



Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 II- LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Online-Shopping Attitude
Attitudes are informed by beliefs needed to engage in the behavior (Ajzen & Fishbein, 1977), It is
define as individual's positive or negative feeling associated with performing a specific behavior.
Attitude towards online shopping was a significant antecedent in forming online purchases, and a
desire was strongly motivated by the intention to own, thereby forming the behavioural intention
to use (Salisbury, Pearson, Pearson, & Miller, 2001).
Online-shopping attitude has been conceptualized in several different ways in the existing
literature. First, it refers to the consumers acceptance of the Internet as a shopping channel ‟ (Jahng
et al., 2001). Second, it refers to consumer attitudes towards a specific Internet store, i.e. the extent
to which consumers think that shopping at this store is appealing. 2.2 Purchase Intention
Purchase intention or referring to willingness to buy is widely defined as the likelihood of a
consumer to purchase a product or service (Dodd & Supa, 2011; Sam & Tahir, 2009). It is also
being defined as a conscious plan made by an individual to make an effort to purchase a brand (Spears & Singh, 2004).
Chang and Chen (2008) investigated the impact of online environmental indications such as the
website's quality and brand identity on consumer shopping intentions towards online sellers and
the mediating effects of consumer trust on the relationship between online environmental
indications and purchasing intentions. Additionally, in the sense of online shopping, Kim, Xu and
Gupta (2012) tested the consequences of confidence on buying intentions. They evaluated two key
factors (price and trust) regarding online buying habits and noticed that trust is much more able to
impact buying intentions than the price of new and repeat customers and that confidence is more
likely to impact new customers' purchasing decisions than repeat customers.
The concept of purchase intention is rooted in psychological and is extensively used in behavioral
studies (Dodd & Supa, 2011). Purchase intention is being characterized as a behavioral tendency
that the consumer will purchase the product (Monroe & Krishnan, 1985) and as an important
indicator for the actual purchasing decision (Tan, 1999). This statement is then further supported lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
by Li, Davies, Edwards, Kinman and Duan (2002), stated that purchase intention is a common
measure that usually employed to assess effectiveness of purchase behavior.
2.3 Hypotheses development 2.3.1 Interactivity
Interactivity is a vital aspect of online business. It is defined as the degree to which consumers
engage in social shopping activities, produce and share knowledge to gain acceptance within the
online community (Steure, 1993). Live streaming enhances interpersonal interactions between the
seller and the customer and interactivity includes the salience of the engagement. This goes above
and beyond what is typical of ordinary e-commerce and s-commerce transactions, where the
seller's private information is seldom or not at all accessible. Customers' trust will rise and
confusion will decrease thanks to the increasing degree of social engagement and social presence
brought about by synchronized two-way communication between buyers and sellers and the
presentation of other viewers' opinions.
Jiang, Chan, Tan, and Chua (2010) believe that the interactivity of social media is an important
environmental stimulus to consumers' purchasing process, and it can stimulate the systematic
elaboration of information related to the repurchase. According to Tajvidi et al. (2017),
interactivity is built via social action and feedback obtained during the forum or group sharing and suggestions sessions.
H1: Interactivity has a positive relationship with purchase intention. 2.3.2 Perceived Trust
Perceived trust, according to Doney and Cannon Doney & Cannon, (1997), was a complex concept
in the marketing and social psychology fields. Trust has long been conceptualized by various
studies in different ways, both theoretically and operationally, and yet there is no universally
accepted definition of trust (Gefen et al., 2003).
Chiles and McMackin (1996) found that perceived trust could reduce the cost of non-monetary
transactions, including the time and effort required by customers to choose the right seller. lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
Perceived trust could also reduce the level of risk in online transactions (Jarvenpaa et al., 2000 &
Kim et al., 2010). Therefore, perceived security affects perceived trust. In addition, perceived trust
is an important factor influencing consumers' willingness to use mobile payments to make purchases.
H2: Perceived trus has a positive relationship with purchase intention.
2.3.3 Electronic word-of-mouth (e-WOM)
Electronic word-of-mouth (e-WOM) is any statement (positive or negative) made by potential,
current or former customers about a product or company which is available to any people and
organizations through the Internet (Byrne, Kearney & MacEvilly, 2017). Consumers found that if
they have a stronger behavioural intention, specifically through the internet environment, they will
be more inclined to perform their purchasing goods and service (Jeong & Koo, 2015). This has led
to the creation of a diverse online word-of-mouth community (Sweeney, J. C., Soutar, G. N., & Mazzarol, T, 2008).
Since then, Electronic Word-of-Mouth (eWOM) has great effects on customers’ behaviour and
decision-making in purchasing process compared to traditional advertising (Goldsmith & Clark,
2008). Consumer purchase intention will grow when there is greater trust in online
recommendation agents, as well as viral messages with a higher level of perceived utility and
adoption, according to Dabholkar & Sheng, (2012) and (Gunawan & Huarng, 2015) research.
Consumers' buying intentions are literally increased by eWOM credibility and trust as a result of
the good influence of eWOM adoption. The higher a person's faith in an electronic vendor, the
more likely he is to buy something. eWOM adoption can assist electronic sellers by transforming
social networking site suggestions into purchases, according to (Erkan & Evans, 2016).
