











Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Downloaded by Lynh Nguyen (lynhn228@gmail.com) lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420 TABLE OF CONTENT
PART I: Background...............................................................1
1. History...............................................................................1
2. General information...........................................................1
3. Organizational structure....................................................2
4. Google mission, vision & values.........................................2
PART II: Case summary.........................................................3
PART III: Answer questions..................................................4
1. Question 1.........................................................................4
2. Question 2.........................................................................5
3. Question 3.........................................................................6
4. Question 4.........................................................................6
Part VI: Related theory.........................................................7
1. Motivation..........................................................................7
2. Communication..................................................................8 Part V:
Lessons......................................................................9
References............................................................................11 TABLE OF FIGURES
Figure 1. Google organizational structure..................................2
Figure 2. Job characteristics model............................................7 lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420 PART I: BACKGROUND 1.History
Google was founded on September 4, 1998, by Larry Page and Sergey
Brin while they were PhD students at Stanford University in California.
Together they own about 14% of its publicly listed shares and control 56% of
the stockholder voting power through super-voting stock. The company went
public via an initial public offering (IPO) in 2004. In 2015, Google was
reorganized as a wholly owned subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. Google is
Alphabet's largest subsidiary and is a holding company for Alphabet's Internet
properties and interests. Sundar Pichai was appointed CEO of Google in 2015,
replacing Larry Page, who became the CEO of Alphabet. In 2019, Pichai also became the CEO of Alphabet. 2.General information
Google is an American multinational technology company that focuses
on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer
software, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. It has
been referred to as the "most powerful company in the world" and one of the
world's most valuable brands due to its market dominance, data collection,
and technological advantages in the area of artificial intelligence. Their
products and services include Google Search, Google Chrome, Google Docs,
Google Calendar, Google Photos, Google Meet, Google Drive, Gmail, YouTube,
…. The company is located across the Americas, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Africa
and the Middle East. Google is headquartered in Mountain View, California, the US. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
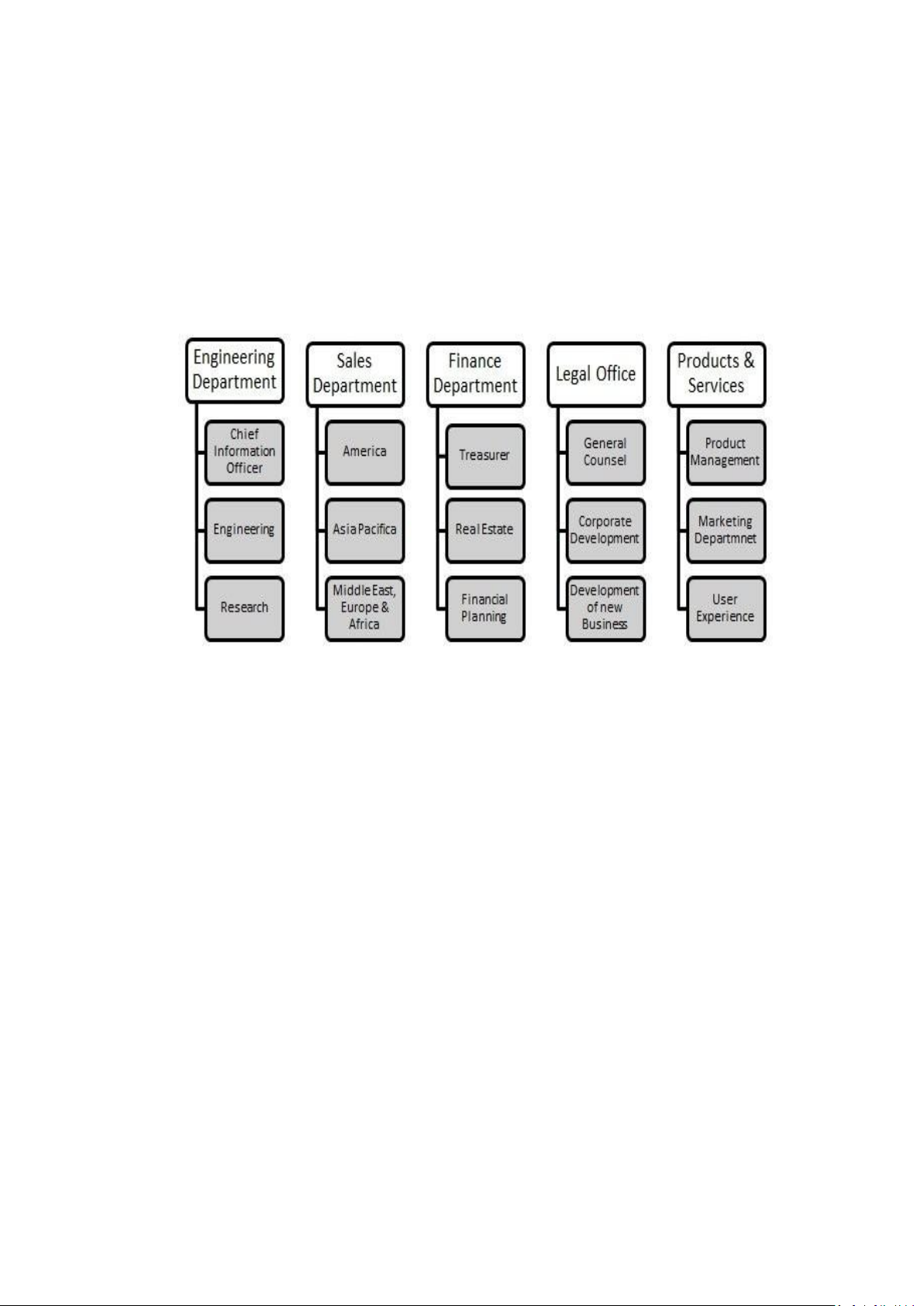
3.Organizational structure
Google uses a functional structure, where the top management team
focuses on employing value-chain activity measures. To ease the management
of the operations, Google’s management team has subdivided the company
into five departments as shown below.
Figure 1: Google organizational structure
Each of the departmental heads reports directly to the executive
