













Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071 Lecture 4
Ethics and Privacy Information Security Objectives
• Define ethics, list and describe the three fundamental tenets of ethics,
and describe the four categories of ethical issues related to information technology. lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
• Identify three places that store personal data, and for each
one, discuss at least one potential threat to the privacy of the data stored there.
• Identify the five factors that contribute to the increasing vulnerability of
information resources, and provide a specific example of each one.
• Compare and contrast human mistakes and social engineering, and
provide a specific example of each one.
• Discuss the 10 types of deliberate attacks • Ref.: Chapter 3 & 4 Ethical Issues
•Ethics refers to the principles of right and wrong
that individuals use to make choices that guide their behavior
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 2 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
•There are many frameworks that can help us make ethical decisions •Ethical Frameworks
•Ethics in the Corporate Environment
•Ethics and Information Technology •Ethical Frameworks 4 standards 5 steps
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 3 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071 ▪ Utilitarian approach • Recognize an ethical ▪ Rights approach issue ▪ Fairness approach • Get the facts
▪ Common good approach • Evaluate alternative actions • Make a decision and test it • Act and reflect on the outcome of your decision
Combine these 4 standards by these 5 steps to develop a general
framework for ethics (or ethical decision making) •Four standards
•The utilitarian approach states that an ethical
action is the one that provides the most good or does the least harm
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 4 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
•The rights approach maintains that an
ethical action is the one that best protects and
respects the moral rights of the affected parties
•The fairness approach posits that ethical actions
treat all human beings equally, or, if unequally, then
fairly, based on some defensible standard.
•the common good approach highlights the
interlocking relationships that underlie all societies
• If we combine these four standards, we can develop a general
framework for ethics (or ethical decision making). This
framework consists of five steps:
• Recognize an ethical issue:
• Could this decision or situation damage someone or some group?
• Does this decision involve a choice between a good and a bad alternative?
• Does this issue involve more than simply legal considerations? If so, then in what way? • Get the facts:
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 5 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
• What are the relevant facts of the situation?
• Do I have sufficient information to make a decision?
• Which individuals and/or groups have an important stake in the outcome?
• Have I consulted all relevant persons and groups?
• Evaluate alternative actions:
• Which option will produce the most good and do the least harm? (the utilitarian approach)
• Which option best respects the rights of all stakeholders? (the rights approach)
• Which option treats people equally or proportionately? (the fairness approach)
• Which option best serves the community as a whole, and not just some
members? (the common good approach)
• Make a decision and test it:
• Considering all the approaches, which option best addresses the situation?
• Act and reflect on the outcome of your decision:
• How can I implement my decision with the greatest care and attention to
the concerns of all stakeholders?
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 6 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
• How did my decision turn out, and what did I learn from this specific situation?
•Ethics in the Corporate Environment:
•A code of ethics is a collection of principles
intended to guide decision making by members of the organization
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 7 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
•Fundamental tenets of ethics:
•Responsibility means that you accept the
consequences of your decisions and actions.
•Accountability refers to determining who is
responsible for actions that were taken.
•Liability is a legal concept that gives individuals the
right to recover the damages done to them by other
individuals, organizations, or systems.
