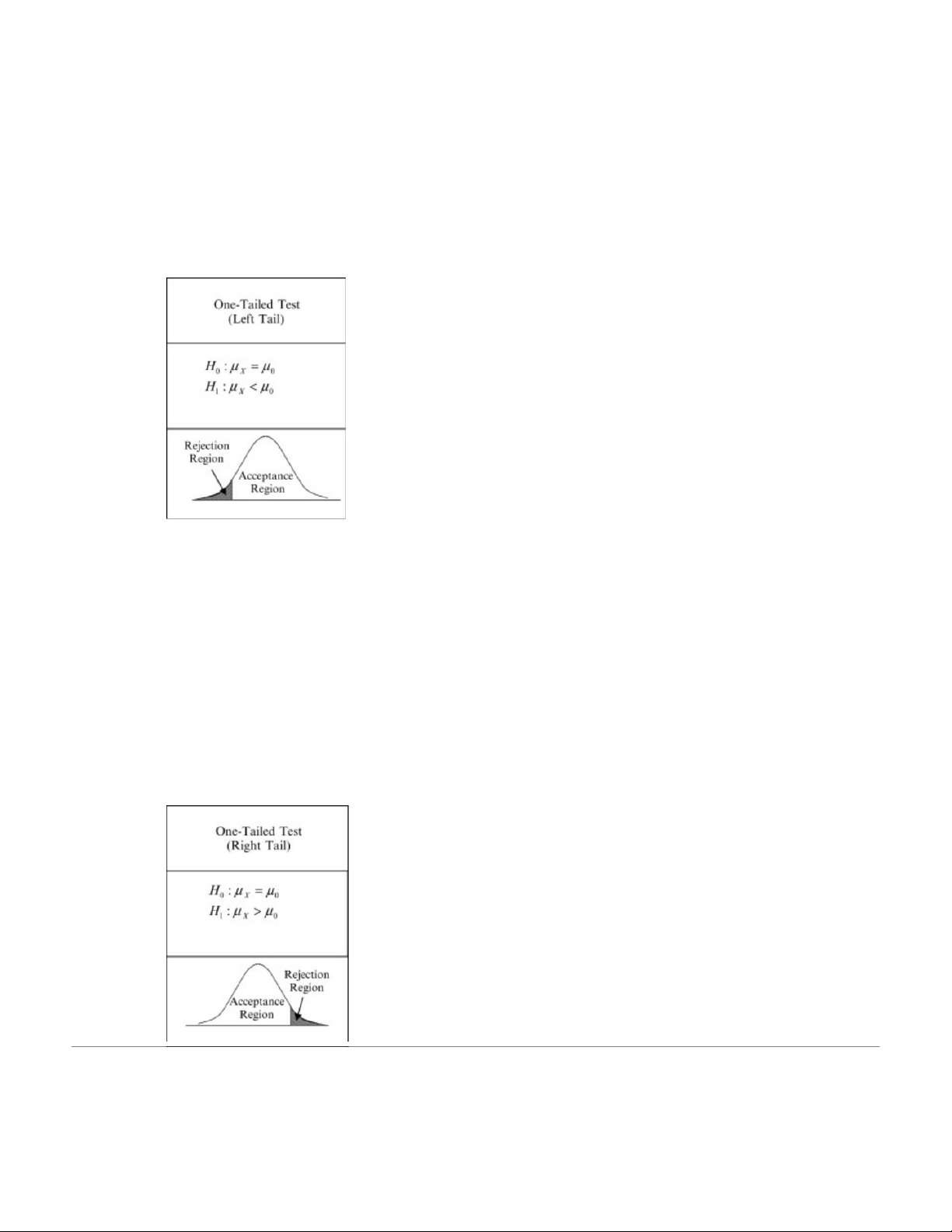
9. What is the null and alternative hypothesis?
Null Hypothesis (H_0): hypothesis which can possibly be disproved using sample information or
evidence. Any null hypothesis must contain the hypothesis value (μ_0 or p_0) (must have equal sign).
Alternative Hypothesis (H_α): alternative to the null hypothesis.
9. Reject or do not reject for a particular value for alpha?
Hypothesis testing on with test statistic z
+ Specify the and (level of significance) + Find the Standard Error of + Specify the test statistics
+ Compute the Critical Value: CV NORM.S.INV() + If CV, reject .
+ Compute the P-value: NORM.S.DIST(, TRUE) + If P-value , reject .