management team, and the team reports to the board of directors. The small
business units obtain a chance to innovate and invent things within the larger
company. The multidivisional structure with small business units facilitates
centralized planning for a large company as Google.
4.Google mission, vision & values
• The mission statement to organize the world's information and make it useful and accessible to all.
• The vision statement is to provide access to the world’s information in one click. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
• The values are “Great isn’t good enough”, “It’s best to do one thing really well”,
“Fast is better than slow”, “You can be serious without a suit”, “You don’t need to be at your desk”, … PART II: CASE SUMMARY
While Google has grown exponentially since its founding, it retains the
aura of an informal, small company in which highly motivated Googlers work
on projects to achieve organizational objectives of speed and cost-
containment, projects that they have the autonomy to pursue and a sense of
ownership to see through to completion. Google's executives think that
brilliant ideas can arrive from anyone and at any time, thus all Googlers are
encouraged to come up with their next big idea. They are all granted one day
per week to engage on their own projects or products in which they are deeply
involved; also, top management hold office hours during which employees can
drop in to discuss new ideas and projects, as well as receive feedback.
Googlers are motivated to have such a mantra since they know their ideas will
be listened to and heard, and what they are doing is critical not only for the
firm but also for Google's global users.
The Ramussen brothers are an identical example of management
offering greater levels of autonomy and resources to pursue initiatives on their
own that are highly inventive. Their ideas for a new type of communication
system are given full access to all necessary resources, including dozens of
employees, by founders Page and Brin, as well as Eric, Chairman of the Board
and Chief Executive Officer. As a result, Googler's overarching goal of
"providing the best user experience possible" benefits the company, its
management and staff, as well as users. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
The report will explain why Google's employee motivation model works
so well in two important areas: motivation and communication.
PART III: ANSWER QUESTIONS
1. How would you characterize engineers' jobs at Google in terms of the job characteristics model?
Developed by Hackman and Oldman, the Job
Characteristic Model identifies five core characteristics that affect the overall
motivation shown by employees. These five core characteristics which affect
intrinsic motivation are skills variety, task significance, task identity, autonomy, and feedback.
To begin with, the skill Variety model means a person has many different
skills and talents to finish the job. For example, in order to achieve
organizational objectives of speed and cost-containment of a project, Google
engineers with PhDs and managers with MBAs are participating in this project
that ensures the project is the best.
The Task Identity model shows a clearly defined beginning, middle, and
end to a given task. For example, Google's engineers are provided with 1 day
a week to work on their own projects. The Task Significance model indicates a
substantial impact on the work. For instance, Mayer puts it, "I like to launch
(products) early and often. That has become my mantra." And having such a
mantra is motivational for Googlers as they know their ideas will be listened
to and heard and what they are doing is important not only for the company
but also for users around the globe.