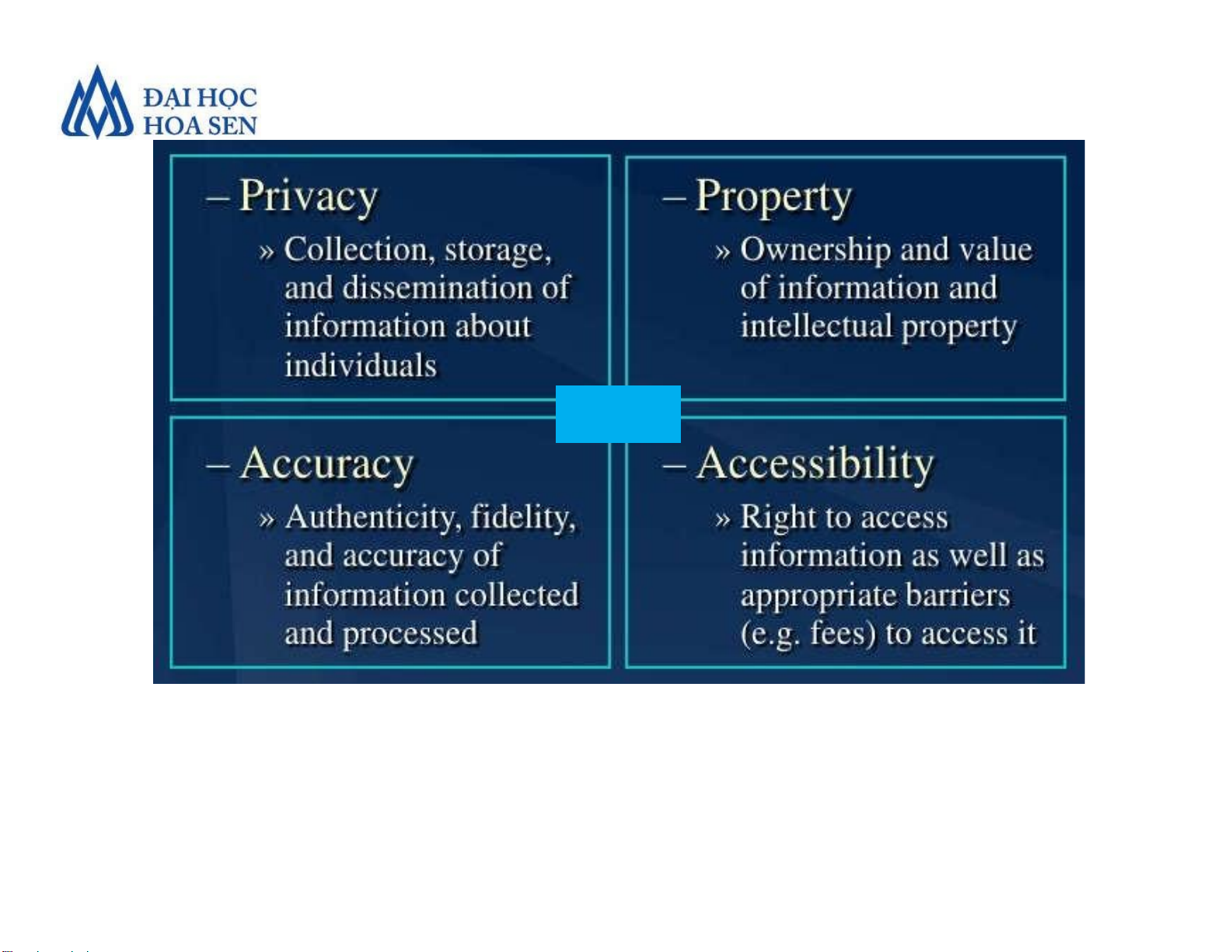
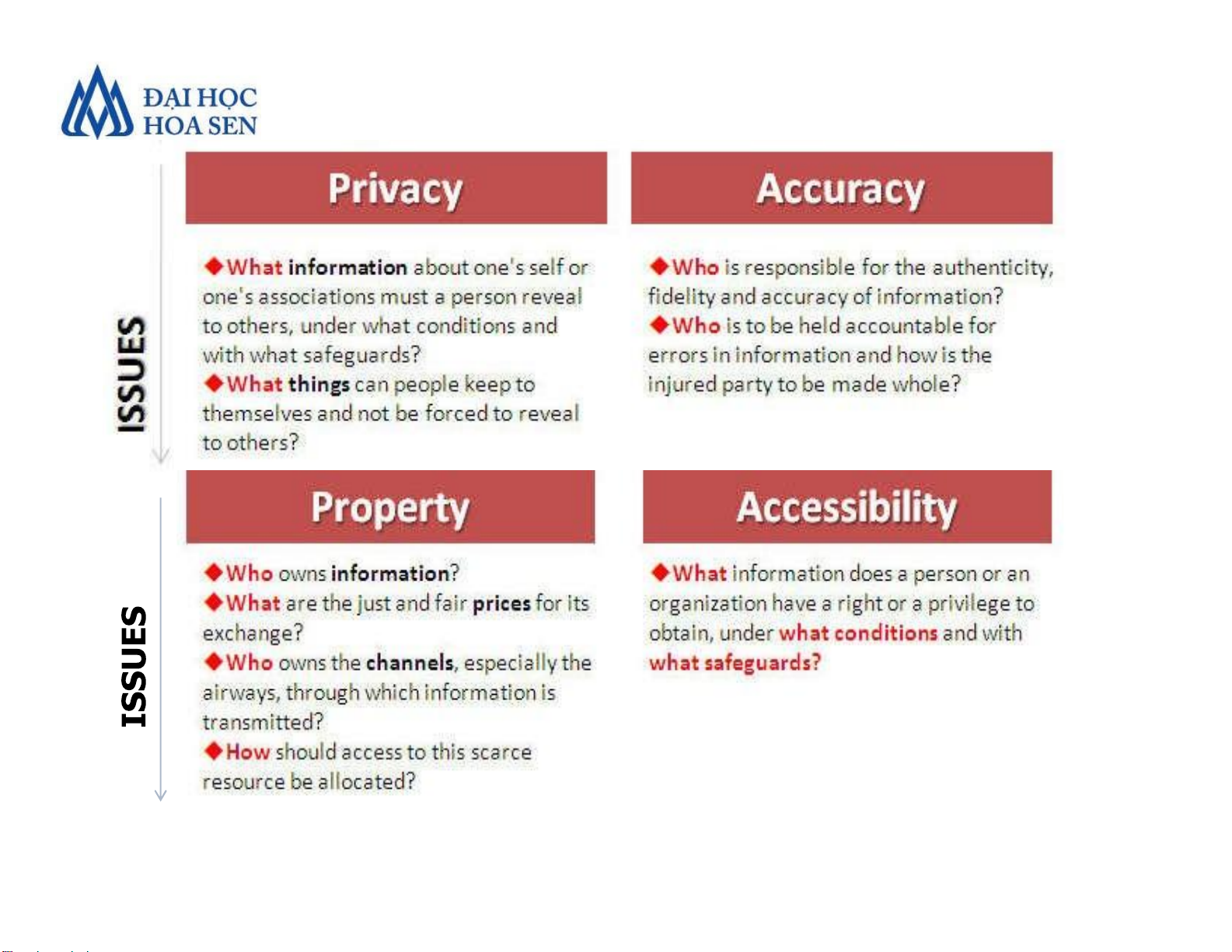
•Ethics and Information Technology
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 8 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071 PAPA
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 9 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 10 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071 Privacy
•Privacy is the right to be left alone and to be free
of unreasonable personal intrusions
•Information privacy is the right to determine when,
and to what extent, information about you can be
gathered and/or communicated to others. •Two rules
•The right of privacy is not absolute. Privacy must be
balanced against the needs of society.
•The public’s right to know supersedes the
individual’s right of privacy. •Electronic Surveillance
•Personal Information in Databases
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 11 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
•Information on Internet Bulletin Boards,
Newsgroups, and Social Networking Sites •Privacy Codes and Policies
•International Aspects of Privacy
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 12 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071 •Privacy Policy Guidelines:
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 13 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071 A Sampler
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 14 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071 Information Security
•Introduction to Information Security
•It is difficult for organizations to provide perfect security for their data.