H3: E-WOM has a positive relationship with purchase intention. 2.3.4 Product Quality
Product quality is the product's ability to perform its functions, including durability, reliability, and
accuracy obtained by the product as a whole (Kotler & Keller, 2016). Product quality is the
physical condition, function and nature of a product that is related and can meet consumer tastes
and needs satisfactorily according to the value of money spent (Prawirosentono, 2002). If a product lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
meets the standards, the customer will be satisfied and assume that the product is reasonable or
even high quality. Conversely, the product is perceived as poor quality if the customer’s
requirements are not met, implying that a product’s quality determines the product’s ability to
satisfy the consumer’s needs and expectations (Ariffin et al., 2016)
The findings from Kotler and Keller (2012) demonstrated that product attributes such as product
quality, and price positively impacted purchasing intention
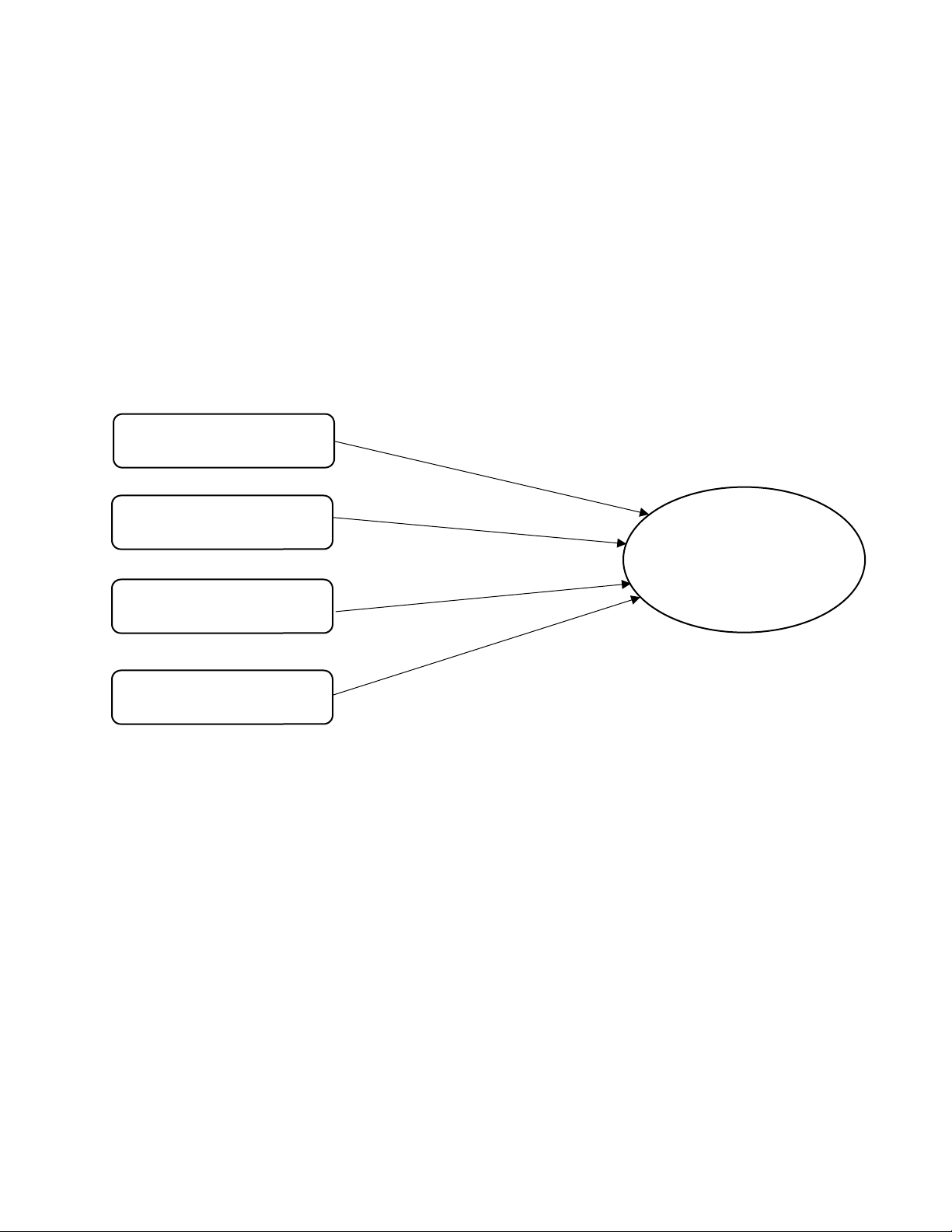
H4: Product Quality has a positive relationship with purchase intention. 2.4 Research Model Interactivity H1 H2 Perceived Trust Purchase Intention H3 E-WOM H4 Product Quality Hypotheses:
H1: Interactivity has a positive relationship with purchase intention.
H2: Perceived trus has a positive relationship with purchase intention.
H3: E-WOM has a positive relationship with purchase intention.
H4: Product Quality has a positive relationship with purchase intention. References: lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336
http://jabes.ueh.edu.vn/Content/ArticleFiles/oldbv_en/2012/Thang %207/8hoangthiphuongthao.pdf
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/234694779.pdf
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4161915
https://scholarhub.ui.ac.id/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1031&context=amj
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/
250174320_Interactivity_and_Its_Facets_Revisited_Theory_and_Empirical_Test
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/
220580368_Effects_of_Interactivity_on_Website_Involvement_and_Purchase_Intention
https://www.ukessays.com/essays/marketing/the-theoretical-foundation-of-purchase-
intentionmarketing-essay.php https://www.researchgate.net/publication/
327221068_The_Role_of_Live_Streaming_in_Building_Consumer_Trust_and_Engagement_wit
h_Social_Commerce_Sellers https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Wan_Mohamad/publication/
358444323_FACEBOOK_LIVE_HOW_IT_AFFECTS_THE_PURCHASE_INTENTION_OF_
GENERATION_Y_IN_MALAYSIA/links/63eb2b2dd0e0b25ca7f3e7e0/FACEBOOK-LIVE-
HOW-IT-AFFECTS-THE-PURCHASE-INTENTION-OF-GENERATION-Y-IN-
MALAYSIA.pdf?origin=publication_detail



