





Preview text:
LESSON 6: ADVERBIAL CLAUSES
(PURPOSE, CONCESSION, CONTRAST) I-LANGUAGE FOCUS 1.1. Purpose clauses
An adverb purpose clause states the purpose of the action in the independent clause. A
purpose normally follows the independent clause, but you may put it at the beginning
of a sentence if you want to especially emphasize it.
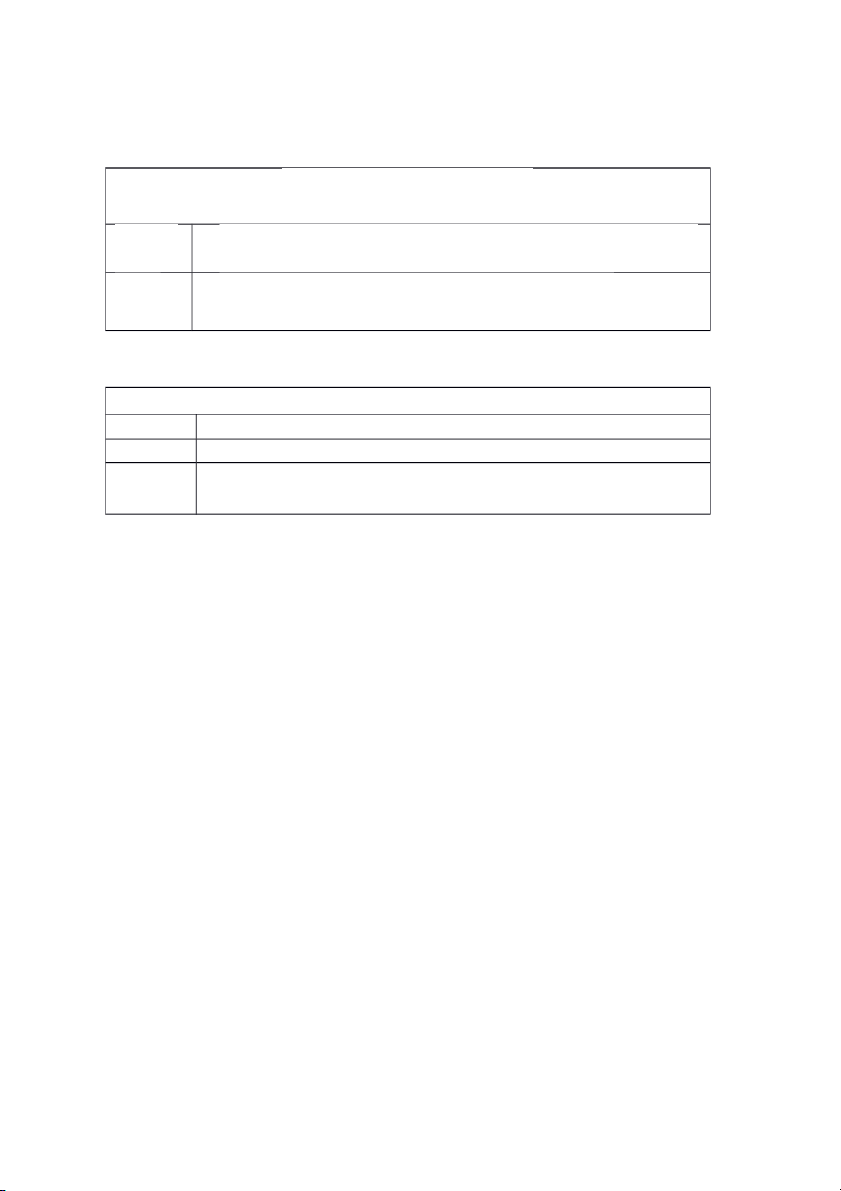
Table 1.8. Purpose Subordinators Purpose Subordinators so that
Farmers use chemical pesticides so that they can get higher crop yields. in order
In order that consumers can enjoy perfect fruits and vegetables, that
farmers also spray their fields.
- In order that is formal.
- The modals may/might, can/could, will/would, or have to usually occur in a purpose clause.
- We often use the phrase in order to to + + a base verb or simply a base verb when the
subjects of both the independent clause and the purpose clause are the same person or thing.
We prefer to + verb over in order to + verb because it is shorter. The first example above
could be written as follows because the two subjects (farmers and they) refer to the same people.
Ex: Farmers use chemical pesticides in order to get higher crop yields.
Farmers use chemical pesticides to get higher crop yields.
In the second example, the two subjects (farmers and consumers) are different, so it is not
possible to use an in order to + verb or a to + verb phrase. 1.2. Contrast clauses
There are two types of adverb clauses that express contrast: direct opposition clauses and concession clauses.