At Google, autonomy, feedback, and task identity are the most important
dimensions considered in each task. According to Hisham and Aerni (2018), lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
autonomy refers to the level of freedom an employee has toward completing
a certain task. This means that the specific worker has control over the
scheduling of the work, the procedure of completing the task, and the
discretion they have towards the assignment. At Google, autonomy is highly
valued, with each employee having a day to complete tasks of their wish.
Finally, the feedback model means their performance during their work
whether or not to communicate. For example, top managers have office hours
during which employees can drop in, discuss new ideas and projects, and receive feedback.
2. Why are engineers at Google given one day a week to work on their own projects?
Google has been well known for its unique approach to innovation – from
its open culture, its radical work environment in its Googleplex campus to its
methods for innovation. One of its best-known innovation mechanisms was
its policy of ' 20% time' which allowed its engineers to spend 20% of their time on personal projects.
Google engineers get one day a week to work on their own projects that
they are very involved in. Google ‘20% time’ resulted in some of the company’s
most successful products such as Gmail, AdSense and Google Talk. Google’s
founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin highlighted the importance of this
management method in a Founders’ IPO letter to prospective investors in
2004: “We encourage our employees, in addition to their regular projects, to
spend 20% of their time working on what they think will most benefit Google,”
the pair wrote. “This empowers them to be more creative and innovative.
Many of our significant advances have happened in this manner.”
On a company-wide mailing list, Googlers can submit proposals for new
projects. Employees can visit top managers' offices during office hours to lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
discuss new projects and ideas and get feedback. Peer support for an idea is
certainly an important criterion in evaluating an idea’s business potential.
These projects often require a variety of employee skills. For example,
Google's international webmaster in the mid2000s, who invented the site's
holiday logo, translated the entire site into Korean, and the chief operations
engineer at the time was also a neurosurgeon. Engineers work together on
their projects and with managers
3. Why do you think Page, Brin, and Schmidt gave theRasmussen brother's
high levels of autonomy to develop Google Wave?
Some engineers at Google have been given higher levels of autonomy
and resources to pursue projects on their own that managers hope will be
highly innovative. For example, Lars and Jens Rasmussen are Google
employees in Australia who work on Google Maps and also happen to be
brothers. A project they were pursuing on the side focused on a new kind of
communication system that might even be thought of as a replacement or
substitute for email and allows for collaboration and communication in real time.
Founders Page and Brin and Eric Schmidt, Chairman of the Board and
Chief Executive Officer of Google, thought the idea sounded interesting, told
the brothers to pursue it, and gave them all the resources they needed,
including dozens of employees. Rasmussen’s project, Google Wave, was in a
limited preview in May 2010. For this and the many other projects ongoing at
Google, engineers, managers, and all employees have the overall objective of
“providing the best user experience possible.” Given the popularity of Google,
this objective is serving Google, its managers and employees, and its users very well. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
4. How might Google's overarching objective of providing the best user
experience influence the goals engineers set for themselves as they pursue new projects?
Google needs to retain its original spirits and continue developing the five
models of job characteristics.
For instance, Google gives engineers higher levels of autonomy and
resources so that they can pursue projects on their own that managers hope
will be highly innovative. And Google recruits new employees with different
kinds of skills in the future. Google creates a motivating work setting for its
employees. They can achieve their goal of providing excellent service to
Google's managers, employees, and users.
Part IV: RELATED THEORY
Through the article about the working environment of Google, we can
see the effects of motivation and communication on the behavior as well as
the relationship between managers and employees when operating the company together. 1. Motivation
It can be seen that Google managers have created motivation by
encouraging their employees to work efficiently and quickly so that they can
respond to users' searches with "breakneck speed". First, they gave
employees a sense of involvement and voice in the work environment by
providing them with opportunities to adapt, experiment, take risks, and even
fail (Safety-security and Social-belongingness). When Googlers have been
encouraged to fail so that they can learn and gain experiences, they
automatically have bigger, more creative thoughts and ideas, and have more
"courage" to express their own opinions with colleagues as well as managers. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
In addition to other company jobs in general, Google engineers are given
one day a week to develop their projects and these ideas will be included in
the mailing list and sent to other employees in the future. Google. This can
help Googlers build their Esteem, they know that their opinions are known to
everyone and have a potential to be built on a platform that can be developed
in the future. After the projects are effectively implemented, this can help not
only the Googler who came up with that idea to "find" his capacity
(Selfactualization), but also create a motivation for other employees so that
Google is always innovating with ideas that are relevant to the situation
around the world as well as making full use of the company's resources.