•There is a growing danger that countries are
engaging in economic cyberwarfare among themselves
•Security is the degree of protection against
criminal activity, danger, damage, and/or loss
•Information security refers to all of the processes
and policies designed to protect an organization’s
information and information systems (IS) from
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 15 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
unauthorized access, use, disclosure,
disruption, modification, or destruction
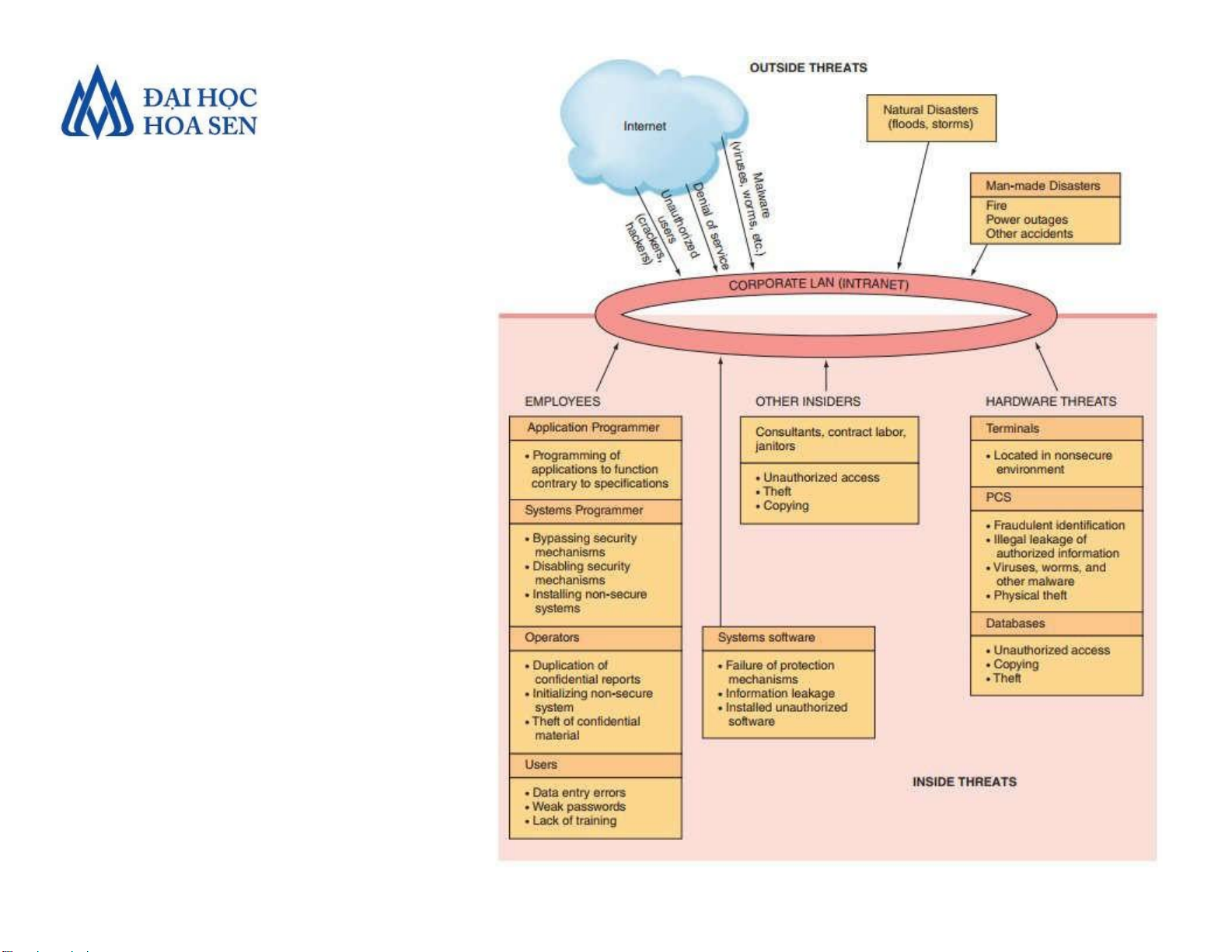
•A threat to an information resource is any danger