Hypothesis test on with test statistics ( is unknown)
+ Specify the and (level of significance) + Find the Standard Error of + Specify the test statistics
+ Compute the Critical Value: CV T.INV(, deg_freedom) or P-value: T.DIST(, deg_freedom, TRUE) + If CV, or P-value , reject
Hypothesis test on with test statistics
+ Specify the sample proportion: =
+ Specify the and (level of significance) + Find the Standard Error of + Specify the test statistics
+ Compute the Critical Value: CV NORM.S.INV() or P-value: NORM.S.DIST(, TRUE)
+ If CV, or P-value , reject . Hypothesis testing on with tes t statistic z
+ Specify the and (level of significance) + Find the Standard Error of + Specify the test statistics
+ Compute the Critical Value: CV NORM.S.INV() + If CV, reject .
+ Compute the P-value: NORM.S.DIST(, TRUE) + If P-value , reject .
Hypothesis test on with test statistics ( is unknown)
+ Specify the and (level of significance) + Find the Standard Error of + Specify the test statistics
+ Compute the Critical Value: CV T.INV(, deg_freedom) or P-value: T.DIST(, deg_freedom, TRUE) + If CV, or P-value , reject
Hypothesis test on with test statistics
+ Specify the sample proportion: =
+ Specify the and (level of significance) + Find the Standard Error of + Specify the test statistics
+ Compute the Critical Value: CV or P NORM.S.INV() -value: NORM.S.DIST(, TRUE)
+ If CV, or P-value , reject .
Hypothesis testing on with test statistic z
+ Specify the and (level of significance) + Find the Standard Error of + Specify the test statistics
+ Compute the Critical Value: CV NORM.S.INV() + If CV or CV, reject .
+ P-value NORM.S.DIST(, deg_freedom, TRUE) if
+ P-value NORM.S.DIST(, deg_freedom, TRUE) if + If P-value , reject .
Hypothesis test on with test statistics ( is unknown)
+ Specify the and (level of significance) + Find the Standard Error of + Specify the test statistics
* Using the Critical Value approach
+ Compute the Critical Value: CV T.INV(, deg_freedom) + If CV or CV, reject .
+ P-value T.DIST(, deg_freedom, TRUE) if
+ P-value T.DIST(, deg_freedom, TRUE) if + If P-value , reject .
Hypothesis test on with test statistics
+ Specify the sample proportion: =
+ Specify the and (level of significance) + Find the Standard Error of + Specify the test statistics
* Using the Critical Value approach
+ Compute the Critical Value: CV NORM.S.INV() + If CV or CV, reject .
+ P-value NORM.S.DIST(, deg_freedom, TRUE) if
+ P-value NORM.S.DIST(, deg_freedom, TRUE) if + If P-value , reject .
Questions 12-18 linear regression
12. What is the null and alternative hypothesis?
Test whether or not a linear relation exists:
H0: β = 0 (No linear relation exists) 1 Hα: β ≠ 0 (A 1 linear relation does exists) α = 0.05
12. Calculate the test statistic
CV = tα/2 = -T.INV(α/2, n-2) 12. Calculate the p-value
p-value = 2 * P( t > t-stat) 12. Reject or do not reject? 12. Interpret slope 12. Interpret the R^2 value
R2 = 1: perfect (positive or negative) relation i.e. points fit exactly along the regression line
R2 close to 0: very little relation
=> The higher the value of R2 the better the model fits the data
12. Use the estimated regression equation to solve for a value
Questions 19-22 matched samples
19. What is the null and alternative hypothesis?
19. Calculate degrees of freedom
19. Given a value of alpha reject or do not reject?
19. Evaluate result from question 21
Questions 23-27 Single Factor ANOVA
23. What is the null hypothesis? 23. Calculate MSTR 23. Calculate F-statistic 23. Calculate p-value 23. Reject or do not reject? Questions 28-31 ANOVA 28. What is the factor?
28. What is the alternative hypothesis?
28. What are the degrees of freedom for treatment?
28. What are the degrees of freedom for error? Questions 32-36 ANOV A blocking
32. What is the null hypothesis? 32. Calculate MSTR 32. Calculate F-statistic 32. What is the p-value? 32. Reject or do not reject? Questions 37-38 ANOVA 37. What is the factor
37. What are the factor levels? Questions 39-40 ANOVA
39. What is the null hypothesis 39. Reject or do not reject?
39. Identify whether data given is positively skewed, negatively skewed, or normally distributed 39. Know how to apply z-score
39. Calculate probability given mean, variance, and x value
39. Identify the null and alternative hypothesis
39. How does changing sample size, mean, and SD affect confidence interval
39. What is the formula on excel to solve for z value?
39. Confidence interval formula
39. How to know if you reject or do not reject in hypothesis testing
39. Definition of histogram, scatter plot, pie chart, and box plot
39. Identify independent variable and dependent variable