Motivations from managers will help Googlers have a healthy working
environment, good work experience as well as achieve high job satisfaction
(according to Job characteristics model). lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Figure 2: Job characteristics model 2. Communication
As a big company specializing in providing information around the world,
so the information system inside Google is also extremely enormous.
Therefore, to be able to create a connection between people, communication
in this working environment is also extremely important. As we already knew,
Google has a company-wide email system to help employees get the latest
information and learn more about the projects and ideas of their colleagues,
this is highly connected when everyone can share freely and easily while
working. From here, the relationships between Googlers can be more
cohesive when everyone respects each other's opinions, making team work
for projects to be effective and achieve the productivity and desired results.
Not only that, the fact that managers allow employees to come to their
offices at any time during office hours to present ideas, discuss and receive
feedback helps both sides get the latest information, the most spontaneous
and creative ideas and solutions to problems at the earliest. Speed and
efficiency are important to Google, and only when communication between
employees and management achieves a high level of cohesion and agility in
order to maintained and stabilized the company and the search engine for
users from all around the world. Part V: LESSONS
As can be seen from the case, we learn that the working environment of
a company can affect labor productivity and product quality of that company.
From the collaboration of two graduate students in computer science, Google
now is the name that anyone will think of when mentioning search engines.
This fruitful result is mostly thanks to a motivating work setting that Google lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
created. By creating a motivating work setting, big ideas and projects are
introduced and worked on, which mostly came from employees. That is
because they are listened to, encouraged and supported by their managers.
However, having a strong culture like Google has some unintended
consequences. First off, Google's distinct "college" culture may eventually
harm its employees. Strong cultures are also known to promote homogeneity
by compelling employees to comply, making their organization inflexible to
changes in a dynamic environment. Nevertheless, Google succeeds in
overcoming the usual issues of workplace rigidity and uniformity. Although
homogeneity typically reduces effectiveness, Google intentionally recruits
individuals with similar attributes, which promotes heterogeneity. For
instance, Google looks for applicants who are passionate and innovative,
qualities that support diversity. Given that they share some traits, Google
employees may appear to be "homogenous" in this situation, yet these traits
combine to create a distinctive and diverse workforce. In Google employees,
characteristics like originality, spontaneity, and new thinking tend to boost
effectiveness rather than decrease it. The bulk of Google's staff members are
also quite youthful, making them adaptable to new surroundings and
accepting of people who are different. Following study of the qualities Google
seeks in new hiring, it is noticeable that the company's employees' underlying
degree of homogeneity does not limit diversity but rather strengthens it.
With the above summaries, you must have harvested your own lessons.
Motivation and communication are two important factors in a work
environment. Promoting motivation and encouraging communication will
increase worker productivity at work. A manager should be willing to listen
and give feedback to your subordinates’ opinions or ideas. A creative and
enthusiastic working environment will be created, and you might have lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
opportunities to develop your team project with some fantastic ideas of your members! REFERENCES 1.
Claburn, T. (September 24, 2008). Google Founded By Sergey Brin, Larry Page...
And Hubert Chang? Retrieved from informationweek:
https://www.informationweek.com/applications/google-foundedby-sergey-
brin-larry-page-and-hubert-chang!/d/d-id/1072309 2. Corporate Overview.
(n.d.). Retrieved from Google, Inc:
http://www.google.com/corporate/index.html
3. Google Mission, Vision & Values. (n.d.). Retrieved from Comparably:
https://www.comparably.com/companies/google/mission
4. Ngoc, P. T. (n.d.). slides organizational behavior for advanced program.
5. Schneider, L. (2019, 6 25). Company Profile and Job Information for Google.
Retrieved from liveabout: https://www.liveabout.com/google-overview-
company-cultureand-history2071320#:~:text=Google%20was%20founded
%20by%20Larry,billion%20in%20August%20of%202004.
6. Schroeder, S. (2010). Google Employees Explain What It s Like Working at
Google. Retrieved from mashable:
http://mashable.com/2010/07/05/google-employees-workinggoogle
7. Towler, D. A. (2020). The Job Characteristics Model: What it is and why it matters more than ever. ckju.
8. Writer, G. T. (2009). employee review google. Retrieved from Glassdoor:
http://www.glassdoor.com/Reviews/EmployeeReview-Google-
RVW144182.htm (accessed November 29, 2010