to which a system may be exposed
•The exposure of an information resource is the
harm, loss, or damage that can result if a threat compromises that resource
•An information resource’s vulnerability is the
possibility that the system will be harmed by a threat
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 16 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
• Unintentional Threats to Information Systems
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 17 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071 • Human Errors • Social Engineering
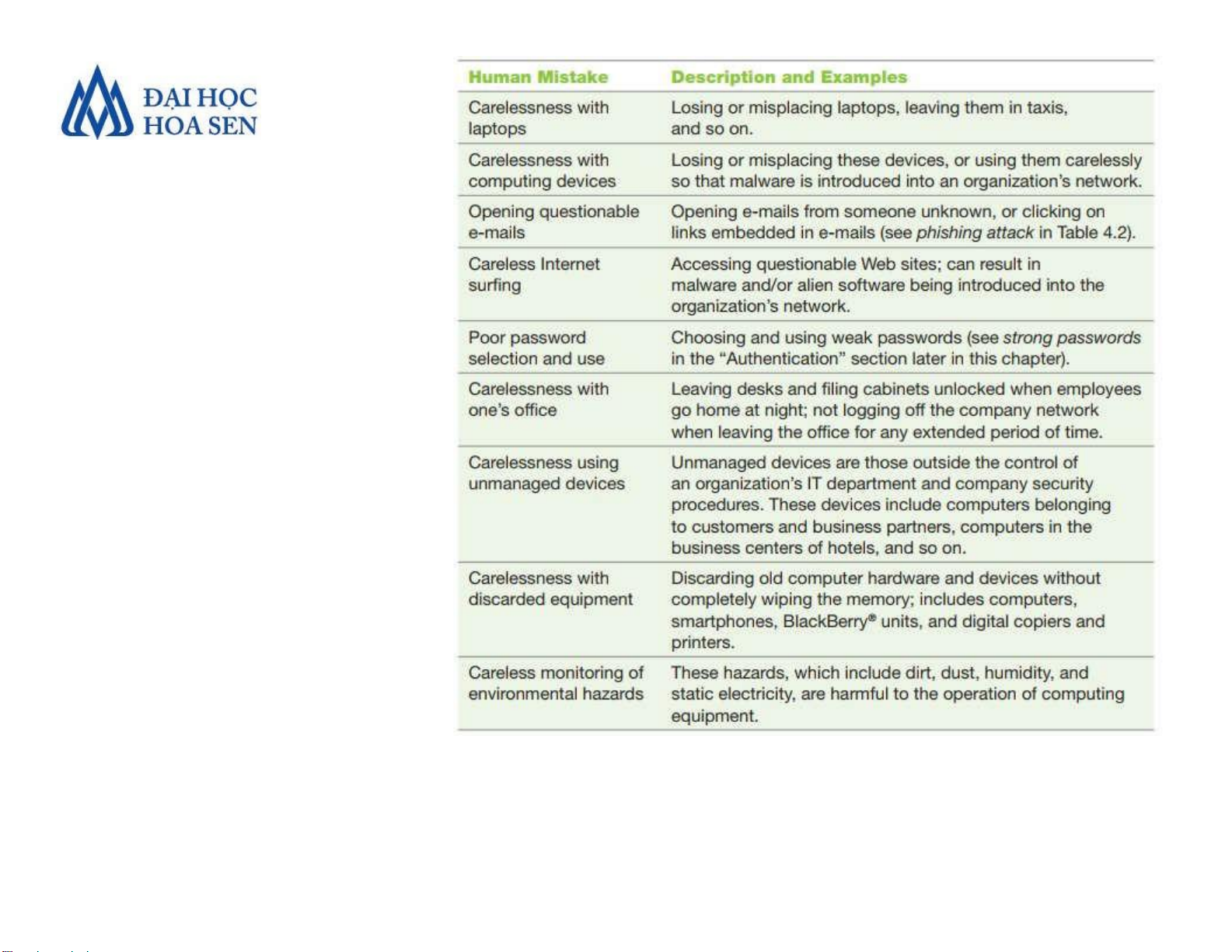