In this type, the information in the adverb clause and the information in the dependent
clause are in direct contrast.
Table 1.9. Direct Opposition Subordinators
Direct Opposition Subordinators whereas
San Francisco is cool during the summer, whereas Los Angeles is generally hot. While
While most homes in San Francisco do not have air conditioning, it i it i L A l
Table 1.10. Concession Subordinators
Concession Subordinators
although Although I had studied all night, 1 failed the test. even
Our house is quite comfortable even though it is small. though
Though the citizens had despised the old regime, they disliked the new government even more. Notes
1. Although, even though, and though have almost the same meaning. Though is less
formal. Even though is a little stronger than although.
2. Be careful about which clause you use the subordinator with. Sometimes you can use it
with either clause, but not always.
Incorrect: He loves sports cars, although he drives a sedan.
CORRECT: Although he loves sports cars, he drives a sedan. II-LANGUAGE PRACTICE
2.1. Match sentences beginning 1-5 with the endings a-e
1. Although he is standing on a ladder, b a. they still go for a walk.
2. The people seem to enjoy themselves, c
b. he still can’t reach the book.
3. Even though it is raining heavily, a
c. though the weather is terrible.
4. The woman is dressed formally, e
d. they still won the competition.
5. In spite of the fact that they lost the last
e. whereas the man’s clothes are more game, d casual.
2.2. Fill in the gaps with “so that (in order that)/ to (in order to)/ not to (in order not to)”
1. I'm studying very hard at the moment … in order to ….pass my exams next month.
2. I bought a dictionary… in order to … help with my vocabulary.
3. I went to bed early…… so that ….. I wouldn't be tired in the morning.
4. I have to get up early. I set the alarm for five o'clock… in order not to …….. oversleep.
5. I waited for an hour … so that ….I could meet her. III-PRACTICE IN TOEIC 3.1. Building Language Picture 1 Picture 2 Picture 3
a- Give some words which may be used to describe pictures 1-3. Compare with your friends.
b- Complete the following about pictures 1-3 sentences with the given words: 6.tries 2.others 1.discuss 5.drive 4.inside 3.getting
1.Three employees have gathered together around an oval table to .…………something.
2. The man is standing, whereas the two ……….. are sitting.
3. He is …………out of the car so that he can get better reception.
4. Though he can listen to the phone ………… the car, he gets outside.
5. A man is clearing snow away from his car in order to………………...it.
6. Although there is a lot of snow, the man still………to clear it. 3.2. Tactic Practice
3.2.1. Put the words in the correct order Picture 1
1. examining/ The people/ are/how to/
the/ so that/ they/there/ can/map/ check/ get.
The people are examining the map so that they can check how to get there
2. the way/although/ time/ a map/
People are waiting in line so
they/ spend/ have/ they/ much/ that they can get into the looking for. building
They spend much time looking
for the way although they have Picture 3 a map Picture 2
5. The/ written/ specials/ are/ on/ so
that/read about/the board/ diners/ can/ them.
The specials are written on the
3. takes/ Though/ it/ standing/ a long board so that diners can read
time/ many/in line/ people/ are/ to them get/ building / to the.
Though it takes a long time,
6. comes/ though/is/ beautiful/ no one many people are standing in / the restaurant . line to get to the building Though the restaurant is beautiful, no one comes
4. in line/ People/ are/ get/ into/
waiting/ so that/ they/ can/ the building. .
3.2.2. Make sentences about the pictures with the suggested words
1. so that/ sit/ portrait
The girls are sitting so that the man can draw their portrait 1. big/ whereas/ foot
The shoe is big whereas the foot of the little boy/ the little boy’s foot is small 3. food/ though/ want
Though the food is delicious, the boy doesn’t want to eat it 3.3. Test Practice
In this part of the test, you will write ONE sentence that is based on a picture. With
each picture, you will be given two words or phrases that you must use in your sentence.
You can change the forms of the words and you can use the words in any order.
1. even though/ bag/ help
…………………………………………
Even though the bags are very heavy, the woman doesn’t need any help/ no one helps the woman 2. although/ wet/ fast
Although the road are very wet, the car is running so fast 3. modern/whereas/ ancient
-The building on the left of the picture is modern whereas the others are ancient
-The building is so modern whereas the city is ancient
-The tower looks modern whereas the building is quite ancient 4. although/ open/ come
Although the coffee shop is open, no one comes/ no customer comes. 5. although/ vacation/ work
Although the man is on vacation, he is still busy with his work/ he is still working 6. laptop/ whereas/ look
The man is working on the laptop whereas the woman is looking at him