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 18 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071 •Human Mistakes
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 19 lOMoAR cPSD| 47206071
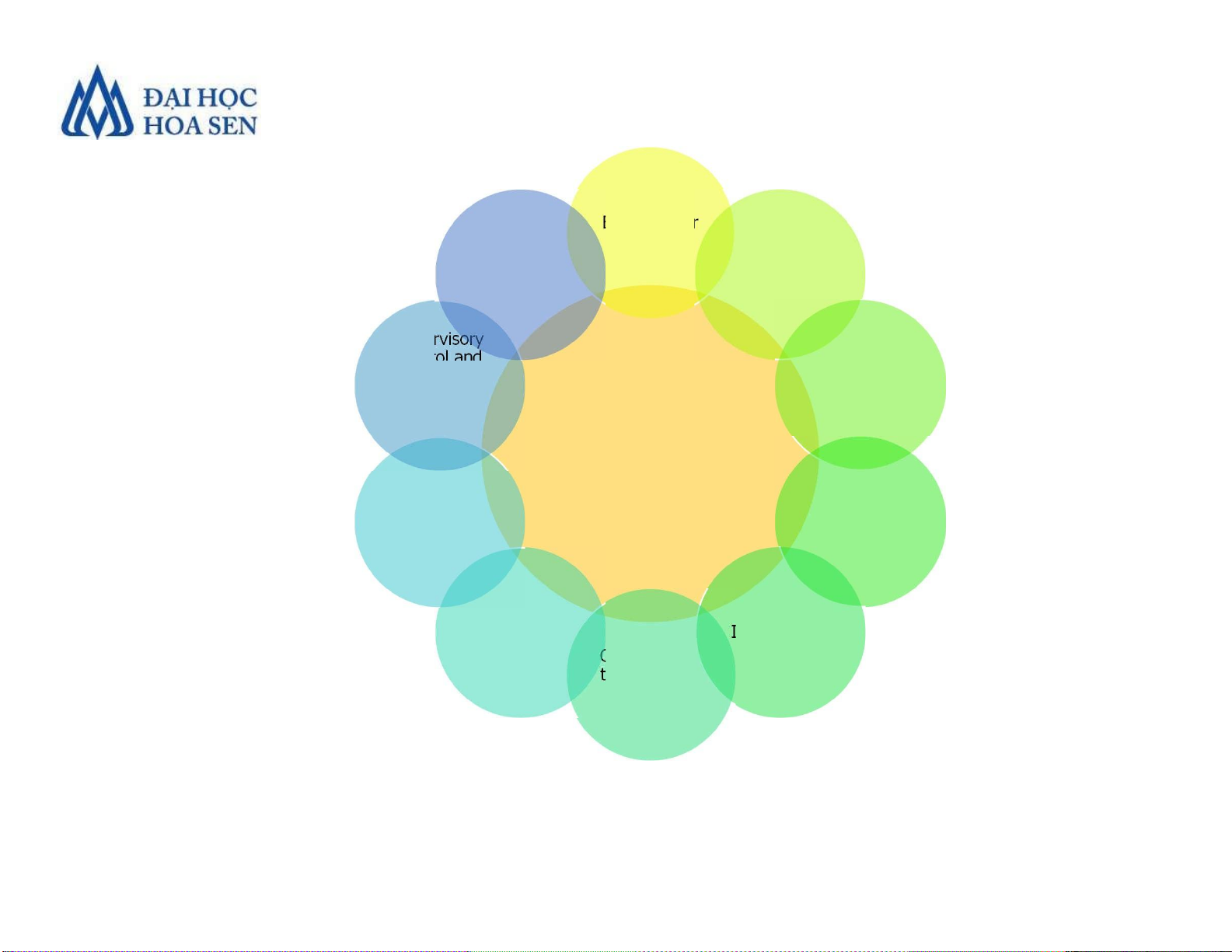
Deliberate Threats to Information Systems Espionage or trespass Cyberterrorism Information and extortion cyberwarfare Supervisory control and data Sabotage or acquisition vandalism ( SCADA) attacks Deliberate Threats Theft of Alien software equipment or information Software Identity theft attacks Compromises to intellectual property •Software Attacks
Faculty of Economics and Business Introduction to MIS 20



